Isochron Dating on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Isochron dating is a common technique of
Isochron dating is a common technique of
Basics of radioactive isotope geochemistry from Cornell
at the
 Isochron dating is a common technique of
Isochron dating is a common technique of radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
and is applied to date certain events, such as crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
lization, metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of ch ...
, shock events, and differentiation of precursor melts, in the history of rocks. Isochron dating can be further separated into ''mineral isochron dating'' and ''whole rock isochron dating''; both techniques are applied frequently to date terrestrial and also extraterrestrial rocks (meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object ...
s). The advantage of isochron dating as compared to simple radiometric dating techniques is that no assumptions are needed about the initial amount of the daughter nuclide
A nuclide (or nucleide, from atomic nucleus, nucleus, also known as nuclear species) is a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was co ...
in the radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
sequence. Indeed, the initial amount of the daughter product can be determined using isochron dating. This technique can be applied if the daughter element has at least one stable isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass num ...
other than the daughter isotope into which the parent nuclide decays.
Basis for method
All forms of isochron dating assume that the source of the rock or rocks contained unknown amounts of both radiogenic and non-radiogenic isotopes of the daughter element, along with some amount of the parent nuclide. Thus, at the moment of crystallization, the ratio of the concentration of the radiogenic isotope of the daughter element to that of the non-radiogenic isotope is some value independent of the concentration of the parent. As time goes on, some amount of the parent decays into the radiogenic isotope of the daughter, increasing the ratio of the concentration of the radiogenic isotope to that of the daughter. The greater the initial concentration of the parent, the greater the concentration of the radiogenic daughter isotope will be at some particular time. Thus, the ratio of the daughter to non-radiogenic isotope will become larger with time, while the ratio of parent to daughter will become smaller. For rocks that start out with a small concentration of the parent, the daughter/non-radiogenic ratio will not change quickly as compared to rocks starting with a large concentration of the parent.Assumptions
An isochron diagram will only give a valid age if all samples are ''cogenetic'', which means they have ''the same initial isotopic composition'' (that is, the rocks are from the same unit, the minerals are from the same rock, etc.), all samples have the same initial isotopic composition (at t0), and the system has remainedclosed
Closed may refer to:
Mathematics
* Closure (mathematics), a set, along with operations, for which applying those operations on members always results in a member of the set
* Closed set, a set which contains all its limit points
* Closed interval, ...
.
Isochron plots
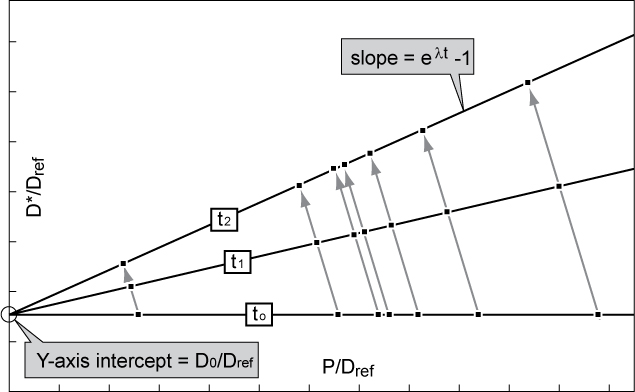
The mathematical expression from which the isochron is derived is where : ''t'' is age of the sample, : ''D''* is number of atoms of the radiogenic daughter isotope in the sample, : ''D''0 is number of atoms of the daughter isotope in the original or initial composition, : n is number of atoms of the parent isotope in the sample at the present, : ''λ'' is thedecay constant
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and (lambda) is a positive rate ...
of the parent isotope, equal to the inverse of the radioactive half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
of the parent isotope times the natural logarithm of 2, and
: (''e''λ''t''-1) is the slope of the isochron which defines the age of the system.
Because the isotopes are measured by mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
, ratios are used instead of absolute concentrations since mass spectrometers usually measure the former rather than the latter. (See the section on isotope ratio
The term stable isotope has a meaning similar to stable nuclide, but is preferably used when speaking of nuclides of a specific element. Hence, the plural form stable isotopes usually refers to isotopes of the same element. The relative abundanc ...
mass spectrometry.) As such, isochrons are typically defined by the following equation, which normalizes the concentration of parent and radiogenic daughter isotopes to the concentration of a non-radiogenic isotope of the daughter element that is assumed to be constant:
where
: is the concentration of the non-radiogenic isotope of the daughter element (assumed constant),
:
: is the present concentration of the radiogenic daughter isotope,
:
: is the initial concentration of the radiogenic daughter isotope, and
: is the present concentration of the parent isotope that has decayed over time .
To perform dating, a rock is crushed to a fine powder, and minerals are separated by various physical and magnetic means. Each mineral has different ratios between parent and daughter concentrations. For each mineral, the ratios are related by the following equation:
: (1)
where
: is the initial concentration of the parent isotope, and
:
: is the total amount of the parent isotope which has decayed by time .
The proof of (1) amounts to simple algebraic manipulation. It is useful in this form because it exhibits the relationship between quantities that actually exist at present. To wit, , and respectively correspond to the concentrations of parent, daughter and non-radiogenic isotopes found in the rock at the time of measurement.
The ratios or (relative concentration of present daughter and non-radiogenic isotopes) and or (relative concentration of present parent and non-radiogenic isotope) are measured by mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
and plotted against each other in a three-isotope plot known as an ''isochron plot''.
If all data points lie on a straight line, this line is called an isochron. The better the fit of the data points to a line, the more reliable the resulting age estimate. Since the ratio of the daughter and non-radiogenic isotopes is proportional to the ratio of the parent and non-radiogenic isotopes, the slope of the isochron gets steeper with time. The change in slope from initial conditions—assuming an initial isochron slope of zero (a horizontal isochron) at the point of intersection (intercept) of the isochron with the y-axis—to the current computed slope gives the age of the rock. The slope of the isochron, or , represents the ratio of daughter to parent as used in standard radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
and can be derived to calculate the age of the sample at time ''t''. The y-intercept of the isochron line yields the initial radiogenic daughter ratio, .
Whole rock isochron dating uses the same ideas but instead of different minerals obtained from one rock uses different types of rocks that are derived from a common reservoir; e.g. the same precursor melt. It is possible to date the differentiation of the precursor melt which then cooled and crystallized into the different types of rocks.
One of the best known isotopic systems for isochron dating is the rubidium–strontium system. Other systems that are used for isochron dating include samarium–neodymium, and uranium–lead. Some isotopic systems based on short-living extinct radionuclides such as 53Mn, 26Al, 129I, 60Fe and others are used for isochron dating of events in the early history of the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
. However, methods using extinct radionuclides give only relative ages and have to be calibrated with radiometric dating techniques based on long-living radionuclides like Pb-Pb dating to give absolute ages.
Application
Isochron dating is useful in the determination of the age ofigneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
s, which have their initial origin in the cooling of liquid magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
. It is also useful to determine the time of metamorphism, shock events (such as the consequence of an asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. ...
impact) and other events depending on the behaviour of the particular isotopic systems under such events. It can be used to determine the age of grains in sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particle ...
and understand their origin by a method known as a provenance study.
See also
*Radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Basics of radioactive isotope geochemistry from Cornell
at the
TalkOrigins Archive
The TalkOrigins Archive is a website that presents mainstream science perspectives on the antievolution claims of young-earth, old-earth, and "intelligent design" creationists. With sections on evolution, creationism, geology, astronomy and homin ...
Radiometric dating