Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th
president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected to the office of president or vice president as well as the only president to date from
Michigan. He previously served as the leader of the
Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
*Republican Party (Liberia)
* Republican Part ...
in the
House of Representatives, and was appointed to be the 40th
vice president in 1973. When President
Richard Nixon resigned in 1974, Ford succeeded to the presidency, but was defeated for election to a full term in
1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
.
Born in
Omaha, Nebraska, and raised in
Grand Rapids, Michigan, Ford attended the
University of Michigan, where he was a member of the school's
football team, winning two national championships. Following his senior year, he turned down offers from the
Detroit Lions
The Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit. The Lions compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) North Division. The team play their home games at Ford ...
and
Green Bay Packers
The Green Bay Packers are a professional American football team based in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The Packers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC North, North division. It ...
, instead opting to go to
Yale Law School. After the
attack on Pearl Harbor, he enlisted in the
U.S. Naval Reserve, serving from 1942 to 1946; he left as a
lieutenant commander. Ford began his political career in 1949 as the
U.S. representative from
Michigan's 5th congressional district. He served in this capacity for nearly 25 years, the final nine of them as the
House minority leader. In December 1973, two months after the resignation of
Spiro Agnew, Ford became the first person appointed to the vice presidency under the terms of the
25th Amendment
The Twenty-fifth Amendment (Amendment XXV) to the United States Constitution deals with presidential succession and disability.
It clarifies that the vice president becomes president if the president dies, resigns, or is removed from office, a ...
. After the subsequent resignation of President Nixon in August 1974, Ford immediately assumed the presidency.
As president, Ford signed the
Helsinki Accords, which marked a move toward
détente in the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. With the collapse of
South Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam ( vi, Việt Nam Cộng hòa), was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975, the period when the southern portion of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of th ...
nine months into his presidency,
US involvement in the Vietnam War
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
essentially ended. Domestically, Ford presided over the worst economy in the four decades since the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, with growing inflation and a
recession during his tenure.
In one of his most controversial acts, he granted a
presidential pardon to Richard Nixon
Proclamation 4311 was a presidential proclamation issued by president of the United States Gerald Ford on September 8, 1974, granting a full and unconditional pardon to Richard Nixon, his predecessor, for any crimes that he might have committe ...
for his role in the
Watergate scandal. During Ford's presidency, foreign policy was characterized in procedural terms by the increased role Congress began to play, and by the corresponding curb on the powers of the president.
In the 1976 Republican presidential primary campaign, Ford defeated former California Governor
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
for the Republican nomination, but narrowly lost the
presidential election to the
Democratic
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
challenger, former Georgia Governor
Jimmy Carter. Surveys of historians and political scientists have ranked Ford as a below-average president.
Following his years as president, Ford remained active in the Republican Party. His moderate views on various social issues increasingly put him at odds with conservative members of the party in the 1990s and early 2000s. In retirement, Ford set aside the enmity he had felt towards Carter following the 1976 election, and the two former presidents developed a close friendship. After experiencing a series of health problems, he
died at home on December 26, 2006, at age 93.
Early life
Ford was born Leslie Lynch King Jr. on July 14, 1913, at
3202 Woolworth Avenue
The Gerald R. Ford Birthsite and Gardens in Omaha, Nebraska marks the location of the house at 3202 Woolworth Avenue where U.S. President Gerald R. Ford lived for a couple of weeks after his birth in July 1913. It was the home of his paternal g ...
in
Omaha, Nebraska, where his parents lived with his paternal grandparents. He was the only child of
Dorothy Ayer Gardner
Dorothy Ayer Gardner King Ford (February 27, 1892 – September 17, 1967) was the mother of U.S. President Gerald Ford.
Early life and marriage
Dorothy Ayer Gardner was born in the small town of Harvard, Illinois to Levi Addison Gardner, a ...
and
Leslie Lynch King Sr., a wool trader. His father was the son of prominent banker
Charles Henry King and Martha Alicia King (née Porter). Gardner separated from King just sixteen days after her son's birth. She took her son with her to
Oak Park, Illinois, home of her sister Tannisse and brother-in-law, Clarence Haskins James. From there, she moved to the home of her parents, Levi Addison Gardner and Adele Augusta Ayer, in
Grand Rapids, Michigan. Gardner and King divorced in December 1913, and she gained full custody of her son. Ford's paternal grandfather Charles Henry King paid child support until shortly before his death in 1930.
Ford later said that his biological father had a history of hitting his mother.
In a biography of Ford,
James M. Cannon
James M. Cannon (February 26, 1918 – September 15, 2011) was an American historian, author and former assistant to the President of the United States for foreign affairs during the Gerald Ford administration. Before his work with Ford, he was ...
wrote that the separation and divorce of Ford's parents was sparked when, a few days after Ford's birth, Leslie King took a
butcher knife
A butcher knife or butcher's knife is a knife designed and used primarily for the butchering or dressing of animal carcasses.
Use
Today, the butcher knife is used throughout the world in the meat processing trade. The heftier blade works well f ...
and threatened to kill his wife, infant son, and Ford's nursemaid. Ford later told confidants that his father had first hit his mother when she had smiled at another man during their honeymoon.
After living with her parents for two and a half years, on February 1, 1917, Gardner married
Gerald Rudolff Ford, a salesman in a family-owned paint and varnish company. Though never formally
adopted
Adoption is a process whereby a person assumes the parenting of another, usually a child, from that person's biological or legal parent or parents. Legal adoptions permanently transfer all rights and responsibilities, along with filiation, from ...
, her young son was referred to as Gerald Rudolff Ford Jr. from then on; the
name change
Name change is the legal act by a person of adopting a new name different from their current name.
The procedures and ease of a name change vary between jurisdictions. In general, common law jurisdictions have loose procedures for a name chang ...
was formalized on December 3, 1935.
He was raised in
Grand Rapids
Grand Rapids is a city and county seat of Kent County in the U.S. state of Michigan. At the 2020 census, the city had a population of 198,917 which ranks it as the second most-populated city in the state after Detroit. Grand Rapids is the ...
with his three half-brothers from his mother's second marriage:
Thomas Gardner "Tom" Ford (1918–1995), Richard Addison "Dick" Ford (1924–2015), and James Francis "Jim" Ford (1927–2001).
Ford was involved in the
Boy Scouts of America, and earned that program's highest rank,
Eagle Scout.
He is the only Eagle Scout to have ascended to the U.S. presidency.
Ford attended Grand Rapids South High School, where he was a star athlete and
captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
of the
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
team. In 1930, he was selected to the All-City team of the
Grand Rapids City League. He also attracted the attention of college recruiters.
College and law school
Ford attended the
University of Michigan, where he played
center,
linebacker, and
long snapper for the school's football team and helped the
Wolverines to two undefeated seasons and
national titles in
1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident (1932), Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort ...
and
1933
Events
January
* January 11 – Sir Charles Kingsford Smith makes the first commercial flight between Australia and New Zealand.
* January 17 – The United States Congress votes in favour of Philippines independence, against the wis ...
. In his senior year of
1934
Events
January–February
* January 1 – The International Telecommunication Union, a specialist agency of the League of Nations, is established.
* January 15 – The 8.0 1934 Nepal–Bihar earthquake, Nepal–Bihar earthquake strik ...
, the team suffered a steep decline and won only one game, but Ford was still the team's star player. In one of those games, Michigan held heavily favored
Minnesota—the eventual national champion—to a scoreless tie in the first half. After the game, assistant coach
Bennie Oosterbaan said, "When I walked into the dressing room at halftime, I had tears in my eyes I was so proud of them. Ford and
edricSweet played their hearts out. They were everywhere on defense." Ford later recalled, "During 25 years in the rough-and-tumble world of politics, I often thought of the experiences before, during, and after that game in 1934. Remembering them has helped me many times to face a tough situation, take action, and make every effort possible despite adverse odds." His teammates later voted Ford their most valuable player, with one assistant coach noting, "They felt Jerry was one guy who would stay and fight in a losing cause."
During Ford's senior year, a controversy developed when
Georgia Tech said that it would not play a scheduled game with Michigan if a black player named
Willis Ward
Willis Franklin Ward (December 28, 1912 – December 30, 1983) was a track and field athlete and American football player who was inducted into the University of Michigan Athletic Hall of Honor in 1981.
Ward was the Michigan High School Athlete o ...
took the field. Students, players and alumni protested, but university officials capitulated and kept Ward out of the game. Ford was Ward's best friend on the team, and they roomed together while on road trips. Ford reportedly threatened to quit the team in response to the university's decision, but he eventually agreed to play against
Georgia Tech when Ward personally asked him to play.
In 1934, Ford was selected for the Eastern Team on the Shriner's
East–West Shrine Game
East West (or East and West) may refer to:
*East–West dichotomy, the contrast between Eastern and Western society or culture
Arts and entertainment
Books, journals and magazines
*'' East, West'', an anthology of short stories written by Salm ...
at San Francisco (a benefit for physically disabled children), played on January 1, 1935. As part of the 1935 Collegiate All-Star football team, Ford played against the
Chicago Bears
The Chicago Bears are a professional American football team based in Chicago. The Bears compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) North division. The Bears have won nine NF ...
in the
Chicago College All-Star Game at
Soldier Field.
In honor of his athletic accomplishments and his later political career, the University of Michigan retired Ford's No. 48 jersey in 1994. With the blessing of the Ford family, it was placed back into circulation in 2012 as part of the
Michigan Football Legends program and issued to sophomore linebacker
Desmond Morgan
Desmond Morgan (born September 9, 1992) is a former American football linebacker and current coach. He played college football for the Michigan Wolverines football team from 2011 to 2015. He was a 2011 ESPN.com and BTN.com Big Ten All-Freshma ...
before a home game against
Illinois on October 13.
Throughout life, Ford remained interested in his school and football; he occasionally attended games. Ford also visited with players and coaches during practices; at one point, he asked to join the players in the huddle. Before state events, Ford often had the Navy band play the University of Michigan fight song, "
The Victors," instead of "
Hail to the Chief."
Ford graduated from Michigan in 1935 with a
Bachelor of Arts degree in
economics. He turned down offers from the
Detroit Lions
The Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit. The Lions compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) North Division. The team play their home games at Ford ...
and
Green Bay Packers
The Green Bay Packers are a professional American football team based in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The Packers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the National Football Conference (NFC) NFC North, North division. It ...
of the
National Football League. Instead, he took a job in September 1935 as the boxing coach and assistant varsity football coach at
Yale University and applied to its law school.
Ford hoped to attend Yale Law School beginning in 1935. Yale officials at first denied his admission to the law school because of his full-time coaching responsibilities. He spent the summer of 1937 as a student at the
University of Michigan Law School and was eventually admitted in the spring of 1938 to
Yale Law School.
That year he was also promoted to the position of junior varsity head football coach at Yale. While at Yale, Ford began working as a model. He initially worked with the
John Robert Powers agency before investing in Harry Conover's agency, with whom he modelled until 1941.
While attending Yale Law School, Ford joined a group of students led by
R. Douglas Stuart Jr.
Robert Douglas Stuart Jr. (April 26, 1916 – May 8, 2014) was the son of Quaker Oats Company co-founder R. Douglas Stuart, the founder of the America First Committee in 1940, the CEO of Quaker Oats from 1966 to 1981, and United States Ambassado ...
, and signed a petition to enforce the 1939
Neutrality Act. The petition was circulated nationally and was the inspiration for the
America First Committee, a group determined to keep the U.S. out of
World War II.
[ p. 7] His introduction into politics was in the summer of 1940 when he worked for the Republican presidential campaign of
Wendell Willkie.
Ford graduated in the top third of his class in 1941, and was admitted to the
Michigan bar shortly thereafter. In May 1941, he opened a Grand Rapids law practice with a friend,
Philip W. Buchen
Philip William Buchen (February 27, 1916 – May 21, 2001) was an American attorney who served as White House counsel during the Ford Administration.
Early life and education
Buchen was born in Sheboygan, Wisconsin, the son of State Senator ...
.
U.S. Naval Reserve
Following the
December 7, 1941, attack on Pearl Harbor, Ford enlisted in the Navy.
He received a commission as
ensign in the
U.S. Naval Reserve on April 13, 1942. On April 20, he reported for active duty to the V-5 instructor school at
Annapolis, Maryland
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
. After one month of training, he went to Navy Preflight School in
Chapel Hill, North Carolina
Chapel Hill is a town in Orange, Durham and Chatham counties in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Its population was 61,960 in the 2020 census, making Chapel Hill the 17th-largest municipality in the state. Chapel Hill, Durham, and the state ca ...
, where he was one of 83 instructors and taught elementary navigation skills, ordnance, gunnery, first aid, and military drill. In addition, he coached all nine sports that were offered, but mostly swimming, boxing, and football. During the year he was at the Preflight School, he was promoted to
Lieutenant, Junior Grade, on June 2, 1942, and to lieutenant, in March 1943.
Sea duty
After Ford applied for sea duty, he was sent in May 1943 to the pre-commissioning detachment for the new aircraft carrier , at New York Shipbuilding Corporation,
Camden, New Jersey
Camden is a city in and the county seat of Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. Camden is part of the Delaware Valley metropolitan area and is located directly across the Delaware River from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At the 2020 ...
. From the ship's commissioning on June 17, 1943, until the end of December 1944, Ford served as the assistant navigator, Athletic Officer, and antiaircraft battery officer on board the ''Monterey''. While he was on board, the carrier participated in many actions in the
Pacific Theater
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
with the
Third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* Second#Sexagesimal divisions of calendar time and day, 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (d ...
and
Fifth Fleets in late 1943 and 1944. In 1943, the carrier helped secure
Makin Island in the Gilberts, and participated in carrier strikes against
Kavieng, New Ireland in 1943. During the spring of 1944, the ''Monterey'' supported landings at
Kwajalein and
Eniwetok and participated in carrier strikes in the
Marianas
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
,
Western Carolines
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the centra ...
, and northern
New Guinea, as well as in the
Battle of the Philippine Sea.
After an overhaul, from September to November 1944, aircraft from the ''Monterey'' launched strikes against
Wake Island, participated in strikes in the Philippines and
Ryukyus, and supported the landings at
Leyte and
Mindoro.
Although the ship was not damaged by the
Empire of Japan's forces, the ''Monterey'' was one of several ships damaged by
Typhoon Cobra that hit Admiral
William Halsey's Third Fleet on December 18–19, 1944. The Third Fleet lost three
destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s and over 800 men during the typhoon. The ''Monterey'' was damaged by a fire, which was started by several of the ship's aircraft tearing loose from their cables and colliding on the
hangar deck. Ford was serving as General Quarters Officer of the Deck and was ordered to go below to assess the raging fire. He did so safely, and reported his findings back to the ship's commanding officer, Captain
Stuart H. Ingersoll. The ship's crew was able to contain the fire, and the ship got underway again.
After the fire, the ''Monterey'' was declared unfit for service. Ford was detached from the ship and sent to the Navy Pre-Flight School at
Saint Mary's College of California, where he was assigned to the Athletic Department until April 1945. From the end of April 1945 to January 1946, he was on the staff of the Naval Reserve Training Command,
Naval Air Station, Glenview, Illinois, at the rank of
lieutenant commander.
Ford received the following military awards: the
American Campaign Medal, the
Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal with nine
" bronze stars (for operations in the
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
,
Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
, Marshall Islands, Asiatic and Pacific carrier raids,
Hollandia Hollandia may refer to:
* HVV Hollandia, Dutch football team
* Hollandia Victoria Combinatie, defunct Dutch football team
* ''Hollandia'' (1742 ship), a ship of the Dutch East India Company, wrecked in 1743 on her maiden voyage
* Jayapura, a city ...
, Marianas, Western Carolines, Western New Guinea, and the Leyte Operation), the
Philippine Liberation Medal with two " bronze stars (for Leyte and Mindoro), and the
World War II Victory Medal.
He was honorably discharged in February 1946.
U.S. House of Representatives (1949–1973)

After Ford returned to Grand Rapids in 1946, he became active in local Republican politics, and supporters urged him to challenge
Bartel J. Jonkman, the incumbent Republican congressman. Military service had changed his view of the world. "I came back a converted
internationalist", Ford wrote, "and of course our congressman at that time was an avowed, dedicated
isolationist. And I thought he ought to be replaced. Nobody thought I could win. I ended up winning two to one."
During his first campaign in 1948, Ford visited voters at their doorsteps and as they left the factories where they worked.
Ford also visited local farms where, in one instance, a wager resulted in Ford spending two weeks milking cows following his election victory.
Ford was a member of the House of Representatives for 25 years, holding
Michigan's 5th congressional district seat from 1949 to 1973. It was a tenure largely notable for its modesty. As an editorial in ''
The New York Times'' described him, Ford "saw himself as a negotiator and a reconciler, and the record shows it: he did not write a single piece of major legislation in his entire career."
Appointed to the
House Appropriations Committee two years after being elected, he was a prominent member of the
Defense Appropriations Subcommittee. Ford described his philosophy as "a moderate in domestic affairs, an internationalist in foreign affairs, and a conservative in fiscal policy." He voted in favor of the
Civil Rights Acts of 1957,
1960
It is also known as the "Year of Africa" because of major events—particularly the independence of seventeen African nations—that focused global attention on the continent and intensified feelings of Pan-Africanism.
Events
January
* Ja ...
,
1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
, and
1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – "Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Januar ...
, as well as the
24th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution and the
Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
. Ford was known to his colleagues in the House as a "Congressman's Congressman".
In the early 1950s, Ford declined offers to run for either the Senate or the Michigan governorship. Rather, his ambition was to become
Speaker of the House, which he called "the ultimate achievement. To sit up there and be the head honcho of 434 other people and have the responsibility, aside from the achievement, of trying to run the greatest legislative body in the history of mankind ... I think I got that ambition within a year or two after I was in the House of Representatives".
Warren Commission
On November 29, 1963, President
Lyndon B. Johnson appointed Ford to the
Warren Commission, a special task force set up to investigate the
assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of President
John F. Kennedy.
Ford was assigned to prepare a biography of accused assassin
Lee Harvey Oswald. He and
Earl Warren
Earl Warren (March 19, 1891 – July 9, 1974) was an American attorney, politician, and jurist who served as the 14th Chief Justice of the United States from 1953 to 1969. The Warren Court presided over a major shift in American constitution ...
also interviewed
Jack Ruby
Jack Leon Ruby (born Jacob Leon Rubenstein; April 25, 1911January 3, 1967) was an American nightclub owner and alleged associate of the Chicago Outfit who murdered Lee Harvey Oswald on November 24, 1963, two days after Oswald was accused of th ...
, Oswald's killer. According to a 1963
FBI memo that was released to the public in 2008, Ford was in contact with the FBI throughout his time on the Warren Commission and relayed information to the deputy director,
Cartha DeLoach, about the panel's activities.
In the preface to his book, ''A Presidential Legacy and The Warren Commission'', Ford defended the work of the commission and reiterated his support of its conclusions.
House Minority Leader (1965–1973)

In 1964, Lyndon Johnson led a landslide victory for his party, secured another term as president and took 36 seats from Republicans in the House of Representatives. Following the election, members of the Republican caucus looked to select a new minority leader. Three members approached Ford to see if he would be willing to serve; after consulting with his family, he agreed. After a closely contested election, Ford was chosen to replace
Charles Halleck
Charles Abraham Halleck (August 22, 1900 – March 3, 1986) was an American politician. He was the History of the United States Republican Party, Republican leader of the United States House of Representatives from the Indiana's 2nd congressional ...
of
Indiana as minority leader.
The members of the Republican caucus that encouraged and eventually endorsed Ford to run as the House minority leader were later known as the "
Young Turks" and one of the members of the Young Turks was congressman
Donald H. Rumsfeld from
Illinois's 13th congressional district, who later on would serve in Ford's administration as the
chief of staff
The title chief of staff (or head of staff) identifies the leader of a complex organization such as the armed forces, institution, or body of persons and it also may identify a principal staff officer (PSO), who is the coordinator of the supporti ...
and
secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
.
With a Democratic majority in both the House of Representatives and the Senate, the Johnson Administration proposed and passed a series of programs that was called by Johnson the "
Great Society". During the first session of the
Eighty-ninth Congress
The 89th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1965, ...
alone, the Johnson Administration submitted 87 bills to Congress, and Johnson signed 84, or 96%, arguably the most successful legislative agenda in Congressional history.
[Unger, Irwin, 1996: 'The Best of Intentions: the triumphs and failures of the Great Society under Kennedy, Johnson, and Nixon': Doubleday, p. 104.]
In 1966, criticism over the Johnson Administration's handling of the
Vietnam War began to grow, with Ford and Congressional Republicans expressing concern that the United States was not doing what was necessary to win the war. Public sentiment also began to move against Johnson, and the
1966 midterm elections produced a 47-seat swing in favor of the Republicans. This was not enough to give Republicans a majority in the House, but the victory gave Ford the opportunity to prevent the passage of further Great Society programs.
Ford's private criticism of the Vietnam War became public knowledge after he spoke from the floor of the House and questioned whether the White House had a clear plan to bring the war to a successful conclusion.
The speech angered President Johnson, who accused Ford of having played "too much football without a helmet".
As minority leader in the House, Ford appeared in a popular series of televised press conferences with
Illinois Senator
Everett Dirksen, in which they proposed Republican alternatives to Johnson's policies. Many in the press jokingly called this "The Ev and Jerry Show."
Johnson said at the time, "Jerry Ford is so dumb he can't fart and chew gum at the same time."
The press, used to sanitizing Johnson's salty language, reported this as "Gerald Ford can't walk and chew gum at the same time."
After
Richard Nixon was elected president in November 1968, Ford's role shifted to being an advocate for the White House agenda. Congress passed several of Nixon's proposals, including the
National Environmental Policy Act and the
Tax Reform Act of 1969. Another high-profile victory for the Republican minority was the State and Local Fiscal Assistance act. Passed in 1972, the act established a
Revenue Sharing program for state and local governments. Ford's leadership was instrumental in shepherding revenue sharing through Congress, and resulted in a bipartisan coalition that supported the bill with 223 votes in favor (compared with 185 against).
During the eight years (1965–1973) that Ford served as minority leader, he won many friends in the House because of his fair leadership and inoffensive personality.
Vice presidency (1973–1974)

In his effort to become House Speaker, Ford worked to help Republicans across the country get a majority in the chamber, often traveling on the
rubber chicken circuit
A rubber chicken is a prop used in comedy. The phrase is also used as a description for food served at speeches, conventions, and other large meetings, and as a metaphor for speechmaking.
Description
A rubber chicken is an imitation plucked fowl ...
. After a decade of failing to do so, he promised his wife that he would try again in 1974 then retire in 1976. On October 10, 1973, Vice President
Spiro Agnew resigned and then pleaded
no contest to a single count of tax evasion over his failure to report $29,500 in income received while he was
governor of Maryland. According to ''The New York Times'', Nixon "sought advice from senior Congressional leaders about a replacement." The advice was unanimous.
House Speaker
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hungerfo ...
Carl Albert recalled later, "We gave Nixon no choice but Ford."
Ford agreed to the nomination, telling his wife that the vice presidency would be "a nice conclusion" to his career.
Ford was nominated to take Agnew's position on October 12, the first time the vice-presidential vacancy provision of the
25th Amendment
The Twenty-fifth Amendment (Amendment XXV) to the United States Constitution deals with presidential succession and disability.
It clarifies that the vice president becomes president if the president dies, resigns, or is removed from office, a ...
had been implemented. The
United States Senate voted 92 to 3 to confirm Ford on November 27. On December 6, 1973, the House confirmed Ford by a vote of 387 to 35. After the confirmation vote in the House, Ford took the oath of office as vice president.
Ford became vice president as the
Watergate scandal was unfolding. On Thursday, August 1, 1974,
Chief of Staff
The title chief of staff (or head of staff) identifies the leader of a complex organization such as the armed forces, institution, or body of persons and it also may identify a principal staff officer (PSO), who is the coordinator of the supporti ...
Alexander Haig contacted Ford to tell him to prepare for the presidency.
At the time, Ford and his wife, Betty, were living in suburban Virginia, waiting for their expected move into the newly designated
vice president's residence in Washington, D.C. However, "Al Haig asked to come over and see me", Ford later said, "to tell me that there would be a new tape released on a Monday, and he said the evidence in there was devastating and there would probably be either an impeachment or a resignation. And he said, 'I'm just warning you that you've got to be prepared, that things might change dramatically and you could become President.' And I said, 'Betty, I don't think we're ever going to live in the vice president's house.
Presidency (1974–1977)
Swearing-in
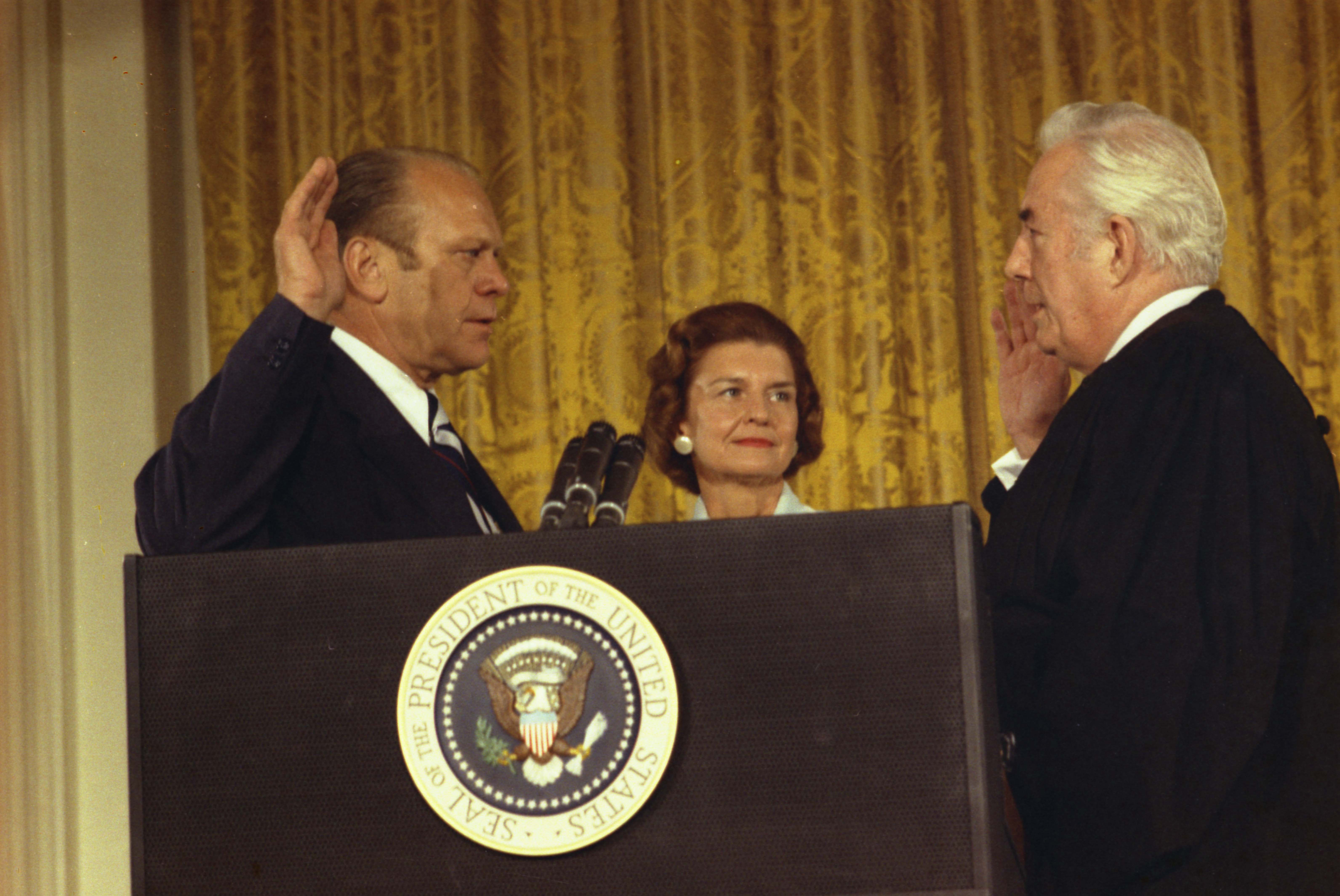

When Nixon resigned on August 9, 1974, Ford automatically assumed the presidency. This made him the only person to become the nation's chief executive without having been previously voted into either the presidential or vice-presidential office by the
Electoral College. Immediately after Ford took the oath of office in the
East Room
The East Room is an event and reception room in the Executive Residence, which is a building of the White House complex, the home of the president of the United States. The East Room is the largest room in the Executive Residence; it is used for ...
of the White House, he spoke to the assembled audience in a speech that was broadcast live to the nation.
[“Gerald R. Ford Events Timeline,”](_blank)
''The American Presidency Project,'' University of California, Santa Barbara, Gerhard Peters and John T. Woolley, last edited Feb. 2, 2021 Ford noted the peculiarity of his position: "I am acutely aware that you have not elected me as your president by your ballots, and so I ask you to confirm me as your president with your prayers."
He went on to state:
He also stated:
A portion of the speech would later be memorialized with a plaque at the entrance to
his presidential museum.
On August 20, Ford nominated former New York Governor
Nelson Rockefeller
Nelson Aldrich Rockefeller (July 8, 1908 – January 26, 1979), sometimes referred to by his nickname Rocky, was an American businessman and politician who served as the 41st vice president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. A member of t ...
to fill the vice presidency he had vacated. Rockefeller's top competitor had been
George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
. Rockefeller underwent extended hearings before Congress, which caused embarrassment when it was revealed he made large gifts to senior aides, such as
Henry Kissinger. Although conservative Republicans were not pleased that Rockefeller was picked, most of them voted for his confirmation, and his nomination passed both the House and Senate. Some, including
Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for presiden ...
, voted against him.
Pardon of Nixon

On September 8, 1974, Ford issued
Proclamation 4311, which gave Nixon a full and unconditional
pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the ju ...
for any crimes he might have committed against the United States while president.
In a televised broadcast to the nation, Ford explained that he felt the pardon was in the best interests of the country, and that the Nixon family's situation "is a tragedy in which we all have played a part. It could go on and on and on, or someone must write the end to it. I have concluded that only I can do that, and if I can, I must."
Ford's decision to pardon Nixon was highly controversial. Critics derided the move and said a "
corrupt bargain" had been struck between the two men,
in which Ford's pardon was granted in exchange for Nixon's resignation, elevating Ford to the presidency. Ford's first press secretary and close friend
Jerald terHorst resigned his post in protest after the pardon. According to
Bob Woodward, Nixon Chief of Staff Alexander Haig proposed a pardon deal to Ford. He later decided to pardon Nixon for other reasons, primarily the friendship he and Nixon shared.
Regardless, historians believe the controversy was one of the major reasons Ford lost the
1976 presidential election, an observation with which Ford agreed.
In an editorial at the time, ''The New York Times'' stated that the Nixon pardon was a "profoundly unwise, divisive and unjust act" that in a stroke had destroyed the new president's "credibility as a man of judgment, candor and competence".
On October 17, 1974, Ford testified before Congress on the pardon. He was the first sitting president since
Abraham Lincoln to testify before the
House of Representatives.
In the months following the pardon, Ford often declined to mention President
Nixon by name, referring to him in public as "my predecessor" or "the former president." When Ford was pressed on the matter on a 1974 trip to California, White House correspondent
Fred Barnes recalled that he replied "I just can't bring myself to do it."
After Ford left the White House in January 1977, he privately justified his pardon of Nixon by carrying in his wallet a portion of the text of ''
Burdick v. United States
''Burdick v. United States'', 236 U.S. 79 (1915), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that:
* A pardoned person must introduce the pardon into court proceedings, otherwise the pardon must be disregarded by the court ...
'', a 1915
U.S. Supreme Court decision which stated that a pardon indicated a presumption of guilt, and that acceptance of a pardon was tantamount to a confession of that guilt. In 2001, the
John F. Kennedy Library
The John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum is the presidential library and museum of John Fitzgerald Kennedy (1917–1963), the 35th president of the United States (1961–1963). It is located on Columbia Point in the Dorchester neighb ...
Foundation awarded the John F. Kennedy
Profile in Courage Award to Ford for his pardon of Nixon.
In presenting the award to Ford, Senator
Edward Kennedy said that he had initially been opposed to the pardon, but later decided that history had proven Ford to have made the correct decision.
["Sen. Ted Kennedy crossed political paths with Grand Rapids' most prominent Republican, President Gerald R. Ford"](_blank)
'' The Grand Rapids Press'', August 26, 2009. Retrieved January 5, 2010.
Draft dodgers and deserters
On September 16 (shortly after he pardoned Nixon), Ford issued Presidential Proclamation 4313, which introduced a conditional
amnesty program for military deserters and Vietnam War
draft dodgers who had fled to countries such as Canada. The conditions of the amnesty required that those reaffirm their allegiance to the United States and serve two years working in a public service job or a total of two years service for those who had served less than two years of honorable service in the military.
The program for the Return of Vietnam Era Draft Evaders and Military Deserters established a Clemency Board to review the records and make recommendations for receiving a Presidential Pardon and a change in
Military discharge status.
Full pardon for draft dodgers came in the
Carter administration
Jimmy Carter's tenure as the 39th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 1977, and ended on January 20, 1981. A Democrat from Georgia, Carter took office after defeating incumbent Republican President ...
.
Administration
When Ford assumed office, he inherited Nixon's
Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
. During his brief administration, he replaced all members except
Secretary of State Kissinger and
Secretary of the Treasury William E. Simon. Political commentators have referred to Ford's dramatic reorganization of his Cabinet in the fall of 1975 as the "
Halloween Massacre
"Halloween Massacre" is the term associated with the major reorganization of United States President of the United States, president Gerald Ford's United States Cabinet, cabinet on November 4, 1975, which was an attempt to address multiple high-lev ...
". One of Ford's appointees,
William Coleman—the
Secretary of Transportation—was the second black man to serve in a presidential cabinet (after
Robert C. Weaver
Robert Clifton Weaver (December 29, 1907 – July 17, 1997) was an American economist, academic, and political administrator who served as the first United States secretary of housing and urban development (HUD) from 1966 to 1968, when the depart ...
) and the first appointed in a Republican administration.
Ford selected George H. W. Bush as
Chief of the US Liaison Office to the People's Republic of China in 1974, and then
Director of the
Central Intelligence Agency in late 1975.
Ford's transition chairman and first Chief of Staff was former congressman and ambassador
Donald Rumsfeld
Donald Henry Rumsfeld (July 9, 1932 – June 29, 2021) was an American politician, government official and businessman who served as Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under president Gerald Ford, and again from 2001 to 2006 under Presi ...
. In 1975, Rumsfeld was named by Ford as the youngest-ever
Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
. Ford chose a young
Wyoming politician,
Richard Cheney, to replace Rumsfeld as his new Chief of Staff; Cheney became the
campaign manager
{{Political campaigning
A campaign manager, campaign chairman, or campaign director is a paid or volunteer individual whose role is to coordinate a political campaign's operations such as fundraising, advertising, polling, getting out the vote ( ...
for Ford's
1976 presidential campaign.
Midterm elections
The 1974 Congressional midterm elections took place in the wake of the Watergate scandal and less than three months after Ford assumed office. The Democratic Party turned voter dissatisfaction into large gains in the
House elections, taking 49 seats from the Republican Party, increasing their majority to 291 of the 435 seats. This was one more than the number needed (290) for a two-thirds majority, the number necessary to override a Presidential veto or to propose a constitutional amendment. Perhaps due in part to this fact, the
94th Congress
The 94th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1975, ...
overrode the highest percentage of vetoes since
Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a Dem ...
was President of the United States (1865–1869). Even Ford's former, reliably Republican House seat was won by a Democrat,
Richard Vander Veen
Richard Franklin Vander Veen (November 26, 1922 – March 3, 2006) was a politician from the U.S. state of Michigan.
Early life and education
Born in Grand Rapids, Michigan, Vander Veen attended the local public schools and graduated from Muskego ...
, who defeated
Robert VanderLaan
Robert "Robbie" VanderLaan (c. 1930-November 1, 2015) was a former majority leader of the Michigan State Senate. A Republican, he ran to replace Gerald Ford as representative for Michigan's 5th congressional district in a 1974 special election, ...
. In the
Senate elections, the Democratic majority became 61 in the 100-seat body.
Domestic policy
Inflation

The
economy was a great concern during the Ford administration. One of the first acts the new president took to deal with the economy was to create, by
Executive Order on September 30, 1974, the Economic Policy Board.
[Greene, John Robert. ''The Presidency of Gerald R. Ford''. University Press of Kansas, 1995] In October 1974, in response to rising inflation, Ford went before the American public and asked them to "Whip Inflation Now". As part of this program, he urged people to wear "
WIN" buttons. At the time, inflation was believed to be the primary threat to the economy, more so than growing unemployment; there was a belief that controlling inflation would help reduce unemployment.
To rein in inflation, it was necessary to control the public's spending. To try to mesh service and sacrifice, "WIN" called for Americans to reduce their spending and consumption. On October 4, 1974, Ford gave a speech in front of a joint session of Congress; as a part of this speech he kicked off the "WIN" campaign. Over the next nine days, 101,240 Americans mailed in "WIN" pledges.
In hindsight, this was viewed as simply a
public relations gimmick which had no way of solving the underlying problems.
The main point of that speech was to introduce to Congress a one-year, five-percent income tax increase on corporations and wealthy individuals. This plan would also take $4.4 billion out of the budget, bringing federal spending below $300 billion.
[Crain, Andrew Downer. ''The Ford Presidency''. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland, 2009] At the time, inflation was over twelve percent.
Budget

The federal budget ran a
deficit
A deficit is the amount by which a sum falls short of some reference amount.
Economics
* Balance of payments deficit, when the balance of payments is negative
* Government budget deficit
* Deficit spending, the amount by which spending exceeds ...
every year Ford was president.
[CRS Report RL33305, The Crude Oil Windfall Profit Tax of the 1980s: Implications for Current Energy Policy](_blank)
, by Salvatore Lazzari, p. 5. Despite his reservations about how the program ultimately would be funded in an era of tight
public budgeting, Ford signed the
Education for All Handicapped Children Act of 1975, which established
special education throughout the United States. Ford expressed "strong support for full educational opportunities for our handicapped children" according to the official White House press release for the bill signing.
The economic focus began to change as the country sank into the worst
recession since the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
four decades earlier. The focus of the Ford administration turned to stopping the rise in unemployment, which reached nine percent in May 1975. In January 1975, Ford proposed a 1-year tax reduction of $16 billion to stimulate economic growth, along with spending cuts to avoid inflation.
Ford was criticized for abruptly switching from advocating a tax increase to a tax reduction. In Congress, the proposed amount of the tax reduction increased to $22.8 billion in tax cuts and lacked spending cuts.
In March 1975, Congress passed, and Ford signed into law, these
income tax rebates as part of the
Tax Reduction Act of 1975. This resulted in a federal deficit of around $53 billion for the 1975 fiscal year and $73.7 billion for 1976.
When New York City faced bankruptcy in 1975,
Mayor Abraham Beame
Abraham David Beame (March 20, 1906February 10, 2001) was the 104th mayor of New York City from 1974 to 1977. As mayor, he presided over the city during its fiscal crisis of the mid-1970s, when the city was almost forced to declare bankruptcy.
...
was unsuccessful in obtaining Ford's support for a federal bailout. The incident prompted the New York ''
Daily News'' famous headline "Ford to City: Drop Dead", referring to a speech in which "Ford declared flatly ... that he would veto any bill calling for 'a federal bail-out of New York City.
Swine flu
Ford was confronted with a potential
swine flu pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease wi ...
. In the early 1970s, an
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
strain
H1N1 shifted from a form of flu that affected primarily pigs and crossed over to humans. On February 5, 1976, an
army recruit at
Fort Dix
Fort Dix, the common name for the Army Support Activity (ASA) located at Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst, is a United States Army post. It is located south-southeast of Trenton, New Jersey. Fort Dix is under the jurisdiction of the Air Force A ...
mysteriously died and four fellow soldiers were hospitalized;
health officials announced that "swine flu" was the cause. Soon after, public health officials in the Ford administration urged that every person in the United States be
vaccinated. Although the vaccination program was plagued by delays and public relations problems, some 25% of the population was vaccinated by the time the program was canceled in December 1976.
Equal rights and abortion

Ford was an outspoken supporter of the
Equal Rights Amendment
The Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) is a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution designed to guarantee equal legal rights for all American citizens regardless of sex. Proponents assert it would end legal distinctions between men and ...
, issuing Presidential Proclamation no. 4383 in 1975:
As president, Ford's position on abortion was that he supported "a federal constitutional amendment that would permit each one of the 50 States to make the choice". This had also been his position as House Minority Leader in response to the 1973 Supreme Court case of ''
Roe v. Wade'', which he opposed. Ford came under criticism when First Lady Betty Ford entered the debate over abortion during an
August 1975 interview for ''60 Minutes'', in which she stated that ''Roe v. Wade'' was a "great, great decision". During his later life, Ford would identify as
pro-choice.
Foreign policy

Ford continued the détente policy with both the
Soviet Union and China, easing the tensions of the Cold War. Still in place from the Nixon administration was the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT).
The thawing relationship brought about by
Nixon's visit to China
The 1972 visit by United States President Richard Nixon to the People's Republic of China (PRC) was an important strategic and diplomatic overture that marked the culmination of the Nixon administration's resumption of harmonious relations betwe ...
was reinforced by Ford's own visit in December 1975.
The Administration entered into the Helsinki Accords
with the Soviet Union in 1975, creating the framework of the
Helsinki Watch, an independent non-governmental organization created to monitor compliance which later evolved into
Human Rights Watch.
Ford attended the inaugural meeting of the
Group of Seven (G7) industrialized nations (initially the G5) in 1975 and secured membership for Canada. Ford supported international solutions to issues. "We live in an interdependent world and, therefore, must work together to resolve common economic problems," he said in a 1974 speech.
In November 1975, Ford adopted the global
human population control recommendations of
National Security Study Memorandum 200 – a
national security directive initially commissioned by Nixon – as United States policy in the subsequent NSDM 314.
The plan explicitly states the goal was population control and not improving the lives of individuals despite instructing organizers to "emphasize development and improvements in the quality of life of the poor", later explaining the projects were "primarily for other reasons". Upon approving the plan, Ford stated "United States leadership is essential to combat population growth, to implement the World Population Plan of Action and to advance United States security and overseas interests".
Population control policies were adopted to protect American economic and military interests, with the memorandum arguing that
population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
in
developing countries resulted with such nations gaining global political power, that more citizens posed a risk to accessing foreign natural resources while also making American businesses vulnerable to governments seeking to fund a growing population, and that younger generations born would be prone to
anti-establishment behavior, increasing political instability.
Middle East
In the Middle East and eastern Mediterranean, two ongoing international disputes developed into crises. The
Cyprus dispute
The Cyprus problem, also known as the Cyprus dispute, Cyprus issue, Cyprus question or Cyprus conflict, is an ongoing dispute between Greek Cypriots in the south and Turkish Cypriots in the north. Initially, with the Modern history of Cyprus#In ...
turned into a crisis with the
Turkish invasion of Cyprus in July 1974, causing extreme strain within the
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) alliance. In mid-August, the
Greek government withdrew Greece from the NATO military structure; in mid-September, the Senate and House of Representatives overwhelmingly voted to halt military aid to Turkey. Ford, concerned with both the effect of this on Turkish-American relations and the deterioration of security on NATO's eastern front, vetoed the bill. A second bill was then passed by Congress, which Ford also vetoed, fearing that it might impede negotiations in Cyprus, although a compromise was accepted to continue aid until December 10, 1974, provided Turkey would not send American supplies to Cyprus.
U.S. military aid to Turkey was suspended on February 5, 1975.

In the continuing
Arab–Israeli conflict, although the initial
cease fire had been implemented to end active conflict in the
Yom Kippur War, Kissinger's continuing
shuttle diplomacy was showing little progress. Ford considered it "stalling" and wrote, "Their
sraelitactics frustrated the Egyptians and made me mad as hell." During Kissinger's shuttle to Israel in early March 1975, a last minute reversal to consider further withdrawal, prompted a cable from Ford to Prime Minister
Yitzhak Rabin, which included:
On March 24, Ford informed congressional leaders of both parties of the reassessment of the administration's policies in the Middle East. In practical terms, "reassessment" meant canceling or suspending further aid to Israel. For six months between March and September 1975, the United States refused to conclude any new arms agreements with Israel. Rabin notes it was "an innocent-sounding term that heralded one of the worst periods in American-Israeli relations". The announced reassessments upset the American Jewish community and Israel's well-wishers in Congress. On May 21, Ford "experienced a real shock" when seventy-six U.S. senators wrote him a letter urging him to be "responsive" to Israel's request for $2.59 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ) in military and economic aid. Ford felt truly annoyed and thought the chance for peace was jeopardized. It was, since the September 1974 ban on arms sales to Turkey, the second major congressional intrusion upon the President's foreign policy prerogatives. The following summer months were described by Ford as an American-Israeli "war of nerves" or "test of wills". After much bargaining, the
Sinai Interim Agreement (Sinai II) was formally signed on September 1, and aid resumed.
Vietnam

One of Ford's greatest challenges was dealing with the continuing
Vietnam War. American offensive operations against North Vietnam had ended with the
Paris Peace Accords
The Paris Peace Accords, () officially titled the Agreement on Ending the War and Restoring Peace in Viet Nam (''Hiệp định về chấm dứt chiến tranh, lập lại hòa bình ở Việt Nam''), was a peace treaty signed on January 27, 1 ...
, signed on January 27, 1973. The accords declared a cease-fire across both North and South Vietnam, and required the release of American
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
. The agreement guaranteed the territorial integrity of Vietnam and, like the
Geneva Conference Geneva Conference may refer to:
* Geneva Naval Conference (1927), on naval arms limitation
* World Economic Conference (423 May 1927), on international trade
* World Population Conference (29 August3 September 1927), on demography
* Geneva Confer ...
of 1954, called for national elections in the North and South. The Paris Peace Accords stipulated a sixty-day period for the total withdrawal of U.S. forces.
The agreements were negotiated by
US National Security Advisor
The Assistant to the President for National Security Affairs (APNSA), commonly referred to as the National Security Advisor (NSA),The National Security Advisor and Staff: p. 1. is a senior aide in the Executive Office of the President, based at t ...
Henry Kissinger and North Vietnamese
Politburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the executive committee for communist parties. It is present in most former and existing communist states.
Names
The term "politburo" in English comes from the Russian ''Politbyuro'' (), itself a contraction ...
member
Lê Đức Thọ. South Vietnamese President
Nguyen Van Thieu was not involved in the final negotiations, and publicly criticized the proposed agreement. However, anti-war pressures within the United States forced Nixon and Kissinger to pressure Thieu to sign the agreement and enable the withdrawal of American forces. In multiple letters to the South Vietnamese president, Nixon had promised that the United States would defend Thieu's government, should the North Vietnamese violate the accords.
In December 1974, months after Ford took office, North Vietnamese forces invaded the province of
Phuoc Long. General
Trần Văn Trà sought to gauge any South Vietnamese or American response to the invasion, as well as to solve logistical issues, before proceeding with the invasion.
As North Vietnamese forces advanced, Ford requested Congress approve a $722 million aid package for South Vietnam, funds that had been promised by the Nixon administration. Congress voted against the proposal by a wide margin.
Senator
Jacob K. Javits
Jacob Koppel Javits ( ; May 18, 1904 – March 7, 1986) was an American lawyer and politician. During his time in politics, he represented the state of New York in both houses of the United States Congress. A member of the Republican Party, he a ...
offered "...large sums for evacuation, but not one nickel for military aid".
President Thieu resigned on April 21, 1975, publicly blaming the lack of support from the United States for the fall of his country.
Two days later, on April 23, Ford gave a speech at
Tulane University. In that speech, he announced that the Vietnam War was over "...as far as America is concerned".
The announcement was met with thunderous applause.
1,373 U.S. citizens and 5,595
Vietnamese and third-country nationals were evacuated from the South Vietnamese capital of
Saigon
, population_density_km2 = 4,292
, population_density_metro_km2 = 697.2
, population_demonym = Saigonese
, blank_name = GRP (Nominal)
, blank_info = 2019
, blank1_name = – Total
, blank1_ ...
during
Operation Frequent Wind. Many of the Vietnamese evacuees were allowed to enter the United States under the
Indochina Migration and Refugee Assistance Act
The Indochina Migration and Refugee Assistance Act, passed on May 23, 1975, under President Gerald Ford, was a response to the Fall of Saigon and the end of the Vietnam War. Under this act, approximately 130,000 refugees from South Vietnam, Laos a ...
. The 1975 Act appropriated $455 million toward the costs of assisting the settlement of Indochinese refugees. In all, 130,000 Vietnamese refugees came to the United States in 1975. Thousands more escaped in the years that followed.
East Timor

The former Portuguese colony of
East Timor declared its independence in 1975.
Indonesian president
Suharto
Suharto (; ; 8 June 1921 – 27 January 2008) was an Indonesian army officer and politician, who served as the second and the longest serving president of Indonesia. Widely regarded as a military dictator by international observers, Suharto ...
was a strong U.S. ally in Southeast Asia. In December 1975, Suharto discussed the plans to invade East Timor during a meeting with Ford and Henry Kissinger in the Indonesian capital of
Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
. Both Ford and Kissinger made clear that the U.S. would not object to the proposed
Indonesian annexation of East Timor. According to
Ben Kiernan
Benedict F. "Ben" Kiernan (born 1953) is an Australian-born American academic and historian who is the Whitney Griswold Professor Emeritus of History, Professor of International and Area Studies and Director of the Genocide Studies Program at Yal ...
, the invasion and occupation resulted in the
deaths of nearly a quarter of the Timorese population from 1975 to 1981.
''Mayaguez'' incident
North Vietnam's victory over the South led to a considerable shift in the political winds in Asia, and Ford administration officials worried about a consequent loss of U.S. influence there. The administration proved it was willing to respond forcefully to challenges to its interests in the region when
Khmer Rouge
The Khmer Rouge (; ; km, ខ្មែរក្រហម, ; ) is the name that was popularly given to members of the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK) and by extension to the regime through which the CPK ruled Cambodia between 1975 and 1979. ...
forces seized an American ship in
international waters. The main crisis was the
''Mayaguez'' incident. In May 1975, shortly after the fall of Saigon and the Khmer Rouge conquest of
Cambodia, Cambodians seized the American merchant ship ''Mayaguez'' in international waters. Ford dispatched
Marines to rescue the crew, but the Marines landed on the wrong island and met unexpectedly stiff resistance just as, unknown to the U.S., the ''Mayaguez'' sailors were being released. In the operation, two military transport helicopters carrying the Marines for the assault operation were shot down, and 41 U.S. servicemen were killed and 50 wounded, while approximately 60 Khmer Rouge soldiers were killed.
Despite the American losses, the operation was seen as a success in the United States, and Ford enjoyed an 11-point boost in his approval ratings in the aftermath. The Americans killed during the operation became the last to have their names inscribed on the
Vietnam Veterans Memorial wall in Washington, D.C.
Some historians have argued that the Ford administration felt the need to respond forcefully to the incident because it was construed as a Soviet plot. But work by Andrew Gawthorpe, published in 2009, based on an analysis of the administration's internal discussions, shows that Ford's national security team understood that the seizure of the vessel was a local, and perhaps even accidental, provocation by an immature Khmer government. Nevertheless, they felt the need to respond forcefully to discourage further provocations by other Communist countries in Asia.
Assassination attempts

Ford was the target of two assassination attempts during his presidency. In
Sacramento, California, on September 5, 1975,
Lynette "Squeaky" Fromme
Lynette Alice "Squeaky" Fromme (born October 22, 1948) is an American criminal who was a member of the Manson family, a cult led by Charles Manson. Though not involved in the Tate–LaBianca murders for which the Manson family is best known, ...
, a follower of
Charles Manson
Charles Milles Manson (; November 12, 1934November 19, 2017) was an American criminal and musician who led the Manson Family, a cult based in California, in the late 1960s. Some of the members committed a series of nine murders at four loca ...
, pointed a
Colt .45-caliber handgun at Ford and pulled the trigger at
point-blank range.
As she did,
Larry Buendorf
Larry Buendorf (born November 18, 1937) is a former Chief Security Officer of the United States Olympic Committee, United States Navy aviator, and Secret Service agent. He is best known for his successful intervention during an assassination att ...
, a Secret Service agent, grabbed the gun, and Fromme was taken into custody. She was later convicted of attempted assassination of the President and was sentenced to life in prison; she was paroled on August 14, 2009, after serving 34 years.
In reaction to this attempt, the Secret Service began keeping Ford at a more secure distance from anonymous crowds, a strategy that may have saved his life seventeen days later. As he left the
St. Francis Hotel in downtown San Francisco,
Sara Jane Moore, standing in a crowd of onlookers across the street, fired a
.38-caliber revolver at him. The shot missed Ford by a few feet.
Before she fired a second round, retired Marine
Oliver Sipple grabbed at the gun and deflected her shot; the bullet struck a wall about six inches above and to the right of Ford's head, then ricocheted and hit a taxi driver, who was slightly wounded. Moore was later sentenced to life in prison. She was paroled on December 31, 2007, after serving 32 years.
Judicial appointments
Supreme Court
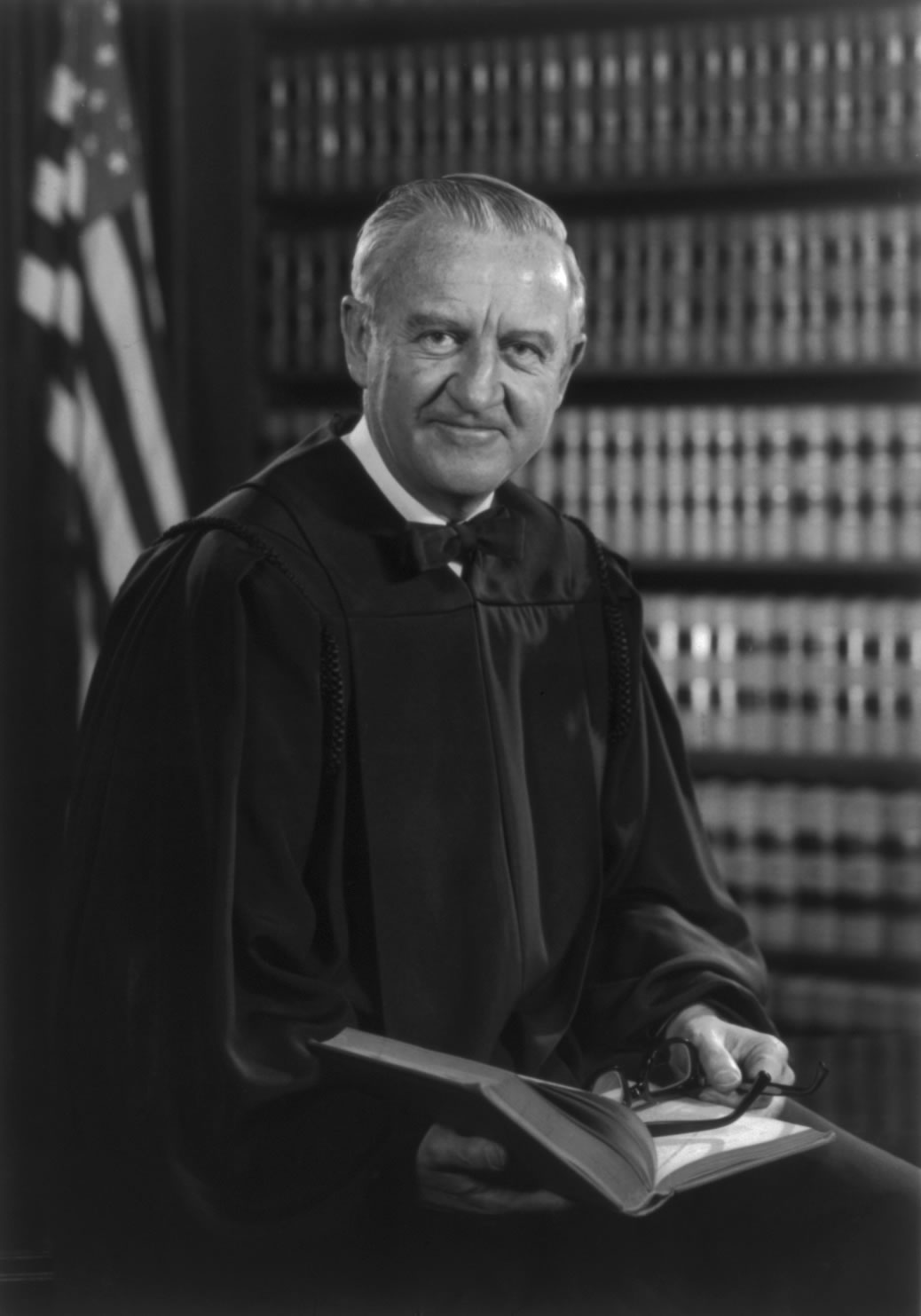

In 1975, Ford appointed
John Paul Stevens
John Paul Stevens (April 20, 1920 – July 16, 2019) was an American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1975 to 2010. At the time of his retirement, he was the second-oldes ...
as
Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States
An associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States is any member of the Supreme Court of the United States other than the chief justice of the United States. The number of associate justices is eight, as set by the Judiciary Act of 18 ...
to replace retiring Justice
William O. Douglas. Stevens had been a judge of the
United States Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit, appointed by President Nixon.
During his tenure as House Republican leader, Ford had led efforts to have Douglas impeached. After being confirmed, Stevens eventually disappointed some conservatives by siding with the Court's liberal wing regarding the outcome of many key issues.
Nevertheless, in 2005 Ford praised Stevens. "He has served his nation well," Ford said of Stevens, "with dignity, intellect and without partisan political concerns."
Other judicial appointments
Ford appointed 11 judges to the United States Courts of Appeals, and 50 judges to the
United States district courts.
1976 presidential election

Ford reluctantly agreed to run for office in 1976, but first he had to counter a challenge for the Republican party nomination. Former
Governor of California
The governor of California is the head of government of the U.S. state of California. The governor is the commander-in-chief of the California National Guard and the California State Guard.
Established in the Constitution of California, the g ...
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
and the party's
conservative wing faulted Ford for failing to do more in
South Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam ( vi, Việt Nam Cộng hòa), was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975, the period when the southern portion of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of th ...
, for signing the Helsinki Accords, and for negotiating to cede the
Panama Canal. (Negotiations for the canal continued under President Carter, who eventually signed the
Torrijos–Carter Treaties.) Reagan launched his campaign in autumn of 1975 and won numerous
primaries, including
North Carolina,
Texas,
Indiana, and
California, but failed to get a majority of delegates; Reagan withdrew from the race at the
Republican Convention
The Republican National Convention (RNC) is a series of U.S. presidential nominating convention, presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1856 by the United States Republican Party. They are administered by the Republican N ...
in
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
,
Missouri. The conservative insurgency did lead to Ford dropping the more
liberal Vice President Nelson Rockefeller in favor of U.S. Senator
Bob Dole
Robert Joseph Dole (July 22, 1923 – December 5, 2021) was an American politician and attorney who represented Kansas in the United States Senate from 1969 to 1996. He was the Republican Leader of the Senate during the final 11 years of his te ...
of
Kansas.
In addition to the pardon dispute and lingering anti-Republican sentiment, Ford had to counter a plethora of negative media imagery.
Chevy Chase often did
pratfalls on ''
Saturday Night Live'',
imitating Ford, who had been seen stumbling on two occasions during his term. As Chase commented, "He even mentioned in his own autobiography it had an effect over a period of time that affected the election to some degree."
Ford's 1976 election campaign benefitted from his being an incumbent president during several anniversary events held during the period leading up to the
United States Bicentennial. The Washington, D.C.
fireworks display on the
Fourth of July was presided over by the President and televised nationally. On July 7, 1976, the President and First Lady served as hosts at a White House state dinner for
Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. She was queen ...
and
Prince Philip of the United Kingdom, which was televised on the
Public Broadcasting Service
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educati ...
network. The 200th anniversary of the
Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord ...
in Massachusetts gave Ford the opportunity to deliver a speech to 110,000 in Concord acknowledging the need for a strong national defense tempered with a plea for "reconciliation, not recrimination" and "reconstruction, not rancor" between the United States and those who would pose "threats to peace". Speaking in New Hampshire on the previous day, Ford condemned the growing trend toward big government bureaucracy and argued for a return to "basic American virtues".

Televised
presidential debates were reintroduced for the first time since the 1960 election. As such, Ford became the first incumbent president to participate in one. Carter later attributed his victory in the election to the debates, saying they "gave the viewers reason to think that Jimmy Carter had something to offer". The turning point came in the second debate when Ford blundered by stating, "There is no Soviet domination of Eastern Europe and there never will be under a Ford Administration." Ford also said that he did not "believe that the Poles consider themselves dominated by the Soviet Union". In an interview years later, Ford said he had intended to imply that the Soviets would never crush the ''spirits'' of eastern Europeans seeking independence. However, the phrasing was so awkward that questioner
Max Frankel was visibly incredulous at the response.

In the end, Carter won the election, receiving 50.1% of the popular vote and 297
electoral votes compared with 48.0% and 240 electoral votes for Ford.
Post-presidency (1977–2006)
The Nixon pardon controversy eventually subsided. Ford's successor, Jimmy Carter, opened his 1977
inaugural address by praising the outgoing president, saying, "For myself and for our Nation, I want to thank my predecessor for all he has done to heal our land."
After leaving the White House, the Fords moved to Denver, Colorado. Ford successfully invested in oil with
Marvin Davis, which later provided an income for Ford's children.
He continued to make appearances at events of historical and ceremonial significance to the nation, such as presidential inaugurals and memorial services. In January 1977, he became the president of
Eisenhower Fellowships in
Philadelphia, then served as the chairman of its board of trustees from 1980 to 1986. Later in 1977, he reluctantly agreed to be interviewed by James M. Naughton, a ''New York Times'' journalist who was given the assignment to write the former president's advance obituary, an article that would be updated prior to its eventual publication.
In 1979, Ford published his autobiography, ''A Time to Heal'' (Harper/Reader's Digest, 454 pages). A review in ''Foreign Affairs'' described it as, "Serene, unruffled, unpretentious, like the author. This is the shortest and most honest of recent presidential memoirs, but there are no surprises, no deep probings of motives or events. No more here than meets the eye."
During the term of office of his successor, Jimmy Carter, Ford received monthly briefs by President Carter's senior staff on international and domestic issues, and was always invited to lunch at the White House whenever he was in Washington, D.C. Their close friendship developed after Carter had left office, with the catalyst being their trip together to the funeral of
Anwar el-Sadat in 1981.
Until Ford's death, Carter and his wife,
Rosalynn, visited the Fords' home frequently. Ford and Carter served as honorary co-chairs of the National Commission on Federal Election Reform in 2001 and of the
Continuity of Government Commission in 2002.
Like Presidents Carter,
George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
, and
Bill Clinton, Ford was an honorary co-chair of the
Council for Excellence in Government The Council for Excellence in Government was a public/private partnership organization initiated in the 1980s designed to improve the effectiveness of federal, state, and local government in the United States. The organization ceased to operate in ...
, a group dedicated to excellence in government performance, which provides leadership training to top federal employees. He also devoted much time to his love of golf, often playing both privately and in public events with comedian
Bob Hope, a longtime friend. In 1977, he shot a
hole in one during a Pro-am held in conjunction with the
Danny Thomas Memphis Classic at
Colonial Country Club in
Memphis, Tennessee. He hosted the
Jerry Ford Invitational
The Jerry Ford Invitational was a celebrity pro-am golf tournament hosted by former President Gerald Ford. It was played in Vail, Colorado
Vail is a home rule municipality in Eagle County, Colorado, United States. The population of the tow ...
in
Vail, Colorado from 1977 to 1996.
In 1977, Ford established the Gerald R. Ford Institute of Public Policy at
Albion College in
Albion, Michigan, to give undergraduates training in public policy. In April 1981, he opened the
Gerald R. Ford Library
The Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library is a repository located on the north campus of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The library houses archival materials on the life, career, and presidency of Gerald Ford, the 38th president of th ...
in
Ann Arbor, Michigan
Ann Arbor is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of Washtenaw County, Michigan, Washtenaw County. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census recorded its population to be 123,851. It is the principal city of the Ann Arbor ...
, on the north campus of his alma mater, the
University of Michigan, followed in September by the
Gerald R. Ford Museum in Grand Rapids.
Ford considered a run for the Republican nomination in
1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – ...
, forgoing numerous opportunities to serve on corporate boards to keep his options open for a rematch with Carter. Ford attacked Carter's conduct of the SALT II negotiations and foreign policy in the Middle East and Africa. Many have argued that Ford also wanted to exorcise his image as an "Accidental President" and to win a term in his own right. Ford also believed the more conservative Ronald Reagan would be unable to defeat Carter and would hand the incumbent a second term. Ford was encouraged by his former Secretary of State, Henry Kissinger as well as
Jim Rhodes of Ohio and
Bill Clements of Texas to make the race. On March 15, 1980, Ford announced that he would forgo a run for the Republican nomination, vowing to support the eventual nominee.
After securing the Republican nomination in 1980, Ronald Reagan considered his former rival Ford as a potential vice-presidential running mate, but negotiations between the Reagan and Ford camps at the
Republican National Convention
The Republican National Convention (RNC) is a series of presidential nominating conventions held every four years since 1856 by the United States Republican Party. They are administered by the Republican National Committee. The goal of the Repu ...
were unsuccessful. Ford conditioned his acceptance on Reagan's agreement to an unprecedented "co-presidency",
giving Ford the power to control key executive branch appointments (such as Kissinger as Secretary of State and
Alan Greenspan as Treasury Secretary). After rejecting these terms, Reagan offered the vice-presidential nomination instead to George H. W. Bush. Ford did appear in a campaign commercial for the Reagan-Bush ticket, in which he declared that the country would be "better served by a Reagan presidency rather than a continuation of the weak and politically expedient policies of Jimmy Carter". On October 8, 1980, Ford said former President Nixon's involvement in the general election potentially could negatively impact the Reagan campaign: "I think it would have been much more helpful if Mr. Nixon had stayed in the background during this campaign. It would have been much more beneficial to Ronald Reagan."
On October 3, 1980, Ford cast blame on Carter for the latter's charges of ineffectiveness on the part of the
Federal Reserve Board due to his appointing of most of its members: "President Carter, when the going gets tough, will do anything to save his own political skin. This latest action by the president is cowardly."
Following the
attempted assassination of Ronald Reagan, Ford told reporters while appearing at a fundraiser for
Thomas Kean that criminals who use firearms should get the death penalty in the event someone is injured with the weapon.
In September 1981, Ford advised Reagan against succumbing to
Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
demands and follow his own agenda for the economic policies of the US during an appearance on ''
Good Morning America
''Good Morning America'' (often abbreviated as ''GMA'') is an American morning television program that is broadcast on ABC. It debuted on November 3, 1975, and first expanded to weekends with the debut of a Sunday edition on January 3, 1993. Th ...
'': "He shouldn't let the gurus of Wall Street decide what the economic future of this country is going to be. They are wrong in my opinion." On October 20, 1981, Ford stated stopping the Reagan administration's Saudi arms package could have a large negative impact to American relations in the Middle East during a news conference.
On March 24, 1982, Ford offered an endorsement of President Reagan's economic policies while also stating the possibility of Reagan being met with a stalemate by Congress if not willing to compromise while in Washington.
Ford founded the annual
AEI World Forum The AEI World Forum is an annual meeting of business and financial executives, heads of government, government officials, and intellectuals. Held every spring in Sea Island, Georgia, it is sponsored by the American Enterprise Institute (AEI) and the ...
in 1982, and joined the
American Enterprise Institute as a distinguished fellow. He was also awarded an
honorary doctorate at Central Connecticut State University on March 23, 1988.
During an August 1982 fundraising reception, Ford stated his opposition to a constitutional amendment requiring the US to have a balanced budget, citing a need to elect "members of the House and Senate who will immediately when Congress convenes act more responsibly in fiscal matters." Ford was a participant in the 1982 midterm elections, traveling to
Tennessee in October of that year to help Republican candidates.
In January 1984, a letter signed by Ford and Carter and urging world leaders to extend their failed effort to end world hunger was released and sent to
Secretary-General of the United Nations Javier Pérez de Cuéllar.
In 1987, Ford testified before the
Senate Judiciary Committee in favor of
District of Columbia Circuit Court judge and former
Solicitor General Robert Bork after Bork was
nominated by President Reagan to be an
Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court. Bork's nomination was rejected by a vote of 58–42.
In 1987, Ford's ''Humor and the Presidency'', a book of humorous political anecdotes, was published.
By 1988, Ford was a member of several corporate boards including Commercial Credit, Nova Pharmaceutical,
The Pullman Company,
Tesoro Petroleum, and Tiger International, Inc.
Ford also became an honorary director of
Citigroup
Citigroup Inc. or Citi (Style (visual arts), stylized as citi) is an American multinational investment banking, investment bank and financial services corporation headquartered in New York City. The company was formed by the merger of banking ...
, a position he held until his death.
In October 1990, Ford appeared in
Gettysburg, Pennsylvania with
Bob Hope to commemorate the centennial anniversary of the birth of former President
Dwight D. Eisenhower, where the two unveiled a plaque with the signatures of each living former president.
In April 1991, Ford joined former presidents
Richard Nixon,
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
, and
Jimmy Carter, in supporting the
Brady Bill
The Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act ( Pub.L. 103–159, 107 Stat. 1536, enacted November 30, 1993), often referred to as the Brady Act or the Brady Bill, is an Act of the United States Congress that mandated federal background checks on ...
.
Three years later, he wrote to the
U.S. House of Representatives, along with Carter and Reagan, in support of the
assault weapons ban.
At the
1992 Republican National Convention
The 1992 Republican National Convention was held in the Astrodome in Houston, Texas, from August 17 to August 20, 1992. The convention nominated President George H. W. Bush and Vice President Dan Quayle for reelection. It was Bush's fourth co ...
, Ford compared the election cycle to his 1976 loss to Carter and urged attention be paid to electing a Republican Congress: "If it's change you want on Nov. 3, my friends, the place to start is not at the White House but in the United States' Capitol. Congress, as every school child knows, has the power of the purse. For nearly 40 years, Democratic majorities have held to the time-tested New Deal formula, tax and tax, spend and spend, elect and elect." (The Republicans would later win both Houses of Congress at the
1994 mid-term elections.)
In April 1997, Ford joined President
Bill Clinton, former President Bush, and
Nancy Reagan
Nancy Davis Reagan (; born Anne Frances Robbins; July 6, 1921 – March 6, 2016) was an American film actress and First Lady of the United States from 1981 to 1989. She was the second wife of president Ronald Reagan.
Reagan was born in N ...
in signing the "Summit Declaration of Commitment" in advocating for participation by private citizens in solving domestic issues within the United States.
On January 20, 1998, during an interview at his Palm Springs home, Ford said the Republican Party's nominee in the 2000 presidential election would lose if the party turned ultra-conservative in their ideals: "If we get way over on the hard right of the political spectrum, we will not elect a Republican President. I worry about the party going down this ultra-conservative line. We ought to learn from the Democrats: when they were running ultra-liberal candidates, they didn't win."
In the prelude to the impeachment of President Clinton, Ford conferred with former President Carter and the two agreed to not speak publicly on the controversy, a pact broken by Carter when answering a question from a student at
Emory University.
In October 2001, Ford broke with conservative members of the Republican Party by stating that gay and lesbian couples "ought to be treated equally. Period." He became the highest-ranking Republican to embrace full equality for gays and lesbians, stating his belief that there should be a federal amendment outlawing anti-gay job discrimination and expressing his hope that the Republican Party would reach out to gay and lesbian voters. He also was a member of the Republican Unity Coalition, which ''
The New York Times'' described as "a group of prominent Republicans, including former President Gerald R. Ford, dedicated to making sexual orientation a non-issue in the Republican Party".
On November 22, 2004, New York Republican Governor
George Pataki named Ford and the other living former Presidents (Carter, George H. W. Bush and Bill Clinton) as honorary members of the board rebuilding the
World Trade Center.
In a pre-recorded
embargoed interview with
Bob Woodward of ''
The Washington Post'' in July 2004, Ford stated that he disagreed "very strongly" with the Bush administration's choice of Iraq's alleged weapons of mass destruction as justification for its decision to
invade Iraq, calling it a "big mistake" unrelated to the national security of the United States and indicating that he would not have gone to war had he been president. The details of the interview were not released until after Ford's death, as he requested.
Health problems
On April 4, 1990, Ford was admitted to
Eisenhower Medical Center for surgery to replace his left knee, orthopedic surgeon Dr. Robert Murphy saying, "Ford's entire left knee was replaced with an artificial joint, including portions of the adjacent femur, or thigh bone, and tibia, or leg bone."
Ford suffered two minor strokes at the
2000 Republican National Convention
The 2000 Republican National Convention convened at the First Union Center (now the Wells Fargo Center) in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from July 31 to August 3, 2000. The 2000 delegates assembled at the convention nominated Texas Governor George ...
, but made a quick recovery after being admitted to
Hahnemann University Hospital. In January 2006, he spent 11 days at the
Eisenhower Medical Center near his residence at
Rancho Mirage, California, for treatment of
pneumonia. On April 23, 2006, President
George W. Bush visited Ford at his home in Rancho Mirage for a little over an hour. This was Ford's last public appearance and produced the last known public photos, video footage, and voice recording.
While vacationing in
Vail, Colorado, Ford was hospitalized for two days in July 2006 for shortness of breath. On August 15 he was admitted to St. Mary's Hospital of the
Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic () is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff, ...
in
Rochester, Minnesota
Rochester is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Olmsted County. Located on rolling bluffs on the Zumbro River's south fork in Southeast Minnesota, the city is the home and birthplace of the renowned Mayo Clinic.
Acco ...
, for testing and evaluation. On August 21, it was reported that he had been fitted with a
pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart eith ...
. On August 25, he underwent an
angioplasty procedure at the Mayo Clinic. On August 28, Ford was released from the hospital and returned with his wife Betty to their California home. On October 13, he was scheduled to attend the dedication of a building of his namesake, the
Gerald R. Ford School of Public Policy
The Gerald R. Ford School of Public Policy, often referred to as the Ford School, is the public policy school at the University of Michigan. Founded in 1914 to train municipal administration experts, the school was named after University of Mi ...
at the University of Michigan, but due to poor health and on the advice of his doctors he did not attend. The previous day, Ford had entered the Eisenhower Medical Center for undisclosed tests; he was released on October 16. By November 2006, he was confined to a bed in his study.
Death and legacy

Ford died on December 26, 2006, at his home in
Rancho Mirage, California, of arteriosclerotic
cerebrovascular disease and diffuse
arteriosclerosis. He had end-stage coronary artery disease and severe
aortic stenosis and insufficiency, caused by calcific alteration of one of his heart valves. At the time of his death, Ford was the
longest-lived U.S. president, having lived 93 years and 165 days (45 days longer than Ronald Reagan, whose record he surpassed).
He died on the 34th anniversary of President
Harry S. Truman's death; he was the last surviving member of the
Warren Commission.
On December 30, 2006, Ford became the 11th U.S. president to
lie in state in the
Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol. A state funeral and memorial services were held at the
National Cathedral in Washington, D.C., on Tuesday, January 2, 2007. After the service, Ford was interred at his
Presidential Museum in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Scouting was so important to Ford that his family asked for Scouts to participate in his funeral. A few selected Scouts served as ushers inside the National Cathedral. About 400 Eagle Scouts were part of the funeral procession, where they formed an honor guard as the casket went by in front of the museum.
Ford selected the song to be played during his funeral procession at the U.S. Capitol. After his death in December 2006, the
University of Michigan Marching Band
The Michigan Marching Band (also known as the University of Michigan Marching Band or simply MMB) is the official marching band of the University of Michigan. The band performs at all Michigan Wolverines football home games, select away games, an ...
played the school's fight song for him one final time, for his last ride from the
Gerald R. Ford Airport
Gerald R. Ford International Airport is a commercial airport in Cascade Township approximately southeast of Grand Rapids, Michigan, United States. The facility is owned by the Kent County Board of Commissioners and managed by an independent ...
in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
The State of Michigan commissioned and submitted a
statue of Ford to the
National Statuary Hall Collection, replacing
Zachariah Chandler. It was unveiled on May 3, 2011, in the Capitol Rotunda. On the proper right side is inscribed a quotation from a tribute by
Tip O'Neill, Speaker of the House at the end of Ford's presidency: "God has been good to America, especially during difficult times. At the time of the Civil War, he gave us Abraham Lincoln. And at the time of Watergate, he gave us Gerald Ford—the right man at the right time who was able to put our nation back together again." On the proper left side are words from Ford's swearing-in address: "Our constitution works. Our great republic is a government of laws and not of men. Here the people rule."
Ford's wife, Betty Ford, died on July 8, 2011.
Personal life
Family
When speaking of his mother and stepfather, Ford said that "My stepfather was a magnificent person and my mother equally wonderful. So I couldn't have written a better prescription for a superb family upbringing."
Ford had three half-siblings from the second marriage of Leslie King Sr., his biological father: Marjorie King (1921–1993), Leslie Henry King (1923–1976), and Patricia Jane King (1925–1980). They never saw one another as children, and he did not know them at all until 1960. Ford was not aware of his biological father until he was 17, when his parents told him about the circumstances of his birth. That year his biological father, whom Ford described as a "carefree, well-to-do man who didn't really give a damn about the hopes and dreams of his firstborn son", approached Ford while he was waiting tables in a Grand Rapids restaurant. The two "maintained a sporadic contact" until Leslie King Sr.'s death in 1941.

On October 15, 1948, Ford married
Elizabeth Bloomer
Elizabeth Anne Ford (; formerly Warren; April 8, 1918 – July 8, 2011) was the first lady of the United States from 1974 to 1977, as the wife of President Gerald Ford. As first lady, she was active in social policy and set a precedent as a pol ...
(1918–2011) at Grace
Episcopal Church in Grand Rapids; it was his first and only marriage and her second marriage. She had previously been married and, after a five‐year marriage, divorced from William Warren.
Originally from Grand Rapids herself, she had lived in New York City for several years, where she worked as a
John Robert Powers fashion model and a dancer in the auxiliary troupe of the
Martha Graham
Martha Graham (May 11, 1894 – April 1, 1991) was an American modern dancer and choreographer. Her style, the Graham technique, reshaped American dance and is still taught worldwide.
Graham danced and taught for over seventy years. She wa ...
Dance Company. At the time of their engagement, Ford was campaigning for what would be his first of 13 terms as a member of the United States House of Representatives. The wedding was delayed until shortly before the
election because, as ''
The New York Times'' reported in a 1974 profile of Betty Ford, "Jerry Ford was running for Congress and wasn't sure how voters might feel about his marrying a divorced exdancer."
[
The couple had four children: Michael Gerald, born in 1950, John Gardner (known as Jack) born in 1952, Steven Meigs, born in 1956, and Susan Elizabeth, born in 1957.]
Civic and fraternal organizations
Ford was a member of several civic and fraternal organizations, including the Junior Chamber of Commerce (Jaycees), American Legion
The American Legion, commonly known as the Legion, is a non-profit organization of U.S. war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militi ...
, AMVETS, Benevolent and Protective Order of Elks, Sons of the Revolution,Veterans of Foreign Wars
The Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW), formally the Veterans of Foreign Wars of the United States, is an organization of US war veterans, who, as military service members fought in wars, campaigns, and expeditions on foreign land, waters, or a ...
, and was an alumnus of Delta Kappa Epsilon at Michigan.
Freemasonry
Ford was initiated into Freemasonry on September 30, 1949.[The Supreme Council](_blank)
Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite, Southern Jurisdiction, USA. He later said in 1975, "When I took my obligation as a master mason—incidentally, with my three younger brothers—I recalled the value my own father attached to that order. But I had no idea that I would ever be added to the company of the Father of our Country and 12 other members of the order who also served as Presidents of the United States."
Public image
 Ford is the only person to hold the presidential office without being elected as either president or vice president. The choice of Ford to fill the vacant vice-presidency was based on Ford's reputation for openness and honesty.
Ford is the only person to hold the presidential office without being elected as either president or vice president. The choice of Ford to fill the vacant vice-presidency was based on Ford's reputation for openness and honesty.Emmy
The Emmy Awards, or Emmys, are an extensive range of awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international television industry. A number of annual Emmy Award ceremonies are held throughout the calendar year, each with the ...
-winning 1987 ABC biographical television movie ''The Betty Ford Story
''The Betty Ford Story'' is a 1987 television film directed by David Greene and written by Karen Hall. This biographical film was based on the book ''The Times of My Life'' written by Chris Chase and Betty Ford. The film originally aired on A ...
'' and the 2022 Showtime television series '' The First Lady''.
Honors
Foreign honors
*:
** First Class of the Order of the Cross of Terra Mariana (7 January 1997)
*Ford received the Distinguished Eagle Scout Award in May 1970, as well as the Silver Buffalo Award, from the Boy Scouts of America.
*In 1974, he also received the highest distinction of the Scout Association of Japan, the Golden Pheasant Award.
First Class of the Order of the Cross of Terra Mariana (7 January 1997)
*Ford received the Distinguished Eagle Scout Award in May 1970, as well as the Silver Buffalo Award, from the Boy Scouts of America.
*In 1974, he also received the highest distinction of the Scout Association of Japan, the Golden Pheasant Award.Profiles in Courage Award
The Profile in Courage Award is a private award given to recognize displays of courage similar to those John F. Kennedy originally described in his Profiles in Courage, book of the same name. It is given to individuals (often elected officials) wh ...
for his decision to pardon Richard Nixon to stop the agony America was experiencing over Watergate.Gerald R. Ford International Airport
Gerald R. Ford International Airport is a commercial airport in Cascade Township approximately southeast of Grand Rapids, Michigan, United States. The facility is owned by the Kent County Board of Commissioners and managed by an independent ...
in Grand Rapids, Michigan
* Gerald R. Ford Library
The Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library is a repository located on the north campus of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The library houses archival materials on the life, career, and presidency of Gerald Ford, the 38th president of th ...
in Ann Arbor, Michigan
* Gerald R. Ford Museum in Grand Rapids, Michigan
* Gerald R. Ford School of Public Policy
The Gerald R. Ford School of Public Policy, often referred to as the Ford School, is the public policy school at the University of Michigan. Founded in 1914 to train municipal administration experts, the school was named after University of Mi ...
, University of Michigan
* Gerald R. Ford Institute of Public Policy, Albion College
* USS ''Gerald R. Ford'' (CVN-78)
* Gerald R. Ford Middle School, Grand Rapids, Michigan
* President Gerald R. Ford Park in Alexandria, Virginia, located in the neighborhood where Ford lived while serving as a Representative and Vice President
* President Ford Field Service Council, Boy Scouts of America The council where he was awarded the rank of Eagle Scout. Serves 25 counties in Western and Northern Michigan with its headquarters located in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
See also
* List of Freemasons
This "List of Freemasons" page provides links to alphabetized lists of notable Freemasons. Freemasonry is a fraternal organisation which exists in a number of forms worldwide. Throughout history some members of the fraternity have made no secre ...
* List of members of the American Legion
* List of presidents of the United States
* List of presidents of the United States by previous experience
* Presidents of the United States on U.S. postage stamps
References
Bibliography
* short biography
* Cannon, James. ''Gerald R. Ford: An Honorable Life'' (Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2013) 482 pp. official biography by a member of the Ford administration
** older full-scale biography
* Congressional Quarterly. ''President Ford: the man and his record'' (1974
online
*
*
* , the major scholarly study
* Hersey, John Richard. The President: A Minute-By-Minute Account of a Week in the Life of Gerald Ford. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. 1975.
* Hult, Karen M. and Walcott, Charles E. ''Empowering the White House: Governance under Nixon, Ford, and Carter''. University Press of Kansas, 2004.
* Jespersen, T. Christopher. "Kissinger, Ford, and Congress: the Very Bitter End in Vietnam". ''Pacific Historical Review'' 2002 71#3: 439–473
Online
* Jespersen, T. Christopher. "The Bitter End and the Lost Chance in Vietnam: Congress, the Ford Administration, and the Battle over Vietnam, 1975–76". ''Diplomatic History'' 2000 24#2: 265–293
Online
* latest full-scale biography
* Parmet, Herbert S. "Gerald R. Ford" in Henry F Graff ed., ''The Presidents: A Reference History'' (3rd ed. 2002); short scholarly overview
* Randolph, Sallie G. ''Gerald R. Ford, president'' (1987
online
for secondary schools
* Schoenebaum, Eleanora. ''Political Profiles: The Nixon/Ford years'' (1979
online
short biographies of over 500 political and national leaders.
* Williams, Daniel K. ''The Election of the Evangelical: Jimmy Carter, Gerald Ford, and the Presidential Contest of 1976'' (University Press of Kansas, 2020
online review
Primary sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
Official sites
Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library and Museum
Gerald R. Ford Presidential Foundation
Media coverage
*
*
*
"Life Portrait of Gerald R. Ford"
from C-SPAN
Cable-Satellite Public Affairs Network (C-SPAN ) is an American cable and satellite television network that was created in 1979 by the cable television industry as a nonprofit public service. It televises many proceedings of the United States ...
's '' American Presidents: Life Portraits'', November 22, 1999
Other
*
Gerald Ford: A Resource Guide
from the Library of Congress.
Essays on Gerald Ford, each member of his cabinet and First Lady
from the Miller Center of Public Affairs
*
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ford, Gerald
1913 births
2006 deaths
20th-century American Episcopalians
21st-century American Episcopalians
20th-century presidents of the United States
20th-century vice presidents of the United States
American adoptees
American athlete-politicians
American football centers
United States Navy personnel of World War II
American people of English descent
American shooting survivors
Burials in Michigan
Congressional Gold Medal recipients
Deaths from cerebrovascular disease
Deaths from arteriosclerosis
East Grand Rapids, Michigan
American Freemasons
Gerald Ford family
Members of the Warren Commission
Michigan lawyers
Michigan Wolverines football players
Military personnel from Michigan
Military personnel from Omaha, Nebraska
Minority leaders of the United States House of Representatives
Nixon administration cabinet members
People from Kent County, Michigan
People from Rancho Mirage, California
Players of American football from Michigan
Politicians from Grand Rapids, Michigan
Politicians from Omaha, Nebraska
Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients
Presidents of the United States
Republican Party (United States) presidential nominees
Republican Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Michigan
Republican Party presidents of the United States
Republican Party vice presidents of the United States
Sons of the American Revolution
University of Michigan Law School alumni
United States Navy officers
Candidates in the 1976 United States presidential election
Vice presidents of the United States
Yale Bulldogs football coaches
Yale Law School alumni
People of the Cold War
 After Ford returned to Grand Rapids in 1946, he became active in local Republican politics, and supporters urged him to challenge Bartel J. Jonkman, the incumbent Republican congressman. Military service had changed his view of the world. "I came back a converted internationalist", Ford wrote, "and of course our congressman at that time was an avowed, dedicated isolationist. And I thought he ought to be replaced. Nobody thought I could win. I ended up winning two to one."
During his first campaign in 1948, Ford visited voters at their doorsteps and as they left the factories where they worked. Ford also visited local farms where, in one instance, a wager resulted in Ford spending two weeks milking cows following his election victory.
Ford was a member of the House of Representatives for 25 years, holding Michigan's 5th congressional district seat from 1949 to 1973. It was a tenure largely notable for its modesty. As an editorial in '' The New York Times'' described him, Ford "saw himself as a negotiator and a reconciler, and the record shows it: he did not write a single piece of major legislation in his entire career." Appointed to the House Appropriations Committee two years after being elected, he was a prominent member of the Defense Appropriations Subcommittee. Ford described his philosophy as "a moderate in domestic affairs, an internationalist in foreign affairs, and a conservative in fiscal policy." He voted in favor of the Civil Rights Acts of 1957,
After Ford returned to Grand Rapids in 1946, he became active in local Republican politics, and supporters urged him to challenge Bartel J. Jonkman, the incumbent Republican congressman. Military service had changed his view of the world. "I came back a converted internationalist", Ford wrote, "and of course our congressman at that time was an avowed, dedicated isolationist. And I thought he ought to be replaced. Nobody thought I could win. I ended up winning two to one."
During his first campaign in 1948, Ford visited voters at their doorsteps and as they left the factories where they worked. Ford also visited local farms where, in one instance, a wager resulted in Ford spending two weeks milking cows following his election victory.
Ford was a member of the House of Representatives for 25 years, holding Michigan's 5th congressional district seat from 1949 to 1973. It was a tenure largely notable for its modesty. As an editorial in '' The New York Times'' described him, Ford "saw himself as a negotiator and a reconciler, and the record shows it: he did not write a single piece of major legislation in his entire career." Appointed to the House Appropriations Committee two years after being elected, he was a prominent member of the Defense Appropriations Subcommittee. Ford described his philosophy as "a moderate in domestic affairs, an internationalist in foreign affairs, and a conservative in fiscal policy." He voted in favor of the Civil Rights Acts of 1957,  In 1964, Lyndon Johnson led a landslide victory for his party, secured another term as president and took 36 seats from Republicans in the House of Representatives. Following the election, members of the Republican caucus looked to select a new minority leader. Three members approached Ford to see if he would be willing to serve; after consulting with his family, he agreed. After a closely contested election, Ford was chosen to replace
In 1964, Lyndon Johnson led a landslide victory for his party, secured another term as president and took 36 seats from Republicans in the House of Representatives. Following the election, members of the Republican caucus looked to select a new minority leader. Three members approached Ford to see if he would be willing to serve; after consulting with his family, he agreed. After a closely contested election, Ford was chosen to replace  In his effort to become House Speaker, Ford worked to help Republicans across the country get a majority in the chamber, often traveling on the
In his effort to become House Speaker, Ford worked to help Republicans across the country get a majority in the chamber, often traveling on the  When Nixon resigned on August 9, 1974, Ford automatically assumed the presidency. This made him the only person to become the nation's chief executive without having been previously voted into either the presidential or vice-presidential office by the Electoral College. Immediately after Ford took the oath of office in the
When Nixon resigned on August 9, 1974, Ford automatically assumed the presidency. This made him the only person to become the nation's chief executive without having been previously voted into either the presidential or vice-presidential office by the Electoral College. Immediately after Ford took the oath of office in the  On September 8, 1974, Ford issued Proclamation 4311, which gave Nixon a full and unconditional
On September 8, 1974, Ford issued Proclamation 4311, which gave Nixon a full and unconditional  The economy was a great concern during the Ford administration. One of the first acts the new president took to deal with the economy was to create, by Executive Order on September 30, 1974, the Economic Policy Board.Greene, John Robert. ''The Presidency of Gerald R. Ford''. University Press of Kansas, 1995 In October 1974, in response to rising inflation, Ford went before the American public and asked them to "Whip Inflation Now". As part of this program, he urged people to wear " WIN" buttons. At the time, inflation was believed to be the primary threat to the economy, more so than growing unemployment; there was a belief that controlling inflation would help reduce unemployment. To rein in inflation, it was necessary to control the public's spending. To try to mesh service and sacrifice, "WIN" called for Americans to reduce their spending and consumption. On October 4, 1974, Ford gave a speech in front of a joint session of Congress; as a part of this speech he kicked off the "WIN" campaign. Over the next nine days, 101,240 Americans mailed in "WIN" pledges. In hindsight, this was viewed as simply a public relations gimmick which had no way of solving the underlying problems. The main point of that speech was to introduce to Congress a one-year, five-percent income tax increase on corporations and wealthy individuals. This plan would also take $4.4 billion out of the budget, bringing federal spending below $300 billion.Crain, Andrew Downer. ''The Ford Presidency''. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland, 2009 At the time, inflation was over twelve percent.
The economy was a great concern during the Ford administration. One of the first acts the new president took to deal with the economy was to create, by Executive Order on September 30, 1974, the Economic Policy Board.Greene, John Robert. ''The Presidency of Gerald R. Ford''. University Press of Kansas, 1995 In October 1974, in response to rising inflation, Ford went before the American public and asked them to "Whip Inflation Now". As part of this program, he urged people to wear " WIN" buttons. At the time, inflation was believed to be the primary threat to the economy, more so than growing unemployment; there was a belief that controlling inflation would help reduce unemployment. To rein in inflation, it was necessary to control the public's spending. To try to mesh service and sacrifice, "WIN" called for Americans to reduce their spending and consumption. On October 4, 1974, Ford gave a speech in front of a joint session of Congress; as a part of this speech he kicked off the "WIN" campaign. Over the next nine days, 101,240 Americans mailed in "WIN" pledges. In hindsight, this was viewed as simply a public relations gimmick which had no way of solving the underlying problems. The main point of that speech was to introduce to Congress a one-year, five-percent income tax increase on corporations and wealthy individuals. This plan would also take $4.4 billion out of the budget, bringing federal spending below $300 billion.Crain, Andrew Downer. ''The Ford Presidency''. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland, 2009 At the time, inflation was over twelve percent.
 The federal budget ran a
The federal budget ran a  Ford was an outspoken supporter of the
Ford was an outspoken supporter of the  Ford continued the détente policy with both the Soviet Union and China, easing the tensions of the Cold War. Still in place from the Nixon administration was the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT). The thawing relationship brought about by
Ford continued the détente policy with both the Soviet Union and China, easing the tensions of the Cold War. Still in place from the Nixon administration was the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT). The thawing relationship brought about by  In the continuing Arab–Israeli conflict, although the initial cease fire had been implemented to end active conflict in the Yom Kippur War, Kissinger's continuing shuttle diplomacy was showing little progress. Ford considered it "stalling" and wrote, "Their sraelitactics frustrated the Egyptians and made me mad as hell." During Kissinger's shuttle to Israel in early March 1975, a last minute reversal to consider further withdrawal, prompted a cable from Ford to Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin, which included:
On March 24, Ford informed congressional leaders of both parties of the reassessment of the administration's policies in the Middle East. In practical terms, "reassessment" meant canceling or suspending further aid to Israel. For six months between March and September 1975, the United States refused to conclude any new arms agreements with Israel. Rabin notes it was "an innocent-sounding term that heralded one of the worst periods in American-Israeli relations". The announced reassessments upset the American Jewish community and Israel's well-wishers in Congress. On May 21, Ford "experienced a real shock" when seventy-six U.S. senators wrote him a letter urging him to be "responsive" to Israel's request for $2.59 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ) in military and economic aid. Ford felt truly annoyed and thought the chance for peace was jeopardized. It was, since the September 1974 ban on arms sales to Turkey, the second major congressional intrusion upon the President's foreign policy prerogatives. The following summer months were described by Ford as an American-Israeli "war of nerves" or "test of wills". After much bargaining, the Sinai Interim Agreement (Sinai II) was formally signed on September 1, and aid resumed.
In the continuing Arab–Israeli conflict, although the initial cease fire had been implemented to end active conflict in the Yom Kippur War, Kissinger's continuing shuttle diplomacy was showing little progress. Ford considered it "stalling" and wrote, "Their sraelitactics frustrated the Egyptians and made me mad as hell." During Kissinger's shuttle to Israel in early March 1975, a last minute reversal to consider further withdrawal, prompted a cable from Ford to Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin, which included:
On March 24, Ford informed congressional leaders of both parties of the reassessment of the administration's policies in the Middle East. In practical terms, "reassessment" meant canceling or suspending further aid to Israel. For six months between March and September 1975, the United States refused to conclude any new arms agreements with Israel. Rabin notes it was "an innocent-sounding term that heralded one of the worst periods in American-Israeli relations". The announced reassessments upset the American Jewish community and Israel's well-wishers in Congress. On May 21, Ford "experienced a real shock" when seventy-six U.S. senators wrote him a letter urging him to be "responsive" to Israel's request for $2.59 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ) in military and economic aid. Ford felt truly annoyed and thought the chance for peace was jeopardized. It was, since the September 1974 ban on arms sales to Turkey, the second major congressional intrusion upon the President's foreign policy prerogatives. The following summer months were described by Ford as an American-Israeli "war of nerves" or "test of wills". After much bargaining, the Sinai Interim Agreement (Sinai II) was formally signed on September 1, and aid resumed.
 One of Ford's greatest challenges was dealing with the continuing Vietnam War. American offensive operations against North Vietnam had ended with the
One of Ford's greatest challenges was dealing with the continuing Vietnam War. American offensive operations against North Vietnam had ended with the  The former Portuguese colony of East Timor declared its independence in 1975. Indonesian president
The former Portuguese colony of East Timor declared its independence in 1975. Indonesian president  Ford was the target of two assassination attempts during his presidency. In Sacramento, California, on September 5, 1975,
Ford was the target of two assassination attempts during his presidency. In Sacramento, California, on September 5, 1975,  In 1975, Ford appointed
In 1975, Ford appointed  Ford reluctantly agreed to run for office in 1976, but first he had to counter a challenge for the Republican party nomination. Former
Ford reluctantly agreed to run for office in 1976, but first he had to counter a challenge for the Republican party nomination. Former  Televised presidential debates were reintroduced for the first time since the 1960 election. As such, Ford became the first incumbent president to participate in one. Carter later attributed his victory in the election to the debates, saying they "gave the viewers reason to think that Jimmy Carter had something to offer". The turning point came in the second debate when Ford blundered by stating, "There is no Soviet domination of Eastern Europe and there never will be under a Ford Administration." Ford also said that he did not "believe that the Poles consider themselves dominated by the Soviet Union". In an interview years later, Ford said he had intended to imply that the Soviets would never crush the ''spirits'' of eastern Europeans seeking independence. However, the phrasing was so awkward that questioner Max Frankel was visibly incredulous at the response.
Televised presidential debates were reintroduced for the first time since the 1960 election. As such, Ford became the first incumbent president to participate in one. Carter later attributed his victory in the election to the debates, saying they "gave the viewers reason to think that Jimmy Carter had something to offer". The turning point came in the second debate when Ford blundered by stating, "There is no Soviet domination of Eastern Europe and there never will be under a Ford Administration." Ford also said that he did not "believe that the Poles consider themselves dominated by the Soviet Union". In an interview years later, Ford said he had intended to imply that the Soviets would never crush the ''spirits'' of eastern Europeans seeking independence. However, the phrasing was so awkward that questioner Max Frankel was visibly incredulous at the response.
 Ford died on December 26, 2006, at his home in Rancho Mirage, California, of arteriosclerotic cerebrovascular disease and diffuse arteriosclerosis. He had end-stage coronary artery disease and severe aortic stenosis and insufficiency, caused by calcific alteration of one of his heart valves. At the time of his death, Ford was the longest-lived U.S. president, having lived 93 years and 165 days (45 days longer than Ronald Reagan, whose record he surpassed). He died on the 34th anniversary of President Harry S. Truman's death; he was the last surviving member of the Warren Commission.
On December 30, 2006, Ford became the 11th U.S. president to lie in state in the Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol. A state funeral and memorial services were held at the National Cathedral in Washington, D.C., on Tuesday, January 2, 2007. After the service, Ford was interred at his Presidential Museum in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Scouting was so important to Ford that his family asked for Scouts to participate in his funeral. A few selected Scouts served as ushers inside the National Cathedral. About 400 Eagle Scouts were part of the funeral procession, where they formed an honor guard as the casket went by in front of the museum.
Ford selected the song to be played during his funeral procession at the U.S. Capitol. After his death in December 2006, the
Ford died on December 26, 2006, at his home in Rancho Mirage, California, of arteriosclerotic cerebrovascular disease and diffuse arteriosclerosis. He had end-stage coronary artery disease and severe aortic stenosis and insufficiency, caused by calcific alteration of one of his heart valves. At the time of his death, Ford was the longest-lived U.S. president, having lived 93 years and 165 days (45 days longer than Ronald Reagan, whose record he surpassed). He died on the 34th anniversary of President Harry S. Truman's death; he was the last surviving member of the Warren Commission.
On December 30, 2006, Ford became the 11th U.S. president to lie in state in the Rotunda of the U.S. Capitol. A state funeral and memorial services were held at the National Cathedral in Washington, D.C., on Tuesday, January 2, 2007. After the service, Ford was interred at his Presidential Museum in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Scouting was so important to Ford that his family asked for Scouts to participate in his funeral. A few selected Scouts served as ushers inside the National Cathedral. About 400 Eagle Scouts were part of the funeral procession, where they formed an honor guard as the casket went by in front of the museum.
Ford selected the song to be played during his funeral procession at the U.S. Capitol. After his death in December 2006, the  On October 15, 1948, Ford married
On October 15, 1948, Ford married  Ford is the only person to hold the presidential office without being elected as either president or vice president. The choice of Ford to fill the vacant vice-presidency was based on Ford's reputation for openness and honesty. "In all the years I sat in the House, I never knew Mr. Ford to make a dishonest statement nor a statement part-true and part-false. He never attempted to shade a statement, and I never heard him utter an unkind word," said Martha Griffiths.
The trust the American public had in him was rapidly and severely tarnished by his pardon of Nixon. Nonetheless, many grant in hindsight that he had respectably discharged with considerable dignity a great responsibility that he had not sought.
In spite of his athletic record and remarkable career accomplishments, Ford acquired a reputation as a clumsy, likable, and simple-minded everyman. An incident in 1975, when he tripped while exiting Air Force One in Austria, was famously and repeatedly parodied by Chevy Chase on '' Saturday Night Live'', cementing Ford's image as a klutz. Other pieces of the everyman image were attributed to his inevitable comparison with Nixon, his Midwestern stodginess and his self-deprecation.
Ford has notably been portrayed in two television productions which included a central focus on his wife: the
Ford is the only person to hold the presidential office without being elected as either president or vice president. The choice of Ford to fill the vacant vice-presidency was based on Ford's reputation for openness and honesty. "In all the years I sat in the House, I never knew Mr. Ford to make a dishonest statement nor a statement part-true and part-false. He never attempted to shade a statement, and I never heard him utter an unkind word," said Martha Griffiths.
The trust the American public had in him was rapidly and severely tarnished by his pardon of Nixon. Nonetheless, many grant in hindsight that he had respectably discharged with considerable dignity a great responsibility that he had not sought.
In spite of his athletic record and remarkable career accomplishments, Ford acquired a reputation as a clumsy, likable, and simple-minded everyman. An incident in 1975, when he tripped while exiting Air Force One in Austria, was famously and repeatedly parodied by Chevy Chase on '' Saturday Night Live'', cementing Ford's image as a klutz. Other pieces of the everyman image were attributed to his inevitable comparison with Nixon, his Midwestern stodginess and his self-deprecation.
Ford has notably been portrayed in two television productions which included a central focus on his wife: the  First Class of the Order of the Cross of Terra Mariana (7 January 1997)
*Ford received the Distinguished Eagle Scout Award in May 1970, as well as the Silver Buffalo Award, from the Boy Scouts of America.
*In 1974, he also received the highest distinction of the Scout Association of Japan, the Golden Pheasant Award. In 1985, he received the 1985 Old Tom Morris Award from the Golf Course Superintendents Association of America, GCSAA's highest honor. In 1992, the U.S. Navy Memorial Foundation awarded Ford its Lone Sailor Award for his naval service and his subsequent government service. In 1999, Ford was honored with a Golden Palm Star on the Palm Springs Walk of Stars. Also in 1999, Ford was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Bill Clinton. In 2001, he was presented with the John F. Kennedy
First Class of the Order of the Cross of Terra Mariana (7 January 1997)
*Ford received the Distinguished Eagle Scout Award in May 1970, as well as the Silver Buffalo Award, from the Boy Scouts of America.
*In 1974, he also received the highest distinction of the Scout Association of Japan, the Golden Pheasant Award. In 1985, he received the 1985 Old Tom Morris Award from the Golf Course Superintendents Association of America, GCSAA's highest honor. In 1992, the U.S. Navy Memorial Foundation awarded Ford its Lone Sailor Award for his naval service and his subsequent government service. In 1999, Ford was honored with a Golden Palm Star on the Palm Springs Walk of Stars. Also in 1999, Ford was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Bill Clinton. In 2001, he was presented with the John F. Kennedy