jobless growth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A jobless recovery or jobless growth is an economic phenomenon in which a macroeconomy experiences
 In addition to employment growth, population growth must also be considered concerning the perception of jobless recoveries. Immigrants and new entrants to the workforce will often accept lower wages, causing persistent unemployment among those who were previously employed.
Surprisingly, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not offer data-sets isolated to the working-age population (ages 16 to 65). Including retirement age individuals in most BLS data-sets may tend to obfuscate the analysis of employment creation in relation to population growth. Additionally, incorrect assumptions about the term, Labor force, might also occur when reading BLS publications, millions of employable persons are not included within the official definition. The Labor force, as defined by the BLS, is a strict definition of those officially unemployed (U-3), and those who are officially employed (1 hour or more).
The following table and included chart depicts year-to-year employment growth in comparison to population growth for those persons under 65 years of age. As such,
In addition to employment growth, population growth must also be considered concerning the perception of jobless recoveries. Immigrants and new entrants to the workforce will often accept lower wages, causing persistent unemployment among those who were previously employed.
Surprisingly, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not offer data-sets isolated to the working-age population (ages 16 to 65). Including retirement age individuals in most BLS data-sets may tend to obfuscate the analysis of employment creation in relation to population growth. Additionally, incorrect assumptions about the term, Labor force, might also occur when reading BLS publications, millions of employable persons are not included within the official definition. The Labor force, as defined by the BLS, is a strict definition of those officially unemployed (U-3), and those who are officially employed (1 hour or more).
The following table and included chart depicts year-to-year employment growth in comparison to population growth for those persons under 65 years of age. As such,
Exploding Productivity Growth: Context, Causes, and Implications
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jobless Recovery Impact of Automation Universal basic income Economic growth Unemployment Unemployment in the United States
growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
while maintaining or decreasing its level of employment. The term was coined by the economist Nick Perna in the early 1990s.
Causes
Economists are still divided about the causes and cures of a jobless recovery: some argue that increasedproductivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
through automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
has allowed economic growth without reducing unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
. Other economists state that blaming automation is an example of the luddite fallacy
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment.
Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficie ...
and that jobless recoveries stem from structural changes in the labor market, leading to unemployment as workers change jobs or industries.
Industrial consolidation
Some have argued that the recent lack of job creation in the United States is due to increased industrial consolidation and growth ofmonopoly
A monopoly (from Greek el, ╬╝Žī╬Į╬┐Žé, m├│nos, single, alone, label=none and el, ŽĆŽē╬╗╬Ąß┐¢╬Į, p┼Źle├«n, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a speci ...
or oligopoly power. The argument is twofold: firstly, small businesses create most American jobs, and secondly, small businesses have more difficulty starting and growing in the face of entrenched existing businesses (compare infant industry argument
The infant industry argument is an economic rationale for trade protectionism. The core of the argument is that nascent industries often do not have the economies of scale that their older competitors from other countries may have, and thus need ...
, applied at the level of industries, rather than individual firms).
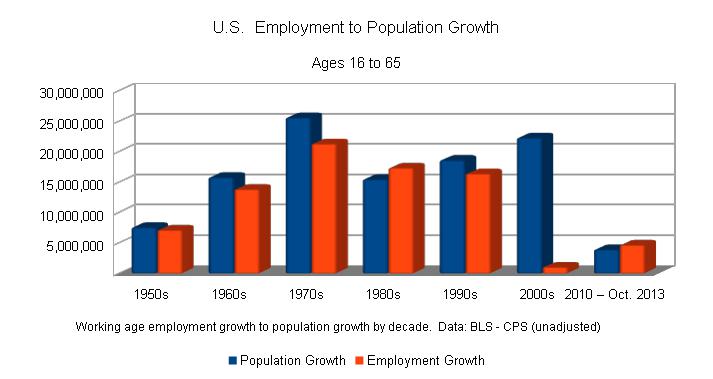
Population growth vs. employment growth
 In addition to employment growth, population growth must also be considered concerning the perception of jobless recoveries. Immigrants and new entrants to the workforce will often accept lower wages, causing persistent unemployment among those who were previously employed.
Surprisingly, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not offer data-sets isolated to the working-age population (ages 16 to 65). Including retirement age individuals in most BLS data-sets may tend to obfuscate the analysis of employment creation in relation to population growth. Additionally, incorrect assumptions about the term, Labor force, might also occur when reading BLS publications, millions of employable persons are not included within the official definition. The Labor force, as defined by the BLS, is a strict definition of those officially unemployed (U-3), and those who are officially employed (1 hour or more).
The following table and included chart depicts year-to-year employment growth in comparison to population growth for those persons under 65 years of age. As such,
In addition to employment growth, population growth must also be considered concerning the perception of jobless recoveries. Immigrants and new entrants to the workforce will often accept lower wages, causing persistent unemployment among those who were previously employed.
Surprisingly, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) does not offer data-sets isolated to the working-age population (ages 16 to 65). Including retirement age individuals in most BLS data-sets may tend to obfuscate the analysis of employment creation in relation to population growth. Additionally, incorrect assumptions about the term, Labor force, might also occur when reading BLS publications, millions of employable persons are not included within the official definition. The Labor force, as defined by the BLS, is a strict definition of those officially unemployed (U-3), and those who are officially employed (1 hour or more).
The following table and included chart depicts year-to-year employment growth in comparison to population growth for those persons under 65 years of age. As such, baby boomer
Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the Western demographic cohort following the Silent Generation and preceding Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964, during the mid-20th century baby boom. ...
retirements are removed from the data as a factor for consideration. The table includes the Bureau of Labor Statistics, Current Population Survey
The Current Population Survey (CPS) is a monthly survey of about 60,000 U.S. households conducted by the United States Census Bureau for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The BLS uses the data to publish reports early each month called the Em ...
, for the Civilian noninstitutional population
In the United States, the civilian noninstitutional population refers to people 16 years of age and older residing in the 50 States and the District of Columbia who are not inmates of institutions ( penal, mental facilities, homes for the aged), an ...
and corresponding Employment Levels, dating from 1948 and includes October 2013, the age groups are 16 years & over, and 65 years & over. The working-age population is then determined by subtracting those age 65 and over from the Civilian noninstitutional population and Employment Levels respectively. Isolated into the traditional working-age subset, growth in both employment levels and population levels are totaled by decade, an employment percentage rate is also displayed for comparison by decade.
When examined, by decade, the first decade of the 2000s, the United States suffered a 5% jobless rate when compared to the added working age population.
See also
* Deindustrialization * Involuntary unemployment *Lost Decade (Japan)
The was a period of economic stagnation in Japan caused by the asset price bubble's collapse in late 1991. The term originally referred to the 1990s, but the 2000s (Lost 20 Years, Õż▒ŃéÅŃéīŃü¤20Õ╣┤) and the 2010s (Lost 30 Years, Õż▒ŃéÅŃéīŃ ...
* Structural unemployment
Notes and references
External links
Exploding Productivity Growth: Context, Causes, and Implications
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jobless Recovery Impact of Automation Universal basic income Economic growth Unemployment Unemployment in the United States