Jack Kelly Sr. (rower) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
John Brendan Kelly Sr. (October 4, 1889 – June 20, 1960) was an American triple
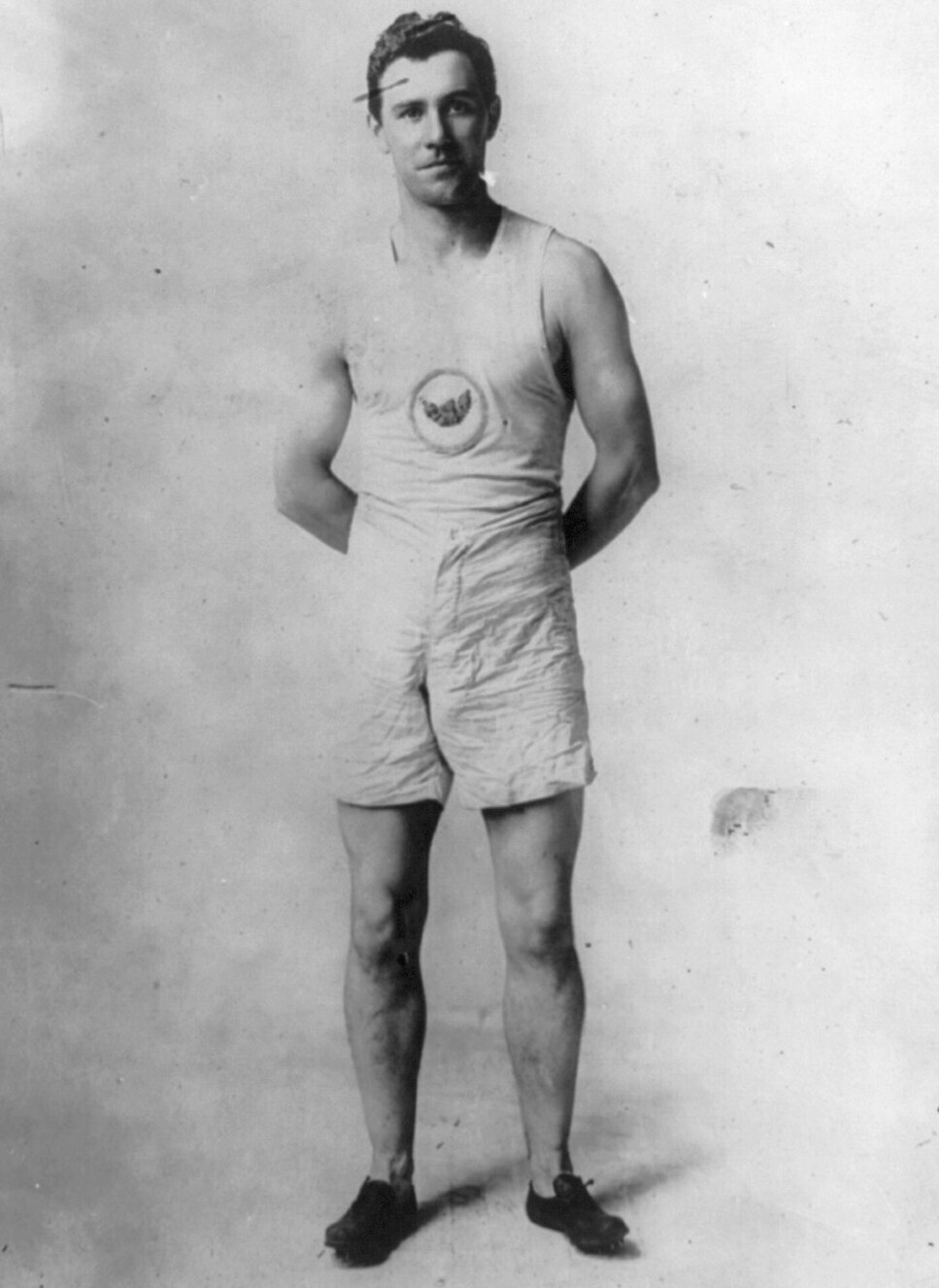 Kelly was born in
Kelly was born in
 After a long courtship, Kelly married Margaret Katherine Majer (1898–1990) in 1924, daughter of German immigrants. Well known herself in the world of sports, she was the founder of
After a long courtship, Kelly married Margaret Katherine Majer (1898–1990) in 1924, daughter of German immigrants. Well known herself in the world of sports, she was the founder of
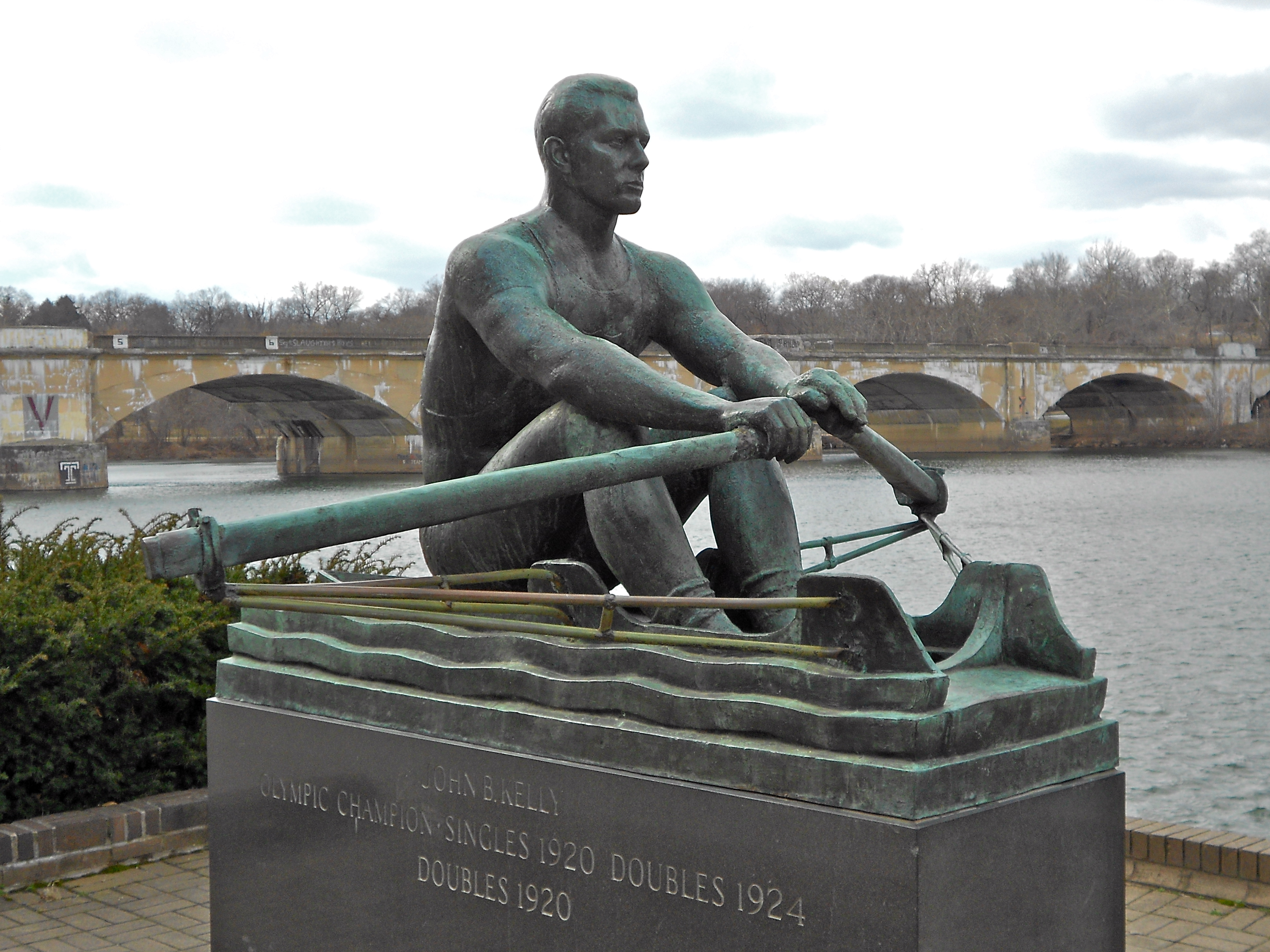 * Gold Medal, Single Scull, 1920 Olympic Games
* Gold Medal, Double Scull, 1920 Olympic Games
* Gold Medal, Double Scull, 1924 Olympic Games
* 126 consecutive victories in the single scull
* Member, United States Olympic Hall of Fame
* Member, United States Rowing Hall of Fame, Single Scull (elected 1956 at the same time as his son, Jack Jr.)
* Member, United States Rowing Hall of Fame, Double Scull (elected 1956)
* National Physical Fitness Director (World War II)
* Member Philadelphia Sports Hall of Fame, (elected in the charter class of 2003 with Wilt Chamberlain,
* Gold Medal, Single Scull, 1920 Olympic Games
* Gold Medal, Double Scull, 1920 Olympic Games
* Gold Medal, Double Scull, 1924 Olympic Games
* 126 consecutive victories in the single scull
* Member, United States Olympic Hall of Fame
* Member, United States Rowing Hall of Fame, Single Scull (elected 1956 at the same time as his son, Jack Jr.)
* Member, United States Rowing Hall of Fame, Double Scull (elected 1956)
* National Physical Fitness Director (World War II)
* Member Philadelphia Sports Hall of Fame, (elected in the charter class of 2003 with Wilt Chamberlain,
Schuylkill Navy site on Kelly, et al.
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Kelly, John B. 1889 births 1960 deaths United States Army personnel of World War I American bricklayers American people of Irish descent Burials at Holy Sepulchre Cemetery Catholics from Pennsylvania Deaths from cancer in Pennsylvania Deaths from colorectal cancer Kelly family Olympic gold medalists for the United States in rowing Rowers from Philadelphia Rowers at the 1920 Summer Olympics Rowers at the 1924 Summer Olympics United States Army officers United States Army soldiers Holmesburg Athletic Club players American male rowers Medalists at the 1920 Summer Olympics Medalists at the 1924 Summer Olympics People associated with the Philadelphia Museum of Art Pennsylvania Democrats Military personnel from Philadelphia
Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece b ...
champion, the first in the sport of rowing. The Philadelphia-based Kelly also was a multimillionaire in the bricklaying and construction industry. He also was involved in politics, serving as Pennsylvania secretary of revenue
The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue (DOR) is an agency of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The department is responsible for collecting all Pennsylvania taxes, including all corporate taxes and taxes on inheritance, personal income, sales and us ...
and running unsuccessfully for mayor of Philadelphia
The mayor of Philadelphia is the chief executive of the government of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
as stipulated by the Charter of the City of Philadelphia. The current mayor of Philadelphia is Jim Kenney.
History
The first mayor of Philadelphia, ...
in the 1935 Philadelphia mayoral election.
Kelly was the father of actress Grace Kelly, Princess of Monaco (thus maternal grandfather of Albert II, Prince of Monaco
Albert II – Website of the Palace of Monaco (Albert Alexandre Louis Pierre Grimaldi; born 14 March 1958) is Prince of Monaco, since 2005.
Albert was born at the Prince's Palace of Monaco, and he is the second child and only son of Prince Rai ...
), and of Jack Kelly Jr., an accomplished rower who served as president of the U.S. Olympic Committee
The United States Olympic & Paralympic Committee (USOPC) is the National Olympic Committee and the National Paralympic Committee for the United States. It was founded in 1895 as the United States Olympic Committee, and is headquartered in Col ...
.
Early life
 Kelly was born in
Kelly was born in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, one of 10 children of Irish immigrants John Henry Kelly (1847–1917), who emigrated from his homestead near Newport, County Mayo, in 1869, and Mary Ann Costello (1852–1926), who arrived in the U.S. in 1867. He attended public schools and at night attended the Spring Garden Institute.
In 1907, he began bricklaying in Philadelphia as an apprentice at his brother Patrick's construction firm. Standing 6'2", he was a gifted athlete and competed in football and basketball in addition to rowing, which he learned on the Schuylkill River. By 1916, Kelly was a national rowing champion and the best sculler in the United States. As part of the World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
callup, Kelly joined the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
as a private in October 1917. He rose to the rank of lieutenant by the time he was discharged in April 1919. While in the Army, Kelly entered the armed forces boxing tournament as a heavyweight and ran up a 12–0 record before being waylaid by a broken ankle. Future world professional boxing champion Gene Tunney won the tournament. In later years, Kelly would kid Tunney: "Aren't you lucky I broke my ankle?"
Following his Army discharge in 1919, Kelly continued his dominance in the single scull. He also started a brickwork contracting company in Philadelphia, John B. Kelly, Inc, with a $7,000 loan from his brothers George
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Presiden ...
, a future Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made h ...
-winning playwright, and Walter
Walter may refer to:
People
* Walter (name), both a surname and a given name
* Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Walter Jacobs (1930–1968)
* Gunther (wrestler), Austrian professional wrestler and trainer Walter Hahn (born 19 ...
, who was a popular vaudeville
Vaudeville (; ) is a theatrical genre of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century. A vaudeville was originally a comedy without psychological or moral intentions, based on a comical situation: a dramatic composition ...
actor. A self-promoter, Kelly coined the slogan "Kelly for Brickwork", which was often seen at local construction sites.
Kelly developed a technique to ensure payment for his brickwork from less-than-trustworthy real estate developers. Kelly's crews would mortar a single pane of glass into each chimney they built. When new home owners would complain to realtors about smoke backing into their houses from the fireplaces, and the developers would then complain to Kelly, he would reply, "I'll take care of it when your check clears." Once paid, Kelly would send crews out to drop a brick down each chimney they'd constructed, smashing the glass panes and solving the problem.
In 1919, Kelly played professional football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
for the Holmesburg Athletic Club
The Holmesburg Athletic Club was a professional football team from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, that was in existence from around 1915 until 1923. The team laid claim to the Philadelphia City Championship in 1919 and 1920.
Alumni
The ...
. The team would go on to win the 1919 and 1920 Philadelphia City Championship. In a 1919 game against a team from Camden, New Jersey
Camden is a city in and the county seat of Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. Camden is part of the Delaware Valley metropolitan area and is located directly across the Delaware River from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At the 2020 ...
, Kelly scored three touchdown
A touchdown (abbreviated as TD) is a scoring play in gridiron football. Whether running, passing, returning a kickoff or punt, or recovering a turnover, a team scores a touchdown by advancing the ball into the opponent's end zone. In Ameri ...
s in just the first quarter of the game.
Rowing career
Kelly won 126 straight races in the single scull in 1919 and 1920, a six-time U.S. national champion who was one of the most popular figures in the sport.Rejection by the Henley Royal Regatta
In 1920, amid his winning streak, Kelly applied to race in theDiamond Sculls
The Diamond Challenge Sculls is a rowing event for men's single sculls at the annual Henley Royal Regatta on the River Thames at Henley-on-Thames in England. First run in 1844, it is open to male scullers from all eligible rowing clubs.
at the Henley Royal Regatta
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It differs from the thre ...
. Held annually on the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
in Henley, England, it was the most prestigious event in rowing. But the event's organizers rejected his application, citing an earlier dispute with his rowing club and the fact that he had worked as a manual laborer.
The minutes of the regatta's Committee of Management for June 3, 1920, read: "The list of entries ... outside of the United Kingdom under Rule iv was presented ... and received with the exception of Mr J.B. Kelly of the Vesper Boat Club to compete in the Diamond Sculls, which was refused under the resolution passed by the Committee on 7th June, 1906 'viz' 'That no entry from the Vesper Boat Club of Philadelphia, or from any member of their 1905 crew be accepted in future': Mr Kelly was also not qualified under Rule I (e) of the General Rules (manual labour)."
That 1906 resolution banned members of the Vesper Boat Club from the event because their eight-man team in the Grand Challenge Cup
The Grand Challenge Cup is a rowing competition for men's eights. It is the oldest and best-known event at the annual Henley Royal Regatta on the River Thames at Henley-on-Thames in England. It is open to male crews from all eligible rowing cl ...
had used a public subscription to raise the money to travel to London, breaching the regatta's rule on amateurism
An amateur () is generally considered a person who pursues an avocation independent from their source of income. Amateurs and their pursuits are also described as popular, informal, self-taught, user-generated, DIY, and hobbyist.
History
Hist ...
.
The regatta committee's minutes also note that they rejected Kelly because he had worked as a bricklayer. The regatta's rules on amateurism excluded anyone "who is or ever has been...by trade or employment for wages a mechanic, artisan or labourer." Two days before Kelly was due to sail to the UK, with his passage booked and his boat boxed, he received a telegram which said: "Entry rejected; letter follows." He never received the letter. The Henley Stewards later declared that they had informed the governing board for U.S. rowing as soon as Kelly's entry was processed, and that it was not their fault if the information was not passed on.
The affair was widely reported, especially in London, New York and Philadelphia. The Stewards of Henley Royal Regatta came in for heavy criticism. One interpretation was that they had excluded Kelly because they did not want an American to win the Diamonds. The publicity made Kelly widely popular and would later help his bricklaying business. The ban on Vesper Boat Club was rescinded soon afterward and in 1937 the references in the Henley rules excluding manual labourers, mechanics, artisans and menial duties were deleted.
In 2003, the Princess Grace Challenge Cup
The Princess Grace Challenge Cup is a rowing event for women's quadruple sculls at the annual Henley Royal Regatta on the Thames at Henley-on-Thames in England. It is open to female crews from all eligible rowing clubs. Two or more clubs may comb ...
was launched as an event for women's quadruple sculls both in recognition of John B. Kelly and in memory of his daughter, Grace.
Kelly was surprised that his entry was rejected. Kelly always maintained that he had been assured by United States rowing officials that his entry would be accepted. In the 1950s he wrote to Jack Beresford
Jack Beresford, CBE (1 January 1899 – 3 December 1977), born Jack Beresford-Wiszniewski, was a British rower who won five medals at five Olympic Games in succession. This record in Olympic rowing was not matched until 2000 when Sir Steve Red ...
, the winner of the 1920 Henley Diamond Sculls race, the following:
: "Russell Johnson, secretary of the NAAO he governing board for U.S. rowinghad an arrangement with the Henley officials that they would approve all entries from the United States, which he had made during his visit to England in the winter of 1919–20... I asked him to check with the Stewards to see if they would accept my entry because in my earlier days I had served an apprenticeship as a bricklayer. He contacted four of them and they told him to send my entry in; the war had changed the old rule and everything would be all right".
:This led Kelly to seek and gain redemption by going to the 1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
in Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Belgium, which he had originally not planned to attend.
Redemption at the 1920 Olympics
When he first made his application to race at Henley, Kelly told the press that if his entry was accepted, he would go to Henley and most likely would skip the Olympics. On learning of his rejection, Kelly was surprised and angered and stated: "I had made all the arrangements to sail for England ... I'll go to the Olympics now for sure. I want to get a crack at the man who wins the diamond sculls." Kelly soon had his chance, representing the United States at the1920 Summer Olympics
The 1920 Summer Olympics (french: Jeux olympiques d'été de 1920; nl, Olympische Zomerspelen van 1920; german: Olympische Sommerspiele 1920), officially known as the Games of the VII Olympiad (french: Jeux de la VIIe olympiade; nl, Spelen van ...
in Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Belgium. In a hard-fought race, he won the single scull event, extracting a measure of revenge by defeating the winner of the Diamond Sculls, British sculler Jack Beresford
Jack Beresford, CBE (1 January 1899 – 3 December 1977), born Jack Beresford-Wiszniewski, was a British rower who won five medals at five Olympic Games in succession. This record in Olympic rowing was not matched until 2000 when Sir Steve Red ...
. Beresford was one of the most talented oarsmen of the day and would go on to win medals at five Olympics. The race, one of the closest in Olympic history, featured a dramatic duel down the stretch with Kelly winning by a second. Kelly and Beresford would go on to become good friends. Half an hour after the singles final, Kelly teamed with his cousin Paul Costello
Paul Vincent Costello (December 27, 1894 – April 17, 1986) was an American triple Olympic Gold Medal winner in rowing. He was the first rower to win a gold medal in the same event, double sculls, at three consecutive Olympics. He also won num ...
to win the double scull (2x) race, a feat which has never been repeated at the Olympic games. After his Olympic victory, Kelly purportedly mailed his racing cap to King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Que ...
with the note, "Greetings from a bricklayer", for having been snubbed at Henley.
Repeat at the 1924 Olympics
In 1924, Kelly and Costello repeated their success, winning the double-scull event at theSummer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The inau ...
in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
. This made Kelly the first rower to win three Olympic gold medals and one of the most famous and successful athletes of his generation.
Personal life
 After a long courtship, Kelly married Margaret Katherine Majer (1898–1990) in 1924, daughter of German immigrants. Well known herself in the world of sports, she was the founder of
After a long courtship, Kelly married Margaret Katherine Majer (1898–1990) in 1924, daughter of German immigrants. Well known herself in the world of sports, she was the founder of Women's sports
The participation of women and girls in sports, physical Physical fitness, fitness and exercise, has been recorded to have existed throughout history. However, participation rates and activities vary in accordance with nation, era, geography, ...
in the University of Pennsylvania. Majer's family was Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
and she converted to Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
prior to the marriage. They had four children: Margaret "Peggy" Katherine (1925–1991), John "Kell" Brendan Jr. (1927–1985), Grace Patricia (1929–1982) and Elizabeth "Lizanne" Anne (1933–2009).
John B. Kelly Jr. won the Diamond Sculls at Henley in 1947 and 1949. Jack Jr., as he was also known, won the James E. Sullivan Award as the best amateur athlete in the U.S. in 1947 for his accomplishments. He would go on to represent the United States at the 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
, 1952
Events January–February
* January 26 – Black Saturday in Egypt: Rioters burn Cairo's central business district, targeting British and upper-class Egyptian businesses.
* February 6
** Princess Elizabeth, Duchess of Edinburgh, becomes m ...
, 1956
Events
January
* January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan.
* January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian Missionary, missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim ...
and 1960 Olympic Games The 1960 Olympics may refer to:
*The 1960 Winter Olympics, which were held in Squaw Valley, United States
*The 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics ( it, Giochi Olimpici estivi del 1960), officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympi ...
. Jack Jr. won the bronze medal in the single scull at the 1956 Olympics and continue to be involved in amateur sports, eventually being appointed President of the United States Olympic Committee shortly before his sudden death from a heart attack in 1985.
Kelly's daughter Grace was an Academy Award
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
-winning actress who became Princess consort of Monaco when she married Prince Rainier in 1956. Kelly purportedly gave Prince Rainier a $2 million dowry for his daughter's marriage. Kelly is the maternal grandfather of Albert II, the reigning prince of Monaco. When Grace's engagement to Prince Rainier was announced, Kelly quipped: "I told the Prince that royalty didn't mean that much to us, and that I hoped he wouldn't run around the way some Princes do."
Kelly was the model for the character of George Kittredge, Tracy Lord's brash, up-and-coming, man-of-the-people fiancé, in Philip Barry
Philip Jerome Quinn Barry (June 18, 1896 – December 3, 1949) was an American dramatist best known for his plays ''Holiday (play), Holiday'' (1928) and ''The Philadelphia Story (play), The Philadelphia Story'' (1939), which were both made into ...
's 1939 Broadway comedy '' The Philadelphia Story''. Grace Kelly played Tracy Lord in the 1956 Cole Porter
Cole Albert Porter (June 9, 1891 – October 15, 1964) was an American composer and songwriter. Many of his songs became standards noted for their witty, urbane lyrics, and many of his scores found success on Broadway and in film.
Born to ...
movie musical version, '' High Society''. Grace visited her grandfather's cottage, the Kelly homestead, near Newport, County Mayo during her 1961 state visit to Ireland.
Later life
Kelly was actively involved in city politics, including chairmanship of the Philadelphia County Democratic Party in 1937 and ran for mayor of Philadelphia in 1935. At the time, Philadelphia was a heavily Republican city, but he came close to winning, losing by fewer than 50,000 votes compared with the usual margin of 300,000. From January 1936 until June 1937, Kelly served asPennsylvania secretary of revenue
The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue (DOR) is an agency of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The department is responsible for collecting all Pennsylvania taxes, including all corporate taxes and taxes on inheritance, personal income, sales and us ...
under Governor George Howard Earle III.
He was a commissioner and later president of the Fairmount Park Commission
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
, which administered Fairmount Park in Philadelphia, one of the largest municipal parks in the world. In 1941, President Roosevelt named the still popular Kelly as the National Physical Fitness Director, a post he held throughout World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Kelly was a strong advocate for physical fitness for all Americans, and in particular those inducted into the military.
Kelly was Commodore of the Schuylkill Navy from 1935 to 1940, and was president of the NAAO, the then governing board for U.S. rowing, from 1954 through 1955. Kelly is the only rower who is a member of the U.S. Olympic Hall of Fame
The United States Olympic & Paralympic Hall of Fame is an honor roll of the top American Olympic and Paralympic athletes headquartered at the United States Olympic & Paralympic Museum, opened in April 2020 in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
The Hall ...
. He is also a member of the United States Rowing Hall of Fame, having been elected in 1956 at the same time as his son Jack Jr.
Kelly died of intestinal cancer at his home in Philadelphia, age 70. He was interred at Holy Sepulchre Cemetery in Cheltenham, Pennsylvania
Cheltenham is an unincorporated area, unincorporated community in Cheltenham Township, Pennsylvania, United States, with a ZIP code of 19012. It is located directly over the city line (Cheltenham Avenue) of Philadelphia. It also borders Northeast ...
.
In 1967, Philadelphia erected a prominent statue of Kelly by artist Harry Rosin near the finish line of the Schuylkill River course that Kelly rowed. It is located just off of the scenic Kelly Drive, which is named for Kelly's son, Jack Jr. Every year, USRowing, as the governing board is now known, bestows the Jack Kelly Award on an individual who represents the ideals that Kelly exemplified, including superior achievement in rowing, service to amateur athletics and success in their chosen profession.
Achievements and awards
Joe Frazier
Joseph William Frazier (January 12, 1944November 7, 2011), nicknamed "Smokin' Joe", was an American professional boxer who competed from 1965 to 1981. He was known for his strength, durability, formidable left hand, and relentless pressure fi ...
, Jimmie Foxx, et al.)
References
External links
*Schuylkill Navy site on Kelly, et al.
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Kelly, John B. 1889 births 1960 deaths United States Army personnel of World War I American bricklayers American people of Irish descent Burials at Holy Sepulchre Cemetery Catholics from Pennsylvania Deaths from cancer in Pennsylvania Deaths from colorectal cancer Kelly family Olympic gold medalists for the United States in rowing Rowers from Philadelphia Rowers at the 1920 Summer Olympics Rowers at the 1924 Summer Olympics United States Army officers United States Army soldiers Holmesburg Athletic Club players American male rowers Medalists at the 1920 Summer Olympics Medalists at the 1924 Summer Olympics People associated with the Philadelphia Museum of Art Pennsylvania Democrats Military personnel from Philadelphia