Jagiellonian dynasty on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a 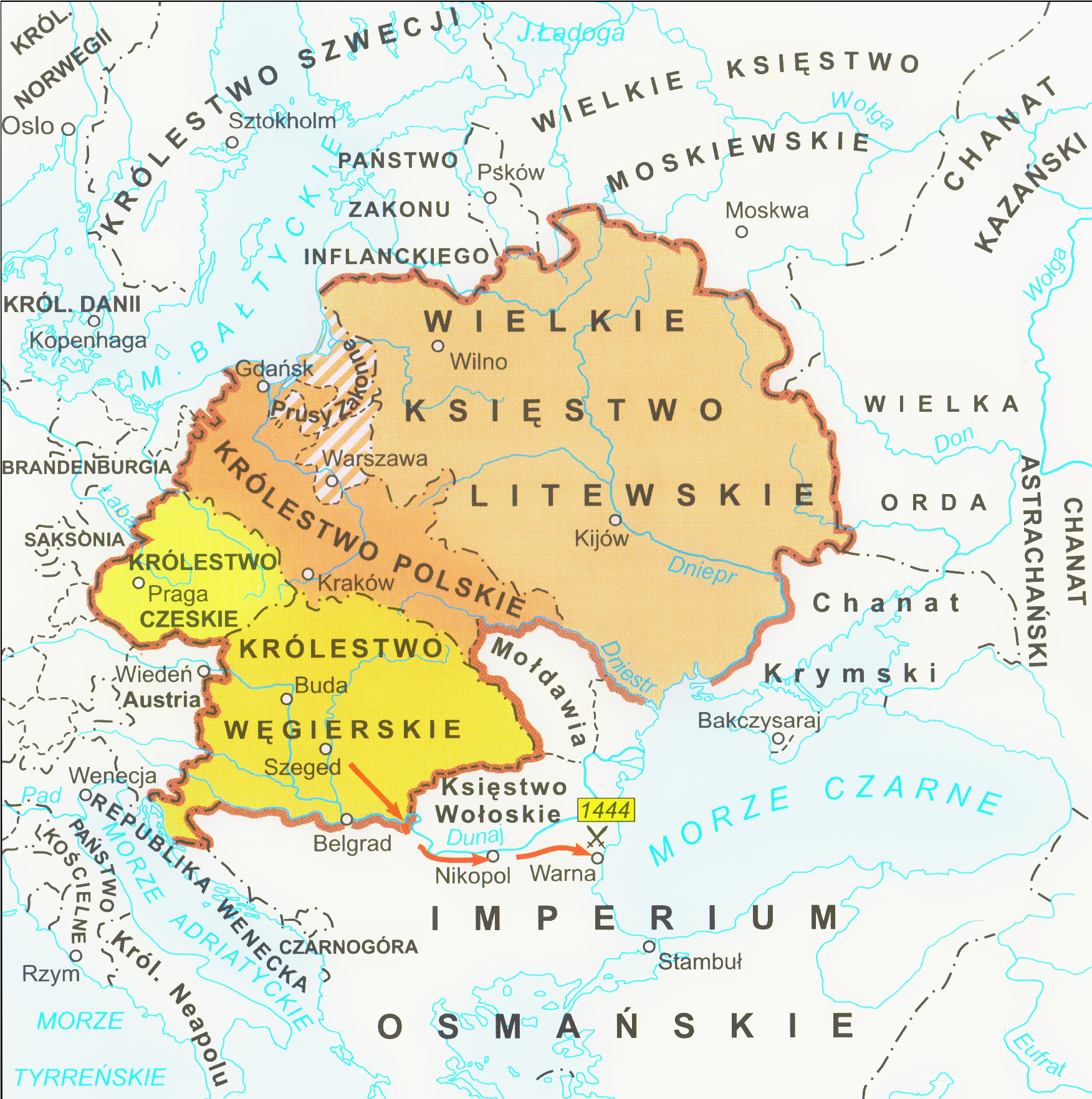
 In 1385 the
In 1385 the
 The Great War of 1409–1411, precipitated by the Lithuanian uprising in the Order controlled
The Great War of 1409–1411, precipitated by the Lithuanian uprising in the Order controlled
 The sudden death of Sigismund Kęstutaitis left the office of the
The sudden death of Sigismund Kęstutaitis left the office of the
cadet branch
In history and heraldry, a cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets—realm, ti ...
of the Lithuanian ducal dynasty of Gediminids
The House of Gediminid or simply the Gediminids ( lt, Gediminaičiai, sgs, Gedėmėnātē, be, Гедзімінавічы, pl, Giedyminowicze, uk, Гедиміновичі;) were a dynasty of monarchs in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that reig ...
upon reception by Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Kingdom of Lithuania, Lithuania, which was established as an Absolute monarchy, absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three Duke, ducal D ...
, of baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
as Władysław in 1386, which paved the way to his ensuing marriage to the Queen Regnant
A queen regnant (plural: queens regnant) is a female monarch, equivalent in rank and title to a king, who reigns '' suo jure'' (in her own right) over a realm known as a "kingdom"; as opposed to a queen consort, who is the wife of a reigni ...
Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Great ...
, resulting in his ascension to the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło (initially ruling ''jure uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title '' suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could beco ...
'' jointly with Hedwig until her death), and the effective promotion of his branch to a royal dynasty. The Jagiellons reigned in several Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
an countries between the 14th and 16th centuries. Members of the dynasty were Kings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
(1386–1572), Grand Dukes of Lithuania (1377–1392 and 1440–1572), Kings of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
(1440–1444 and 1490–1526), and Kings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
of Bohemia and imperial electors
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prin ...
(1471–1526).
The personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more State (polity), states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some e ...
between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (converted in 1569 with the Treaty of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the ...
into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ...
) is the reason for the common appellation " Poland–Lithuania" in discussions about the area from the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
onward. One Jagiellon, Władysław III of Poland, briefly ruled both Poland and Hungary (1440–1444), and two others ruled both Bohemia and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
(1490–1526) and then continued in the distaff line as a branch of the House of Habsburg.
The Polish "Golden Age", the period of the reigns of Sigismund I and Sigismund II, the last two Jagiellonian kings, or more generally the 16th century, is most often identified with the rise of the culture of Polish Renaissance. The cultural flowering had its material base in the prosperity of the elites, both the landed nobility and urban patriciate at such centers as Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 159 ...
and Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
.

Name
The name comes from Jogaila (), the first Grand Duke of Lithuania to become King of Poland. In Polish, the dynasty is known as and the patronymic form: ; inLithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
it is called , in Belarusian
Belarusian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Belarus
* Belarusians, people from Belarus, or of Belarusian descent
* A citizen of Belarus, see Demographics of Belarus
* Belarusian language
* Belarusian culture
* Belarusian cuisine
* Byelor ...
(), in Hungarian , and in Czech , as well as or in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
. Etymologically, the name Jogaila means "strong rider," from the Lithuanian words (to ride) and (strong, powerful).
Pre-dynasty background
The rule of Piasts, the earlier Polish ruling house (c. 962–1370) had ended with the death of KingCasimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great ( pl, Kazimierz III Wielki; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, and fought to retain the title in the Galicia-Volhynia Wars. He w ...
. Gediminids
The House of Gediminid or simply the Gediminids ( lt, Gediminaičiai, sgs, Gedėmėnātē, be, Гедзімінавічы, pl, Giedyminowicze, uk, Гедиміновичі;) were a dynasty of monarchs in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that reig ...
, the immediate predecessors of the first Jagiellonian, were rulers of medieval Lithuania with the title of '' Grand Duke''. Their realm, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
, was chiefly inhabited by Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Ame ...
and Ruthenians
Ruthenian and Ruthene are exonyms of Latin origin, formerly used in Eastern and Central Europe as common ethnonyms for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. The Latin term Rutheni was used in medieval sourc ...
.
Jogaila, the eponymous
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
first ruler of the Jagiellonian dynasty, started as the Grand Duke of Lithuania. As a result of the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; be, Крэўская унія, translit=Kreŭskaja unija; pl, unia w Krewie; lt, Krėvos sutartis) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made ...
he then converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
and married the 11-year-old Queen Jadwiga of Poland (daughter of King Louis I of Hungary from the Angevins Dynasty). Thereby he became jure uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title '' suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could beco ...
King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
as her co-ruler and founded the dynasty. Angevin rulers were the second and Jagiellonian
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
third dynasty of Polish Kings.
Kingdom of Poland
Jogaila and Władysław III
Polish–Lithuanian union
 In 1385 the
In 1385 the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; be, Крэўская унія, translit=Kreŭskaja unija; pl, unia w Krewie; lt, Krėvos sutartis) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made ...
was signed between Queen Jadwiga of Poland and Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, the last pagan state in Europe. The act arranged for Jogaila's baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
(after which Jogaila was known in Poland by his baptismal name, Władysław, and the Polish version of his Lithuanian name, Jagiełło) (Zamoyski, the Polish Way) and for the couple's marriage and constituted the beginning of the Polish–Lithuanian union Polish–Lithuanian can refer to:
* Polish–Lithuanian union (1385–1569)
* Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795)
* Polish-Lithuanian identity as used to describe groups, families, or individuals with histories in the Polish–Lithuani ...
. The Union strengthened both nations in their shared opposition to the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
and the growing threat of the Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Russia, Muscovite Rus' or Grand Principality of Moscow (russian: Великое княжество Московское, Velikoye knyazhestvo Moskovskoye; also known in English simply as Muscovy from the Lat ...
. Uniquely in Europe, the union connected two states geographically located on the opposite sides of the great civilizational divide between the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
* Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that i ...
or Latin, and the Eastern or Byzantine worlds. Krzysztof Baczkowski – ''Dzieje Polski późnośredniowiecznej (1370–1506)'' (History of Late Medieval Poland (1370–1506)), p. 55; Fogra, Kraków 1999,
The intention of the Union was to create a common state under Władysław II Jagiełło, but the Polish ruling oligarchy's idea of incorporation of Lithuania into Poland turned out to be unrealistic. There would be territorial disputes and warfare between Poland and Lithuania or Lithuanian factions; the Lithuanians at times had even found it expedient to conspire with the Teutonic Knights against the Poles. Geographic consequences of the dynastic union and the preferences of the Jagiellonian kings accelerated the process of reorientation of Polish territorial priorities to the east. The political influence of the Jagiellonian kings was diminishing during this period, which was accompanied by the ever-increasing role in central government and national affairs of landed nobility. The royal dynasty, however, had a stabilizing effect on Poland's politics. The Jagiellonian Era is often regarded as a period of maximum political power, great prosperity, and in its later stage, the Golden Age of Polish culture.
Struggle with the Teutonic Knights
 The Great War of 1409–1411, precipitated by the Lithuanian uprising in the Order controlled
The Great War of 1409–1411, precipitated by the Lithuanian uprising in the Order controlled Samogitia
Samogitia or Žemaitija ( Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
, included the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respe ...
(Tannenberg), where the Polish and Lithuanian-Rus' armies completely defeated the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
. The offensive that followed lost its impact with the ineffective siege of Malbork (Marienburg). The failure to take the fortress and eliminate the Teutonic (later Prussian) state had for Poland dire historic consequences in the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries. The Peace of Thorn (1411) had given Poland and Lithuania rather modest territorial adjustments, including Samogitia. Afterwards there were negotiations and peace deals that didn't hold, more military campaigns and arbitrations. One attempted, unresolved arbitration took place at the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance was a 15th-century ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance in present-day Germany. The council ended the Western Schism by deposing or accepting the res ...
.
Polish–Hungarian union
During theHussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the ...
(1420–1434), Jagiełło, Vytautas
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great (Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', Ol ...
and Sigismund Korybut
Sigismund Korybut ( lt, Žygimantas Kaributaitis; be, Жыгімонт Карыбутавіч; pl, Zygmunt Korybutowicz; cz, Zikmund Korybutovič; uk, Жиґимонт Корибутович or Сигізмунд Корибутович, 1395 � ...
were involved in political and military maneuvering concerning the Czech crown, offered by the Hussites
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Hu ...
first to Jagiełło in 1420. Zbigniew Oleśnicki became known as the leading opponent of a union with the Hussite Czech state.
The Jagiellonian dynasty was not entitled to automatic hereditary succession, as each new king had to be approved by nobility consensus. Władysław Jagiełło had two sons late in life from his last wife, Sophia of Halshany. In 1430 the nobility agreed to the succession of the future Władysław III, only after the King gave in and guaranteed the satisfaction of their new demands. In 1434 the old monarch died and his minor son Władysław was crowned; the Royal Council led by Bishop Oleśnicki undertook the regency duties. In 1438 the Czech anti- Habsburg opposition, mainly Hussite factions, offered the Czech crown to Jagiełło's younger son Casimir IV. The idea, accepted in Poland over Oleśnicki's objections, resulted in two unsuccessful Polish military expeditions to Bohemia.
After Vytautas
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great (Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', Ol ...
' death in 1430 Lithuania became embroiled in internal wars and conflicts with Poland. Casimir IV, sent as a boy by Władysław III on a mission there in 1440, was surprisingly proclaimed by the Lithuanians as a Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Kingdom of Lithuania, Lithuania, which was established as an Absolute monarchy, absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three Duke, ducal D ...
, and he stayed in Lithuania.
Oleśnicki gained the upper hand again and pursued his long-term objective of Poland's union with Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
. At that time the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
embarked on a new round of European conquests and threatened Hungary, which needed the powerful Polish–Lithuanian ally. In 1440 Władysław III assumed the Hungarian throne. Influenced by Julian Cesarini, the young king led the Hungarian army against the Ottomans in 1443 and again in 1444. Like Cesarini, Władysław III was killed at the Battle of Varna. Beginning toward the end of Jagiełło's life, Poland was practically governed by a magnate oligarchy led by Oleśnicki. The rule of the dignitaries was actively opposed by various ''szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
'' groups. Their leader Spytek of Melsztyn was killed during an armed confrontation in 1439, which allowed Oleśnicki to purge Poland of the remaining Hussite sympathizers and pursue his other objectives without significant opposition.
Casimir IV Jagiellon
In 1445Casimir
Casimir is classically an English, French and Latin form of the Polish name Kazimierz. Feminine forms are Casimira and Kazimiera. It means "proclaimer (from ''kazać'' to preach) of peace (''mir'')."
List of variations
*Belarusian: Казі ...
, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, was asked to assume the Polish throne vacated by the death of his brother Władysław. Casimir was a tough negotiator and did not accept the Polish nobility's conditions for his election. Casimir Jagiellon was the third and youngest son of King Władysław II Jagiełło and his fourth wife, Sophia of Halshany
Sophia (Sonka) of Halshany or Sophia Holshanska ( be, Соф'я Гальшанская, translit=Sofja Halšanskaja; lt, Sofija Alšėniškė; pl, Zofia Holszańska; – September 21, 1461 in Kraków) was a princess of Halshany and was Queen ...
. His father was already 65 at the time of Casimir's birth, and his brother Władysław III, three years his senior, was expected to become king before his majority. Strangely, little was done for his education; he was never taught Latin, nor was he trained for the responsibilities of office, despite the fact he was the only brother of the rightful sovereign. He often relied on his instinct and feelings and had little political knowledge, but shared a great interest in the diplomacy and economic affairs of the country. Throughout Casimir's youth, Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki was his mentor and tutor, however, the cleric felt a strong reluctance towards him, believing that he would be an unsuccessful monarch following Władysław's death.
 The sudden death of Sigismund Kęstutaitis left the office of the
The sudden death of Sigismund Kęstutaitis left the office of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
empty. The Voivode of Trakai
Trakai (; see names section for alternative and historic names) is a historic town and lake resort in Lithuania. It lies west of Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. Because of its proximity to Vilnius, Trakai is a popular tourist destination. ...
, Jonas Goštautas, and other magnates of Lithuania, supported Casimir as a candidate to the throne. However many Polish noblemen hoped that the thirteen-year-old boy would become a Vice-regent for the Polish King in Lithuania. Casimir was invited by the Lithuanian magnates to Lithuania, and when he arrived in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional u ...
in 1440, he was proclaimed as the Grand Duke of Lithuania on 29 June 1440 by the Council of Lords. Casimir succeeded his brother Władysław III (killed at the Battle of Varna in 1444) as King of Poland after a three-year interregnum on 25 June 1447. In 1454, he married Elisabeth of Austria, daughter of the late King of the Romans Albert II of Habsburg by his late wife Elisabeth of Bohemia. Her distant relative Frederick of Habsburg became Holy Roman Emperor and reigned as Frederick III until after Casimir's own death. The marriage strengthened the ties between the house of Jagiellon and the sovereigns of Hungary-Bohemia and put Casimir at odds with the Holy Roman Emperor through internal Habsburg rivalry. Becoming a King of Poland Casimir also freed himself from the control the Lithuaniaszlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
''. In time Kazimierz Jagiellończyk was able to remove from power Cardinal Oleśnicki and his group, basing his own power on the younger middle nobility camp instead. A conflict with the pope and the local Church hierarchy over the right to fill vacant bishop positions Casimir also resolved in his favor.
Thirteen Years' War (1454–66)
That same year, Casimir was approached by thePrussian Confederation
The Prussian Confederation (german: Preußischer Bund, pl, Związek Pruski) was an organization formed on 21 February 1440 at Kwidzyn (then officially ''Marienwerder'') by a group of 53 nobles and clergy and 19 cities in Prussia, to oppose the ...
for aid against the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
, which he promised, by making the separatist Prussian regions a protectorate of the Polish Kingdom
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central