Joseph Martin (general) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Joseph Martin, Jr. (1740–1808) was a
Joseph Martin, Jr. (1740–1808) was a
 The son of planter Capt. Joseph Martin Sr. and his wife Susannah Chiles, great-granddaughter of
The son of planter Capt. Joseph Martin Sr. and his wife Susannah Chiles, great-granddaughter of
 Martin's Station stood along the Wilderness Trail near Rose Hill, Virginia. The first fort was built in 1769, but Martin's party were attacked by the local Native Americans. He returned a few years later in 1775 and built a new "Martin's station". Again he was attacked by the Indians and had to leave. Moving closer to the
Martin's Station stood along the Wilderness Trail near Rose Hill, Virginia. The first fort was built in 1769, but Martin's party were attacked by the local Native Americans. He returned a few years later in 1775 and built a new "Martin's station". Again he was attacked by the Indians and had to leave. Moving closer to the
 "Martin was a robust figure in the history of the early frontier," according to the
"Martin was a robust figure in the history of the early frontier," according to the 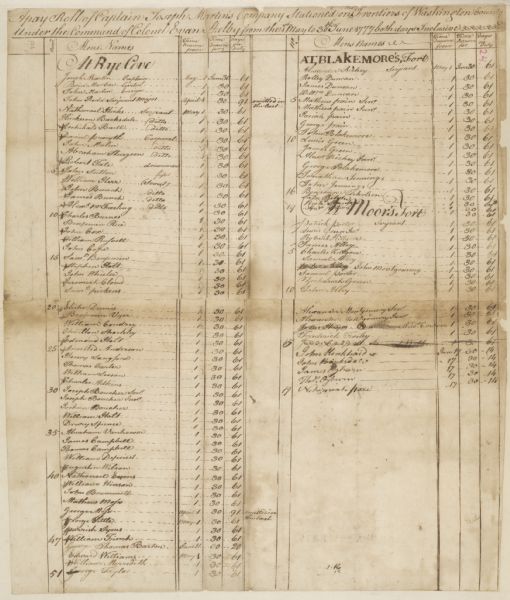 "General Martin's conduct so far as I could discern in that affair was really praise-worthy," Henry wrote to
"General Martin's conduct so far as I could discern in that affair was really praise-worthy," Henry wrote to
 Ultimately, General Martin lost his appointment as chief Indian agent. Martin's "manner of treating with the Indians necessarily prevented his appointment," Senator Richard Henry Lee informed Patrick Henry in September 1789. "At present no such office as a standing Indian agent is appointed. The Government of the Western Territory is charged with such affairs."
In some quarters Martin was seen as too lenient with the Indians, especially after an incident in 1786 when several young Cherokee warriors were said to have murdered two white settlers near
Ultimately, General Martin lost his appointment as chief Indian agent. Martin's "manner of treating with the Indians necessarily prevented his appointment," Senator Richard Henry Lee informed Patrick Henry in September 1789. "At present no such office as a standing Indian agent is appointed. The Government of the Western Territory is charged with such affairs."
In some quarters Martin was seen as too lenient with the Indians, especially after an incident in 1786 when several young Cherokee warriors were said to have murdered two white settlers near  Martin's attempts to restrain the
Martin's attempts to restrain the  Later Judgments on Martin's career as an Indian agent have been mixed. Writing in 1894,
Later Judgments on Martin's career as an Indian agent have been mixed. Writing in 1894,
 Initially known as Henry Courthouse, the town of
Initially known as Henry Courthouse, the town of
 *
*
General Joseph Martin, An Unsung Hero of the Virginia Frontier
', William Allen Pusey, Filson Club History Quarterly 10, April 1936
* [https://books.google.com/books?id=ItIRAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA347&lpg=PA347&dq=%22brice+martin%22+%22joseph+martin%22&source=web&ots=jrmku3nLDA&sig=PluFiq0NsVdDfOXwrNMwP1auHhE&hl=en&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=7&ct=result A Biographical Sketch of General Joseph Martin, by His Son, Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Virginia Historical Society, Richmond, Va., 1901]
General Joseph Martin, by John Redd, Publications of the Southern History Association, Published by the Association, Washington, D.C., 1903
Reminiscences of Western Virginia: General Joseph Martin, John Redd, The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Vol. VII, October 1899, The Virginia Historical Society, Richmond, Va., 1899A Short History of the Wilderness Road WildernessRoadHistory.pdfMurders in the Cumberland Gap, Papers of the War Department, 1784–1800, Center for History and New Media, National Historical Publications and Records CommissionGeneral Joseph Martin, Martinsville-Henry County Historical SocietyGeneral Joseph Martin, Papers of the War Department, 1784–1800, Center for History and New Media, George Mason University''General Joseph Martin'', Lawrence J. Fleenor Jr., Daniel Boone Wilderness Trail Historical SiteLetter from Thomas Jefferson to Joseph Martin, Envisaging the West, Thomas Jefferson and the Roots of Lewis and Clark
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Martin, Joseph 1740 births 1808 deaths People from Albemarle County, Virginia American people of English descent American explorers American hunters American pioneers American planters American surveyors Martinsville, Virginia American city founders Members of the Georgia General Assembly Members of the North Carolina General Assembly North Carolina state senators Members of the Tennessee General Assembly Members of the Virginia House of Delegates Militia generals in the American Revolution Page family of Virginia People from Henry County, Virginia People from Martinsville, Virginia People of Tennessee in the American Revolution People of Virginia in the French and Indian War People in Dunmore's War Virginia colonial people Virginia militiamen in the American Revolution American slave owners People from Rose Hill, Virginia
 Joseph Martin, Jr. (1740–1808) was a
Joseph Martin, Jr. (1740–1808) was a brigadier general
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
in the Virginia militia during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, in which Martin's frontier diplomacy with the Cherokee people is credited with not only averting Indian attacks on the Scotch-Irish American
Scotch-Irish (or Scots-Irish) Americans are American descendants of Ulster Protestants who emigrated from Ulster in northern Ireland to America during the 18th and 19th centuries, whose ancestors had originally migrated to Ireland mainly from t ...
and English American
English Americans (historically known as Anglo-Americans) are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in England.
In the 2020 American Community Survey, 25.21 million self-identified as being of English origin.
The term is distin ...
settlers who helped win the battles of Kings Mountain and Cowpens Cowpens may refer to:
* Battle of Cowpens, a battle in the American Revolution
* Cowpens National Battlefield, a unit of the National Park Service that protects the battlefield.
* Cowpens, South Carolina
* USS Cowpens (CG-63), USS ''Cowpens'' (CG-63 ...
, but with also helping to keep the Indians' position neutral and from siding with the British troops during those crucial battles. Historians agree that the settlers' success at these two battles signaled the turning of the tide of the Revolutionary War—in favor of the Americans.
Martin was born in Caroline County, Virginia
Caroline County is a United States county located in the eastern part of the Commonwealth of Virginia. The northern boundary of the county borders on the Rappahannock River, notably at the historic town of Port Royal. The Caroline county sea ...
, and later lived at Albemarle County and then at Henry County, Virginia, at his plantation, ''Belmont'', on Leatherwood Creek in Martinsville, not far from the plantation of his friend Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Patrick Henry
Patrick Henry (May 29, 1736June 6, 1799) was an American attorney, planter, politician and orator known for declaring to the Second Virginia Convention (1775): " Give me liberty, or give me death!" A Founding Father, he served as the first an ...
, ''Leatherwood Plantation Leatherwood Plantation of 10,000 acres (40 km2) was located in Henry County, Virginia, where American Founding Father Patrick Henry lived from 1779 until 1784. The plantation is probably named after Leatherwood Creek, a tributary to the Smith River ...
''.
General Martin held many positions during his public life. As a very young man he first tried his hand at farming, next he worked for three years as an overseer on the huge plantation of his local Virginia kin, next he was a longhunter
A longhunter (or long hunter) was an 18th-century explorer and hunter who made expeditions into the American frontier for as much as six months at a time. Historian Emory Hamilton says that "The Long Hunter was peculiar to Southwest Virginia onl ...
, and an explorer on the frontier for friend Patrick Henry, then an early pioneer and builder of Martin's Station in the "wild west," a surveyor of the KY/NC and TN/VA borders, an Indian agent/Indian fighter for Patrick Henry, a member at peace treaties with the Indians, and along with Dr. Thomas Walker, Joseph Martin named the Cumberland region and the Cumberland River
The Cumberland River is a major waterway of the Southern United States. The U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 8, 2011 river drains almost of southern Kentucky and ...
, he served as a member of the legislatures of Virginia, Georgia, and North Carolina, he was lifelong friends with Gen. Thomas Sumter, he was also friends and brothers-in-law with Col. Benjamin Cleveland (both married Graves sisters), he was unsuccessfully nominated by Patrick Henry to the position of the first governor of the Southwest Territory, was the holder of some 80,000 acres across the Southeastern U.S. at one point. The city of Martinsville, Virginia
Martinsville is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,485. A community of both Southside and Southwest Virginia, it is the county seat of Henry County, althou ...
, was named in his honor during his lifetime.
Early life
Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
John Page, Joseph Martin Jr. was raised in a Virginia gentry family in Caroline and Albemarle Counties. His father, Joseph Martin Sr., was the son of wealthy British merchant William Martin in Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
, England, who sent his son to Virginia as supercargo
A supercargo (from Spanish ''sobrecargo'') is a person employed on board a vessel by the owner of cargo carried on the ship. The duties of a supercargo are defined by admiralty law and include managing the cargo owner's trade, selling the merchand ...
aboard his ship the ''Brice''. Martin Sr. wrote to his English father that he planned to marry the daughter of a common Virginia colonist. Even though she was from the Chiles family and was a descendant of Virginia's Col. John Page, to Martin's wealthy father back in England all American colonists were inferior to the English. William Martin of Bristol was himself Lord Mayor of Bristol and owner of a ship building company, a glass manufacturing plant, importer and exporter with the new world; including tobacco. The father wrote back disinheriting young Joseph Martin Sr., who never returned to England.
Joseph Martin Sr. was "a perfect Englishman", recalled his grandson later, "large and athletic; bold, daring, self-willed and supercilious. And in him was depicted, as my father has told me, the most complete form of the aristocracy of the British government." Capt. Martin arrived in Albemarle County in 1745, one of the original patentees. Joseph Martin Sr. left some 300 acres of his landholdings to son Joseph Jr. at his death in 1762. Nearby neighbors Dr. Thomas Walker, Peter Jefferson
Peter Jefferson (February 29, 1708 – August 17, 1757) was a planter, cartographer and politician in colonial Virginia best known for being the father of the third president of the United States, Thomas Jefferson. The "Fry-Jefferson Map", creat ...
, James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
, and the Lewis and Clark clans and kin including Lewis, Carr, Waller, Dabney, Hammock, Hughes, etc.
But Joseph Martin Jr., the grandson of the English immigrant, was not cut out for a Virginia gentry planter's life. "Gambling was a favorite pastime." Martin's son, Revolutionary War officer Col. William Martin, in his accounts of his father's life in the, "Lyman Draper
Lyman Copeland Draper (September 4, 1815August 26, 1891) was a librarian and historian who served as secretary for the State Historical Society of Wisconsin at Madison, Wisconsin. Draper also served as Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisco ...
Manuscript Collection," writes that although his father gambled, he was not much of a drinker and let his son in on his secret; Martin sometimes pretended to over-drink so he might appear to be drunk in order that fellow gamblers would let down their guard. As a youth, Joseph Martin ran off from an apprenticeship during the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
of 1756, and joined the army at Fort Pitt, where he served alongside another Virginia youth, Thomas Sumter
Thomas Sumter (August 14, 1734June 1, 1832) was a soldier in the Colony of Virginia militia; a brigadier general in the South Carolina militia during the American Revolution, a planter, and a politician. After the United States gained independe ...
. Following his early army service, Martin lit out for the rigors of the frontier, where he dressed in buckskin and was an early real estate speculator, trapper and fur trader and Indian fighter.
But this time on the frontier was after Martin had bought a large plot of land in Henry County with his earnings working for three years as an overseer for an uncle. Martin also gained 20,000 acres of land from Patrick Henry in a surveying contest at Powell Valley. Martin's youthful adventures on the frontier were grist for later stories... some of which were written by Martin's political foes and were slanted to paint a picture of him in an unkind light. One writer, a fan of Martin's political enemy, called him lazy and refused to describe him by his military ranking. General Joseph Martin may have been many things in his lifetime, but a quick study of his history and his accomplishments show that he was far from lazy. Eventually the soldiering, trapping and Indian fighting transformed the young Martin into a fearsome explorer.
Among Martin's earliest excursions on the frontier was one made on behalf of family friend Dr. Thomas Walker. Martin's son, Revolutionary War officer Col. William Martin, describes the naming of the area and the river in a letter to historian Lyman Draper
Lyman Copeland Draper (September 4, 1815August 26, 1891) was a librarian and historian who served as secretary for the State Historical Society of Wisconsin at Madison, Wisconsin. Draper also served as Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisco ...
, "A treaty with the Cherokees was held at Fort Chiswell, Virginia
Fort Chiswell is a census-designated place (CDP) in Wythe County, Virginia, United States. The population was 939 at the 2010 census.
Fort Chiswell is located at the junction of Interstates 77 and 81. Going west from Fort Chiswell, drivers find ...
on New River, then a frontier. On the return of the chiefs home, Dr.homas
In the Vedic Hinduism, a homa (Sanskrit: होम) also known as havan, is a fire ritual performed on special occasions by a Hindu priest usually for a homeowner (" grihastha": one possessing a home). The grihasth keeps different kinds of fire ...
Walker, a gentleman of distinction, and my father, eneralJoseph Martin, accompanied them. The Indians being guides, they passed through the place now called Cumberland Gap, where they discovered a fine spring. They still had a little rum remaining, and they drank to the health of the Duke of Cumberland. This gave rise to the name of Cumberland Mountain and Cumberland River."
In 1769, Martin journeyed to Powell's Valley to attempt a settlement, a full ahead of any previous settlement. Martin and his party – which included his brother Brice and Mordecai Hord – had hoped to secure the granted to Dr. Walker and themselves. Martin's Creek in the region where Joseph Martin attempted his settlement is today named for him. (Martin's Station, as the settlement was known, became a well-known stopover for westward-bound settlers for many years.) The settlement ultimately failed, which some historians have blamed on the inability of the Loyal Company to defend its title to the tract.
But in the foray to Powell's Valley, Martin had established his credentials as a hard-bitten explorer. Daniel Boone
Daniel Boone (September 26, 1820) was an American pioneer and frontiersman whose exploits made him one of the first folk heroes of the United States. He became famous for his exploration and settlement of Kentucky, which was then beyond the we ...
and his party of explorers were stunned in 1769 when, upon their arrival in Powell's Valley, they discovered that Martin and his 20-man party had beaten them there. It was beyond the farthest reaches that Boone and his long hunters had explored. Following Martin's feat, the Albemarle County native became a force to be reckoned with in exploration circles, even though Martin's settlement was soon broken up by the Cherokees, who pushed back against the westernmost settlement yet attempted.
By 1775, when North Carolina merchant Richard Henderson purchased an immense tract of land from the Cherokees to found the short-lived Transylvania colony
The Transylvania Colony, also referred to as the Transylvania Purchase, was a short-lived, extra-legal colony founded in early 1775 by North Carolina land speculator Richard Henderson, who formed and controlled the Transylvania Company. Henders ...
, in what is today Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, Henderson turned to Martin as his agent in Powell's Valley. It was one of several such roles that the explorer, accustomed to trapping, longhunting and traveling in the Appalachian wilderness inhabited by the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, would hold over the years.
Martin's Station
 Martin's Station stood along the Wilderness Trail near Rose Hill, Virginia. The first fort was built in 1769, but Martin's party were attacked by the local Native Americans. He returned a few years later in 1775 and built a new "Martin's station". Again he was attacked by the Indians and had to leave. Moving closer to the
Martin's Station stood along the Wilderness Trail near Rose Hill, Virginia. The first fort was built in 1769, but Martin's party were attacked by the local Native Americans. He returned a few years later in 1775 and built a new "Martin's station". Again he was attacked by the Indians and had to leave. Moving closer to the Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
, he built another new "Martin's Station", his third, in 1783. The small fort provided protection plus supplies for hunters and immigrant families moving into Kentucky. He was able to finally sell his fort and lands in Powell County, Kentucky
Powell County is a county located in the U.S. Commonwealth of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,129. Its county seat is Stanton. The county was formed January 7, 1852, by Kentucky Governor Lazarus W. Powell from parts of ...
in 1788, and moved back to the town in Henry County, Virginia
Henry County is a county located in the U.S. state of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 50,948. The county seat is usually identified as Martinsville; however, the administration building (where county offices are located an ...
, that would soon be renamed in his honor: Martinsville.
A "fourth" Martin's Station was recently constructed at the Wilderness Road State Park. "Builders of the hand-hewn log replica, constructed in 2002, used only the kinds of tools that Martin would have used in the wild frontier in the later 1700s. Workers carted logs into the construction site with oxen and then used ropes and horses to set those logs in place. At times, reenactors came on the scene and made the construction yet more authentic by staging spontaneous Indian attacks."
Life along the frontier
 "Martin was a robust figure in the history of the early frontier," according to the
"Martin was a robust figure in the history of the early frontier," according to the WPA
WPA may refer to:
Computing
*Wi-Fi Protected Access, a wireless encryption standard
*Windows Product Activation, in Microsoft software licensing
* Wireless Public Alerting (Alert Ready), emergency alerts over LTE in Canada
* Windows Performance An ...
guide to the Old Dominion. "He was born in Albemarle County in 1740, ran away to fight Indians at 17, became an Indian agent, land agent, and officer of militia, fighting Indians all up and down the frontier. In 1774 he came to Henry County, established himself at Belle Monte on Leatherwood Creek, for nine years sat for his district in the general assembly, and in 1793 was made a brigadier general of state militia. He was a brawny, picturesque man, more than six feet tall and the father of 18 children; wore buckled knee breeches and a great beard, braided and thrust inside his shirt."
Martin first married Sarah Lucas in Orange County, Virginia
Orange County is a county located in the Central Piedmont region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 36,254. Its county seat is Orange. Orange County includes Montpelier, the estate of James Madison, the ...
. After her death in Henry County, Martin married Susannah
Graves, a descendant of Captain Thomas Graves Thomas Graves (c. 1580–1635) was one of the original Adventurers (stockholders) of the Virginia Company of London, and one of the very early Planters (settlers) who founded Jamestown, Virginia, the first permanent English settlement in North Ameri ...
. Susannah Graves, of Spotsylvania County, Virginia, the wife of Joseph Martin, and her second cousin Mary Graves, who was married to Benjamin Cleveland
Benjamin Cleveland (May 28, 1738 – October 1806) was an American pioneer and officer in the North Carolina militia. He is best remembered for his service as a colonel in the Wilkes County Regiment of the North Carolina militia during the War ...
, Susannah Graves was the daughter of William Graves and Mary unk, Mary was the daughter of Joseph Graves and Sarah Bunyard. Both are direct descendants of Thomas Graves and Anna Davenport, common ancestor, is Capt. Thomas Graves. ef; Wills of Joseph Graves and Thomas Graves
While married to Sarah Lucas and then to Susannah Graves, Martin was simultaneously married to his half-Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
wife, Elizabeth Ward, the daughter of Nancy Ward
''Nanyehi'' (Cherokee: ᎾᏅᏰᎯ: "One who goes about"), known in English as Nancy Ward (c. 1738 – 1822 or 1824), was a Beloved Woman and political leader of the Cherokee. She advocated for peaceful coexistence with European Americans and, ...
, a power within the Cherokee tribes, and her husband, English trapper Bryan Ward. The polygamous relationship, justified by Martin as common practice among frontiersmen operating among the tribes, caused considerable consternation to General Martin's son, Col. William Martin. Joseph Martin and Betsy Ward had two children. (Joseph Martin's son by his Cherokee wife was educated in Virginia schools, but afterwards elected to return to the Cherokee.)
On November 3, 1777, Martin was commissioned by Governor Patrick Henry as Agent and Superintendent for Indian Affairs for the State of Virginia. (Martin served in the same capacity with the state of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
from 1783 to 1789.) Gov. Henry instructed Martin that he was "to reside at some place in that Nation in order to negotiate and direct all things relating to the Commonwealth and which concern the interest thereof, using your best endeavors from time to time to preserve peace with that Nation and to cultivate their present good Disposition." It was an appointment Martin would continue to hold until 1789.
During his time on the frontier, Martin became acquainted at an early age with two other Revolutionary War patriots and frontiersmen: Benjamin Cleveland
Benjamin Cleveland (May 28, 1738 – October 1806) was an American pioneer and officer in the North Carolina militia. He is best remembered for his service as a colonel in the Wilkes County Regiment of the North Carolina militia during the War ...
, who was his brother-in-law, [They were not related, just lifetime friends. Susannah Graves, the wife of Joseph Martin and Mary Graves the wife of Benjamin Cleveland were second cousins, common ancestor Capt. Thomas Graves. <\ref> Wills of Joseph Graves, Thomas Graves and Benjamin Graves. Grace S. Green] Cleveland having married the sister of Susannah Graves; and Thomas Sumter
Thomas Sumter (August 14, 1734June 1, 1832) was a soldier in the Colony of Virginia militia; a brigadier general in the South Carolina militia during the American Revolution, a planter, and a politician. After the United States gained independe ...
, who had been a companion of Martin's during his early adventures on the frontier. Both men were fellow Virginia natives who struck out for the wilds, and both were ardent patriots.
During the Revolutionary War it was the efforts of Joseph Martin (then a Major) that helped prevent the Overhill Cherokee
Overhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 1 ...
from launching widespread attacks on American colonists, which Loyalist agents had attempted to incite. Following the British capture of Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the Canopy (forest), canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to rea ...
and Augusta, Georgia
Augusta ( ), officially Augusta–Richmond County, is a consolidated city-county on the central eastern border of the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. The city lies across the Savannah River from South Carolina at the head of its navig ...
in 1778–1779, English goods made their way to the Cherokee on the Savannah River, prompting some tribesmen to rejoin the English cause.
Martin's diplomacy with the Cherokees in 1780–81, wrote the American Historical Association, enabled the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
to achieve victory over the English at the Battle of Kings Mountain
The Battle of Kings Mountain was a military engagement between Patriot and Loyalist militias in South Carolina during the Southern Campaign of the American Revolutionary War, resulting in a decisive victory for the Patriots. The battle took pla ...
, thus hastening the end of the conflict. On the eve of the Battle of Guilford Court House, in February 1781, General Nathanael Greene
Nathanael Greene (June 19, 1786, sometimes misspelled Nathaniel) was a major general of the Continental Army in the American Revolutionary War. He emerged from the war with a reputation as General George Washington's most talented and dependab ...
wrote Martin and seven other officers – including John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
, Arthur Campbell, and William Christian – appointing them agents to treat with the Cherokees and Chicasaws "to afford the Said Tribes of Indians every mark of our good disposition towards them." Foremost in Greene's thinking, apparently, was keeping the Indians on the sidelines as the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
and its militia forces fought the British in the last days of the war. Greene was probably mindful of previous British attempts at sending large quantities of ammunition, weapons, horses, cash and goods to their Indian allies through their Florida redoubts.
At the same time – and complicating Martin's legacy – Martin and his sons were prime movers behind the settlement of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
by removing obdurate Cherokees from the territory.
By the end of the Revolution, Martin's place as chief colonial Indian agent seemed secure. In January 1780, Virginia governor
The governor of the Commonwealth of Virginia serves as the head of government of Virginia for a four-year term. The incumbent, Glenn Youngkin, was sworn in on January 15, 2022.
Oath of office
On inauguration day, the Governor-elect takes th ...
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
directed Martin to negotiate with the Cherokees to secure land around a new fort being overseen by General George Rogers Clark at the mouth of the Ohio River ( Fort Jefferson). In the fall of 1783, the State of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are s ...
built a new fort at the Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
, replacing an older fort which was adjudged to lie within the boundaries of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. The new Virginia fort was designed as the primary residence for Martin while he was in the region on official business. And in 1784, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
directed Martin to use his connections with the Cherokees to negotiate for more land between the Carolinas and the Mississippi to establish American sovereignty over the region.
Later, in a twist overlooked by most historians, Martin corresponded with Alexander McGillivray
Alexander McGillivray, also known as ''Hoboi-Hili-Miko'' (December 15, 1750February 17, 1793), was a Muscogee (Creek) leader. The son of a Muscogee mother and a Scottish father, he had skills no other Creek of his day had: he was not only liter ...
, the leader of the Creek Indians, who had Loyalist sentiments. In 1788 a letter from Martin to McGillivray was intercepted in which Martin professed to be interested in settling abroad. When the letter was discovered, the North Carolina General Assembly launched an investigation into Martin's conduct. But he was later exonerated when it turned out that he was acting as a spy on Patrick Henry's instructions to ferret out the nature of McGillivray's ties to the Spanish, who were then active in Florida.
 "General Martin's conduct so far as I could discern in that affair was really praise-worthy," Henry wrote to
"General Martin's conduct so far as I could discern in that affair was really praise-worthy," Henry wrote to United States Senator
The United States Senate is the Upper house, upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives being the Lower house, lower chamber. Together they compose the national Bica ...
from Virginia Richard Henry Lee
Richard Henry Lee (January 20, 1732June 19, 1794) was an American statesman and Founding Father from Virginia, best known for the June 1776 Lee Resolution, the motion in the Second Continental Congress calling for the colonies' independence from ...
. "He artin
Artin may refer to:
* Artin (name), a surname and given name, including a list of people with the name
** Artin, a variant of Harutyun, an Armenian given name
* 15378 Artin, a main-belt asteroid
See also
{{disambiguation, surname ...
frequently gave me Intelligence of Creek Indian affairs, and of the intercourse between other Indians and the Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance peoples, Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of National and regional identity in Spain, national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex Hist ...
that was interesting.
General Martin and Governor Patrick Henry kept a long-running correspondence through the years, some of which concerned real estate speculation. Other letters recounted Martin's dealings with the Indian tribes, as well as settlement efforts in Tennessee. As late as 1790, Patrick Henry wrote Joseph Martin concerning a real estate investment, holding out that the hope, Henry noted, that Martin might finally capitalize on his long service to Virginia. "After all the Hazards you have run," Henry wrote, "that you have not acquired so much property as many others would have done in your situation, I was desirous to throw something in your way by which some fine lands would have been offered to you in our purchase."
Career as an Indian agent
 Ultimately, General Martin lost his appointment as chief Indian agent. Martin's "manner of treating with the Indians necessarily prevented his appointment," Senator Richard Henry Lee informed Patrick Henry in September 1789. "At present no such office as a standing Indian agent is appointed. The Government of the Western Territory is charged with such affairs."
In some quarters Martin was seen as too lenient with the Indians, especially after an incident in 1786 when several young Cherokee warriors were said to have murdered two white settlers near
Ultimately, General Martin lost his appointment as chief Indian agent. Martin's "manner of treating with the Indians necessarily prevented his appointment," Senator Richard Henry Lee informed Patrick Henry in September 1789. "At present no such office as a standing Indian agent is appointed. The Government of the Western Territory is charged with such affairs."
In some quarters Martin was seen as too lenient with the Indians, especially after an incident in 1786 when several young Cherokee warriors were said to have murdered two white settlers near Clinch Mountain
Clinch Mountain is a mountain ridge in the U.S. states of Tennessee and Virginia, lying in the ridge-and-valley section of the Appalachian Mountains. From its southern terminus at Kitts Point, which lies at the intersection of Knox, Union and Gr ...
. The killings set off calls for retribution within the secessionist
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics lea ...
State of Franklin, and Martin found himself trying to mediate the dispute, and calm the settlers, while trying to prevent the angry Cherokees from joining with the Creeks. Martin did little to disguise his contempt for the authorities of the State of Franklin, who, Martin wrote Henry, "immediately marched into the above mentioned Town, where they killed one Young ndian
Ndian is a department of Southwest Region in Cameroon. It is located in the humid tropical rainforest zone about southeast of Yaoundé, the capital.
History
Ndian division was formed in 1975 from parts of Kumba and Victoria divisions and is ...
woman, and Shot Several others."
But Martin himself had not hesitated to wield military power against the Cherokees, especially when they killed several colonists at the instigation of Loyalist and English agents during the Revolution. In 1781, following a running battle between Indian forces and those of the colonists, Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Arthur Campbell, Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colone ...
John Sevier
John Sevier (September 23, 1745 September 24, 1815) was an American soldier, frontiersman, and politician, and one of the founding fathers of the State of Tennessee. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, he played a leading role in Tennes ...
and Martin addressed a letter to the Indian chiefs, warning them about their actions. "You know you began the war," the bulletin began, "by listening to the bad councils of the King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ...
and the falsehoods told you by his agents." Further hostilities, the three colonial leaders warned, would result in a military campaign against the Indian villages. Seven years later, in 1788, Martin again fought the Overmountain Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, as well as the Chickamauga Cherokee
The Chickamauga Cherokee refers to a group that separated from the greater body of the Cherokee during the American Revolutionary War. The majority of the Cherokee people wished to make peace with the Americans near the end of 1776, following se ...
, in a battle at Lookout Mountain
Lookout Mountain is a mountain ridge located at the northwest corner of the U.S. state of Georgia, the northeast corner of Alabama, and along the southeastern Tennessee state line in Chattanooga. Lookout Mountain was the scene of the 18th-cen ...
, during the Cherokee–American wars
The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American se ...
.
But having eventually struck a hard-won peace with the tribes, Martin bridled at the actions of the State of Franklin
The State of Franklin (also the Free Republic of Franklin or the State of Frankland)Landrum, refers to the proposed state as "the proposed republic of Franklin; while Wheeler has it as ''Frankland''." In ''That's Not in My American History Boo ...
. Henry empathized with Martin, writing the General in May 1785 that "the disorderly behavior of the Franklin people, as they call themselves, gives me concern. If they will not be subservient to the Rules and Regulations respecting Indian affairs, which prevail in all the States, they must expect none of the advantages of the Union."
"Partisans of the State in Nrth Rth or RTH may refer to:
Business
* Regular trading hours
* ICAO symbol for Artis (airline)
* Exchange symbol for VanEck Vectors Retail, an exchange-traded fund
Media
* Radio y Televisión de Hidalgo, Mexico
Other uses
* Equivalent res ...
Carolina afterwards found him obnoxious to their views," former Governor Henry wrote Virginia Senator William Grayson
William Grayson (1742 – March 12, 1790) was a planter, lawyer and statesman from Virginia. After leading a Virginia regiment in the Continental Army, Grayson served in the Virginia House of Delegates before becoming one of the first two U ...
in urging Martin's reappointment in 1789, "and as I believe often endangered his Life For his duty called him to discourage their Disorderly conduct ndthwart their favorite Schemes." Henry then commended Martin for his efforts to impose restraints upon the actions of the State of Franklin settlers, whose "frequent Butcherys of Indians & Refinement in cruelty sufficiently characterize these people who are Mr Martins decided Foes."
 Martin's attempts to restrain the
Martin's attempts to restrain the State of Franklin
The State of Franklin (also the Free Republic of Franklin or the State of Frankland)Landrum, refers to the proposed state as "the proposed republic of Franklin; while Wheeler has it as ''Frankland''." In ''That's Not in My American History Boo ...
settlers from a more-belligerent course made Martin unacceptable in some quarters, where he was seen as too 'soft' on the tribesmen. Martin also became controversial in some quarters after the Treaty of Hopewell
Three agreements, each known as the Treaty of Hopewell, were signed between representatives of the Congress of the United States and the Cherokee, Choctaw, and Chickasaw peoples, were negotiated and signed at the Hopewell plantation in South Car ...
in 1785, when Martin, Andrew Pickens and Benjamin Hawkins
Benjamin Hawkins (August 15, 1754June 6, 1816) was an American planter, statesman and a U.S. Indian agent He was a delegate to the Continental Congress and a United States Senator from North Carolina, having grown up among the planter elite ...
, acting as government agents, concluded treaties with the Cherokees and the Choctaws. The Cherokee treaty particularly engendered later enmity from the Indian signatories, as well as the colonial state governments. The Indians saw the treaty as a thinly-veiled land grab, and the state governments saw the treaty as an attempt to encroach on local government authority, and attempts were made in Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
to void it. "No action of Martin's life brought down on him more condemnation than this he Hopewell Treaty" wrote historian Stephen B. Weeks of the incident.
Consequently, his appointment as agent was not renewed, despite Henry's repeated entreaties to political allies for Martin's reinstatement. (In a 1789 letter to Senator William Grayson, Henry reminded his political ally that Martin had been so effective in his Indian dealings during the Revolutionary War that British agents had offered rewards to their Indian allies for Martin's scalp.)
But the forces allied against Martin overwhelmed Henry's defense, and in 1789, his career as Indian agent finished, General Martin sold his large holdings in the Powell's Valley and near Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
and returned to his lands in Henry County next door to Henry's to spend the rest of his life. A year later, in 1790, when the governorship of the Southwest Territory
The Territory South of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Southwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1790, until June 1, 1796, when it was admitted to the United States a ...
opened up, Patrick Henry suggested Gen. Martin, along with George Mason
George Mason (October 7, 1792) was an American planter, politician, Founding Father, and delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787, one of the three delegates present who refused to sign the Constitution. His writings, including ...
, for the job, but both were passed over in favor of William Blount
William Blount (March 26, 1749March 21, 1800) was an American Founding Father, statesman, farmer and land speculator who signed the United States Constitution. He was a member of the North Carolina delegation at the Constitutional Convention o ...
.
 Later Judgments on Martin's career as an Indian agent have been mixed. Writing in 1894,
Later Judgments on Martin's career as an Indian agent have been mixed. Writing in 1894, Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
called Martin "a firm friend of the red race, hohad earnestly striven to secure justice for them."
Legislative service
In his peripatetic life on the frontier, Martin was called upon to serve in the legislatures of several states. He served as a member of theNorth Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
Convention called to approve the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
, and served several times in the North Carolina General Assembly. Martin was subsequently elected to the Virginia House of Delegates
The Virginia House of Delegates is one of the two parts of the Virginia General Assembly, the other being the Senate of Virginia. It has 100 members elected for terms of two years; unlike most states, these elections take place during odd-numbe ...
, until he finally chose to retire because of advanced age. (In 1787 the North Carolina assembly chose Martin as Brigadier General of the Washington District.) During his time in the Virginia legislature, Martin was one of the primary supporters of James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
's Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
The Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions were political statements drafted in 1798 and 1799 in which the Kentucky and Virginia legislatures took the position that the federal Alien and Sedition Acts were unconstitutional. The resolutions argued ...
. During his military service in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Martin was elected to the Georgia legislature in 1783.
Martin was also initially a member of the Watauga Association
The Watauga Association (sometimes referred to as the Republic of Watauga) was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. Although it lasted only a few ...
, which supported the founding of the State of Franklin. Martin subsequently resigned his membership when he saw that it might compromise his role as Indian agent.
In 1799, Martin and his old friend Major John Redd of Henry County served as the two county representatives on the Virginia commission relating to the Alien and Sedition Acts
The Alien and Sedition Acts were a set of four laws enacted in 1798 that applied restrictions to immigration and speech in the United States. The Naturalization Act increased the requirements to seek citizenship, the Alien Friends Act allowed th ...
.
Family life, legacy, and descendants
Gen. Joseph Martin, Jr.'s first wife was Sarah Lucas. They were both born in Virginia and together had seven children, including Revolutionary War officer, Col. William L. Martin, who eventually moved to Smith County, in Middle Tennessee. After Sarah Lucas Martin's death, Joseph Martin, Jr. married Susannah Graves in Henry County, Virginia. They had 11 children, all of whom were born in Virginia, including: Col. Joseph Martin of Henry County, Va. He was one of five of Gen. Martin's sons who served in theWar of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
.
Another Martin son, and veteran of the War of 1812, was Patrick Henry Martin. He was a young, trained lawyer, and died a bachelor on his trip home after the war. He was named in honor of Gen. Martin's friend and neighbor, Governor Patrick Henry. Gen. Martin's son, Capt. Lewis Graves Martin, also a veteran of the War of 1812, moved from Henry County, Virginia to Rutherford/Cannon County in Middle Tennessee, in 1816, where he married Belinda Rucker (daughter of Gideon Rucker, Sr. & Joyce Reade; both of whom were born in Va. and moved to Middle Tennessee). They had a large family before Belinda's death in the late 1830s. Capt. Lewis G. Martin remarried and removed to Missouri in 1840. Another Martin son, and veteran of the War of 1812, was Thomas Martin. He also moved to Middle Tennessee where he married Georgia Carr (daughter of Dabney Carr). Alexander Martin, another son and veteran of the War of 1812, also moved to Middle Tennessee. He married Elizabeth Carr (daughter of John Fyndall Carr, also a Tennessean from Virginia), and after some years, moved to Missouri. Another son of Gen. Martin and Susannah Graves was Esq. Judge John C. Martin, who also moved to Middle Tennessee in the days following the War of 1812, where he became a judge and chairman of the Cannon County courts, and served five terms as county executive. He was also responsible for the construction of the original Cannon County court house, erected in 1830. He married Sophia Rucker, sister to his brother Lewis' wife, Belinda.
Other children of Gen. Martin include: George Martin (1763 - 1799), Martha Martin Cleveland, Elizabeth Martin Waller (1768 - 1805), Brice Martin (1770 - 1856), Jesse Martin (1786 - 1836), and Susan Martin King (1799 - 1867).
Gen. Martin also had two children with his half-Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, common law wife
Common-law marriage, also known as non-ceremonial marriage, marriage, informal marriage, or marriage by habit and repute, is a legal framework where a couple may be considered married without having formally registered their relation as a civil ...
("frontier wife"), Elizabeth Ward, daughter of frontiersman Bryant Ward and his wife Nancy, "the beloved woman of the Cherokee." One of their children may have been Nancy Martin Hildebrand (1778 - 1837).
The Native Indian connection of two members of the Martin family has created some confusion for some Martin genealogy researchers; Gen. Joseph Martin's brother, Capt. John "Jack" Calvin Martin, Sr., of his N.C. Rock House Plantation, a.k.a. Rock Castle Plantation, is often confused with his brother Gen. Joseph Martin. Capt. John "Jack" Martin, Sr. moved from Virginia to N.C. with his brother William Martin, Sr.. In N.C. Capt. John "Jack" Martin, Sr. married a Miss Emory, who was half Native American. She died early in their marriage. Her widower, "Jack," then married her sister, a second Miss Emory. This same Capt. John "Jack" Martin, Sr. and his Emory wife were the parents of a John Calvin Martin, Jr. who served as a judge on the supreme court of the Cherokee Nation in Oklahoma, although he was only 1/4 Cherokee. This Oklahoma judge was the older cousin of the Tennessee judge of the same name; the son of Gen. Joseph Martin and wife Susannah Graves, as mentioned earlier; Esq. Judge, John C. Martin of Tennessee. There were two Martin cousins with the same name who both served as judges. Although they were born many miles and many years apart, their identities are sometimes confused by modern researchers looking at the names alone.
Another brother of Gen. Joseph Martin, William Martin, Sr., was the father of Gen. William "Buck" Martin, Jr., who served in the War of 1812 on Andrew Jackson's staff.
Gen. Martin, after helping adjudicate the western boundary line between North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
, and Virginia as far as the Cumberland Mountains
The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the ...
, retired to his plantation ''Belmont'' on Leatherwood Creek, which he had purchased in 1796 from Benjamin Harrison V
Benjamin Harrison V (April 5, 1726April 24, 1791) was an American planter, merchant, and politician who served as a legislator in colonial Virginia, following his namesakes’ tradition of public service. He was a signer of the Continental As ...
of Berkeley Plantation
Berkeley Plantation, one of the first plantations in America, comprises about on the banks of the James River on State Route 5 in Charles City County, Virginia. Berkeley Plantation was originally called Berkeley Hundred, named after the Berkele ...
, which was originally built by a Capt. John Martin who was possibly the great-uncle of General Joseph Martin. General Joseph Martin died at his plantation on December 18, 1808, and was buried there in the family cemetery. Buried in the family graveyard are three other Joseph Martins: Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Joseph Martin, son of the general, his son Joseph, and his grandson Joseph, who lived at ''Greenwood'' plantation. Initially known as Henry Courthouse, the town of
Initially known as Henry Courthouse, the town of Martinsville, Virginia
Martinsville is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,485. A community of both Southside and Southwest Virginia, it is the county seat of Henry County, althou ...
, was later renamed in honor of this early soldier, planter, pioneer, and real estate speculator. For many years afterwards, General Martin remained an obscure figure, until Lyman Draper
Lyman Copeland Draper (September 4, 1815August 26, 1891) was a librarian and historian who served as secretary for the State Historical Society of Wisconsin at Madison, Wisconsin. Draper also served as Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisco ...
began collecting reminiscences about him, including those of Major John Redd, a prominent Henry County planter who served under Martin, and who also wrote about his early recollections of General Nathanael Greene
Nathanael Greene (June 19, 1786, sometimes misspelled Nathaniel) was a major general of the Continental Army in the American Revolutionary War. He emerged from the war with a reputation as General George Washington's most talented and dependab ...
, George Rogers Clark, Daniel Boone
Daniel Boone (September 26, 1820) was an American pioneer and frontiersman whose exploits made him one of the first folk heroes of the United States. He became famous for his exploration and settlement of Kentucky, which was then beyond the we ...
, Col. Benjamin Cleveland
Benjamin Cleveland (May 28, 1738 – October 1806) was an American pioneer and officer in the North Carolina militia. He is best remembered for his service as a colonel in the Wilkes County Regiment of the North Carolina militia during the War ...
, Dr. John Walker, and other early prominent Virginia figures.
Martin's descendants include his second eldest son Col. William Martin, Tennessee pioneer, and member of the South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
legislatures; son Col. Joseph Martin, member of the Virginia House of Delegates
The Virginia House of Delegates is one of the two parts of the Virginia General Assembly, the other being the Senate of Virginia. It has 100 members elected for terms of two years; unlike most states, these elections take place during odd-numbe ...
, the Virginia State Senate
The Senate of Virginia is the upper house of the Virginia General Assembly. The Senate is composed of 40 senators representing an equal number of single-member constituent districts. The Senate is presided over by the lieutenant governor of Virg ...
and the Virginia Constitutional Convention 1829–1830; daughter Martha Martin, who was the 1st wife of William Cleveland, son of John (Preacher John) Cleveland, Jr., brother of Benjamin Cleveland, hero of the Battle of King's Mountain; William Cleveland was a nephew of Benjamin Cleveland; son Major Brice Martin, Tennessee pioneer and surveyor in 1801 of the disputed boundary between Virginia and Tennessee;. Other descendants: Dr. Jesse Martin Shackelford, founder of Martinsville's Shackelford Hospital, later Martinsville Memorial; Judge Nicholas H. Hairston of Roanoke.; United States Senator from Virginia Thomas Staples Martin from Charlottesville, Virginia
Charlottesville, colloquially known as C'ville, is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is the county seat of Albemarle County, which surrounds the city, though the two are separate legal entities. It is named after Queen Ch ...
.; Judge John Dillard
John Dillard (August 12, 1760 – June 5, 1842) was an American soldier and pioneer settler, and a prominent figure in the establishment of Buncombe County, North Carolina and Dillard, Georgia.
Dillard was born in Culpeper County, Virginia and ...
of the North Carolina Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the State of North Carolina is the state of North Carolina's highest appellate court. Until the creation of the North Carolina Court of Appeals in the 1960s, it was the state's only appellate court. The Supreme Court consists ...
; American theologian and Biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
scholar Archibald Thomas Robertson
Archibald Thomas Robertson (November 6, 1863 – September 24, 1934) was a Southern Baptist preacher and biblical scholar whose work focused on the New Testament and Koine Greek.
Biography
Robertson was born at Cherbury near Chatham, Virgi ...
.; Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
Governors Joshua L. Martin, Gabriel Moore
Gabriel Moore (1785 – August 6, 1844) was a Democratic-Republican, later Jacksonian and National Republican politician and fifth governor of the U.S. state of Alabama (1829–1831).
Life and politics
Moore was born in Stokes County, North ...
, John A. Winston
John Anthony Winston (September 4, 1812 – December 21, 1871) was a planter, military officer, and politician who became the List of Governors of Alabama, 15th Governor of Alabama, Governor of Alabama (1853 to 1857) after serving as president ...
, and Charles Henderson; as well as Alfred M. Scales
Alfred Moore Scales (November 26, 1827 – February 9, 1892) was a North Carolina state legislator, Confederate States Army, Confederate General officer, general in the American Civil War, and the List of Governors of North Carolina, 45th G ...
, Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
in the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, and subsequently Governor of North Carolina. Also descended from Martin was Henry Smith Pritchett
Henry Smith Pritchett (April 16, 1857 – August 28, 1939) was an American astronomer and educator.
Biography
Pritchett was born on April 16, 1857 in Fayette, Missouri, the son of Carr Waller Pritchett, Sr., and attended Pritchett Colleg ...
, an educator born in Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
who served as president of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
.
Toby's freedom
General Joseph Martin, Jr. owned a slave named 'Toby' from the time Toby was about 25 years old, and in his letters to historianLyman Draper
Lyman Copeland Draper (September 4, 1815August 26, 1891) was a librarian and historian who served as secretary for the State Historical Society of Wisconsin at Madison, Wisconsin. Draper also served as Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisco ...
, Martin's son Col. William Martin told Draper that Toby, "a bright mulatto, a little under middle stature, of great physical powers, as well as mental" had served his father for many years and had distinguished himself in several battles. It was General Martin's intention, noted his son, that Toby be freed at Joseph Martin's death, but the General died intestate
Intestacy is the condition of the estate of a person who dies without having in force a valid will or other binding declaration. Alternatively this may also apply where a will or declaration has been made, but only applies to part of the estat ...
. Taking note of the General's affection for his longtime servant, as well as the Martin's family members' sentiments toward Martin's constant companion, the family elected "by mutual consent" to leave Toby out of the inventory of General Martin's estate, and Toby "has ever since been free, and has made himself a good estate." In his letter to Draper, Col. William Martin calls the freed slave "my fine old brother Toby."
Recent monument
On June 27–29, 2008, 200 descendants of General Joseph Martin gathered in the city named for him to unveil a monument in his honor, at the Gen. Joseph Martin, Jr. Bicentennial Celebration.See also
 *
* Martinsville, Virginia
Martinsville is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,485. A community of both Southside and Southwest Virginia, it is the county seat of Henry County, althou ...
* Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
* Patrick Henry
Patrick Henry (May 29, 1736June 6, 1799) was an American attorney, planter, politician and orator known for declaring to the Second Virginia Convention (1775): " Give me liberty, or give me death!" A Founding Father, he served as the first an ...
* Rose Hill, Lee County, Virginia
Rose Hill is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Lee County, Virginia, United States. The population was 799 at the 2010 census, up from 714 at the 2000 census.
Geography
Rose Hill is located in western Lee County a ...
* Battle of Kings Mountain
The Battle of Kings Mountain was a military engagement between Patriot and Loyalist militias in South Carolina during the Southern Campaign of the American Revolutionary War, resulting in a decisive victory for the Patriots. The battle took pla ...
* Wilderness Road
* Wilderness Road State Park
* Thomas Sumter
Thomas Sumter (August 14, 1734June 1, 1832) was a soldier in the Colony of Virginia militia; a brigadier general in the South Carolina militia during the American Revolution, a planter, and a politician. After the United States gained independe ...
* Benjamin Cleveland
Benjamin Cleveland (May 28, 1738 – October 1806) was an American pioneer and officer in the North Carolina militia. He is best remembered for his service as a colonel in the Wilkes County Regiment of the North Carolina militia during the War ...
* Richard Henderson (American pioneer)
Richard Henderson (April 20, 1735 – January 30, 1785) was an American jurist, land speculator and politician who was best known for attempting to create the Transylvania Colony in frontier Kentucky. Henderson County and its seat Henderson, ...
* Treaty of Hopewell
Three agreements, each known as the Treaty of Hopewell, were signed between representatives of the Congress of the United States and the Cherokee, Choctaw, and Chickasaw peoples, were negotiated and signed at the Hopewell plantation in South Car ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* ''Brig. General Joseph Martin'', Carol Gehrs Mitchell, C. G. Mitchell, 1998 * ''General Joseph Martin and the War of the Revolution in the West'', Stephen Beauregard Weeks, Contributor Samuel Cole Williams, Published by G.P.O., 1894 * ''Joseph Martin and the Southern Frontier'', Denise Pratt Morrison, Womack Press, 1976 * ''The Wilderness Road'', Robert L. Kinkaid, Kessinger Publishing LLC, 2008, *General Joseph Martin, An Unsung Hero of the Virginia Frontier
', William Allen Pusey, Filson Club History Quarterly 10, April 1936
External links
* [https://books.google.com/books?id=ItIRAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA347&lpg=PA347&dq=%22brice+martin%22+%22joseph+martin%22&source=web&ots=jrmku3nLDA&sig=PluFiq0NsVdDfOXwrNMwP1auHhE&hl=en&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=7&ct=result A Biographical Sketch of General Joseph Martin, by His Son, Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Virginia Historical Society, Richmond, Va., 1901]
General Joseph Martin, by John Redd, Publications of the Southern History Association, Published by the Association, Washington, D.C., 1903
Reminiscences of Western Virginia: General Joseph Martin, John Redd, The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Vol. VII, October 1899, The Virginia Historical Society, Richmond, Va., 1899
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Martin, Joseph 1740 births 1808 deaths People from Albemarle County, Virginia American people of English descent American explorers American hunters American pioneers American planters American surveyors Martinsville, Virginia American city founders Members of the Georgia General Assembly Members of the North Carolina General Assembly North Carolina state senators Members of the Tennessee General Assembly Members of the Virginia House of Delegates Militia generals in the American Revolution Page family of Virginia People from Henry County, Virginia People from Martinsville, Virginia People of Tennessee in the American Revolution People of Virginia in the French and Indian War People in Dunmore's War Virginia colonial people Virginia militiamen in the American Revolution American slave owners People from Rose Hill, Virginia