Jackie Robinson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jack Roosevelt Robinson (January 31, 1919 – October 24, 1972) was an American professional
 After graduating from PJC in spring 1939, Robinson enrolled at UCLA, where he became the school's first athlete to win
After graduating from PJC in spring 1939, Robinson enrolled at UCLA, where he became the school's first athlete to win
 After receiving his commission, Robinson was reassigned to
After receiving his commission, Robinson was reassigned to
 In early 1945, while Robinson was at Sam Huston College, the
In early 1945, while Robinson was at Sam Huston College, the
 Robinson's presence was controversial in racially segregated Florida. He was not allowed to stay with his white teammates at the team hotel, and instead lodged at the home of Joe and Dufferin Harris, a politically active African American couple who introduced the Robinsons to civil rights activist
Robinson's presence was controversial in racially segregated Florida. He was not allowed to stay with his white teammates at the team hotel, and instead lodged at the home of Joe and Dufferin Harris, a politically active African American couple who introduced the Robinsons to civil rights activist
p. 163
 Later in spring training, after some less-than-stellar performances, Robinson was shifted from shortstop to second base, allowing him to make shorter throws to first base. Robinson's performance soon rebounded. On April 18, 1946,
Later in spring training, after some less-than-stellar performances, Robinson was shifted from shortstop to second base, allowing him to make shorter throws to first base. Robinson's performance soon rebounded. On April 18, 1946,
pp. 12
336. Black fans began flocking to see the Dodgers when they came to town, abandoning their Negro league teams. Robinson's promotion met a generally positive, although mixed, reception among newspapers and white major league players. However, racial tension existed in the Dodger clubhouse. Some Dodger players insinuated they would sit out rather than play alongside Robinson. The brewing mutiny ended when Dodgers management took a stand for Robinson. Manager
 Racial pressure on Robinson eased in 1948 when a number of other black players entered the major leagues.
Racial pressure on Robinson eased in 1948 when a number of other black players entered the major leagues.  In 1950, Robinson led the National League in
In 1950, Robinson led the National League in
 Despite Robinson's regular-season heroics, on October 3, 1951, the Dodgers lost the pennant on
Despite Robinson's regular-season heroics, on October 3, 1951, the Dodgers lost the pennant on
 Robinson's major league debut brought an end to approximately sixty years of segregation in professional baseball, known as the
Robinson's major league debut brought an end to approximately sixty years of segregation in professional baseball, known as the
pp. 502–503
After playing his rookie season at first base, Robinson spent most of his career as a second baseman. He led the league in fielding among second basemen in 1950 and 1951. Toward the end of his career, he played about 2,000 innings at third base and about 1,175 innings in the outfield, excelling at both. Assessing himself, Robinson said, "I'm not concerned with your liking or disliking me ... all I ask is that you respect me as a human being." Regarding Robinson's qualities on the field,
 Robinson portrayed himself in the 1950 motion picture ''
Robinson portrayed himself in the 1950 motion picture ''
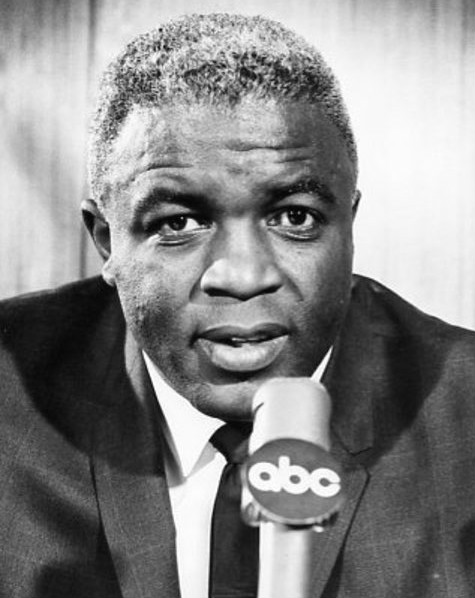 In 1965, Robinson served as an analyst for Major League Baseball on ABC, ABC's ''Major League Baseball Game of the Week'' telecasts, the first black person to do so. In 1966, Robinson was hired as general manager for the short-lived Brooklyn Dodgers (Continental Football League), Brooklyn Dodgers of the Continental Football League. In 1972, he served as a part-time commentator on Montreal Expos telecasts.
On June 4, 1972, the Dodgers retired his uniform number, 42, alongside those of Roy Campanella (39) and Sandy Koufax (32). From 1957 to 1964, Robinson was the vice president for personnel at
In 1965, Robinson served as an analyst for Major League Baseball on ABC, ABC's ''Major League Baseball Game of the Week'' telecasts, the first black person to do so. In 1966, Robinson was hired as general manager for the short-lived Brooklyn Dodgers (Continental Football League), Brooklyn Dodgers of the Continental Football League. In 1972, he served as a part-time commentator on Montreal Expos telecasts.
On June 4, 1972, the Dodgers retired his uniform number, 42, alongside those of Roy Campanella (39) and Sandy Koufax (32). From 1957 to 1964, Robinson was the vice president for personnel at  Robinson protested against the major leagues' ongoing lack of minority managers and central office personnel, and he turned down an invitation to appear in an Old-Timers' Day, old-timers' game at Yankee Stadium in 1969. He made his final public appearance on October 15, 1972, nine days before his death, throwing the ceremonial first pitch before Game 2 of the 1972 World Series, World Series at Riverfront Stadium in Cincinnati. He gratefully accepted a plaque honoring the twenty-fifth anniversary of his MLB debut, but also commented, "I'm going to be tremendously more pleased and more proud when I look at that third base coaching line one day and see a black face managing in baseball." This wish was only fulfilled after Robinson's death: following the 1974 season, the
Robinson protested against the major leagues' ongoing lack of minority managers and central office personnel, and he turned down an invitation to appear in an Old-Timers' Day, old-timers' game at Yankee Stadium in 1969. He made his final public appearance on October 15, 1972, nine days before his death, throwing the ceremonial first pitch before Game 2 of the 1972 World Series, World Series at Riverfront Stadium in Cincinnati. He gratefully accepted a plaque honoring the twenty-fifth anniversary of his MLB debut, but also commented, "I'm going to be tremendously more pleased and more proud when I look at that third base coaching line one day and see a black face managing in baseball." This wish was only fulfilled after Robinson's death: following the 1974 season, the
 Robinson's eldest son, Jackie Robinson Jr., had emotional trouble during his childhood and entered special education at an early age. He enlisted in the Army in search of a disciplined environment, served in the Vietnam War, and was wounded in action on November 19, 1965. After his discharge, he struggled with drug problems. Robinson Jr. eventually completed the treatment program at Daytop Village in Seymour, Connecticut, and became a counselor at the institution. Robinson, Rachel, p. 201. On June 17, 1971, he was killed in an automobile accident at age 24. The experience with his son's drug addiction turned Robinson Sr. into an avid anti-drug crusader toward the end of his life.
Robinson did not outlive his son by very long. In 1968, he suffered a heart attack. Complications from Cardiovascular disease, heart disease and
Robinson's eldest son, Jackie Robinson Jr., had emotional trouble during his childhood and entered special education at an early age. He enlisted in the Army in search of a disciplined environment, served in the Vietnam War, and was wounded in action on November 19, 1965. After his discharge, he struggled with drug problems. Robinson Jr. eventually completed the treatment program at Daytop Village in Seymour, Connecticut, and became a counselor at the institution. Robinson, Rachel, p. 201. On June 17, 1971, he was killed in an automobile accident at age 24. The experience with his son's drug addiction turned Robinson Sr. into an avid anti-drug crusader toward the end of his life.
Robinson did not outlive his son by very long. In 1968, he suffered a heart attack. Complications from Cardiovascular disease, heart disease and
 Major League Baseball has honored Robinson many times since his death. In 1987, both the National and American League MLB Rookie of the Year Award, Rookie of the Year Awards were renamed the "Jackie Robinson Award" in honor of the first recipient (Robinson's Major League Rookie of the Year Award in 1947 encompassed both leagues). On April 15, 1997, Robinson's jersey number, 42, was retired throughout Major League Baseball, the first time any jersey number had been retired throughout one of the Major North American professional sports teams, four major American sports leagues. Under the terms of the retirement, a grandfather clause allowed the handful of players who wore number 42 to continue doing so in tribute to Robinson, until such time as they subsequently changed teams or jersey numbers. This affected players such as the Mets' Butch Huskey and Boston's Mo Vaughn. The Yankees' Mariano Rivera, who retired at the end of the 2013 season, was the last player in Major League Baseball to wear jersey number 42 on a regular basis. Since 1997, only Wayne Gretzky's number 99, retired by the National Hockey League, NHL in 2000, and Bill Russell's number 6, retired by the National Basketball Association, NBA in 2022, have been retired league-wide in any of the four major sports. There have also been calls for MLB to retire number 21 league-wide in honor of Roberto Clemente, a sentiment opposed by the Robinson family.
As an exception to the retired-number policy, MLB began honoring Robinson by allowing players to wear number 42 on April 15, Jackie Robinson Day, which is an annual observance that started in 2004. For the 60th anniversary of Robinson's major league debut, MLB invited players to wear the number 42 on Jackie Robinson Day in 2007. The gesture was originally the idea of outfielder Ken Griffey Jr., who sought Rachel Robinson's permission to wear the number. After Griffey received her permission, Commissioner Bud Selig not only allowed Griffey to wear the number, but also extended an invitation to all major league teams to do the same. Ultimately, more than 200 players wore number 42, including the entire rosters of the Los Angeles Dodgers, New York Mets, Houston Astros,
Major League Baseball has honored Robinson many times since his death. In 1987, both the National and American League MLB Rookie of the Year Award, Rookie of the Year Awards were renamed the "Jackie Robinson Award" in honor of the first recipient (Robinson's Major League Rookie of the Year Award in 1947 encompassed both leagues). On April 15, 1997, Robinson's jersey number, 42, was retired throughout Major League Baseball, the first time any jersey number had been retired throughout one of the Major North American professional sports teams, four major American sports leagues. Under the terms of the retirement, a grandfather clause allowed the handful of players who wore number 42 to continue doing so in tribute to Robinson, until such time as they subsequently changed teams or jersey numbers. This affected players such as the Mets' Butch Huskey and Boston's Mo Vaughn. The Yankees' Mariano Rivera, who retired at the end of the 2013 season, was the last player in Major League Baseball to wear jersey number 42 on a regular basis. Since 1997, only Wayne Gretzky's number 99, retired by the National Hockey League, NHL in 2000, and Bill Russell's number 6, retired by the National Basketball Association, NBA in 2022, have been retired league-wide in any of the four major sports. There have also been calls for MLB to retire number 21 league-wide in honor of Roberto Clemente, a sentiment opposed by the Robinson family.
As an exception to the retired-number policy, MLB began honoring Robinson by allowing players to wear number 42 on April 15, Jackie Robinson Day, which is an annual observance that started in 2004. For the 60th anniversary of Robinson's major league debut, MLB invited players to wear the number 42 on Jackie Robinson Day in 2007. The gesture was originally the idea of outfielder Ken Griffey Jr., who sought Rachel Robinson's permission to wear the number. After Griffey received her permission, Commissioner Bud Selig not only allowed Griffey to wear the number, but also extended an invitation to all major league teams to do the same. Ultimately, more than 200 players wore number 42, including the entire rosters of the Los Angeles Dodgers, New York Mets, Houston Astros,  At the November 2006 groundbreaking for Citi Field, the new ballpark for the New York Mets, it was announced that the main entrance, modeled on the one in Brooklyn's old
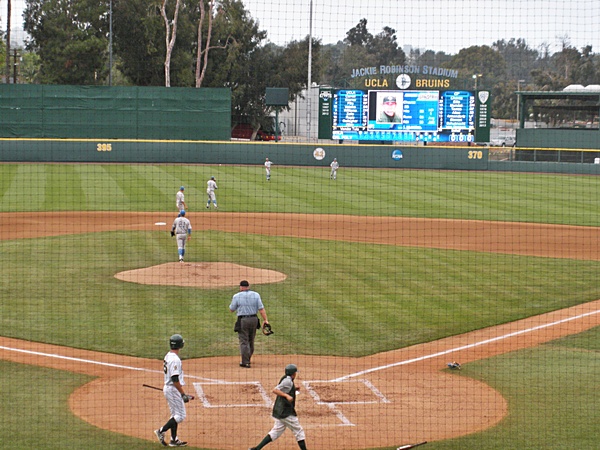
At the November 2006 groundbreaking for Citi Field, the new ballpark for the New York Mets, it was announced that the main entrance, modeled on the one in Brooklyn's old  A number of buildings have been named in Robinson's honor. The UCLA Bruins baseball team plays in Jackie Robinson Stadium (UCLA baseball), Jackie Robinson Stadium, which, because of the efforts of Jackie's brother Mack, features a memorial statue of Robinson by sculptor Richard H. Ellis. The stadium also unveiled a new mural of Robinson by Mike Sullivan on April 14, 2013. City Island Ballpark in
A number of buildings have been named in Robinson's honor. The UCLA Bruins baseball team plays in Jackie Robinson Stadium (UCLA baseball), Jackie Robinson Stadium, which, because of the efforts of Jackie's brother Mack, features a memorial statue of Robinson by sculptor Richard H. Ellis. The stadium also unveiled a new mural of Robinson by Mike Sullivan on April 14, 2013. City Island Ballpark in
Retrosheet
o
Seamheads
* * His life is retold in the radio drama
The Rhyme of the Ancient Dodger
, a presentation from ''Destination Freedom'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Robinson, Jackie Jackie Robinson, 1919 births 1972 deaths Activists for African-American civil rights African-American baseball players African-American male track and field athletes African-American Methodists African-American sports history American expatriate baseball players in Canada American male long jumpers American men's basketball players Baseball players from Georgia (U.S. state) Baseball players from Pasadena, California Basketball players from Pasadena, California Brooklyn Dodgers players Burials at Cypress Hills Cemetery Canadian Baseball Hall of Fame inductees College men's basketball head coaches in the United States Congressional Gold Medal recipients Guards (basketball) Kansas City Monarchs players Major League Baseball broadcasters Major League Baseball first basemen Major League Baseball players with retired numbers Major League Baseball Rookie of the Year Award winners Major League Baseball second basemen Military personnel from Georgia (U.S. state) Montreal Expos announcers Montreal Royals players National Baseball Hall of Fame inductees National College Baseball Hall of Fame inductees National League All-Stars National League batting champions National League Most Valuable Player Award winners National League stolen base champions New York State Athletic Commissioners Nonviolence advocates Pasadena City Lancers baseball players Pasadena City Lancers football players Pasadena City Lancers men's basketball players People from Cairo, Georgia People with type 1 diabetes Players of American football from Pasadena, California Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients Spingarn Medal winners Sportspeople from Pasadena, California UCLA Bruins baseball players UCLA Bruins football players UCLA Bruins men's basketball players UCLA Bruins men's track and field athletes United States Army officers United States Army personnel of World War II United States Army personnel who were court-martialed Writers from Georgia (U.S. state)
baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding tea ...
player who became the first African American to play in Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
(MLB) in the modern era. Robinson broke the baseball color line
The color line, also known as the color barrier, in American baseball excluded players of black African descent from Major League Baseball and its affiliated Minor Leagues until 1947 (with a few notable exceptions in the 19th century before the li ...
when he started at first base
A first baseman, abbreviated 1B, is the player on a baseball or softball team who fields the area nearest first base, the first of four bases a baserunner must touch in succession to score a run. The first baseman is responsible for the majori ...
for the Brooklyn Dodgers
The Brooklyn Dodgers were a Major League Baseball team founded in 1884 as a member of the American Association (19th century), American Association before joining the National League in 1890. They remained in Brooklyn until 1957, after which the ...
on April 15, 1947. When the Dodgers signed Robinson, it heralded the end of racial segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against hum ...
in professional baseball that had relegated black players to the Negro leagues
The Negro leagues were United States professional baseball leagues comprising teams of African Americans and, to a lesser extent, Latin Americans. The term may be used broadly to include professional black teams outside the leagues and it may be ...
since the 1880s. Robinson was inducted into the Baseball Hall of Fame
The National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum is a history museum and hall of fame in Cooperstown, New York, operated by private interests. It serves as the central point of the history of baseball in the United States and displays baseball-r ...
in 1962.
During his 10-year MLB career, Robinson won the inaugural Rookie of the Year Award
A rookie is a person new to an occupation, profession, or hobby. In sports, a ''rookie'' is a professional athlete in their first season (or year).
In contrast with a veteran who has experience and expertise, a rookie is usually inexperienced ...
in 1947, was an All-Star for six consecutive seasons from 1949 through 1954, and won the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team s ...
Most Valuable Player Award
In team sports, a most valuable player award, abbreviated 'MVP award', is an honor typically bestowed upon an individual (or individuals, in the instance of a tie) whose individual performance is the greatest in an entire league, for a particu ...
in 1949—the first black player so honored. Robinson played in six World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, contested since 1903 between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winner of the World ...
and contributed to the Dodgers' 1955 World Series championship.
In 1997, MLB retired
Retirement is the withdrawal from one's position or occupation or from one's active working life. A person may also semi-retire by reducing work hours or workload.
Many people choose to retire when they are elderly or incapable of doing their j ...
his uniform number 42 across all major league teams; he was the first professional athlete in any sport to be so honored. MLB also adopted a new annual tradition, " Jackie Robinson Day", for the first time on April 15, 2004, on which every player on every team wears No. 42.
Robinson's character, his use of nonviolence
Nonviolence is the personal practice of not causing harm to others under any condition. It may come from the belief that hurting people, animals and/or the environment is unnecessary to achieve an outcome and it may refer to a general philosoph ...
, and his talent challenged the traditional basis of segregation that had then marked many other aspects of American life. He influenced the culture of and contributed significantly to the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
. Robinson also was the first black television analyst in MLB and the first black vice president of a major American corporation, Chock full o'Nuts
Chock full o'Nuts is an American brand of coffee that originated from a chain of New York City coffee shops.
Its unusual name derives from the 18 nut shops that founder William Black (c. 1902 – 1983) established under that banner in the city ...
. In the 1960s, he helped establish the Freedom National Bank Freedom National Bank was an African-American owned bank in Harlem (New York City) founded in 1964 and shut down in 1990. Freedom National served Harlem's Black community and was one of the largest Black owned banks in the U.S. Its main office was a ...
, an African-American-owned financial institution based in Harlem
Harlem is a neighborhood in Upper Manhattan, New York City. It is bounded roughly by the Hudson River on the west; the Harlem River and 155th Street (Manhattan), 155th Street on the north; Fifth Avenue on the east; and 110th Street (Manhattan), ...
, New York. After his death in 1972, Robinson was posthumously awarded the Congressional Gold Medal
The Congressional Gold Medal is an award bestowed by the United States Congress. It is Congress's highest expression of national appreciation for distinguished achievements and contributions by individuals or institutions. The congressional pract ...
and Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merito ...
in recognition of his achievements on and off the field.
Early life
Family and personal life
Jack Roosevelt Robinson was born on January 31, 1919, into a family ofsharecroppers
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement with regard to agricultural land in which a landowner allows a tenant to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land.
Sharecropping has a long history and there are a wide range ...
in Cairo, Georgia
Cairo () is a city in Grady County, Georgia, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 10,179. The city is the county seat of Grady County.
History
Cairo was founded in 1835. It was incorporated as a town in 1870 and as ...
. He was the youngest of five children born to Mallie (McGriff) and Jerry Robinson, after siblings Edgar, Frank, Matthew
Matthew may refer to:
* Matthew (given name)
* Matthew (surname)
* ''Matthew'' (ship), the replica of the ship sailed by John Cabot in 1497
* ''Matthew'' (album), a 2000 album by rapper Kool Keith
* Matthew (elm cultivar), a cultivar of the Ch ...
(nicknamed "Mack"), and Willa Mae. Bigelow, p. 225. His middle name was in honor of former President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
, who died 25 days before Robinson was born. After Robinson's father left the family in 1920, they moved to Pasadena, California
Pasadena ( ) is a city in Los Angeles County, California, northeast of downtown Los Angeles. It is the most populous city and the primary cultural center of the San Gabriel Valley. Old Pasadena is the city's original commercial district.
I ...
. Robinson, Jackie (1995), p. 9.
The extended Robinson family established itself on a residential plot containing two small houses at 121 Pepper Street in Pasadena. Robinson's mother worked various odd jobs to support the family. Growing up in relative poverty in an otherwise affluent community, Robinson and his minority friends were excluded from many recreational opportunities. Robinson, Rachel, p. 17. As a result, Robinson joined a neighborhood gang, but his friend Carl Anderson persuaded him to abandon it. Eig, p. 10.
John Muir High School
In 1935, Robinson graduated from Washington Junior High School and enrolled atJohn Muir High School
John Muir High School is a four-year comprehensive secondary school in Pasadena, California, United States and is a part of the Pasadena Unified School District. The school is named after preservationist John Muir.
History
In 1926 the Pasadena ...
(Muir Tech). Recognizing his athletic talents, Robinson's older brothers Mack (himself an accomplished athlete and silver medalist at the 1936 Summer Olympics
The 1936 Summer Olympics (German: ''Olympische Sommerspiele 1936''), officially known as the Games of the XI Olympiad (German: ''Spiele der XI. Olympiade'') and commonly known as Berlin 1936 or the Nazi Olympics, were an international multi-sp ...
) and Frank inspired Jackie to pursue his interest in sports.
At Muir Tech, Robinson played numerous sports at the varsity level and lettered
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "t ...
in four of them: football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
, basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
, track
Track or Tracks may refer to:
Routes or imprints
* Ancient trackway, any track or trail whose origin is lost in antiquity
* Animal track, imprints left on surfaces that an animal walks across
* Desire path, a line worn by people taking the shorte ...
, and baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding tea ...
. He played shortstop
Shortstop, abbreviated SS, is the baseball or softball fielding position between second and third base, which is considered to be among the most demanding defensive positions. Historically the position was assigned to defensive specialists who ...
and catcher
Catcher is a Baseball positions, position in baseball and softball. When a Batter (baseball), batter takes their at bat, turn to hit, the catcher crouches behind home plate, in front of the (home plate, home) Umpire (baseball), umpire, and recei ...
on the baseball team, quarterback
The quarterback (commonly abbreviated "QB"), colloquially known as the "signal caller", is a position in gridiron football. Quarterbacks are members of the offensive platoon and mostly line up directly behind the offensive line. In modern Ame ...
on the football team, and guard
Guard or guards may refer to:
Professional occupations
* Bodyguard, who protects an individual from personal assault
* Crossing guard, who stops traffic so pedestrians can cross the street
* Lifeguard, who rescues people from drowning
* Prison ...
on the basketball team. With the track and field squad, he won awards in the broad jump
The long jump is a track and field event in which athletes combine speed, strength and agility in an attempt to leap as far as possible from a takeoff point. Along with the triple jump, the two events that measure jumping for distance as a gr ...
. He was also a member of the tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
team.
In 1936, Robinson won the junior boys singles championship in the annual Pacific Coast Negro Tennis Tournament and earned a place on the Pomona annual baseball tournament all-star team, which included future Hall of Famers Ted Williams
Theodore Samuel Williams (August 30, 1918 – July 5, 2002) was an American professional baseball player and manager. He played his entire 19-year Major League Baseball (MLB) career, primarily as a left fielder, for the Boston Red Sox from 1939 ...
and Bob Lemon
Robert Granville Lemon (September 22, 1920 – January 11, 2000) was an American right-handed pitcher and manager (baseball), manager in Major League Baseball (MLB). Lemon was elected to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum, National Ba ...
.Rampersad
Rampersad also spelt as Ramprasad or Rampersaud is a surname common in Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, Suriname, the Caribbean, Fiji, South Africa, and Mauritius. It is of Indian and Hindu origin, derived from the Sanskrit words Rama Prasada, and is n ...
, p. 37. In late January 1937, the ''Pasadena Star-News
The ''Pasadena Star-News'' is a paid local daily newspaper for the greater Pasadena, California area. The Pasadena ''Star-News'' is a member of Southern California News Group (formerly the Los Angeles Newspaper Group), since 1996. It is also part ...
'' newspaper reported that Robinson "for two years has been the outstanding athlete at Muir, starring in football, basketball, track, baseball and tennis."
Pasadena Junior College
After Muir, Robinson attendedPasadena Junior College
Pasadena City College (PCC) is a public community college in Pasadena, California.
History
Pasadena City College was founded in 1924 as Pasadena Junior College. From 1928 to 1953, it operated as a four-year junior college, combining the la ...
(PJC), where he continued his athletic career by participating in basketball, football, baseball, and track. On the football team, he played quarterback and safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to risk management, the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are ...
. He was a shortstop and leadoff hitter for the baseball team, and he broke an American junior college broad-jump record held by his brother Mack with a jump of 25 ft. in. on May 7, 1938. As at Muir High School, most of Jackie's teammates were white. While playing football at PJC, Robinson suffered a fractured ankle, complications from which would eventually delay his deployment status while in the military. In 1938, he was elected to the All-Southland Junior College Team for baseball and selected as the region's Most Valuable Player. Robinson, Rachel, p. 20.
That year, Robinson was one of 10 students named to the school's Order of the Mast and Dagger (''Omicron Mu Delta''), awarded to students performing "outstanding service to the school and whose scholastic and citizenship record is worthy of recognition." Also while at PJC, he was elected to the Lancers, a student-run police organization responsible for patrolling various school activities.
An incident at PJC illustrated Robinson's impatience with authority figures he perceived as racist
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism ...
—a character trait that would resurface repeatedly in his life. On January 25, 1938, he was arrested after vocally disputing the detention of a black friend by police.Linge
The Linge is a river in the Betuwe that is 99.8 km long, which makes it one of the longest rivers that flow entirely within the Netherlands.
It starts near the village Doornenburg near the German border. A legend tells us that if there w ...
, p. 18. Robinson received a two-year suspended sentence, but the incident—along with other rumored run-ins between Robinson and police—gave Robinson a reputation for combativeness in the face of racial antagonism. While at PJC, he was motivated by a preacher (the Rev. Karl Downs) to attend church on a regular basis, and Downs became a confidant for Robinson, a Christian. Toward the end of his PJC tenure, Frank Robinson (to whom Robinson felt closest among his three brothers) was killed in a motorcycle accident. The event motivated Jackie to pursue his athletic career at the nearby University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California St ...
(UCLA), where he could remain closer to Frank's family.
UCLA and afterward
 After graduating from PJC in spring 1939, Robinson enrolled at UCLA, where he became the school's first athlete to win
After graduating from PJC in spring 1939, Robinson enrolled at UCLA, where he became the school's first athlete to win varsity letter
A varsity letter (or monogram) is an award earned in the United States for excellence in school activities. A varsity letter signifies that its recipient was a qualified varsity team member, awarded after a certain standard was met.
Description ...
s in four sports: baseball, basketball, football, and track.
He was one of four black players on the Bruins' 1939 football team; the others were Woody Strode
Woodrow Wilson Woolwine Strode (July 25, 1914 – December 31, 1994) was an American athlete and actor. He was a decathlete and football star who was one of the first Black American players in the National Football League in the postwar era. Aft ...
, Kenny Washington, and Ray Bartlett. Washington, Strode, and Robinson made up three of the team's four backfield players. At a time when only a few black students played mainstream college football, this made UCLA college football's most They went undefeated with four ties at Robinson finished the season with 12.2 yards per attempt on 42 carries, which is the school football record for highest rushing yards per carry in a season as of 2022. Robinson also led the NCAA in punt return average in the 1939 and 1940 seasons.
In track and field
Track and field is a sport that includes athletic contests based on running, jumping, and throwing skills. The name is derived from where the sport takes place, a running track and a grass field for the throwing and some of the jumping events ...
, Robinson won the 1940 NCAA championship in the long jump
The long jump is a track and field event in which athletes combine speed, strength and agility in an attempt to leap as far as possible from a takeoff point. Along with the triple jump, the two events that measure jumping for distance as a gr ...
at . Baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding tea ...
was Robinson's "worst sport" at UCLA; he hit .097 in his only season, although in his first game he went 4-for-4 and twice stole home.
While a senior at UCLA, Robinson met his future wife, Rachel Isum (b.1922), a UCLA freshman who was familiar with Robinson's athletic career He played football as a senior, but the 1940 Bruins won only one game. In the spring, Robinson left college just shy of graduation, despite the reservations of his mother and Isum. He took a job as an assistant athletic director with the government's National Youth Administration
The National Youth Administration (NYA) was a New Deal agency sponsored by Franklin D. Roosevelt during his presidency. It focused on providing work and education for Americans between the ages of 16 and 25. It operated from June 26, 1935 to ...
(NYA)
After the government ceased NYA operations, Robinson traveled to Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
in the fall of 1941 to play football for the semi-professional, racially integrated Honolulu After a short season, Robinson returned to California in December 1941 to pursue a career as running back for the Los Angeles Bulldogs
The Los Angeles Bulldogs were a professional American football team that competed from 1936 to 1948 (the last year as the Long Beach Bulldogs). Formed with the intention of joining the National Football League in 1937 (and turned down in favor of ...
of the Pacific Coast Football League. By that time, however, the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
had taken place, which drew the United States into World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and ended Robinson's nascent football career.
Military career
In 1942, Robinson was drafted and assigned to a segregated Army cavalry unit atFort Riley
Fort Riley is a United States Army installation located in North Central Kansas, on the Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, between Junction City and Manhattan. The Fort Riley Military Reservation covers 101,733 acres (41,170 ha) in Gear ...
(in Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
). Having the requisite qualifications, Robinson and several other black soldiers applied for admission to an Officer Candidate School
An officer candidate school (OCS) is a military school which trains civilians and Enlisted rank, enlisted personnel in order for them to gain a Commission (document), commission as Commissioned officer, officers in the armed forces of a country. ...
(OCS) then located at Fort Riley. Although the Army's initial July 1941 guidelines for OCS had been drafted as race neutral, few black applicants were admitted into OCS until after subsequent directives by Army leadership. As a result, the applications of Robinson and his colleagues were delayed for several months. Robinson, Jackie (1995), p. 13. After protests by heavyweight boxing champion Joe Louis (then stationed at Fort Riley) and with the help of Truman Gibson
Truman Kella Gibson, Jr. (January 22, 1912 – December 23, 2005) was an African-American businessman, attorney, government advisor, and later influential boxing promoter who played a unique and unheralded role in the Civil Rights Movement, pr ...
(then an assistant civilian aide to the Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
), the men were accepted into OCS. The experience led to a personal friendship between Robinson and Louis. Upon finishing OCS, Robinson was commissioned as a second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
in January 1943. Shortly afterward, Robinson and Isum were formally engaged.
 After receiving his commission, Robinson was reassigned to
After receiving his commission, Robinson was reassigned to Fort Hood
Fort Hood is a United States Army post located near Killeen, Texas. Named after Confederate General John Bell Hood, it is located halfway between Austin and Waco, about from each, within the U.S. state of Texas. The post is the headquarter ...
, Texas, where he joined the 761st "Black Panthers" Tank Battalion. While at Fort Hood, Robinson often used his weekend leave to visit the Rev. Karl Downs, President of Sam Huston College (now Huston–Tillotson University
Huston–Tillotson University (HT) is a private historically black university in Austin, Texas. Established in 1875, Huston–Tillotson University was the first institution of higher learning in Austin. The university is affiliated with the Unit ...
) in nearby Austin, Texas
Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of Texas, as well as the county seat, seat and largest city of Travis County, Texas, Travis County, with portions extending into Hays County, Texas, Hays and Williamson County, Texas, Williamson co ...
; in California, Downs had been Robinson's pastor at Scott United Methodist Church while Robinson attended PJC.
An event on July 6, 1944, derailed Robinson's military career. While awaiting results of hospital tests on the ankle he had injured in junior college, Robinson boarded an Army bus with a fellow officer's wife; although the Army had commissioned its own unsegregated bus line, the bus driver ordered Robinson to move to the back of the bus. (also published at Tygiel (2002), pp. 14–23). Robinson refused. The driver backed down, but after reaching the end of the line, summoned the military police
Military police (MP) are law enforcement agencies connected with, or part of, the military of a state. In wartime operations, the military police may support the main fighting force with force protection, convoy security, screening, rear recon ...
, who took Robinson into custody. When Robinson later confronted the investigating duty officer about racist questioning by the officer and his assistant, the officer recommended Robinson be court-martialed
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of memb ...
.
After Robinson's commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
in the 761st, Paul L. Bates, refused to authorize the legal action, Robinson was summarily transferred to the 758th Battalion—where the commander quickly consented to charge Robinson with multiple offenses, including, among other charges, public drunkenness, even though Robinson did not drink.
By the time of the court-martial in August 1944, the charges against Robinson had been reduced to two counts of insubordination during questioning. Robinson was acquitted by an all-white panel of nine officers.
Although his former unit, the 761st Tank Battalion, became the first black tank unit to see combat in World War II, Robinson's court-martial proceedings prohibited him from being deployed overseas; thus, he never saw combat action.
After his acquittal, he was transferred to Camp Breckinridge, Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, where he served as a coach for army athletics until receiving an honorable discharge
A military discharge is given when a member of the armed forces is released from their obligation to serve. Each country's military has different types of discharge. They are generally based on whether the persons completed their training and th ...
in November 1944. While there, Robinson met a former player for the Kansas City Monarchs
The Kansas City Monarchs were the longest-running franchise in the history of baseball's Negro leagues. Operating in Kansas City, Missouri, and owned by J. L. Wilkinson, they were charter members of the Negro National League from 1920 to 19 ...
of the Negro American League
The Negro American League was one of the several Negro leagues created during the time organized American baseball was segregated. The league was established in 1937, and disbanded after its 1962 season.
Negro American League franchises
:''Ann ...
, who encouraged Robinson to write the Monarchs and ask for a tryout. Robinson took the former player's advice and wrote to Monarchs co-owner Thomas Baird.
Post-military
After his discharge, Robinson briefly returned to his old football club, the Los Angeles Bulldogs. Robinson then accepted an offer from his old friend and pastor Rev. Karl Downs to be the athletic director atSamuel Huston College
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bi ...
in Austin, then of the Southwestern Athletic Conference.Rampersad
Rampersad also spelt as Ramprasad or Rampersaud is a surname common in Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, Suriname, the Caribbean, Fiji, South Africa, and Mauritius. It is of Indian and Hindu origin, derived from the Sanskrit words Rama Prasada, and is n ...
, p. 114. The job included coaching the school's basketball team for the 1944–45 season. As it was a fledgling program, few students tried out for the basketball team, and Robinson even resorted to inserting himself into the lineup for exhibition games. Although his teams were outmatched by opponents, Robinson was respected as a disciplinarian coach, and drew the admiration of, among others, Langston University
Langston University (LU) is a public land-grant historically black university in Langston, Oklahoma. It is the only historically black college in the state. Though located in a rural setting east of Guthrie, Langston also serves an urban mis ...
basketball player Marques Haynes
Marques Haynes (March 10, 1926 – May 22, 2015) was an American professional basketball player and member of the Harlem Globetrotters, notable for his ability to dribble the ball and keep it away from defenders. According to the 1988 film ''Harl ...
, a future member of the Harlem Globetrotters.
Playing career
Negro leagues and major league prospects
 In early 1945, while Robinson was at Sam Huston College, the
In early 1945, while Robinson was at Sam Huston College, the Kansas City Monarchs
The Kansas City Monarchs were the longest-running franchise in the history of baseball's Negro leagues. Operating in Kansas City, Missouri, and owned by J. L. Wilkinson, they were charter members of the Negro National League from 1920 to 19 ...
sent him a written offer to play professional baseball in the Negro leagues. Robinson accepted a contract for $400 per month. Although he played well for the Monarchs, Robinson was frustrated with the experience. He had grown used to a structured playing environment in college, and the Negro leagues' disorganization and embrace of gambling interests appalled him. The hectic travel schedule also placed a burden on his relationship with Isum, with whom he could now communicate only by letter. In all, Robinson played 47 games at shortstop
Shortstop, abbreviated SS, is the baseball or softball fielding position between second and third base, which is considered to be among the most demanding defensive positions. Historically the position was assigned to defensive specialists who ...
for the Monarchs, hitting .387 with five home runs, and registering 13 stolen bases. He also appeared in the 1945 East–West All-Star Game, going hitless in five at-bats.
During the season, Robinson pursued potential major league interests. No black man had played in the major leagues since Moses Fleetwood Walker
Moses Fleetwood Walker (October 7, 1856 – May 11, 1924) was an American professional baseball catcher who, historically, was credited with being the first black man to play in Major League Baseball (MLB). A native of Mount Pleasant, Ohio, an ...
in 1884, but the Boston Red Sox
The Boston Red Sox are an American professional baseball team based in Boston. The Red Sox compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. Founded in as one of the American League's eight ...
nevertheless held a tryout at Fenway Park
Fenway Park is a baseball stadium located in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, near Kenmore Square. Since 1912, it has been the home of the Boston Red Sox, the city's American League baseball team, and since 1953, its only Major League Base ...
for Robinson and other black players on April 16. Bryant, p. 31. The tryout, however, was a farce chiefly designed to assuage the desegregationist sensibilities of powerful Boston City Councilman Isadore H. Y. Muchnick
Isadore Harry Yaver Muchnick (January 11, 1908 – September 15, 1963) was an American politician who served as a member of the Boston City Council from 1942 to 1947 and Boston School Committee from 1948 to 1953.
Early life
Muchnick was born on ...
. Even with the stands limited to management, Robinson was subjected to racial epithets. He left the tryout humiliated, and more than 14 years later, in July 1959, the Red Sox became the final major league team to integrate its roster.
Other teams, however, had more serious interest in signing a black ballplayer. In the mid-1940s, Branch Rickey
Wesley Branch Rickey (December 20, 1881 – December 9, 1965) was an American baseball player and sports executive. Rickey was instrumental in breaking Major League Baseball's color barrier by signing black player Jackie Robinson. He also creat ...
, club president and general manager
A general manager (GM) is an executive who has overall responsibility for managing both the revenue and cost elements of a company's income statement, known as profit & loss (P&L) responsibility. A general manager usually oversees most or all of ...
of the Brooklyn Dodgers
The Brooklyn Dodgers were a Major League Baseball team founded in 1884 as a member of the American Association (19th century), American Association before joining the National League in 1890. They remained in Brooklyn until 1957, after which the ...
, began to scout the Negro leagues for a possible addition to the Dodgers' roster. Rickey selected Robinson from a list of promising black players and interviewed him for possible assignment to Brooklyn's International League
The International League (IL) is a Minor League Baseball league that operates in the United States. Along with the Pacific Coast League, it is one of two leagues playing at the Triple-A level, which is one grade below Major League Baseball ...
farm club
In sports, a farm team, farm system, feeder team, feeder club, or nursery club is generally a team or club whose role is to provide experience and training for young players, with an agreement that any successful players can move on to a higher ...
, the Montreal Royals
The Montreal Royals were a minor league professional baseball team in Montreal, Quebec, during 1897–1917 and 1928–1960. A member of the International League, the Royals were the top farm club (Class AAA) of the Brooklyn Dodgers from 1939; pi ...
. Rickey was especially interested in making sure his eventual signee could withstand the inevitable racial abuse that would be directed at him. In a famous three-hour exchange on August 28, 1945, Rickey asked Robinson if he could face the racial animus without taking the bait and reacting angrily—a concern given Robinson's prior arguments with law enforcement officials at PJC and in the military. Robinson was aghast: "Are you looking for a Negro who is afraid to fight back?" Rickey replied that he needed a Negro player "with guts enough not to fight back." Robinson, Jackie (1995), p. 33. After obtaining a commitment from Robinson to "turn the other cheek" to racial antagonism, Rickey agreed to sign him to a contract for $600 a month, equal to $ today. Robinson, Jackie (1995), p. 34. Rickey did not offer compensation to the Monarchs, instead believing all Negro league players were free agents due to the contracts not containing a reserve clause. Among those with whom Rickey discussed prospects was Wendell Smith Wendell Smith may refer to:
* Wendell Smith (sportswriter) (1914–1972), American baseball writer
*Wendell Smith (actor)
Wendell Smith is a Canadian actor born in Antigonish, Nova Scotia.
History
Originally based in Nova Scotia, Wendell Smit ...
, writer for the black weekly ''Pittsburgh Courier
The ''Pittsburgh Courier'' was an African-American weekly newspaper published in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, from 1907 until October 22, 1966. By the 1930s, the ''Courier'' was one of the leading black newspapers in the United States.
It was acqu ...
'', who, according to Cleveland Indians
The Cleveland Guardians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Guardians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. Since , they have played at Progressive F ...
owner and team president Bill Veeck
William Louis Veeck Jr. ( ; February 9, 1914 – January 2, 1986), also known as "Sport Shirt Bill", was an American Major League Baseball franchise owner and promoter. Veeck was at various times the owner of the Cleveland Indians, St. Louis Br ...
, "influenced Rickey to take Jack Robinson, for which he's never completely gotten credit."
Although he required Robinson to keep the arrangement a secret for the time being, Rickey committed to formally signing Robinson before November 1, 1945. On October 23, it was publicly announced that Robinson would be assigned to the Royals for the 1946 season. On the same day, with representatives of the Royals and Dodgers present, Robinson formally signed his contract with the Royals. In what was later referred to as "The Noble Experiment", Robinson was the first black baseball player in the International League since the 1880s. He was not necessarily the best player in the Negro leagues, and black talents Satchel Paige
Leroy Robert "Satchel" Paige (July 7, 1906 – June 8, 1982) was an American professional baseball pitcher who played in Negro league baseball and Major League Baseball (MLB). His career spanned five decades and culminated with his induction in ...
and Josh Gibson
Joshua Gibson (December 21, 1911 – January 20, 1947) was an American baseball catcher primarily in the Negro leagues. Baseball historians consider Gibson among the best power hitters and catchers in baseball history. In 1972, he became the se ...
were upset when Robinson was selected first. Larry Doby
Lawrence Eugene Doby (December 13, 1923 – June 18, 2003) was an American professional baseball player in the Negro leagues and Major League Baseball (MLB) who was the second black player to break baseball's color barrier and the first black pl ...
, who broke the color line in the American League
The American League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the American League (AL), is one of two leagues that make up Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada. It developed from the Western League, a minor league ...
the same year as Robinson, said, "One of the things that was disappointing and disheartening to a lot of the black players at the time was that Jack was not the best player. The best was Josh Gibson. I think that's one of the reasons why Josh died so early—he was heartbroken."
Rickey's offer allowed Robinson to leave behind the Monarchs and their grueling bus rides, and he went home to Pasadena.
That September, he signed with Chet Brewer
Chester Arthur Brewer (January 14, 1907 – March 26, 1990) was an American right-handed pitcher in baseball's Negro leagues. Born in Leavenworth, Kansas, he played for the Kansas City Monarchs, and from 1957 to 1974 he scouted for the Pittsburgh ...
's Kansas City Royals, a post-season barnstorming
Barnstorming was a form of entertainment in which stunt pilots performed tricks individually or in groups that were called flying circuses. Devised to "impress people with the skill of pilots and the sturdiness of planes," it became popular in t ...
team in the California Winter League. Later that off-season, he briefly toured South America with another barnstorming team, while his fiancée Isum pursued nursing opportunities in New York City. On February 10, 1946, Robinson and Isum were married by their old friend, the Rev. Karl Downs.
Minor leagues
In 1946, Robinson arrived atDaytona Beach, Florida
Daytona Beach, or simply Daytona, is a coastal Resort town, resort-city in east-central Florida. Located on the eastern edge of Volusia County, Florida, Volusia County near the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic coastline, its population ...
, for spring training
Spring training is the preseason in Major League Baseball (MLB), a series of practices and exhibition games preceding the start of the regular season. Spring training allows new players to try out for Schedule (workplace), roster and position spo ...
with the Montreal Royals
The Montreal Royals were a minor league professional baseball team in Montreal, Quebec, during 1897–1917 and 1928–1960. A member of the International League, the Royals were the top farm club (Class AAA) of the Brooklyn Dodgers from 1939; pi ...
of the Class AAA
Triple-A (officially Class AAA) has been the highest level of play in Minor League Baseball in the United States since 1946. Currently, two leagues operate at the Triple-A level, the International League (IL) and the Pacific Coast League (PCL). ...
International League
The International League (IL) is a Minor League Baseball league that operates in the United States. Along with the Pacific Coast League, it is one of two leagues playing at the Triple-A level, which is one grade below Major League Baseball ...
. Clay Hopper
Robert Clay Hopper (October 3, 1902 – April 17, 1976) was an American professional baseball player and manager in minor league baseball. Hopper played from 1926 through 1941 and continued managing through 1956.
Managing the Montreal Royals ...
, the manager of the Royals, asked Rickey to assign Robinson to any other Dodger affiliate, but Rickey refused.
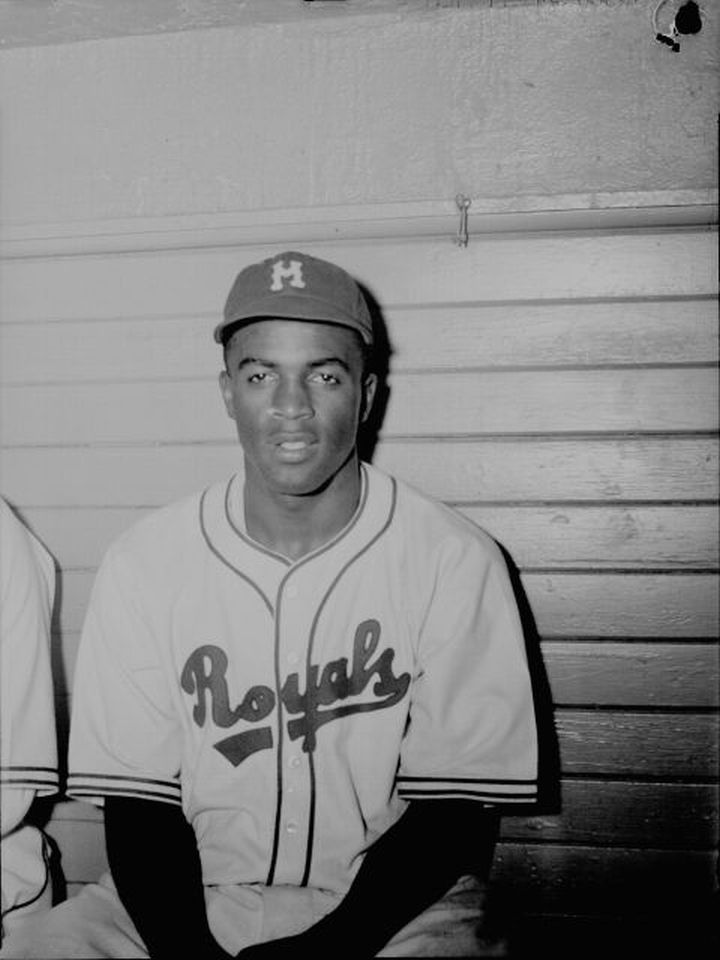
 Robinson's presence was controversial in racially segregated Florida. He was not allowed to stay with his white teammates at the team hotel, and instead lodged at the home of Joe and Dufferin Harris, a politically active African American couple who introduced the Robinsons to civil rights activist
Robinson's presence was controversial in racially segregated Florida. He was not allowed to stay with his white teammates at the team hotel, and instead lodged at the home of Joe and Dufferin Harris, a politically active African American couple who introduced the Robinsons to civil rights activist Mary McLeod Bethune
Mary Jane McLeod Bethune ( McLeod; July 10, 1875 – May 18, 1955) was an American educator, philanthropist, humanitarian, Womanism, womanist, and civil rights activist. Bethune founded the National Council of Negro Women in 1935, established th ...
. Since the Dodgers organization did not own a spring training facility, scheduling was subject to the whim of area localities, several of which turned down any event involving Robinson or Johnny Wright, another black player whom Rickey had signed to the Dodgers' organization in January. In Sanford, Florida
Sanford is a city in the central region of the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Seminole County. As of the 2020 census, its population was 61,051.
Known as the "Historic Waterfront Gateway City", Sanford sits on the southern shore ...
, the police chief threatened to cancel games if Robinson and Wright did not cease training activities there; as a result, Robinson was sent back to Daytona Beach. In Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
, the stadium
A stadium ( : stadiums or stadia) is a place or venue for (mostly) outdoor sports, concerts, or other events and consists of a field or stage either partly or completely surrounded by a tiered structure designed to allow spectators to stand o ...
was padlocked shut without warning on game day, by order of the city's Parks and Public Property director. In DeLand, a scheduled day game was postponed, ostensibly because of issues with the stadium's electrical lighting.
After much lobbying of local officials by Rickey himself, the Royals were allowed to host a game involving Robinson in Daytona Beach. Robinson made his Royals debut at Daytona Beach's City Island Ballpark on March 17, 1946, in an exhibition game against the team's parent club, the Dodgers. Robinson thus became the first black player to openly play for a minor league team against a major league team since the ''de facto'' baseball color line had been implemented in the 1880s. Loewenp. 163
 Later in spring training, after some less-than-stellar performances, Robinson was shifted from shortstop to second base, allowing him to make shorter throws to first base. Robinson's performance soon rebounded. On April 18, 1946,
Later in spring training, after some less-than-stellar performances, Robinson was shifted from shortstop to second base, allowing him to make shorter throws to first base. Robinson's performance soon rebounded. On April 18, 1946, Roosevelt Stadium
Roosevelt Stadium was a baseball stadium at Droyer's Point in Jersey City, New Jersey. It opened in April 1937 and hosted high-minor league baseball, 15 major league baseball games, plus championship boxing matches, top-name musical acts, an ...
hosted the Jersey City Giants {{about, the baseball team, the football team, American Association (American football)
The Jersey City Giants was the name of a high-level American minor league baseball franchise that played in Jersey City, New Jersey, as the top farm system a ...
' season opener against the Montreal Royals
The Montreal Royals were a minor league professional baseball team in Montreal, Quebec, during 1897–1917 and 1928–1960. A member of the International League, the Royals were the top farm club (Class AAA) of the Brooklyn Dodgers from 1939; pi ...
, marking the professional debut of the Royals' Jackie Robinson and the first time the color barrier had been broken in a game between two minor league clubs. Pitching against Robinson was Warren Sandel who had played against him when they both lived in California. During Robinson's first at bat, the Jersey City catcher, Dick Bouknight, demanded that Sandel throw at Robinson, but Sandel refused. Although Sandel induced Robinson to ground out at his first at bat, Robinson ended up with four hits in his five trips to the plate; his first hit was a three-run home run in the game's third inning. He also scored four runs, drove in three, and stole two bases in the Royals' 14–1 victory. Robinson proceeded to lead the International League that season with a .349 batting average and .985 fielding percentage
In baseball statistics, fielding percentage, also known as fielding average, is a measure that reflects the percentage of times a defensive player properly handles a batted or thrown ball. It is calculated by the sum of putouts and assists, div ...
, and he was named the league's Most Valuable Player. Although he often faced hostility while on road trips (the Royals were forced to cancel a Southern exhibition tour, for example), the Montreal fan base enthusiastically supported Robinson. Whether fans supported or opposed it, Robinson's presence on the field was a boon to attendance; more than one million people went to games involving Robinson in 1946, an astounding figure by International League standards. In the fall of 1946, following the baseball season, Robinson returned home to California and briefly played professional basketball for the short-lived Los Angeles Red Devils.
Major leagues
Breaking the color barrier (1947)
In 1947, the Dodgers called Robinson up to the major leagues six days before the start of the season. WithEddie Stanky
Edward Raymond Stanky (born Stankiewicz (September 3, 1915 – June 6, 1999) was an American professional baseball second baseman, shortstop, and manager. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Chicago Cubs, Brooklyn Dodgers, Boston ...
entrenched at second base for the Dodgers, Robinson played his initial major league season as a first baseman
A first baseman, abbreviated 1B, is the player on a baseball or softball team who fields the area nearest first base, the first of four bases a baserunner must touch in succession to score a run. The first baseman is responsible for the majori ...
. Robinson made his debut in a Dodgers uniform wearing number 42 on April 11, 1947, in a preseason exhibition game against the New York Yankees at Ebbets Field
Ebbets Field was a Major League Baseball stadium in the Flatbush section of Brooklyn, New York. It is mainly known for having been the home of the Brooklyn Dodgers baseball team of the National League (1913–1957). It was also home to five p ...
with 24,237 in attendance. On April 15, Robinson made his major league debut at the relatively advanced age of 28 at Ebbets Field before a crowd of 26,623 spectators, more than 14,000 of whom were black. Although he failed to get a base hit, he walked and scored a run in the Dodgers' 5–3 victory. McNeil, p. 357. Robinson became the first player since 1884 to openly break the major league baseball color line. Kirsch, Harris & Noltepp. 12
336. Black fans began flocking to see the Dodgers when they came to town, abandoning their Negro league teams. Robinson's promotion met a generally positive, although mixed, reception among newspapers and white major league players. However, racial tension existed in the Dodger clubhouse. Some Dodger players insinuated they would sit out rather than play alongside Robinson. The brewing mutiny ended when Dodgers management took a stand for Robinson. Manager
Leo Durocher
Leo Ernest Durocher (French spelling Léo Ernest Durocher) (; July 27, 1905 – October 7, 1991), nicknamed "Leo the Lip" and "Lippy", was an American professional baseball player, manager (baseball), manager and coach (baseball), coach. He playe ...
informed the team, "I do not care if the guy is yellow or black, or if he has stripes like a fuckin' zebra. I'm the manager of this team, and I say he plays. What's more, I say he can make us all rich. And if any of you cannot use the money, I will see that you are all traded."
Robinson was also derided by opposing teams. According to a press report, the St. Louis Cardinals
The St. Louis Cardinals are an American professional baseball team based in St. Louis. The Cardinals compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) Central division. Since the 2006 season, the Cardinals ha ...
threatened to strike
Strike may refer to:
People
* Strike (surname)
Physical confrontation or removal
*Strike (attack), attack with an inanimate object or a part of the human body intended to cause harm
*Airstrike, military strike by air forces on either a suspected ...
if Robinson played and spread the walkout across the entire National League. Existence of the plot was said to have been leaked by the Cardinals' team physician, Robert Hyland, to a friend, the ''New York Herald Tribune
The ''New York Herald Tribune'' was a newspaper published between 1924 and 1966. It was created in 1924 when Ogden Mills Reid of the ''New-York Tribune'' acquired the ''New York Herald''. It was regarded as a "writer's newspaper" and competed ...
''s Rutherford "Rud" Rennie. The reporter, concerned about protecting Hyland's anonymity and job, in turn leaked it to his ''Tribune'' colleague and editor, Stanley Woodward, whose own subsequent reporting with other sources protected Hyland.Giglio, pp. 152–153. The Woodward article made national headlines. After it was published, National League President Ford Frick
Ford Christopher Frick (December 19, 1894 – April 8, 1978) was an American sportswriter and baseball executive. After working as a teacher and as a sportswriter for the ''New York American'', he served as public relations director of the Natio ...
and Baseball Commissioner
The Commissioner of Baseball is the chief executive officer of Major League Baseball (MLB) and the associated Minor League Baseball (MiLB) – a constellation of leagues and clubs known as "organized baseball". Under the direction of the Commiss ...
Happy Chandler let it be known that any striking players would be suspended. "You will find that the friends that you think you have in the press box will not support you, that you will be outcasts," Frick was quoted as saying. "I do not care if half the league strikes. Those who do it will encounter quick retribution. All will be suspended and I don't care if it wrecks the National League for five years. This is the United States of America and one citizen has as much right to play as another." Woodward's article received the E. P. Dutton
E. P. Dutton was an American book publishing company. It was founded as a book retailer in Boston, Massachusetts, in 1852 by Edward Payson Dutton. Since 1986, it has been an imprint of Penguin Group.
Creator
Edward Payson Dutton (January 4, ...
Award in 1947 for Best Sports Reporting. The Cardinals players denied that they were planning to strike, and Woodward later told author Roger Kahn that Frick was his true source; writer Warren Corbett said that Frick's speech "never happened". Regardless, the report led to Robinson receiving increased support from the sports media. Even ''The Sporting News
The ''Sporting News'' is a website and former magazine publication owned by Sporting News Holdings, which is a U.S.-based sports media company formed in December 2020 by a private investor consortium. It was originally established in 1886 as a pr ...
'', a publication that had backed the color line, came out against the idea of a strike.
Robinson nonetheless became the target of rough physical play by opponents (particularly the Cardinals). At one time, he received a seven-inch gash in his leg from Enos Slaughter
Enos Bradsher Slaughter (April 27, 1916 – August 12, 2002), nicknamed "Country", was an American Major League Baseball (MLB) right fielder. He played for 19 seasons on four major league teams from 1938 to 1942 and 1946 to 1959. He is noted prima ...
. On April 22, 1947, during a game between the Dodgers and the Philadelphia Phillies
The Philadelphia Phillies are an American professional baseball team based in Philadelphia. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) National League East, East division. Since 2004, the team's home sta ...
, Phillies players and manager Ben Chapman called Robinson a "nigger
In the English language, the word ''nigger'' is an ethnic slur used against black people, especially African Americans. Starting in the late 1990s, references to ''nigger'' have been progressively replaced by the euphemism , notably in cases ...
" from their dugout and yelled that he should "go back to the cotton fields". Rickey later recalled that Chapman "did more than anybody to unite the Dodgers. When he poured out that string of unconscionable abuse, he solidified and united thirty men."
However, Robinson received significant encouragement from several major league players. Robinson named Lee "Jeep" Handley, who played for the Phillies at the time, as the first opposing player to wish him well. Dodgers teammate Pee Wee Reese
Harold Peter Henry "Pee Wee" Reese (July 23, 1918 – August 14, 1999) was an American professional baseball player. He played in Major League Baseball as a shortstop for the Brooklyn / Los Angeles Dodgers from 1940 to 1958. A ten-time All-Star ...
once came to Robinson's defense with the famous line, "You can hate a man for many reasons. Color is not one of them." In 1947 or 1948, Reese is said to have put his arm around Robinson in response to fans who shouted racial slurs at Robinson before a game in Boston or Cincinnati. A statue by sculptor William Behrends, unveiled at KeySpan Park
Maimonides Park (formerly MCU Park and KeySpan Park) is a minor league baseball stadium on the Riegelmann Boardwalk in Coney Island, Brooklyn, New York City. The home team and primary tenant is the New York Mets-affiliated Brooklyn Cyclones of ...
on November 1, 2005, depicts Reese with his arm around Robinson. Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
baseball star Hank Greenberg
Henry Benjamin Greenberg (born Hyman Greenberg; January 1, 1911 – September 4, 1986), nicknamed "Hammerin' Hank", "Hankus Pankus", or "The Hebrew Hammer", was an American professional baseball player and team executive. He played in Major Leagu ...
, who had to deal with ethnic epithets during his career, also encouraged Robinson. Following an incident where Greenberg collided with Robinson at first base, he "whispered a few words into Robinson's ear", which Robinson later characterized as "words of encouragement." Greenberg had advised him to overcome his critics by defeating them in games. Robinson also talked frequently with Larry Doby
Lawrence Eugene Doby (December 13, 1923 – June 18, 2003) was an American professional baseball player in the Negro leagues and Major League Baseball (MLB) who was the second black player to break baseball's color barrier and the first black pl ...
, who endured his own hardships since becoming the first black player in the American League
The American League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the American League (AL), is one of two leagues that make up Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada. It developed from the Western League, a minor league ...
with the Cleveland Indians
The Cleveland Guardians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Guardians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. Since , they have played at Progressive F ...
, as the two spoke to one another via telephone throughout the season.
Robinson finished the season having played in 151 games for the Dodgers
The Los Angeles Dodgers are an American professional baseball team based in Los Angeles. The Dodgers compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) West division. Established in 1883 in the city of Brooklyn ...
, with a batting average
Batting average is a statistic in cricket, baseball, and softball that measures the performance of batters. The development of the baseball statistic was influenced by the cricket statistic.
Cricket
In cricket, a player's batting average is ...
of .297, an on-base percentage
In baseball statistics, on-base percentage (OBP) measures how frequently a batter reaches base. An official Major League Baseball (MLB) statistic since 1984, it is sometimes referred to as on-base average (OBA), as it is rarely presented as a ...
of .383, and a .427 slugging percentage
In baseball statistics, slugging percentage (SLG) is a measure of the batting productivity of a hitter. It is calculated as total bases divided by at bats, through the following formula, where ''AB'' is the number of at bats for a given player, ...
. He had 175 hits (scoring 125 runs) including 31 doubles, 5 triples, and 12 home runs, driving in 48 runs for the year. Robinson led the league in sacrifice hits
In baseball, a sacrifice bunt (also called a sacrifice hit) is a batter's act of deliberately bunting the ball, before there are two outs, in a manner that allows a baserunner to advance to another base. The batter is almost always put out, and ...
, with 28, and in stolen bases, with 29. His cumulative performance earned him the inaugural Major League Baseball Rookie of the Year Award
In Major League Baseball, the Rookie of the Year Award is given annually to two outstanding rookie players, one each for the American League (AL) and National League (NL), as voted on by the Baseball Writers' Association of America (BBWAA). The a ...
(separate National and American League Rookie of the Year honors were not awarded until 1949).
MVP, Congressional testimony, and film biography (1948–1950)
Following Stanky's trade to the Boston Braves in March 1948, Robinson took over second base, where he logged a .980fielding percentage
In baseball statistics, fielding percentage, also known as fielding average, is a measure that reflects the percentage of times a defensive player properly handles a batted or thrown ball. It is calculated by the sum of putouts and assists, div ...
that year (second in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team s ...
at the position, fractionally behind Stanky). McNeil, p. 94. Robinson had a batting average of .296 and 22 stolen bases for the season. In a 12–7 win against the St. Louis Cardinals on August 29, 1948, he hit for the cycle
In baseball, hitting for the cycle is the accomplishment of one batter who hits a single, a double, a triple, and a home run in the same game. Collecting the hits in that order is known as a "natural cycle". Cycles are rare in Major League B ...
—a home run
In baseball, a home run (abbreviated HR) is scored when the ball is hit in such a way that the batter is able to circle the bases and reach home plate safely in one play without any errors being committed by the defensive team. A home run i ...
, a triple
Triple is used in several contexts to mean "threefold" or a " treble":
Sports
* Triple (baseball), a three-base hit
* A basketball three-point field goal
* A figure skating jump with three rotations
* In bowling terms, three strikes in a row
* ...
, a double
A double is a look-alike or doppelgänger; one person or being that resembles another.
Double, The Double or Dubble may also refer to:
Film and television
* Double (filmmaking), someone who substitutes for the credited actor of a character
* Th ...
, and a single
Single may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Single (music), a song release
Songs
* "Single" (Natasha Bedingfield song), 2004
* "Single" (New Kids on the Block and Ne-Yo song), 2008
* "Single" (William Wei song), 2016
* "Single", by ...
in the same game. The Dodgers briefly moved into first place in the National League in late August 1948, but they ultimately finished third as the Braves went on to win the league title and lose to the Cleveland Indians in the World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, contested since 1903 between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winner of the World ...
.
 Racial pressure on Robinson eased in 1948 when a number of other black players entered the major leagues.
Racial pressure on Robinson eased in 1948 when a number of other black players entered the major leagues. Larry Doby
Lawrence Eugene Doby (December 13, 1923 – June 18, 2003) was an American professional baseball player in the Negro leagues and Major League Baseball (MLB) who was the second black player to break baseball's color barrier and the first black pl ...
(who broke the color barrier in the American League
The American League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the American League (AL), is one of two leagues that make up Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada. It developed from the Western League, a minor league ...
on July 5, 1947, just 11 weeks after Robinson) and Satchel Paige
Leroy Robert "Satchel" Paige (July 7, 1906 – June 8, 1982) was an American professional baseball pitcher who played in Negro league baseball and Major League Baseball (MLB). His career spanned five decades and culminated with his induction in ...
played for the Cleveland Indians
The Cleveland Guardians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Guardians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. Since , they have played at Progressive F ...
, and the Dodgers had three other black players besides Robinson. In February 1948, he signed a $12,500 contract (equal to $ today) with the Dodgers; while a significant amount, this was less than Robinson made in the off-season from a vaudeville
Vaudeville (; ) is a theatrical genre of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century. A vaudeville was originally a comedy without psychological or moral intentions, based on a comical situation: a dramatic composition ...
tour, where he answered pre-set baseball questions and a speaking tour of the South. Between the tours, he underwent surgery on his right ankle. Because of his off-season activities, Robinson reported to training camp overweight. He lost the weight during training camp, but dieting left him weak at the plate. In 1948, Wendell Smith's book, ''Jackie Robinson: My Own Story'', was released.
In the spring of 1949, Robinson turned to Hall of Famer George Sisler
George Harold Sisler (March 24, 1893 – March 26, 1973), nicknamed "Gorgeous George", was an American professional baseball first baseman and player-manager. From 1915 through 1930, he played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the St. Louis B ...
, working as an advisor to the Dodgers, for batting help. At Sisler's suggestion, Robinson spent hours at a batting tee, learning to hit the ball to right field. Sisler taught Robinson to anticipate a fastball, on the theory that it is easier to subsequently adjust to a slower curveball. Robinson also noted that "Sisler showed me how to stop lunging, how to check my swing until the last fraction of a second". The tutelage helped Robinson raise his batting average from .296 in 1948 to .342 in 1949. In addition to his improved batting average, Robinson stole 37 bases that season, was second place in the league for both doubles and triples, and registered 124 runs batted in
A run batted in (RBI; plural RBIs ) is a statistic in baseball and softball that credits a batter for making a play that allows a run to be scored (except in certain situations such as when an error is made on the play). For example, if the bat ...
with 122 runs scored. For the performance Robinson earned the Most Valuable Player Award
In team sports, a most valuable player award, abbreviated 'MVP award', is an honor typically bestowed upon an individual (or individuals, in the instance of a tie) whose individual performance is the greatest in an entire league, for a particu ...
for the National League. Baseball fans also voted Robinson as the starting second baseman for the 1949 All-Star Game—the first All-Star Game to include black players.
That year, a song about Robinson by Buddy Johnson
Woodrow Wilson "Buddy" Johnson (January 10, 1915 – February 9, 1977) was an American jump blues pianist and bandleader active from the 1930s through the 1960s. His songs were often performed by his sister Ella Johnson, most notably "Since I F ...
, "Did You See Jackie Robinson Hit That Ball?", reached number 13 on the charts; Count Basie
William James "Count" Basie (; August 21, 1904 – April 26, 1984) was an American jazz pianist, organist, bandleader, and composer. In 1935, he formed the Count Basie Orchestra, and in 1936 took them to Chicago for a long engagement and the ...
recorded a famous version. Ultimately, the Dodgers won the National League pennant, but lost in five games to the New York Yankees
The New York Yankees are an American professional baseball team based in the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of the Bronx. The Yankees compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Amer ...
in the 1949 World Series.
Summer 1949 brought an unwanted distraction for Robinson. In July, he was called to testify before the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the Lower house, lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States Senate, Senate being ...
' Committee on Un-American Activities
The House Committee on Un-American Activities (HCUA), popularly dubbed the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC), was an investigative committee of the United States House of Representatives, created in 1938 to investigate alleged disloy ...
(HUAC) concerning statements made that April by black athlete and actor Paul Robeson
Paul Leroy Robeson ( ; April 9, 1898 – January 23, 1976) was an American bass-baritone concert artist, stage and film actor, professional football player, and activist who became famous both for his cultural accomplishments and for his p ...
. Robinson was reluctant to testify, but he eventually agreed to do so, fearing it might negatively affect his career if he declined.
 In 1950, Robinson led the National League in
In 1950, Robinson led the National League in double play
In baseball and softball, a double play (denoted as DP in baseball statistics) is the act of making two outs during the same continuous play. Double plays can occur any time there is at least one baserunner and fewer than two outs.
In Major Leag ...
s made by a second baseman with 133. His salary that year was the highest any Dodger had been paid to that point: $35,000 ($ in dollars). He finished the year with 99 runs scored, a .328 batting average, and 12 stolen bases. The year saw the release of a film biography of Robinson's life, ''The Jackie Robinson Story
''The Jackie Robinson Story'' is a 1950 biographical film directed by Alfred E. Green (who had directed ''The Jolson Story'', "one of the biggest hits of the 40s") and starring Jackie Robinson as himself. The film focuses on Robinson's struggle ...
'', in which Robinson played himself, and actress Ruby Dee played Rachel "Rae" (Isum) Robinson. The project had been previously delayed when the film's producers refused to accede to demands of two Hollywood studios that the movie include scenes of Robinson being tutored in baseball by a white man. ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' wrote that Robinson, "doing that rare thing of playing himself in the picture's leading role, displays a calm assurance and composure that might be envied by many a Hollywood star."
Robinson's Hollywood exploits, however, did not sit well with Dodgers co-owner Walter O'Malley
Walter Francis O'Malley (October 9, 1903 – August 9, 1979) was an American sports executive who owned the Brooklyn/Los Angeles Dodgers team in Major League Baseball from 1950 to 1979. In 1958, as owner of the Dodgers, he brought major league b ...
, who referred to Robinson as "Rickey's prima donna
In opera or commedia dell'arte, a prima donna (; Italian for "first lady"; plural: ''prime donne'') is the leading female singer in the company, the person to whom the prime roles would be given.
''Prime donne'' often had grand off-stage pers ...
". In late 1950, Rickey's contract as the Dodgers' team President expired. Weary of constant disagreements with O'Malley, and with no hope of being re-appointed as President of the Dodgers, Rickey cashed out his one-quarter financial interest in the team, leaving O'Malley in full control of the franchise. Rickey shortly thereafter became general manager of the Pittsburgh Pirates
The Pittsburgh Pirates are an American professional baseball team based in Pittsburgh. The Pirates compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) Central division. Founded as part of the American Associati ...
. Robinson was disappointed at the turn of events and wrote a sympathetic letter to Rickey, whom he considered a father figure, stating, "Regardless of what happens to me in the future, it all can be placed on what you have done and, believe me, I appreciate it."
Pennant races and outside interests (1951–1953)
Before the 1951 season, O'Malley reportedly offered Robinson the job of manager of the Montreal Royals, effective at the end of Robinson's playing career. O'Malley was quoted in the ''Montreal Standard'' as saying, "Jackie told me that he would be both delighted and honored to tackle this managerial post"—although reports differed as to whether a position was ever formally offered. During the 1951 season, Robinson led the National League in double plays made by a second baseman for the second year in a row, with 137. He also kept the Dodgers in contention for the 1951 pennant. During the last game of the regular season, in the 13th inning, he had a hit to tie the game and then hit a home run in the 14th inning, which proved to be the winning margin. This forced a best-of-three playoff series against the crosstown rivalNew York Giants
The New York Giants are a professional American football team based in the New York metropolitan area. The Giants compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) East division. ...
.
 Despite Robinson's regular-season heroics, on October 3, 1951, the Dodgers lost the pennant on
Despite Robinson's regular-season heroics, on October 3, 1951, the Dodgers lost the pennant on Bobby Thomson
Robert Brown Thomson (October 25, 1923 – August 16, 2010) was a Scottish-born American professional baseball player, nicknamed the "Staten Island Scot". He was an outfielder and right-handed batter for the New York Giants (1946–53, 1957), M ...
's famous home run, known as the Shot Heard 'Round the World. Overcoming his dejection, Robinson dutifully observed Thomson's feet to ensure he touched all the bases. Dodgers sportscaster Vin Scully
Vincent Edward Scully (November 29, 1927 – August 2, 2022) was an American sportscaster. He was best known for his 67 seasons calling games for Major League Baseball's Los Angeles Dodgers, beginning in 1950 (when the franchise was located ...
later noted that the incident showed "how much of a competitor Robinson was." He finished the season with 106 runs scored, a batting average of .335, and 25 stolen bases.
Robinson had what was an average year for him in 1952. He finished the year with 104 runs, a .308 batting average, and 24 stolen bases. He did, however, record a career-high on-base percentage
In baseball statistics, on-base percentage (OBP) measures how frequently a batter reaches base. An official Major League Baseball (MLB) statistic since 1984, it is sometimes referred to as on-base average (OBA), as it is rarely presented as a ...
of .436. The Dodgers improved on their performance from the year before, winning the National League pennant before losing the 1952 World Series to the New York Yankees in seven games. That year, on the television show ''Youth Wants to Know'', Robinson challenged the Yankees' general manager, George Weiss, on the racial record of his team, which had yet to sign a black player. Sportswriter Dick Young, whom Robinson had described as a "bigot", said, "If there was one flaw in Jackie, it was the common one. He believed that everything unpleasant that happened to him happened because of his blackness." The 1952 season was the last year Robinson was an everyday starter at second base. Afterward, Robinson played variously at first, second, and third bases, shortstop, and in the outfield
The outfield, in cricket, baseball and softball is the area of the field of play further from the batsman or batter than the infield. In association football, the outfield players are positioned outside the goal area.
In cricket, baseball and ...
, with Jim Gilliam
James William "Junior" Gilliam (October 17, 1928 – October 8, 1978) was an American second baseman, third baseman, and coach in Negro league and Major League Baseball who spent his entire major league career with the Brooklyn / Los Angeles Dod ...
, another black player, taking over everyday second base duties. Robinson's interests began to shift toward the prospect of managing a major league team. He had hoped to gain experience by managing in the Puerto Rican Winter League, but according to the ''New York Post
The ''New York Post'' (''NY Post'') is a conservative daily tabloid newspaper published in New York City. The ''Post'' also operates NYPost.com, the celebrity gossip site PageSix.com, and the entertainment site Decider.com.
It was established ...
'', Commissioner Happy Chandler denied the request. Tygiel (2002), p. 34.
In 1953, Robinson had 109 runs, a .329 batting average, and 17 steals, leading the Dodgers to another National League pennant (and another World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, contested since 1903 between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winner of the World ...
loss to the Yankees, this time in six games). Robinson's continued success spawned a string of death threats. He was not dissuaded, however, from addressing racial issues publicly. That year, he served as editor for ''Our Sports'' magazine, a periodical focusing on Negro sports issues; contributions to the magazine included an article on golf course segregation by Robinson's old friend Joe Louis. Robinson also openly criticized segregated hotels and restaurants that served the Dodger organization; a number of these establishments integrated as a result, including the five-star Chase Park Hotel in St. Louis.
World Championship and retirement (1954–1956)
In 1954, Robinson had 62 runs scored, a .311 batting average, and 7 steals. His best day at the plate was on June 17, when he hit two home runs and two doubles. The following autumn, Robinson won his only championship when the Dodgers beat the New York Yankees in the 1955 World Series. Although the team enjoyed ultimate success, 1955 was the worst year of Robinson's individual career. He hit .256 and stole only 12 bases. The Dodgers tried Robinson in the outfield and as athird baseman
A third baseman, abbreviated 3B, is the player in baseball or softball whose responsibility is to defend the area nearest to third base — the third of four bases a baserunner must touch in succession to score a run. In the scoring system us ...
, both because of his diminishing abilities and because Gilliam was established at second base. Robinson, then 36 years old, missed 49 games and did not play in Game 7 of the World Series. Robinson missed the game because manager Walter Alston
Walter Emmons Alston (December 1, 1911 – October 1, 1984), nicknamed "Smokey", was an American baseball player and manager in Major League Baseball He is best known for managing the Brooklyn/Los Angeles Dodgers from 1954 through 1976, and si ...
decided to play Gilliam at second and Don Hoak
Donald Albert Hoak (February 5, 1928 – October 9, 1969), nicknamed "Tiger", was an American professional baseball third baseman and coach. He played eleven seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) (–) for the Brooklyn Dodgers, Chicago Cubs, ...
at third base. That season, the Dodgers' Don Newcombe
Donald Newcombe (June 14, 1926 – February 19, 2019), nicknamed "Newk", was an American professional baseball pitcher in Negro league and Major League Baseball who played for the Newark Eagles (1944–45), Brooklyn/Los Angeles Dodgers (1949–1 ...
became the first black major league pitcher to win twenty games in a year.
In 1956, Robinson had 61 runs scored, a .275 batting average, and 12 steals. By then, he had begun to exhibit the effects of diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
and to lose interest in the prospect of playing or managing professional baseball. Robinson ended his major league career when he struck out to end Game 7 of the 1956 World Series. After the season, the Dodgers traded Robinson to the arch-rival New York Giants
The New York Giants are a professional American football team based in the New York metropolitan area. The Giants compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) East division. ...
for Dick Littlefield
Richard Bernard Littlefield (March 18, 1926 – November 20, 1997) was an American Major League Baseball pitcher with the Boston Red Sox, Chicago White Sox, Detroit Tigers, St. Louis Browns / Baltimore Orioles, Pittsburgh Pirates, St. Louis Card ...
and $35,000 cash (equal to $ today). The trade, however, was never completed; unbeknownst to the Dodgers, Robinson had already agreed with the president of Chock full o'Nuts
Chock full o'Nuts is an American brand of coffee that originated from a chain of New York City coffee shops.
Its unusual name derives from the 18 nut shops that founder William Black (c. 1902 – 1983) established under that banner in the city ...
to quit baseball and become an executive with the company.Linge
The Linge is a river in the Betuwe that is 99.8 km long, which makes it one of the longest rivers that flow entirely within the Netherlands.
It starts near the village Doornenburg near the German border. A legend tells us that if there w ...
, p. 114. Since Robinson had sold exclusive rights to any retirement story to ''Look'' magazine two years previously, his retirement decision was revealed through the magazine, instead of through the Dodgers organization.
Legacy
 Robinson's major league debut brought an end to approximately sixty years of segregation in professional baseball, known as the
Robinson's major league debut brought an end to approximately sixty years of segregation in professional baseball, known as the baseball color line
The color line, also known as the color barrier, in American baseball excluded players of black African descent from Major League Baseball and its affiliated Minor Leagues until 1947 (with a few notable exceptions in the 19th century before the li ...
. After World War II, several other forces were also leading the country toward increased equality for blacks, including their accelerated migration to the North, where their political clout grew, and President Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
's desegregation of the military in 1948. Robinson's breaking of the baseball color line and his professional success symbolized these broader changes and demonstrated that the fight for equality was more than simply a political matter. Civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
leader Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister and activist, one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968 ...
said that he was "a legend and a symbol in his own time", and that he "challenged the dark skies of intolerance and frustration." According to historian Doris Kearns Goodwin
Doris Helen Kearns Goodwin (born January 4, 1943) is an American biographer, historian, former sports journalist, and political commentator. She has written biographies of several U.S. presidents, including ''Lyndon Johnson and the American Drea ...
, Robinson's "efforts were a monumental step in the civil-rights revolution in America ... isaccomplishments allowed black and white Americans to be more respectful and open to one another and more appreciative of everyone's abilities."
Beginning his major league career at the relatively advanced age of 28, he played only ten seasons from 1947 to 1956, all of them for the Brooklyn Dodgers. During his career, the Dodgers played in six World Series, and Robinson himself played in six All-Star Games. In 1999, he was posthumously named to the Major League Baseball All-Century Team.
Robinson's career is generally considered to mark the beginning of the post–"long ball" era in baseball, in which a reliance on raw power-hitting gave way to balanced offensive strategies that used footspeed to create runs through aggressive baserunning. Robinson exhibited the combination of hitting ability and speed which exemplified the new era. He scored more than 100 runs in six of his ten seasons (averaging more than 110 runs from 1947 to 1953), had a .311 career batting average, a .409 career on-base percentage, a .474 slugging percentage, and substantially more walks than strikeout
In baseball or softball, a strikeout (or strike-out) occurs when a batter accumulates three strikes during a time at bat. It usually means that the batter is out. A strikeout is a statistic recorded for both pitchers and batters, and is deno ...
s (740 to 291). Robinson was one of only two players during the span of 1947–56 to accumulate at least 125 steals while registering a slugging percentage over .425 (Minnie Miñoso
Orestes "Minnie" Miñoso (, ; born Saturnino Orestes Armas Miñoso Arrieta; November 29, 1923 – March 1, 2015), nicknamed "The Cuban Comet" and "Mr. White Sox", was a Cuban professional baseball player. He began his baseball career in the Neg ...
was the other). He accumulated 197 stolen bases in total, including 19 steals of home. None of the latter were double steals (in which a player stealing home is assisted by a player stealing another base at the same time). Robinson has been referred to by author David Falkner as "the father of modern base-stealing".
Historical statistical analysis indicates Robinson was an outstanding fielder throughout his ten years in the major leagues and at virtually every position he played. James and Wirthpp. 502–503
After playing his rookie season at first base, Robinson spent most of his career as a second baseman. He led the league in fielding among second basemen in 1950 and 1951. Toward the end of his career, he played about 2,000 innings at third base and about 1,175 innings in the outfield, excelling at both. Assessing himself, Robinson said, "I'm not concerned with your liking or disliking me ... all I ask is that you respect me as a human being." Regarding Robinson's qualities on the field,
Leo Durocher
Leo Ernest Durocher (French spelling Léo Ernest Durocher) (; July 27, 1905 – October 7, 1991), nicknamed "Leo the Lip" and "Lippy", was an American professional baseball player, manager (baseball), manager and coach (baseball), coach. He playe ...
said, "Ya want a guy that comes to play. This guy didn't just come to play. He come to beat ya. He come to stuff the goddamn bat right up your ass."
Portrayals on stage, film and television
 Robinson portrayed himself in the 1950 motion picture ''
Robinson portrayed himself in the 1950 motion picture ''The Jackie Robinson Story
''The Jackie Robinson Story'' is a 1950 biographical film directed by Alfred E. Green (who had directed ''The Jolson Story'', "one of the biggest hits of the 40s") and starring Jackie Robinson as himself. The film focuses on Robinson's struggle ...
''. Other portrayals include:
* John Lafayette, in the 1978 ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
television special "A Home Run for Love" (broadcast as an ''ABC Afterschool Special
''ABC Afterschool Special'' is an American television anthology series that aired on American Broadcasting Company, ABC from October 4, 1972, to January 23, 1997, usually in the late afternoon on weekdays. Most episodes were dramatically presen ...
'').
* David Alan Grier, in the 1981 Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
production of the musical
Musical is the adjective of music.
Musical may also refer to:
* Musical theatre, a performance art that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance
* Musical film and television, a genre of film and television that incorporates into the narr ...
'' The First''.
* Michael-David Gordon, in the 1989 Off-Broadway
An off-Broadway theatre is any professional theatre venue in New York City with a seating capacity between 100 and 499, inclusive. These theatres are smaller than Broadway theatres, but larger than off-off-Broadway theatres, which seat fewer tha ...
production of the musical '' Play to Win''.
* Andre Braugher
Andre Keith Braugher (; born July 1, 1962) is an American actor. He is best known for his roles as Detective Frank Pembleton in the police drama series '' Homicide: Life on the Street'' (1993–1999), used car salesman Owen Thoreau Jr. in the com ...
, in the 1990 TNT
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagen ...
television movie ''The Court-Martial of Jackie Robinson
''The Court-Martial of Jackie Robinson'' is a 1990 American drama film directed by Larry Peerce and written by L. Travis Clark, Steve Duncan, Clay Frohman and Dennis Lynton Clark. The film stars Andre Braugher, Daniel Stern, Ruby Dee, Stan Sha ...
''.
* Blair Underwood
Blair Erwin Underwood (born August 25, 1964) is an American actor. He made his debut in the 1985 musical film ''Krush Groove'' and from 1987 to 1994 starred as attorney Jonathan Rollins in the NBC legal drama series '' L.A. Law''.
Underwood has ...
, in the 1996 HBO
Home Box Office (HBO) is an American premium television network, which is the flagship property of namesake parent subsidiary Home Box Office, Inc., itself a unit owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. The overall Home Box Office business unit is ba ...
television movie ''Soul of the Game
''Soul of the Game'' (also known as ''Field of Honour'') is a 1996 television film about Negro league baseball.
The film stars Blair Underwood as Jackie Robinson, Delroy Lindo as Satchel Paige, Mykelti Williamson as Josh Gibson, and Harvey W ...
''.
* Antonio Todd in "Colors", a 2005 episode of the CBS
CBS Broadcasting Inc., commonly shortened to CBS, the abbreviation of its former legal name Columbia Broadcasting System, is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the CBS Entertainm ...
television series ''Cold Case
A cold case is a crime, or a suspected crime, that has not yet been fully resolved and is not the subject of a current criminal investigation, but for which new information could emerge from new witness testimony, re-examined archives, new or re ...
''.
* Chadwick Boseman, in the 2013 motion picture ''42 (film), 42''.
* Robert Hamilton in "Sundown", a 2020 episode of the HBO
Home Box Office (HBO) is an American premium television network, which is the flagship property of namesake parent subsidiary Home Box Office, Inc., itself a unit owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. The overall Home Box Office business unit is ba ...
television series ''Lovecraft Country (TV series), Lovecraft Country''.
Robinson was also the subject of a 2016 PBS documentary, ''Jackie Robinson (film), Jackie Robinson'', which was directed by Ken Burns and features Jamie Foxx doing voice-over as Robinson.
Post-baseball life
Robinson once told future Hall of Fame inductee Hank Aaron that "the game of baseball is great, but the greatest thing is what you do after your career is over." Robinson retired from baseball at age 37 on January 5, 1957. Later that year, after he complained of numerous physical ailments, he was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, diabetes, a disease that also afflicted his brothers. Although Robinson adopted an insulin injection regimen, the state of medicine at the time could not prevent the continued deterioration of Robinson's physical condition from the disease. In October 1959, Robinson entered the Greenville Downtown Airport, Greenville Municipal Airport's whites-only waiting room. Airport police asked Robinson to leave, but he refused. At a National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) speech in Greenville, South Carolina, Robinson urged "complete freedom" and encouraged black citizens to vote and to protest their second-class citizenship. The following January, approximately 1,000 people New Year's Day March (Greenville, 1960), marched on New Year's Day to the airport, which was desegregated shortly thereafter. In his first year of eligibility for theBaseball Hall of Fame
The National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum is a history museum and hall of fame in Cooperstown, New York, operated by private interests. It serves as the central point of the history of baseball in the United States and displays baseball-r ...
in 1962, Robinson encouraged voters to consider only his on-field qualifications, rather than his cultural impact on the game. He was 1962 Baseball Hall of Fame balloting, elected on the first ballot, becoming the first black player inducted into the Cooperstown, New York, Cooperstown museum.
 In 1965, Robinson served as an analyst for Major League Baseball on ABC, ABC's ''Major League Baseball Game of the Week'' telecasts, the first black person to do so. In 1966, Robinson was hired as general manager for the short-lived Brooklyn Dodgers (Continental Football League), Brooklyn Dodgers of the Continental Football League. In 1972, he served as a part-time commentator on Montreal Expos telecasts.
On June 4, 1972, the Dodgers retired his uniform number, 42, alongside those of Roy Campanella (39) and Sandy Koufax (32). From 1957 to 1964, Robinson was the vice president for personnel at
In 1965, Robinson served as an analyst for Major League Baseball on ABC, ABC's ''Major League Baseball Game of the Week'' telecasts, the first black person to do so. In 1966, Robinson was hired as general manager for the short-lived Brooklyn Dodgers (Continental Football League), Brooklyn Dodgers of the Continental Football League. In 1972, he served as a part-time commentator on Montreal Expos telecasts.
On June 4, 1972, the Dodgers retired his uniform number, 42, alongside those of Roy Campanella (39) and Sandy Koufax (32). From 1957 to 1964, Robinson was the vice president for personnel at Chock full o'Nuts
Chock full o'Nuts is an American brand of coffee that originated from a chain of New York City coffee shops.
Its unusual name derives from the 18 nut shops that founder William Black (c. 1902 – 1983) established under that banner in the city ...
; he was the first black person to serve as vice president of a major American corporation. Robinson always considered his business career as advancing the cause of black people in commerce and industry. Robinson also chaired the NAACP's million-dollar Freedom Fund Drive in 1957, and served on the organization's board until 1967. In 1964, he helped found, with Harlem
Harlem is a neighborhood in Upper Manhattan, New York City. It is bounded roughly by the Hudson River on the west; the Harlem River and 155th Street (Manhattan), 155th Street on the north; Fifth Avenue on the east; and 110th Street (Manhattan), ...
businessman Dunbar McLaurin, Freedom National Bank Freedom National Bank was an African-American owned bank in Harlem (New York City) founded in 1964 and shut down in 1990. Freedom National served Harlem's Black community and was one of the largest Black owned banks in the U.S. Its main office was a ...
—a black-owned and operated commercial bank based in Harlem. He also served as the bank's first chairman of the board. In 1970, Robinson established the Jackie Robinson Construction Company to build housing for low-income families.
Robinson was active in politics throughout his post-baseball life. He identified himself as a political independent, although he held conservative opinions on several issues, including the Vietnam War (he once wrote to Martin Luther King Jr. to defend the Lyndon B. Johnson, Johnson Administration's military policy). After supporting Richard Nixon in his 1960 United States presidential election, 1960 presidential race against John F. Kennedy, Robinson later praised Kennedy effusively for his stance on civil rights. Robinson was angered by the 1964 United States presidential election, 1964 presidential election candidacy of conservative Republican Senator Barry Goldwater of Arizona, who had opposed the Civil Rights Act of 1964. He became one of six national directors for Nelson Rockefeller's unsuccessful campaign to be nominated as the Republican candidate for the election. After the party nominated Goldwater instead, Robinson left the party's convention commenting that he now had "a better understanding of how it must have felt to be a Jew in Hitler's Germany". He later became special assistant for community affairs when Rockefeller was re-elected governor of New York in 1966 and in 1971 was appointed to the New York State Athletic Commission by Rockefeller. In 1968 he broke with the Republican party and supported Hubert Humphrey against Nixon in 1968 United States presidential election, that year's presidential election.
 Robinson protested against the major leagues' ongoing lack of minority managers and central office personnel, and he turned down an invitation to appear in an Old-Timers' Day, old-timers' game at Yankee Stadium in 1969. He made his final public appearance on October 15, 1972, nine days before his death, throwing the ceremonial first pitch before Game 2 of the 1972 World Series, World Series at Riverfront Stadium in Cincinnati. He gratefully accepted a plaque honoring the twenty-fifth anniversary of his MLB debut, but also commented, "I'm going to be tremendously more pleased and more proud when I look at that third base coaching line one day and see a black face managing in baseball." This wish was only fulfilled after Robinson's death: following the 1974 season, the
Robinson protested against the major leagues' ongoing lack of minority managers and central office personnel, and he turned down an invitation to appear in an Old-Timers' Day, old-timers' game at Yankee Stadium in 1969. He made his final public appearance on October 15, 1972, nine days before his death, throwing the ceremonial first pitch before Game 2 of the 1972 World Series, World Series at Riverfront Stadium in Cincinnati. He gratefully accepted a plaque honoring the twenty-fifth anniversary of his MLB debut, but also commented, "I'm going to be tremendously more pleased and more proud when I look at that third base coaching line one day and see a black face managing in baseball." This wish was only fulfilled after Robinson's death: following the 1974 season, the Cleveland Indians
The Cleveland Guardians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Guardians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. Since , they have played at Progressive F ...
gave their managerial post to Frank Robinson (no relation to Jackie), a Hall of Fame-bound player who would go on to manage three other teams. Despite the success of these two Robinsons and other black players, the number of African-American players in Major League Baseball has declined since the 1970s.
Family life and death
After Robinson's retirement from baseball, his wife Rachel Robinson pursued a career in academic nursing. She became an assistant professor at the Yale School of Nursing and director of nursing at the Connecticut Mental Health Center. She also served on the board of the Freedom National Bank until it closed in 1990. She and Jackie had three children: Jackie Robinson Jr. (1946–1971), Sharon Robinson (b. 1950), and David Robinson (b. 1952). Robinson's eldest son, Jackie Robinson Jr., had emotional trouble during his childhood and entered special education at an early age. He enlisted in the Army in search of a disciplined environment, served in the Vietnam War, and was wounded in action on November 19, 1965. After his discharge, he struggled with drug problems. Robinson Jr. eventually completed the treatment program at Daytop Village in Seymour, Connecticut, and became a counselor at the institution. Robinson, Rachel, p. 201. On June 17, 1971, he was killed in an automobile accident at age 24. The experience with his son's drug addiction turned Robinson Sr. into an avid anti-drug crusader toward the end of his life.
Robinson did not outlive his son by very long. In 1968, he suffered a heart attack. Complications from Cardiovascular disease, heart disease and
Robinson's eldest son, Jackie Robinson Jr., had emotional trouble during his childhood and entered special education at an early age. He enlisted in the Army in search of a disciplined environment, served in the Vietnam War, and was wounded in action on November 19, 1965. After his discharge, he struggled with drug problems. Robinson Jr. eventually completed the treatment program at Daytop Village in Seymour, Connecticut, and became a counselor at the institution. Robinson, Rachel, p. 201. On June 17, 1971, he was killed in an automobile accident at age 24. The experience with his son's drug addiction turned Robinson Sr. into an avid anti-drug crusader toward the end of his life.
Robinson did not outlive his son by very long. In 1968, he suffered a heart attack. Complications from Cardiovascular disease, heart disease and diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
weakened Robinson and made him almost blind by middle age. On October 24, 1972, Robinson died of a Myocardial infarction, heart attack at his home on 95 Cascade Road in North Stamford, Connecticut; he was 53 years old. Robinson's funeral service on October 27, 1972, at Upper Manhattan's Riverside Church in Morningside Heights, attracted 2,500 mourners.Linge
The Linge is a river in the Betuwe that is 99.8 km long, which makes it one of the longest rivers that flow entirely within the Netherlands.
It starts near the village Doornenburg near the German border. A legend tells us that if there w ...
, p. 149. Many of his former teammates, other famous baseball players, and basketball star Bill Russell served as pallbearers, and the Rev. Jesse Jackson gave the eulogy. Tens of thousands of people lined the subsequent procession route to Robinson's interment site at Cypress Hills Cemetery in Brooklyn, New York, where he was buried next to his son Jackie and mother-in-law Zellee Isum. Twenty-five years after Robinson's death, the Interboro Parkway was renamed the Jackie Robinson Parkway in his memory. This parkway bisects the cemetery in close proximity to Robinson's gravesite.
After Robinson's death, his widow founded the Jackie Robinson Foundation, and she remains an officer as of 2021. On April 15, 2008, she announced that in 2010 the foundation would open a museum devoted to Jackie in Lower Manhattan. Robinson's daughter, Sharon, became a midwife, educator, director of educational programming for MLB, and the author of two books about her father. His youngest son, David, who has ten children, is a coffee grower and social activist in Tanzania.
Awards and recognition
According to a poll conducted in 1947, Robinson was the second most popular man in the country, behind Bing Crosby. In 1999, he was named by ''Time (magazine), Time'' on its list of the Time 100: The Most Important People of the Century, 100 most influential people of the 20th century. Also in 1999, he ranked number 44 on the ''Sporting News'' list of Baseball's 100 Greatest Players and was elected to the Major League Baseball All-Century Team as the top vote-getter among second basemen. Baseball writer Bill James, in ''The New Bill James Historical Baseball Abstract'', ranked Robinson as the 32nd greatest player of all time strictly on the basis of his performance on the field, noting that he was one of the top players in the league throughout his career. Robinson was among the 25 charter members of UCLA's Athletics Hall of Fame in 1984. In 2002, Molefi Kete Asante included Robinson on his list of 100 Greatest African Americans. Robinson has also been honored by the United States Postal Service on three separate postage stamps, in 1982, 1999, and 2000. The City of Pasadena has recognized Robinson with a baseball diamond and stadium named Jackie Robinson Field in Brookside Park/Arroyo Terrace, Pasadena, California, Brookside Park next to the Rose Bowl (stadium), Rose Bowl, and with the Jackie Robinson Center (a community outreach center providing health services). In 1997, a $325,000 bronze sculpture (equal to $ today) by artists Ralph Helmick, Stu Schecter, and John Outterbridge depicting oversized nine-foot busts of Robinson and his brother Mack was erected at Garfield Avenue, across from the main entrance of Pasadena City Hall; a granite footprint lists multiple donors to the commission project, which was organized by the Robinson Memorial Foundation and supported by members of the Robinson family. Major League Baseball has honored Robinson many times since his death. In 1987, both the National and American League MLB Rookie of the Year Award, Rookie of the Year Awards were renamed the "Jackie Robinson Award" in honor of the first recipient (Robinson's Major League Rookie of the Year Award in 1947 encompassed both leagues). On April 15, 1997, Robinson's jersey number, 42, was retired throughout Major League Baseball, the first time any jersey number had been retired throughout one of the Major North American professional sports teams, four major American sports leagues. Under the terms of the retirement, a grandfather clause allowed the handful of players who wore number 42 to continue doing so in tribute to Robinson, until such time as they subsequently changed teams or jersey numbers. This affected players such as the Mets' Butch Huskey and Boston's Mo Vaughn. The Yankees' Mariano Rivera, who retired at the end of the 2013 season, was the last player in Major League Baseball to wear jersey number 42 on a regular basis. Since 1997, only Wayne Gretzky's number 99, retired by the National Hockey League, NHL in 2000, and Bill Russell's number 6, retired by the National Basketball Association, NBA in 2022, have been retired league-wide in any of the four major sports. There have also been calls for MLB to retire number 21 league-wide in honor of Roberto Clemente, a sentiment opposed by the Robinson family.
As an exception to the retired-number policy, MLB began honoring Robinson by allowing players to wear number 42 on April 15, Jackie Robinson Day, which is an annual observance that started in 2004. For the 60th anniversary of Robinson's major league debut, MLB invited players to wear the number 42 on Jackie Robinson Day in 2007. The gesture was originally the idea of outfielder Ken Griffey Jr., who sought Rachel Robinson's permission to wear the number. After Griffey received her permission, Commissioner Bud Selig not only allowed Griffey to wear the number, but also extended an invitation to all major league teams to do the same. Ultimately, more than 200 players wore number 42, including the entire rosters of the Los Angeles Dodgers, New York Mets, Houston Astros,
Major League Baseball has honored Robinson many times since his death. In 1987, both the National and American League MLB Rookie of the Year Award, Rookie of the Year Awards were renamed the "Jackie Robinson Award" in honor of the first recipient (Robinson's Major League Rookie of the Year Award in 1947 encompassed both leagues). On April 15, 1997, Robinson's jersey number, 42, was retired throughout Major League Baseball, the first time any jersey number had been retired throughout one of the Major North American professional sports teams, four major American sports leagues. Under the terms of the retirement, a grandfather clause allowed the handful of players who wore number 42 to continue doing so in tribute to Robinson, until such time as they subsequently changed teams or jersey numbers. This affected players such as the Mets' Butch Huskey and Boston's Mo Vaughn. The Yankees' Mariano Rivera, who retired at the end of the 2013 season, was the last player in Major League Baseball to wear jersey number 42 on a regular basis. Since 1997, only Wayne Gretzky's number 99, retired by the National Hockey League, NHL in 2000, and Bill Russell's number 6, retired by the National Basketball Association, NBA in 2022, have been retired league-wide in any of the four major sports. There have also been calls for MLB to retire number 21 league-wide in honor of Roberto Clemente, a sentiment opposed by the Robinson family.
As an exception to the retired-number policy, MLB began honoring Robinson by allowing players to wear number 42 on April 15, Jackie Robinson Day, which is an annual observance that started in 2004. For the 60th anniversary of Robinson's major league debut, MLB invited players to wear the number 42 on Jackie Robinson Day in 2007. The gesture was originally the idea of outfielder Ken Griffey Jr., who sought Rachel Robinson's permission to wear the number. After Griffey received her permission, Commissioner Bud Selig not only allowed Griffey to wear the number, but also extended an invitation to all major league teams to do the same. Ultimately, more than 200 players wore number 42, including the entire rosters of the Los Angeles Dodgers, New York Mets, Houston Astros, Philadelphia Phillies
The Philadelphia Phillies are an American professional baseball team based in Philadelphia. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) National League East, East division. Since 2004, the team's home sta ...
, St. Louis Cardinals
The St. Louis Cardinals are an American professional baseball team based in St. Louis. The Cardinals compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) Central division. Since the 2006 season, the Cardinals ha ...
, Milwaukee Brewers, and Pittsburgh Pirates
The Pittsburgh Pirates are an American professional baseball team based in Pittsburgh. The Pirates compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) Central division. Founded as part of the American Associati ...
. The tribute was continued in 2008, when, during games on April 15, all members of the Mets, Cardinals, Washington Nationals, and Tampa Bay Rays wore Robinson's number 42. On June 25, 2008, MLB installed a new plaque for Robinson at the Baseball Hall of Fame
The National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum is a history museum and hall of fame in Cooperstown, New York, operated by private interests. It serves as the central point of the history of baseball in the United States and displays baseball-r ...
commemorating his off-the-field impact on the game as well as his playing statistics. In 2009, all of MLB's uniformed personnel (including players) wore number 42 on April 15; this tradition has continued every year since on that date.
 At the November 2006 groundbreaking for Citi Field, the new ballpark for the New York Mets, it was announced that the main entrance, modeled on the one in Brooklyn's old
At the November 2006 groundbreaking for Citi Field, the new ballpark for the New York Mets, it was announced that the main entrance, modeled on the one in Brooklyn's old Ebbets Field
Ebbets Field was a Major League Baseball stadium in the Flatbush section of Brooklyn, New York. It is mainly known for having been the home of the Brooklyn Dodgers baseball team of the National League (1913–1957). It was also home to five p ...
, would be called the Jackie Robinson Rotunda. The rotunda was dedicated at the opening of Citi Field on April 16, 2009. It honors Robinson with large quotations spanning the inner curve of the facade and features a large freestanding statue of his number, 42, which has become an attraction in itself. Mets owner Fred Wilpon announced that the Mets—in conjunction with Citigroup and the Jackie Robinson Foundation—will create a Jackie Robinson Museum and Learning Center, located at the headquarters of the Jackie Robinson Foundation at One Hudson Square, along Canal Street (Manhattan), Canal Street in lower Manhattan. Along with the museum, scholarships will be awarded to "young people who live by and embody Jackie's ideals." The museum hopes to open by 2020. At Dodger Stadium in Los Angeles, a statue of Robinson was introduced in 2017. The New York Yankees honor Robinson with a plaque in Monument Park (Yankee Stadium), Monument Park.
Since 2004, the Aflac#Award programs, Aflac National High School Baseball Player of the Year has been presented the "Jackie Robinson Award".
Robinson has also been recognized outside of baseball. In December 1956, the NAACP recognized him with the Spingarn Medal, which it awards annually for the highest achievement by an African-American. President Ronald Reagan posthumously awarded Robinson the Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merito ...
on March 26, 1984, and on March 2, 2005, President George W. Bush gave Robinson's widow the Congressional Gold Medal
The Congressional Gold Medal is an award bestowed by the United States Congress. It is Congress's highest expression of national appreciation for distinguished achievements and contributions by individuals or institutions. The congressional pract ...
, the highest civilian award bestowed by Congress; Robinson was only the second baseball player to receive the award, after Roberto Clemente. On August 20, 2007, California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger and his wife, Maria Shriver, announced that Robinson was inducted into the California Hall of Fame, located at The California Museum for History, Women and the Arts in Sacramento.
 A number of buildings have been named in Robinson's honor. The UCLA Bruins baseball team plays in Jackie Robinson Stadium (UCLA baseball), Jackie Robinson Stadium, which, because of the efforts of Jackie's brother Mack, features a memorial statue of Robinson by sculptor Richard H. Ellis. The stadium also unveiled a new mural of Robinson by Mike Sullivan on April 14, 2013. City Island Ballpark in
A number of buildings have been named in Robinson's honor. The UCLA Bruins baseball team plays in Jackie Robinson Stadium (UCLA baseball), Jackie Robinson Stadium, which, because of the efforts of Jackie's brother Mack, features a memorial statue of Robinson by sculptor Richard H. Ellis. The stadium also unveiled a new mural of Robinson by Mike Sullivan on April 14, 2013. City Island Ballpark in Daytona Beach, Florida
Daytona Beach, or simply Daytona, is a coastal Resort town, resort-city in east-central Florida. Located on the eastern edge of Volusia County, Florida, Volusia County near the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic coastline, its population ...
was renamed Jackie Robinson Ballpark in 1990 and a statue of Robinson with two children stands in front of the ballpark. His wife Rachel was present for the dedication on September 15. 1990. A number of facilities at Pasadena City College (successor to PJC) are named in Robinson's honor, including Robinson Field, a football/soccer/track facility named jointly for Robinson and his brother Mack. The New York Public School system has named a middle school after Robinson, and Susan Miller Dorsey High School, Dorsey High School plays at a Los Angeles football stadium named after him. His home in Brooklyn, the Jackie Robinson House, was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1976, and Brooklyn residents sought to turn his home into a city landmark. In 1978, Jackie Robinson Park, Colonial Park in Harlem
Harlem is a neighborhood in Upper Manhattan, New York City. It is bounded roughly by the Hudson River on the west; the Harlem River and 155th Street (Manhattan), 155th Street on the north; Fifth Avenue on the east; and 110th Street (Manhattan), ...
was renamed after Robinson. Robinson also has an asteroid named after him, 4319 Jackierobinson. In 1997, the United States Mint issued a Jackie Robinson commemorative silver dollar, and five-dollar gold coin. That same year, New York City renamed the Jackie Robinson Parkway, Interboro Parkway in his honor. A Jackie Robinson (statue), statue of Robinson at Journal Square Transportation Center in Jersey City, New Jersey, was dedicated in 1998.
In 2011, the U.S. placed a plaque at Robinson's Montreal home to honor the ending of segregation in baseball. The house, at 8232 avenue de Gaspé near Jarry Park, was Robinson's residence when he played for the Montreal Royals
The Montreal Royals were a minor league professional baseball team in Montreal, Quebec, during 1897–1917 and 1928–1960. A member of the International League, the Royals were the top farm club (Class AAA) of the Brooklyn Dodgers from 1939; pi ...
during 1946. In a letter read during the ceremony, Rachel Robinson, Jackie's widow, wrote: "I remember Montreal and that house very well and have always had warm feeling for that great city. Before Jack and I moved to Montreal, we had just been through some very rough treatment in the racially biased South during spring training in Florida. In the end, Montreal was the perfect place for him to get his start. We never had a threatening or unpleasant experience there. The people were so welcoming and saw Jack as a player and as a man."
On November 22, 2014, UCLA announced that it would officially retire the number 42 across all university sports, effective immediately. While Robinson wore several different numbers during his UCLA career, the school chose 42 because it had become indelibly identified with him. The only sport this did not affect was UCLA Bruins men's basketball, men's basketball, which had UCLA Bruins men's basketball retired numbers, previously retired the number for Walt Hazzard (although Kevin Love was actually the last player in that sport to wear 42, with Hazzard's blessing). In a move paralleling that of MLB when it retired the number, UCLA allowed three athletes (in women's soccer, softball, and football) who were already wearing 42 to continue to do so for the remainder of their UCLA careers. The school also announced it would prominently display the number at all of its athletic venues.
A jersey that Robinson brought home with him after his rookie season ended in 1947 was sold at an auction for $2.05 million on November 19, 2017. The price was the highest ever paid for a post-World War II jersey.
See also
* Civil Rights Game (including MLB Beacon Awards) * DHL Hometown Heroes * Glass ceiling * List of African-American firsts * List of first black Major League Baseball players * List of Major League Baseball annual stolen base leaders * List of Major League Baseball batting champions * List of Major League Baseball career stolen bases leaders * List of Major League Baseball players who spent their entire career with one franchise * List of Major League Baseball players to hit for the cycle * List of Major League Baseball retired numbers * List of NCAA major college football yearly rushing leaders * List of NCAA major college yearly punt and kickoff return leaders * List of Negro league baseball players who played in Major League Baseball * List of sports desegregation firsts * List of University of California, Los Angeles people * Los Angeles Dodgers award winners and league leadersReferences
Bibliography
* * * * (2002 CASEY Award winner). * * * * (2007 CASEY Award nominee). * * * * * * * * * * * * * , ''quoting'' * * * * (1997 CASEY Award nominee). * * * (1996 CASEY Award nominee). * * * * * * (1983 CASEY Award nominee). * *Further reading
*External links
* * , oRetrosheet
o
Seamheads
* * His life is retold in the radio drama
The Rhyme of the Ancient Dodger
, a presentation from ''Destination Freedom'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Robinson, Jackie Jackie Robinson, 1919 births 1972 deaths Activists for African-American civil rights African-American baseball players African-American male track and field athletes African-American Methodists African-American sports history American expatriate baseball players in Canada American male long jumpers American men's basketball players Baseball players from Georgia (U.S. state) Baseball players from Pasadena, California Basketball players from Pasadena, California Brooklyn Dodgers players Burials at Cypress Hills Cemetery Canadian Baseball Hall of Fame inductees College men's basketball head coaches in the United States Congressional Gold Medal recipients Guards (basketball) Kansas City Monarchs players Major League Baseball broadcasters Major League Baseball first basemen Major League Baseball players with retired numbers Major League Baseball Rookie of the Year Award winners Major League Baseball second basemen Military personnel from Georgia (U.S. state) Montreal Expos announcers Montreal Royals players National Baseball Hall of Fame inductees National College Baseball Hall of Fame inductees National League All-Stars National League batting champions National League Most Valuable Player Award winners National League stolen base champions New York State Athletic Commissioners Nonviolence advocates Pasadena City Lancers baseball players Pasadena City Lancers football players Pasadena City Lancers men's basketball players People from Cairo, Georgia People with type 1 diabetes Players of American football from Pasadena, California Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients Spingarn Medal winners Sportspeople from Pasadena, California UCLA Bruins baseball players UCLA Bruins football players UCLA Bruins men's basketball players UCLA Bruins men's track and field athletes United States Army officers United States Army personnel of World War II United States Army personnel who were court-martialed Writers from Georgia (U.S. state)