Kawasaki Ha9-II-Ko on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The BMW VI was a
 ;BMW VI 5.5
: Compression ratio 5.5:1, at up to 1600 rpm at sea level
;BMW VI 6.0
: Compression ratio 6:1, at up to 1650 rpm at sea level,
;BMW VI 5.5
: Compression ratio 5.5:1, at up to 1600 rpm at sea level
;BMW VI 6.0
: Compression ratio 6:1, at up to 1650 rpm at sea level,  ;
;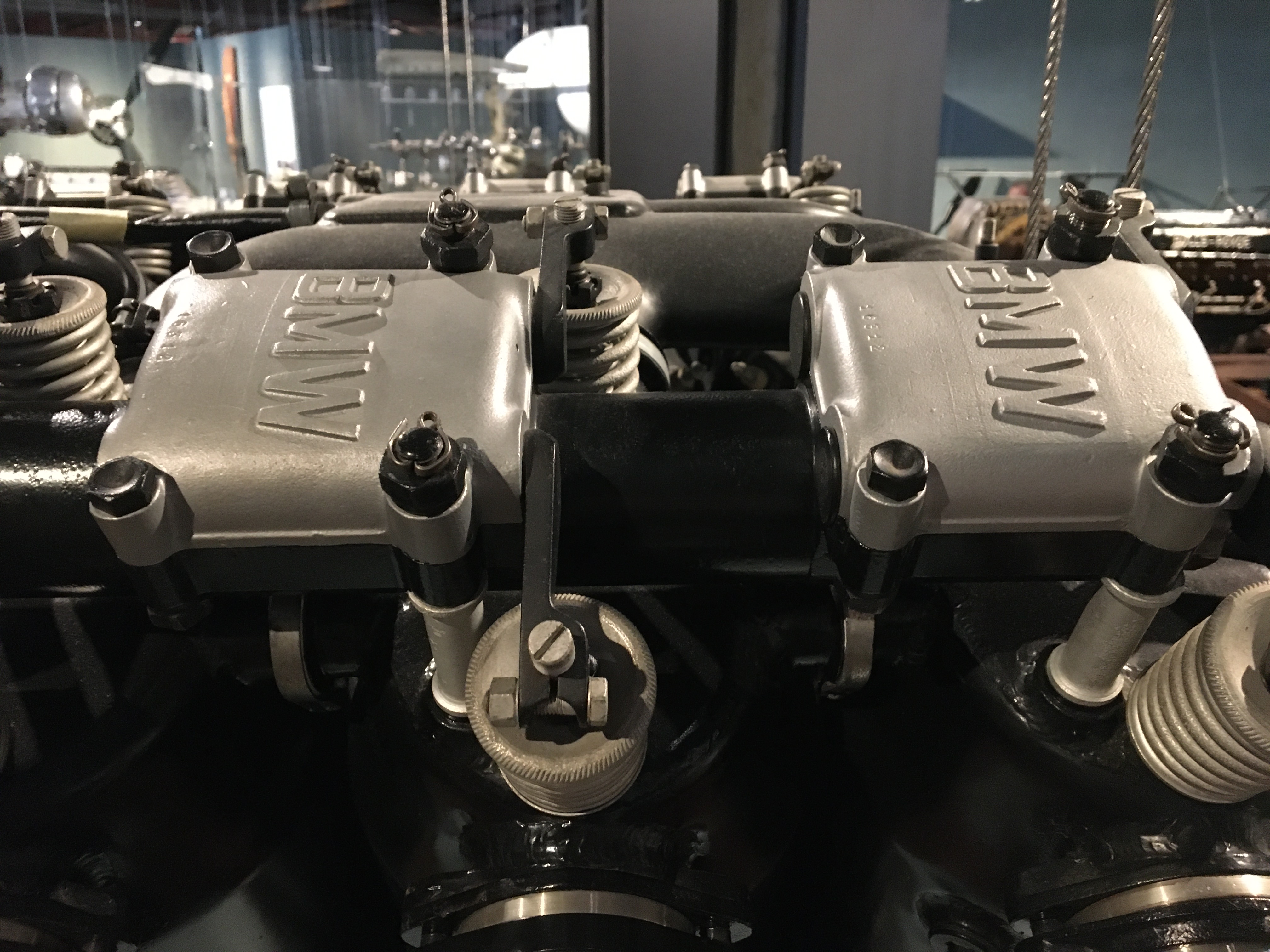 ;Kawasaki Ha9: (long designation:- Army Type 98 850hp Liquid Cooled In-line) licence production in Japan by Kawasaki
;Kawasaki Ha9: (long designation:- Army Type 98 850hp Liquid Cooled In-line) licence production in Japan by Kawasaki

water-cooled
Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant
Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and no ...
V-12 aircraft engine built in Germany in the 1920s. It was one of the most important German aero engines in the years leading up to World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, with thousands built. It was further developed as the BMW VII
__NOTOC__
The BMW VII was a water-cooled twelve-cylinder engine derived from the successful BMW VI. The engine was not as popular as the VI, due in no small part to the Great Depression, and only a small number were built. Experiments with super ...
and BMW IX
The BMW iX is a battery-electric mid-size luxury crossover SUV manufactured and marketed by the German automobile manufacturer BMW. It was unveiled in concept form named Vision iNext at the 2018 Paris Motor Show, and then as fully production-rea ...
, although these saw considerably less use. It was also produced in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
as the M-17 and Japan as the Kawasaki Ha-9.
Design and development
The BMW VI was the first twelve-cylinder engine built by the BMW. It essentially consisted of twocylinder bank
The engine configuration describes the fundamental operating principles by which internal combustion engines are categorized.
Piston engines are often categorized by their cylinder layout, valves and camshafts. Wankel engines are often categorize ...
s from the six-cylinder BMW IV
The BMW IV was a six-cylinder, water-cooled inline aircraft engine built in Germany in the 1920s. Power was in the 180 kW (250 hp) range.
World record
On 17 June 1919 Franz Zeno Diemer flew a DFW F37, powered by a BMW IV engine to ...
bolted to a common cast aluminium crankcase at a 60-degree included angle between the cylinder banks. Series production commenced in 1926 after type approval had been granted. From 1930 on, after 1000 engines of the BMW VI type had already been delivered, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
was again permitted to construct military aircraft. The sudden additional demand resulted in the production figures increasing rapidly. In 1933 the BMW VI was used for BMW's first experiments with direct fuel injection.
The BMW VI was the chosen source of power for numerous record-breaking and long-distance flights, including an east-to-west crossing of the Atlantic in 1930 and a round-the world flight in 1932, both by Wolfgang von Gronau
Hans Wolfgang von Gronau (25 February 1893 - 17 March 1977) was a German aviation pioneer.
Biography
Wolfgang von Gronau was born in Berlin in a family hailing from the ancient dynasty of the House of Berg. He was the son of artillery General Han ...
in an open Dornier Wal flying boat powered by two BMW VI engines.
The BMW VI was put to unusual use as a power unit for the " Rail Zeppelin" high-speed railcar.
Many versions of the BMW VI engine were developed, and it was built under license in Japan and the Soviet Union. This was further evidence of the reliability of an engine with which BMW made a fundamental contribution to the build-up of German air transport. At least 9,200 were built between 1926 and 1938. The engine was license-built in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
under the supervision of Mikulin, who then further developed it as the M-17. More license built engines were produced by Kawasaki Heavy Industries
(or simply Kawasaki) is a Japanese public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, heavy equipment, aerospace and defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headquartered in Chūō, Kobe and Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is ...
in Japan as the Kawasaki Ha9 (long designation:- Army Type 98 850hp Liquid Cooled In-line).
Variants
5.5, 6 or 7.3 denotes compression ratio. No additional letter denotes BMW carburetor and direct-drive propeller (7.3), u denotes a propeller reduction gear (7.3u), z denotes Zenith carburetor (7.3z), zu denotes Zenith carburetor and propeller reduction gear (7.3zu). ;BMW VI 5.5
: Compression ratio 5.5:1, at up to 1600 rpm at sea level
;BMW VI 6.0
: Compression ratio 6:1, at up to 1650 rpm at sea level,
;BMW VI 5.5
: Compression ratio 5.5:1, at up to 1600 rpm at sea level
;BMW VI 6.0
: Compression ratio 6:1, at up to 1650 rpm at sea level, 80 Octane
An octane rating, or octane number, is a standard measure of a fuel's ability to withstand compression in an internal combustion engine without detonating. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonat ...
fuel
;BMW VI 7.3
: Compression ratio 7.3:1 at up to 1700 rpm at sea level, 87 Octane fuel
 ;
;Mikulin M-17
The Mikulin M-17 was a Soviet-licensed copy of the German BMW VI V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft piston engine, further developed by Alexander Mikulin and used by Soviet aircraft and tanks during World War II. Production began in 1930 and continue ...
: Licence production in the USSR
 ;Kawasaki Ha9: (long designation:- Army Type 98 850hp Liquid Cooled In-line) licence production in Japan by Kawasaki
;Kawasaki Ha9: (long designation:- Army Type 98 850hp Liquid Cooled In-line) licence production in Japan by Kawasaki
Applications
* Albatros L 77v * Arado Ar 64 *Arado Ar 65
The Arado Ar 65 was the single-seat biplane fighter successor to the Ar 64. Both looked very similar. The only major difference was the use of a 12-cylinder inline engine versus the Ar 64's radial. The wingspan was also increased.
The Ar 65 ...
* Arado Ar 68
The Arado Ar 68 was a German single-seat biplane fighter developed in the mid-1930s. It was among the first fighters produced when Germany abandoned the restrictions of the Treaty of Versailles and began rearming.
Design and development
Designe ...
* Arado SSD I __NOTOC__
The Arado SSD I was a biplane fighter seaplane developed in Germany in 1930, intended to be launched from catapults on warships. This was an all-new design from Walter Rethel, sharing nothing with his other fighter designs for Arado ...
* Dornier Do 10
The Dornier Do 10, originally designated Dornier Do C4, was the name given by the '' Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM) of a pre-World War II German aircraft.
It was a two-seat parasol-wing monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft co ...
* Dornier Do 14
* Dornier Do 17
The Dornier Do 17 is a twin-engined light bomber produced by Dornier Flugzeugwerke for the German Luftwaffe during World War II. Designed in the early 1930s as a '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") intended to be fast enough to outrun opposing a ...
* Focke-Wulf Fw 42
The Focke-Wulf Fw 42 was a design for a twin-engined medium bomber, of canard configuration, that was designed by Focke-Wulf Flugzeugbau AG in Germany in the early 1930s. Several air forces expressed interest in the aircraft. However, despite ...
* Heinkel He 45
* Heinkel He 51
The Heinkel He 51 was a German single-seat biplane which was produced in a number of different versions. It was initially developed as a fighter; a seaplane variant and a ground-attack version were also developed. It was a development of th ...
* Heinkel He 59
The Heinkel He 59 was a twin-engined German biplane designed in 1930, resulting from a requirement for a torpedo bomber and reconnaissance aircraft able to operate on wheeled landing gear or twin-floats.
Development
In 1930, Ernst Heinkel bega ...
* Heinkel He 60
The Heinkel He 60 was a German single-engined biplane reconnaissance seaplane designed to be catapulted from ''Kriegsmarine'' (German navy) warships of the 1930s.
Development and design
The Heinkel He 60 was designed by Heinkel engineer Reinh ...
* Heinkel He 70
The Heinkel He 70 ''Blitz'' ("lightning") was a German mail plane and fast passenger monoplane aircraft of the 1930s designed by Heinkel Flugzeugwerke, which was later used as a bomber and for aerial reconnaissance. It had a brief commercial car ...
* Heinkel He 111
* Junkers F.24ko
* Kawasaki Type 92
* Kawasaki Ki-10
The was the last biplane fighter used by the Imperial Japanese Army, entering service in 1935. Built by Kawasaki Kōkūki Kōgyō K.K. for the Imperial Japanese Army, it saw combat service in Manchukuo and in North China during the early stage ...
* Messerschmitt M.20
* Polikarpov R-5
The Polikarpov R-5 (russian: Р-5) was a Soviet reconnaissance bomber aircraft of the 1930s. It was the standard light bomber and reconnaissance aircraft of the Soviet Air Force for much of the 1930s, while also being used heavily as a civilian l ...
prototype
* Schienenzeppelin
The () or rail zeppelin was an experimental railcar which resembled a Zeppelin airship in appearance. It was designed and developed by the German aircraft engineer Franz Kruckenberg in 1929. Propulsion was by means of a pusher propeller locate ...
* Tupolev TB-3
The Tupolev TB-3 (russian: Тяжёлый Бомбардировщик, Tyazhyolyy Bombardirovshchik, Heavy Bomber, civilian designation ANT-6) was a monoplane heavy bomber deployed by the Soviet Air Force in the 1930s and used during the early ...
Specifications (BMW VI 7.3z )

See also
References
Further reading
* {{Japanese Imperial Army aeroengines BMW aircraft engines 1920s aircraft piston engines