Kappa-carbides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
κ-Carbides are a special class of carbide structures. They are most known for appearing in steels containing manganese and aluminium where they have the molecular formula .
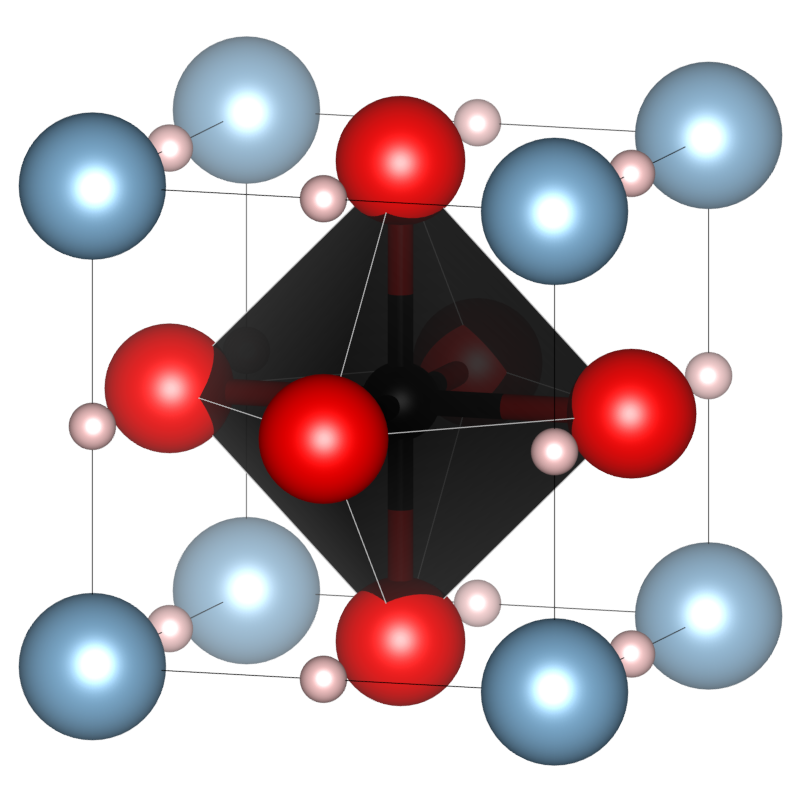
 κ-Carbides crystallise in the perovskite structure type with the space group ''Pm3m'' (Nr. 221). This structure was, inter alia, elucidated with XRD-measurements on
κ-Carbides crystallise in the perovskite structure type with the space group ''Pm3m'' (Nr. 221). This structure was, inter alia, elucidated with XRD-measurements on

 κ-carbides are typically found as precipitates in high-performance steels. A common example is the TRIPLEX
κ-carbides are typically found as precipitates in high-performance steels. A common example is the TRIPLEX
κ Carbide in Steels] (Phase Transformations & Complex Properties Research Group, University of Cambridge) Carbides
Properties
Structure
 κ-Carbides crystallise in the perovskite structure type with the space group ''Pm3m'' (Nr. 221). This structure was, inter alia, elucidated with XRD-measurements on
κ-Carbides crystallise in the perovskite structure type with the space group ''Pm3m'' (Nr. 221). This structure was, inter alia, elucidated with XRD-measurements on steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
alloys containing κ-carbide precipitates but also on single crystals of manganese-κ-carbides with a molecular formula of Mn3.1Al0.9C and a lattice parameter of ''a=3.87Å''. In steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
alloys where diverse arrangements of the atoms are possible, a considerable effect of the short range ordering, e.g. of iron and manganese on the microscopic properties of the alloy, has been observed. This is especially important for the role as hydrogen-traps in steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
s.
Composition
A first glance at the composition of a steel alloy is achieved by analysing its surface with EDX-technique. Depending on the content of the alloying elements of thesteel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
, different types of κ-carbides can form. They occur in both ferritic (α-Fe) and austenitic (γ-Fe) steels. Typical alloying elements are iron, manganese, aluminium, carbon, and silicon.
Magnetism
SQUID
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting t ...
measurements on polycrystalline Mn3.1Al0.9C revealed a soft ferromagnetic behaviour of this κ-carbide with a Curie temperature of 295±13 K, a remanent
Remanence or remanent magnetization or residual magnetism is the magnetization left behind in a ferromagnetic material (such as iron) after an external magnetic field is removed. Colloquially, when a magnet is "magnetized", it has remanence. Th ...
magnetic moment of 3.22 ''μB'' and a coercive field of 1.9 mT. DFT-simulations confirmed these findings and indicated that other κ-carbides behave similarly.
Occurrence
 κ-carbides are typically found as precipitates in high-performance steels. A common example is the TRIPLEX
κ-carbides are typically found as precipitates in high-performance steels. A common example is the TRIPLEX steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
with the generic composition FexMnyAlzC containing 18-28 % manganese, 9-12 % aluminium and 0.7-1.2 % carbon (in mass %). It is a high-strength, low- density steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
consisting of austenitic γ– solid solution, nano size κ-carbides and α– ferrite. Other similar steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
s are known for their high ductility. κ-carbides are usually formed from areas enriched in carbon through spinodal decomposition and are key determinants of the properties of these steels. The low density is e.g. obtained after a hot rolling
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is simil ...
post-process. Upon cooling, different domains of austenite and ferrite are formed and κ-carbides form at the boundaries of these domains. Continuing the cooling process leads to a phase transition of austenite to ferrite and the κ-carbides are released as a result of an eutectoid transformation in form of a precipitate.
The κ-carbides can have an additional strengthening effect on steels because they can function as a hydrogen trap to counteract hydrogen embrittlement. Ab-initio
''Ab initio'' ( ) is a Latin term meaning "from the beginning" and is derived from the Latin ''ab'' ("from") + ''initio'', ablative singular of ''initium'' ("beginning").
Etymology
Circa 1600, from Latin, literally "from the beginning", from ab ...
DFT-simulations have shown that hydrogen can occupy the same site as carbon in the κ-carbide precipitates or an initially empty interstitial lattice site. Hereby, it was found that an increased Mn content enhances the H-trapping by attractive short-range interactions. The aforementioned short-range ordering of Fe and Mn in the κ-carbide has a significant influence on the strength of this effect. This behaviour can be used as an additional method to cope with hydrogen embrittlement which is normally prevented by simply minimising the contact of metal and hydrogen.
See also
* Contemporary steel *Carbon steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
* Alloy steels
References
{{reflistExternal links
κ Carbide in Steels] (Phase Transformations & Complex Properties Research Group, University of Cambridge) Carbides