Joseph (Hebrew Bible) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Joseph (; he, יוֹסֵף, , He shall add;
File:Joseph dreams of wheat.JPG, Joseph's dream of grain
File:Owen Jones - Joseph dreams of stars.JPG, Joseph's dream of stars
 Joseph's half-brothers were jealous of him; () wherefore, in
Joseph's half-brothers were jealous of him; () wherefore, in
 The warden put Joseph in charge of the other prisoners, and soon afterward Pharaoh's chief
The warden put Joseph in charge of the other prisoners, and soon afterward Pharaoh's chief
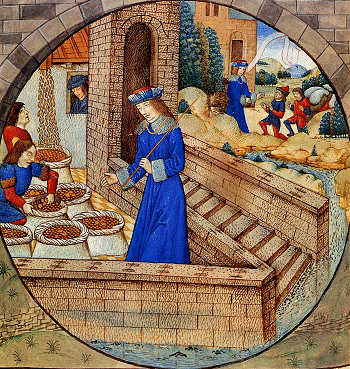 In the second year of famine, Joseph's half brothers were sent to Egypt to buy goods. When they came to Egypt, they stood before the Vizier but did not recognize him as their brother Joseph, who was now in his late 30s; but Joseph ''did'' recognize them and did not speak at all to them in his native tongue of
In the second year of famine, Joseph's half brothers were sent to Egypt to buy goods. When they came to Egypt, they stood before the Vizier but did not recognize him as their brother Joseph, who was now in his late 30s; but Joseph ''did'' recognize them and did not speak at all to them in his native tongue of
 Upon their return to Egypt, the brothers were received by the steward of the house of Joseph. When they were brought to Joseph's house, they were apprehensive about the returned money in their money sacks. They thought that the missed transaction would somehow be used against them as way to induct them as slaves and confiscate their possessions. So they immediately informed the steward of what had transpired to get a feel of the situation. The steward put them at ease, telling them not to worry about the money, and brought out their brother Simeon. Then he brought the brothers into the house of Joseph and received them hospitably. When the Vizier (Joseph) appeared, they gave him gifts from their father. Joseph saw and inquired of Benjamin and was overcome by emotion but did not show it. He withdrew to his chambers and wept. When he regained control of himself, he returned and ordered a meal to be served. The Egyptians would not dine with Hebrews at the same table, as doing so was considered loathsome, so the sons of Israel were served at a separate table ().
That night, Joseph ordered his steward to load the brothers' donkeys with food and all their money. The money they brought was double what they had from the first trip. Deceptively, Joseph also ordered that his silver cup be put in Benjamin's sack. The following morning the brothers began their journey back to Canaan. Joseph ordered the steward to go after the brothers and question them about the "missing" silver cup. When the steward caught up with the brothers, he seized them and searched their sacks. The steward found the cup in Benjamin's sack just as he had planted it the night before. This caused a stir amongst the brothers. However, they agreed to be escorted back to Egypt. When the Vizier (Joseph) confronted them about the silver cup, he demanded that the one who possessed the cup in his bag become his slave. In response, Judah pleaded with the Vizier that Benjamin be allowed to return to his father, and he himself be kept in Benjamin's place as a slave ().
Upon their return to Egypt, the brothers were received by the steward of the house of Joseph. When they were brought to Joseph's house, they were apprehensive about the returned money in their money sacks. They thought that the missed transaction would somehow be used against them as way to induct them as slaves and confiscate their possessions. So they immediately informed the steward of what had transpired to get a feel of the situation. The steward put them at ease, telling them not to worry about the money, and brought out their brother Simeon. Then he brought the brothers into the house of Joseph and received them hospitably. When the Vizier (Joseph) appeared, they gave him gifts from their father. Joseph saw and inquired of Benjamin and was overcome by emotion but did not show it. He withdrew to his chambers and wept. When he regained control of himself, he returned and ordered a meal to be served. The Egyptians would not dine with Hebrews at the same table, as doing so was considered loathsome, so the sons of Israel were served at a separate table ().
That night, Joseph ordered his steward to load the brothers' donkeys with food and all their money. The money they brought was double what they had from the first trip. Deceptively, Joseph also ordered that his silver cup be put in Benjamin's sack. The following morning the brothers began their journey back to Canaan. Joseph ordered the steward to go after the brothers and question them about the "missing" silver cup. When the steward caught up with the brothers, he seized them and searched their sacks. The steward found the cup in Benjamin's sack just as he had planted it the night before. This caused a stir amongst the brothers. However, they agreed to be escorted back to Egypt. When the Vizier (Joseph) confronted them about the silver cup, he demanded that the one who possessed the cup in his bag become his slave. In response, Judah pleaded with the Vizier that Benjamin be allowed to return to his father, and he himself be kept in Benjamin's place as a slave ().
 Judah appealed to the Vizier begging that Benjamin be released and that he be enslaved in his stead, because of the silver cup found in Benjamin's sack. The Vizier broke down into tears. He could not control himself any longer and so he sent the Egyptian men out of the house. Then he revealed to the Hebrews that he was in fact their brother, Joseph. He wept so loudly that even the Egyptian household heard it outside. The brothers were frozen and could not utter a word. He brought them closer and relayed to them the events that had happened and told them not to fear, that what they had meant for evil, God had meant for good. Then he commanded them to go and bring their father and his entire household into Egypt to live in the province of Goshen, because there were five more years of famine left. So Joseph supplied them Egyptian transport wagons, new garments, silver money, and twenty additional donkeys carrying provisions for the journey. ()
Thus, Jacob (also known as Israel) and his entire house of seventy gathered up with all their livestock and began their journey to Egypt. As they approached Egyptian territory, Judah went ahead to ask Joseph where the caravan should unload. They were directed into the province of Goshen and Joseph readied his chariot to meet his father there. It had been over twenty years since Joseph had last seen his father. When they met, they embraced each other and wept together for quite a while. His father then remarked, "Now let me die, since I have seen your face, because you are still alive." ()
Afterward, Joseph's family personally met the
Judah appealed to the Vizier begging that Benjamin be released and that he be enslaved in his stead, because of the silver cup found in Benjamin's sack. The Vizier broke down into tears. He could not control himself any longer and so he sent the Egyptian men out of the house. Then he revealed to the Hebrews that he was in fact their brother, Joseph. He wept so loudly that even the Egyptian household heard it outside. The brothers were frozen and could not utter a word. He brought them closer and relayed to them the events that had happened and told them not to fear, that what they had meant for evil, God had meant for good. Then he commanded them to go and bring their father and his entire household into Egypt to live in the province of Goshen, because there were five more years of famine left. So Joseph supplied them Egyptian transport wagons, new garments, silver money, and twenty additional donkeys carrying provisions for the journey. ()
Thus, Jacob (also known as Israel) and his entire house of seventy gathered up with all their livestock and began their journey to Egypt. As they approached Egyptian territory, Judah went ahead to ask Joseph where the caravan should unload. They were directed into the province of Goshen and Joseph readied his chariot to meet his father there. It had been over twenty years since Joseph had last seen his father. When they met, they embraced each other and wept together for quite a while. His father then remarked, "Now let me die, since I have seen your face, because you are still alive." ()
Afterward, Joseph's family personally met the
 Joseph lived to the age of 110, living to see his great-grandchildren. Before he died, he made the
Joseph lived to the age of 110, living to see his great-grandchildren. Before he died, he made the
 The majority of modern scholars agree that the Joseph story is a
The majority of modern scholars agree that the Joseph story is a
 In the
In the
 Jewish tradition holds that Joseph had his steward plant his personal silver cup in Benjamin's sack to test his brothers. He wanted to know if they would be willing to risk danger in order to save their half brother Benjamin. Since Joseph and Benjamin were born from Rachel, this test was necessary to reveal if they would betray Benjamin as they did with Joseph when he was seventeen. Because ''Joseph the Dreamer'' predicts the future by analyzing dreams, alternative Jewish tradition claims that he practiced divination using this silver cup as the steward charged and as Joseph himself claimed in .
Jewish tradition holds that Joseph had his steward plant his personal silver cup in Benjamin's sack to test his brothers. He wanted to know if they would be willing to risk danger in order to save their half brother Benjamin. Since Joseph and Benjamin were born from Rachel, this test was necessary to reveal if they would betray Benjamin as they did with Joseph when he was seventeen. Because ''Joseph the Dreamer'' predicts the future by analyzing dreams, alternative Jewish tradition claims that he practiced divination using this silver cup as the steward charged and as Joseph himself claimed in .
 Joseph ( ar, يوسُف, ') is regarded by
Joseph ( ar, يوسُف, ') is regarded by
/ref> But in Islam they returned leaving behind Benjamin because the mizzen bowl of the king was found in his bag. Similarly, the eldest son of Jacob had decided not to leave the land because of the oath taken to protect Benjamin beforehand. When Jacob learned their story after their return, he wept in grief till he lost his eyesight because of sorrow. He thus charged his sons to go and inquire about Joseph and his brother and despair not of God's mercy. It was during this return to Egypt that Joseph disclosed his real identity to his brothers. He admonished and forgave them, he sent also his garment which healed the patriarch's eyes as soon as it was cast unto his face. The remaining verses describe the migration of Jacob's family to Egypt and the emotional meeting of Jacob and his long lost son, Joseph. The family prostrated before him hence the fulfilment of his dream aforetime. The story concludes by Joseph praying, "My lord you have indeed bestowed upon me of the sovereignty and taught me something of the interpretation of dreams- the (only) creator of heavens and the earth! You are my Guardian in this world and in the Hereafter. Cause me to die as a Muslim and join me with the righteous" (Qur'an 12:101).
The Composition of Genesis 37: Incoherence and Meaning in the Exposition of the Joseph Story
'. Forschungen zum Alten Testament 2. Reihe. 95. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. . * * * * * * *
BBC - Joseph
{{DEFAULTSORT:Joseph Biblical figures in rabbinic literature Book of Genesis people Burials in Israel Children of Jacob Christian saints from the Old Testament Divination Founders of biblical tribes People whose existence is disputed
Standard Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object th ...
: ''Yōsef'', Tiberian
Tiberian may refer to:
* Tiberian vocalization, an oral tradition within the Hebrew language
* Tiberian Hebrew, the variety of Hebrew based on Tiberian vocalization
* Tiberias, a city in Lower Galilee, Israel
* Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesa ...
: ''Yōsēp̄''; alternatively: יְהוֹסֵף, lit. 'Yahweh
Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he posse ...
shall add'; Standard: ''Yəhōsef'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōsēp̄''; ar, يوسف, Yūsuf; grc, Ἰωσήφ, Iōsēph) is an important figure in the Bible's Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning") ...
. He was the first of the two sons of Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
and Rachel
Rachel () was a Biblical figure, the favorite of Jacob's two wives, and the mother of Joseph and Benjamin, two of the twelve progenitors of the tribes of Israel. Rachel's father was Laban. Her older sister was Leah, Jacob's first wife. Her aun ...
(Jacob's twelfth child and eleventh son). He is the founder of the Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
Tribe of Joseph
The Tribe of Joseph is one of the Tribes of Israel in biblical tradition. Since Ephraim and Manasseh (often called the "two half-tribes of Joseph") together traditionally constituted the tribe of Joseph, it was often not listed as one of th ...
. His story functions as an explanation for Israel's residence in Egypt. He is the favourite son of the patriarch Jacob, and his jealous brothers sell him into slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in Egypt, where he eventually ends up incarcerated. After correctly interpreting the dreams of Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
, however, he rises to second-in-command
Second-in-command (2i/c or 2IC) is a title denoting that the holder of the title is the second-highest authority within a certain organisation.
Usage
In the British Army or Royal Marines, the second-in-command is the deputy commander of a unit, ...
in Egypt and saves Egypt during a famine. Jacob's family travel to Egypt to escape the famine, and it is through him that they are given leave to settle in the Land of Goshen
The land of Goshen ( he, אֶרֶץ גֹּשֶׁן, Modern: ''ʾEreẓ Gōšen'', Tiberian: ''ʾEreṣ Gōšen'') is named in the Hebrew Bible as the place in Egypt given to the Hebrews by the pharaoh of Joseph (Book of Genesis, ), and the la ...
(the eastern part of the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Po ...
).
The composition of the story can be dated to the period between the 7th century BCE and the third quarter of the 5th century BCE, which is roughly the period to which scholars date the Book of Genesis.
In rabbinic tradition, he is considered the ancestor of a second Messiah called " Mashiach ben Yosef", who will wage war against the forces of evil alongside Mashiach ben David
The Messiah in Judaism () is a savior and liberator figure in Jewish eschatology, who is believed to be the future redeemer of the Jewish people. The concept of messianism originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible a messiah is a king or H ...
and die in combat with the enemies of God and Israel.
Etymology
The Bible offers two explanations of the name ''Yōsēf:'' first it is compared to the Hebrew root אסף (''ʾ-s-p''), meaning "to gather, remove, take away": "And she conceived, and bore a son; and said, God hath ''taken away'' my reproach" (Genesis 30:23); ''Yōsēf'' is then identified with the similar root יסף (''y-s-p''), meaning "to add": "And she called his name Joseph; and said, The LORD shall ''add'' to me another son." (Genesis 30:24).Friedman, R.E., ''The Bible With Sources Revealed'', (2003), p. 80Biblical narrative
Birth and family
Joseph, son ofJacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
and Rachel
Rachel () was a Biblical figure, the favorite of Jacob's two wives, and the mother of Joseph and Benjamin, two of the twelve progenitors of the tribes of Israel. Rachel's father was Laban. Her older sister was Leah, Jacob's first wife. Her aun ...
, lived in the land of Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
with ten half-brothers, one full brother, and at least one half-sister. He was Rachel's firstborn and Jacob's eleventh son. Of all the sons, Joseph was preferred by his father, who gave him a "long coat of many colors
In the Hebrew Bible, the coat of many colors ( he, כְּתֹנֶת פַּסִּים, ketonet passim) is the name for the garment that Joseph (Hebrew Bible), Joseph owned, which was given to him by his father, Jacob.
Biblical narrative
Joseph' ...
". When Joseph was seventeen years old, he shared with his brothers two dreams he had had: in the first dream, Joseph and his brothers gathered bundles of grain, of which those his brothers gathered, bowed to his own. In the second dream, the sun (father), the moon (mother), and eleven stars (brothers) bowed to Joseph himself. These dreams, implying his supremacy, angered his brothers () and made the brothers plot his demise.
Plot against Joseph
 Joseph's half-brothers were jealous of him; () wherefore, in
Joseph's half-brothers were jealous of him; () wherefore, in Dothan Dothan is a place-name from the Hebrew Bible, identified with Tel Dothan. It may refer to:
* Dothan, Alabama, a city in Dale, Henry, and Houston counties in the U.S. state of Alabama
* Dani Dothan, lyricist and vocalist for the Israeli rock and ne ...
, most of them plotted to kill him, with the exception of Reuben
Reuben or Reuven is a Biblical male first name from Hebrew רְאוּבֵן (Re'uven), meaning "behold, a son". In the Bible, Reuben was the firstborn son of Jacob.
Variants include Rúben in European Portuguese; Rubens in Brazilian Portugue ...
, who suggested to have Joseph thrown into an empty cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by t ...
, intending to rescue Joseph himself. Unaware of this secondary intention, the others obeyed him first. Upon imprisoning Joseph, the brothers saw a camel caravan carrying spices and perfumes to Egypt, and sold Joseph to these merchants. Thereafter the guilty brothers painted goat's blood on Joseph's coat and showed it to Jacob, who therefore believed Joseph had died ().
Potiphar's house
Ultimately, Joseph was sold toPotiphar
Potiphar ( ; Egyptian origin: ''pꜣ-dj-pꜣ-rꜥ'' "he whom Ra gave") is a figure in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran. Potiphar is possibly the same name as Potiphera () from Late Egyptian ''pꜣ-dj-pꜣ-rꜥ'' "he whom Ra has given."
Potiphar ...
, the captain of Pharaoh's guard (, ). Later, Joseph became Potiphar's personal servant, and subsequently his household's superintendent. Here, Potiphar's wife (called Zuleika in later tradition) tried to seduce Joseph, which he refused. Angered by his running away from her, she made a false accusation of rape
A false accusation of rape happens when a person states that they or another person have been raped when no rape has occurred.
Although some studies attempt to characterize the prevalence of false accusation of rape, according to a 2013 book o ...
, and thus assured his imprisonment ().
Joseph in prison
 The warden put Joseph in charge of the other prisoners, and soon afterward Pharaoh's chief
The warden put Joseph in charge of the other prisoners, and soon afterward Pharaoh's chief cup-bearer
A cup-bearer was historically an officer of high rank in royal courts, whose duty was to pour and serve the drinks at the royal table. On account of the constant fear of plots and intrigues (such as poisoning), a person must have been regarded as ...
and chief baker, who had offended the Pharaoh, were thrown into the prison. Both men had dreams, and Joseph, being able to interpret dreams, asked to hear them. The cup-bearer's dream was about a vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselv ...
with three branches that was budding. And as it was budding, its blossoms came out and they produced grapes. The cup-bearer took those grapes and squeezed them into Pharaoh's cup, and placed the cup in Pharaoh's hand. Joseph interpreted this dream as the cup-bearer being restored as cup-bearer to the Pharaoh within three days. The baker's dream was about three baskets full of bread for the Pharaoh, and birds were eating the bread out of those baskets. Joseph interpreted this dream as the baker being hanged within three days and having his flesh eaten by birds. Joseph requested that the cup-bearer mention him to Pharaoh to secure his release from prison, but the cup-bearer, reinstalled in office, forgot Joseph. After two more years, the Pharaoh dreamt of seven lean cows which devoured seven fat cows; and of seven withered ears of grain which devoured seven fat ears. When the Pharaoh's advisers failed to interpret these dreams, the cup-bearer remembered Joseph. Joseph was then summoned. He interpreted the dream as seven years of abundance followed by seven years of famine, and advised the Pharaoh to store surplus grain.
Vizier of Egypt
Following the prediction, Joseph becameVizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was a ...
, under the name of Zaphnath-Paaneah
Zaphnath-Paaneah ( hbo, צָפְנַת פַּעְנֵחַ , grc, label= LXX, Ψονθομφανήχ ) is the name given by Pharaoh to Joseph in the Genesis narrative ().
The name may be of Egyptian origins, but there is no straightforward ety ...
( Hebrew: צָפְנַת פַּעְנֵחַ ''Ṣāp̄naṯ Paʿnēaḥ''), and was given Asenath
Asenath (, ; Koine Greek: Ἀσενέθ, ''Asenéth'') is a minor figure in the Book of Genesis. Asenath was a high-born, aristocratic Egyptian woman. She was the wife of Joseph and the mother of his sons, Manasseh and Ephraim. There are two R ...
, the daughter of Potipherah, priest of On, to be his wife. During the seven years of abundance, Joseph ensured that the storehouses were full and that all produce was weighed. In the sixth year, Asenath bore two children to Joseph: Manasseh
Manasseh () is both a given name and a surname. Its variants include Manasses and Manasse.
Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Ezekiel Saleh Manasseh (died 1944), Singaporean rice and opium merchant and hotelier
* Jacob Manasseh (die ...
and Ephraim
Ephraim (; he, ''ʾEp̄rayīm'', in pausa: ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was, according to the Book of Genesis, the second son of Joseph ben Jacob and Asenath. Asenath was an Ancient Egyptian woman whom Pharaoh gave to Joseph as wife, and the daughte ...
. When the famine came, it was so severe that people from surrounding nations came to Egypt to buy bread. The narrative also indicates that they went straight to Joseph or were directed to him, even by the Pharaoh himself (). As a last resort, all of the inhabitants of Egypt, less the Egyptian priestly class, sold their properties and later themselves (as slaves) to Joseph for seed; wherefore Joseph set a mandate that, because the people would be sowing and harvesting seed on government property, a fifth of the produce should go to the Pharaoh. This mandate lasted until the days of Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
().
Brothers sent to Egypt
 In the second year of famine, Joseph's half brothers were sent to Egypt to buy goods. When they came to Egypt, they stood before the Vizier but did not recognize him as their brother Joseph, who was now in his late 30s; but Joseph ''did'' recognize them and did not speak at all to them in his native tongue of
In the second year of famine, Joseph's half brothers were sent to Egypt to buy goods. When they came to Egypt, they stood before the Vizier but did not recognize him as their brother Joseph, who was now in his late 30s; but Joseph ''did'' recognize them and did not speak at all to them in his native tongue of Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
. After questioning them, he accused them of being spies. After they mentioned a younger brother at home, the Vizier (Joseph) demanded that he be brought to Egypt as a demonstration of their veracity. This was Joseph's full brother, Benjamin
Benjamin ( he, ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel (Jacob's thir ...
. Joseph placed his brothers in prison for three days. On the third day, he brought them out of prison to reiterate that he wanted their youngest brother brought to Egypt to demonstrate their veracity. The brothers conferred amongst themselves speaking in Hebrew, reflecting on the wrong they had done to Joseph. Joseph understood what they were saying and removed himself from their presence because he was caught in emotion. When he returned, the Vizier took Simeon
Simeon () is a given name, from the Hebrew (Biblical ''Šimʿon'', Tiberian ''Šimʿôn''), usually transliterated as Shimon. In Greek it is written Συμεών, hence the Latinized spelling Symeon.
Meaning
The name is derived from Simeon, so ...
and bound him as a hostage. Then he had their donkeys prepared with grain and sent the other brothers back to Canaan. Unbeknownst to them, Joseph had also returned their money to their money sacks ().
The silver cup
The remaining brothers returned to their father in Canaan, and told him all that had transpired in Egypt. They also discovered that all of their money sacks still had money in them, and they were dismayed. Then they informed their father that the Vizier demanded that Benjamin be brought before him to demonstrate that they were honest men. Jacob became greatly distressed feeling that they treated him badly. After they had consumed all of the grain that they brought back from Egypt, Jacob told his sons to go back to Egypt for more grain. With Reuben and Judah's persistence, they persuaded their father to let Benjamin join them for fear of Egyptian retribution (). Upon their return to Egypt, the brothers were received by the steward of the house of Joseph. When they were brought to Joseph's house, they were apprehensive about the returned money in their money sacks. They thought that the missed transaction would somehow be used against them as way to induct them as slaves and confiscate their possessions. So they immediately informed the steward of what had transpired to get a feel of the situation. The steward put them at ease, telling them not to worry about the money, and brought out their brother Simeon. Then he brought the brothers into the house of Joseph and received them hospitably. When the Vizier (Joseph) appeared, they gave him gifts from their father. Joseph saw and inquired of Benjamin and was overcome by emotion but did not show it. He withdrew to his chambers and wept. When he regained control of himself, he returned and ordered a meal to be served. The Egyptians would not dine with Hebrews at the same table, as doing so was considered loathsome, so the sons of Israel were served at a separate table ().
That night, Joseph ordered his steward to load the brothers' donkeys with food and all their money. The money they brought was double what they had from the first trip. Deceptively, Joseph also ordered that his silver cup be put in Benjamin's sack. The following morning the brothers began their journey back to Canaan. Joseph ordered the steward to go after the brothers and question them about the "missing" silver cup. When the steward caught up with the brothers, he seized them and searched their sacks. The steward found the cup in Benjamin's sack just as he had planted it the night before. This caused a stir amongst the brothers. However, they agreed to be escorted back to Egypt. When the Vizier (Joseph) confronted them about the silver cup, he demanded that the one who possessed the cup in his bag become his slave. In response, Judah pleaded with the Vizier that Benjamin be allowed to return to his father, and he himself be kept in Benjamin's place as a slave ().
Upon their return to Egypt, the brothers were received by the steward of the house of Joseph. When they were brought to Joseph's house, they were apprehensive about the returned money in their money sacks. They thought that the missed transaction would somehow be used against them as way to induct them as slaves and confiscate their possessions. So they immediately informed the steward of what had transpired to get a feel of the situation. The steward put them at ease, telling them not to worry about the money, and brought out their brother Simeon. Then he brought the brothers into the house of Joseph and received them hospitably. When the Vizier (Joseph) appeared, they gave him gifts from their father. Joseph saw and inquired of Benjamin and was overcome by emotion but did not show it. He withdrew to his chambers and wept. When he regained control of himself, he returned and ordered a meal to be served. The Egyptians would not dine with Hebrews at the same table, as doing so was considered loathsome, so the sons of Israel were served at a separate table ().
That night, Joseph ordered his steward to load the brothers' donkeys with food and all their money. The money they brought was double what they had from the first trip. Deceptively, Joseph also ordered that his silver cup be put in Benjamin's sack. The following morning the brothers began their journey back to Canaan. Joseph ordered the steward to go after the brothers and question them about the "missing" silver cup. When the steward caught up with the brothers, he seized them and searched their sacks. The steward found the cup in Benjamin's sack just as he had planted it the night before. This caused a stir amongst the brothers. However, they agreed to be escorted back to Egypt. When the Vizier (Joseph) confronted them about the silver cup, he demanded that the one who possessed the cup in his bag become his slave. In response, Judah pleaded with the Vizier that Benjamin be allowed to return to his father, and he himself be kept in Benjamin's place as a slave ().
Family reunited
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
of Egypt. The Pharaoh honored their stay and even proposed that if there were any qualified men in their house, then they may elect a chief herdsman to oversee Egyptian livestock. Because the Pharaoh had such a high regard for Joseph, practically making him his equal, it had been an honor to meet his father. Thus, Israel was able to bless the Pharaoh. () The family was then settled in Goshen.
Father's blessing and passing
The house of Israel acquired many possessions and multiplied exceedingly during the course of seventeen years, even through the worst of the seven-year famine. At this time, Joseph's father was 147 years old and bedridden. He had fallen ill and lost most of his vision. Joseph was called into his father's house and Israel pleaded with his son that he not be buried in Egypt. Rather, he requested to be carried to the land of Canaan to be buried with his forefathers. Joseph was sworn to do as his father asked of him. () Later, Joseph came to visit his father having with him his two sons, Ephraim and Manasseh. Israel declared that they would be heirs to the inheritance of the house of Israel, as if they were his own children, just as Reuben and Simeon were. Then Israel laid his left hand on the eldest Mannasseh's head and his right hand on the youngest Ephraim's head and blessed Joseph. However, Joseph was displeased that his father's right hand was not on the head of his firstborn, so he switched his father's hands. But Israel refused saying, "but truly his younger brother shall be greater than he," a declaration he made just as Israel himself was to his firstborn brother Esau. To Joseph, he gave a portion more of Canaanite property than he had to his other sons; land that he fought for against theAmorite
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied lar ...
s. ()
Then Israel called all of his sons in and prophesied their blessings or curses to all twelve of them in order of their ages. To Joseph he declared:
After relaying his prophecies, Israel died. The family, including the Egyptians, mourned him seventy days. Joseph had his father embalmed, a process that took forty days. Then he prepared a great ceremonial journey to Canaan leading the servants of the Pharaoh, and the elders of the houses Israel and Egypt beyond the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
. They stopped at Atad
Atad is an Old Testament Hebrew name meaning buckthorn.
Atad was the place where Joseph and his brothers, when on their way from Egypt to Hebron with the remains of their father Jacob, made for seven days a "great and very sore lamentation". On ...
where they observed seven days of mourning. Here, their lamentation was so great that it caught the attention of surrounding Canaanites who remarked "This is a deep mourning of the Egyptians." So they named this spot Abel Mizraim
Abel-mizraim (, ''’Āḇêl-Mitsrayim,''; the "meadow of Egypt", or "mourning of Egypt") is a place "beyond," or east, of the Jordan river, at the "threshing-floor of Atad." Here Joseph and his 11 brothers (representing the future 12 tribes of I ...
. Then Joseph buried Israel in the cave of Machpelah
, alternate_name = Tomb of the Patriarchs, Cave of Machpelah, Sanctuary of Abraham, Ibrahimi Mosque (Mosque of Abraham)
, image = Palestine Hebron Cave of the Patriarchs.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Southern view of the complex, 2009
, map ...
, the property of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
when he bought it from the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centra ...
. ()
After their father died, the brothers of Joseph feared retribution for being responsible for Joseph's deliverance into Egypt as a slave. Joseph wept as they spoke and told them that what had happened was God's purpose to save lives and the lives of his family. He comforted them and their ties were reconciled. ()
Joseph's burial
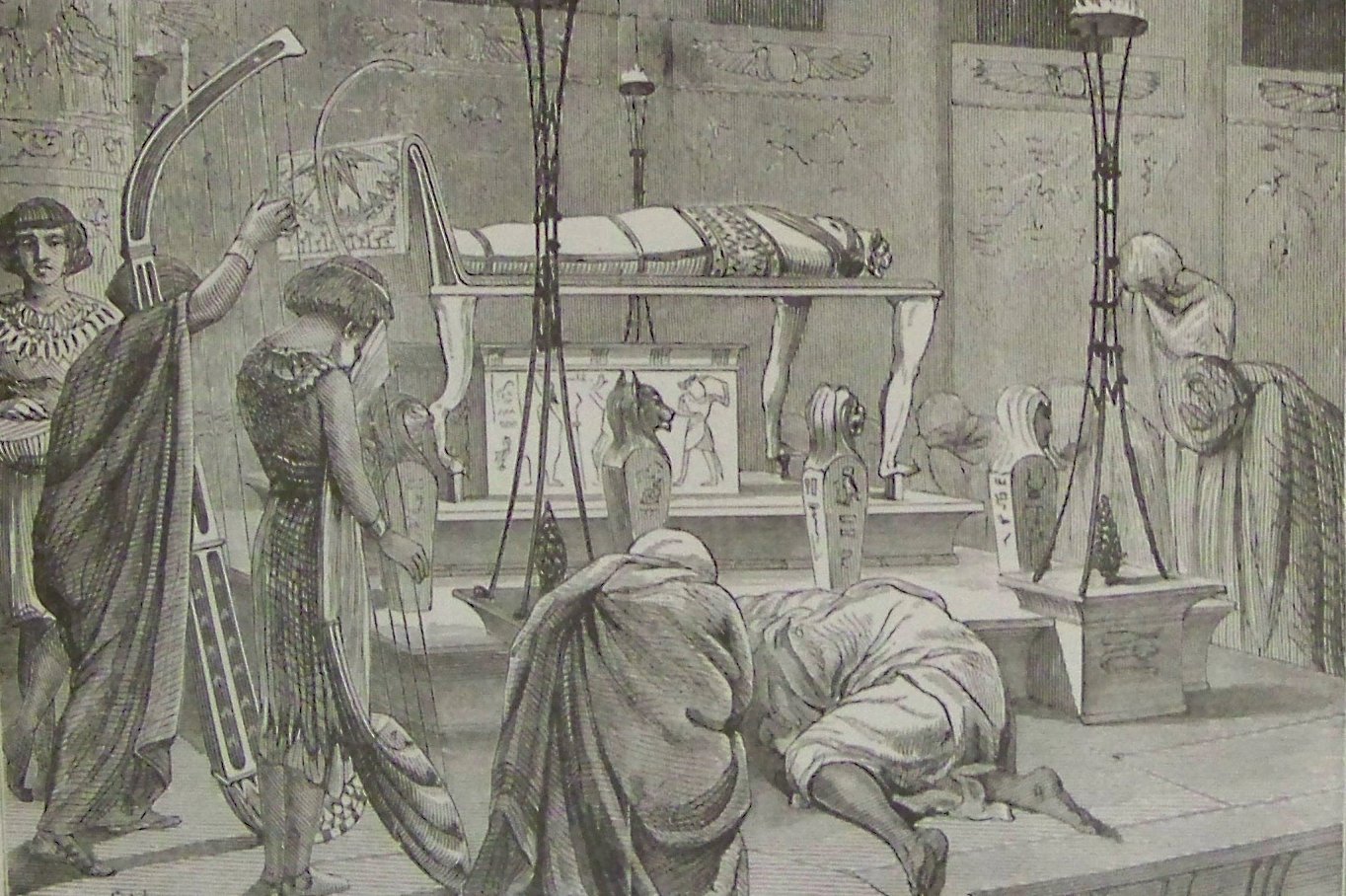
 Joseph lived to the age of 110, living to see his great-grandchildren. Before he died, he made the
Joseph lived to the age of 110, living to see his great-grandchildren. Before he died, he made the children of Israel
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
swear that when they left the land of Egypt they would take his bones with them, and on his death his body was embalmed and placed in a coffin in Egypt. ()
The children of Israel
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
remembered their oath, and when they left Egypt during the Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew language, Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yeẓi’at Miẓrayim'': ) is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four books of the Torah (or Pentateuch, corresponding to the first five books of the ...
, Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
took Joseph's bones with him. () The bones were buried at Shechem
Shechem ( ), also spelled Sichem ( ; he, שְׁכֶם, ''Šəḵem''; ; grc, Συχέμ, Sykhém; Samaritan Hebrew: , ), was a Canaanite and Israelite city mentioned in the Amarna Letters, later appearing in the Hebrew Bible as the first cap ...
, in the parcel of ground which Jacob bought from the sons of Hamor
In the Book of Genesis, Dinah (; ) was the seventh child and only daughter of Leah and Jacob, and one of the matriarchs of the Israelites. The episode of her violation by Shechem, son of a Canaanite or Hivite prince, and the subsequent vengean ...
(), which has traditionally been identified with site of Joseph's Tomb
Joseph's Tomb ( he, קבר יוסף, ''Qever Yosef''; ar, قبر يوسف, ''Qabr Yūsuf'') is a funerary monument located in Balata village at the eastern entrance to the valley that separates Mounts Gerizim and Ebal, 300 metres northwest of ...
, before Jacob and all his family moved to Egypt. Shechem was in the land which was allocated by Joshua to the Tribe of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim ( he, אֶפְרַיִם, ''ʾEp̄rayīm,'' in pausa: אֶפְרָיִם, ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was one of the tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim formed the ''House of ...
, one of the tribes of the House of Joseph
The Tribe of Joseph is one of the Tribes of Israel in biblical tradition. Since Ephraim and Manasseh (often called the "two half-tribes of Joseph") together traditionally constituted the tribe of Joseph, it was often not listed as one of the ...
, after the alleged conquest of Canaan
The Book of Joshua ( he, סֵפֶר יְהוֹשֻׁעַ ', Tiberian: ''Sēp̄er Yŏhōšūaʿ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israe ...
.
Composition and literary motifs
 The majority of modern scholars agree that the Joseph story is a
The majority of modern scholars agree that the Joseph story is a Wisdom
Wisdom, sapience, or sagacity is the ability to contemplate and act using knowledge, experience, understanding, common sense and insight. Wisdom is associated with attributes such as unbiased judgment, compassion, experiential self-knowledge, ...
novella constructed by a single author and that it reached its current form in the 5th century BCE at the earliest. Its redaction history may have included a first "Reuben version" originating in the northern kingdom of Israel and intended to justify the domination by the "house of Joseph" over the other tribes, this was followed by a later "Judah-expansion" (chapters 38 and 49) elevating Judah as the rightful successor to Jacob, and finally various embellishments so that the novella would function as the bridge between the Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
and the story of Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
and the Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* Ex ...
.
The motif of dreams/dream interpretation contributes to a strong story-like narrative. The plot begins by showing Joseph as a dreamer; this leads him into trouble as, out of jealousy, his brothers sell him into slavery. The next two instances of dream interpretation establish his reputation as a great interpreter of dreams; first, he begins in a low place, interpreting the dreams of prisoners. Then Joseph is summoned to interpret the dreams of Pharaoh himself. Impressed with Joseph's interpretations, Pharaoh appoints him as second-in-command (Gen 41:41). This sets up the climax of the story, which many regard to be the moment Joseph reveals his identity to his brothers (Gen 45:3).
Jewish tradition
Selling Joseph
 In the
In the midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
, the selling of Joseph was part of God's divine plan for him to save his tribes. The favoritism Israel showed Joseph and the plot against him by his brothers were divine means of getting him into Egypt. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
comments that even the villager in Shechem, about whom Joseph inquired his brother's whereabouts, was a "divine messenger" working behind the scene.
A midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
asked, ''How many times was Joseph sold?'' In analyzing , there are five different Hebrew names used to describe five different groups of people involved in the transaction of selling Joseph, according to Rabbi Judah and ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
Rav Huna
Rav Huna (Hebrew: רב הונא) was a Jewish Talmud, Talmudist and Exilarch who lived in Babylonia, known as an Amoraim, amora of the second generation and head of the Talmudic Academies in Babylonia, Academy of Sura; he was born about 216 (212 ...
. The first group identified, are Joseph's brothers when Judah brings up the idea of selling Joseph in verses 26 and 27. The first mention of Ishmaelites (Yishma'elîm) is in verse 25. Then the Hebrew phrase ''ʼnāshîm midyanîm sōĥrîm'' in verse 28 describes Midianite traders. A fourth group in verse 36 is named in Hebrew as ''m‘danîm'' that is properly identified as Medanites. The final group, where a transaction is made, is among the Egyptians in the same verse.
After identifying the Hebrew names, Rabbi Judah claims that Joseph was sold four times: First his brothers sold Joseph to the Ishmaelites (Yishma'elîm), then the Ishmaelites sold him to the Midianite traders (ʼnāshîm midyanîm sōĥrîm), the Midianite traders to the Medanites (m‘danîm), and the Medanites into Egypt. Rav Huna
Rav Huna (Hebrew: רב הונא) was a Jewish Talmud, Talmudist and Exilarch who lived in Babylonia, known as an Amoraim, amora of the second generation and head of the Talmudic Academies in Babylonia, Academy of Sura; he was born about 216 (212 ...
adds one more sale by concluding that after the Medanites sold him to the Egyptians, a fifth sale occurred when the Egyptians sold him to Potiphar
Potiphar ( ; Egyptian origin: ''pꜣ-dj-pꜣ-rꜥ'' "he whom Ra gave") is a figure in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran. Potiphar is possibly the same name as Potiphera () from Late Egyptian ''pꜣ-dj-pꜣ-rꜥ'' "he whom Ra has given."
Potiphar ...
. (Genesis Rabbah
Genesis Rabbah (Hebrew: , ''B'reshith Rabba'') is a religious text from Judaism's classical period, probably written between 300 and 500 CE with some later additions. It is a midrash comprising a collection of ancient rabbinical homiletical inter ...
84:22)
Potiphar's wife
Joseph had good reasons not to have an affair with Potiphar's wife: he did not want to abuse his master's trust; he believed in the sanctity of marriage; and it went against his ethical, moral and religious principles taught to him by his father Jacob. According to theMidrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
, Joseph would have been immediately executed by the sexual assault charge against him by Potiphar's wife. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
Abravanel
The Abravanel family ( he, ''ʾAbravanʾēl'' or ''ʾAbarbənəʾēl''), also spelled as ''Abarbanel'', ''Abrabanel'', ''Avravanel'', ''Barbernell'', or ''Barbanel'' – literally meaning ''Ab'' ("father") ''rabban'' ("priest") ''el'' ("of God" ...
explains that she had accused other servants of the same crime in the past. Potiphar believed that Joseph was incapable of such an act and petitioned Pharaoh to spare his life. However, punishment could not have been avoided because of her class status and limited public knowledge of her scheme.
According to '' Legend of the Jews'', the name of Potiphar's wife is Zuleikha
Potiphar's wife is a figure in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran. She was the wife of Potiphar, the captain of Pharaoh's guard in the time of Jacob and his twelve sons. According to the Book of Genesis, she falsely accused Joseph of attempted r ...
and when she was enticing Joseph to give up to her sinful passion, God appeared unto him, holding the foundation of earth (''Eben Shetiyah''), that He would destroy the world if Joseph touched her.
Silver cup for divination
 Jewish tradition holds that Joseph had his steward plant his personal silver cup in Benjamin's sack to test his brothers. He wanted to know if they would be willing to risk danger in order to save their half brother Benjamin. Since Joseph and Benjamin were born from Rachel, this test was necessary to reveal if they would betray Benjamin as they did with Joseph when he was seventeen. Because ''Joseph the Dreamer'' predicts the future by analyzing dreams, alternative Jewish tradition claims that he practiced divination using this silver cup as the steward charged and as Joseph himself claimed in .
Jewish tradition holds that Joseph had his steward plant his personal silver cup in Benjamin's sack to test his brothers. He wanted to know if they would be willing to risk danger in order to save their half brother Benjamin. Since Joseph and Benjamin were born from Rachel, this test was necessary to reveal if they would betray Benjamin as they did with Joseph when he was seventeen. Because ''Joseph the Dreamer'' predicts the future by analyzing dreams, alternative Jewish tradition claims that he practiced divination using this silver cup as the steward charged and as Joseph himself claimed in .
Raising Joseph
In oneTalmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cente ...
ic story, Joseph was buried in the Nile river
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
, as there was some dispute as to which province should be honored by having his tomb within its boundaries. Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
, led there by an ancient holy woman named Serach {{about, , the Jewish wife of the Khazar ruler Sabriel, Serach (Khazar), the South Indian actress, Serah (actress), the type of Ancient Egyptian cartouche, Serekh, other meanings, Serach (disambiguation)
Serach bat Asher was, in the Tanakh, a daugh ...
, was able by a miracle to raise the sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek ...
and to take it with him at the time of the Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew language, Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yeẓi’at Miẓrayim'': ) is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four books of the Torah (or Pentateuch, corresponding to the first five books of the ...
.
Christian tradition
Joseph is mentioned in theNew Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christ ...
as an example of faith (). Joseph is commemorated as one of the Holy Forefathers in the Calendar of Saints
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context d ...
of the Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
on 26 July. In the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
and those Eastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of th ...
which follow the Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
Th ...
, he is known as "Joseph the all-comely", a reference not only to his physical appearance, but more importantly to the beauty of his spiritual life. They commemorate him on the Sunday of the Holy Forefathers (two Sundays before Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus, Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by country, around t ...
) and on Holy and Great Monday
Holy Monday or Great and Holy Monday (also Holy and Great Monday) (Greek: ''Μεγάλη Δευτέρα'', ''Megale Deutera'') is a day of the Holy Week, which is the week before Easter. According to the gospels, on this day Jesus Christ cursed ...
(Monday of Holy Week
Holy Week ( la, Hebdomada Sancta or , ; grc, Ἁγία καὶ Μεγάλη Ἑβδομάς, translit=Hagia kai Megale Hebdomas, lit=Holy and Great Week) is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. In Eastern Churches, w ...
). In icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The most ...
s, he is sometimes depicted wearing the nemes
Nemes were pieces of striped head cloth worn by pharaohs in ancient Egypt. It covered the whole crown and behind of the head and nape of the neck (sometimes also extending a little way down the back) and had lappets, two large flaps which hung ...
headdress of an Egyptian vizier. The Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod
The Lutheran Church—Missouri Synod (LCMS), also known as the Missouri Synod, is a traditional, confessional Lutheran denomination in the United States. With 1.8 million members, it is the second-largest Lutheran body in the United States. The LC ...
commemorates him as a patriarch on 31 March.
In addition to honoring him, there was a strong tendency in the patristic
Patristics or patrology is the study of the early Christian writers who are designated Church Fathers. The names derive from the combined forms of Latin ''pater'' and Greek ''patḗr'' (father). The period is generally considered to run from ...
period to view his life as a typological precursor to Christ. This tendency is represented in John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Χρυσόστομος; 14 September 407) was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his homilies, preaching and public speaking, his denunciat ...
who said that Joseph's suffering was "a type of things to come", Caesarius of Arles
Caesarius of Arles ( la, Caesarius Arelatensis; 468/470 27 August 542 AD), sometimes called "of Chalon" (''Cabillonensis'' or ''Cabellinensis'') from his birthplace Chalon-sur-Saône, was the foremost ecclesiastic of his generation in Merovingia ...
who interpreted Joseph's famous coat as representative of the diverse nations who would follow Christ, Ambrose of Milan
Ambrose of Milan ( la, Aurelius Ambrosius; ), venerated as Saint Ambrose, ; lmo, Sant Ambroeus . was a theologian and statesman who served as Bishop of Milan from 374 to 397. He expressed himself prominently as a public figure, fiercely promot ...
who interpreted the standing sheaf as prefiguring the resurrection of Christ, and others.
This tendency, although greatly diminished, was followed throughout late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, the Medieval Era
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, and into the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
. Even John Calvin, sometimes hailed as the father of modern grammatico-historical
The historical-grammatical method is a modern Christian hermeneutical method that strives to discover the biblical authors' original intended meaning in the text. According to the historical-grammatical method, if based on an analysis of the gram ...
exegesis
Exegesis ( ; from the Ancient Greek, Greek , from , "to lead out") is a critical explanation or interpretation (logic), interpretation of a text. The term is traditionally applied to the interpretation of Bible, Biblical works. In modern usage, ...
, writes "in the person of Joseph, a lively image of Christ is presented."
In addition, some Christian authors have argued that this typological interpretation finds its origin in the speech of Stephen
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; ...
in Acts
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its message ...
, as well as the Gospel of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-volu ...
and the parables of Jesus
The parables of Jesus are found in the Synoptic Gospels and some of the non-canonical gospels. They form approximately one third of his recorded teachings. Christians place great emphasis on these parables, which they generally regard as the word ...
, noting strong verbal and conceptual collocation between the Greek translation of the portion of Genesis concerning Joseph and the Parable of the Wicked Tenants
The Parable of the Wicked Husbandmen, also known as the Parable of the Bad Tenants, is a parable of Jesus found in the Gospel of Matthew (), the Gospel of Mark () and the Gospel of Luke (). It is also found in the non-canonical Gospel of Thomas ...
and the Parable of the Prodigal Son.
Islamic tradition
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s as a prophet (Quran, suras vi. 84, xl. 34), and a whole chapter Yusuf
Yusuf ( ar, يوسف ') is a male name of Arabic origin meaning "God increases" (in piety, power and influence).From the Hebrew יהוה להוסיף ''YHWH Lhosif'' meaning "YHWH will increase/add". It is the Arabic equivalent of the Hebrew name ...
(sura xii.) is devoted to him, the only instance in the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Classical Arabic, Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation in Islam, revelation from God in Islam, ...
in which an entire chapter is devoted to a complete story of a prophet. It is described in the Quran as the 'best of stories'. Joseph is said to have been extremely handsome, which attracted his Egyptian master's wife to attempt to seduce him. Muhammad is believed to have once said, "One half of all the beauty God apportioned for mankind went to Joseph and his mother; the other one half went to the rest of mankind." The story has a lot in common with the biblical narrative, but with certain differences. In the Quran the brothers ask Jacob ("Yaqub
Yaqub ibn Ishaq ibn Ibrahim (Arabic: يَعْقُوب ابْنُ إِسْحَٰق ابْنُ إِبْرَاهِيم, literally: "''Jacob, son of Isaac, son of Abraham''" ar, يَعْقُوب , translit=Yaqub; also later ''Israil'', Arabic: إ ...
") to let Joseph go with them. Joseph is thrown into a well, and was taken as a slave by a passing caravan. When the brothers claimed to the father that a wolf had eaten Joseph, he observed patience.
In the Bible, Joseph discloses himself to his brethren before they return to their father the second time after buying grain.Differences of Tradition/ref> But in Islam they returned leaving behind Benjamin because the mizzen bowl of the king was found in his bag. Similarly, the eldest son of Jacob had decided not to leave the land because of the oath taken to protect Benjamin beforehand. When Jacob learned their story after their return, he wept in grief till he lost his eyesight because of sorrow. He thus charged his sons to go and inquire about Joseph and his brother and despair not of God's mercy. It was during this return to Egypt that Joseph disclosed his real identity to his brothers. He admonished and forgave them, he sent also his garment which healed the patriarch's eyes as soon as it was cast unto his face. The remaining verses describe the migration of Jacob's family to Egypt and the emotional meeting of Jacob and his long lost son, Joseph. The family prostrated before him hence the fulfilment of his dream aforetime. The story concludes by Joseph praying, "My lord you have indeed bestowed upon me of the sovereignty and taught me something of the interpretation of dreams- the (only) creator of heavens and the earth! You are my Guardian in this world and in the Hereafter. Cause me to die as a Muslim and join me with the righteous" (Qur'an 12:101).
Baha'i tradition
There are numerous mentions of Joseph in Bahá'í writings. These come in the forms of allusions written by theBáb
The Báb (b. ʿAlí Muḥammad; 20 October 1819 – 9 July 1850), was the messianic founder of Bábism, and one of the central figures of the Baháʼí Faith. He was a merchant from Shiraz in Qajar Iran who, in 1844 at the age of 25, claimed ...
and Bahá'u'lláh. In the ''Kitáb-i-Aqdas
The Kitáb-i-Aqdas (Arabic: The Most Holy Book) is the central religious text of the Baháʼí Faith, written by Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the religion, in 1873. Though it is the main source of Baháʼí laws and practices, much of the co ...
'', Bahá'u'lláh states that "from my laws, the sweet-smelling savour of my garment can be smelled" and, in the '' Four Valleys'', states that "the fragrance of his garment blowing from the Egypt of Baha," referring to Joseph.
Bahá'í commentaries have described these as metaphors with the garment implying the recognition of a manifestation of God. In the '' Qayyumu'l-Asma''', the Báb refers to Bahá'u'lláh as the true Joseph and makes an analogous prophecy regarding Bahá'u'lláh suffering at the hands of his brother, Mírzá Yahyá.
Literature and culture
* ''Somnium morale Pharaonis
Somnium was originally a Latin language, Latin word meaning "dream", and may refer to:
* Somnium (novel), ''Somnium'' (novel), a scientific fantasy in Latin by Johannes Kepler
* Somnium, a brand name for the drug lorazepam
* Somnium (album), ''Somn ...
'' (13th century), by Cistercian monk Jean de Limoges, is a collection of fictional letters exchanged between Pharaoh, Joseph, and other characters of the narrative regarding the interpretation of Pharaoh's dream.
* '' Joseph and his Brethren'', 1743, an oratorio
An oratorio () is a large musical composition for orchestra, choir, and soloists. Like most operas, an oratorio includes the use of a choir, soloists, an instrumental ensemble, various distinguishable characters, and arias. However, opera is mus ...
by George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque music, Baroque composer well known for his opera#Baroque era, operas, oratorios, anthems, concerto grosso, concerti grossi, ...
.
* ''Josephslegende
''Josephslegende'' (''The Legend of Joseph''), Op. 63, is a ballet in one act for the Ballets Russes based on the story of Potiphar's Wife, with a libretto by Hugo von Hofmannsthal and Harry Graf Kessler and music by Richard Strauss. Composed in ...
'' (The Legend of Joseph) is a 1914 work by Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wag ...
for the Ballets Russes
The Ballets Russes () was an itinerant ballet company begun in Paris that performed between 1909 and 1929 throughout Europe and on tours to North and South America. The company never performed in Russia, where the Revolution disrupted society. A ...
.
*''Joseph and His Brothers
''Joseph and His Brothers'' (''Joseph und seine Brüder'') is a four-part novel by Thomas Mann, written over the course of 16 years. Mann retells the familiar stories of Genesis, from Jacob to Joseph (chapters 27–50), setting it in the hi ...
'' (1933–43), a four-novel omnibus by Thomas Mann
Paul Thomas Mann ( , ; ; 6 June 1875 – 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novella ...
, retells the Genesis stories surrounding Joseph, identifying Joseph with the figure of Osarseph
Osarseph or Osarsiph ( grc-koi, Ὀσαρσίφ) is a legendary figure of Ancient Egypt who has been equated with Moses. His story was recounted by the Ptolemaic Egyptian historian Manetho in his ''Aegyptiaca'' (first half of the 3rd century ...
known from Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly d ...
, and the pharaoh with Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dy ...
.
*1961 film, ''The Story of Joseph and His Brethren
''The Story of Joseph and His Brethren'' (Italian: ''Giuseppe venduto dai fratelli'') is a 1961 Yugoslavian/Italian film directed by Irving Rapper and Luciano Ricci.
The film is also known as ''Joseph Sold by His Brothers'', ''Joseph and His Bre ...
'' (Giuseppe venduto dai fratelli)
*1974 film, ''The Story of Jacob and Joseph
''The Story of Jacob and Joseph'' is a 1974 American Biblical drama television film directed by Michael Cacoyannis, based on the Biblical ''Book of Genesis'' with a screenplay written by Ernest Kinoy. It stars Keith Michell as Jacob, Tony Lo Bianc ...
''
*1979, New Media Bible Genesis Project (TV)-cap. Joseph And His Brothers
* The long-running musical ''Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat
''Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat'' (often colloquially known as ''Joseph'') is a sung-through musical with lyrics by Tim Rice and music by Andrew Lloyd Webber, based on the character of Joseph from the Bible's Book of Genesis. Thi ...
'' by Andrew Lloyd Webber
Andrew Lloyd Webber, Baron Lloyd-Webber (born 22 March 1948), is an English composer and impresario of musical theatre. Several of his musicals have run for more than a decade both in the West End and on Broadway. He has composed 21 musicals, ...
and Tim Rice
Sir Timothy Miles Bindon Rice (born 10 November 1944) is an English lyricist and author. He is best known for his collaborations with Andrew Lloyd Webber, with whom he wrote, among other shows, ''Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat'', ' ...
is based on the biblical story of Joseph, up through Genesis chapter 46. It was adapted into the 1999 film of the same name.
* In 1995, Turner Network Television
TNT (originally an abbreviation for Turner Network Television) is an American basic cable television channel
A television channel is a terrestrial frequency or virtual number over which a television station or television network is dist ...
released the made-for-television movie ''Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
'' starring Ben Kingsley
Sir Ben Kingsley (born Krishna Pandit Bhanji; 31 December 1943) is an English actor. He has received various accolades throughout his career spanning five decades, including an Academy Award, a British Academy Film Award, a Grammy Award, and two ...
as Potiphar, Lesley Ann Warren
Lesley Ann Warren (born August 16, 1946) is an American actress and singer.
She made her Broadway debut in 1963, aged 17, in '' 110 in the Shade''. In 1965 she received wide recognition for playing the title role in the television musical prod ...
as Potiphar's wife, Paul Mercurio
Paul Joseph Mercurio (born 31 March 1963) is an Australian actor, dancer, TV presenter and politician. Mercurio is best known for his lead role in '' Strictly Ballroom'' 1992 and his role as a judge on TV series ''Dancing with the Stars''.
H ...
as Joseph and Martin Landau
Martin James Landau (; June 20, 1928 – July 15, 2017) was an American actor, acting coach, producer, and editorial cartoonist. His career began in the 1950s, with early film appearances including a supporting role in Alfred Hitchcock's ''North ...
as Jacob.
* In 2000, ''DreamWorks Animation
DreamWorks Animation LLC (DWA, also known as DreamWorks Animation Studios and simply known as DreamWorks) is an American animation studio that produces animated films and television programs and is a subsidiary of Universal Pictures, a division ...
'' released a direct-to-video animated musical film based on the life of Joseph, titled '' Joseph: King of Dreams''. American Actor Ben Affleck
Benjamin Géza Affleck (born August 15, 1972) is an American actor and filmmaker. His accolades include two Academy Awards, three Golden Globe Awards and a Volpi Cup.
Affleck began his career as a child when he starred in the PBS educationa ...
provided the speaking voice of Joseph, with Australian Theater Singer David Campbell providing the singing voice
* '' Yousuf e Payambar'' or Joseph, the Prophet is an Iranian television series from 2008, directed by Farajullah Salahshur, which tells the story of Prophet Joseph from the Quran and Islamic traditions.
* The cultural impact of the Joseph story in early-modern times is discussed in
* ''Rappresentatione di Giuseppe e i suoi Fratelli / Joseph and his Brethren'' - a musical drama in three acts composed by Elam Rotem for ensemble Profeti della Quinta
Profeti della Quinta (Prophets of the Perfect Fifth) is a male vocal ensemble, specializing in the music of the Renaissance and Baroque periods. Founded in the Galilee region of Israel by Elam Rotem, the ensemble is currently based in Basel, Switz ...
(2013, Pan Classics).
* ''José do Egito
''José do Egito'' (English: ''Joseph from Egypt'') is a Brazilian miniseries produced and broadcast by RecordTV. It premiered on January 30, 2013 and ended on October 9, 2013. It is based on the biblical account of the book of Genesis that deals ...
'' (English: Joseph from Egypt) is a Brazilian miniseries produced and broadcast by RecordTV
RecordTV (), formerly known as Rede Record, is a Brazilian free-to-air television network. It is currently the second largest commercial TV station in Brazil, and the 28th largest in the 2012 world ranking. In 2010, it was elected by the adverti ...
. It premiered on January 30, 2013 and ended on October 9, 2013. It is based on the biblical account of the book of Genesis that deals with the patriarch Joseph, son of Jacob.
* The 2003 VeggieTales
''VeggieTales'' is an American Christian media, computer generated musical children's animation, and book franchise created by Phil Vischer and Mike Nawrocki under Big Idea Entertainment. The series sees fruit and vegetable characters retelling ...
children's video "The Ballad of Little Joe" retells Joseph's Genesis stories in the style and setting of an American Western film.
* The 2019 novel ''Joseph and the Way of Forgiveness
''Joseph and the Way of Forgiveness: A Biblical Tale Retold'' is a 2019 novel by Stephen Mitchell, retelling the story of Joseph from the Book of Genesis. Written in the style of a midrash, the novel expands on the Genesis narrative as it follows ...
'' by Stephen Mitchell retells the story of Joseph in the form of a midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
with emphasis on the thoughts and beliefs of a flawed Joseph.
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
See also
* Book of Joseph (Latter Day Saints) *Joseph's tomb
Joseph's Tomb ( he, קבר יוסף, ''Qever Yosef''; ar, قبر يوسف, ''Qabr Yūsuf'') is a funerary monument located in Balata village at the eastern entrance to the valley that separates Mounts Gerizim and Ebal, 300 metres northwest of ...
* List of slaves
Slavery is a social-economic system under which people are enslaved: deprived of personal freedom and forced to perform labor or services without compensation. These people are referred to as slaves, or as enslaved people.
The following is a ...
* Yousuf-e Payambar
''Prophet Joseph'' ( fa, یوسف پيامبر, Yūsofe Payāmbar, Joseph the Prophet) is an Iranian Islamic television series produced, written, and directed by Farajollah Salahshoor. It is based on the Joseph in Islam, Islamic account of Joseph ...
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * Genung, Matthew C. (2017).The Composition of Genesis 37: Incoherence and Meaning in the Exposition of the Joseph Story
'. Forschungen zum Alten Testament 2. Reihe. 95. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. . * * * * * * *
External links
*BBC - Joseph
{{DEFAULTSORT:Joseph Biblical figures in rabbinic literature Book of Genesis people Burials in Israel Children of Jacob Christian saints from the Old Testament Divination Founders of biblical tribes People whose existence is disputed