Javelin Throw At The African Championships In Athletics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a
Samnite and early Roman ''pilum''-type javelins
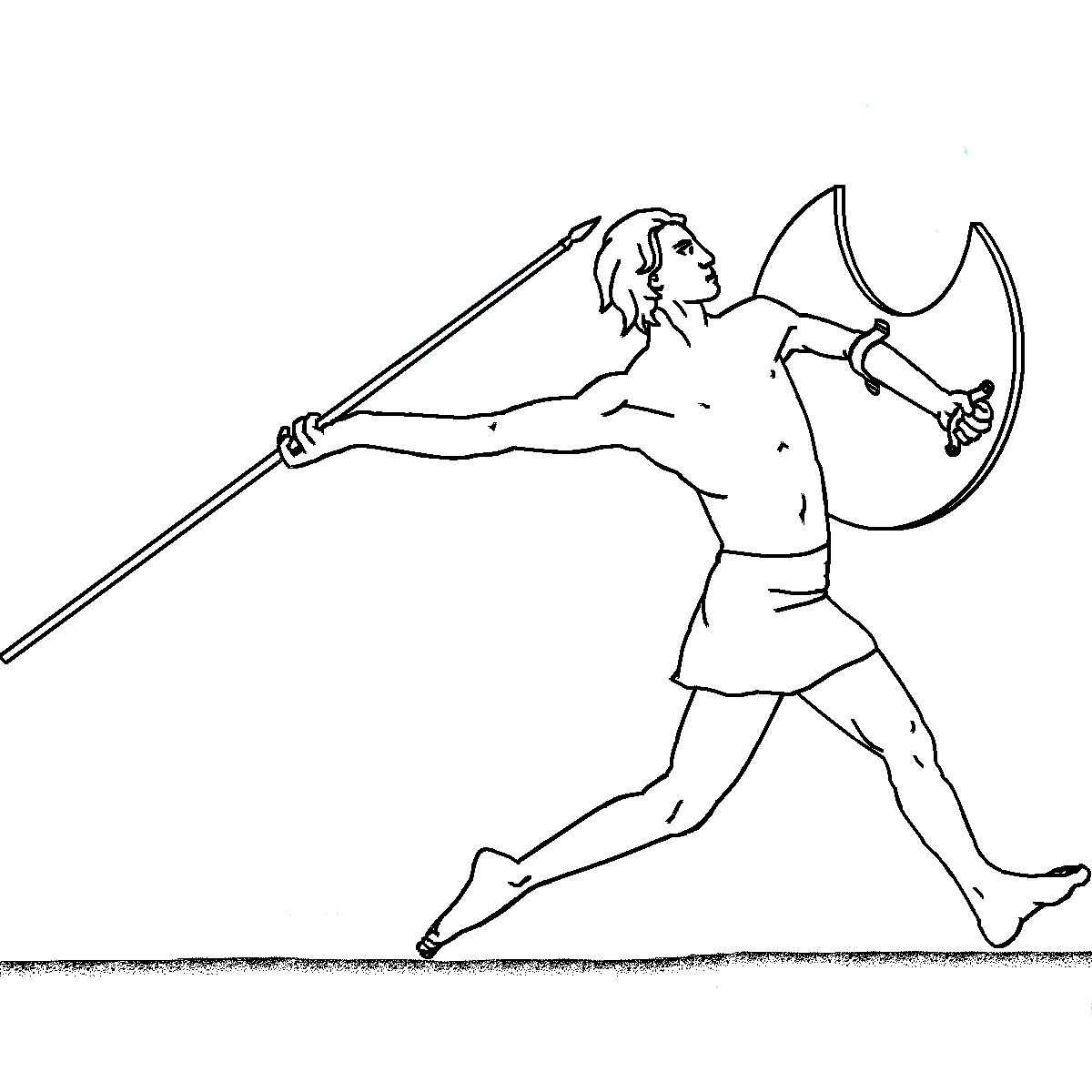
Picture of a Thracian Peltast with one javelin in his throwing hand and four javelins in his Pelte hand as additional ammunition
{{Pole weapons Projectiles Throwing weapons Ancient weapons Ancient Greek military equipment Ancient Roman legionary equipment Roman spears
 A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon
A ranged weapon is any weapon that can engage targets beyond hand-to-hand distance, i.e. at distances greater than the physical reach of the user holding the weapon itself. The act of using such a weapon is also known as shooting. It is someti ...
, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling
sling may refer to:
Places
*Sling, Anglesey, Wales
*Sling, Gloucestershire, England, a small village in the Forest of Dean
People with the name
* Otto Šling (1912–1952), repressed Czech communist functionary
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ...
, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum
An ''amentum'' (Greek ''ἀγκύλη'') was a leather strap attached to a javelin used in ancient Greek athletics, hunting, and warfare, which helped to increase the range and the stability of the javelin in flight. Stability in flight was impor ...
.
A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer.
The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages.
Prehistory
There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of theLower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in ...
. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen
Schöningen is a town of about 11,000 inhabitants in the district of Helmstedt, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Geography
The town is located on the southeastern rim of the Elm hill range, near the border with the state of Saxony-Anhalt. In its curren ...
, Germany. Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are about 400,000 years old. The excavated items were made of spruce (Picea) trunk and were between 1.83 and 2.25 metres long. They were manufactured with the maximum thickness and weight situated at the front end of the wooden shaft. The frontal centre of gravity suggests that these weapons were used as javelins. A fossilized horse shoulder blade with a projectile wound, dated to 500,000 years ago, was revealed in a gravel quarry in the village of Boxgrove
Boxgrove is a village, ecclesiastical parish and civil parish in the Chichester District of the English county of West Sussex, about north east of the city of Chichester. The village is just south of the A285 road which follows the line of the R ...
, England. Studies suggested that the wound was probably caused by a javelin.
Classical age
Ancient Egypt
In ''History of Ancient Egypt'': Volume 1 (1882), George Rawlinson depicts the javelin as an offensive weapon used by the Ancient Egyptian military. It was lighter in weight than that used by other nations. He describes the Ancient Egyptian javelin's features:It consisted of a long thin shaft, sometimes merely pointed, but generally armed with a head, which was either leaf-shaped, or like the head of a spear, or else four-sided, and attached to the shaft by projections at the angles.A strap or tasseled head was situated at the lower end of the javelin: it allowed the javelin thrower to recover his javelin after throwing it. Egyptian military trained from a young age in special military schools. Focusing on gymnastics to gain strength, hardiness and endurance in childhood, they learned to throw the javelin – along with practicing archery and the battle-axe – when they grew older, before entering a specific regiment. Javelins were carried by Egyptian light infantry, as a main weapon, and as an alternative to a spear or a bow and arrow, generally along with a shield. They also carried a curved sword, a club or a hatchet as a side-arm. An important part in battles is often assigned to javelin-men, "whose weapons seem to inflict death at every blow". One or multiple javelins were also sometimes carried by Egyptian war-chariots, in the quiver and/or the bow case. Beyond its military purpose, the javelin was likely also a hunting instrument, both to seek food and as a sport.
Ancient Greece
The peltasts, usually serving asskirmishers
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They are usually deployed in a skirmish line, an i ...
, were armed with several javelins, often with throwing straps to increase stand-off power. The peltasts hurled their javelins at the enemy's heavier troops, the hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with ...
phalanx, in order to break their lines so that their own army's hoplites could destroy the weakened enemy formation. In the battle of Lechaeum
The Battle of Lechaeum (391 BC) was an Athenian victory in the Corinthian War. In the battle, the Athenian general Iphicrates took advantage of the fact that a Spartan hoplite regiment operating near Corinth was moving in the open without the ...
, the Athenian general Iphicrates
Iphicrates ( grc-gre, Ιφικράτης; c. 418 BC – c. 353 BC) was an Athenian general, who flourished in the earlier half of the 4th century BC. He is credited with important infantry reforms that revolutionized ancient Greek warfare by ...
took advantage of the fact that a Spartan hoplite phalanx operating near Corinth was moving in the open field without the protection of any missile-throwing troops. He decided to ambush it with his force of peltasts. By launching repeated hit-and-run attacks against the Spartan formation, Iphicrates and his men were able to wear the Spartans down, eventually routing them and killing just under half. This marked the first recorded occasion in ancient Greek military history in which a force entirely made up of peltasts had defeated a force of hoplites.
The thureophoroi
The ''thyreophoroi'' or ''thureophoroi'' ( el, θυρεοφόροι; singular: ''thureophoros''/''thyreophoros'', θυρεοφόρος) were a type of infantry soldier, common in the 3rd to 1st centuries BC, who carried a large oval shield called a ...
and thorakitai, who gradually replaced the peltasts, carried javelins in addition to a long thrusting spear and a short sword.
Javelins were often used as an effective hunting weapon, the strap adding enough power to take down large game. Javelins were also used in the Ancient Olympics
The ancient Olympic Games (Ὀλυμπιακοὶ ἀγῶνες; la, Olympia, neuter plural: "the Olympics") were a series of Athletics (sport), athletic competitions among representatives of polis, city-states and were one of the Panhellenic ...
and other Panhellenic games
Panhellenic Games is the collective term for four separate sports festivals held in ancient Greece. The four Games were:
Description
The Olympiad was one of the ways the Greeks measured time. The Olympic Games were used as a starting point, year ...
. They were hurled in a certain direction and whoever hurled it the farthest, as long as it hit tip-first, won that game.
Ancient Rome
Republic and early empire
In 387 BC, the Gauls invaded Italy, inflicted a crushing defeat on theRoman Republican army
The Roman army of the mid-Republic, also called the manipular Roman army or the Polybian army, refers to the armed forces deployed by the mid-Roman Republic, from the end of the Samnite Wars (290 BC) to the end of the Social War (91–88 BC), Soc ...
, and sacked Rome. After this defeat, the Romans undertook a comprehensive reform of their army and changed the basic tactical formation from the Greek-style phalanx armed with the ''hasta
Hasta may refer to:
Latin
*Hasta (spear)
*Hasta Pompeia, a Roman town today known as Asti
Sanskrit
*Hasta (hand), a Sanskrit word meaning hand gesture or position
*Hasta (unit), a measure of length
*Hasta (nakshatra), the thirteenth nakshatra of ...
'' spear and the '' clipeus'' round shield to a more flexible three-line formation. The '' hastati'' stood in the first line, the '' principes'' in the second line and the '' triarii'' in the third line. While the ''triarii'' were still armed with ''hastae'', the ''hastati'' and the ''principes'' were rearmed with short swords and heavy javelins. Each soldier from the ''hastati'' and ''principes'' lines carried two javelins. This heavy javelin, known as a ''pilum
The ''pilum'' (; plural ''pila'') was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about long overall, consisting of an iron shank about in diameter and long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft ...
'' (plural ''pila''), was about two metres long overall, consisting of an iron shank, about 7 mm in diameter and 60 cm long, with pyramidal head, secured to a wooden shaft. The iron shank was either socketed or, more usually, widened to a flat tang
Tang or TANG most often refers to:
* Tang dynasty
* Tang (drink mix)
Tang or TANG may also refer to:
Chinese states and dynasties
* Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) b ...
. A ''pilum'' usually weighed between , with the versions produced during the empire being somewhat lighter. Pictorial evidence suggests that some versions of the weapon were weighted with a lead ball at the base of the shank in order to increase penetrative power, but no archaeological specimens have been found. Recent experiments have shown ''pila'' to have a range of about 30 metres, although the effective range is only 15 to 20 metres. ''Pila'' were sometimes referred to as "javelins", but the archaic term for the javelin was "'' verutum''".
From the third century BC, the Roman legion added a skirmisher type of soldier to its tactical formation. The '' velites'' were light infantry armed with short swords (the '' gladius'' or '' pugio''), small round shields, and several small javelins. These javelins were called "''veruta''" (singular ''verutum''). The ''velites'' typically drew near the enemy, hurled javelins against their formation, and then retreated behind the legion's heavier infantry. The ''velites'' were considered highly effective in turning back war elephants, on account of discharging a hail of javelins at some range and not presenting a "block" that could be trampled on or otherwise smashed – unlike the close-order infantry behind them. At the Battle of Zama in 202 BC, the javelin-throwing ''velites'' proved their worth and were no doubt critical in helping to herd Hannibal's war elephants through the formation to be slaughtered. The ''velites'' would slowly have been either disbanded or re-equipped as more-heavily armed legionaries from the time when Gaius Marius and other Roman generals reorganised the army in the late second and early first centuries BC. Their role would most likely have been taken by irregular auxiliary troops as the republic expanded overseas. The '' verutum'' was a cheaper missile weapon than the ''pilum''. The ''verutum'' was a short-range weapon, with a simply made head of soft iron.
Legionaries of the late republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
and early empire often carried two ''pila'', with one sometimes being lighter than the other. Standard tactics called for a Roman soldier to throw his ''pilum'' (both if there was time) at the enemy just before charging to engage with his '' gladius''. Some ''pila'' had small hand-guards, to protect the wielder if he intended to use it as a melee weapon, but it does not appear that this was common.
Late Empire
In the late Roman Empire, the Roman infantry came to use a differently-shaped javelin from the earlierpilum
The ''pilum'' (; plural ''pila'') was a javelin commonly used by the Roman army in ancient times. It was generally about long overall, consisting of an iron shank about in diameter and long with a pyramidal head, attached to a wooden shaft ...
. This javelin was lighter and had a greater range. Called a plumbata
''Plumbatae'' or ''martiobarbuli'' were lead-weighted darts carried by infantrymen in Antiquity and the Middle Ages.
History
The first examples seem to have been carried by the Ancient Greeks from about 500 BC onwards, but the best-known us ...
, it resembled a thick stocky arrow, fletched with leather vanes to provide stability and rotation in flight (which increased accuracy). To overcome its comparatively small mass, the plumbata was fitted with an oval-shaped lead weight socketed around the shaft just forward of the center of balance, giving the weapon its name. Even so, plumbatae were much lighter than pila, and would not have had the armour penetration or shield transfixing capabilities of their earlier counterparts.
Two or three plumbatae were typically clipped to a small wooden bracket on the inside of the large oval or round shields used at the time. Massed troops would unclip and hurl plumbatae as the enemy neared, hopefully stalling their movement and morale by making them clump together and huddle under their shields. With the enemy deprived of rapid movement and their visibility impaired by their own raised shields, the Roman troops were then better placed to exploit the tactical situation. It is unlikely plumbatae were viewed by the Romans as the killing blow, but more as a means of stalling the enemy at ranges greater than previously provided by the heavier and shorter ranged pilum.
Gaul
The Gallic cavalry used to hurl several javelin volleys to soften the enemy before a frontal attack. The Gallic cavalry used their javelins in a tactic similar to that of horse archers' Parthian shot. The Gauls knew how to turn on horseback to throw javelins backwards while appearing to retreat.Iberia
The Hispanic cavalry was a light cavalry armed with '' falcatas'' and several light javelins. The Cantabri tribes invented a military tactic to maximize the advantages of the combination between horse and javelin. In this tactic the horsemen rode around in circles, toward and away from the enemy, continually hurling javelins. The tactic was usually employed against heavy infantry. The constant movement of the horsemen gave them an advantage against slow infantry and made them hard to target. The maneuver was designed to harass and taunt the enemy forces, disrupting close formations. This was commonly used against enemy infantry, especially the heavily armed and slow moving legions of the Romans. This tactic came to be known as the Cantabrian circle. In the late Republic various auxiliary cavalry completely replaced the Italian cavalry contingents and the Hispanic auxiliary cavalry was considered the best.Numidia
The Numidians were indigenous tribes of northwest Africa. The Numidian cavalry was a light cavalry usually operating as skirmishers. The Numidian horseman was armed with a small shield and several javelins. The Numidians had a reputation as swift horsemen, cunning soldiers and excellent javelin throwers. It is said that Jugurtha, the Numidian king "...took part in the national pursuits of riding, javelin throwing and competed with other young men in running." allust The Jugurthine War: 6 The Numidian Cavalry served as mercenaries in theCarthaginian Army The term Carthaginian ( la, Carthaginiensis ) usually refers to a citizen of Ancient Carthage.
It can also refer to:
* Carthaginian (ship), a three-masted schooner built in 1921
* Insurgent privateer
Insurgent privateers ( es, corsarios insurgen ...
and played a key role in assisting both Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
and Scipio during the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
.
Middle ages
Norse
There is some literary and archeological evidence that the Norse were familiar with and used the javelin for hunting and warfare, but they commonly used a spear designed for both throwing and thrusting. The Old Norse word for javelin was ''frakka''.Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxon term for javelin was ''france''. InAnglo-Saxon warfare
The period of Anglo-Saxon warfare spans the 5th century AD to the 11th in England. Its technology and tactics resemble those of other European cultural areas of the Early Medieval Period, although the Anglo-Saxons, unlike the Continental Germani ...
, soldiers usually formed a shield wall
A shield wall ( or in Old English, in Old Norse) is a military formation that was common in ancient and medieval warfare. There were many slight variations of this formation,
but the common factor was soldiers standing shoulder to shoulder ...
and used heavy weapons like Danish axes, sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
s and spears. Javelins, including barbed angon
The ''angon'' (Medieval Greek , Old High German ''ango'', Old English ''anga'' "hook, point, spike") was a type of javelin used during the Early Middle Ages by the Anglo-Saxons, Franks, Goths, and other Germanic peoples. It was similar to, and p ...
s, were used as an offensive weapon from behind the shield wall or by warriors who left the protective formation and attacked the enemy as skirmishers.
Designed to be difficult to remove from either flesh or wood, the Angon
The ''angon'' (Medieval Greek , Old High German ''ango'', Old English ''anga'' "hook, point, spike") was a type of javelin used during the Early Middle Ages by the Anglo-Saxons, Franks, Goths, and other Germanic peoples. It was similar to, and p ...
javelin used by Anglo-Saxon warriors was an effective means of disabling an opponent or his shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of a ...
, thus having the potential to disrupt opposing shield-walls.
Iberia
The Almogavars were a class of Aragonese infantrymen armed with a short sword, a shield and two heavy javelins, known as azcona. The equipment resembled that of a Roman legionary and the use of the heavy javelins was much the same. TheJinetes
''Jinete'' () is Spanish for " horseman", especially in the context of light cavalry.
Etymology
The word Jinete (of Berber ''zenata'') designates, in Castilian and the Provençal dialect of Occitan language, those who show great skill and riding ...
were Arabic light horsemen armed with several javelins, a sword, and a shield. They were proficient at skirmishing and rapid maneuver, and played an important role in Arabic mounted warfare throughout the Reconquista until the sixteenth century. These units were widespread among the Italian infantrymen of the fifteenth century.
Wales
TheWelsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
, particularly those of North Wales, used the javelin as one of their main weapons. During the Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
and later English invasions, the primary Welsh tactic was to rain javelins on the tired, hungry, and heavily armoured English troops and then retreat into the mountains or woods before the English troops could pursue and attack them. This tactic was very successful, since it demoralized and damaged the English armies while the Welsh ranks suffered little.
Ireland
The '' kern'' of Ireland used javelins as their main weapon as they accompanied the more heavily armoured '' galloglass''.Chinese
Various kingdoms and dynasties inChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
have used javelins, such as the iron-headed javelin of the Qing dynasty.
Qi Jiguang
Qi Jiguang (, November 12, 1528 – January 17, 1588), courtesy name Yuanjing, art names Nantang and Mengzhu, posthumous name Wuyi, was a Chinese military general and writer of the Ming dynasty. He is best known for leading the defense on the ...
's anti-pirate army included javelin throwers with shields.
Modern age
Africa
Many African kingdoms have used the javelin as their main weapon since ancient times. TypicalAfrican warfare
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
was based on ritualized stand-off encounters involving throwing javelins without advancing for close combat. In the flag of Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
there is a shield and two javelins, which symbolize the protection from the country's enemies.
Zulu
The Zulu warriors used a long version of theassegai
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber languages, Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", French language, Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, ...
javelin as their primary weapon. The Zulu legendary leader Shaka initiated military reforms
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
in which a short stabbing spear, with a long, swordlike spearhead named iklwa
An assegai or assagai (Arabic ''az-zaġāyah'', Berber ''zaġāya'' "spear", Old French ''azagaie'', Spanish ''azagaya'', Italian ''zagaglia'', Middle English ''lancegay'') is a pole weapon used for throwing, usually a light spear or javelin m ...
, had become the Zulu warrior's main weapon and was used as a mêlée weapon
A melee weapon, hand weapon or close combat weapon is any handheld weapon used in hand-to-hand combat, i.e. for use within the direct physical reach of the weapon itself, essentially functioning as an additional (and more impactful) extension of t ...
. The assegai was not discarded, but was used for an initial missile assault. With the larger shields, introduced by Shaka to the Zulu army, the short spears used as stabbing swords and the opening phase of javelin attack; the Zulu regiments were quite similar to the Roman legion with its Scutum
The ''scutum'' (; plural ''scuta'') was a type of shield used among Italic peoples in antiquity, most notably by the army of ancient Rome starting about the fourth century BC.
The Romans adopted it when they switched from the military formati ...
, Gladius and Pilum tactical combination.
Mythology
Norse mythology
In Norse mythology, Odin, the chief god, carried a javelin or spear called Gungnir. It was created by a group of dwarves known as theSons of Ivaldi
In Norse mythology, the Sons of Ivaldi are a group of dwarfs who fashion Skíðblaðnir, the flying ship of Freyr, Gungnir, the spear belonging to Odin, along with the golden hair for Sif to replace what Loki had cut off.
According to ''Skál ...
who also fashioned the ship of Freyr called Skidbladnir and the golden hair of Sif. It had the property of always finding its mark ("the spear never stopped in its thrust"). During the final conflict of Ragnarok between the gods and giants, Odin will use Gungnir to attack the wolf Fenrir before being devoured by him.
During the war (and subsequent alliance) between the Aesir and Vanir at the dawn of time, Odin hurled a javelin over the enemy host which, according to custom, was thought to bring good fortune or victory to the thrower. Odin also wounded himself with a spear while hanging from Yggdrasil, the World Tree
The world tree is a motif present in several religions and mythologies, particularly Indo-European religions, Siberian religions, and Native American religions. The world tree is represented as a colossal tree which supports the heavens, thereb ...
, in his ritual quest for knowledge but in neither case is the weapon referred to specifically as Gungnir.
When the god Baldr
Baldr (also Balder, Baldur) is a god in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, Baldr (Old Norse: ) is a son of the god Odin and the goddess Frigg, and has numerous brothers, such as Thor and Váli. In wider Germanic mythology, the god was kno ...
began to have prophetic dreams of his own death, his mother Frigg extracted an oath from all things in nature not to harm him. However, she neglected the mistletoe
Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemiparasitic plants in the order Santalales. They are attached to their host tree or shrub by a structure called the haustorium, through which they extract water and nutrients from the host plant.
...
, thinking it was too young to make, let alone respect, such a solemn vow. When Loki
Loki is a god in Norse mythology. According to some sources, Loki is the son of Fárbauti (a jötunn) and Laufey (mentioned as a goddess), and the brother of Helblindi and Býleistr. Loki is married to Sigyn and they have two sons, Narfi or Na ...
learned of this weakness, he had a javelin or dart
Dart or DART may refer to:
* Dart, the equipment in the game of darts
Arts, entertainment and media
* Dart (comics), an Image Comics superhero
* Dart, a character from ''G.I. Joe''
* Dart, a ''Thomas & Friends'' railway engine character
* Dar ...
made from one of its branches and tricked Hod
Hod or HOD may refer to:
* Brick hod, a long-handled box for carrying bricks or mortar
* Coal scuttle, bucket-like container for carrying coal
* Hawk (plasterer's tool), used to hold plaster
* a container used to hold clams when clam digging
* ...
, the blind god, into hurling it at Baldr and causing his death.Faulkes (1995), pp. 48–49.
Lusitanian mythology
The godRunesocesius
Runesocesius was a deity whose name appears on an inscription from the region of Évora, the Roman ''Ebora'' in modern Portugal in the area inhabited by the Celtici in Lusitania. He has generally been thought of as a Lusitanians, Lusitanian god.
D ...
is identified as a "god of the javelin".
See also
Notes
Further reading
* Anglim, Simon et al., (2003), Fighting Techniques of the Ancient World (3000 B.C. to 500 A.D.): Equipment, Combat Skills, and Tactics, Thomas Dunne Books. *Bennett, Matthew et al., (2005), Fighting Techniques of the Medieval World: Equipment, Combat Skills and Tactics, Thomas Dunne Books. * Connolly, Peter, (2006), Greece and Rome at War, Greenhill Books, 2nd edition. * Jorgensen, rister et al., (2006), Fighting Techniques of the Early Modern World: Equipment, Combat Skills, and Tactics, Thomas Dunne Books. * Saunders, J. J., (1972), A History of Medieval Islam, Routledge. * Warry, John Gibson, (1995), Warfare in the Classical World: An Illustrated Encyclopedia of Weapons, Warriors and Warfare in the Ancient Civilisations of Greece and Rome, University of Oklahoma Press. *Rawlinson, G., (1882), History of Ancient Egypt, E. Cassino. *Bothwell Gosse, A. (1915), The Civilization of the Ancient Egyptians, T.C. & E.C. Jack.External links
Samnite and early Roman ''pilum''-type javelins
Picture of a Thracian Peltast with one javelin in his throwing hand and four javelins in his Pelte hand as additional ammunition
{{Pole weapons Projectiles Throwing weapons Ancient weapons Ancient Greek military equipment Ancient Roman legionary equipment Roman spears