Isdud on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Isdud ( ar, اسدود) is a former
 In 950 BCE Ashdod was destroyed during Pharaoh Siamun's conquest of the region. The city was not rebuilt until at least 815 BCE.
''Asdûdu'' led the revolt of Philistines, Judeans, Edomites, and Moabites against Assyria after expulsion of king Ahimiti, whom Sargon had installed instead of his brother Azuri. Gath (''Gimtu'') belonged to the kingdom of Ashdod at that time. Assyrian king
In 950 BCE Ashdod was destroyed during Pharaoh Siamun's conquest of the region. The city was not rebuilt until at least 815 BCE.
''Asdûdu'' led the revolt of Philistines, Judeans, Edomites, and Moabites against Assyria after expulsion of king Ahimiti, whom Sargon had installed instead of his brother Azuri. Gath (''Gimtu'') belonged to the kingdom of Ashdod at that time. Assyrian king
The Towns of Palestine under Muslim Rule: AD 600-1600
", BAR International Series 1381, 2005, pp
90
-91 With the destruction of the port city, its inland counterpart regains its importance.
 The location of the village on
The location of the village on
4
.
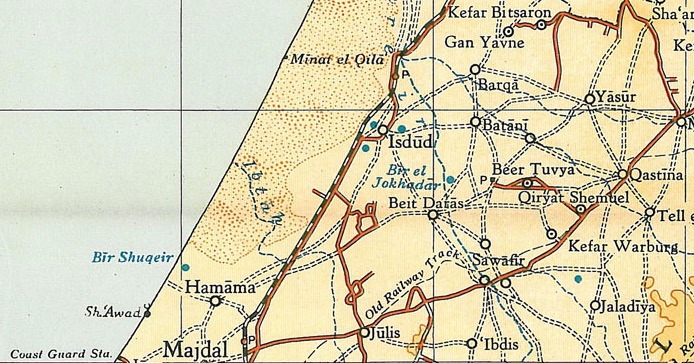 During the Mandatory period, Isdud had two elementary schools; one for boys which was opened in 1922, and one for girls which started in 1942. By the mid-1940s the boy-school had 371 students, while the girl-school had 74.
The official
During the Mandatory period, Isdud had two elementary schools; one for boys which was opened in 1922, and one for girls which started in 1942. By the mid-1940s the boy-school had 371 students, while the girl-school had 74.
The official
31
No. 33 Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p
45
Of this, 3,277 dunams were used citrus and bananas, 8,327 for plantations and irrigable land, 23,762 for cereals, while 131 dunams were built-on land.
 The village of Isdud was occupied by the Egyptian army on May 29, 1948, and became the Egyptians' northernmost position during the
The village of Isdud was occupied by the Egyptian army on May 29, 1948, and became the Egyptians' northernmost position during the
File:Isdud 1946 BOA.jpg, Detailed village map, 1946
File:ISDUD.jpg, Ruins of the Isdud mosque
File:Air views of Palestine. Air route over Cana of Galilee, Nazareth, Plain of Sharon, etc. Ashdod. Home of Dagon. Encroaching sand waves in distance LOC matpc.15882.jpg, Aerial view of Isdud, 1932
File:Isdud 08, ruins 1900.jpg, Ruins of medieval Isdud, in 1900
File:Isdud After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War (D281-049).jpg, Isdud in 1948
"Memoirs"
in ''
“Memoirs of the First Palestine War” in 2, no. 2 (Win. 73): 3-32
pdf-file, downloadable *Petersen, Andrew (2002):
A Gazetteer of Buildings in Muslim Palestine: Volume I (British Academy Monographs in Archaeology)
' (Isdud, p. 155-158) * (Isdud
p.124
from the
Tour and signposting in Isdud
by Eitan Bronstein, 15.8.03,
Untold stories: Ahmad Joudah
IMEU, Apr 24, 2008 {{Palestinian Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War District of Gaza Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War Ashdod
Palestinian
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
village and the site of the ancient and classical-era Levantine metropolis of Ashdod. The Arab village, which had a population of 4,910 in 1945, was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
. Today the ruins are located in the Be'er Tuvia region, 6 km southwest of the modern Israeli city of Ashdod
Ashdod ( he, ''ʾašdōḏ''; ar, أسدود or إسدود ''ʾisdūd'' or '' ʾasdūd'' ; Philistine: 𐤀𐤔𐤃𐤃 *''ʾašdūd'') is the sixth-largest city in Israel. Located in the country's Southern District, it lies on the Mediterran ...
. The archaeological site is known as Tel Ashdod, and remnants of the settlement's ancient and modern remains are visible.
The first documented urban settlement at Isdud dates to the 17th century BCE, when it was a fortified Canaanite city. It was destroyed at the end of the Late Bronze Age. During the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, it was a prominent Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
city, one of the five Philistine city-states. It is mentioned 13 times in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
. After being captured by ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Uzziah
Uzziah (; he, עֻזִּיָּהוּ ''‘Uzzīyyāhū'', meaning "my strength is Yah"; el, Ὀζίας; la, Ozias), also known as Azariah (; he, עֲזַרְיָה ''‘Azaryā''; el, Αζαρίας; la, Azarias), was the tenth king of t ...
, it was briefly ruled by the Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Ce ...
before it was taken by the Assyrians. During the Persian period
Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta (), was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a self-governing region under its local Jewish population. The province was a part ...
, Nehemiah
Nehemiah is the central figure of the Book of Nehemiah, which describes his work in rebuilding Jerusalem during the Second Temple period. He was governor of Persian Judea under Artaxerxes I of Persia (465–424 BC). The name is pronounced ...
condemned the returning Jews for intermarrying Ashdod's residents. Under Hellenistic rule, the city was known as ''Azotus''. It was later incorporated into the Hasmonean kingdom
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, an ...
. During the 1st century BCE, Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
removed the city from Judean rule and annexed it to the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
province of Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great.
Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into tetr ...
. Ashdod was a bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
under Byzantine rule, but its importance gradually slipped and by the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
it was a village.
Today, the site is an archaeological site open to the public, with visible remains of Isdud and earlier historical ruins, thought to be Philistine. The central village mosque stands at the top of the site, as does the khan and the tomb of Sheikh Abu Al-Kabel.
History
Bronze Age archaeology
The site of Isdud is today an archaeological tell known as "Tel Ashdod". It is a few km south of the modern Israel city ofAshdod
Ashdod ( he, ''ʾašdōḏ''; ar, أسدود or إسدود ''ʾisdūd'' or '' ʾasdūd'' ; Philistine: 𐤀𐤔𐤃𐤃 *''ʾašdūd'') is the sixth-largest city in Israel. Located in the country's Southern District, it lies on the Mediterran ...
. It was excavated by archaeologists in nine seasons between 1962 and 1972. The effort was led during the first few years by David Noel Freedman
David Noel Freedman (May 12, 1922 – April 8, 2008) was an American biblical scholar, author, editor, archaeologist, and, after his conversion from Judaism, a Presbyterian minister. He was one of the first Americans to work on the Dead Sea Scroll ...
of the Pittsburgh Theological Seminary
Pittsburgh Theological Seminary (PTS) is a Presbyterian graduate seminary in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1794, it houses one of the largest theological libraries in the tri-state area.
History
Pittsburgh Theological Seminary was formed ...
and Moshe Dothan. The remaining seasons were headed by Dothan for the Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, he, רשות העתיקות ; ar, داﺌرة الآثار, before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of ...
.Moshe Dothan, Ashdod VI: The Excavations of Areas H and K (1968–1969) (Iaa Reports) (v. 6), Israel Antiquities Authority, 2005,
Middle Bronze
The earliest major habitation in Ashdod dates to the 17th century BCE. Ashdod was fortified in MBIIC with a two-entryway city gate (similar to Shechem).Late Bronze
Ashdod is first mentioned in written documents fromLate Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
Ugarit
)
, image =Ugarit Corbel.jpg
, image_size=300
, alt =
, caption = Entrance to the Royal Palace of Ugarit
, map_type = Near East#Syria
, map_alt =
, map_size = 300
, relief=yes
, location = Latakia Governorate, Syria
, region = F ...
, which indicate that the city was a center of export for dyed woolen purple fabric and garments. At the end of the 13th century BCE the Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the Fren ...
conquered and destroyed Ashdod. By the beginning of the 12th century BCE, the Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
, generally thought to have been one of the Sea Peoples, ruled the city. During their reign, the city prospered and was a member of the Philistine Pentapolis (i.e. five cities), which included Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border with ...
and Gaza on the coast and Ekron
Ekron (Philistine: 𐤏𐤒𐤓𐤍 ''*ʿAqārān'', he, עֶקְרוֹן, translit=ʿEqrōn, ar, عقرون), in the Hellenistic period known as Accaron ( grc-gre, Ακκαρων, Akkarōn}) was a Philistine city, one of the five cities o ...
and Gath farther inland, in addition to Ashdod.
Iron Age
 In 950 BCE Ashdod was destroyed during Pharaoh Siamun's conquest of the region. The city was not rebuilt until at least 815 BCE.
''Asdûdu'' led the revolt of Philistines, Judeans, Edomites, and Moabites against Assyria after expulsion of king Ahimiti, whom Sargon had installed instead of his brother Azuri. Gath (''Gimtu'') belonged to the kingdom of Ashdod at that time. Assyrian king
In 950 BCE Ashdod was destroyed during Pharaoh Siamun's conquest of the region. The city was not rebuilt until at least 815 BCE.
''Asdûdu'' led the revolt of Philistines, Judeans, Edomites, and Moabites against Assyria after expulsion of king Ahimiti, whom Sargon had installed instead of his brother Azuri. Gath (''Gimtu'') belonged to the kingdom of Ashdod at that time. Assyrian king Sargon II
Sargon II (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is general ...
's commander-in-chief (''turtanu "Turtanu" or "Turtan" (Akkadian: 𒌉𒋫𒉡 ''tur-ta-nu''; he, תַּרְתָּן ''tartān''; el, Θαρθαν; la, Tharthan; arc, ܬܵܪܬܵܢ ''tartan'') is an Akkadian word/title meaning 'commander in chief' or 'prime minister'. In Assyri ...
''), whom the King James Bible
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an Bible translations into English, English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and publis ...
calls simply "Tartan" (), regained control of Ashdod in 712/711 BCE and forced the usurper Yamani to flee. Sargon's general destroyed the city and exiled its residents, including some Israelites who were subsequently settled in Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass el ...
and Elam
Elam (; Linear Elamite: ''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ; Akkadian: ; he, עֵילָם ''ʿēlām''; peo, 𐎢𐎺𐎩 ''hūja'') was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran, stretc ...
.
Mitinti Mitinti (Philistine: 𐤌𐤕𐤕NAVEH, JOSEPH. “Writing and Scripts in Seventh-Century B.C.E. Philistia: The New Evidence from Tell Jemmeh.” Israel Exploration Journal, vol. 35, no. 1, Israel Exploration Society, 1985, pp. 8–21, http://www.j ...
(Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ...
: 𒈪𒋾𒅔𒋾 ''mi-ti-in-ti''; Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
: 𐤌𐤕𐤕 *''Mītīt'' or *''Matīt'') was king at the time of Sargon's son Sennacherib
Sennacherib (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynast ...
(r. 705–681 BCE), and Akhimilki in the reign of Sennacherib's son Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his ...
(r. 681–669 BCE).
Psamtik I
Wahibre Psamtik I ( Ancient Egyptian: ) was the first pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the Saite period, ruling from the city of Sais in the Nile delta between 664–610 BC. He was installed by Ashurbanipal of the Neo-Assyrian Empire ...
of Egypt (r. 664 – 610 BCE) is reported to have besieged the great city Azotus for twenty-nine years (Herodotus, ii. 157); the biblical references to ''the remnant of Ashdod'' (; cf. ) are interpreted as allusions to this event.
The city absorbed another blow in 605 BCE, when Nebuchadnezzar
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
of Babylonia conquered it.
In 539 BCE the city was rebuilt by the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
. In 332 BCE it was conquered in the wars of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
.
The Book of Nehemiah
The Book of Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, largely takes the form of a first-person memoir concerning the rebuilding of the walls of Jerusalem after the Babylonian exile by Nehemiah, a Jew who is a high official at the Persian court, and the dedic ...
, referring to events in the 5th century BCE, mentions the ''Ashdodites'' and the ''speech of Ashdod'', which half of the children from mixed families are described as adopting. Hugo Winckler
Hugo Winckler (4 July 1863 – 19 April 1913) was a German archaeologist and historian who uncovered the capital of the Hittite Empire (Hattusa) at Boğazkale, Turkey.
A student of the languages of the ancient Middle East, he wrote extens ...
explains the use of that name by the fact that Ashdod was the nearest of the Philistine cities to Jerusalem.
In the Hebrew Bible
There are Biblical episodes referencing Ashdod but they remain uncorroborated by archaeological finds: * UponJoshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Yēšūaʿ''; syr, ܝܫܘܥ ܒܪ ܢܘܢ ''Yəšūʿ bar Nōn''; el, Ἰησοῦς, ar , يُوشَعُ ٱبْنُ نُونٍ '' Yūšaʿ ...
's conquest of the Promised Land
The Promised Land ( he, הארץ המובטחת, translit.: ''ha'aretz hamuvtakhat''; ar, أرض الميعاد, translit.: ''ard al-mi'ad; also known as "The Land of Milk and Honey"'') is the land which, according to the Tanakh (the Hebrew ...
, Ashdod was allotted to the Tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe of Judah (, ''Shevet Yehudah'') was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel, named after Judah, the son of Jacob. Judah was the first tribe to take its place in the Land of Israel, occupying the southern ...
(Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua ( he, סֵפֶר יְהוֹשֻׁעַ ', Tiberian: ''Sēp̄er Yŏhōšūaʿ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Isra ...
15:46).
* In I Samuel 6:17 Ashdod is mentioned among the principal Philistine cities. After capturing the Ark of the covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an e ...
from the Israelites, the Philistines took it to Ashdod and placed it in the temple of Dagon
Dagon ( he, דָּגוֹן, ''Dāgōn'') or Dagan ( sux, 2= dda-gan, ; phn, 𐤃𐤂𐤍, Dāgān) was a god worshipped in ancient Syria across the middle of the Euphrates, with primary temples located in Tuttul and Terqa, though many attes ...
. The next morning Dagon was found prostrate before the Ark; on being restored to his place, he was on the following morning again found prostrate and broken. The people of Ashdod were smitten with boils; a plague of mice was sent over the land (1 Samuel 6:5).
* According to the Bible, during the 10th century BCE Ashdod became, along with all the kingdom of Philistia
Philistia (; Koine Greek (LXX): Γῆ τῶν Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''gê tôn Phulistieìm''), also known as the Philistine Pentapolis, was a confederation of cities in the Southwest Levant, which included the cities of Ashdod, Ash ...
, a patronage area of the Kingdom of Israel under the control of King David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
.
* The capture of the city by King Uzziah of Judah
Uzziah (; he, עֻזִּיָּהוּ ''‘Uzzīyyāhū'', meaning "my strength is Yah"; el, Ὀζίας; la, Ozias), also known as Azariah (; he, עֲזַרְיָה ''‘Azaryā''; el, Αζαρίας; la, Azarias), was the tenth king of ...
shortly after 815 BCE is mentioned within 2 Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( he, דִּבְרֵי־הַיָּמִים ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third sect ...
(26:6) and in the Book of Zechariah
The Book of Zechariah, attributed to the Hebrew prophet Zechariah, is included in the Twelve Minor Prophets in the Hebrew Bible.
Historical context
Zechariah's prophecies took place during the reign of Darius the Great and were contempora ...
(9:6), speaking of the false Jews.
* In the Book of Nehemiah
The Book of Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, largely takes the form of a first-person memoir concerning the rebuilding of the walls of Jerusalem after the Babylonian exile by Nehemiah, a Jew who is a high official at the Persian court, and the dedic ...
(), some 5th century BCE residents of Jerusalem are said to have married women from Ashdod, and half of the children of these unions were reportedly unable to understand Hebrew; instead, they spoke "the language of Ashdod".
Hellenistic period
OnceHellenised
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek Greek culture, culture, Religion in Greece, religion, Greek language, language and Ethnic identity, identity by non-Greeks. In the Ancient Greece, ancient ...
, the city changed its name to the more Greek-sounding ''Αzotus'' ( gr, Άζωτος) and prospered until the Hasmonean Revolt. During the rebellion Judas Maccabeus
Judah Maccabee (or Judas Maccabeus, also spelled Machabeus, or Maccabæus, Hebrew: יהודה המכבי, ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') was a Jewish priest (''kohen'') and a son of the priest Mattathias. He led the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleuci ...
"took it, and laid it waste" (''Antiquities of the Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' ( la, Antiquitates Iudaicae; el, Ἰουδαϊκὴ ἀρχαιολογία, ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by historian Flavius Josephus in the 13th year of the re ...
'' Book 12, 8:6) His brother Jonathan
Jonathan may refer to:
*Jonathan (name), a masculine given name
Media
* ''Jonathan'' (1970 film), a German film directed by Hans W. Geißendörfer
* ''Jonathan'' (2016 film), a German film directed by Piotr J. Lewandowski
* ''Jonathan'' (2018 ...
conquered it again in 147 BCE and destroyed the temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
of Dagon
Dagon ( he, דָּגוֹן, ''Dāgōn'') or Dagan ( sux, 2= dda-gan, ; phn, 𐤃𐤂𐤍, Dāgān) was a god worshipped in ancient Syria across the middle of the Euphrates, with primary temples located in Tuttul and Terqa, though many attes ...
of biblical fame (''Antiquities'' Book 13, 4:4; ). During the rule of Alexander Jannæus
Alexander Jannaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξανδρος Ἰανναῖος ; he, ''Yannaʾy''; born Jonathan ) was the second king of the Hasmonean dynasty, who ruled over an expanding kingdom of Judea from 103 to 76 BCE. A son of John Hyrcanus, h ...
, Ashdod was part of his territory (''Antiquities'' Book 13, 15:4).
Roman period
After the destruction wreaked during the succession wars betweenHyrcanus II
John Hyrcanus II (, ''Yohanan Hurqanos'') (died 30 BCE), a member of the Hasmonean dynasty, was for a long time the Jewish High Priest in the 1st century BCE. He was also briefly King of Judea 67–66 BCE and then the ethnarch (ruler) of J ...
and Aristobulus II
Aristobulus II (, grc, Ἀριστόβουλος ''Aristóboulos'') was the Jewish High Priest and King of Judea, 66 BCE to 63 BCE, from the Hasmonean dynasty.
Family
Aristobulus was the younger son of Alexander Jannaeus, King and High Priest ...
, Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
restored the independence of Azotus, as he did with all Hellenising coastal cities (''Antiquities'' Book 14, 4:4). A few years later, in 55 BCE, after more fighting, Roman general Gabinius
The gens Gabinia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens first appear in the second century BC.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', pp. 192 ''ff''. ("Gabinia gens"). The ''nomen'' derives from the city of ...
helped rebuild Ashdod and several other cities left without protective walls (''Antiquities'' Book 14, 5:2). In 30 BCE Ashdod came under the rule of King Herod, who then bequeathed it to his sister Salome
Salome (; he, שְלוֹמִית, Shlomit, related to , "peace"; el, Σαλώμη), also known as Salome III, was a Jewish princess, the daughter of Herod II, son of Herod the Great, and princess Herodias, granddaughter of Herod the Great, an ...
(''Antiquities'' Book 17, 8:1). By the time of the First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
(66-70), there must have been a large enough Jewish presence in Ashdod for Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
to feel compelled to place a garrison in the city.
Despite its location four miles (6 km) from the coast, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
(c. 90 – c. 168 CE) described it as a maritime city, as did Josephus in ''Antiquities'' Book 13, 15:4. The same Josephus though describes Ashdod as "in the inland parts" (''Antiquities'' Book 14, 4:4). This curious contradiction may refer to Ashdod's control of a separate harbor, called Azotus Paralios, or Ashdod-on-the-Sea (παράλιος - "paralios", Greek for "on the coast"). The landlocked city was called by the Romans Hippinos, "of the horsemen", and by the Greeks until late in the medieval period, Azotus mesogaios or "inland Azotus".
In the New Testament
The 1st century CEBook of Acts
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its message ...
refers to Azotus as the place in which Philip the Evangelist
Philip the Evangelist ( el, Φίλιππος, ''Philippos'') appears several times in the Acts of the Apostles. He was one of the Seven chosen to care for the poor of the Christian community in Jerusalem (). He preached and reportedly perform ...
reappeared after he converted the Ethiopian eunuch
The Ethiopian eunuch ( gez, ኢትዮጵያዊው ጃንደረባ) is a figure in the New Testament of the Bible; the story of his conversion to Christianity is recounted in Acts 8.
Biblical narrative
Philip the Evangelist was told by an angel ...
to Christianity. Philip preached the gospel throughout the area until he reached Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
, about 90 km to the north.
Byzantine, Crusader, Ayyubid and Mamluk periods
During the Byzantine period,Ashdod-Yam
Ashdod-Yam (lit. "Ashdod on the Sea" in Hebrew) is an archaeological site on the Mediterranean coast of Israel. It is located in the southern part of the modern city of Ashdod, and about 5 kilometres northwest of where Ashdod stood in the time ...
overshadowed its inland counterpart in size and importance. The 6th-century Madaba Map shows both under their respective names.
The prominence of Hellenised, then Christian Azotus continued until the 7th century, when it came under Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
rule. The city was represented at the Council of Chalcedon
The Council of Chalcedon (; la, Concilium Chalcedonense), ''Synodos tēs Chalkēdonos'' was the fourth ecumenical council of the Christian Church. It was convoked by the Roman emperor Marcian. The council convened in the city of Chalcedon, Bith ...
by Heraclius of Azotus.
The geographer Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l-Qasim Ubaydallah ibn Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh ( ar, ابوالقاسم عبیدالله ابن خرداذبه; 820/825–913), commonly known as Ibn Khordadbeh (also spelled Ibn Khurradadhbih; ), was a high-ranking Persian bureaucrat and ...
(c. 820 – 912) referred to the inland city as "Azdud" and described it as a postal station between al-Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
and Gaza.
The port stops being mentioned during the Ayyubid and Mamluk periods, making it likely that it was destroyed by the Muslims along with the other port cities, due to fears that they might again be used by Crusader invasions from the sea.Andrew Petersen, The Towns of Palestine under Muslim Rule: AD 600-1600
", BAR International Series 1381, 2005, pp
90
-91 With the destruction of the port city, its inland counterpart regains its importance.
Ottoman period
 The location of the village on
The location of the village on Via Maris
Via Maris is one modern name for an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia — along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Egypt, Israel, Turkey and Syr ...
enhanced the city's importance during the Ottoman rule. In 1596 CE, administrated by ''nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( ar, , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division w ...
'' ("subdistrict") of Gaza under the ''liwa'
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг ('' okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province") ...
'' ("district") of Gaza, the population of Ashdod (named ''Sdud'') numbered 75 households, about 413 persons, all Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s. The villagers paid a fixed tax rate of 33,3% on wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
, sesame
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus ''Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
and fruit crops, as well as goats and beehives; a total of 14,000 Akçe
The ''akçe'' or ''akça'' (also spelled ''akche'', ''akcheh''; ota, آقچه; ) refers to a silver coin which was the chief monetary unit of the Ottoman Empire. The word itself evolved from the word "silver or silver money", this word is deri ...
.
In 1838, ''Esdud'' was noted as a Muslim village in the Gaza district.
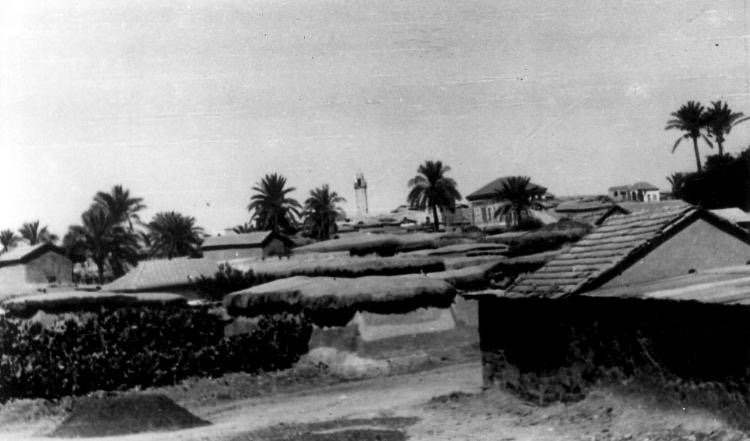
In the late nineteenth century, Isdud was described as a village spread across the eastern slope of a low hill, covered with gardens. A ruined khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
stood southwest of the village. Its houses were one-storey high with walls and enclosures built of adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of e ...
brick. There were two main sources of water: a pond and a masonry well. Both were surrounded by groves of date-palm and fig-trees.
British Mandate
In the1922 census of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922.
The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The divisi ...
, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Isdud had a population of 2,566 inhabitants; 2,555 Muslims and 11 Christians, where the Christians were all Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The population increased in the 1931 census to 3,240; 3,238 Muslims and 2 Christians, in a total of 764 houses.Mills, 1932, p4
.

 During the Mandatory period, Isdud had two elementary schools; one for boys which was opened in 1922, and one for girls which started in 1942. By the mid-1940s the boy-school had 371 students, while the girl-school had 74.
The official
During the Mandatory period, Isdud had two elementary schools; one for boys which was opened in 1922, and one for girls which started in 1942. By the mid-1940s the boy-school had 371 students, while the girl-school had 74.
The official Village Statistics, 1945
Village Statistics, 1945 was a joint survey work prepared by the Government Office of Statistics and the Department of Lands of the British Mandate Government for the Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry on Palestine which acted in early 1946. The ...
for "Isdûd" gave a population of 4,620 Arabs and 290 Jews in a total land area of 47,871 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; tr, dönüm; he, דונם), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount ...
s [].Department of Statistics, 1945, p31
No. 33 Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p
45
Of this, 3,277 dunams were used citrus and bananas, 8,327 for plantations and irrigable land, 23,762 for cereals, while 131 dunams were built-on land.
1948 War

 The village of Isdud was occupied by the Egyptian army on May 29, 1948, and became the Egyptians' northernmost position during the
The village of Isdud was occupied by the Egyptian army on May 29, 1948, and became the Egyptians' northernmost position during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
. While the Israelis failed to capture territory, and suffered heavy casualties, Egypt changed its strategy from offensive to defensive, thus halting their advance northwards. Egyptian and Israeli forces clashed in the surrounding area, with the Egyptians being unable to hold the Ad Halom
Ad Halom ( he, עַד הֲלוֹם) is a site at the eastern entrance to the city of Ashdod, Israel, where three bridges cross the Lakhish River.
Battle
Ad Halom (lit. "no further" or "up to here") refers to the northernmost point reached by ...
bridge over the Lachish River
Lakhish River ( he, נחל לכיש, ''Naḥal Lakhish'') is a river in Israel that flows into the Mediterranean Sea at the city of Ashdod. It is also known as Wadi Kabiba (inland section) and Wadi Sukhrir (Ashdod section) in Arabic. History
The Dr ...
. Israeli forces surrounded the town during Operation Pleshet
Operation Pleshet ( he, מִבְצָע פְּלֶשֶׁת, ''Mivtza Pleshet'', lit. "Operation Philistia"), named after the Pleshet, geographical region where it took place, was an Israeli military operation during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. It ...
, and shelled and bombed it from the air. For three nights from 18 October the Israeli Air Force
The Israeli Air Force (IAF; he, זְרוֹעַ הָאֲוִיר וְהֶחָלָל, Zroa HaAvir VeHahalal, tl, "Air and Space Arm", commonly known as , ''Kheil HaAvir'', "Air Corps") operates as the aerial warfare branch of the Israel Defense ...
bombed Isdud and several other locations. Fearing encirclement, Egyptian forces retreated on October 28, 1948, and the majority of the residents fled. The 300 townspeople who remained were driven southwards by the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the Israel, State of Israel. It consists of three servic ...
. The village was part of territory that was granted to Israel in the 1949 Armistice Agreements
The 1949 Armistice Agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt,moshav
A moshav ( he, מוֹשָׁב, plural ', lit. ''settlement, village'') is a type of Israeli town or settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 an ...
im, Sde Uziyahu
Sde Uziyahu ( he, שְׂדֵה עוֹזִיָּהוּ, lit. ''Uzziah Field'') is a moshav in southern Israel. Located near the city of Ashdod, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In it had a population of .
History ...
and Shtulim
Shtulim ( he, שְׁתוּלִים, lit. ''Planted'') is a moshav in south-central Israel. Located near Ashdod, it falls under the jurisdiction of Be'er Tuvia Regional Council. In it had a population of .
History
The moshav was founded in 1950 b ...
, were established to the east of Isdud, on village land. Bnei Darom
Bnei Darom ( he, בְּנֵי דָּרוֹם, ''lit.'' Sons of the South) is a religious moshav shitufi in central Israel. Located near the Mediterranean coast, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hevel Yavne Regional Council. In it had a popula ...
(in 1949) and Gan HaDarom
Gan HaDarom ( he, גַּן הַדָּרוֹם, ''lit.'' Garden of the South) is a moshav in southern Israel. Located on the coastal plain near Ashdod, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gederot Regional Council. In it had a population of .
Hist ...
(in 1953) were established north of Isdud, on village land.Khalidi, 1992, pp. 112-13 The city of Ashdod
Ashdod ( he, ''ʾašdōḏ''; ar, أسدود or إسدود ''ʾisdūd'' or '' ʾasdūd'' ; Philistine: 𐤀𐤔𐤃𐤃 *''ʾašdūd'') is the sixth-largest city in Israel. Located in the country's Southern District, it lies on the Mediterran ...
was founded in 1956 north of Isdud.
According to Khalidi, the site of Isdud is now covered in sand dunes.
Gallery
See also
* List of Arab towns and villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli WarReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * Nasser, Gamal Abdul (1955/1973)"Memoirs"
in ''
Journal of Palestine Studies
The ''Journal of Palestine Studies (JPS)'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal established in 1971. It is published by Taylor and Francis on behalf of the Institute for Palestine Studies, having previously been published by the University ...
''
“Memoirs of the First Palestine War” in 2, no. 2 (Win. 73): 3-32
pdf-file, downloadable *Petersen, Andrew (2002):
A Gazetteer of Buildings in Muslim Palestine: Volume I (British Academy Monographs in Archaeology)
' (Isdud, p. 155-158) * (Isdud
p.124
External links
from the
Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center
Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center () is a leading Palestinian arts and culture organization that aims to create a pluralistic, critical liberating culture through research, query, and participation, and that provides an open space for the community ...
Tour and signposting in Isdud
by Eitan Bronstein, 15.8.03,
Zochrot
Zochrot ( he, זוכרות; "Remembering"; ar, ذاكرات; "Memories") is an Israeli nonprofit organization founded in 2002. Based in Tel Aviv, its aim is to promote awareness of the Palestinian ''Nakba'' ("Catastrophe"), including the 1948 Pa ...
Untold stories: Ahmad Joudah
IMEU, Apr 24, 2008 {{Palestinian Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Palestine War District of Gaza Arab villages depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War Ashdod