Joseph Plunkett on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Joseph Mary Plunkett (
 Sometime in 1915, Joseph Plunkett joined the
Sometime in 1915, Joseph Plunkett joined the
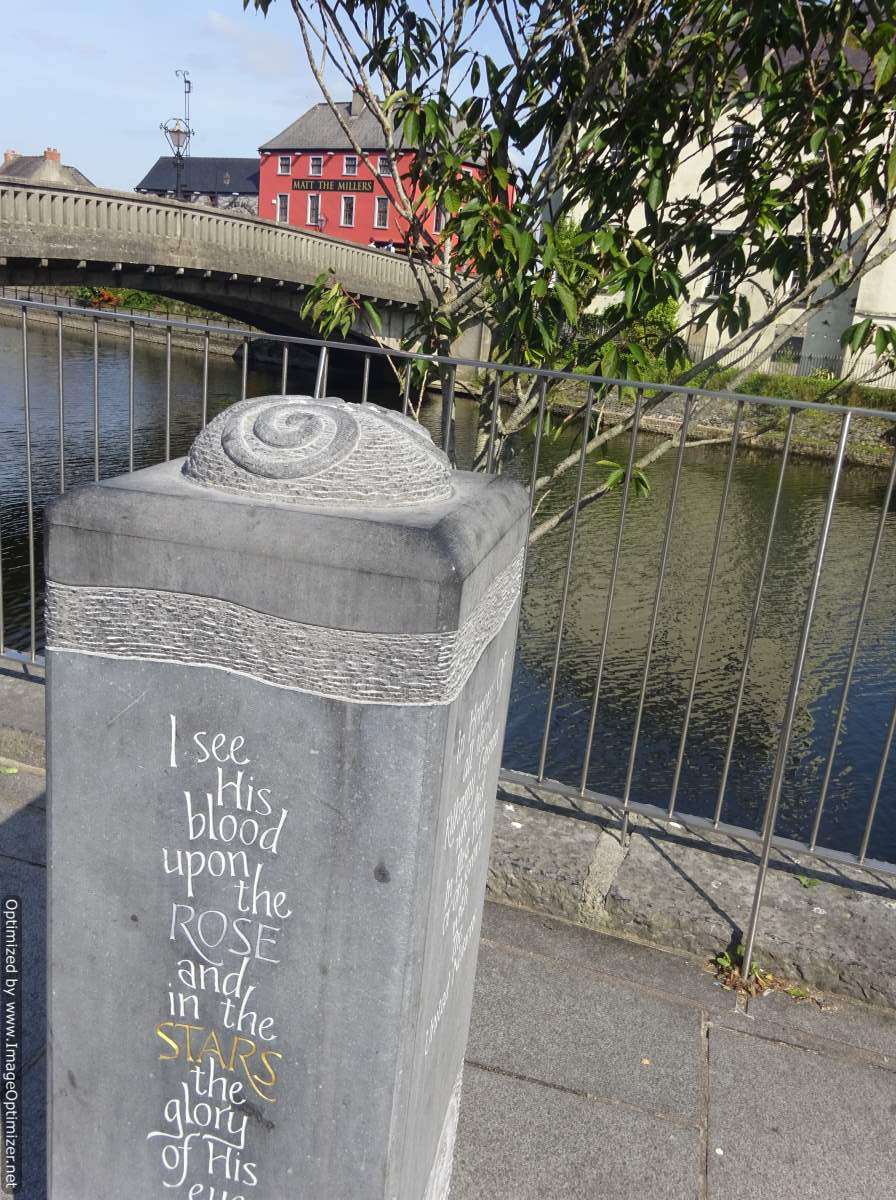 His brothers
His brothers
Grace – By Seán and Frank O' Meara
{{DEFAULTSORT:Plunkett, Joseph Mary 1887 births 1916 deaths 20th-century poets Executed participants in the Easter Rising Executed writers Irish Catholic poets Irish Esperantists Irish nationalists Irish poets Irish republicans Members of the Irish Republican Brotherhood People educated at Belvedere College People educated at Stonyhurst College People from County Dublin Signatories of the Proclamation of the Irish Republic People educated at Catholic University School
Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
: ''Seosamh Máire Pluincéid''; 21 November 1887 – 4 May 1916) was an Irish nationalist, republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
, poet, journalist, revolutionary and a leader of the 1916 Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the a ...
. Joseph Mary Plunkett married Grace Gifford
Grace Evelyn Gifford Plunkett (4 March 1888 – 13 December 1955) was an Irish artist and cartoonist who was active in the Republican movement, who married her fiancé Joseph Plunkett in Kilmainham Gaol only a few hours before he was executed f ...
in 1916, seven hours before his execution.
Background
Plunkett was born at 26 Upper Fitzwilliam Street in one ofDublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
's most affluent districts. Both his parents came from wealthy backgrounds, and his father, George Noble Plunkett
George Noble Plunkett (3 December 1851 – 12 March 1948) was an Irish nationalist politician, museum director and biographer, who served as Minister for Fine Arts from 1921 to 1922, Minister for Foreign Affairs from 1919 to 1921 and Ceann Comh ...
, had been made a papal count
The papal nobility are the aristocracy of the Holy See, composed of persons holding titles bestowed by the Pope. From the Middle Ages into the nineteenth century, the papacy held direct temporal power in the Papal States, and many titles of papal ...
.
Plunkett contracted tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
(TB) at a young age and spent part of his youth in the warmer climates of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. He spent time in Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
where he studied Arabic literature
Arabic literature ( ar, الأدب العربي / ALA-LC: ''al-Adab al-‘Arabī'') is the writing, both as prose and poetry, produced by writers in the Arabic language. The Arabic word used for literature is '' Adab'', which is derived from ...
and language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
and composed poetry in Arabic. He was educated at the Catholic University School
Catholic University School ''(C.U.S.)'' is a private (voluntary) secondary school for boys in Dublin, Ireland. The school was founded in 1867 by Bartholomew Woodlock as a preparatory school for the Catholic University of Ireland, the predecess ...
(CUS) and by the Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
at Belvedere College
Belvedere College S.J. (sometimes St Francis Xavier's College) is a voluntary secondary school for boys in Dublin, Ireland. The school has numerous alumni in the arts, politics, sports, science, and business.
History
Belvedere owes its origin ...
in Dublin and later at Stonyhurst College
Stonyhurst College is a co-educational Catholic Church, Roman Catholic independent school, adhering to the Society of Jesus, Jesuit tradition, on the Stonyhurst, Stonyhurst Estate, Lancashire, England. It occupies a Grade I listed building. Th ...
, in Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancashi ...
, England where he acquired some military knowledge from the Officers' Training Corps
The Officers' Training Corps (OTC), more fully called the University Officers' Training Corps (UOTC), are military leadership training units operated by the British Army. Their focus is to develop the leadership abilities of their members whilst ...
. Throughout his life, Joseph Plunkett took an active interest in Irish heritage and the Irish language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was ...
, and also studied Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communi ...
. Plunkett was one of the founders of the Irish Esperanto League. He joined the Gaelic League
(; historically known in English as the Gaelic League) is a social and cultural organisation which promotes the Irish language in Ireland and worldwide. The organisation was founded in 1893 with Douglas Hyde as its first president, when it emer ...
and began studying with Thomas MacDonagh
Thomas Stanislaus MacDonagh ( ga, Tomás Anéislis Mac Donnchadha; 1 February 1878 – 3 May 1916) was an Irish political activist, poet, playwright, educationalist and revolutionary leader. He was one of the seven leaders of the Easter Rising o ...
, with whom he formed a lifelong friendship. The two were both poets with an interest in theatre, and both were early members of the Irish Volunteers
The Irish Volunteers ( ga, Óglaigh na hÉireann), sometimes called the Irish Volunteer Force or Irish Volunteer Army, was a military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists and republicans. It was ostensibly formed in respons ...
, joining their provisional committee. Plunkett's interest in Irish nationalism spread throughout his family, notably to his younger brothers George and John, as well as his father, who allowed his property in Kimmage
Kimmage ( or ''Camaigh uisce'', meaning "crooked water-meadow", possibly referring to the meandering course of the River Poddle), is a suburb on the south side of the city of Dublin in Ireland.
Location
Kimmage is to the south of Dublin city c ...
, south Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
, to be used as a training camp for young men who wished to escape conscription in Britain during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
IRB involvement
 Sometime in 1915, Joseph Plunkett joined the
Sometime in 1915, Joseph Plunkett joined the Irish Republican Brotherhood
The Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB; ) was a secret oath-bound fraternal organisation dedicated to the establishment of an "independent democratic republic" in Ireland between 1858 and 1924.McGee, p. 15. Its counterpart in the United States ...
and soon after was sent to Germany to meet with Roger Casement
Roger David Casement ( ga, Ruairí Dáithí Mac Easmainn; 1 September 1864 – 3 August 1916), known as Sir Roger Casement, CMG, between 1911 and 1916, was a diplomat and Irish nationalist executed by the United Kingdom for treason during Worl ...
, who was negotiating with the German government on behalf of Ireland. Casement's role as emissary was self-appointed, and, as he was not a member of the IRB, that organisation's leadership wished to have one of their own contact Germany to negotiate German aid for an uprising the following year. He was seeking (but not limiting himself to) a shipment of arms. Casement, on the other hand, spent most of his energies recruiting Irish prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
in Germany to form a brigade to fight instead for Ireland. Some nationalists in Ireland saw this as a fruitless endeavour and preferred to seek weapons. Plunkett successfully got a promise of a German arms shipment to coincide with the Rising.
According to Ernest Blythe
Ernest Blythe (; 13 April 1889 – 23 February 1975) was an Irish journalist, managing director of the Abbey Theatre, and politician who served as Minister for Finance from 1923 to 1932, Minister for Posts and Telegraphs and Vice-President of t ...
, Plunkett's republicanism did not prevent him from suggesting, at a briefing of Irish Volunteer organisers in January 1915, that in certain circumstances it would be in Irish interests for a German Catholic prince to be crowned king of Ireland
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
, nor did anyone present object. During the Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the a ...
, Plunkett and Patrick Pearse
Patrick Henry Pearse (also known as Pádraig or Pádraic Pearse; ga, Pádraig Anraí Mac Piarais; 10 November 1879 – 3 May 1916) was an Irish teacher, barrister, poet, writer, nationalist, republican political activist and revolutionary who ...
argued in a conversation with Desmond Fitzgerald that it would be beneficial for Prince Joachim of Prussia
Prince Joachim Franz Humbert of Prussia (17 December 1890 – 18 July 1920) was the youngest son and sixth child of Wilhelm II, German Emperor, by his first wife, Augusta Victoria of Schleswig-Holstein. He committed suicide at age 29.
Prince J ...
to be crowned king.
Easter Rising
Plunkett was one of the original members of the IRB Military Committee that was responsible for planning the Easter Rising, and it was largely his plan that was followed. Shortly before the rising was to begin, Plunkett was hospitalised following a turn for the worse in his health. He had an operation on his neck glands (probablygoiter
A goitre, or goiter, is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly.
Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are caused by iodine deficiency. The term is ...
) days before Easter and had to struggle out of bed to take part in what was to follow. Still bandaged, he took his place in the General Post Office
The General Post Office (GPO) was the state postal system and telecommunications carrier of the United Kingdom until 1969. Before the Acts of Union 1707, it was the postal system of the Kingdom of England, established by Charles II in 1660. ...
with several other of the rising's leaders such as Patrick Pearse and Tom Clarke, though his health prevented him from being active. His '' aide de camp'' was Michael Collins Michael Collins or Mike Collins most commonly refers to:
* Michael Collins (Irish leader) (1890–1922), Irish revolutionary leader, soldier, and politician
* Michael Collins (astronaut) (1930–2021), American astronaut, member of Apollo 11 and Ge ...
.
Marriage and execution
Following the surrender, Plunkett was held inKilmainham Gaol
Kilmainham Gaol ( ga, Príosún Chill Mhaighneann) is a former prison in Kilmainham, Dublin, Ireland. It is now a museum run by the Office of Public Works, an agency of the Government of Ireland. Many Irish revolutionaries, including the leade ...
, and faced a court martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of memb ...
. Seven hours before his execution by firing squad
Execution by firing squad, in the past sometimes called fusillading (from the French ''fusil'', rifle), is a method of capital punishment, particularly common in the military and in times of war. Some reasons for its use are that firearms are us ...
at the age of 28, he was married in the prison chapel to his sweetheart Grace Gifford
Grace Evelyn Gifford Plunkett (4 March 1888 – 13 December 1955) was an Irish artist and cartoonist who was active in the Republican movement, who married her fiancé Joseph Plunkett in Kilmainham Gaol only a few hours before he was executed f ...
, a Protestant convert to Catholicism, whose sister, Muriel, had married his best friend Thomas MacDonagh
Thomas Stanislaus MacDonagh ( ga, Tomás Anéislis Mac Donnchadha; 1 February 1878 – 3 May 1916) was an Irish political activist, poet, playwright, educationalist and revolutionary leader. He was one of the seven leaders of the Easter Rising o ...
, who was also executed for his role in the Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the a ...
. Grace never married again.
Aftermath
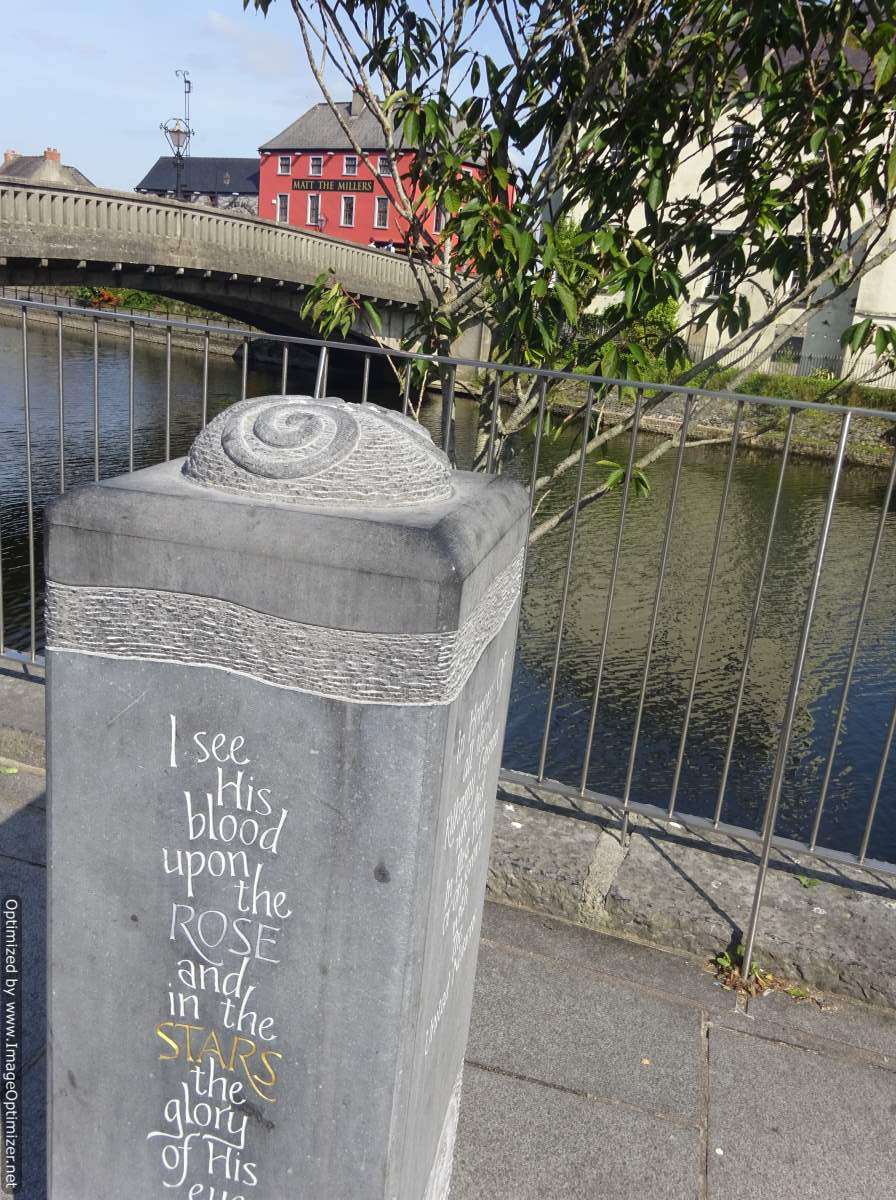 His brothers
His brothers George Oliver Plunkett
George Oliver Plunkett (; 5 July 1894 – 21 January 1944), known to his contemporaries as Seoirse Plunkett,p94, Ernie O'Malley, ''The Singing Flame'', Anvil Books Limited, 1978 was a militant Irish republican. He was sentenced to death with hi ...
and Jack Plunkett joined him in the Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the a ...
and later became important IRA
Ira or IRA may refer to:
*Ira (name), a Hebrew, Sanskrit, Russian or Finnish language personal name
*Ira (surname), a rare Estonian and some other language family name
*Iran, UNDP code IRA
Law
*Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, US, on status of ...
men. His father's cousin, Horace Plunkett
Sir Horace Curzon Plunkett (24 October 1854 – 26 March 1932), was an Anglo-Irish agricultural reformer, pioneer of agricultural cooperatives, Unionist MP, supporter of Home Rule, Irish Senator and author.
Plunkett, a younger brother of Jo ...
, was a Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
and unionist who sought to reconcile unionists and nationalists. Horace Plunkett's home was burned down by the Anti-Treaty IRA
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-Éireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the ...
during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.
Plunkett named his sister, Geraldine, literary executor of his will. She published a volume of his poetry a month after his execution in June 1916.
The main railway station in Waterford City
"Waterford remains the untaken city"
, mapsize = 220px
, pushpin_map = Ireland#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption = Location within Ireland##Location within Europe
, pushpin_relief = 1
, coordinates ...
is named after him as was Joseph Plunkett Tower in Ballymun
Ballymun () is an outer suburb of Dublin, Ireland, at the northern edge of the Northside, the green-field development of which began in the 1960s to accommodate a housing crisis in inner city areas of Dublin. While the newly built housing was ...
which has since been demolished. Plunkett barracks in the Curragh Camp
The Curragh Camp ( ga, Campa an Churraigh) is an army base and military college in The Curragh, County Kildare, Ireland. It is the main training centre for the Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish Defence Forces and is home to 2,000 military personnel ...
, County Kildare is also named after him.
In popular culture
The Irish ballad "Grace", written by Seán and Frank O'Meara, is a monologue of Plunkett expressing his love to Grace and his love for the cause of Irish independence in the small hours before his execution. The ballad has been notably covered by Jim McCann. He is also mentioned in the Irish rebel song “Seán South of Garryowen”. American composerFlorence Turner-Maley
Florence Turner-Maley (August 23, 1871 – January 3, 1962) was an American composer, singer, and teacher.
Florence Turner was born in Jersey City, New Jersey, to William Hayward and Mathilde (Holwill) Turner. Her father had been a boy soprano. ...
used Plunkett’s text in her song “I See Him Everywhere.”
His religious poem "I See His Blood upon the Rose" is well-known in Ireland.
References
Further reading
* Augusteijn, Joost (ed.), ''The Irish Revolution 1913-1923'' (Basingstoke 2002) * Boyce, George D., ''Nationalism in Ireland'' (London 1982) * Kee, Robert, ''The Green Flag: A History of Irish Nationalism'' (London 1972) * Kelly, Matthew, ''The Fenian Ideal and Irish Nationalism 1882-1916'' (Woodbridge 2006) *Mansergh, Nicholas
Philip Nicholas Seton Mansergh (27 June 1910 – 16 January 1991) was a historian. His focus was on Ireland and the British Commonwealth. As the Smuts Professor of Commonwealth History at Cambridge University after 1953, he trained many of the ...
, ''The Unresolved Question: The Anglo-Irish Settlement and its Undoing'' (New Haven and London 1991)
* Martin, F.X. (ed.), ''Leaders and Men of the Easter Rising: Dublin 1916'' (London 1967)
* Novick, Ben, ''Concerning Revolution: Irish Nationalist Propaganda during the First World War'' (Dublin 2001)
* O Brolchain, Honor, ''Joseph Plunkett'' (Dublin 2012)
* Plunkett Dillon, Geraldine (edited Honor O Brolchain): All in the Blood (A. & A. Farmar)
* Townshend, Charles, ''Easter 1916: The Irish Rebellion'' (London 2005)
External links
* * *Grace – By Seán and Frank O' Meara
{{DEFAULTSORT:Plunkett, Joseph Mary 1887 births 1916 deaths 20th-century poets Executed participants in the Easter Rising Executed writers Irish Catholic poets Irish Esperantists Irish nationalists Irish poets Irish republicans Members of the Irish Republican Brotherhood People educated at Belvedere College People educated at Stonyhurst College People from County Dublin Signatories of the Proclamation of the Irish Republic People educated at Catholic University School