Kansas () is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the
Midwestern
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
. Its
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
is
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
, and its largest city is
Wichita. Kansas is a
landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
state bordered by
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
to the north;
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
to the east;
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
to the south; and
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
to the west. Kansas is named after the
Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
, which in turn was named after the
Kansa Native Americans who lived along its banks. The
tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English language, English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in p ...
's name (natively ') is often said to mean "people of the (south) wind" although this was probably not the term's original meaning. For thousands of years, what is now Kansas was home to numerous and diverse
Native American tribes. Tribes in the eastern part of the state generally lived in villages along the river valleys. Tribes in the western part of the state were semi-nomadic and hunted large herds of
bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
.
The first Euro-American settlement in Kansas occurred in 1827 at
Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., an ...
. The pace of settlement accelerated in the 1850s, in the midst of political wars over the
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slaveŌĆösomeone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
debate. When it was officially opened to settlement by the U.S. government in 1854 with the
KansasŌĆōNebraska Act
The KansasŌĆōNebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
, abolitionist
Free-Staters from
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
and pro-slavery settlers from neighboring Missouri rushed to the territory to determine whether Kansas would become a
free state or a slave state. Thus, the area was a hotbed of violence and chaos in its early days as these forces collided, and was known as
Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the ...
. The abolitionists prevailed, and on January 29, 1861, Kansas entered the
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
as a free state, hence the unofficial nickname "The Free State".
By 2015, Kansas was one of the most productive
agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
states, producing high yields of
wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
,
corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, ma├Łz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
,
sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
, and
soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu an ...
s. Kansas, which has an area of is the
15th-largest state by area and is the
36th most-populous of the 50 states, with a population of 2,940,865 according to the 2020 census. Residents of Kansas are called ''Kansans''.
Mount Sunflower
Mount Sunflower, although not a true mountain, is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Kansas. At , it is above the state's topographic low point, which lies on the opposite side of the state. Located in Wallace County, it is less tha ...
is Kansas's highest point at .
Etymology
The name ''Kansas'' derives from the
Algonquian term, ''Akansa'', for the
Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Ohi ...
people. These were a
Dhegiha Siouan
The Dhegihan languages are a group of Siouan languages that include Kansa language, KansaŌĆōOsage language, Osage, OmahaŌĆōPonca language, OmahaŌĆōPonca, and Quapaw language, Quapaw. Their historical region included parts of the Ohio and Mississi ...
-speaking people who settled in Arkansas around the 13th century. The stem -''kansa'' is named after the
Kaw people
The Kaw Nation (or Kanza or Kansa) is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Oklahoma and parts of Kansas. It comes from the central Midwestern United States. It has also been called the "People of the South wind", , also known as the ''Kansa'', a federally recognized Native American tribe.
History
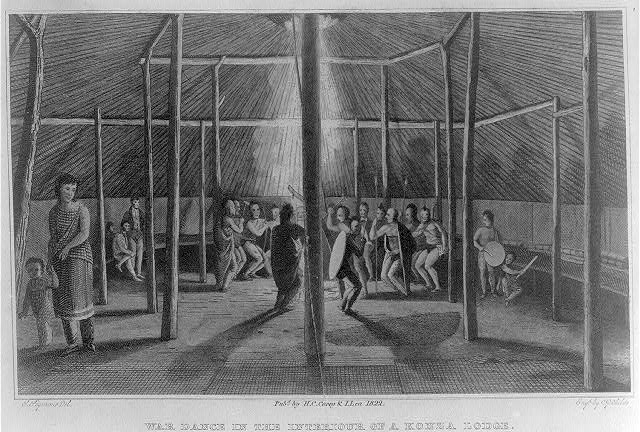

Before
European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
, Kansas was occupied by the
Caddoan
The Caddoan languages are a family of languages native to the Great Plains spoken by tribal groups of the central United States, from present-day North Dakota south to Oklahoma. All Caddoan languages are critically endangered, as the number of sp ...
Wichita and later the
Siouan
Siouan or SiouanŌĆōCatawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
Kaw people
The Kaw Nation (or Kanza or Kansa) is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Oklahoma and parts of Kansas. It comes from the central Midwestern United States. It has also been called the "People of the South wind", . The first European to set foot in present-day Kansas was the Spanish
conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
Francisco V├Īzquez de Coronado
Francisco V├Īzquez de Coronado y Luj├Īn (; 1510 ŌĆō 22 September 1554) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer who led a large expedition from what is now Mexico to present-day Kansas through parts of the southwestern United States between 15 ...
, who explored the area in 1541.
Between 1763 and 1803 the territory of Kansas was integrated into
Spanish Louisiana
Spanish Louisiana ( es, link=no, la Luisiana) was a governorate and administrative district of the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1762 to 1801 that consisted of a vast territory in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of t ...
. The governor
Luis de Unzaga
Luis de Unzaga y Am├®zaga (1717ŌĆō1793), also known as Louis Unzaga y Amez├®ga le Conciliateur, Luigi de Unzaga Panizza and Lewis de Onzaga, was governor of Spanish Louisiana from late 1769 to mid-1777, as well as a Captain General of Venezuela ...
'le Conciliateur', during that period, promoted expeditions and good relations with the
Amerindians
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Ame ...
, among the explorers were
Antoine de Marigny
Antoine is a French given name (from the Latin ''Antonius'' meaning 'highly praise-worthy') that is a variant of Danton, Titouan, D'Anton and Antonin.
The name is used in France, Switzerland, Belgium, Canada, West Greenland, Haiti, French Guiana ...
and others who continued trading across the
Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
, especially at its confluence with the
Missouri River, tributaries of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
.
In 1803, most of modern Kansas was
acquired by the United States as part of the
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
. Southwest Kansas, however, was still a part of Spain, Mexico, and the
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, Rep├║blica de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
until the conclusion of the
MexicanŌĆōAmerican War
The MexicanŌĆōAmerican War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
in 1848, when these lands were
ceded to the United States. From 1812 to 1821, Kansas was part of the
Missouri Territory
The Territory of Missouri was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 4, 1812, until August 10, 1821. In 1819, the Territory of Arkansas was created from a portion of its southern area. In 1821, a southeas ...
. The
Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
traversed Kansas from 1821 to 1880, transporting manufactured goods from
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
and silver and furs from
Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , Spanish for 'Holy Faith'; tew, Ogh├Ī P'o'oge, Tewa for 'white shell water place'; tiw, Hulp'├│'ona, label=Tiwa language, Northern Tiwa; nv, Yoot├│, Navajo for 'bead + water place') is the capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico. ...
. Wagon ruts from the trail are still visible in the prairie today.
In 1827,
Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., an ...
became the first permanent settlement of white Americans in the future state. The
KansasŌĆōNebraska Act
The KansasŌĆōNebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
became law on May 30, 1854, establishing
Nebraska Territory
The Territory of Nebraska was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until March 1, 1867, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Nebraska. The Nebraska ...
and
Kansas Territory
The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Slave and ...
, and opening the area to broader settlement by whites.
Kansas Territory
The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Slave and ...
stretched all the way to the Continental Divide and included the sites of present-day
Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
,
Colorado Springs
Colorado Springs is a home rule municipality in, and the county seat of, El Paso County, Colorado, United States. It is the largest city in El Paso County, with a population of 478,961 at the 2020 United States Census, a 15.02% increase since ...
, and
Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
.

The first non-military settlement of Euro-Americans in Kansas Territory consisted of
abolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
from
and other
Free-Staters who founded the town of Lawrence and attempted to stop the spread of slavery from neighboring Missouri.
Missouri and
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
continually sent settlers into Kansas Territory along its eastern border to sway votes in favor of slavery prior to Kansas statehood elections. Directly presaging the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 ŌĆō May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
these forces collided, entering into skirmishes and guerrilla conflicts that earned the territory the nickname
Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the ...
. These included
John Brown John Brown most often refers to:
*John Brown (abolitionist) (1800ŌĆō1859), American who led an anti-slavery raid in Harpers Ferry, Virginia in 1859
John Brown or Johnny Brown may also refer to:
Academia
* John Brown (educator) (1763ŌĆō1842), Ir ...
's
Pottawatomie massacre of 1856.
Kansas was
admitted to the Union
''Admitted'' is a 2020 Indian Hindi-language docudrama film directed by Chandigarh-based director Ojaswwee Sharma. The film is about Dhananjay Chauhan, the first transgender student at Panjab University. The role of Dhananjay Chauhan has been p ...
as a free state on January 29, 1861, making it the 34th state to join the United States. By that time, the violence in Kansas had largely subsided, but during the Civil War, on August 21, 1863,
William Quantrill
William Clarke Quantrill (July 31, 1837 ŌĆō June 6, 1865) was a Confederate guerrilla leader during the American Civil War.
Having endured a tempestuous childhood before later becoming a schoolteacher, Quantrill joined a group of bandits who ...
led several hundred men on a raid into
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
, destroying much of the city and killing nearly 200 people. He was roundly condemned by both the conventional
Confederate military and the partisan rangers commissioned by the
Missouri legislature
The Missouri General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Missouri. The bicameral General Assembly is composed of a 34-member Senate and a 163-member House of Representatives. Members of both houses of the General Assembly are s ...
. His application to that body for a commission was flatly rejected due to his pre-war criminal record.
After the Civil War, many veterans constructed homesteads in Kansas. Many
African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
also looked to Kansas as the land of "
John Brown John Brown most often refers to:
*John Brown (abolitionist) (1800ŌĆō1859), American who led an anti-slavery raid in Harpers Ferry, Virginia in 1859
John Brown or Johnny Brown may also refer to:
Academia
* John Brown (educator) (1763ŌĆō1842), Ir ...
" and, led by
freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
like
Benjamin "Pap" Singleton
Benjamin "Pap" Singleton (1809 ŌĆō February 17, 1900) was an American activist and businessman best known for his role in establishing African American settlements in Kansas. A former slave from Tennessee who escaped to freedom in Ontario, Canada ...
, began establishing black colonies in the state. Leaving southern states in the late 1870s because of increasing discrimination, they became known as
Exodusters
Exodusters was a name given to African Americans who Human migration, migrated from U.S. state, states along the Mississippi River to Kansas in the late nineteenth century, as part of the Exoduster Movement or Exodus of 1879. It was the first Hum ...
.
At the same time, the
Chisholm Trail
The Chisholm Trail was a trail used in the post-Civil War era to drive cattle overland from ranches in Texas to Kansas railheads. The trail was established by Black Beaver, a Lenape guide and rancher, and his friend Jesse Chisholm, a Cheroke ...
was opened and the
Wild West
The American frontier, also known as the Old West or the Wild West, encompasses the geography, history, folklore, and culture associated with the forward wave of American expansion in mainland North America that began with European colonial ...
-era commenced in Kansas.
Wild Bill Hickok
James Butler Hickok (May 27, 1837August 2, 1876), better known as "Wild Bill" Hickok, was a folk hero of the American Old West known for his life on the frontier as a soldier, scout, lawman, gambler, showman, and actor, and for his involvement ...
was a deputy marshal at
Fort Riley
Fort Riley is a United States Army installation located in North Central Kansas, on the Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, between Junction City and Manhattan. The Fort Riley Military Reservation covers 101,733 acres (41,170 ha) in Gear ...
and a marshal at
Hays and
Abilene.
Dodge City
Dodge City is the county seat of Ford County, Kansas, United States, named after nearby Fort Dodge. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 27,788. The city is famous in American culture for its history as a wild frontier town ...
was another wild cowboy town, and both
Bat Masterson
Bartholemew William Barclay "Bat" Masterson (November 26, 1853 ŌĆō October 25, 1921) was a U.S. Army scout, lawman, professional gambler, and journalist known for his exploits in the 19th and early 20th-century American Old West. He was born to ...
and
Wyatt Earp
Wyatt Berry Stapp Earp (March 19, 1848 ŌĆō January 13, 1929) was an American lawman and gambler in the American West, including Dodge City, Deadwood, and Tombstone. Earp took part in the famous gunfight at the O.K. Corral, during which law ...
worked as lawmen in the town. In one year alone, eight million head of cattle from Texas boarded trains in Dodge City bound for the East, earning Dodge the nickname "Queen of the Cowtowns".
In response to demands of
Methodists and other
evangelical Protestants
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "born again", in which an individual experi ...
, in 1881 Kansas became the first U.S. state to adopt a constitutional amendment
prohibiting all
alcoholic beverages
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The cons ...
, which was repealed in 1948.
In 1922, suffragist
Ella Uphay Mowry
Ella Uphay (Herod) Mowry (July 1865 ŌĆō August 2, 1923), also known as Mrs. W.D. Mowry, was an American educator, suffragist, and women's rights activist. A member of the Republican Party, she became the first female gubernatorial candidate in K ...
became the first female gubernatorial candidate in the state when she ran as "Mrs. W.D. Mowry." She later stated that, "Someone had to be the pioneer. I firmly believe that some day a woman will sit in the governor's chair in Kansas."
Geography


Kansas is bordered by
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
to the north;
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
to the east;
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
to the south; and
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
to the west. The state is divided into
105 counties with
628 cities, with its largest county by area being
Butler County. Kansas is located
equidistant
A point is said to be equidistant from a set of objects if the distances between that point and each object in the set are equal.
In two-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the locus of points equidistant from two given (different) points is the ...
from the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The
geographic center of the 48 contiguous states is in
Smith County near
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, ┘ä┘Åž©┘Æ┘å┘Äž¦┘å, translit=lubn─ün, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
. Until 1989, the
Meades Ranch Triangulation Station
The Meades Ranch Triangulation Station is a survey marker in Osborne County in the state of Kansas in the Midwestern United States. The marker was initially placed in 1891. From 1901, it was the reference location for establishing a system of h ...
in
Osborne County was the geodetic center of North America: the central reference point for all maps of North America. The geographic center of Kansas is in
Barton County.
Geology
Kansas is underlain by a sequence of horizontal to gently westward
dipping sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s. A sequence of
Mississippian,
Pennsylvanian and
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
rocks outcrop in the eastern and southern part of the state. The state's western half has exposures of
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
through Tertiary sediments, the latter derived from the
erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
of the
uplifted
''Uplifted'' is the second studio album by Nigerian singer Flavour N'abania. It was released on July 20, 2010, by Obaino Music and 2nite Entertainment. The album features guest appearances from Jay Dey, Oloye, Stormrex, Waga Gee, Asemstone, M-Jay, ...
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
to the west. These are underlain by older Paleozoic and Mesozoic sediments which correlate well with the outcrops to the east. The state's northeastern corner was subjected to
glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
in the
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
and is covered by
glacial drift
In geology, drift is a name for all sediment (clay, silt, sand, gravel, boulders) transported by a glacier and deposited directly by or from the ice, or by glacial meltwater. Drift is often subdivided into (unsorted and) unstratified drift (glaci ...
and
loess
Loess (, ; from german: L├Čss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits.
Loess is a periglacial or aeolian ...
.
Topography
The western two-thirds of the state, lying in the
great central plain of the United States, has a generally flat or undulating surface, while the eastern third has many hills and forests. The land gradually rises from east to west; its altitude ranges from along the
Verdigris River
The Verdigris River is a tributary of the Arkansas River in southeastern Kansas and northeastern Oklahoma in the United States. It is about long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, ...
at
Coffeyville
Coffeyville is a city in southeastern Montgomery County, Kansas, United States, located along the Verdigris River in the state's southeastern region. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 8,826. Coffeyville is the most popul ...
in
Montgomery County, to at
Mount Sunflower
Mount Sunflower, although not a true mountain, is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Kansas. At , it is above the state's topographic low point, which lies on the opposite side of the state. Located in Wallace County, it is less tha ...
, from the Colorado border, in
Wallace County. It is a common misconception that Kansas is the flattest state in the nationŌĆöin 2003, a tongue-in-cheek study famously declared the state "flatter than a pancake". In fact, Kansas has a maximum topographic relief of , making it the 23rd flattest U.S. state measured by maximum relief.
Rivers

Nearly of the state's northeastern boundary is defined by the
Missouri River. The
Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
(locally known as the Kaw), formed by the junction of the
Smoky Hill and
Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
rivers at appropriately-named
Junction City, joins the Missouri River at
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
, after a course of across the northeastern part of the state.
The
Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
(
pronunciation varies), rising in
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
, flows with a bending course for nearly across the western and southern parts of the state. With its tributaries, (the
Little Arkansas,
Ninnescah, Walnut,
Cow Creek,
Cimarron, Verdigris, and the
Neosho), it forms the southern drainage system of the state.
Kansas's other rivers are the
Saline
Saline may refer to:
* Saline (medicine), a liquid with salt content to match the human body
* Saline water, non-medicinal salt water
* Saline, a historical term (especially US) for a salt works or saltern
Places
* Saline, Calvados, a commune in ...
and Solomon Rivers, tributaries of the Smoky Hill River; the
Big Blue,
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, and
Wakarusa Wakarusa can refer to several things in the United States:
* Wakarusa, Indiana
* Wakarusa, Kansas
* The Wakarusa River, a tributary of the Kansas River
* The Wakarusa War, part of the Bleeding Kansas violence before the American Civil War
* Wakarus ...
, which flow into the Kansas River; and the
Marais des Cygnes, a tributary of the Missouri River. Spring River is located between
Riverton and
Baxter Springs
Baxter Springs is a city in Cherokee County, Kansas, United States, and located along Spring River. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 3,888.
History
For thousands of years, indigenous peoples had lived along the waterwa ...
.
National parks and historic sites
Areas under the protection of the
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
include:
*
Brown v. Board of Education National Historic Site
''Brown v. Board of Education'' National Historical Park was established in Topeka, Kansas, on October 26, 1992, by the United States Congress to commemorate the landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in the case ''Brown v. Board of Educatio ...
in Topeka
*
California National Historic Trail
The California Trail was an emigrant trail of about across the western half of the North American continent from Missouri River towns to what is now the state of California. After it was established, the first half of the California Trail f ...
*
Fort Larned National Historic Site
Fort Larned National Historic Site preserves Fort Larned which operated from 1859 to 1878. It is approximately west of Larned, Kansas, United States.
History
The Camp on Pawnee Fork was established on October 22, 1859 to protect traffic al ...
in
Larned
*
Fort Scott National Historic Site
Fort Scott National Historic Site is a historical area under the control of the United States National Park Service in Bourbon County, Kansas, United States. Named after General Winfield Scott, who achieved renown during the MexicanŌĆōAmerican ...
*
Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail
The Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail is a route across the United States commemorating the Lewis and Clark Expedition of 1804 to 1806. It is part of the National Trails System of the United States. It extends for some from Pittsburgh, Pen ...
*
Nicodemus National Historic Site at
Nicodemus
Nicodemus (; grc-gre, ╬Ø╬╣╬║Žī╬┤╬Ę╬╝╬┐Žé, Nik├│d─ōmos) was a Pharisee and a member of the Sanhedrin mentioned in three places in the Gospel of John:
* He first visits Jesus one night to discuss Jesus' teachings ().
* The second time Nicodem ...
*
Oregon National Historic Trail
The Oregon Trail was a eastŌĆōwest, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
*
Pony Express National Historic Trail
The Pony Express was an American express mail service that used relays of horse-mounted riders. It operated from April 3, 1860, to October 26, 1861, between Missouri and California. It was operated by the Central Overland California and Pik ...
*
Santa Fe National Historic Trail
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a Legend, legendary figure originating in Western Christianity, Western Christian culture who is said to Christmas gift-bringer, bring ...
*
Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve
Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in the Flint Hills region of Kansas, north of Strong City. The preserve protects a nationally significant example of the once vast tallgrass prairie ecosystem. O ...
near
Strong City
Flora and fauna
In Kansas, there are currently 238 species of rare animals and 400 rare plants. Among those include: ''
Boechera laevigata
''Boechera laevigata'' is a species of flowering plant in the mustard family known by the common name smooth rockcress. It is native to many areas of the eastern United States and Canada, where it grows in calcareous rocky woods and bluffs. It is ...
'',
Virginia Rail
The Virginia rail (''Rallus limicola'') is a small waterbird, of the family Rallidae.
These birds remain fairly common despite continuing loss of habitat, but are secretive by nature and more often heard than seen. They are also considered a ga ...
,
Cleft Ledge Cleft Ledge () is a flat-topped ridge long and wide between Shaw Trough and Healy Trough in the Labyrinth of Wright Valley, McMurdo Dry Valleys. The ledge rises to and is 0.3 nautical miles northwest of Hoffman Ledge. The name is descriptive a ...
,
Royal Fern,
Turkey-tangle
''Phyla nodiflora'', the frog fruit, sawtooth fogfruit, or turkey tangle, is a flowering plant in the family Verbenaceae, and is native to the area from northern South America to southern United States. It can be found in tropical areas around th ...
,
Bobolink
The bobolink (''Dolichonyx oryzivorus'') is a small New World blackbird and the only member of the genus ''Dolichonyx''. An old name for this species is the "rice bird", from its tendency to feed on cultivated grains during winter and migration. ...
,
Cave Salamander
A cave salamander is a type of salamander that primarily or exclusively inhabits caves, a group that includes several species. Some of these animals have developed special, even extreme, adaptations to their subterranean environments. Some specie ...
,
Peregrine Falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
, and
Black-footed ferret
The black-footed ferret (''Mustela nigripes''), also known as the American polecatHeptner, V. G. (Vladimir Georgievich); Nasimovich, A. A; Bannikov, Andrei Grigorovich; Hoffmann, Robert S. (2001)''Mammals of the Soviet Union''Volume: v. 2, pt. 1 ...
. Common animal species and grasses include:
Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus ''Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifical ...
s,
Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
,
Lesser Prairie Chicken
The lesser prairie chicken (''Tympanuchus pallidicinctus'') is a species in the grouse family.
Description
It is a medium to large bird, striped white and brown, slightly smaller and paler than its near relative the greater prairie chicken (''T. ...
,
Mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
,
Moles Moles can refer to:
*Moles de Xert, a mountain range in the Baix Maestrat comarca, Valencian Community, Spain
*The Moles (Australian band)
*The Moles, alter ego of Scottish band Simon Dupree and the Big Sound
People
*Abraham Moles, French engineer ...
,
Opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North ...
,
Prairie Dogs
Prairie dogs (genus ''Cynomys'') are herbivorous burrowing ground squirrels native to the grasslands of North America. Within the genus are five species: black-tailed, white-tailed, Gunnison's, Utah, and Mexican prairie dogs. In Mexico, p ...
,
Raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
, ''
Tripsacum dactyloides
''Tripsacum dactyloides'', commonly called eastern gamagrass, or Fakahatchee grass, is a warm-season, sod-forming bunch grass. It is widespread in the Western Hemisphere, native from the eastern United States to northern South America. '',
Prairie Dropseed
''Sporobolus heterolepis'', commonly known as prairie dropseed, is a species of prairie grass native to the tallgrass and mixed grass prairies of central North America from Texas to southern Canada. It is also found further east, to the Atlant ...
,
Indian Grass
''Sorghastrum nutans'', commonly known as either Indiangrass or yellow Indiangrass, is a North American prairie grass found in the central and eastern United States and Canada, especially in the Great Plains and tallgrass prairies.
Description
...
,
Little Bluestem
''Schizachyrium scoparium'', commonly known as little bluestem or beard grass, is a species of North American prairie grass native to most of the contiguous United States (except California, Nevada, and Oregon) as well as a small area north of t ...
,
Switch Grass
''Panicum virgatum'', commonly known as switchgrass, is a perennial warm season bunchgrass native to North America, where it occurs naturally from 55┬░N latitude in Canada southwards into the United States and Mexico. Switchgrass is one of the ...
,
Northern Sea Oats,
Tussock Sedge,
Sideoats Grama
''Bouteloua curtipendula'', commonly known as sideoats grama, is a perennial, short prairie grass that is native throughout the temperate and tropical Western Hemisphere, from Canada south to Argentina.
The species epithet comes from Latin "sh ...
, and
Big Bluestem
''Andropogon gerardi'', commonly known as big bluestem, is a species of tall grass native to much of the Great Plains and grassland regions of central and eastern North America. It is also known as tall bluestem, bluejoint, and turkeyfoot.
Taxon ...
.
Climate
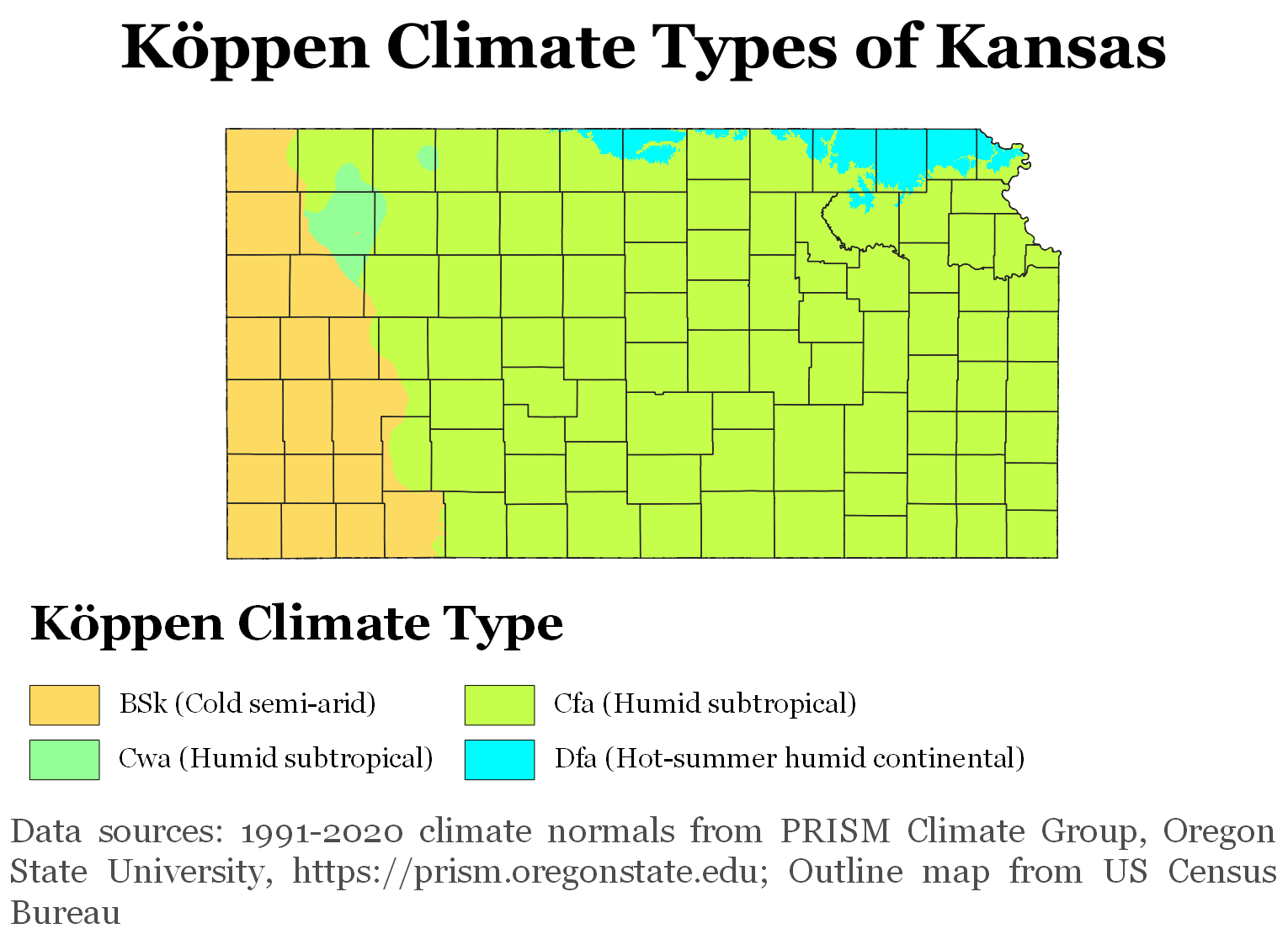


In the
K├Čppen climate classification
The K├Čppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir K├Čppen (1846ŌĆō1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by K├Čppen, notabl ...
, Kansas has three climates: humid continental, semi-arid steppe, and humid subtropical. The eastern two-thirds of the state (especially the northeastern portion) has a
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir K├Čppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
, with cool to cold winters and hot, often humid summers. Most of the precipitation falls during both the summer and the spring.
The western third of the stateŌĆöfrom roughly the
U.S. Route 83
U.S. Route 83 (US 83) is a major northŌĆōsouth United States Numbered Highway that extends in the central United States. Only four other northŌĆōsouth routes are longer: US 1, US 41, US 59, and US 87, while US ...
corridor westwardŌĆöhas a
semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
climate. Summers are hot, often very hot, and generally less humid. Winters are highly changeable between warm and very cold. The western region receives an average of about of precipitation per year.
Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
s in the winter can warm western Kansas all the way into the range.
The south-central and southeastern portions of the state, including the
Wichita area, have a
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25┬░ and 40┬░ ...
with hot and humid summers, milder winters, and more precipitation than elsewhere in Kansas. Some features of all three climates can be found in most of the state, with droughts and changeable weather between dry and humid not uncommon, and both warm and cold spells in the winter.
Temperatures in areas between U.S. Routes 83 and
81, as well as the southwestern portion of the state along and south of
U.S. 50
U.S. Route 50 or U.S. Highway 50 (US 50) is a major eastŌĆōwest route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching from Interstate 80 (I-80) in West Sacramento, California, to Maryland Route 528 (MD 528) in Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlantic O ...
, reach or above on most days of June, July, and August. High humidity added to the high temperatures sends the heat index into life-threatening territory, especially in Wichita, Hutchinson, Kansas, Hutchinson, Salina, Kansas, Salina, Russell, Kansas, Russell,
Hays, and Great Bend, Kansas, Great Bend. Temperatures are often higher in
Dodge City
Dodge City is the county seat of Ford County, Kansas, United States, named after nearby Fort Dodge. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 27,788. The city is famous in American culture for its history as a wild frontier town ...
, Garden City, Kansas, Garden City, and Liberal, Kansas, Liberal, but the heat index in those three cities is usually lower than the actual air temperature.
Although temperatures of or higher are not as common in areas east of U.S. 81, higher humidity and the urban heat island effect lead most summer days to heat indices between and in
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
,
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
, and the Kansas City metropolitan area. Also, combined with humidity between 85 and 95 percent, dangerous heat indices can be experienced at every hour of the day.
Precipitation ranges from about annually in the state's southeast corner to about in the southwest. Snowfall ranges from around in the fringes of the south, to in the far northwest. Frost-free days range from more than 200 days in the south, to 130 days in the northwest. Thus, Kansas is the country's ninth or tenth sunniest state, depending on the source. Western Kansas is as sunny as parts of California and Arizona.
Kansas is prone to severe weather, especially in the spring and the early-summer. Despite the frequent sunshine throughout much of the state, due to its location at a climatic boundary prone to intrusions of multiple air masses, the state is vulnerable to strong and severe thunderstorms. Some of these storms become supercell thunderstorms; these can produce some tornadoes, occasionally those of Enhanced Fujita scale, EF3 strength or higher. Kansas averages more than 50 tornadoes annually.
Severe thunderstorms sometimes drop some very large hail over Kansas as well. Furthermore, these storms can even bring in flash flooding and damaging straight line winds.
According to NOAA, the all-time highest temperature recorded in Kansas is () on July 24, 1936, near Alton, Kansas, Alton in
Osborne County, and the all-time low is on February 13, 1905, near
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, ┘ä┘Åž©┘Æ┘å┘Äž¦┘å, translit=lubn─ün, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
in
Smith County. Alton and Lebanon are approximately apart.
Kansas's record high of ties with North Dakota for the fifth-highest record high in an American state, behind California (), Arizona (), Nevada (), and New Mexico ().
Demographics
The United States Census Bureau estimates that the population of Kansas was 2,913,314 on July 1, 2019, a 2.11% increase since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census and an increase of 58,387, or 2.05%, since 2010.
This includes a natural increase since the last census of 93,899 (246,484 births minus 152,585 deaths) and a decrease due to net migration of 20,742 people out of the state. Immigration to the United States, Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 44,847 people, and migration within the country produced a net loss of 65,589 people.
The population density of Kansas is 52.9 people per square mile. The center of population of Kansas is located in Chase County, Kansas, Chase County, at , approximately north of the community of
Strong City.
The focus on labor-efficient grain-based agricultureŌĆösuch as a large wheat farm that requires only one or a few people with large farm machinery, machinery to operate, rather than a Vegetable farming, vegetable farm that requires many peopleŌĆöis causing the Depopulation of the Great Plains, de-population of rural areas across Kansas.
Ancestry

According to the 2020 United States census, 2021 United States census estimates, the racial makeup of the population was:
* White American, White American, non-Hispanic - 74.7%
* Hispanic or Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino - 12.7%
* Black or African American - 6.2%
* Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander - 0.1%
* Two or more races - 3.3%
* Asian people, Asian - 3.2%
* American Indian and Alaska Native - 1.2%

As of 2004, the population included 149,800 foreign-born (5.5% of the state population). The ten largest reported ancestry groups, which account for nearly 90% of the population, in the state are: German American, German (33.75%), Irish American, Irish (14.4%), English American, English (14.1%), American ancestry, American (7.5%), French American, French (4.4%), Scottish American, Scottish (4.2%), Dutch American, Dutch (2.5%), Swedish American, Swedish (2.4%), Italian American, Italian (1.8%), and Polish American, Polish (1.5%). German descendants are especially present in the northwest and northeast with German immigrants settling and founding towns such as Nortonville, Kansas, Nortonville, Holton, Kansas, Holton, Sabetha, Kansas, Sabetha and Horton, Kansas, Horton. Descendants of English and of white Americans from other states are especially present in the southeast.
Mexicans are present in the southwest and make up nearly half the population in certain counties. Many African Americans in Kansas are descended from the
Exodusters
Exodusters was a name given to African Americans who Human migration, migrated from U.S. state, states along the Mississippi River to Kansas in the late nineteenth century, as part of the Exoduster Movement or Exodus of 1879. It was the first Hum ...
, newly freed blacks who fled the South for land in Kansas following the Civil War.
As of 2011, 35.0% of Kansas's population younger than one year of age belonged to minority groups (i.e., did not have two parents of non-Hispanic white ancestry).

Language
English is the most-spoken language in Kansas, with 91.3% of the population speaking only English at home as of the year 2000. 5.5% speak Spanish, 0.7% speak German, and 0.4% speak Vietnamese.
Religion
The 2014 Pew Religious Landscape Survey showed the religious makeup of adults in Kansas was as follows:
:Christian 76%
::Protestant 57%
:::Evangelical Protestant 31%
:::Mainline Protestant 24 %
:::Black church, Black Protestant 2%
::Catholic 18%
::Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints 1%
::Jehovah's Witness 1%
:Non-Christian faiths 4%
::Jewish < 1%
::Muslim 1%
::Buddhist 1%
::Hindu < 1%
:Other World Religions < 1%
:Other Faiths 2%
:Unaffiliated 20%
::Atheist 2%
::Agnostic 3%
::Nothing in particular 14%
:Don't know < 1%

As of 2010, the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) reported that the Catholic Church has the highest number of adherents in Kansas (at 426,611), followed by the United Methodist Church with 202,989 members, and the Southern Baptist Convention, reporting 99,329 adherents.
Kansas's capital Topeka is sometimes cited as the home of Pentecostalism as it was the site of Charles Fox Parham's Bethel Bible College, where glossolalia was first claimed as the evidence of a spiritual experience referred to as the baptism of the Holy Spirit in 1901. It is also the home of Reverend Charles Sheldon, author of ''In His Steps'', and was the site where the question "What would Jesus do?" originated in a sermon of Sheldon's at Central Congregational Church.
Kansas is the location of the second Baha'i community west of Egypt, when the Baha'i community of Enterprise, KS was started in 1897. From that beginning the Baha'i Faith spread across Kansas.
Topeka is also home of the Westboro Baptist Church, a hate group according to the Southern Poverty Law Center. The church has garnered worldwide media attention for picketing the funerals of U.S. servicemen and women for what church members claim as "necessary to combat the fight for equality for gays and lesbians". They have sometimes successfully raised lawsuits against the city of Topeka.
Settlement
Known as rural flight, the last few decades have been marked by a migratory pattern out of the countryside into cities. Out of all the cities in these Midwestern states, 89% have fewer than 3,000 people, and hundreds of those have fewer than 1,000. In Kansas alone, there are more than 6,000 List of ghost towns in Kansas, ghost towns and dwindling communities, according to one Kansas historian, Daniel C. Fitzgerald. At the same time, some of the communities in Johnson County (metropolitan Kansas City) are among the fastest-growing in the country.
Kansas has 627 Municipal corporation, incorporated cities. By state statute, cities are divided into three classes as determined by the population obtained "by any census of enumeration". A city of the third class has a population of less than 5,000, but cities reaching a population of more than 2,000 may be certified as a city of the second class. The second class is limited to cities with a population of less than 25,000, and upon reaching a population of more than 15,000, they may be certified as a city of the first class. First and second class cities are independent of any Civil township, township and are not included within the township's territory.
Birth data
''Note: Births in table don't add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic and Latino Americans, White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Life expectancy
The residents of Kansas have a life expectancy near the U.S. national average. In 2013, males in Kansas lived an average of 76.6 years compared to a male national average of 76.7 years and females lived an average of 81.0 years compared to a female national average of 81.5 years. Increases in life expectancy between 1980 and 2013 were below the national average for males and near the national average for females. Male life expectancy in Kansas between 1980 and 2014 increased by an average of 5.2 years, compared to a male national average of a 6.7 year increase. Life expectancy for females in Kansas between 1980 and 2014 increased by 4.3 years, compared to a female national average of a 4.0 year increase.
Using 2017ŌĆō2019 data, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation calculated that life expectancy for Kansas counties ranged from 75.8 years for Wyandotte County, Kansas, Wyandotte County to 81.7 years for Johnson County, Kansas, Johnson County. Life expectancy for the state as a whole was 78.5 years.
Life expectancy for the United States as a whole in 2019 was 78.8 years.
Regions
Northeast Kansas


The northeastern portion of the state, extending from the eastern border to
Junction City and from the Nebraska border to south of Johnson County is home to more than 1.5 million people in the Kansas City (Kansas portion), Manhattan, Lawrence, and Topeka metropolitan areas. Overland Park, Kansas, Overland Park, a young city incorporated in 1960, has the largest population and the largest land area in the county. It is home to Johnson County Community College.
Olathe is the county seat and home to Johnson County Executive Airport. The cities of Olathe, Shawnee, Kansas, Shawnee, De Soto, Kansas, De Soto and Gardner, Kansas, Gardner have some of the state's fastest growing populations. The cities of Overland Park, Lenexa, Kansas, Lenexa, Olathe, De Soto, and Gardner are also notable because they lie along the former route of the
Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
. Among cities with at least one thousand residents, Mission Hills, Kansas, Mission Hills has the highest median income in the state.
Several institutions of higher education are located in Northeast Kansas including Baker University (the oldest university in the state, founded in 1858 and affiliated with the United Methodist Church) in Baldwin City, Benedictine College (sponsored by St. Benedict's Abbey and Mount St. Scholastica Monastery and formed from the merger of St. Benedict's College (1858) and Mount St. Scholastica College (1923)) in Atchison, MidAmerica Nazarene University in Olathe, Ottawa University in Ottawa and Overland Park, Kansas City Kansas Community College and KU Medical Center in Kansas City, and KU Edwards Campus in Overland Park. Less than an hour's drive to the west,
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
is home to the University of Kansas, the largest public university in the state, and Haskell Indian Nations University.
To the north,
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
, with the second largest land area in the state, contains a number of diverse ethnic neighborhoods. Its attractions include the Kansas Speedway, Sporting Kansas City, Kansas City Monarchs (American Association), Kansas City Monarchs, and The Legends at Village West retail and entertainment center. Nearby, Kansas's first settlement Bonner Springs, Kansas, Bonner Springs
is home to several national and regional attractions including the Cricket Wireless Amphitheater (Bonner Springs, Kansas), Providence Medical Center Amphitheather, the National Agricultural Center and Hall of Fame, and the annual Kansas City Renaissance Festival. Further up the
Missouri River, the city of Lansing, Kansas, Lansing is the home of the state's first maximum-security prison. Historic Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth, founded in 1854, was the first incorporated city in Kansas. North of the city,
Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., an ...
is the oldest active Army post west of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. The city of Atchison, Kansas, Atchison was an early commercial center in the state and is well known as the birthplace of Amelia Earhart.
To the west, nearly a quarter million people reside in the Topeka metropolitan area.
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
is the state capital and home to Washburn University and Washburn Institute of Technology. Built at a
Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River dr ...
crossing along the old Oregon Trail, this historic city has several nationally registered historic places. Further westward along Interstate 70 (Kansas), Interstate 70 and the Kansas River is
Junction City with its historic limestone and brick buildings and nearby
Fort Riley
Fort Riley is a United States Army installation located in North Central Kansas, on the Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, between Junction City and Manhattan. The Fort Riley Military Reservation covers 101,733 acres (41,170 ha) in Gear ...
, well known as the home to the United States Army, U.S. Army's 1st Infantry Division (United States), 1st Infantry Division (nicknamed "the Big Red One"). A short distance away, the city of Manhattan, Kansas, Manhattan is home to Kansas State University, the second-largest public university in the state and the nation's oldest land-grant university, dating back to 1863. South of the campus, Aggieville dates back to 1889 and is the state's oldest shopping district of its kind.
South Central Kansas

In south-central Kansas, the Wichita metropolitan area, Kansas, Wichita metropolitan area is home to more than 600,000 people.
Wichita is the largest city in the state in terms of both land area and population. 'The Air Capital' is a major manufacturing center for the aircraft industry and the home of Wichita State University. Before Wichita was 'The Air Capital' it was a Cowtown.
With a number of nationally registered historic places, museums, and other entertainment destinations, it has a desire to become a cultural mecca in the Midwest. Wichita's population growth has grown by double digits and the surrounding suburbs are among the fastest growing cities in the state. The population of Goddard, Kansas, Goddard has grown by more than 11% per year since 2000.
Other fast-growing cities include Andover, Kansas, Andover, Maize, Kansas, Maize, Park City, Kansas, Park City, Derby, Kansas, Derby, and Haysville, Kansas, Haysville.
Wichita was one of the first cities to add the city commissioner and city manager in their form of government.
Wichita is also home of the nationally recognized Sedgwick County Zoo.
Up river (the
Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
) from Wichita is the city of Hutchinson, Kansas, Hutchinson. The city was built on one of the world's largest salt deposits (of what would form Strataca), and it has the world's largest and longest wheat elevator. It is also the home of Kansas Cosmosphere and Space Center, Prairie Dunes Country Club and the Kansas State Fair. North of Wichita along Interstate 135 (Kansas), Interstate 135 is the city of Newton, Kansas, Newton, the former western terminal of the Santa Fe Railroad and trailhead for the famed
Chisholm Trail
The Chisholm Trail was a trail used in the post-Civil War era to drive cattle overland from ranches in Texas to Kansas railheads. The trail was established by Black Beaver, a Lenape guide and rancher, and his friend Jesse Chisholm, a Cheroke ...
. To the southeast of Wichita are the cities of Winfield, Kansas, Winfield and Arkansas City, Kansas, Arkansas City with historic architecture and the Cherokee Strip (Kansas), Cherokee Strip Museum (in Ark City). The city of Udall, Kansas, Udall was the site of the deadliest tornado in Kansas on May 25, 1955; it killed 80 people in and near the city.
Southeast Kansas
Southeast Kansas has a unique history with a number of nationally registered historic places in this coal-mining region. Located in Crawford County, Kansas, Crawford County (dubbed the Fried Chicken Capital of Kansas), Pittsburg, Kansas, Pittsburg is the largest city in the region and the home of Pittsburg State University. The neighboring city of Frontenac, Kansas, Frontenac in 1888 was the site of the worst mine disaster in the state in which an underground explosion killed 47 miners. "Big Brutus" is located outside the city of West Mineral, Kansas, West Mineral. Along with the restored fort, historic Fort Scott, Kansas, Fort Scott has a national cemetery designated by President Lincoln in 1862. The region also shares a Media market with Joplin, Missouri, a city in Southwest Missouri.
Central and North-Central Kansas
Salina, Kansas, Salina is the largest city in central and north-central Kansas. South of Salina is the small city of Lindsborg, Kansas, Lindsborg with its numerous Dalecarlian horse, Dala horses. Much of the architecture and decor of this town has a distinctly Sweden, Swedish style. To the east along Interstate 70 (Kansas), Interstate 70, the historic city of
Abilene was formerly a trailhead for the
Chisholm Trail
The Chisholm Trail was a trail used in the post-Civil War era to drive cattle overland from ranches in Texas to Kansas railheads. The trail was established by Black Beaver, a Lenape guide and rancher, and his friend Jesse Chisholm, a Cheroke ...
and was the boyhood home of President Dwight D. Eisenhower, and is the site of his Eisenhower Presidential Center, Presidential Library and the tombs of the former president, First Lady and son who died in infancy. To the west is Lucas, Kansas, Lucas, the Grassroots Art Capital of Kansas.

Northwest Kansas


Westward along the Interstate, the city of Russell, Kansas, Russell, traditionally the beginning of sparsely-populated northwest Kansas, was the base of former U.S. Senator Bob Dole and the boyhood home of U.S. Senator Arlen Specter. The city of
Hays is home to Fort Hays State University and the Sternberg Museum of Natural History, and is the largest city in the northwest with a population of around 20,001.
Two other landmarks are located in smaller towns in Ellis County, Kansas, Ellis County: the "Cathedral of the Plains" is located east of Hays in Victoria, Kansas, Victoria, and the boyhood home of Walter Chrysler is west of Hays in Ellis, Kansas, Ellis. West of Hays, population drops dramatically, even in areas along I-70, and only two towns containing populations of more than 4,000: Colby, Kansas, Colby and Goodland, Kansas, Goodland, which are located apart along I-70.
Southwest Kansas
Dodge City
Dodge City is the county seat of Ford County, Kansas, United States, named after nearby Fort Dodge. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 27,788. The city is famous in American culture for its history as a wild frontier town ...
, famously known for the cattle drive days of the late 19th century, was built along the old
Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
route. The city of Liberal, Kansas, Liberal is located along the southern Santa Fe Trail route. The first wind farm in the state was built east of Montezuma, Kansas, Montezuma. Garden City, Kansas, Garden City has the Lee Richardson Zoo. In 1992, a West Kansas, short-lived secessionist movement advocated the secession of several counties in southwest Kansas.
Around the state
Located midway between Kansas City, Topeka, and Wichita in the heart of the Bluestem Region of the Flint Hills, the city of Emporia, Kansas, Emporia has several nationally registered historic places and is the home of Emporia State University, well known for its Teachers College. It was also the home of newspaper man William Allen White.
Economy
Total Employment of the metropolitan areas in the State of Kansas by total Non-farm Employment in 2016
*Kansas Portion of the Kansas City metropolitan area, Kansas City MO-KS MSA: 468,400 non-farm, accounting for 40.9% of state GDP in 2015
*Wichita, KS Metropolitan Statistical Area, Wichita, KS MSA: 297,300 non-farm
*Topeka metropolitan area, Kansas, Topeka, KS MSA: 112,600 non-farm
*Douglas County, Kansas, Lawrence KS, MSA: 54,000 non-farm
*Manhattan, Kansas, metropolitan area, Manhattan, KS MSA: 44,200 non-farm
*Total employment: 1,184,710
Total Number of employer establishments in 2016: 74,884
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Kansas's total gross domestic product in 2014 was billion. In 2015, the job growth rate in was 0.8%, among the lowest rate in America with only "10,900 total nonfarm jobs" added that year.
According to the Kansas Department of Labor's 2016 report, the average annual wage was $42,930 in 2015.
As of April 2016, the state's unemployment rate was 4.2%.
The State of Kansas had a $350 million budget shortfall in February 2017.
In February 2017, S&P downgraded Kansas's credit rating to AA-.
Nearly 90% of Kansas's land is devoted to agriculture.
The state's agricultural outputs are cattle, sheep,
wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
,
sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
, soybeans, cotton, pig, hogs, maize, corn, and salt. As of 2018, there were 59,600 farms in Kansas, 86 (0.14%) of which are Organic certification, certified organic farms.
The average farm in the state is about 770 acres (more than a square mile), and in 2016, the average cost of running the farm was $300,000.
By far, the most significant agricultural crop in the state is wheat. Eastern Kansas is part of the Grain Belt, an area of major grain production in the central United States. Approximately 40% of all winter wheat grown in the US is grown in Kansas.
Roughly 95% of the wheat grown in the state is hard red winter wheat.
During 2016, farmers of conventionally grown wheat farmed 8.2 million acres and harvested an average of 57 bushels of wheat per acre.
The industrial outputs are transportation equipment, commercial and private aircraft, food processing, publishing, chemical products, machinery, apparel, petroleum, and mining.
The state's economy is also heavily influenced by the aerospace industry. Several large aircraft corporations have manufacturing facilities in Wichita and Kansas City, including Spirit AeroSystems, Bombardier Aerospace (LearJet), and Textron Aviation (a merger of the former Cessna, Hawker Aircraft, Hawker, and Beechcraft brands). Boeing ended a decades-long history of manufacturing in Kansas between 2012 and 2013.
Major companies headquartered in Kansas include the Garmin (Olathe, Kansas, Olathe), YRC Worldwide (Overland Park), Payless Shoes (national headquarters and major distribution facilities in
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
), and Koch Industries (with national headquarters in
Wichita), and Coleman Company, Coleman (headquarters in Wichita).
Kansas is also home to three major military installations:
Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., an ...
(Army),
Fort Riley
Fort Riley is a United States Army installation located in North Central Kansas, on the Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, between Junction City and Manhattan. The Fort Riley Military Reservation covers 101,733 acres (41,170 ha) in Gear ...
(Army), and McConnell Air Force Base (Air Force). Approximately 25,000 active duty soldiers and airmen are stationed at these bases which also employ approximately 8,000 civilian DoD employees. The US Army Reserve also has the 451st Expeditionary Sustainment Command headquartered in Wichita that serves reservists and their units from around the region. The Kansas Air National Guard has units at Forbes Field in Topeka and the 184th Intelligence Wing in Wichita. The Smoky Hill Weapons Range, a detachment of the Intelligence Wing, is one of the largest and busiest bombing ranges in the nation. During World War II, Kansas was home to numerous Army Air Corps training fields for training new pilots and aircrew. Many of those airfields live on today as municipal airports.
Energy
Kansas has vast renewable resources and is a top producer of Wind power in Kansas, wind energy in the US, with an installed capacity of about 6,100 Megawatts (MW) from nearly 3,200 wind turbines in 2019. Wind generated the List of power stations in Kansas, largest share of electricity from the state at 41%. An additional 700 MW of capacity was scheduled to come online during 2020. Kansas is also a leading national producer of renewable ethanol and biodiesel fuels at nearly 600 million gallons per year.
Kansas is ranked eighth in Petroleum in the United States, US petroleum extraction. Production has experienced a steady decline as the state's limited economical reserves especially from the Anadarko Basin are depleted. Since Price of oil, oil prices bottomed in 1999, oil production in Kansas has remained fairly constant, with an average monthly rate of about in 2004. The Oil price increases since 2003, recent higher prices have made carbon sequestration, carbon dioxide sequestration and other oil recovery techniques more economical.
Kansas is also ranked eighth in US natural gas production. Production has steadily declined since the mid-1990s with the gradual depletion of the Hugoton Natural Gas Area, Hugoton Natural Gas FieldŌĆöthe state's largest field which extends into Oklahoma and Texas. In 2004, slower declines in the Hugoton gas fields and increased coalbed methane production contributed to a smaller overall decline. Average monthly production was over .
Taxes
Tax is collected by the Kansas Department of Revenue.
Revenue shortfalls resulting from lower than expected tax collections and slower growth in personal income following a 1998 permanent tax reduction have contributed to the substantial growth in the state's debt level as bonded debt increased from $1.16 billion in 1998 to $3.83 billion in 2006. Some increase in debt was expected as the state continues with its 10-year Comprehensive Transportation Program enacted in 1999.
In 2003, Kansas had three income brackets for income tax calculation, ranging from 3.5% to 6.45%.
The state sales tax in Kansas is 6.15%. Various cities and counties in Kansas have an additional local sales tax. Except during the 2001 recession (MarchŌĆōNovember 2001), when monthly sales tax collections were flat, collections have trended higher as the economy has grown and two rate increases have been enacted. If there had been no change in sales tax rates or in the economy, the total sales tax collections for 2003 would have been $1,797 million, compared to $805.3 million in 1990. However, they instead amounted to $1,630 million an inflation-adjusted reduction of 10%. The state sales tax is a combined destination-based tax, meaning a single tax is applied that includes state, county, and local taxes, and the rate is based on where the consumer takes possession of the goods or services. Thanks to the destination structure and the numerous local special taxing districts, Kansas has 920 separate sales tax rates ranging from 6.5% to 11.5%. This taxing scheme, known as "Streamlined Sales Tax" was adopted on October 1, 2005, under the governorship of Kathleen Sebelius. Groceries are subject to sales tax in the state. All sales tax collected is remitted to the state department of revenue, and local taxes are then distributed to the various taxing agencies.
As of June 2004, Moody's Investors Service ranked the state 14th for net tax-supported debt per capita. As a percentage of personal income, it was at 3.8%ŌĆöabove the median value of 2.5% for all rated states and having risen from a value of less than 1% in 1992. The state has a statutory requirement to maintain cash reserves of at least 7.5% of expenses at the end of each fiscal year; however, lawmakers can vote to override the rule, and did so during the most recent budget agreement.
During his campaign for the 2010 election, Governor Sam Brownback called for a complete "phase out of Kansas's income tax".
In May 2012, Governor Brownback signed into law the Kansas Senate Bill Substitute HB 2117.
Starting in 2013, the "ambitious tax overhaul" trimmed income tax, eliminated some corporate taxes, and created Flow-through entity, pass-through income tax exemptions, he raised the sales tax by one percent to offset the loss to state revenues but that was inadequate. He made cuts to education and some state services to offset lost revenue.
The tax cut led to years of budget shortfalls, culminating in a $350 million budget shortfall in February 2017. From 2013 to 2017, 300,000 businesses were considered to be pass-through income entities and benefited from the tax exemption. The tax reform "encouraged tens of thousands of Kansans to claim their wages and salaries as income from a business rather than from employment."
The economic growth that Brownback anticipated never materialized. He argued that it was because of "low wheat and oil prices and a downturn in aircraft sales".
The state general fund debt load was $83 million in fiscal year 2010 and by fiscal year 2017 the debt load sat at $179 million. In 2016, Governor Brownback earned the title of "most unpopular governor in America". Only 26 percent of Kansas voters approved of his job performance, compared to 65 percent who said they did not. In the summer of 2016 S&P Global Ratings downgraded Kansas's credit rating.
In February 2017, S&P lowered it to AA-.
In February 2017, a bi-partisan coalition presented a bill that would repeal the pass-through income exemption, the "most important provisions of Brownback's overhaul", and raise taxes to make up for the budget shortfall. Brownback vetoed the bill but "45 GOP legislators had voted in favor of the increase, while 40 voted to uphold the governor's veto."
On June 6, 2017, a coalition of Democrats and newly elected Republicans overrode [Brownback's] veto and implemented tax increases to a level close to what it was before 2013.
Brownback's tax overhaul was described in a June 2017 article in ''The Atlantic'' as the United States' "most aggressive experiment in conservative economic policy".
The drastic tax cuts had "threatened the viability of schools and infrastructure" in Kansas.
Transportation

Highways
Kansas is served by two Interstate Highway System, Interstate highways with one Ring road, beltway, two spur routes, and three bypass (road), bypasses, with over in all. The first section of Interstate in the nation was opened on Interstate 70 in Kansas, Interstate 70 (I-70) just west of
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
on November 14, 1956.
I-70 is a major eastŌĆōwest route connecting to
Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Colorado and Kansas City, Missouri. Cities along this route (from west to east) include Colby, Kansas, Colby,
Hays, Salina, Kansas, Salina,
Junction City,
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
,
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
, Bonner Springs, Kansas, Bonner Springs, and
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
.
Interstate 35 in Kansas, I-35 is a major northŌĆōsouth route connecting to Oklahoma City, Oklahoma and Des Moines, Iowa. Cities along this route (from south to north) include
Wichita, El Dorado, Kansas, El Dorado, Emporia, Kansas, Emporia, Ottawa, Kansas, Ottawa, and Kansas City (and suburbs).
Spur routes serve as connections between the two major routes. Interstate 135 (Kansas), I-135, a northŌĆōsouth route, connects I-35 at Wichita to I-70 at Salina. Interstate 335 (Kansas), I-335, a southwestŌĆōnortheast route, connects I-35 at Emporia to I-70 at Topeka. I-335 and portions of I-35 and I-70 make up the Kansas Turnpike. Bypasses include Interstate 470 (Kansas), I-470 around Topeka, Interstate 235 (Kansas), I-235 around Wichita, and Interstate 670 (Kansas), I-670 in downtown Kansas City. Interstate 435 (Kansas), I-435 is a beltway around the Kansas City metropolitan area while Interstate 635 (KansasŌĆōMissouri), I-635 bypasses through Kansas City.
U.S. Route 69 in Kansas, U.S. Route 69 (US-69) travels south to north, from Oklahoma to Missouri. The highway passes through the eastern section of Kansas, traveling through
Baxter Springs
Baxter Springs is a city in Cherokee County, Kansas, United States, and located along Spring River. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 3,888.
History
For thousands of years, indigenous peoples had lived along the waterwa ...
, Pittsburg, Kansas, Pittsburg, Frontenac, Kansas, Frontenac, Fort Scott, Kansas, Fort Scott, Louisburg, Kansas, Louisburg, and the Kansas City area.

Kansas also has the country's third largest state highway system after Texas and California. This is because of the high number of counties and county seats (105) and their intertwining.
In January 2004, the Kansas Department of Transportation (KDOT) announced the new Kansas 5-1-1, 511 traveler information service. By dialing 511, callers will get access to information about road conditions, construction, closures, detours and weather conditions for the state highway system. Weather and road condition information is updated every 15 minutes.
Interstate Highways
*
** (formerly known as I-35W)
**
**
**
**
*
**
**
U.S. Routes
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
*
**
*
**
**
*
Aviation
The state's only major commercial (Airspace class (United States), Class C) airport is Wichita Dwight D. Eisenhower National Airport, located along U.S. Route 54 (Kansas), US-54 on the western edge of the city. Manhattan Regional Airport in Manhattan, Kansas, Manhattan offers daily flights to Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport and Chicago's O'Hare International Airport, making it the second-largest commercial airport in the state. Most air travelers in northeastern Kansas fly out of Kansas City International Airport, located in Platte County, Missouri, as well as Topeka Regional Airport in the state's capital.
In the state's southeastern part, people often use Tulsa International Airport in Tulsa, Oklahoma or Joplin Regional Airport in Joplin, Missouri. For those in the far western part of the state, Denver International Airport is a popular option. Connecting flights are also available from smaller Kansas airports in Dodge City Regional Airport, Dodge City, Garden City Regional Airport, Garden City, Hays Regional Airport, Hays, Hutchinson Municipal Airport (Kansas), Hutchinson, Liberal Mid-America Regional Airport, Liberal, or Salina Municipal Airport, Salina.
Dotted across the state are smaller regional and municipal airports, including the Lawrence Municipal Airport (Kansas), Lawrence Municipal Airport, which houses many aircraft for the city of Lawrence and the University of Kansas, Miami County Airport, Wamego Airport, Osage City Municipal Airport, which is the headquarters of ''Skydive Kansas'', Garden City Regional Airport, Manhattan Regional Airport, and Dodge City Regional Airport.
Rail
The ''Southwest Chief'' Amtrak route runs through the state on its route from Chicago to Los Angeles. Stops in Kansas include Lawrence, Topeka, Newton, Hutchinson, Dodge City, and Garden City. An Amtrak Thruway Motorcoach connects Newton to the Heartland Flyer in Oklahoma City,
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
. Amtrak is proposing to modify the Southwest Chief from its status as a direct passenger rail operation. Plans call for shortening the route to Los Angeles to Albuquerque. Thruway buses would replace the train on the route between Albuquerque and Dodge City, where train service east to Chicago would resume.
Kansas is served by four Class I rail carrier, Class I railroads, Amtrak, BNSF, Kansas City Southern Railway, Kansas City Southern, and Union Pacific, as well as many shortline railroads.
Law and government
State and local politics
Executive branch: The executive branch consists of one officer and five elected officers. The governor and Lieutenant Governor of Kansas, lieutenant governor are elected on the same Ticket (election), ticket. The attorney general, secretary of state, state treasurer, and state insurance commissioner are each elected separately.
Legislative branch: The bicameral Kansas Legislature consists of the Kansas House of Representatives, with 125 members serving two-year terms, and the Kansas Senate, with 40 members serving four-year terms.
Judicial branch: The judicial branch of the state government is state supreme court, headed by the Kansas Supreme Court. The court has seven judges. A vacancy is filled by the Governor picking one of three nominees selected by the nine-member Kansas Supreme Court Nominating Commission. The board consists of five Kansas lawyers elected by other Kansas lawyers and four members selected by the governor.
Political culture
Since the 1930s, Kansas has remained one of the most socially conservative states in the nation. The 1990s brought the defeat of prominent Democrats, including Dan Glickman, and the Kansas State Board of Education's 1999 decision to eliminate evolution from the state teaching standards, a decision that was later reversed. In 2005, voters accepted a constitutional amendment to ban same-sex marriage. The next year, the state passed a law setting a minimum age for marriage at 15 years. Kansas's path to a solid Republican state has been examined by journalist and historian Thomas Frank in his 2004 book ''What's the Matter with Kansas? (book), What's the Matter with Kansas?''.
20th-century state politics
Kansas was the first state to institute a system of workers' compensation (1910) and to regulate the Security (finance), securities industry (1911). Kansas also permitted women's suffrage in 1912, almost a decade before the federal constitution was amended to require it. Suffrage in all states would not be guaranteed until ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution in 1920.
The councilŌĆōmanager government model was adopted by many larger Kansas cities in the years following World War I while many American cities were being run by political machines or organized crime, notably the Tom Pendergast, Pendergast Machine in neighboring Kansas City, Missouri. Kansas was also at the center of ''Brown v. Board of Education of
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
'', a 1954 Supreme Court decision that banned racially segregated schools throughout the U.S, though, infamously, many Kansas residents opposed the decision, and it led to protests in Topeka after the verdict.
The state backed Republican Presidential Candidates Wendell Willkie and Thomas E. Dewey in 1940 United States presidential election in Kansas, 1940 and 1944 United States presidential election in Kansas, 1944, respectively, breaking ranks with the majority of the country in the election of Franklin D. Roosevelt. Kansas also supported Dewey in 1948 United States presidential election in Kansas, 1948 despite the presence of incumbent president Harry S. Truman, who hailed from Independence, Missouri, approximately east of the KansasŌĆōMissouri state line. After Roosevelt carried Kansas in 1936 United States presidential election in Kansas, 1936, only one Democrat has won the state since, Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964 United States presidential election in Kansas, 1964.
21st-century state politics
In 2008, Democrat Governor Kathleen Sebelius vetoed permits for the construction of new coal-fired energy plants in Kansas, saying: "We know that greenhouse gases contribute to climate change. As an agricultural state, Kansas is particularly vulnerable. Therefore, reducing pollutants benefits our state not only in the short termŌĆöbut also for generations of Kansans to come." However, shortly after Mark Parkinson became governor in 2009 upon Sebelius's resignation to become Secretary of U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Parkinson announced a compromise plan to allow construction of a coal-fired plant.
In 2010, Republican Sam Brownback was elected governor with 63 percent of the state vote. He was sworn in as governor in 2011, Kansas's first Republican governor in eight years. Brownback had established himself as a conservative member of the U.S. Senate in years prior, but made several controversial decisions after becoming governor, leading to a 23% approval rating among registered voters - the lowest of any governor in the United States. In May 2011, much to the opposition of art leaders and enthusiasts in the state, Brownback eliminated the Kansas Arts Commission, making Kansas the first state without an arts agency. In July 2011, Brownback announced plans to close the Lawrence branch of the Kansas Department of Social and Rehabilitation Services as a cost-saving measure. Hundreds rallied against the decision. Lawrence City Commission later voted to provide the funding needed to keep the branch open.
Democrat Laura Kelly defeated former Secretary of State of Kansas Kris Kobach in the 2018 Kansas gubernatorial election, 2018 election for Governor with 48.0% of the vote.
In August 2022, Kansas voters rejected the controversial 2022 Kansas Value Them Both Amendment, Value Them Both Amendment, which would have eliminated the right to an abortion in the state constitution. The vote was the first referendum on abortion since Roe v. Wade was overturned earlier that summer, and the result was hailed as a landmark victory for pro-choice advocates in the traditionally socially conservative state.
In a 2020 study, Kansas was ranked as the 13th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
National politics

The state's current delegation to the Congress of the United States includes Republican Party (United States), Republican Senators Jerry Moran of Manhattan, Kansas, Manhattan, and Roger Marshall (politician), Roger Marshall of Great Bend, Kansas, Great Bend. In the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, Kansas is represented by Republican Representatives Tracey Mann of Quinter, Kansas, Quinter (1st Congressional District of Kansas, District 1), Jake LaTurner of Pittsburg, Kansas, Pittsburg (2nd Congressional District of Kansas, District 2), Ron Estes of
Wichita (4th Congressional District of Kansas, District 4), and Democratic Representative Sharice Davids of
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
(3rd Congressional District of Kansas, District 3) Davids is the second Native American to represent Kansas in Congress, after Republican Charles Curtis (Kaw people, Kaw).
Historically, Kansas has been strongly Republican, dating from the Antebellum era, Antebellum age when the Republican Party was created out of the movement opposing the extension of slavery into Kansas Territory. Kansas has not elected a Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to the U.S. Senate since the 1932 election, when Franklin D. Roosevelt won his first term as president in the wake of the Great Depression. This is the longest Senate losing streak for either party in a single state. Senator Sam Brownback was a candidate for the Republican party nomination for president in 2008. Brownback was not a candidate for re-election to a third full term in 2010, but he was elected Governor in that year's general election. Moran defeated Tiahrt for the Republican nomination for Brownback's seat in the August 2010 primary, then won a landslide general election victory over Democrat Lisa Johnston.
The only non-Republican presidential candidates Kansas has given its electoral vote to are Populist James Baird Weaver, James Weaver and Democrats Woodrow Wilson, Franklin Roosevelt (twice), and Lyndon B. Johnson, Lyndon Johnson. In 2004, George W. Bush won the state's six electoral votes by an overwhelming margin of 25 percentage points with 62% of the vote. The only two counties to support Democrat John Kerry in that election were Wyandotte County, Kansas, Wyandotte, which contains
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
, and Douglas County, Kansas, Douglas, home to the University of Kansas, located in
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
. The 2008 election brought similar results as John McCain won the state with 57% of the votes. Douglas, Wyandotte, and Crawford County, Kansas, Crawford County were the only counties in support of President Barack Obama.
Abilene was the boyhood home to Republican president Dwight D. Eisenhower, and he maintained lifelong ties to family and friends there. Kansas was the adult home of two losing Republican candidates (Governor Alf Landon in 1936 United States presidential election, 1936 and Senator Bob Dole in 1996 United States presidential election, 1996).
The ''New York Times'' reported in September 2014 that as the Democratic candidate for Senator has tried to drop out of the race, independent Greg Orman has attracted enough bipartisan support to seriously challenge the reelection bid of Republican Pat Roberts:
:Kansas politics have been roiled in recent years. The rise of the Tea Party and the election of President Obama have prompted Republicans to embrace a purer brand of conservatism and purge what had long been a robust moderate wing from its ranks. Mr. Roberts has sought to adapt to this new era, voting against spending bills that included projects for the state that he had sought.
State laws
The legal drinking age in Kansas is 21. In lieu of the state retail sales tax, a 10% Liquor Drink Tax is collected for liquor consumed on the licensed premises and an 8% Liquor Enforcement Tax is collected on retail purchases. Although the sale of cereal malt beverage (also known as 3.2 beer) was legalized in 1937, the first post-Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition legalization of alcoholic liquor did not occur until the Kansas Constitution, state's constitution was amended in 1948. The following year the Kansas Legislature, Legislature enacted the Liquor Control Act which created a system of regulating, licensing, and taxing, and the Division of Alcoholic Beverage Control (ABC) was created to enforce the act. The power to regulate cereal malt beverage remains with the cities and counties. Liquor-by-the-drink did not become legal until passage of an amendment to the state's constitution in 1986 and additional legislation the following year. As of November 2006, Kansas still has 29 dry county, dry counties and only 17 counties have passed liquor-by-the-drink with no food sales requirement. Today there are more than 2,600 liquor and 4,000 cereal malt beverage licensees in the state.
On May 12, 2022, Gov. Laura Kelly signed legislation (Senate Bill 84) that legalizes sports betting in the state, making Kansas the 35th state to approve sports wagering in the US. This would give the four state-owned casinos the right to partner with online bookmakers and up to 50 retailers, including gas stations and restaurants, to engage in sports betting.
Education
Education in Kansas is governed at the primary and secondary school level by the Kansas State Board of Education. The state's public colleges and universities are supervised by the Kansas Board of Regents.
Twice since 1999 the Board of Education has approved changes in the state science curriculum standards that encouraged the teaching of intelligent design. Both times, the standards were reversed after changes in the composition of the board in the next election.
Culture

Music
The rock band Kansas (band), Kansas was formed in the state capital of
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
, the hometown of several of the band's members.
Joe Walsh, guitarist for the famous rock band the Eagles (band), Eagles, was born in Wichita.
Danny Carey, drummer for the band Tool (band), Tool, was raised in Paola.
Singers from Kansas include Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth native Melissa Etheridge, Sharon, Kansas, Sharon native Martina McBride, Chanute, Kansas, Chanute native Jennifer Knapp (whose first album was titled ''Kansas (Jennifer Knapp album), Kansas''),
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
native Janelle Mon├Īe, and Liberal, Kansas, Liberal native Jerrod Niemann.
The state anthem is the American classic Home on the Range, written by Kansan Brewster Higley. Another song, the official state march adopted by the Kansas Legislature in 1935 is called ''The Kansas March'', which features the lyrics, "Blue sky above us, silken strands of heat, Rim of the far horizon, where earth and heaven meet, Kansas as a temple, stands in velvet sod, Shrine which the sunshine, sanctifies to God."
Literature
The state's most famous appearance in literature was as the home of Dorothy Gale, the main character in the novel ''The Wonderful Wizard of Oz'' (1900). Laura Ingalls Wilder's ''Little House on the Prairie (novel), Little House on the Prairie'', published in 1935, is another well-known tale about Kansas.
Kansas was also the setting of the 1965 best-seller ''In Cold Blood'', described by its author Truman Capote as a "nonfiction novel". Mixing fact and fiction, the book chronicles the events and aftermath of the 1959 murder of a wealthy farmer and his family who lived in the small West Kansas town of Holcomb, Kansas, Holcomb in Finney County.
The fictional town of Smallville, Kansas is the childhood home of Clark Kent/Superman in American comic books published by DC Comics. Also Keystone City is a Kansas city where The Flash works and lives.
The science fiction novella ''A Boy and His Dog'', as well as the A Boy and His Dog (1975 film), film based on it,
take place in post-apocalyptic
Topeka
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, D├│pik╦Će, script=Latn or ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kansas and the seat of Shawnee County. It is along the Kansas River in the central part of Shawnee County, in northeast Kansas, in the Central Un ...
.
The winner of the 2011 Newbery Medal for excellence in children's literature, ''Moon Over Manifest'', tells the story of a young and adventurous girl named Abilene who is sent to the fictional town of Manifest, Kansas, by her father in the summer of 1936. It was written by Kansan Clare Vanderpool.
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
is the setting for a number of science fiction writer James Gunn (author), James Gunn's novels.
Film


The first film theater in Kansas was the Patee Theater in
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
. Most theaters at the time showed films only as part of vaudeville acts but not as an exclusive and stand alone form of entertainment. Though the Patee family had been involved in vaudeville, they believed films could carry the evening without other variety acts, but in order to show the films it was necessary for the Patee's to establish a generating plant (back in 1903 Lawrence was not yet fully electrified). The Patee Theater was one of the first of its kind west of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. The specialized equipment like the projector came from New York City, New York.
Kansas has been the setting of many award-winning and popular American films, as well as being the home of some of the oldest operating cinemas in the world. The Plaza Cinema in Ottawa, Kansas, located in the northeastern portion of the state, was built on May 22, 1907, and it is listed by the Guinness Book of World Records as the oldest operating cinema in the world. In 1926, The Jayhawk Theatre, an art-deco movie house in Topeka opened its doors for the first time to movie going audiences, and today, in addition to screenings of independent films, the theatre acts as a venue for plays and concerts. The Fox Theater in Hutchinson was built in 1930, and was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989. Like the other theaters listed here, The Fox still plays first run movies to this day.
* As was the case with the novel, Dorothy Gale (portrayed by Judy Garland) in the 1939 fantasy film The Wizard of Oz (1939 film), ''The Wizard of Oz'' was a young girl who lived in Kansas with her aunt and uncle. The line, "We're not in Kansas anymore", has entered into the English language, English lexicon as a phrase describing a wholly new and/or unexpected situation.
* The 1967 feature film In Cold Blood (film), ''In Cold Blood'', like the book on which it was based, was set in various locations across Kansas. Many of the scenes in the film were filmed at the exact locations where the events profiled in the book took place. A In Cold Blood (miniseries), 1996 TV miniseries was also based on the book.
* The 1988 film ''Kansas (film), Kansas'' starred Andrew McCarthy as a traveler who met up with a dangerous wanted drifter played by Matt Dillon.
* The 2005 film Capote (film), ''Capote'', for which Philip Seymour Hoffman was awarded the Academy Award for Best Actor for his portrayal of the title character, profiled the author as he traveled across Kansas while writing ''In Cold Blood'' (although most of the film itself was shot in the Canadian province of Manitoba).
* The setting of ''The Day After'', a 1983 made-for-television movie about a fictional nuclear attack, was the city of
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
.
* Due to the super hero Superman growing up in the fictional Smallville, Kansas, multiple films featuring the super hero have been entirely or at least partially set in Kansas including ''Superman (1978 film), Superman'' (1978), ''Superman III'' (1983), ''Man of Steel (film), Man of Steel'' (2013), ''Batman v Superman: Dawn of Justice'' (2016), and ''Justice League (film), Justice League'' (2017).
* The 2012 film Looper (film), ''Looper'' is set in Kansas.
* The 1973 film Paper Moon (film), ''Paper Moon'' in which Tatum O'Neal won an Academy Award for Best Supporting Actress (The youngest to win an Academy Award) was based in and filmed in Kansas. The film was shot in the small towns of
Hays; McCracken, Kansas, McCracken; Wilson, Kansas, Wilson; and St. Joseph, Missouri. Various shooting locations include the Midland Hotel at Wilson; the railway depot at Gorham, Kansas, Gorham; storefronts and buildings on Main Street in White Cloud, Kansas, White Cloud; Hays; sites on both sides of the
Missouri River; Rulo Bridge; and Saint Joseph, Missouri.
* Scenes of the 1996 film Mars Attacks! took place in the fictional town of Perkinsville. Scenes taking place in Kansas were filmed in Burns, Kansas, Burns,
Lawrence
Lawrence may refer to:
Education Colleges and universities
* Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States
* Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States
Preparator ...
, and
Wichita.
* The 2007 film ''The Lookout'' is set mostly in Kansas (although filmed in Canada). Specifically two locations; Kansas City and the fictional town of Noel, Kansas.
* The 2012 documentary ''The Gridiron'' was filmed at The University of Kansas
* The 2014 ESPN documentary ''No Place Like Home (2014 film), No Place Like Home'' was filmed in Lawrence and the countryside of Douglas County, Kansas
* The 2017 film ''Thank You for Your Service (2017 film), Thank You for Your Service'' is primarily set in Kansas, including the cities of Topeka and
Junction City.
* The 2017 documentary ''When Kings Reigned'' was filmed in Lawrence.
* The 2019 film ''Brightburn'' took place in the fictional town of Brightburn. As is evident with scenes in the film depicting mountains (Kansas has no mountain ranges), it was filmed in Georgia instead of in Kansas.
Television
* The protagonist brothers of the 2005 TV show ''Supernatural (U.S. TV series), Supernatural'' hail from Lawrence, with the city referenced numerous times on the show.
* 2006 TV series ''Jericho (2006 TV series), Jericho'' was based in the fictitious town of Jericho, Kansas, surviving post-nuclear America.
* Early seasons of ''Smallville'', about Superman as a teenager, were based in a fictional town of Smallville (comics), Smallville, Kansas. Unlike most other adaptations of the Superman story, the series also places the fictional city of Metropolis (comics), Metropolis in western Kansas, a few hours from Smallville.
* ''Gunsmoke'', a radio series western, ran from 1952 to 1961, took place in Dodge City, Kansas.
* ''Gunsmoke'', television series, the longest running prime time show of the 20th century, ran from September 10, 1955, to March 31, 1975, for a total of 635 episodes.
* The 2009 Showtime (TV channel), Showtime series ''United States of Tara'' is set in Overland Park, a suburb of Kansas City.
Sports
Professional

Sporting Kansas City, who have played their home games at Village West in
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
, since 2008, are the first top-tier Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, professional sports league and first Major League Soccer team to be located within Kansas. In 2011 the team moved to their new home, a $165 million soccer specific stadium now known as Children's Mercy Park.
Historically, Kansans have supported the Major professional sports leagues of Canada and the United States, major league sports teams of Kansas City, Missouri, including the Kansas City Royals (Major League Baseball, MLB), and the Kansas City Chiefs (National Football League, NFL), in part because the home stadiums for these teams are a few miles from the Kansas border. The Chiefs and the Royals play at the Truman Sports Complex, located about from the KansasŌĆōMissouri state line. FC Kansas City, a charter member of the National Women's Soccer League, played the 2013 National Women's Soccer League season, 2013 season, the first for both the team and the league, on the Kansas side of the metropolitan area, but played on the Missouri side until folding after the 2017 National Women's Soccer League season, 2017 season. From 1973 to 1997 the Flagship station, flagship radio station for the Royals was WIBW (AM), WIBW in Topeka.
Some Kansans, mostly from the westernmost parts of the state, support the professional sports teams of
Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
, particularly the Denver Broncos of the NFL.
Two major auto racing facilities are located in Kansas. The Kansas Speedway located in Kansas City hosts races of the NASCAR, IndyCar Series, IndyCar, and Auto Racing Club of America, ARCA circuits. Also, the National Hot Rod Association (NHRA) holds drag racing events at Heartland Park Topeka. The Sports Car Club of America has its national headquarters in Topeka.
=History
=
The history of professional sports in Kansas probably dates from the establishment of the minor league baseball Topeka Capitals and Leavenworth Soldiers in 1886 in the Western League (original), Western League.
The African-American Bud Fowler played on the Topeka team that season, one year before the "Baseball color line, color line" descended on professional baseball.
In 1887, the Western League was dominated by a reorganized Topeka team called the Topeka Golden Giants (1887), Golden Giants: a high-priced collection of major leaguer players, including Bug Holliday, Jim Conway (baseball), Jim Conway, Dan Stearns, Perry Werden and Jimmy Macullar, which won the league by 15┬Į games.
On April 10, 1887, the Golden Giants also won an exhibition game from the defending 1886 World Series, World Series champions, the St. Louis Browns (NL), St. Louis Browns (the present-day Cardinals), by a score of 12ŌĆō9. However, Topeka was unable to support the team, and it disbanded after one year.
The first night game in the history of professional baseball was played in Independence on April 28, 1930, when the Muscogee (Oklahoma) Indians beat the Independence Producers 13ŌĆō3 in a minor league game sanctioned by the Western League of the Western Baseball Association with 1,500 fans attending the game. The permanent lighting system was first used for an exhibition game on April 17, 1930, between the Independence Producers and House of David semi-professional baseball team of Benton Harbor, Michigan with the Independence team winning 9ŌĆō1 before a crowd of 1,700 spectators.
College

The governing body for intercollegiate sports in the United States, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), was headquartered in Johnson County, Kansas from 1952 until moving to Indianapolis in 1999.
=NCAA Division I schools
=


While there are no franchises of the four major professional sports within the state, many Kansans are fans of the state's major college sports teams, especially the Kansas Jayhawks, Jayhawks of the University of Kansas (KU), and the Kansas State Wildcats, Wildcats of Kansas State University (KSU or "K-State"). The teams are rivals in the Big 12 Conference.
Both KU and K-State have tradition-rich programs in men's basketball. The Jayhawks are a perennial national power, ranking first in all-time victories among NCAA programs. The Jayhawks have won six national titles, including NCAA tournament championships in 1952, 1988, 2008, and 2022. They also were retroactively awarded national championships by the Helms Foundation for 1922 and 1923. K-State also had a long stretch of success on the hardwood, lasting from the 1940s to the 1980s, making four Final Fours during that stretch. In 1988, KU and K-State met in the Elite Eight, KU taking the game 71ŌĆō58. After a 12-year absence, the Wildcats returned to the NCAA tournament in 2008, and advanced to the Elite Eight in 2010 and 2018. KU is fifth all-time with 15 Final Four appearances, while K-State's four appearances are tied for 17th.
Conversely, success on the American football, gridiron has been less frequent for both KSU and KU. However, there have been recent breakthroughs for both schools' football teams. The Jayhawks won the Orange Bowl (game), Orange Bowl for the first time in three tries in 2008, capping a 12ŌĆō1 season, the best in school history. And when Bill Snyder arrived to coach at K-State in 1989, he turned the Wildcats from one of the worst college football programs in America,
into a national force for most of the 1990s and early 2000s. The team won the Fiesta Bowl in 1997, achieved an undefeated (11ŌĆō0) regular season and No.1 ranking in 1998, and took the Big 12 Conference championship in 2003. After three seasons in which K-State football languished, Snyder came out of retirement in 2009 and guided them to the top of the college football ranks again, finishing second in the Big 12 in 2011 and earning a berth in the Cotton Bowl Classic, Cotton Bowl, and winning the Big 12 again in 2012.
Wichita State University, which also fields teams (called the Wichita State Shockers, Shockers) in NCAA Division I, Division I of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA, is best known for its baseball and basketball programs. In baseball, the Shockers won the College World Series in 1989. In men's basketball, they appeared in the Final Four in 1965 and 2013, and entered the 2014 NCAA tournament unbeaten. The school also fielded a American football, football team from 1897 to 1986. The Shocker football team is tragically known for a Wichita State University football team plane crash, plane crash in 1970 that killed 31 people, including 14 players.
=NCAA Division II schools
=
Notable success has also been achieved by the state's smaller schools in football. Pittsburg State University, an NCAA Division II participant, has claimed four national titles in football, two in the NAIA and most recently the 2011 NCAA Division II national title. Pittsburg State became the winningest NCAA Division II football program in 1995. PSU passed Hillsdale College at the top of the all-time victories list in the 1995 season on its march to the national runner-up finish. The Gorillas, in 96 seasons of intercollegiate competition, have accumulated 579 victories, posting a 579ŌĆō301ŌĆō48 overall mark.
Washburn University, in Topeka, won the National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics, NAIA Men's Basketball Championship in 1987. The Fort Hays State University men won the 1996 NCAA Division II title with a 34ŌĆō0 record, and the Washburn women won the 2005 NCAA Division II crown. St. Benedict's College (now Benedictine College), in Atchison, won the 1954 and 1967 Men's NAIA Basketball Championships.
The Kansas Collegiate Athletic Conference has its roots as one of the oldest college sport conferences in existence and participates in the NAIA and all ten member schools are in the state of Kansas. Other smaller school conferences that have some members in Kansas are the Mid-America Intercollegiate Athletics Association the Midlands Collegiate Athletic Conference, the Midwest Christian College Conference, and the Heart of America Athletic Conference. Many junior colleges also have active athletic programs.
Emporia State's women's basketball team, under head coach Brandon Schneider, who is now serving as the women's basketball coach at the University of Kansas, has seen success as well. In 2010 the team won the NCAA Division II National Championship. Emporia State and Washburn in Topeka share a heated rivalry in all sports, mostly due to the close proximity of both cities.
=Junior colleges
=
The Kansas Jayhawk Community College Conference has been heralded as one of the best conferences in all of NJCAA football, with Garden City Community College, Independence Community College, and Butler County Community College all consistently in contention for national championships.
High school
The Kansas State High School Activities Association (KSHSAA) is the organization which oversees interscholastic competition in the state of Kansas at the high school level. It oversees both athletic and non-athletic competition, and sponsors championships in several sports and activities. The association is perhaps best known for devising the overtime system now used for almost all football games below the professional level (which has also been adopted at all levels of Canadian football).
See also
* Index of Kansas-related articles
* Outline of Kansas
* List of Kansas landmarks
* List of people from Kansas
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Kansas
Notes
References
Bibliography
* ; 559 pages.
* ; 535 pages.
* ; 1204 pages.
* ; 5 volumes; 2731 pages;
Vol1,
Vol2,
Vol3,
Vol4,
Vol5; the 1919 edition contains additional biographies.
* ; 369 pages.
* ; 3 volumes; 2723 pages;
Vol1,
Vol2,
Vol3
* ; 610 pages.
* ; 3 volumes; 1616 pages;
Hathi TrustInternet Archive
*
External links
State of Kansas*
Kansas Travel and Tourism DivisionKansas Historical SocietyKansas MemoryĆödocuments, photographs, and other primary sources provided by the Kansas Historical Society
Kansas State Agency DatabasesĆöAnnotated list of searchable databases produced by Kansas state agencies
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of KansasKansas State Facts from USDA
Maps
Kansas Department of Transportation maps:* .
:* .
* .
*
* .
{{coord, 38, -98, dim:300000_region:US-KS_type:adm1st, name=State of Kansas, display=title
Kansas,
1861 establishments in Kansas
Midwestern United States
States and territories established in 1861
States of the United States
U.S. states with multiple time zones
Contiguous United States
 Before
Before  The first non-military settlement of Euro-Americans in Kansas Territory consisted of
The first non-military settlement of Euro-Americans in Kansas Territory consisted of 
 Nearly of the state's northeastern boundary is defined by the Missouri River. The
Nearly of the state's northeastern boundary is defined by the Missouri River. The 
 In the
In the  According to the 2020 United States census, 2021 United States census estimates, the racial makeup of the population was:
* White American, White American, non-Hispanic - 74.7%
* Hispanic or Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino - 12.7%
* Black or African American - 6.2%
* Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander - 0.1%
* Two or more races - 3.3%
* Asian people, Asian - 3.2%
* American Indian and Alaska Native - 1.2%
According to the 2020 United States census, 2021 United States census estimates, the racial makeup of the population was:
* White American, White American, non-Hispanic - 74.7%
* Hispanic or Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino - 12.7%
* Black or African American - 6.2%
* Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander - 0.1%
* Two or more races - 3.3%
* Asian people, Asian - 3.2%
* American Indian and Alaska Native - 1.2%

 As of 2010, the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) reported that the Catholic Church has the highest number of adherents in Kansas (at 426,611), followed by the United Methodist Church with 202,989 members, and the Southern Baptist Convention, reporting 99,329 adherents.
Kansas's capital Topeka is sometimes cited as the home of Pentecostalism as it was the site of Charles Fox Parham's Bethel Bible College, where glossolalia was first claimed as the evidence of a spiritual experience referred to as the baptism of the Holy Spirit in 1901. It is also the home of Reverend Charles Sheldon, author of ''In His Steps'', and was the site where the question "What would Jesus do?" originated in a sermon of Sheldon's at Central Congregational Church.
Kansas is the location of the second Baha'i community west of Egypt, when the Baha'i community of Enterprise, KS was started in 1897. From that beginning the Baha'i Faith spread across Kansas.
Topeka is also home of the Westboro Baptist Church, a hate group according to the Southern Poverty Law Center. The church has garnered worldwide media attention for picketing the funerals of U.S. servicemen and women for what church members claim as "necessary to combat the fight for equality for gays and lesbians". They have sometimes successfully raised lawsuits against the city of Topeka.
As of 2010, the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) reported that the Catholic Church has the highest number of adherents in Kansas (at 426,611), followed by the United Methodist Church with 202,989 members, and the Southern Baptist Convention, reporting 99,329 adherents.
Kansas's capital Topeka is sometimes cited as the home of Pentecostalism as it was the site of Charles Fox Parham's Bethel Bible College, where glossolalia was first claimed as the evidence of a spiritual experience referred to as the baptism of the Holy Spirit in 1901. It is also the home of Reverend Charles Sheldon, author of ''In His Steps'', and was the site where the question "What would Jesus do?" originated in a sermon of Sheldon's at Central Congregational Church.
Kansas is the location of the second Baha'i community west of Egypt, when the Baha'i community of Enterprise, KS was started in 1897. From that beginning the Baha'i Faith spread across Kansas.
Topeka is also home of the Westboro Baptist Church, a hate group according to the Southern Poverty Law Center. The church has garnered worldwide media attention for picketing the funerals of U.S. servicemen and women for what church members claim as "necessary to combat the fight for equality for gays and lesbians". They have sometimes successfully raised lawsuits against the city of Topeka.

 The northeastern portion of the state, extending from the eastern border to Junction City and from the Nebraska border to south of Johnson County is home to more than 1.5 million people in the Kansas City (Kansas portion), Manhattan, Lawrence, and Topeka metropolitan areas. Overland Park, Kansas, Overland Park, a young city incorporated in 1960, has the largest population and the largest land area in the county. It is home to Johnson County Community College.
Olathe is the county seat and home to Johnson County Executive Airport. The cities of Olathe, Shawnee, Kansas, Shawnee, De Soto, Kansas, De Soto and Gardner, Kansas, Gardner have some of the state's fastest growing populations. The cities of Overland Park, Lenexa, Kansas, Lenexa, Olathe, De Soto, and Gardner are also notable because they lie along the former route of the
The northeastern portion of the state, extending from the eastern border to Junction City and from the Nebraska border to south of Johnson County is home to more than 1.5 million people in the Kansas City (Kansas portion), Manhattan, Lawrence, and Topeka metropolitan areas. Overland Park, Kansas, Overland Park, a young city incorporated in 1960, has the largest population and the largest land area in the county. It is home to Johnson County Community College.
Olathe is the county seat and home to Johnson County Executive Airport. The cities of Olathe, Shawnee, Kansas, Shawnee, De Soto, Kansas, De Soto and Gardner, Kansas, Gardner have some of the state's fastest growing populations. The cities of Overland Park, Lenexa, Kansas, Lenexa, Olathe, De Soto, and Gardner are also notable because they lie along the former route of the  In south-central Kansas, the Wichita metropolitan area, Kansas, Wichita metropolitan area is home to more than 600,000 people. Wichita is the largest city in the state in terms of both land area and population. 'The Air Capital' is a major manufacturing center for the aircraft industry and the home of Wichita State University. Before Wichita was 'The Air Capital' it was a Cowtown. With a number of nationally registered historic places, museums, and other entertainment destinations, it has a desire to become a cultural mecca in the Midwest. Wichita's population growth has grown by double digits and the surrounding suburbs are among the fastest growing cities in the state. The population of Goddard, Kansas, Goddard has grown by more than 11% per year since 2000. Other fast-growing cities include Andover, Kansas, Andover, Maize, Kansas, Maize, Park City, Kansas, Park City, Derby, Kansas, Derby, and Haysville, Kansas, Haysville.
Wichita was one of the first cities to add the city commissioner and city manager in their form of government. Wichita is also home of the nationally recognized Sedgwick County Zoo.
Up river (the
In south-central Kansas, the Wichita metropolitan area, Kansas, Wichita metropolitan area is home to more than 600,000 people. Wichita is the largest city in the state in terms of both land area and population. 'The Air Capital' is a major manufacturing center for the aircraft industry and the home of Wichita State University. Before Wichita was 'The Air Capital' it was a Cowtown. With a number of nationally registered historic places, museums, and other entertainment destinations, it has a desire to become a cultural mecca in the Midwest. Wichita's population growth has grown by double digits and the surrounding suburbs are among the fastest growing cities in the state. The population of Goddard, Kansas, Goddard has grown by more than 11% per year since 2000. Other fast-growing cities include Andover, Kansas, Andover, Maize, Kansas, Maize, Park City, Kansas, Park City, Derby, Kansas, Derby, and Haysville, Kansas, Haysville.
Wichita was one of the first cities to add the city commissioner and city manager in their form of government. Wichita is also home of the nationally recognized Sedgwick County Zoo.
Up river (the 

 Westward along the Interstate, the city of Russell, Kansas, Russell, traditionally the beginning of sparsely-populated northwest Kansas, was the base of former U.S. Senator Bob Dole and the boyhood home of U.S. Senator Arlen Specter. The city of Hays is home to Fort Hays State University and the Sternberg Museum of Natural History, and is the largest city in the northwest with a population of around 20,001.
Two other landmarks are located in smaller towns in Ellis County, Kansas, Ellis County: the "Cathedral of the Plains" is located east of Hays in Victoria, Kansas, Victoria, and the boyhood home of Walter Chrysler is west of Hays in Ellis, Kansas, Ellis. West of Hays, population drops dramatically, even in areas along I-70, and only two towns containing populations of more than 4,000: Colby, Kansas, Colby and Goodland, Kansas, Goodland, which are located apart along I-70.
Westward along the Interstate, the city of Russell, Kansas, Russell, traditionally the beginning of sparsely-populated northwest Kansas, was the base of former U.S. Senator Bob Dole and the boyhood home of U.S. Senator Arlen Specter. The city of Hays is home to Fort Hays State University and the Sternberg Museum of Natural History, and is the largest city in the northwest with a population of around 20,001.
Two other landmarks are located in smaller towns in Ellis County, Kansas, Ellis County: the "Cathedral of the Plains" is located east of Hays in Victoria, Kansas, Victoria, and the boyhood home of Walter Chrysler is west of Hays in Ellis, Kansas, Ellis. West of Hays, population drops dramatically, even in areas along I-70, and only two towns containing populations of more than 4,000: Colby, Kansas, Colby and Goodland, Kansas, Goodland, which are located apart along I-70.

 The state's current delegation to the Congress of the United States includes Republican Party (United States), Republican Senators Jerry Moran of Manhattan, Kansas, Manhattan, and Roger Marshall (politician), Roger Marshall of Great Bend, Kansas, Great Bend. In the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, Kansas is represented by Republican Representatives Tracey Mann of Quinter, Kansas, Quinter (1st Congressional District of Kansas, District 1), Jake LaTurner of Pittsburg, Kansas, Pittsburg (2nd Congressional District of Kansas, District 2), Ron Estes of Wichita (4th Congressional District of Kansas, District 4), and Democratic Representative Sharice Davids of
The state's current delegation to the Congress of the United States includes Republican Party (United States), Republican Senators Jerry Moran of Manhattan, Kansas, Manhattan, and Roger Marshall (politician), Roger Marshall of Great Bend, Kansas, Great Bend. In the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, Kansas is represented by Republican Representatives Tracey Mann of Quinter, Kansas, Quinter (1st Congressional District of Kansas, District 1), Jake LaTurner of Pittsburg, Kansas, Pittsburg (2nd Congressional District of Kansas, District 2), Ron Estes of Wichita (4th Congressional District of Kansas, District 4), and Democratic Representative Sharice Davids of 

 Sporting Kansas City, who have played their home games at Village West in
Sporting Kansas City, who have played their home games at Village West in  The governing body for intercollegiate sports in the United States, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), was headquartered in Johnson County, Kansas from 1952 until moving to Indianapolis in 1999.
The governing body for intercollegiate sports in the United States, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), was headquartered in Johnson County, Kansas from 1952 until moving to Indianapolis in 1999.
