James Harmon Ward on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In 1860, Ward served at the
In 1860, Ward served at the
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ward, James Harmon Union military personnel killed in the American Civil War Norwich University alumni United States Navy personnel of the Mexican–American War Union Navy officers 1806 births 1861 deaths Military personnel from Hartford, Connecticut People of Connecticut in the American Civil War United States Naval Academy faculty 19th-century American writers American textbook writers 19th-century American male writers
Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
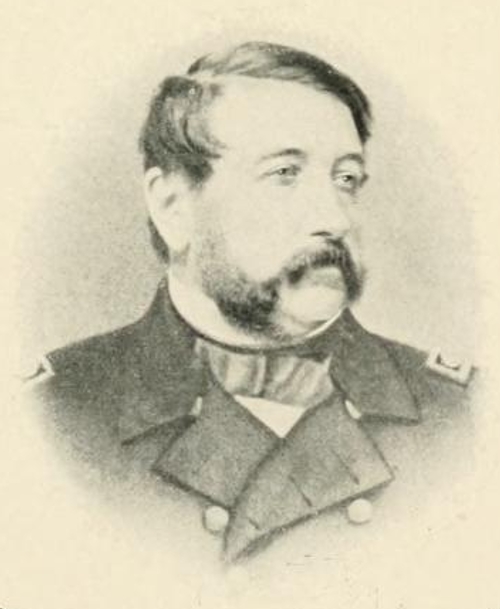
James Harmon Ward (September 25, 1806 – June 27, 1861) was the first officer of the United States Navy who was killed during the American Civil War.
Biography
Born atHartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It was the seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960. It is the core city in the Greater Hartford metropolitan area. Census estimates since the ...
, Ward received his early educational training in Connecticut common schools before attending the American Literary Scientific and Military Academy
Norwich University – The Military College of Vermont is a private senior military college in Northfield, Vermont. It is the oldest private and senior military college in the United States and offers bachelor's and master's degrees on-campus ...
at Norwich, Vermont. After graduating in 1823, Ward accepted an appointment as a midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Afr ...
in the Navy on March 4, 1823. Subsequently, he served on the frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
''Constitution'' during a four-year Mediterranean cruise and then received a year's leave of absence for scientific studies at Washington College, Hartford, Connecticut (now Trinity College).
When Ward returned to sea, he served once more in the Mediterranean and then saw duty off the African coast in interdicting the slave trade. He next served in the West Indies, helping to prevent a resurgence of piracy.
Upon his return to the United States, he taught courses in ordnance and gunnery at the Naval School
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and ...
at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. These courses were later published as ''An Elementary Course of Instruction in Ordnance and Gunnery''.
On October 10, 1845, the new Naval Academy opened in Annapolis, Maryland
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east o ...
; Lt. Ward was one of the five founders of this naval academy. He was one of the first line officers to pass along the benefits of his own experience to young midshipmen. One of the most scholarly officers of the Navy of his day, Ward held the office of executive officer (a post which later became that of the Commandant of Midshipmen), with collateral duties as instructor of gunnery and steam engineering.
The advent of the war with Mexico
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
prompted many naval officers and men to seek assignments on ships serving in Mexican waters. Detached from the Academy, Ward took command of the in 1847 and served in that capacity for the duration of the war. After a period spent waiting for orders, he was given command of the steamer in 1848 and remained on her through 1850.
After intermittent periods awaiting orders and serving at the Washington and Philadelphia Navy Yards, Ward took command of the and took her to the African coast to hunt slave ships. During this time, in his off-duty hours, he proceeded to work on another textbook—''A Manual of Naval Tactics''—a scholarly work which would run to four editions after its initial publication in 1859.


 In 1860, Ward served at the
In 1860, Ward served at the New York Navy Yard
The Brooklyn Navy Yard (originally known as the New York Navy Yard) is a shipyard and industrial complex located in northwest Brooklyn in New York City, New York (state), New York. The Navy Yard is located on the East River in Wallabout Bay, a ...
, where he wrote a popular treatise on steam engineering
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporizatio ...
, entitled ''Steam for the Million''. In the spring of 1861, with the Southern states leaving the Union and Confederate forces mounting a siege at Fort Sumter, South Carolina, Gideon Welles summoned Ward to Washington to plan for a relief expedition for Sumter. Ward volunteered to lead it, but opposition, notably from General Winfield Scott (who perceived it as being futile), forced cancellation of the plans.
Ward pressed for front line service, proposing that a "flying squadron" be established in the Chesapeake Bay for use against Confederate naval and land forces threatening that area south of the Union capital. The idea was approved, and the squadron took shape. With the steamer ''Thomas Freeborn'' serving as Ward's flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
, the steamers ''Freelance'', ''Alliance'' plus three coastal survey ships made up his flotilla.
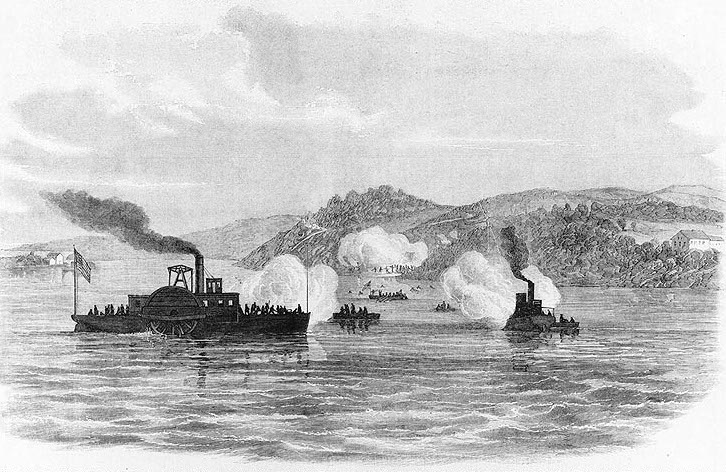
The newly composed unit—later known as the Potomac Flotilla—saw its first action on June 1, when guns from Ward's ships silenced Confederate shore batteries at Aquia Creek
Aquia Creek () is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the tidal segment of the Potomac River and is located in northern Virginia. The creek's h ...
, Virginia during the Battle of Aquia Creek. On June 27, at the Battle of Mathias Point, Ward sent a landing party ashore to dislodge Southern forces from another battery at Mathias Point
Mathias Point () is a point about north of Allen Point, Montagu Island, in the South Sandwich Islands. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for W.A. Mathias, Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval ...
, in King George County, Virginia
King George County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population sits at 26,723. Its county seat is the town of King George.
The county's largest employer is the U.S. Naval Surface Warfare Center ...
, but it encountered heavy resistance. The Federals gave up the attack and retired under heavy sniper and cannon fire to their ships. Ward brought his flotilla in close to the shoreline to provide gunfire support for the retreating landing party. As he was sighting the bow gun in his flagship, ''Thomas Freeborn'', Ward was struck by a bullet in his abdomen and fell to the deck, mortally wounded. He died within an hour.
He was the great-grandfather of actor Andy Devine.
Namesakes
USS ''Ward'' (DD-139) was named for him, as was Fort Ward, one of the defenses of Washington during the American Civil War. Ward Hall, site of the US Naval Academy's computing center, is named after James Ward, first commandant of midshipmen.See also
* Battle of Mathias PointReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ward, James Harmon Union military personnel killed in the American Civil War Norwich University alumni United States Navy personnel of the Mexican–American War Union Navy officers 1806 births 1861 deaths Military personnel from Hartford, Connecticut People of Connecticut in the American Civil War United States Naval Academy faculty 19th-century American writers American textbook writers 19th-century American male writers