invasion of the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The concept of an invasion of the United States relates to military theory and doctrine which address the feasibility and practicality of a foreign power attacking and successfully invading the
The concept of an invasion of the United States relates to military theory and doctrine which address the feasibility and practicality of a foreign power attacking and successfully invading the
 The feasibility of a full-scale invasion of Hawaii and the contiguous United States by Imperial Japan was considered negligible, with Japan possessing neither the manpower nor logistical ability to do so. Minoru Genda of the
The feasibility of a full-scale invasion of Hawaii and the contiguous United States by Imperial Japan was considered negligible, with Japan possessing neither the manpower nor logistical ability to do so. Minoru Genda of the
 During the
During the
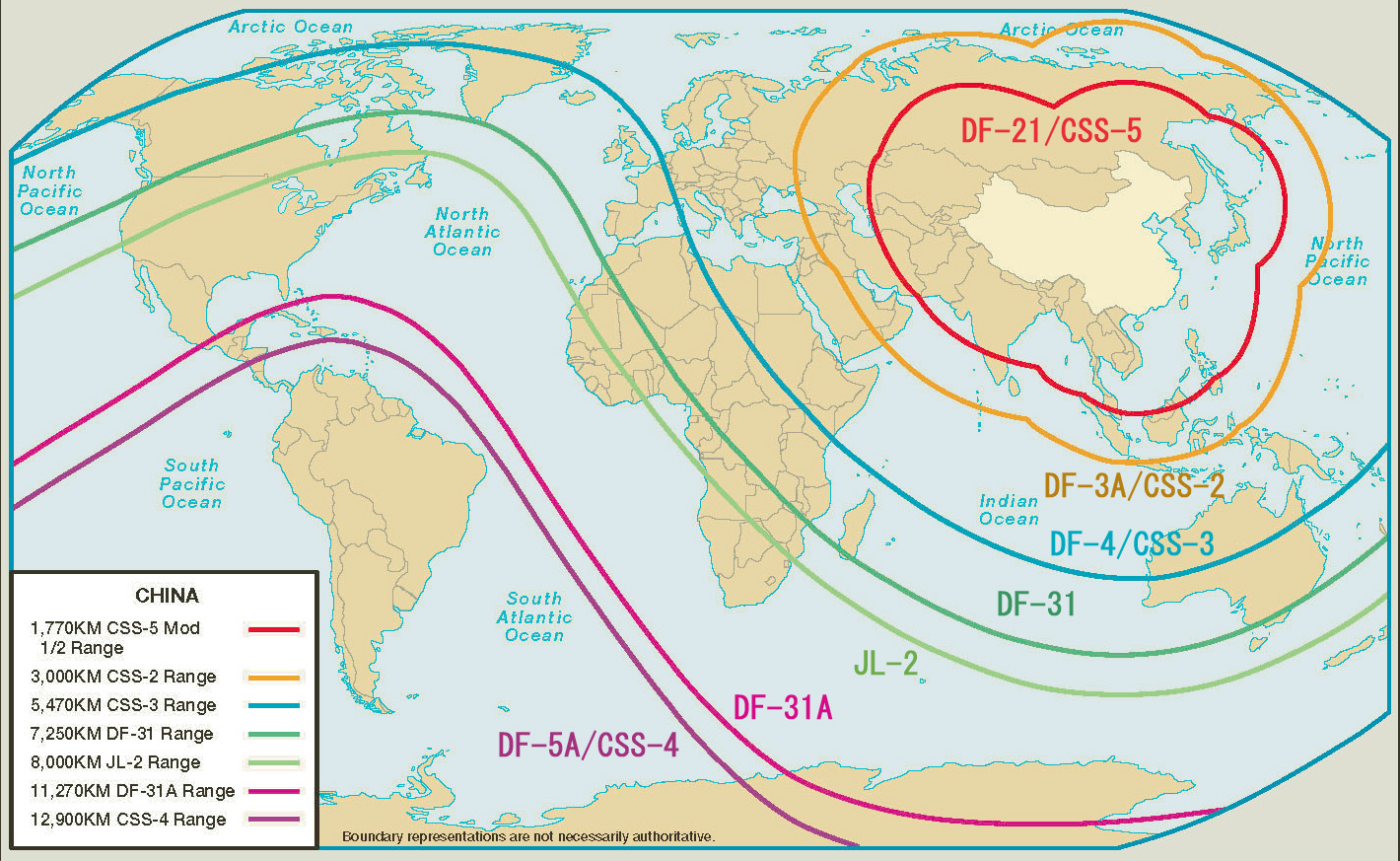 Several modern armies operate nuclear weapons with ranges in the thousands of kilometers. The US is therefore vulnerable to nuclear attack by powers such as the
Several modern armies operate nuclear weapons with ranges in the thousands of kilometers. The US is therefore vulnerable to nuclear attack by powers such as the
We Asked a Military Expert if All the World's Armies Could Shut Down the US
Vice, December 22, 2013.
 The concept of an invasion of the United States relates to military theory and doctrine which address the feasibility and practicality of a foreign power attacking and successfully invading the
The concept of an invasion of the United States relates to military theory and doctrine which address the feasibility and practicality of a foreign power attacking and successfully invading the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. The country has been physically invaded on several occasions—once during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
, once during the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the ...
, several times during the Mexican Border War, and three times during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, two of which were air attacks on American soil. During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, most of the US military strategy was geared towards repelling an attack by the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republi ...
against NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
allies in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
Early attacks
The military history of the United States began with a foreign power on US soil: theBritish Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. After American independence, the next attack on American soil was during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
, also with Britain, the first and only time since the end of the Revolutionary War in which a foreign power occupied the American capital (the capital city of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
was also captured by the British during the Revolution).
On April 25, 1846, Mexican forces invaded Brownsville, Texas, which they had long claimed as Mexican territory, and attacked US troops patrolling the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
in an incident known as the Thornton Affair
The Thornton Affair, also known as the Thornton Skirmish, Thornton's Defeat, or Rancho Carricitos was a battle in 1846 between the military forces of the United States and Mexico west upriver from Zachary Taylor's camp along the Rio Gra ...
, which sparked the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the ...
. The Texas Campaign
The Texas Campaign was the first front in the Mexican–American War, fought between the United States and Mexico. The front started with a Mexican assault near Brownsville. US forces were forced to surrender after hours of resisting, which lead ...
remained the only campaign on American soil, and the rest of the action in that conflict occurred in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, which were then part of Mexico, and in other parts of Mexico.
The American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
may be seen as an invasion of home territory to some extent since both the Confederate and the Union Armies made forays into the other's home territory. After the Civil War, the threat of an invasion from a foreign power was small, and it was not until the 20th century that any real military strategy was developed to address the possibility of an attack on America.
During the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction ...
in the summer of 1915, Mexican and Tejano rebels covertly supported by the Mexican Government of Venustiano Carranza
José Venustiano Carranza de la Garza (; 29 December 1859 – 21 May 1920) was a Mexican wealthy land owner and politician who was Governor of Coahuila when the constitutionally elected president Francisco I. Madero was overthrown in a February ...
, attempted to execute the Plan of San Diego by reconquering Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
and creating a racial utopia for Native Americans, Mexican Americans
Mexican Americans ( es, mexicano-estadounidenses, , or ) are Americans of full or partial Mexican heritage. In 2019, Mexican Americans comprised 11.3% of the US population and 61.5% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans. In 2019, 71% of Mexica ...
, Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian ancestry (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Although this term had historically been used for all the indigenous peopl ...
, and African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
. The plan also called for ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
in the reconquered territories and the summary execution of all white males over the age of sixteen. In order to implement the Plan, the rebels set off the Bandit War and conducted violent raids into Texas from across the Mexican border. Under pressure from his advisors to appease Carranza, U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
recognized the latter as leader of Mexico in return for Carranza's "help" in suppressing the Texas border raids.
On March 9, 1916, Mexican revolutionary Pancho Villa and his ''Villistas'' retaliated for the Wilson Administration's support of Carranza by invading Columbus, New Mexico in the Border War's Battle of Columbus, triggering the Pancho Villa Expedition in response, led by Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
John J. Pershing.
When it was captured and leaked to the American press by British Intelligence, the Imperial German Foreign Office's offer in the Zimmermann Telegram to support Carranza's expansionist aims, as laid out in the Plan of San Diego, in return for a potential wartime alliance against the United States, led the U.S. to declare war on Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
and enter World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
on the Allied side.
European threats
Until the early 20th century, the greatest potential threat to attack the United States was seen as theBritish Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
. Seacoast defense in the United States was organized on that basis, and military strategy was developed to forestall a British attack and attack and occupy Canada. War Plan Red was specifically designed to deal with a British attack on the United States and a subsequent invasion of Canada. Similar plans existed for a 20th-century war with Mexico, although the ability of the Mexican Army to attack and occupy American soil was considered negligible.
Within the British Empire, Canadian Army
The Canadian Army (french: Armée canadienne) is the command responsible for the operational readiness of the conventional ground forces of the Canadian Armed Forces. It maintains regular forces units at bases across Canada, and is also respo ...
Lieutenant Colonel James "Buster" Sutherland Brown drafted the Canadian counterpart of War Plan Red, Defence Scheme No. 1, in 1921. According to the plan, Canada would invade the United States as quickly as possible in the event of war or American invasion. The Canadians would gain a foothold in the Northern US to allow time for Canada to prepare its war effort and receive aid from Britain. According to the plan, Canadian flying columns stationed in Pacific Command would immediately be sent to seize Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region o ...
, Spokane, and Portland. Troops stationed in Prairie Command would attack Fargo and Great Falls and then advance towards Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origin ...
. Troops from Quebec would be sent to seize Albany in a surprise counterattack while troops from the Maritime Provinces would invade Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
. When American resistance grew, the Canadian soldiers would retreat to their own borders, destroying bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
s and railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
s to delay US military pursuit. The plan had detractors, who saw it as unrealistic, but it also had supporters who believed that it could conceivably have worked. On the opposite side of the Atlantic, the British Armed Forces
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, s ...
generally believed that if war with the United States did occur, they could transport troops to Canada if asked, but nonetheless saw it as impossible to defend Canada against the much larger and powerful United States. They did not plan to render any real aid and felt that sacrificing Canada to divert troops and buy time would be in the best military interests of the British Empire. A full invasion of the United States was considered unrealistic and a naval blockade was seen as too slow. The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
also could not afford a defensive strategy because Great Britain was extremely vulnerable to a supply blockade and if the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
approached the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
would be forced to immediately surrender. The British High Command planned instead for a decisive naval battle against the United States Navy by Royal Navy ships based in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the te ...
, likely Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
. Meanwhile, other ships based in Canada and the British West Indies would attack American merchant shipping and protect British and Commonwealth shipping convoys. The British would also attack U.S. coastal bases with bombing, shelling, and amphibious assaults. Soldiers from British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
would provide assistance with an attack on Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
to prevent United States Asiatic Fleet
The United States Asiatic Fleet was a fleet of the United States Navy during much of the first half of the 20th century. Before World War II, the fleet patrolled the Philippine Islands. Much of the fleet was destroyed by the Japanese by Febr ...
attacks against British merchant ships in the Far East and to preempt a potential assault against the Colony of Hong Kong
Hong Kong was a colony and later a dependent territory of the British Empire from 1841 to 1997, apart from a period of occupation under the Japanese Empire from 1941 to 1945 during the Pacific War. The colonial period began with the Briti ...
. The British Government hoped that these policies would make the war unpopular enough among Americans to force the U.S. government to agree to a negotiated peace.
Meanwhile, Imperial German plans for the invasion of the United States were drafted, like most war plans, as military logistical exercises between 1897 and 1906. Early versions planned to engage the United States Atlantic Fleet in a naval battle off Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 census, making it the third-most populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia B ...
, followed by shore bombardment of cities on the Eastern Seaboard. Later versions envisioned amphibious landings to seize control of both New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
. These plans, however, were never seriously considered, because the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
had insufficient soldiers and military resources to carry them out successfully. In reality, the foreign policy of Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
Wilhelm II sought to maintain good relations and avoid unnecessarily antagonizing the United States, while also limiting US ability to intervene in Europe. This policy continued, however, until the U.S. entered World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in 1917, but with one alteration.
From August 1914 until April 6, 1917, when the US ended its neutrality, German military intelligence
Military intelligence is a military discipline that uses information collection and analysis approaches to provide guidance and direction to assist commanders in their decisions. This aim is achieved by providing an assessment of data from a ...
officers and spies under diplomatic cover worked covertly to both delay and destroy military supplies being built by American munitions corporations and shipped to the Allied Powers. These efforts culminated in sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, disruption, or destruction. One who engages in sabotage is a ''saboteur''. Saboteurs typically try to conceal their identitie ...
operations like the Black Tom explosion (July 30, 1916) and the Kingsland explosion (January 11, 1917).
World War II
DuringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the defense of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
and the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
was part of the Pacific theater and American theater respectively. The American Campaign Medal
The American Campaign Medal is a military award of the United States Armed Forces which was first created on November 6, 1942, by issued by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The medal was intended to recognize those military members who had perfo ...
was awarded to military personnel who served in the continental United States in official duties, while those serving in Hawaii were awarded the Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal.
Nazi Germany
When Germany declared war on the U.S. in 1941, the German High Command immediately recognized that current German military strength would be unable to attack or invade the United States directly. Military strategy instead focused onsubmarine warfare
Submarine warfare is one of the four divisions of underwater warfare, the others being anti-submarine warfare, mine warfare and mine countermeasures.
Submarine warfare consists primarily of diesel and nuclear submarines using torpedoes, mis ...
, with U-boats
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare rol ...
striking American shipping in an expanded Battle of the Atlantic, particularly an all-out assault on US merchant shipping during Operation Drumbeat.
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
dismissed the threat of America, stating that the country had no racial purity and thus no fighting strength, and further stated that "the American public is made up of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and Negro
In the English language, ''negro'' is a term historically used to denote persons considered to be of Black African heritage. The word ''negro'' means the color black in both Spanish and in Portuguese, where English took it from. The term can be ...
es." German military and economic leaders held far more realistic views, with some such as Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as the Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of World War II. A close ally of Adolf Hitler, h ...
recognizing the enormous productive capacity of America's factories as well as the rich food supplies which could be harvested from the American heartland.
In 1942, German military leaders did briefly investigate and consider the possibility of a cross Atlantic attack against the US, most cogently expressed with the RLM's '' Amerika Bomber'' trans-Atlantic range bomber design competition, first issued in the spring of 1942, proceeded forward with only five airworthy prototype aircraft created between two of the competitors, but this plan had to be abandoned due to both the lack of staging bases in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the te ...
, and Germany's own rapidly decreasing capacity to produce such aircraft as the war continued. Thereafter, Germany's greatest hope of an attack on America was to wait and see the result its war with Japan. By 1944, with U-boat losses soaring and with the occupation of Greenland and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, it was clear to German military leaders that their dwindling armed forces had no further hope to attack the US directly. In the end, German military strategy was in fact geared toward ''surrendering'' to America, with many of the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
battles fought solely for the purpose of escaping the advance of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
and surrendering instead to the Western Allies, whom German leaders believed would offer more favorable terms.
One of the only officially recognized landings of German soldiers on American soil was during Operation Pastorius, in which eight German sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, disruption, or destruction. One who engages in sabotage is a ''saboteur''. Saboteurs typically try to conceal their identitie ...
agents were landed in the United States (one team landed in New York, the other in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
) via U-boats. The team was quickly captured and put on trial as spies, rather than prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of w ...
, due to the nature of their assignment. After the court found them guilty of espionage, six German agents were executed by electric chair at the Washington, DC
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morg ...
jail; the other two escaped the death penalty and instead received prison terms because they chose to defect to the US and inform the FBI of the mission plans. In 1948, the two were freed and returned to then Allied-occupied Germany
Germany was already de facto occupied by the Allies from the real fall of Nazi Germany in World War II on 8 May 1945 to the establishment of the East Germany on 7 October 1949. The Allies (United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and Franc ...
, later to be divided between West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
and East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In t ...
.
The Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
began planning for possible trans-Atlantic strategic bombing missions early in World War II, with Albert Speer stating in his own post-war book, '' Spandau: The Secret Diaries'', that Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
was fascinated with the idea of New York City in flames. Before his ''Machtergreifung
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Be ...
'' in January 1933, Hitler had already indicated his belief that the United States would be the next serious foe the future Third Reich would need to confront, after the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. The proposal by the RLM to Germany's military aviation firms for the Amerika Bomber project was issued to ''Reichsmarschall'' Hermann Göring in the late spring of 1942, about six months after the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
, for the competition to produce such a strategic bomber design, with only Junkers
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer. It was founded there in Dessau, Ge ...
and Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG () was a German share-ownership limited, aircraft manufacturing corporation named after its chief designer Willy Messerschmitt from mid-July 1938 onwards, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, in parti ...
each building a few airworthy prototype airframes before the war's end.
Imperial Japan
 The feasibility of a full-scale invasion of Hawaii and the contiguous United States by Imperial Japan was considered negligible, with Japan possessing neither the manpower nor logistical ability to do so. Minoru Genda of the
The feasibility of a full-scale invasion of Hawaii and the contiguous United States by Imperial Japan was considered negligible, with Japan possessing neither the manpower nor logistical ability to do so. Minoru Genda of the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
advocated invading Hawaii after attacking Oahu on December 7, 1941, believing that Japan could use Hawaii as a base to threaten the contiguous United States, and perhaps as a negotiating tool for ending the war. The American public in the first months after the attack on Pearl Harbor feared a Japanese landing on the West Coast of the United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
, eventually reacting with alarm to a rumored raid in the Battle of Los Angeles. Although the invasion of Hawaii was never considered by the Japanese military after Pearl Harbor, they did carry out Operation K, a mission on March 4, 1942, involving two Japanese aircraft dropping bombs on Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
to disrupt repair and salvage operations following the attack on Pearl Harbor three months earlier, which only caused minor damage.
On June 3/4, 1942, the Japanese Navy attacked the Alaska Territory
The Territory of Alaska or Alaska Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from August 24, 1912, until Alaska was granted statehood on January 3, 1959. The territory was previously Russian America, 1784–1867; th ...
as part of the Aleutian Islands campaign with the bombing of Dutch Harbor in the city of Unalaska, inflicting destruction and killing 43 Americans. Several days later, a force of six to seven thousand Japanese troops landed and occupied the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large v ...
of Attu and Kiska
Kiska ( ale, Qisxa, russian: Кыска) is one of the Rat Islands, a group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is about long and varies in width from . It is part of Aleutian Islands Wilderness and as such, special permission is requir ...
; they were driven out between May and August 1943 by American and Canadian forces. The Aleutian Islands campaign in early June 1942 was the only foreign invasion of American soil during World War II and the first significant foreign occupation of American soil since the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
. Japan also conducted air attacks through the use of fire balloons. Six American civilians were killed in such attacks; Japan also launched two manned air attacks on Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
as well as two incidents of Japanese submarines shelling the U.S. West Coast.
Although Alaska was the only incorporated territory
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sove ...
invaded by Japan, successful invasions of unincorporated territories in the western Pacific shortly after Pearl Harbor included the battles of Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
In December 1944, the Japanese Naval General Staff, led by Vice-Admiral Jisaburō Ozawa
was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, va ...
, proposed Operation PX
Operation PX, also known as Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night, was a planned Japanese military attack on civilians in the United States using biological weapons, devised during World War II. The proposal was for Imperial Japanese Navy submar ...
, also known as Operation Cherry Blossoms at Night. It called for ''Seiran'' aircraft to be launched by submarine aircraft carriers upon the West Coast of the United States—specifically, the cities of San Diego, Los Angeles, and San Francisco. The planes would spread weaponized bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as wel ...
, cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium '' Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting an ...
, typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. ...
, dengue fever, and other pathogens in a biological terror attack upon the population. The submarine crews would infect themselves and run ashore in a suicide mission. Planning for Operation PX was finalized on March 26, 1945, but shelved shortly thereafter due to the strong opposition of Chief of General Staff Yoshijirō Umezu, who believed the attack would spark "an endless battle of humanity against bacteria" and that it would cause Japan to "earn the derision of the world."
Cold War
 During the
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, the primary threat of an attack on the United States was viewed to be from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and larger Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republi ...
. In the event of such an attack occurring, the resulting war was universally expected to turn nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
almost immediately, mainly in the form of intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapo ...
attacks as well as Soviet Navy launches of SLBMs at US coastal cities.
The first Cold War strategy against a Soviet attack on the United States was developed in 1948, one year after the declaration of the Truman Doctrine, and was made into an even firmer policy after the first Soviet development of a nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
in 1949. By 1950, the United States had developed a defense plan to repel a Soviet nuclear bomber force through the use of interceptors and anti-aircraft missiles and to launch its own bomber fleet into Soviet airspace from bases in Alaska and Europe. By the end of the 1950s, both Soviet and US strategy included nuclear submarines and long-range nuclear missiles, both of which could strike in just ten to thirty minutes; bomber forces took as long as four to six hours to reach their targets and were significantly easier to intercept. This resulted in the development and implementation of the nuclear triad policy, under which all three weapons platforms (land-based, submarine, and bomber) were to be coordinated in unison for a devastating first strike, followed by a counterstrike that would be accompanied by "mopping up" missions of nuclear bombers.
Operation Washtub was a top secret joint operation between the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
and the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice ...
. Primarily lead by FBI director J. Edgar Hoover
John Edgar Hoover (January 1, 1895 – May 2, 1972) was an American law enforcement administrator who served as the first Director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). He was appointed director of the Bureau of Investigation ...
and his then-protégé Joseph F. Carroll, the operation was carried out with the primary goal of leaving stay-behind agents in the Alaska Territory
The Territory of Alaska or Alaska Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from August 24, 1912, until Alaska was granted statehood on January 3, 1959. The territory was previously Russian America, 1784–1867; th ...
for covert intelligence gathering, with a secondary goal of maintaining evasion and escape facilities for US forces.
On June 22, 1955, a US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
P2V Neptune with a crew of eleven was attacked by two Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
along the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific ...
in international waters over the Bering Strait, between the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and w ...
and Alaska. The P2V crashed on the northwestern cape of St. Lawrence Island, near the village of Gambell
Gambell ( ess, Sivuqaq, russian: Гамбелл) is a city
in the Nome Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Located on St. Lawrence Island, it had a population of 640 at the 2020 census, down slightly from 649 in 2000.
History
''S ...
. Villagers rescued the crew, three of whom were wounded by Soviet fire and four of whom were injured in the crash.
American nuclear warfare planning was nearly put to the test during the Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis (of 1962) ( es, Crisis de Octubre) in Cuba, the Caribbean Crisis () in Russia, or the Missile Scare, was a 35-day (16 October – 20 November 1962) confrontation between the United S ...
. The subsequent blockade of Cuba also added a fourth element into American nuclear strategy: surface ships and the possibility of low-yield nuclear attacks against deployed fleets. Indeed, the US had already tested the feasibility of nuclear attacks on ships during Operation Crossroads. Reportedly, one Soviet submarine nearly launched a nuclear torpedo at an American warship, but the three officers required to initiate the launch (the captain, the executive officer Vasily Arkhipov, and the political officer) could not agree to do so.
By the 1970s, the concept of mutually-assured destruction led to an American nuclear strategy that would remain relatively consistent until the end of the Cold War.
Modern era
In of 21st-century warfare, United States strategic planners have been forced to contend with various threats to the United States, including direct attack, terrorism, and unconventional warfare such as a cyberwarfare or economic attack on American investments and financial stability.Direct attack
 Several modern armies operate nuclear weapons with ranges in the thousands of kilometers. The US is therefore vulnerable to nuclear attack by powers such as the
Several modern armies operate nuclear weapons with ranges in the thousands of kilometers. The US is therefore vulnerable to nuclear attack by powers such as the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
,
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
. However, the UK and France are both members of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
and longtime US allies, while India is a Major Defense Partner of the United States and a member of the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, meaning an attack on the US by any of these countries is extremely unlikely. It should also be noted that although relations between China and the United States have been consistently tense, both countries are economically intertwined to an extent that full-scale war between them would be highly unprofitable.
The United States Northern Command and the United States Indo-Pacific Command
United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM) is a unified combatant command of the United States Armed Forces responsible for the Indo-Pacific region.
Formerly known as United States Pacific Command (USPACOM) since its inception in 1947, ...
are the top US military commands overseeing the defense of the Continental US and Hawaii, respectively.
Cyberwarfare and economic attacks
The risk of cyberattacks on civilian, government, and military computer targets was brought to light afterChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
became suspected of using government-funded hackers to disrupt American banking systems, defense industries, telecommunication systems, power grids, utility controls, air traffic and train traffic control systems, and certain military systems such as C4ISR and ballistic missile launch systems.
Attacks on the US economy
The United States is a highly developed mixed-market economy and has the world's largest nominal GDP and net wealth. It has the second-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP) behind China. It has the world's seventh-highest per capita GD ...
, such as efforts to devalue the dollar or corner trade markets to isolate the United States, are currently considered another method by which a foreign power may seek to attack the country.
Geographic feasibility
Many experts have considered the US impossible to invade because of its major industries, reliable and fast supply lines, large geographical size, geographic location, population size, and difficult regional features. For example, the deserts in the Southwest and theGreat Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
in the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
insulate the country's major population centers from threats of invasion. An invasion from outside North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
would require long supply chain
In commerce, a supply chain is a network of facilities that procure raw materials, transform them into intermediate goods and then final products to customers through a distribution system. It refers to the network of organizations, people, activ ...
s across the Pacific or Atlantic Oceans
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
, leading to a dramatic reduction of overall power. Furthermore, no existing nation possesses enough military and economic resources to threaten the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
. It should also be noted that Canada and Mexico enjoy generally friendly relations with the US, are deeply economically intertwined, and are militarily weak in comparison.
Military expert Dylan Lehrke noted that an amphibious assault
Amphibious warfare is a type of offensive military operation that today uses naval ships to project ground and air power onto a hostile or potentially hostile shore at a designated landing beach. Through history the operations were conducted u ...
on either the West Coast or the East Coast is simply too insignificant to acquire a beachhead
A beachhead is a temporary line created when a military unit reaches a landing beach by sea and begins to defend the area as other reinforcements arrive. Once a large enough unit is assembled, the invading force can begin advancing inland. The ...
on both coasts. Even if a foreign power somehow managed to prepare such a massive operation, and do so while remaining undetected despite the unrivaled size of the American intelligence apparatus, it still could not build up a force of any significant size before it was pushed back into the sea. In addition, Hawaii is largely protected by the consistently forty thousand-strong US military presence with valuable assets, which acts as a major deterrent to any foreign invasion of the island state and thereby the contiguous US. Thus, any continental invasion with even a remote hope of success would need to come from the land borders through Canada or Mexico. An attack from the latter would probably be more feasible due to the Great Lakes blocking much of the Canadian border, but California and Texas have the largest concentration of defense industries and military bases in the country and thus provide an effective deterrent from any attack, with the Southwestern desert also effectively dividing any invasion into two. An attack launched from Canada on the Midwest or the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
would be limited to light infantry and would fail to take over population centers or other important strategic points since there are mostly rural farmland and unpopulated national parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
along the border and powerful airbases located hundreds of miles south. That provides US military personnel or militias an advantage to conduct guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run ta ...
. This has resulted in many referring to the US as uninvadable.Oscar RickettWe Asked a Military Expert if All the World's Armies Could Shut Down the US
Vice, December 22, 2013.
In popular culture
A number of films and other related media have dealt with fictitious portrayals of an attack against the US by a foreign power. One of the more well-known films is '' Red Dawn'', detailing an attack against the US by the Soviet Union,Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
, and Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
. A 2012 remake details a similar attack, launched by North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
and ultranationalists controlling Russia. Other films include '' Invasion U.S.A.'', '' Olympus Has Fallen'', and '' White House Down''. '' The Day After'' and '' By Dawn's Early Light'', both of which detail nuclear war between US and Soviet forces. Another film that shows an invasion of the US was the 1999 film '' South Park: Bigger, Longer & Uncut'' in which Canadian forces invade the main characters' hometown in Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
. A bloodless Soviet takeover aftermath is depicted in the 1987 miniseries '' Amerika''.
''Invasion U.S.A.'' is a 1985 American action film made by Cannon Films starring Chuck Norris
Carlos Ray "Chuck" Norris (born March 10, 1940) is an American martial artist and actor. He is a black belt in Tang Soo Do, Brazilian jiu jitsu and judo. After serving in the United States Air Force, Norris won many martial arts championshi ...
. It was directed by Joseph Zito. It involves the star fighting off a force of Soviet and Cuban-led guerrillas.
In Philip K. Dick's '' The Man in the High Castle'', the United States is occupied by both Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan, which are separated by a neutral zone, after invasions of both the West Coast and the East Coast.
A terrorist occupation of Washington, D.C. was the subject of a '' G.I. Joe'' cartoon episode, when Serpentor led Cobra forces to occupy the American capital. A terrorist occupation of the capital was also seen in '' G.I. Joe: Retaliation''. In ''The Simpsons
''The Simpsons'' is an American animated sitcom created by Matt Groening for the Fox Broadcasting Company. The series is a satirical depiction of American life, epitomized by the Simpson family, which consists of Homer, Marge, Bart, ...
episode " You Only Move Twice," series protagonist Homer Simpson goes to work for what he doesn't know is a terrorist organization, whose leader threatens extreme violence and destruction in the mainland if various demands are not met; in the end, the terrorists seize control of the U.S. East Coast
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. The eastern seaboard contains the coa ...
.
In the video game '' Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 2'', Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
invades several parts of the United States, including Washington, D.C., in retaliation for a supposedly U.S.-assisted terrorist attack on a Russian airport. In '' Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 3'', the battle spreads to New York. The video game '' Homefront'' depicts an invasion of the U.S. by a unified Korea while '' Homefront: The Revolution'' depicts North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
invading and occupying the United States. In the real time strategy game '' World in Conflict'', Soviet forces invade and occupy the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
region of the United States, but are unable to make true gains into the mainland before they are eventually thrown back into the sea, only occupying at most, a third of the state of Washington for a few months. In the game '' Turning Point: Fall of Liberty'' is an alternate universe of the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
winning World War II which results in Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan invading the United States in 1953. Bethesda Softworks
Bethesda Softworks LLC is an American video game publisher based in Rockville, Maryland. The company was founded by Christopher Weaver in 1986 as a division of Media Technology Limited, and in 1999 became a subsidiary of ZeniMax Media. In ...
's '' Wolfenstein: The New Order'' and '' The New Colossus'' are set in a world where Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
has won World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, including a mainland invasion of U.S. after a nuclear bomb hit New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
. Part of '' Star Trek: Enterprise'' includes a similar scenario.
The 2003 video game '' Freedom Fighters'' is set in an alternate history where the Soviet Union won the Cold War, conquered most of the world and has invaded the United States from both Alaska and New York City. In the video game '' Command & Conquer: Red Alert 2'' the Soviet Union launches a massive invasion of the United States, with an emphasis on deploying psychic beacons in order to mind control the population.
References
{{Reflist Military history of the United States