Kastina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Qastina ( ar, قسطينة) was a Palestinian village, located 38 kilometers northeast of
156
Also noted it in the Gaza district In 1882, the PEF's '' Survey of Western Palestine'' described Qastina as a village laid out in a northwest–southeast direction on flat ground. It had
9
/ref> increasing in the 1931 census when it had an all-Muslim population of 593 in 147 houses.Mills, 1932, p
5
/ref> The villagers had a
88
/ref> while 37 dunams were built-up, urban, land.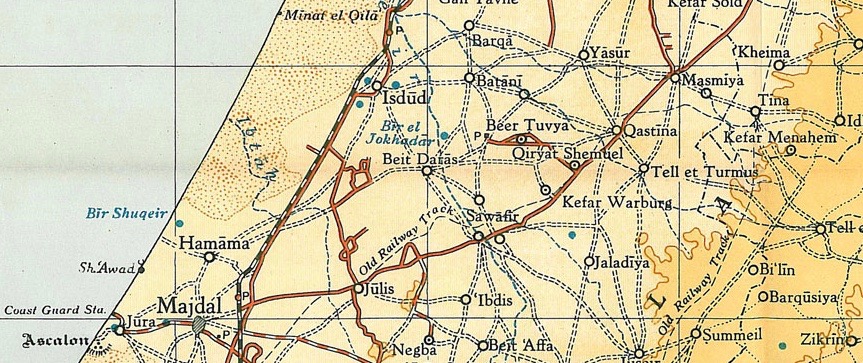
176
/ref> A preparatory order for the conquest of Qastina and other neighbouring villages ( Masmiya al Kabira, Masmiya al Saghira,
436
/ref> On 9 July 1948, the village and its over 147 houses were completely destroyed by
Welcome To QastinaQastina
Zochrot *Survey of Western Palestine, Map 16
IAAWikimedia commons
from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center {{Palestinian Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War District of Gaza Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
Gaza City
Gaza (;''The New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (1998), , p. 761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory in Palestine, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza...". ar, غَزَّة ', ), also referred to as Gaza City, i ...
. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
.
Location
Qastina was situated on an elevated spot in a generally flat area on the coastal plain, on the highway between al-Majdal and theJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
-Jaffa
Jaffa, in Hebrew Yafo ( he, יָפוֹ, ) and in Arabic Yafa ( ar, يَافَا) and also called Japho or Joppa, the southern and oldest part of Tel Aviv-Yafo, is an ancient port city in Israel. Jaffa is known for its association with the b ...
highway. A British military camp, Beer Tuvia, was 3 km. southwest of the village.Khalidi, 1992, pp. 130-131
History
Ottoman period
Qastina was incorporated into theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in 1517 with the rest of Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, and by the 1596 tax records, it was a village in the ''nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( ar, , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division w ...
'' (subdistrict) of Gaza under the '' liwa''' (district) of Gaza, with a population of 55 households and 15 bachelors, an estimated 385 persons. All the villagers were Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. They paid a fixed tax rate of 33,3% on a number of crops, including wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
and sesame, and fruits, as well as goats, beehives and vineyards; a total of 13,100 akçe
The ''akçe'' or ''akça'' (also spelled ''akche'', ''akcheh''; ota, آقچه; ) refers to a silver coin which was the chief monetary unit of the Ottoman Empire. The word itself evolved from the word "silver or silver money", this word is deri ...
. 5/6 of the revenue went to a Muslim charitable endowment.
The Syrian Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
teacher and traveller Mustafa al-Bakri al-Siddiqi (1688-1748/9) reported travelling through the village in the first half of the eighteenth century, on his way to al-Masmiyya al-Kabira
Al-Masmiyya al-Kabira ( ar, المسمية الكبيرة) was a Palestinian people, Palestinian village in the Gaza Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine, Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza City, Gaza. With a land area of 20,687 dunams, the ...
.
In 1838, Edward Robinson saw ''el-Kustineh'' located northwest of Tell es-Safi, where he was staying, and noted it as a Muslim village located in the Gaza district.
In 1863, the French explorer Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Mino ...
visited the village, called ''Kasthineh''. He found it had four hundred inhabitants. Near the mouth of a well were the remains of an antique gray-white marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the ...
column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
, while two palm trees and three acacia mimosas shaded the cemetery.
An Ottoman village list of about 1870 showed that Qastina had 152 houses and a population of 469, though the population count included men only.Socin, 1879, p156
Also noted it in the Gaza district In 1882, the PEF's '' Survey of Western Palestine'' described Qastina as a village laid out in a northwest–southeast direction on flat ground. It had
adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of e ...
brick structures, a well, and gardens.
British Mandate period
In the1922 census of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922.
The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The divisi ...
conducted by the British Mandate authorities, the village had a population of 406 inhabitants, all Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s,Barron, 1923, Table V, Sub-district of Gaza, p9
/ref> increasing in the 1931 census when it had an all-Muslim population of 593 in 147 houses.Mills, 1932, p
5
/ref> The villagers had a
mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
, and in 1936 an elementary school was started, which was shared with the neighbouring village of Tall al-Turmus. By the mid-1940s the school had 161 students.
In 1939 Kfar Warburg
Kfar Warburg ( he, כְּפַר וַרְבּוּרְג, ''lit.'' Warburg Village) is a large moshav in south-central Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi with 98 farms covering an area of 6,000 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia ...
was established on what was traditionally village land, 3 km southwest of the village site.Khalidi, 1992, p. 131
By the 1945 statistics the population was 890, all Muslims, with a total of 12,019 dunams of land. The villagers lived mostly of agriculture. In addition, villagers raised animals and poultry, and worked in the British military camp (Beer Tuvia) nearby.
In 1944–45 a total of 235 dunums was used for citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering plant, flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as Orange (fruit), oranges, Lemon, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and lim ...
and banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
s, 7,317 dunums used for cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
s, 770 dunums were irrigated or used for orchards,Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p88
/ref> while 37 dunams were built-up, urban, land.

1948 war
Qastina was in the territory allotted to the Arab state under the 1947UN Partition Plan
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Re ...
. Upon Israel's declaration of independence on 15 May 1948, the armies of neighbouring Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
states invaded, prompting fresh evacuations of civilians fearful of being caught up in the fighting. The women and children of Qastina were sent away to the village of Tell es-Safi by the menfolk at this time, but they returned after discovering there was insufficient water in the host village to meet the newcomers' needs.Morris, 2004, p176
/ref> A preparatory order for the conquest of Qastina and other neighbouring villages ( Masmiya al Kabira, Masmiya al Saghira,
al Tina
Al-Tina, or Khirbet et-Tineh was a Palestinian people, Palestinian Arab village in the Ramle Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine, Ramle Subdistrict of Mandatory Palestine. The village was located between the Shfela and southern Israeli coastal plain ...
and Tall al Turmus) was drafted by the Giv'ati Brigade
The 84th "Givati" Brigade ( he, חֲטִיבַת גִּבְעָתִי, , "Hill Brigade" or "Highland Brigade") is an Israel Defense Forces infantry brigade. Until 2005, the Brigade used to be stationed within the Gaza Strip and primarily per ...
's 51st Battalion and produced on 29 June 1948. According to Benny Morris
Benny Morris ( he, בני מוריס; born 8 December 1948) is an Israeli historian. He was a professor of history in the Middle East Studies department of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in the city of Beersheba, Israel. He is a member of t ...
, the document recommended "the 'liquidation' (''hisul'') of the two Masmiya villages and 'burning' ('' bi'ur'') the rest."Morris, 2004, p436
/ref> On 9 July 1948, the village and its over 147 houses were completely destroyed by
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
i forces after its inhabitants fled an assault by the Givati Brigade
The 84th "Givati" Brigade ( he, חֲטִיבַת גִּבְעָתִי, , "Hill Brigade" or "Highland Brigade") is an Israel Defense Forces infantry brigade. Until 2005, the Brigade used to be stationed within the Gaza Strip and primarily perf ...
in Operation An-Far. Qastina was used as a rallying point by the IDF seventh Battalion of the 8th Armored Brigade after the failed attack on Iraq al-Manshiyya
Iraq al-Manshiyya ( ar, عراق المنشية) was a Palestinian Arab village located 32 km northeast of Gaza City. The village contained two mosques and a shrine for Shaykh Ahmad al-Arayni. It was depopulated after the 1948 Arab-Israeli Wa ...
in part of the Israeli drive to open a route to the Negev during Operation Yoav.
Israel after 1948 war
In early 1949Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
relief workers reported that many those living in tents in what became Maghazi refugee camp had come from Qastina.Gallagher, Nancy (2007) ‘’Quakers in the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The Dilemmas of NGO Humanitarian Activism’’ The American University in Cairo Press. p 75
Following the war the area was incorporated into the State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and four villages were later established on the lands of Qastina; Arugot
Arugot ( he, עֲרוּגוֹת, , garden terraces or beds), is a moshav in southern Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In its population was .
History
The moshav was founded i ...
and Kfar Ahim
Kfar Ahim ( he, כְּפַר אַחִים, ''lit.'' Village of Brothers) is a moshav in south-central Israel. Located near Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In it had a population of .
History
The m ...
were founded in 1949 after the village had been destroyed. They were followed by Avigdor
Avigdor ( he, אֲבִיגְדוֹר) a small moshav in southern Israel. Located south of Kiryat Malakhi and 11 km north of Kiryat Gat and covering 3.75 km², it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In its pop ...
in 1950 and Kiryat Malakhi in 1951. Be'er Tuvia
Be'er Tuvia ( he, בְּאֵר טוֹבִיָּה, ''Be'er Toviya'', "Tuvia's Well") is a moshav in the Southern District of Israel. Located near the city of Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In its ...
, which was also known by the name Qastina after its establishment in 1887, lies adjacent.
In 1992, Walid Khalidi notes of Qastina that: "All that remains is the debris of houses strewn across the site. The research team investigating the current status of the depopulated villages visited the site and found it overgrown with bushes and tall grasses that were about 2m high."Nowadays, ''Qastina'' is the popular name for
Malakhi Junction
The Malakhi Junction, also known as Qastina ( he, קסטינה) for the Arab village which once stood there, is a major road junction in Israel, between Highway 40 (Israel), Highway 40 and Highway 3 (Israel), 3. It is located on the 37th kilometer ...
.
See also
* Depopulated Palestinian locations in Israel *RAF Qastina
Qastina ( ar, قسطينة) was a Palestinian village, located 38 kilometers northeast of Gaza City. It was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
Location
Qastina was situated on an elevated spot in a generally flat area on the coastal ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Welcome To Qastina
Zochrot *Survey of Western Palestine, Map 16
IAA
from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center {{Palestinian Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War District of Gaza Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War