Irreligion In The United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the United States, between 8% and 15% of citizens polled in 2019 demonstrated nonreligious attitudes and naturalistic worldviews, namely
In America, Nonbelievers Find Strength in Numbers
, Washington Post (September 15, 2007). In the 2008 American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS) report, 15% of the US population identified as having "no religion", almost double the 1990 figure. Irreligiosity is often under-reported in American surveys; many more express lack of faith in god or have alternative views on god (e.g. deism), than those who self-identify as atheists, agnostics and the like.Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar, , March 2009, American Religious Identification Survey
''None of the above: the growth of the “non-religious”''
Derek Michaud (2009) {{DEFAULTSORT:Irreligion In The United States Religion in the United States Religious demographics
atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
s or agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
s.Robert Fuller, ''Spiritual, but not Religious: Understanding Unchurched America'', Oxford University Press (2001). pp. 1-4. The number of self-identified atheists and agnostics was around 4% each, while many persons formally affiliated with a religion are likewise non-believing.
The percentage of Americans without religious affiliation, often labeled as "Nones", is around 20-29% - with people who identify as "nothing in particular" accounting for the growing majority of this demographic and while both atheists and agnostics accounting for the relatively unchanged minority of this demographic. "Nones" is an unclear category. Researchers argue that most of the "Nones" should be considered "unchurched", rather than objectively nonreligious; especially since most "Nones" may still hold some religious and spiritual beliefs. For example, 72% of American "Nones" believe in God or a Higher Power. The "None" response is more of an indicator for lacking affiliation than an active measure for irreligiosity, and a majority of the "Nones" can either be conventionally religious or "spiritual".
Social scientists observe that nonreligious Americans are characterized by indifference. Very few incorporate active irreligion as part of their identity, and only about 1-2% join groups promoting such values.
Demographics
A 2007 Barna group poll found that about 20 million people say they are atheist, have no religious faith, or are agnostic, with 5 million of that number claiming to be atheists. The study also found that " ey tend to be more educated, more affluent and more likely to be male and unmarried than those with active faith" and that "only 6 percent of people over 60 have no faith in God, and one in four adults ages 18 to 22 describe themselves as having no faith."Salmon, Jacqueline.In America, Nonbelievers Find Strength in Numbers
, Washington Post (September 15, 2007). In the 2008 American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS) report, 15% of the US population identified as having "no religion", almost double the 1990 figure. Irreligiosity is often under-reported in American surveys; many more express lack of faith in god or have alternative views on god (e.g. deism), than those who self-identify as atheists, agnostics and the like.Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar, , March 2009, American Religious Identification Survey
RIS 2008 Ris may refer to the following:
* Ris, Puy-de-Dôme, a commune in France
* Ris, Hautes-Pyrénées, a commune in France
* Ris, Norway
* Diane Ris (1932–2013), Catholic nun, educator and author
* Friedrich Ris (1867–1931), Swiss physician and ento ...
Trinity College. In 2012, 23% of religious affiliates did not consider themselves to be "religious", though this is subjective.
The number of atheists and agnostics found in common surveys tends to be quite low since, for instance, according to the 2019 Pew Research Center survey they were 3.1% and 4% respectively and according to the 2014 General Social Survey they were 4% and 5% respectively. However, their self-identification and actual views on God do differ since one study observed that out of people who did not believe in God or a universal spirit, only 24% actually self-identified as "atheists" and 15% as "agnostics". In one 2018 research paper using indirect probabilistic methods with considerable uncertainty estimated that 26% of Americans are atheists, which is much higher than the 3%-11% rates that are consistently found in surveys.
A 2012 study by the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
reported that, of the U.S. adult population, 19.6% had no religious affiliation and an additional 16% identified as "neither spiritual nor religious". Furthermore, atheists made up 2.4% and agnostics made up 3.3% of the US population. It also notes that a third of adults under the age of 30 are religiously unaffiliated. However, out of the religiously unaffiliated demographic: the majority describe themselves either as a religious (18%) or as spiritual but not religious (37%) while a significant minority (42%) considers themselves neither spiritual nor religious. Additionally, out of the unaffiliated: 68% believe in God, 12% are atheists, 17% are agnostics and overall 21% of the religiously unaffiliated pray every day.
The Pew Religious Landscape survey reported that as of 2014, 22.8% of the U.S. population is religiously unaffiliated, atheists made up 3.1% and agnostics made up 4% of the U.S. population. Out of all Americans who identify as unaffiliated including atheists and agnostics, 41% were raised Protestant and 28% were raised Catholic according to the 2014 Pew Religious Landscape survey.
The 2014 General Social Survey reported that 21% of Americans had no religion with 3% being atheist and 5% being agnostic.
Some 20% of Americans considered themselves neither religious nor spiritual. Irreligiousness is highest among young, white, unmarried, educated males.
When asked, around a third (24%-34% in different years) answered they were "not religious", and another 8% as atheist. Many of these identify/affiliate themselves with established religious groups and most believe in God. In one survey, 88% considered themselves as at least moderately spiritual.
According to the 2014 General Social Survey the percentages of the US population that identified as no religion were 21% in 2014, 20% in 2012, just 14% in 2000, and only 8 percent in 1990. Furthermore, the number of atheists and agnostics in the US has remained relatively flat in the past 23 years since in 1991 only 2% identified as atheist and 4% identified as agnostic while in 2014 only 3% identified as atheist and 5% identified as agnostic.
According to the 2008 Pew Religious Landscape report, as 2007, 16.1% of the US population identified as "no religion", atheists made up 1.6% and agnostics made up 2.4% of the US population.
According to a 2012 Pew Report on the "Nones", 19.6% of the population identified as "no religion", atheists made up 2.4% and agnostics made up 3.3% of the US population.
The Pew Religious Landscape survey reported that as of 2014, 22.8% of the American population is religiously unaffiliated, atheists made up 3.1% and agnostics made up 4% of the US population.
A 2010 Pew Research Center study comparing Millennials
Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the Western demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000 ...
to other generations showed that of those between 18 and 29 years old, only 3% self-identified as "atheists" and only 4% as "agnostics". Overall, 25% of Millennials were "Nones" and 74% were religiously affiliated. Though Millennials are less religious than previous generations at the same age frame, they are also much less engaged in many social institutions in general than previous generations.
According to the American Values Atlas from PPRI, 24% of the US Population is unaffiliated with a religion in 2017.
According to the Cooperative Congressional Election Study in 2016 31% were "nones" in 2016 and 29.5% were "nones" in 2018.
According to a Pew study, 7% of those raised Protestant are now unaffiliated whereas 4% of those raised Catholic are now unaffiliated.
In 2019, a Pew study found that 65% of American adults described themselves as Christians while the religiously unaffiliated, including atheist, agnostic or “nothing in particular”, is 26%.
According to a 2018 Pew report, 72% of the "Nones" have belief in God, a higher power, or spiritual force.
Several groups promoting irreligion – including the Freedom From Religion Foundation, American Atheists
American Atheists is a non-profit organization in the United States dedicated to defending the civil liberties of atheists and advocating complete separation of church and state. It provides speakers for colleges, universities, clubs, and the ...
, Camp Quest
Camp Quest is an organisation providing humanist residential summer camps for children in the United States, the United Kingdom,
Switzerland and Norway. It was first held in 1996 in Kentucky to provide an alternative to the traditional religiousl ...
, and the Rational Response Squad – have witnessed large increases in membership numbers in recent years, and the number of nonreligious student organizations at American colleges and universities increased during the 2000s (decade). However, the growth of atheist groups is very limited and will possibly shrink due to atheists normally being non-joiners. The overwhelming majority of the nonreligious in the US do not express their convictions in any manner, and only a negligible percentage joins irreligious organizations. As such, the overwhelming majority on the nonreligious do not join secular groups. Only a very small minority of the nonreligious, around 1% to 2%, actually join these kinds of groups.
Various explanations for trends
Some of the underlying factors in the increases in people identifying as "Nones" seem to not be that significant numbers of people are dropping religion, but rather that, in recent times, it has become more socially acceptable for younger and older generations to identify as a "None" than in previous decades, when identifying as having no religion carried negative stigmas. With young people usually having lower religious observance than older people and them feeling more comfortable identifying as a "None", generational replacement factors could play a role in the increment. Other possible driving factors may be just broader general cultural changes in the American way of life. The growth of the internet and social media has altered the sense of community and spirituality and the growth of self-focused citizenry, as opposed to community-focused citizenry, has broadly led to less civic involvement and less loyalty to many public institutions. Other possible driving forces could be political backlash. Young adults, in particular, have turned away from organized religion because they perceive it as deeply entangled with conservative politics and some seek to distance themselves from polarized systems. Others have suggested that delays in marriage, settling down, and having children among younger people reduces or delays the number and commitment of people participating in traditional religions or religious activities. Robert Fuller argues that the ascendency of science as a way of understanding the world makes it difficult for some people to believe in the supernatural or accept the "blind faith" that religion often requires. That modern biblical scholarship has illuminated the human authorship of the Bible as opposed to divine revelation. And that most educated people are aware of the role that cultural conditioning plays in shaping beliefs. Younger generations as a whole have lost trust and belief in numerous institutions along with religion. For instance,Millennials
Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the Western demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000 ...
, which make up about 1/3 the "Nones" demographic, tend to have less belief and trust in institutions such as the labor market, the economy, government and politics, marriage, the media, along with churches; than previous generations. The Nones tend to be more politically liberal and their growth has resulted in some increases in membership of secular organizations. However, the overwhelming majority of those without religion are not joining secular groups or even aligning with secularism.
Tables

Various beliefs
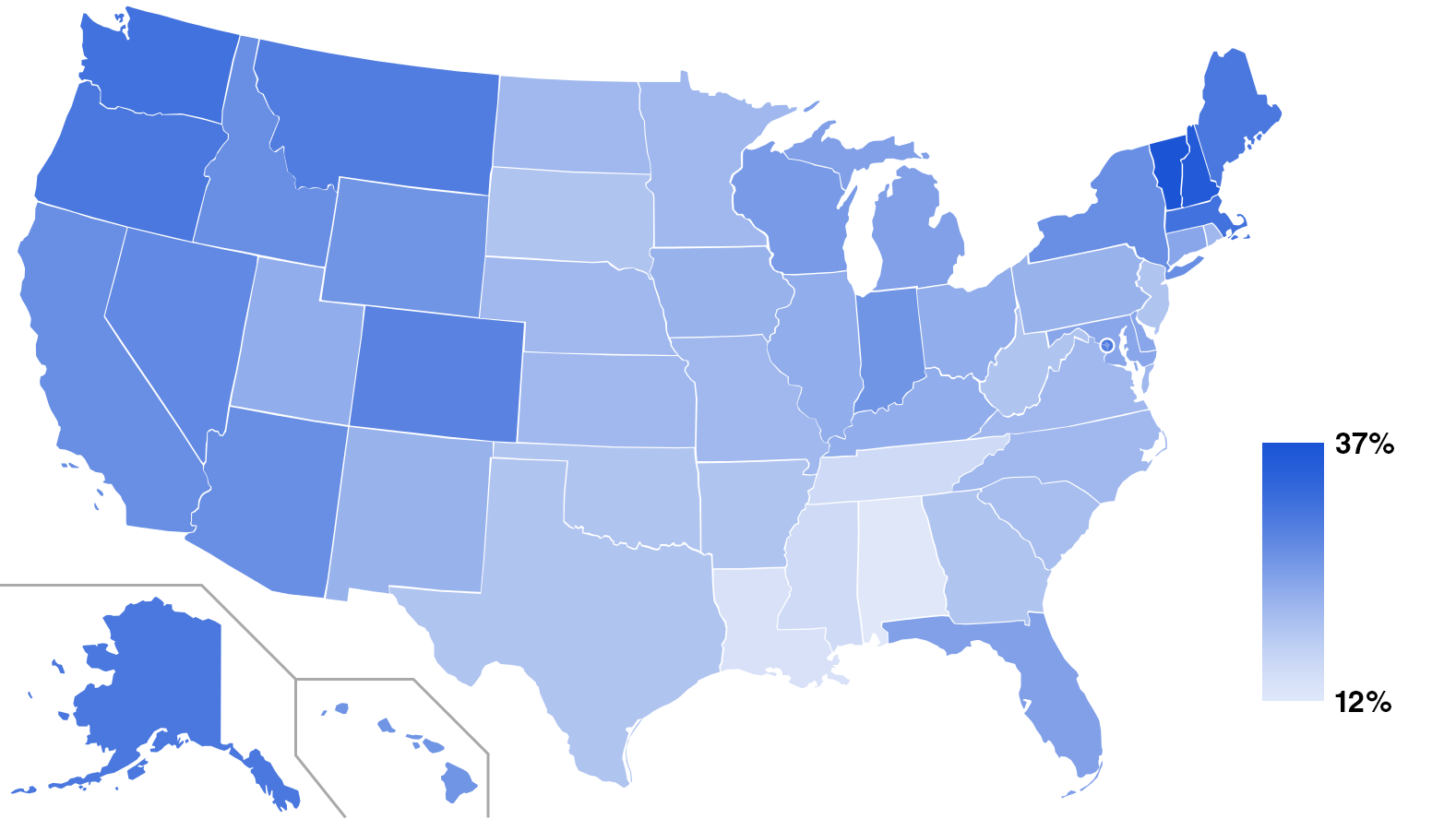
Various beliefs and practices of the "Nones" in 2012."Nones" by state
"Nones" by territory
Territories of the United States with percentage of population claiming no religion in 2010."Nones" by region
A region of the western United States known as the “ Unchurched Belt” is traditionally considered to contain the highest concentration of irreligious people, although this may have been surpassed by New England. Regions of the United States ranked by percentage of population claiming no religion in 2014."None" demographics
Demographics of the religiously unaffiliated in 2012 (as fraction of the named groups).Politics
In the late 2010s, 21% of registered voters were religiously unaffiliated; they are considered to be the largest "religious" voting block. More than six-in-ten religiously unaffiliated registered voters are Democrats (39%) or lean toward the Democratic Party (24%). They are about twice as likely to describe themselves as political liberals than as conservatives, and solid majorities support legal abortion (72%) and same-sex marriage (73%). In the last five years, the unaffiliated have risen from 17% to 24% of all registered voters who are Democrats or lean Democratic. According to a Pew Research exit poll 70% of those who were religiously unaffiliated voted for Barack Obama. In January 2007, California CongressmanPete Stark
Fortney Hillman Stark Jr. (November 11, 1931 – January 24, 2020), known as Pete Stark, was an American businessman and politician who was a member of the United States House of Representatives from 1973 to 2013. A Democrat from California, St ...
became the first openly atheist member of Congress. In January 2013, Kyrsten Sinema became the first openly non-theist Congresswoman, representing the State of Arizona.
See also
*Discrimination against atheists in the United States
Discrimination against atheists, both at present and historically, includes persecution of and discrimination against people who are identified as atheists. Discrimination against atheists may also comprise negative attitudes, prejudice, hostil ...
* Exvangelical
* First Amendment to the United States Constitution
* Religion in the United States
Christianity is the most widely professed religion in the United States, with Protestantism being its largest branch, although the country is believed to be "rapidly secularizing".
References
Bibliography
*Richard Dawkins
Richard Dawkins (born 26 March 1941) is a British evolutionary biologist and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford and was Professor for Public Understanding of Science in the University of Oxford from 1995 to 2008. An ath ...
, "Secularism, the Founding Fathers and the religion of America", in ''The God Delusion
''The God Delusion'' is a 2006 book by British evolutionary biologist, ethologist Richard Dawkins, a professorial fellow at New College, Oxford and, at the time of publication, the Charles Simonyi Chair for the Public Understanding of Science ...
'', Black Swan, 2007 ().
External links
''None of the above: the growth of the “non-religious”''
Derek Michaud (2009) {{DEFAULTSORT:Irreligion In The United States Religion in the United States Religious demographics