Islam in Kosovo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Until the sixteenth century the degree of Islamisation in Kosovo was minimal, and largely confined to urban centres. The pace of conversions to Islam only increased significantly in the second half of the sixteenth century, possibly because high taxes, Ottoman retaliations and forced conversions. Prior to the Ottomans, both Catholic and Orthodox Churches had waged a ruthless war over the hearts, minds and souls of the Albanians, and this situation was exploited by the Ottomans. Both the Serbian Orthodox Church and the Sultan viewed the conversion of Albanians to Islam as something positive as it weakened Balkan Catholic nucleus, and the Sultan received new subjects.
Converts also became exempt from the '' cizje'', a protective tax levied only on non-Muslim males. But that was certainly not the only cause of the people turning to Islam. the tax burden tended to go up as Ottoman power relative to foreign Christian powers came under challenge. So far as Catholic Albanians were concerned, the Catholic church was less powerful and privileged within the Ottoman Empire than the Serbian Orthodox Church (and less well staffed); the Bektashi order of dervishes carried out a conversion campaign which stressed the similarities between their version of Islam and Christianity (the Bektashis drank wine and had a quasi-Trinitarian doctrine). A phenomenon of "crypto-Catholicism" developed in Kosovo Albanian society, where large numbers of people would convert officially to Islam but follow Catholic rites in private. From 1703 ecclesiastical decrees banned this practice and did not accept that crypto-Catholics could receive holy rites. In 1717,
Until the sixteenth century the degree of Islamisation in Kosovo was minimal, and largely confined to urban centres. The pace of conversions to Islam only increased significantly in the second half of the sixteenth century, possibly because high taxes, Ottoman retaliations and forced conversions. Prior to the Ottomans, both Catholic and Orthodox Churches had waged a ruthless war over the hearts, minds and souls of the Albanians, and this situation was exploited by the Ottomans. Both the Serbian Orthodox Church and the Sultan viewed the conversion of Albanians to Islam as something positive as it weakened Balkan Catholic nucleus, and the Sultan received new subjects.
Converts also became exempt from the '' cizje'', a protective tax levied only on non-Muslim males. But that was certainly not the only cause of the people turning to Islam. the tax burden tended to go up as Ottoman power relative to foreign Christian powers came under challenge. So far as Catholic Albanians were concerned, the Catholic church was less powerful and privileged within the Ottoman Empire than the Serbian Orthodox Church (and less well staffed); the Bektashi order of dervishes carried out a conversion campaign which stressed the similarities between their version of Islam and Christianity (the Bektashis drank wine and had a quasi-Trinitarian doctrine). A phenomenon of "crypto-Catholicism" developed in Kosovo Albanian society, where large numbers of people would convert officially to Islam but follow Catholic rites in private. From 1703 ecclesiastical decrees banned this practice and did not accept that crypto-Catholics could receive holy rites. In 1717,
File:Prizren kossovo.jpg, Sinan Pasha Mosque in
Qendra për Studime Islame
Bashkësia Islame e Kosovës
* (dedicated to the study, research, and documentation of the destruction and damage of historic heritage during the Balkan Wars of the 1990s. The website contains judicial documents from the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY)). {{Islam in Europe
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
in Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
has a long-standing tradition dating back to the Ottoman conquest of the Balkans. Before the Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo ( tr, Kosova Savaşı; sr, Косовска битка) took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan ...
in 1389, the entire Balkan region had been Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
by both the Western and Eastern Roman Empire. From 1389 until 1912, Kosovo was officially governed by the Muslim Ottoman Empire and a high level of Islamization
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurre ...
occurred among Catholic and Orthodox Albanians, mainly due to taxes and socio-political opportunism. Despite these events, both Christian and Muslim Albanians intermarried and some lived as "Laramans", also known as Crypto-Christians. During the time period after World War II, Kosovo was ruled by secular socialist authorities in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
(SFRY). During that period, Kosovars became increasingly secularized
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
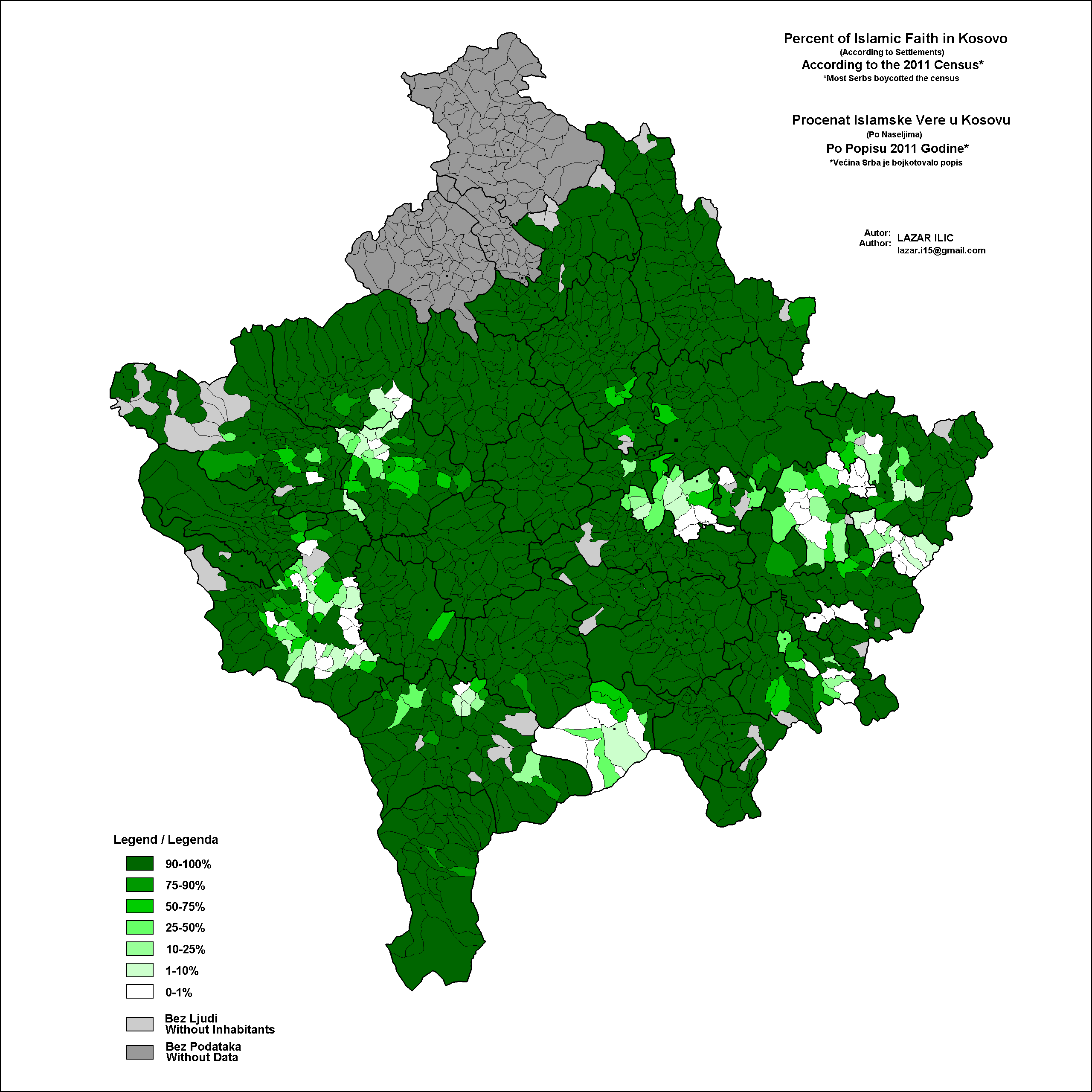
. After the end of Communist period religion had a revival in Kosovo. Today, 95.6% of Kosovo's population are Muslims, most of whom are ethnic Albanians. There are also Slavic speaking Muslims, who define themselves as Bosniaks
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry, cu ...
and Gorani, and Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
.
History
Lady Mary Wortley Montagu
Lady Mary Wortley Montagu (née Pierrepont; 15 May 168921 August 1762) was an English aristocrat, writer, and poet. Born in 1689, Lady Mary spent her early life in England. In 1712, Lady Mary married Edward Wortley Montagu, who later served ...
, wife of the British Ambassador to the Sublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
History
The na ...
wrote that her Albanian escort from Belgrade to Istanbul claimed to go to the mosque on Fridays and church on Sundays. At any rate, by 1750, most Christian families had converted to Islam, for the benefits of social networking of the citizens and for financial soundness. Albanians in Kosovo who had been passing as Muslims were declaring themselves Catholics (to avoid conscription) as late as 1845.Malcolm, Noel, ''Kosovo: A Short History'', pp. 185-86
The Kosovo War
Numerous Albanian cultural sites in Kosovo were destroyed during theKosovo conflict
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the war ...
(1998-1999) which constituted a war crime violating the Hague and Geneva Convention
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conven ...
s.. Of the 498 mosques in Kosovo that were in active use, the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia
The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) was a body of the United Nations that was established to prosecute the war crimes that had been committed during the Yugoslav Wars and to try their perpetrators. The tribuna ...
(ICTY) documented that 225 mosques sustained damage or destruction by the Yugoslav Serb army. In all, eighteen months of the Yugoslav Serb counterinsurgency campaign between 1998-1999 within Kosovo resulted in 225 or a third out of a total of 600 mosques being damaged, vandalised, or destroyed alongside other Islamic architecture during the conflict.. ""The attack on Landovica’s mosque was reprised throughout Kosovo during the eighteen months of the Serb counterinsurgency campaign. Approximately 225 of Kosovo’s 600 mosques were vandalized, damaged, or destroyed during that campaign." "Islamic heritage in general has received meagre legal attention although such heritage was severely damaged during the war. The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) documented that, of 498 mosques that were in active use, approximately 225 of them were damaged or destroyed by Serbian military during the years 1998—1999." Sufi lodges ( tekkes), Muslim theological schools (madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated ...
s) and Islamic libraries sustained damage or destruction resulting in the loss of rare books, manuscripts and other collections of literature. Archives belonging to the Islamic Community of Kosovo with records spanning 500 years were also destroyed. During the war, Islamic architectural heritage posed for Yugoslav Serb paramilitary and military forces as Albanian patrimony with destruction of non-Serbian architectural heritage being a methodical and planned component of ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
in Kosovo.
In the aftermath of the war, a wave of revenge attacks on dozens of Serbian Orthodox churches by Muslim Albanians resulting in being damaged or destroyed. These attacks effectively ended after six weeks, with 35 churches destroyed or damaged, at the end of August 1999, after appeals by Kosovo's political leaders and by the Mufti.
Organization
Since Yugoslav times, the official organisation of Muslims in Kosovo has been theIslamic Community of Kosova
The Islamic Community of Kosovo (ICK; sq, Bashkësia Islame e Kosovës), is an independent religious organization of Muslims in Kosovo and the Preshevo Valley. The community's headquarters are located in Pristina and their current leader, t ...
(Alb: ''Bashkësia Islame e Kosovës''), led by its Grand Mufti
The Grand Mufti (also called Chief Mufti, State Mufti and Supreme Mufti) is the head of regional muftis, Islamic jurisconsults, of a state. The office originated in the early modern era in the Ottoman empire and has been later adopted in a num ...
, currently Naim Tërnava. Bektashi tekkes are subject to the Bektashi order, and in some areas fundings from Saudi Arabia or other countries has led to concern about possible Wahhabi-Salafi attempts to influence Kosovo and its social habits, although such influences are very rarely visible.
Interfaith relations
There have long been contacts between the Islamic Community of Kosovo and the Catholic Church in Kosovo, and in 2011 regular meetings began at the level of Mufti and Bishops both of the Catholic Church and theSerbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous ( ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian churches.
The majority of the population ...
in Kosovo. But for most of Kosovo's history, there has been a rift between Serbian Orthodox Christianity versus Albanian Catholic Christianity and Albanian Sunni Islam, as existing in the country.
Political influence
While individual politicians may be influenced in their attitudes or decisions by Islamic beliefs, only one political party, the Justice Party (Alb: Partia e Drejtësisë), includes in its party programme a commitment to traditional Islamic values. It argued in 2010 for Islamic religious teaching in state schools for children from families with a Muslim family background: this was rejected by the Kosovo Assembly. In the parliamentary elections in Kosovo it took part in an electoral coalition led by the AKR (Alliance for a New Kosovo), together with firmly secular parties, presumably because it was unlikely to reach the threshold for parliamentary representation on its own. The AKR coalition itself came in fourth place in the elections with 7.29% of the total vote. (In the 2001 elections the Kosovo Christian Democratic Party, a Kosovo Albanian political entity, won one seat in the Assembly elections; its leadership included people with Muslim names).Gallery
Prizren
)
, settlement_type = Municipality and city
, image_skyline = Prizren Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 290px
, image_caption = View of Prizren
, image_alt = View of Prizren
, image_flag ...
.
File:Sultan_Mehmet_Fatih_Xhamia.jpg, Imperial Mosque in Pristina
Pristina, ; sr, / (, ) is the capital and largest city of Kosovo. The city's municipal boundaries in Pristina District form the largest urban center in Kosovo. After Tirana, Pristina has the second largest population of ethnic Albanians an ...
.
File:Bajrakli_Xhami.JPG, Bajrakli Mosque, Peja.
File:Inside the Mosque in Kastriot Obilic 3.jpg, Praying at the mosque in Obiliq.
File:Teqja.jpg, Sufi ceremony at the Sheh Emin Teqe, Gjakova
Gjakova, ) and Đakovica ( sr-Cyrl, Ђаковица, ) is the seventh largest city of Kosovo and seat of Gjakova Municipality and Gjakova District. The city has 40,827 inhabitants, while the municipality has 94,556 inhabitants.
Geographicall ...
See also
*Islamic Community of Kosova
The Islamic Community of Kosovo (ICK; sq, Bashkësia Islame e Kosovës), is an independent religious organization of Muslims in Kosovo and the Preshevo Valley. The community's headquarters are located in Pristina and their current leader, t ...
* Bosniaks in Kosovo
* Gorani people
The Gorani (, ) or Goranci (, ), are a Slavic Muslim ethnic group inhabiting the Gora region—the triangle between Kosovo, Albania, and North Macedonia. They number an estimated 60,000 people, and speak a transitional South Slavic dialect, c ...
* Turks in Kosovo
The Turks in Kosovo, also known as Kosovo Turks, and Kosovan Turks, ( tr, ) are the ethnic Turks who constitute a minority group in Kosovo.
History
Turkish settlement into Kosovo began in the late 14th century after the medieval Serbian state l ...
* Religion in Kosovo
* Christianity in Kosovo
Notes
References
Sources
*Further reading
*External links
*Qendra për Studime Islame
Bashkësia Islame e Kosovës
* (dedicated to the study, research, and documentation of the destruction and damage of historic heritage during the Balkan Wars of the 1990s. The website contains judicial documents from the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY)). {{Islam in Europe