Jacob Franquart on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Jacob Franquart or Jacob Franckaert the Younger (1582/83 – 6 January 1651 (buried)) was a Flemish architect, painter, print artist, draftsman, military engineer and poet.Jacques Franckaert (II)
Jacob Franquart or Jacob Franckaert the Younger (1582/83 – 6 January 1651 (buried)) was a Flemish architect, painter, print artist, draftsman, military engineer and poet.Jacques Franckaert (II)
at the
in: Dictionnaire des peintres belges His style is sometimes referred to as the Italo-Flemish style and became very popular in Flanders in the 17th century.J.-P. Esther, ''Francart (Franckaert; Francquart), Jacques (Jacob) (born ?Antwerp, ?1583; d Brussels, buried Jan 6, 1651)''
at Oxford Art Online Only a few paintings are attributed to him.Auguste Schoy, ''Histoire de l'influence italienne sur l'architecture dans les Pays-Bas''
1879, Brussels, F. Hayez, pp 245-262
 Some authors have stated that Franquart worked in the workshop of Rubens in Antwerp and that they were old friends. There is no documentary evidence for this. It is possible that the two artists got to know each other during their residence in Italy. Rubens' later purchase of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture...'' (First book of Architecture) published in 1616 was possibly a sign of his respect for Franquart. Rubens may also have acquired the book purely for practical reasons as at that time he was carrying out renovations on his newly purchased home in Antwerp.
One month after the publication of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' (''Premier livre d'architecture de Iaques Francart : contenant diuerses inuentions de portes seruiables à tous ceux qui désirent bastir et pour sculpteurs, tailleurs de pieres, escriniers, massons et autres : en trois langues'', in English ''First book of architecture of Jaques Francart : containing various inventions of doors useful to all those which wish to build and for sculptors, stone cutters, manufacturers of cases, masons and others: in three languages''), he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). Construction of the church had started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. Franquart's involvement in this project launched his career as an architect. In 1620 he was put in charge of the construction of the Augustine church in Brussels. In June 1621 he designed the funeral procession of the Archduke Albert. In 1629 he was commissioned to design the Beguinage Church in Mechelen. Franquart also rebuilt the church of Our Lady by the Dijle, Mechelen, by adding a choir chapel and two side chapels as a continuation of the 16th-century choir. After Cobergher's death in 1632 Franquart was appointed engineer to the Spanish king. Franquart taught his niece Anna Francisca de Bruyns to paint. The leading Brussels sculptor Jerôme Duquesnoy (II) was appointed as his assistant.Matthias Depoorter, ''Jerôme Duquesnoy II''
Some authors have stated that Franquart worked in the workshop of Rubens in Antwerp and that they were old friends. There is no documentary evidence for this. It is possible that the two artists got to know each other during their residence in Italy. Rubens' later purchase of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture...'' (First book of Architecture) published in 1616 was possibly a sign of his respect for Franquart. Rubens may also have acquired the book purely for practical reasons as at that time he was carrying out renovations on his newly purchased home in Antwerp.
One month after the publication of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' (''Premier livre d'architecture de Iaques Francart : contenant diuerses inuentions de portes seruiables à tous ceux qui désirent bastir et pour sculpteurs, tailleurs de pieres, escriniers, massons et autres : en trois langues'', in English ''First book of architecture of Jaques Francart : containing various inventions of doors useful to all those which wish to build and for sculptors, stone cutters, manufacturers of cases, masons and others: in three languages''), he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). Construction of the church had started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. Franquart's involvement in this project launched his career as an architect. In 1620 he was put in charge of the construction of the Augustine church in Brussels. In June 1621 he designed the funeral procession of the Archduke Albert. In 1629 he was commissioned to design the Beguinage Church in Mechelen. Franquart also rebuilt the church of Our Lady by the Dijle, Mechelen, by adding a choir chapel and two side chapels as a continuation of the 16th-century choir. After Cobergher's death in 1632 Franquart was appointed engineer to the Spanish king. Franquart taught his niece Anna Francisca de Bruyns to paint. The leading Brussels sculptor Jerôme Duquesnoy (II) was appointed as his assistant.Matthias Depoorter, ''Jerôme Duquesnoy II''
at Baroque in the Southern Netherlands He never married and died in Brussels where he was buried on 6 January 1651.
He never married and died in Brussels where he was buried on 6 January 1651.
/ref> The book introduces the principle of Baroque decorative opulence as well as certain recurring themes, such as the cartouche, the horn of opulence, the sheell three superimposed pods.Ralph Dekoninck et Caroline Heering, ''Le permanent et l’éphémère. Ornements d’architecture et arts du spectacle'', in: Th. CORTEMBOS and M.-C. CLAES (dir.), De Saint-Ignace à Saint-Loup. Quatre siècles d’un joyau baroque à Namur, Namur, Société archéologique de Namur (coll. Namur. Histoire et patrimoine), 2021 Like Coberghers unpublished treatise, Franquart's book made a significant contribution to the knowledge of the Italian tradition in the Southern Netherlands. In 1622, he published in Brussels the ''Cent tablettes et escussons d'armes'' or ''Hondert schryftafelkens ende wapeschilden'' (One hundred plaques and escutcheons of arms). The book had 27 pages and plates. It was a model book providing examples of portals and gate designs were included to be realized and adapted. The subtitle of the book was ''pour sculpteurs, peintres et orfebvres, pour s'en servir aux ornemens d'inscriptions, emblemes et armes'' (for sculptors, painters and goldsmiths, to be used for inscriptions, emblems and coats of arms), showing that the intention of the book was to serve as guidelines for painters, sculptors and goldsmiths.
Volume 7, pp. 272-274 One month after the publication of his ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). The church's construction had been started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. His first building design was of great importance both for his own career and for its influence on his contemporaries. His Jesuit church played a key role in the evolution of the Flemish early Baroque even more so than the
One month after the publication of his ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). The church's construction had been started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. His first building design was of great importance both for his own career and for its influence on his contemporaries. His Jesuit church played a key role in the evolution of the Flemish early Baroque even more so than the 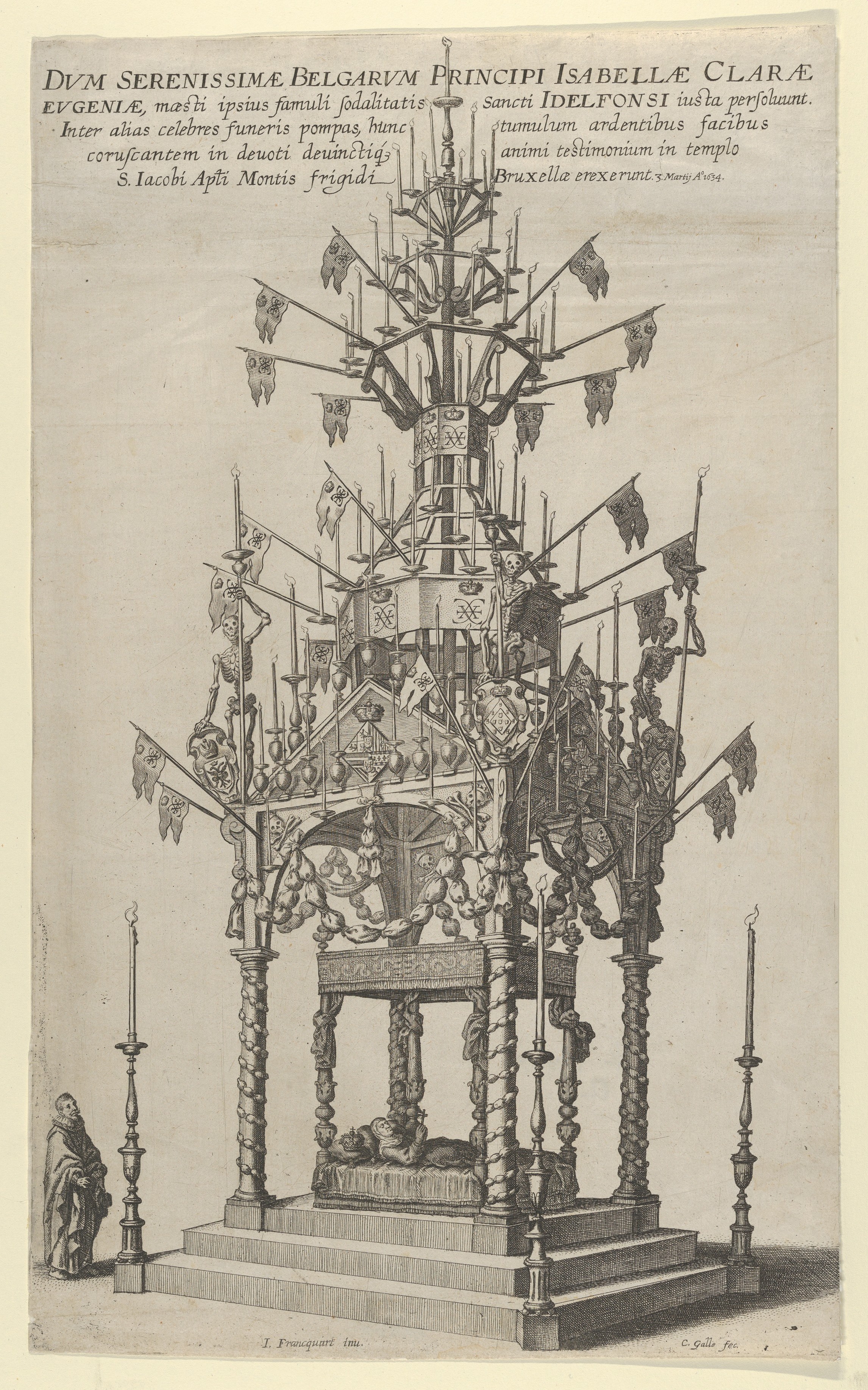 In 1620 Franquart designed the Augustine church in Brussels. Various elements of his design, including the use of consecutive double columns, broken frontons and boldly decorated light-openings in various shapes, established a new architectural style that became known as the Brabant Baroque. He used a comparable design for the facade of the Beguinage church in Mechelen, started in 1629 and completed around 1645 by Lucas Faydherbe. The front facade, which he copied in the church of the Holy Trinity in Brussels, is similar to the Jesuit church and to Cobergher's Augustine church in Antwerp. The architect Lucas Faydherbe of Mechelen was also inspired by this facade in his design for the
In 1620 Franquart designed the Augustine church in Brussels. Various elements of his design, including the use of consecutive double columns, broken frontons and boldly decorated light-openings in various shapes, established a new architectural style that became known as the Brabant Baroque. He used a comparable design for the facade of the Beguinage church in Mechelen, started in 1629 and completed around 1645 by Lucas Faydherbe. The front facade, which he copied in the church of the Holy Trinity in Brussels, is similar to the Jesuit church and to Cobergher's Augustine church in Antwerp. The architect Lucas Faydherbe of Mechelen was also inspired by this facade in his design for the
11 August 2021 He also designed the catafalque below which the body of the Archduchess Isabella Clara was laid in the Saint-Jacques-sur-Coudenberg/church of St. Jacob-on-Koudenberg in Brussels during her funeral ceremony on 3 March 1634. A print of the catafalque made by Cornelis Galle the Elder shows the body of the Archduchess in the habit of the
Cornelis Curtius, ''Virorum illustrium ex ordine eremitarum D. Augustini elogia : cum singulorvm expressis ad viuum iconibus''
/ref> The frames in which the portraits of the Augustines depicted constitute a further development of the door, plaque and escutcheon designs from his design publications.
 Jacob Franquart or Jacob Franckaert the Younger (1582/83 – 6 January 1651 (buried)) was a Flemish architect, painter, print artist, draftsman, military engineer and poet.Jacques Franckaert (II)
Jacob Franquart or Jacob Franckaert the Younger (1582/83 – 6 January 1651 (buried)) was a Flemish architect, painter, print artist, draftsman, military engineer and poet.Jacques Franckaert (II)at the
Netherlands Institute for Art History
The Netherlands Institute for Art History or RKD (Dutch: RKD-Nederlands Instituut voor Kunstgeschiedenis), previously Rijksbureau voor Kunsthistorische Documentatie (RKD), is located in The Hague and is home to the largest art history center i ...
He is known for his altarpieces and publications on contemporary Italian architecture. He was employed by the court of the Archdukes Albert and Isabella
Isabella may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Isabella (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Isabella (surname), including a list of people
Places
United States
* Isabella, Alabama, an unincorpor ...
in Brussels as a painter and architect. He was responsible for the design of ephemeral decorations and structure for important occasions at the court such as funerals. As an architect and decorator, he introduced the Baroque in the buildings of the Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austr ...
.Brigitte de Patoul, ''Jacques Francart II''in: Dictionnaire des peintres belges His style is sometimes referred to as the Italo-Flemish style and became very popular in Flanders in the 17th century.J.-P. Esther, ''Francart (Franckaert; Francquart), Jacques (Jacob) (born ?Antwerp, ?1583; d Brussels, buried Jan 6, 1651)''
at Oxford Art Online Only a few paintings are attributed to him.Auguste Schoy, ''Histoire de l'influence italienne sur l'architecture dans les Pays-Bas''
1879, Brussels, F. Hayez, pp 245-262
Life
Franquart was born in Antwerp or possiblyBrussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
as the son of Jacob Franckaert the Elder
Jacob Franckaert or Jacob Franquart (the Elder) (1550–51 – 6 September 1601 (buried)) was a Flemish painter and draftsman.Guild of Saint Luke
The Guild of Saint Luke was the most common name for a city guild for painters and other artists in early modern Europe, especially in the Low Countries. They were named in honor of the Evangelist Luke, the patron saint of artists, who was ide ...
in 1571. A sister of Jacob the Younger named Suzanna was born around 1584. Jacob the Elder is still mentioned in Antwerp in 1585. His father took his family via Paris to Italy in 1591. In Naples Jacob the Elder started a collaboration with Wenceslas Cobergher
Wenceslas Cobergher (1560 – 23 November 1634), sometimes called Wenzel Coebergher, was a Flemish Renaissance architect, engineer, painter, antiquarian, numismatist and economist. Faded somewhat into the background as a painter, he is chiefly ...
, a Flemish painter who had trained in Antwerp with Maerten de Vos
Maerten de Vos, Maerten de Vos the Elder or Marten de Vos (1532 – 4 December 1603)Maerten de Vos
at the Net ...
. They executed several paintings for the city's churches.
Jacob the Elder moved with his family to Rome in 1594. Cobergher joined them and the two artists continued their collaboration. Four months after the death of his first wife, Cobergher married Suzanna Franckaert, the daughter of his collaborator, in Rome on 20 November 1599. At the time the Franquart family was registered in the register of the parish of San Lorenzo in Rome. In March 1601 the family was registered in the marriage register of the parish of San Lorenzo in Rome. It is difficult to discern in these works the contribution of either artist. Jacob started to study painting, likely with his father. In Rome he had the opportunity to study the Antique and Renaissance architecture. He particularly admired the works of Michelangelo, at the Net ...
Giacomo della Porta
Giacomo della Porta (1532–1602) was an Italian architect and sculptor, who worked on many important buildings in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica. He was born at Porlezza, Lombardy and died in Rome.
Biography
Giacomo Della Porta was ...
, Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola
Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola ( , , ; 1 October 15077 July 1573), often simply called Vignola, was one of the great Italian architects of 16th century Mannerism. His two great masterpieces are the Villa Farnese at Caprarola and the Jesuits' Churc ...
and Carlo Maderno
Carlo Maderno (Maderna) (1556 – 30 January 1629) was an Italian architect, born in today's Ticino, who is remembered as one of the fathers of Baroque architecture. His façades of Santa Susanna, St. Peter's Basilica and Sant'Andrea della Vall ...
.
Both parents of Jacob had died by September 1601 after which he lived with his sister Susanna and her husband Cobergher. At this time the Archdukes Albert
Albert may refer to:
Companies
* Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic
* Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands
* Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia
* Albert Productions, a record label
* Alber ...
and Isabella invited Cobergher to work for them at the court in Brussels causing him to leave Italy with his family. Jacob remained in Rome. At some point he got involved in a lawsuit regarding some stolen precious stones. The stones were rediscovered before the end of the trial. In the years 1607 and 1608 he was residing near the Santa Maria della Pace in Rome. Franquart returned to his homeland at the end of the trial and before the summer of 1611.
 Some authors have stated that Franquart worked in the workshop of Rubens in Antwerp and that they were old friends. There is no documentary evidence for this. It is possible that the two artists got to know each other during their residence in Italy. Rubens' later purchase of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture...'' (First book of Architecture) published in 1616 was possibly a sign of his respect for Franquart. Rubens may also have acquired the book purely for practical reasons as at that time he was carrying out renovations on his newly purchased home in Antwerp.
One month after the publication of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' (''Premier livre d'architecture de Iaques Francart : contenant diuerses inuentions de portes seruiables à tous ceux qui désirent bastir et pour sculpteurs, tailleurs de pieres, escriniers, massons et autres : en trois langues'', in English ''First book of architecture of Jaques Francart : containing various inventions of doors useful to all those which wish to build and for sculptors, stone cutters, manufacturers of cases, masons and others: in three languages''), he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). Construction of the church had started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. Franquart's involvement in this project launched his career as an architect. In 1620 he was put in charge of the construction of the Augustine church in Brussels. In June 1621 he designed the funeral procession of the Archduke Albert. In 1629 he was commissioned to design the Beguinage Church in Mechelen. Franquart also rebuilt the church of Our Lady by the Dijle, Mechelen, by adding a choir chapel and two side chapels as a continuation of the 16th-century choir. After Cobergher's death in 1632 Franquart was appointed engineer to the Spanish king. Franquart taught his niece Anna Francisca de Bruyns to paint. The leading Brussels sculptor Jerôme Duquesnoy (II) was appointed as his assistant.Matthias Depoorter, ''Jerôme Duquesnoy II''
Some authors have stated that Franquart worked in the workshop of Rubens in Antwerp and that they were old friends. There is no documentary evidence for this. It is possible that the two artists got to know each other during their residence in Italy. Rubens' later purchase of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture...'' (First book of Architecture) published in 1616 was possibly a sign of his respect for Franquart. Rubens may also have acquired the book purely for practical reasons as at that time he was carrying out renovations on his newly purchased home in Antwerp.
One month after the publication of Franquart's ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' (''Premier livre d'architecture de Iaques Francart : contenant diuerses inuentions de portes seruiables à tous ceux qui désirent bastir et pour sculpteurs, tailleurs de pieres, escriniers, massons et autres : en trois langues'', in English ''First book of architecture of Jaques Francart : containing various inventions of doors useful to all those which wish to build and for sculptors, stone cutters, manufacturers of cases, masons and others: in three languages''), he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). Construction of the church had started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. Franquart's involvement in this project launched his career as an architect. In 1620 he was put in charge of the construction of the Augustine church in Brussels. In June 1621 he designed the funeral procession of the Archduke Albert. In 1629 he was commissioned to design the Beguinage Church in Mechelen. Franquart also rebuilt the church of Our Lady by the Dijle, Mechelen, by adding a choir chapel and two side chapels as a continuation of the 16th-century choir. After Cobergher's death in 1632 Franquart was appointed engineer to the Spanish king. Franquart taught his niece Anna Francisca de Bruyns to paint. The leading Brussels sculptor Jerôme Duquesnoy (II) was appointed as his assistant.Matthias Depoorter, ''Jerôme Duquesnoy II''at Baroque in the Southern Netherlands
 He never married and died in Brussels where he was buried on 6 January 1651.
He never married and died in Brussels where he was buried on 6 January 1651.
Work
General
Franquart was a prolific artist who worked as an architect, painter, print designer, draftsman, military engineer and poet. His most important contributions are his publication on contemporary Italian architecture and introduction of the Baroque style in architecture in the Habsburg Netherlands.. He was employed by the court of the Archdukes Albert and Isabella in Brussels as a painter and architect. He was responsible for the design of ephemeral decorations and structure for important occasions at the court such as funerals. As an architect and decorator, he introduced early Baroque into the buildings of the Habsburg Netherlands. Only a few paintings are attributed to him. He was further active as a civil and military engineer.Publications
Franquart's ''Premier Livre d’Architecture'' was published in 1617 and dedicated to Archduke Albert. Four volumes were planned but only one was ever published. This treatise features an introduction and 18 designs for doors for civil architecture. The designs are illustrated in scale drawings, elevations and in profile with the additions of a few measurements. Three illustrations show additional details. The engravings were made by Michel Lasne. The text was in three languages: Latin, French and Dutch. The book reflects the tradition ofHans Vredeman de Vries
Hans Vredeman de Vries (1527 – c. 1607) was a Dutch Renaissance architect, painter, and engineer. Vredeman de Vries is known for his publication in 1583 on garden design and his books with many examples on ornaments (1565) and perspective (1604 ...
' pattern books. It also reflects the influence of van Sebastiano Serlio
Sebastiano Serlio (6 September 1475 – c. 1554) was an Italian Mannerist architect, who was part of the Italian team building the Palace of Fontainebleau. Serlio helped canonize the classical orders of architecture in his influential trea ...
's ''Extraordinario Libro''. The door designs are all based on designs by Michelangelo and later Mannerist architects. Two types of models are provided in the book: for refined doors and for rustic doors. The importance of door design at that time is that doors were typically the only modern element added to civil buildings whose design remained otherwise traditional.Krista De Jonge and Annemie De Vos, ''Francart, Jacques, Michel Lasne (engraver), "Premier livre d’architecture"...''/ref> The book introduces the principle of Baroque decorative opulence as well as certain recurring themes, such as the cartouche, the horn of opulence, the sheell three superimposed pods.Ralph Dekoninck et Caroline Heering, ''Le permanent et l’éphémère. Ornements d’architecture et arts du spectacle'', in: Th. CORTEMBOS and M.-C. CLAES (dir.), De Saint-Ignace à Saint-Loup. Quatre siècles d’un joyau baroque à Namur, Namur, Société archéologique de Namur (coll. Namur. Histoire et patrimoine), 2021 Like Coberghers unpublished treatise, Franquart's book made a significant contribution to the knowledge of the Italian tradition in the Southern Netherlands. In 1622, he published in Brussels the ''Cent tablettes et escussons d'armes'' or ''Hondert schryftafelkens ende wapeschilden'' (One hundred plaques and escutcheons of arms). The book had 27 pages and plates. It was a model book providing examples of portals and gate designs were included to be realized and adapted. The subtitle of the book was ''pour sculpteurs, peintres et orfebvres, pour s'en servir aux ornemens d'inscriptions, emblemes et armes'' (for sculptors, painters and goldsmiths, to be used for inscriptions, emblems and coats of arms), showing that the intention of the book was to serve as guidelines for painters, sculptors and goldsmiths.
Architectural designs
In 1620 he designed the Augustine church which stood on Place de Broukere in Brussels from its completion in 1642 to its demolition in 1893. The facade of the building now forms part of the Church of the Holy Trinity on Parvis de la Trinite inBrussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
.Adolphe Siret, ''Jacques Franquart'' in: Biographie Nationale BelgeVolume 7, pp. 272-274
 One month after the publication of his ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). The church's construction had been started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. His first building design was of great importance both for his own career and for its influence on his contemporaries. His Jesuit church played a key role in the evolution of the Flemish early Baroque even more so than the
One month after the publication of his ''Premier Livre d'Architecture'' he was asked to complete the Jesuit church in Brussels (destroyed in 1812). The church's construction had been started in 1606 with Hendrik Hoeimaker as the building master. His first building design was of great importance both for his own career and for its influence on his contemporaries. His Jesuit church played a key role in the evolution of the Flemish early Baroque even more so than the Saint Carolus Borromeus Church
St. Charles Borromeo Church (Dutch: ''Sint-Carolus Borromeuskerk'') is a church in central Antwerp, located on the Hendrik Conscience square. It was built in 1615-1621 as the Jesuit church of Antwerp, which was closed in 1773. It was rededicated ...
in Antwerp which was designed by Franciscus Aguilonius and Peter Huyssens and was built at the same time. His Baroque church showsthe influence of his Roman models. The primary Roman models include the Church of Saint Susanna by Carlo Maderno
Carlo Maderno (Maderna) (1556 – 30 January 1629) was an Italian architect, born in today's Ticino, who is remembered as one of the fathers of Baroque architecture. His façades of Santa Susanna, St. Peter's Basilica and Sant'Andrea della Vall ...
, the designs of Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola
Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola ( , , ; 1 October 15077 July 1573), often simply called Vignola, was one of the great Italian architects of 16th century Mannerism. His two great masterpieces are the Villa Farnese at Caprarola and the Jesuits' Churc ...
for the Jesuit Church which were not executed and the facade of the Jesuit Church which were built by Giacomo della Porta
Giacomo della Porta (1532–1602) was an Italian architect and sculptor, who worked on many important buildings in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica. He was born at Porlezza, Lombardy and died in Rome.
Biography
Giacomo Della Porta was ...
in 1577. Franquart's sole original contribution to these models is the addition of an attic (a story above the cornice of the façade), which adds an extra dimension to the facade, while not entirely breaking with the horizantality of Renaissance architecture.Rutger Tijs, ''Renaissance- en barokarchitectuur in België: Vitruvius' erfenis en de ontwikkeling van de bouwkunst in de Zuidelijke Nederlanden van renaissance tot barok'', Lannoo Uitgeverij, 1999, pp. 144-146 Franquart's Jesuit Church also incorporated local traditions as the facade hid a Flemish Late Gothic building (in part inherited from Hoeimaker's original design) characterised by its verticalism and interior rib-vaulting. Tuscan columns carried the rib-vaults, decorated in the centre by escutcheons, a treatment of the nave that was echoed by many, including Huyssens at St. Walburga Church in Bruges.
 In 1620 Franquart designed the Augustine church in Brussels. Various elements of his design, including the use of consecutive double columns, broken frontons and boldly decorated light-openings in various shapes, established a new architectural style that became known as the Brabant Baroque. He used a comparable design for the facade of the Beguinage church in Mechelen, started in 1629 and completed around 1645 by Lucas Faydherbe. The front facade, which he copied in the church of the Holy Trinity in Brussels, is similar to the Jesuit church and to Cobergher's Augustine church in Antwerp. The architect Lucas Faydherbe of Mechelen was also inspired by this facade in his design for the
In 1620 Franquart designed the Augustine church in Brussels. Various elements of his design, including the use of consecutive double columns, broken frontons and boldly decorated light-openings in various shapes, established a new architectural style that became known as the Brabant Baroque. He used a comparable design for the facade of the Beguinage church in Mechelen, started in 1629 and completed around 1645 by Lucas Faydherbe. The front facade, which he copied in the church of the Holy Trinity in Brussels, is similar to the Jesuit church and to Cobergher's Augustine church in Antwerp. The architect Lucas Faydherbe of Mechelen was also inspired by this facade in his design for the Basilica of Our Lady of Hanswijk
The Basilica of Our Lady of Hanswijk is a Roman Catholic basilica in Mechelen, Belgium. The basilica is a famous place of pilgrimage in Belgium, the statue was crowned on 30 July 1876 by Cardinal Deschamps by request of pope Pius IX.
Description ...
in Mechelen. The interior of which is characterized by the round-arched arcades with Corinthian pilasters supporting an entablature, as in the Our Lady of Saint Peter's Church in Ghent designed by Huyssens. Franquart contributed to the extension of the church of Our Lady by the Dijle in Mechelen, by adding a choir chapel and two side chapels as a continuation of the 16th-century choir (executed from 1642 to 1652). Through these designs, Franquart was, together with Cobergher, Aguilonius and Huyssens, one of the foremost church architects in the Southern Netherlands in the early 17th century, by pioneering the introduction and dissemination of the Roman early Baroque style. His style, sometimes referred to as the Italo-Flemish style, became very popular in Flanders in the 17th century.
Ephemeral designs
As a leading court artist, Franquart was often tasked with designing ephemeral decorations and structures for important occasions at the court. He designed the various decorations and monumental, ephemeral architecture and structures for the funeral of Archduke Albert held in the church of Saint Gudula in Brussels on 12 March 1622.Zoe Cooke, ''Ephemeral Architecture Eternalised in Print: The Documentation of the Funeral Procession for Archduke Albert VII of Austria, 1622.''11 August 2021 He also designed the catafalque below which the body of the Archduchess Isabella Clara was laid in the Saint-Jacques-sur-Coudenberg/church of St. Jacob-on-Koudenberg in Brussels during her funeral ceremony on 3 March 1634. A print of the catafalque made by Cornelis Galle the Elder shows the body of the Archduchess in the habit of the
Poor Clares
The Poor Clares, officially the Order of Saint Clare ( la, Ordo sanctae Clarae) – originally referred to as the Order of Poor Ladies, and later the Clarisses, the Minoresses, the Franciscan Clarist Order, and the Second Order of Saint Francis ...
laid out in a four-poster bed, her crown beside her on the pillow. The catafalque is richly decorated with lit candles and flags with Isabella's monogram.
Franquart designed the festive architecture in honor of the Joyous Entry
A Joyous Entry ( nl, Blijde Intrede, Blijde Inkomst, or ; ) is the official name used for the ceremonial royal entry, the first official peaceable visit of a reigning monarch, prince, duke or governor into a city, mainly in the Duchy of Braban ...
into Ghent on 26 January 1635 of the Governor of the Habsburg Netherlands Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria
Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand (also known as Don Fernando de Austria, Cardenal-Infante Fernando de España and as Ferdinand von Österreich; May 1609 or 1610 – 9 November 1641) was Governor of the Spanish Netherlands, Cardinal of the Holy Catholic ...
. He was invited to do so by the local magistrates of Ghent. The event itself was organized by the Jesuit College which provided research into emblems, allegories and classical Humanism to build the image of the Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria and to link him to Emperor Charles V, who was born in Ghent. Francart designed two triumphal arches, respectively of Emperor Charles V and the Cardinal-Infant Ferdinand that took into account this research. The arches were erected on the Friday Market. The arches were not built under the supervision of Franquart, but under that of engineer Melchior de Somer and master Pieter Plumion. The Joyous Entry was described in detail in the book ''Serenissimi Principis Ferdinandi Hispaniarum Infantis S.R.E. Cardinalis Triumphalis introitus in Flandriae Metropolim Gandavum'' written by the Jesuit Willem van der Beke (Guilielmus Becanus). It was printed in Antwerp in 1636 by the printing press of Jan van Meurs.
Print designs
Franquart designed the illustrations for a book commemorating the funeral ceremony of Archduke Albert held in the church of Saint Gudula in Brussels on 12 March 1622. The title of the book is ''Pompa funebris optimi potentissimiq eprincipis Alberti Pii, Archiducis Austriae, ducis Burg. Bra. &c.'' While the work was published inBrussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
at the Jan Mommaert
Jan Mommaert was the name of two 17th-century printers in Brussels, father (active 1585–1627) and son (active 1646–1669). Between the dates of their activity, Martine van Straeten operated a printing house under the name Widow of Jan Mommaert. ...
press, the copper engravings were cut by Antwerp's eminent printmaker Cornelis Galle the Elder. It is therefore generally regarded as one of the eminent works of the golden age of Antwerp copperplate engraving
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that ...
. The text was principally derived from the book ''Phoenix Principum...'' written by the Dutch writer and historian Erycius Puteanus and published in Leuven in 1622. The engravings use a hatching table of heraldic tincture
A tincture is typically an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Solvent concentrations of 25–60% are common, but may run as high as 90%.Groot Handboek Geneeskrachtige Planten by Geert Verhelst In chemistr ...
s which is the earliest hatching system in heraldry after Zangrius. According to some authors it was the inspiration for the later hatching system of de la Colombière. The engravings in the book present the 1621 funeral procession in 64 tables. The total length of the print is close to 1 meter. It depicts more than 700 different persons with the banner of their countries. It also has depictions of monumental, ephemeral architecture that was designed for the funeral by Franquart himself. The volume is an important record of the role of ephemeral architecture in courtly ceremonies in this period in Europe.
He collaborated on a collection of biographies of prominent members of the Augustinian order published by Antwerp printer Joannes Cnobbaert under the title ''Virorum illustrium ex ordine eremitarum D. Augustini elogia : cum singulorvm expressis ad viuum iconibus''. Written by the Augustinian monk Cornelis Curtius, it contained biographies and short-title listings of the works of prominent Augustians. It was illustrated with 30 full-page portraits engraved by Cornelius Galle after designs by Franquart./ref> The frames in which the portraits of the Augustines depicted constitute a further development of the door, plaque and escutcheon designs from his design publications.
Paintings
n 1611 Franquart received his first painting commission for the convent of theDiscalced Carmelites
The Discalced Carmelites, known officially as the Order of the Discalced Carmelites of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Mount Carmel ( la, Ordo Fratrum Carmelitarum Discalceatorum Beatae Mariae Virginis de Monte Carmelo) or the Order of Discalced Carme ...
in Brussels. The painting is lost. In 1613, Franquart was appointed court painter to the Brussels court. In the 1620s, Archdukes Albert and Isabella commissioned Franquart, Rubens, Cobergher, Salomon de Claus and Jerôme Duquesnoy (II) to decorate their palace in Brussels. Franquart mainly worked on the old and new oratories of the Archduchess and the finishing and detailing of the palace. Between 1612 and 1614, he created ceiling paintings in the first oratory and also restored its older scenes. He was also responsible for other decorative commissions at the court.Anthony Blunt, ''Rubens and Architecture'', The Burlington Magazine, Vol 119, No. 894, pp. 620-629+631+645
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Franquart, Jacob 1580s births 1651 deaths Heraldists Flemish Baroque painters Flemish architects Engineers of the Spanish Netherlands Flemish military engineers Artists from Antwerp Artists from Brussels