Integrated Truss Structure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the
The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the
 All
All
 ISS truss segments were fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at
ISS truss segments were fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at

 The first truss piece, the Z1 truss, launched aboard STS-92 in October 2000. It contains the control moment gyroscope (CMG) assemblies, electrical wiring, communications equipment, and two plasma contactors designed to neutralize the static electrical charge of the space station.
Another objective of the Z1 truss was to serve as a temporary mounting position for the "P6 truss and solar array" until its relocation to the end of the P5 truss during STS-120. Though not a part of the main truss, the Z1 truss was the first permanent lattice-work structure for the ISS, very much like a girder, setting the stage for the future addition of the station's major trusses or backbones. It is made from stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum alloys.
While the bulk of the Z1 truss is unpressurized, it features a Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) port that connects its nadir to the zenith port of ''Unity'' and contains a small pressurized dome that allowed astronauts to connect electrical ground straps between ''Unity'' and the truss without an EVA. In addition, the dome inside the CBM of Z1 can be used as storage space.
The Z1 truss also features a forward-facing Manual Berthing Mechanism (MBM) ring. This MBM is not a port and is not pressurized or electrically powered, but it can be operated with a handheld tool to berth any passive CBM to it. The Z1 truss's MBM was used only once, to temporarily hold PMA-2, while the ''Destiny'' lab was being berthed onto the ''Unity'' node during STS-98. Since the installation of the nearby S0 truss in April 2002, access to the MBM has been blocked.
In October 2007, the P6 truss element was disconnected from Z1 and moved to P5; P6 will now be permanently connected with P5. The Z1 truss is now solely used to house the CMGs, communications equipment, and the plasma contactors; furthermore, Z1 connects now solely to ''Unity'' (Node 1) and no longer houses other space station elements.
In December 2008, the Ad Astra Rocket Company announced an agreement with NASA to place a flight test version of its VASIMR ion thruster on the station to take over reboost duties. In 2013, the thruster module was intended to be placed on top of the Z1 truss in 2015. NASA and Ad Astra signed a contract for development of the VASIMR engine for up to three years in 2015. However, in 2015 NASA ended plans for flying the VF-200 to the ISS. A NASA spokesperson stated that the ISS "was not an ideal demonstration platform for the desired performance level of the engines".NASA nixes Ad Astra rocket test on the space station
The first truss piece, the Z1 truss, launched aboard STS-92 in October 2000. It contains the control moment gyroscope (CMG) assemblies, electrical wiring, communications equipment, and two plasma contactors designed to neutralize the static electrical charge of the space station.
Another objective of the Z1 truss was to serve as a temporary mounting position for the "P6 truss and solar array" until its relocation to the end of the P5 truss during STS-120. Though not a part of the main truss, the Z1 truss was the first permanent lattice-work structure for the ISS, very much like a girder, setting the stage for the future addition of the station's major trusses or backbones. It is made from stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum alloys.
While the bulk of the Z1 truss is unpressurized, it features a Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) port that connects its nadir to the zenith port of ''Unity'' and contains a small pressurized dome that allowed astronauts to connect electrical ground straps between ''Unity'' and the truss without an EVA. In addition, the dome inside the CBM of Z1 can be used as storage space.
The Z1 truss also features a forward-facing Manual Berthing Mechanism (MBM) ring. This MBM is not a port and is not pressurized or electrically powered, but it can be operated with a handheld tool to berth any passive CBM to it. The Z1 truss's MBM was used only once, to temporarily hold PMA-2, while the ''Destiny'' lab was being berthed onto the ''Unity'' node during STS-98. Since the installation of the nearby S0 truss in April 2002, access to the MBM has been blocked.
In October 2007, the P6 truss element was disconnected from Z1 and moved to P5; P6 will now be permanently connected with P5. The Z1 truss is now solely used to house the CMGs, communications equipment, and the plasma contactors; furthermore, Z1 connects now solely to ''Unity'' (Node 1) and no longer houses other space station elements.
In December 2008, the Ad Astra Rocket Company announced an agreement with NASA to place a flight test version of its VASIMR ion thruster on the station to take over reboost duties. In 2013, the thruster module was intended to be placed on top of the Z1 truss in 2015. NASA and Ad Astra signed a contract for development of the VASIMR engine for up to three years in 2015. However, in 2015 NASA ended plans for flying the VF-200 to the ISS. A NASA spokesperson stated that the ISS "was not an ideal demonstration platform for the desired performance level of the engines".NASA nixes Ad Astra rocket test on the space station
''SEN News'', Irene Klotz. 17 March 2015. (An example of a spacecraft that used an

 The S0 truss, (also called the ''Center Integrated Truss Assembly Starboard 0 Truss'') forms the central backbone of the Space Station. It was attached on the top of the Destiny Laboratory Module during STS-110 in April 2002. S0 is used to route power to the pressurized station modules and conduct heat away from the modules to the S1 and P1 Trusses. The S0 truss is not docked to the ISS but is connected with four Module to Truss Structure (MTS) stainless steel struts.
The S0 truss, (also called the ''Center Integrated Truss Assembly Starboard 0 Truss'') forms the central backbone of the Space Station. It was attached on the top of the Destiny Laboratory Module during STS-110 in April 2002. S0 is used to route power to the pressurized station modules and conduct heat away from the modules to the S1 and P1 Trusses. The S0 truss is not docked to the ISS but is connected with four Module to Truss Structure (MTS) stainless steel struts.

 The P1 and S1 trusses (also called the ''Port and Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Trusses'') are attached to the S0 truss and contain carts to transport the
The P1 and S1 trusses (also called the ''Port and Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Trusses'') are attached to the S0 truss and contain carts to transport the

 The P3/P4 truss assembly was installed by the
The P3/P4 truss assembly was installed by the

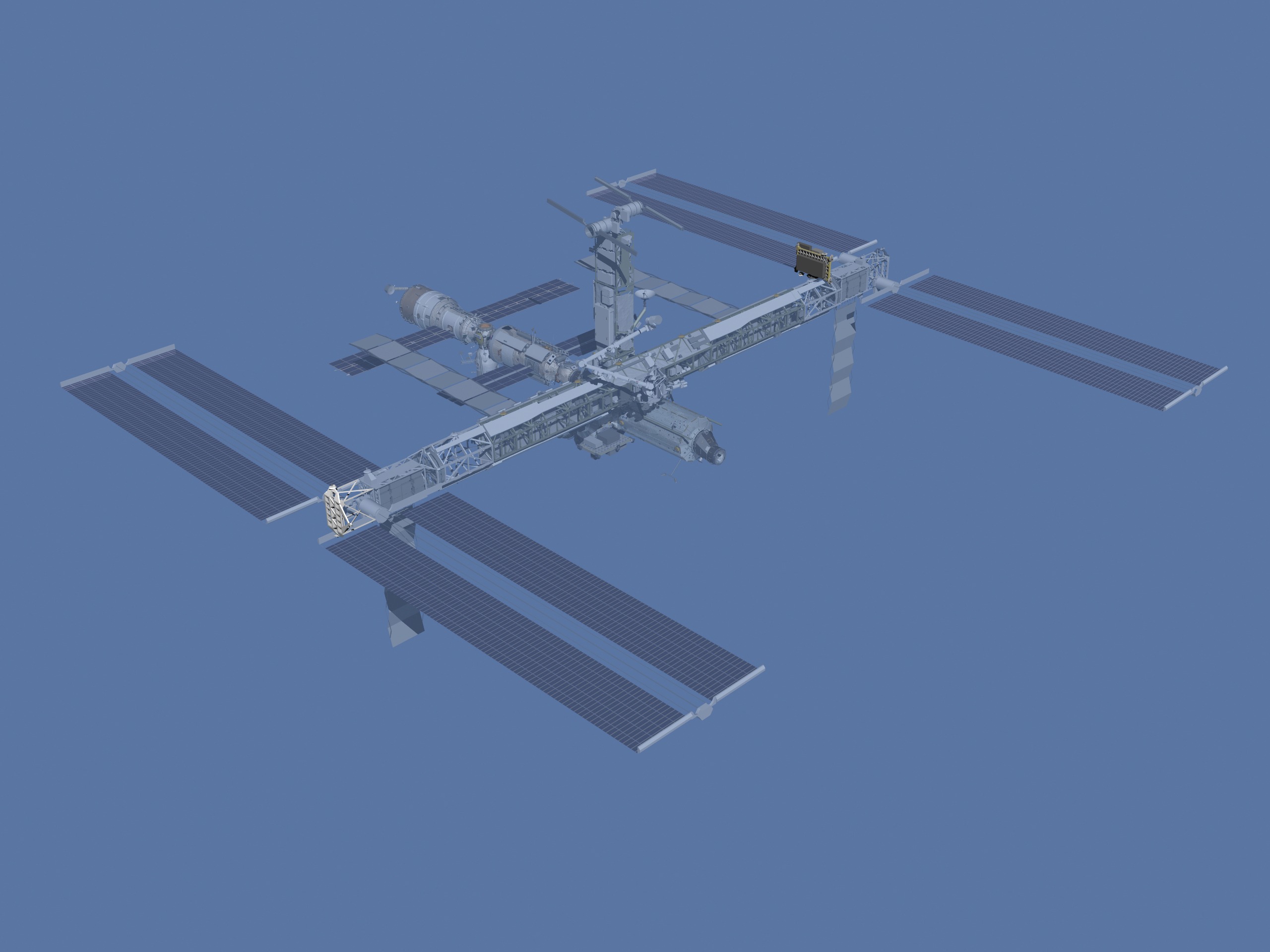 The P5 and S5 trusses are connectors that support the P6 and S6 trusses, respectively. The P3/P4 and S3/S4 truss assemblies' length was limited by the cargo bay capacity of the
The P5 and S5 trusses are connectors that support the P6 and S6 trusses, respectively. The P3/P4 and S3/S4 truss assemblies' length was limited by the cargo bay capacity of the

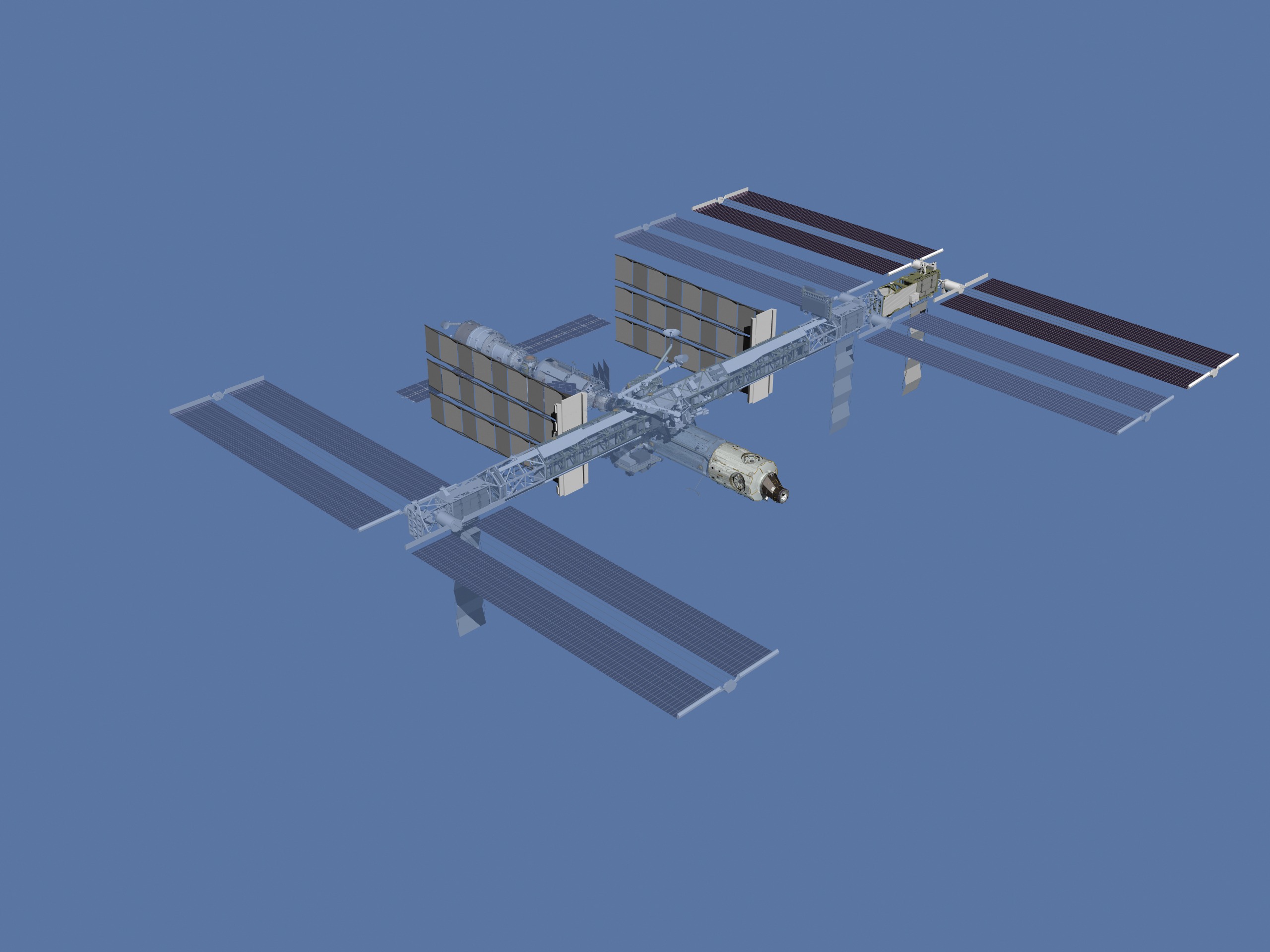
 The P6 truss was the second truss segment to be added because it contains a large Solar Array Wing (SAW) that generated essential electricity for the station, prior to activation of the SAW on the P4 truss. It was originally mounted to the Z1 truss and had its SAW extended during
The P6 truss was the second truss segment to be added because it contains a large Solar Array Wing (SAW) that generated essential electricity for the station, prior to activation of the SAW on the P4 truss. It was originally mounted to the Z1 truss and had its SAW extended during
Image:ISS Unity and Z1 truss structure from STS-92.jpg, Z1 truss (above) and Unity Module (below) from STS-92 in October 2000
Image:ISS after installation of S0 Truss element.jpg, The S0 truss (above) from STS-110 April 17, 2002
Image:ISS S1 Truss.jpg, ISS S1 truss element being installed on STS-112 October 10, 2002
Image:ISS Truss structure.jpg, ISS P1 truss element being installed on STS-113 November 28, 2002
Image:STS-115 EVA 2 on Day 5.jpg, The P3/P4 truss assembly being installed during STS-115 September 13, 2006. Astronauts give scale to the image.
Image:S3-S4 Truss Installed 2.jpg, The newly installed S3/S4 truss assembly during the first EVA of mission STS-117 on June 11, 2007.
Image:STS-116 - P5 Truss hand-off to ISS (NASA S116-E-05765).jpg, Space Shuttle ''Discovery'''s Canadarm-1 robotic arm hands off the P5 truss section to the International Space Station's Canadarm-2 during shuttle mission STS-116 in December 2006.
Image:STS-118 approaching ISS.jpg, Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' approaches the International Space Station during mission STS-118 with the S5 truss section ready to be installed.
Image:ISS_connecting_struts_and_frames.jpg, EVA view of structural steel framework
File:ISS_S3_truss_manufacturing_at_Michoud.jpg, S3 truss end piece manufacturing at NASA Michoud
Image:ISS after STS-120 in November 2007.jpg,
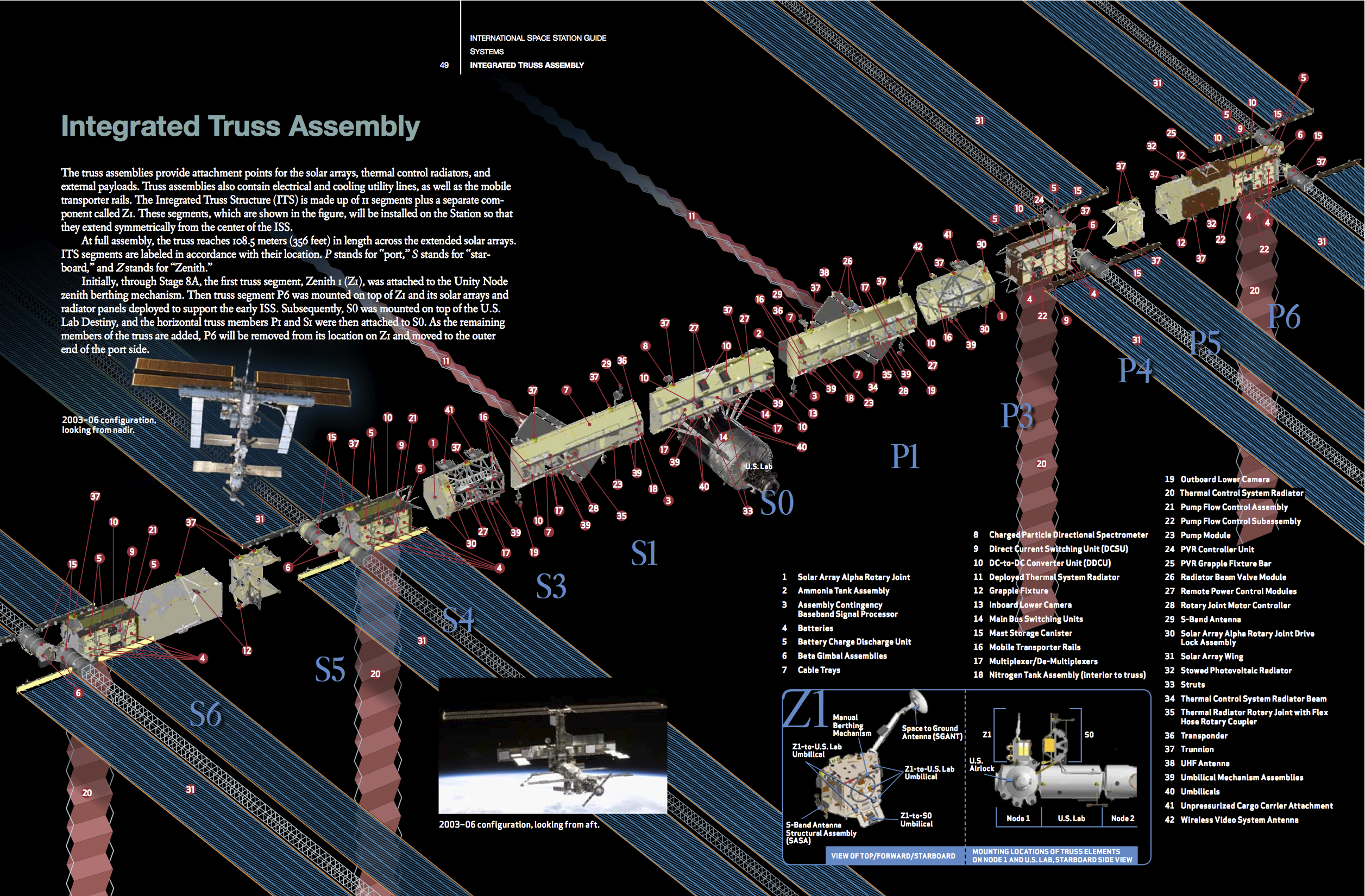
Image:01a Z1 Truss.jpg, Z1 Truss design
Image:05 SO Truss.jpg, S0 Truss design
File:06 S1 TrrussA.jpg, P1 / S1 Truss design
Image:07 P3 4 Truss.jpg, P3/4 / S3/4 Truss design
Image:08 P5 Truss.jpg, P5 / S5 Truss design
Image:02 P6.jpg, P6 / S6 Truss design
 The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the
The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
(ISS) consists of a linear arranged sequence of connected truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assembl ...
es on which various unpressurized components are mounted such as logistics carriers, radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.
A radiator is always ...
s, solar arrays, and other equipment. It supplies the ISS with a bus architecture. It is approximately 110 meters long and is made from aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
and stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's r ...
.
Truss components
 All
All truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assembl ...
components were named after their planned end-positions: Z for zenith, S for starboard and P for port, with the number indicating the sequential position. The S0 truss might be considered a misnomer, as it is mounted centrally on the zenith position of ''Destiny'' and is neither starboard nor port side.
Manufacturing
 ISS truss segments were fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at
ISS truss segments were fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at Huntington Beach, California
Huntington Beach is a seaside city in Orange County in Southern California, located southeast of Downtown Los Angeles. The city is named after American businessman Henry E. Huntington. The population was 198,711 during the 2020 census, mak ...
(formerly McDonnell Douglas), Michoud Assembly Facility
The Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) is an manufacturing complex owned by NASA in New Orleans East, a district within New Orleans, Louisiana, in the United States. Organizationally it is part of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, and is curren ...
in , Marshall Space Flight Center
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville postal address), is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's firs ...
in Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city in Madison County, Limestone County, and Morgan County, Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Madison County. Located in the Appalachian region of northern Alabama, Huntsville is the most populous city in ...
, and in Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa () is the second-largest city in the state of Oklahoma and 47th-most populous city in the United States. The population was 413,066 as of the 2020 census. It is the principal municipality of the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, a region wit ...
. The trusses were then transported or shipped to Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility for final assembly and checkout.
The structural framework was made using several manufacturing processes, including the investment casting
Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes.
Investment casting has been used in vari ...
, steel hot rolling
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is simi ...
, friction-stir, and TIG welding processes.
Z1 truss

 The first truss piece, the Z1 truss, launched aboard STS-92 in October 2000. It contains the control moment gyroscope (CMG) assemblies, electrical wiring, communications equipment, and two plasma contactors designed to neutralize the static electrical charge of the space station.
Another objective of the Z1 truss was to serve as a temporary mounting position for the "P6 truss and solar array" until its relocation to the end of the P5 truss during STS-120. Though not a part of the main truss, the Z1 truss was the first permanent lattice-work structure for the ISS, very much like a girder, setting the stage for the future addition of the station's major trusses or backbones. It is made from stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum alloys.
While the bulk of the Z1 truss is unpressurized, it features a Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) port that connects its nadir to the zenith port of ''Unity'' and contains a small pressurized dome that allowed astronauts to connect electrical ground straps between ''Unity'' and the truss without an EVA. In addition, the dome inside the CBM of Z1 can be used as storage space.
The Z1 truss also features a forward-facing Manual Berthing Mechanism (MBM) ring. This MBM is not a port and is not pressurized or electrically powered, but it can be operated with a handheld tool to berth any passive CBM to it. The Z1 truss's MBM was used only once, to temporarily hold PMA-2, while the ''Destiny'' lab was being berthed onto the ''Unity'' node during STS-98. Since the installation of the nearby S0 truss in April 2002, access to the MBM has been blocked.
In October 2007, the P6 truss element was disconnected from Z1 and moved to P5; P6 will now be permanently connected with P5. The Z1 truss is now solely used to house the CMGs, communications equipment, and the plasma contactors; furthermore, Z1 connects now solely to ''Unity'' (Node 1) and no longer houses other space station elements.
In December 2008, the Ad Astra Rocket Company announced an agreement with NASA to place a flight test version of its VASIMR ion thruster on the station to take over reboost duties. In 2013, the thruster module was intended to be placed on top of the Z1 truss in 2015. NASA and Ad Astra signed a contract for development of the VASIMR engine for up to three years in 2015. However, in 2015 NASA ended plans for flying the VF-200 to the ISS. A NASA spokesperson stated that the ISS "was not an ideal demonstration platform for the desired performance level of the engines".NASA nixes Ad Astra rocket test on the space station
The first truss piece, the Z1 truss, launched aboard STS-92 in October 2000. It contains the control moment gyroscope (CMG) assemblies, electrical wiring, communications equipment, and two plasma contactors designed to neutralize the static electrical charge of the space station.
Another objective of the Z1 truss was to serve as a temporary mounting position for the "P6 truss and solar array" until its relocation to the end of the P5 truss during STS-120. Though not a part of the main truss, the Z1 truss was the first permanent lattice-work structure for the ISS, very much like a girder, setting the stage for the future addition of the station's major trusses or backbones. It is made from stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum alloys.
While the bulk of the Z1 truss is unpressurized, it features a Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) port that connects its nadir to the zenith port of ''Unity'' and contains a small pressurized dome that allowed astronauts to connect electrical ground straps between ''Unity'' and the truss without an EVA. In addition, the dome inside the CBM of Z1 can be used as storage space.
The Z1 truss also features a forward-facing Manual Berthing Mechanism (MBM) ring. This MBM is not a port and is not pressurized or electrically powered, but it can be operated with a handheld tool to berth any passive CBM to it. The Z1 truss's MBM was used only once, to temporarily hold PMA-2, while the ''Destiny'' lab was being berthed onto the ''Unity'' node during STS-98. Since the installation of the nearby S0 truss in April 2002, access to the MBM has been blocked.
In October 2007, the P6 truss element was disconnected from Z1 and moved to P5; P6 will now be permanently connected with P5. The Z1 truss is now solely used to house the CMGs, communications equipment, and the plasma contactors; furthermore, Z1 connects now solely to ''Unity'' (Node 1) and no longer houses other space station elements.
In December 2008, the Ad Astra Rocket Company announced an agreement with NASA to place a flight test version of its VASIMR ion thruster on the station to take over reboost duties. In 2013, the thruster module was intended to be placed on top of the Z1 truss in 2015. NASA and Ad Astra signed a contract for development of the VASIMR engine for up to three years in 2015. However, in 2015 NASA ended plans for flying the VF-200 to the ISS. A NASA spokesperson stated that the ISS "was not an ideal demonstration platform for the desired performance level of the engines".NASA nixes Ad Astra rocket test on the space station''SEN News'', Irene Klotz. 17 March 2015. (An example of a spacecraft that used an
ion thruster
An ion thruster, ion drive, or ion engine is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. It creates thrust by accelerating ions using electricity.
An ion thruster ionizes a neutral gas by extracting some electrons out of ...
to maintain its orbit was the Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer
The Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) was the first of ESA's Living Planet Programme satellites intended to map in unprecedented detail the Earth's gravity field. The spacecraft's primary instrumentation was a hi ...
, whose engine allowed it to maintain a very low orbit.)
S0 truss

 The S0 truss, (also called the ''Center Integrated Truss Assembly Starboard 0 Truss'') forms the central backbone of the Space Station. It was attached on the top of the Destiny Laboratory Module during STS-110 in April 2002. S0 is used to route power to the pressurized station modules and conduct heat away from the modules to the S1 and P1 Trusses. The S0 truss is not docked to the ISS but is connected with four Module to Truss Structure (MTS) stainless steel struts.
The S0 truss, (also called the ''Center Integrated Truss Assembly Starboard 0 Truss'') forms the central backbone of the Space Station. It was attached on the top of the Destiny Laboratory Module during STS-110 in April 2002. S0 is used to route power to the pressurized station modules and conduct heat away from the modules to the S1 and P1 Trusses. The S0 truss is not docked to the ISS but is connected with four Module to Truss Structure (MTS) stainless steel struts.
P1, S1 trusses

 The P1 and S1 trusses (also called the ''Port and Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Trusses'') are attached to the S0 truss and contain carts to transport the
The P1 and S1 trusses (also called the ''Port and Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Trusses'') are attached to the S0 truss and contain carts to transport the Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, su ...
and astronauts to worksites along with the space station. They each flow 290 kg (637 lb) of anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achi ...
ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
through three heat rejection radiators. The S1 truss was launched on STS-112 in October 2002 and the P1 truss was launched on STS-113 in November 2002. Detailed design, test, and construction of the S1 and P1 structures were conducted by McDonnell Douglas (now Boeing) in Huntington Beach, CA. First parts were cut for the structure in 1996, and delivery of the first truss occurred in 1999.
P2, S2 trusses
The P2 and S2 trusses were planned as locations for rocket thrusters in the original design for Space Station Freedom. Since the Russian parts of the ISS also provided that capability, the reboost capability of the Space Station Freedom design was no longer needed at that location. So P2 and S2 were canceled.P3/P4, S3/S4 truss assemblies

 The P3/P4 truss assembly was installed by the
The P3/P4 truss assembly was installed by the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
'' Atlantis'' STS-115 mission, launched September 9, 2006, and attached to the P1 segment. The P3 and P4 segments together contain a pair of solar arrays, a radiator, and a rotary joint that will aim the solar arrays, and connects P3 to P4. Upon its installation, no power was flowing across the rotary joint, so the electricity generated by the P4 solar array wings was only being used on the P4 segment and not the rest of the station. Then in December 2006, a major electrical rewiring of the station by STS-116 routed this power to the entire grid. The S3/S4 truss assembly—a mirror-image of P3/P4—was installed on June 11, 2007 also by Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
''Atlantis'' during flight STS-117, mission 13A and mounted to the S1 truss segment.
Major P3 and S3 subsystems include the Segment-to-Segment Attach System (SSAS), Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ), and Unpressurized Cargo Carrier Attach System (UCCAS). The primary functions of the P3 truss segment are to provide mechanical, power and data interfaces to payloads attached to the two UCCAS platforms; axial indexing for solar tracking, or rotating of the arrays to follow the sun, via the SARJ; movement and worksite accommodations for the Mobile Transporter. The P3/S3 primary structure is made of a hexagonal-shaped aluminum structure and includes four bulkheads and six longeron
In engineering, a longeron and stringer is the load-bearing component of a framework.
The term is commonly used in connection with aircraft fuselages and automobile chassis. Longerons are used in conjunction with stringers to form structural ...
s. The S3 truss also supports EXPRESS Logistics Carrier locations, first to be launched and installed in the 2009 time frame.
Major subsystems of the P4 and S4 Photovoltaic Modules (PVM) include the two Solar Array Wings (SAW), the Photovoltaic Radiator (PVR), the Alpha Joint Interface Structure (AJIS), and Modified Rocketdyne Truss Attachment System (MRTAS), and Beta Gimbal Assembly (BGA).
P5, S5 trusses

 The P5 and S5 trusses are connectors that support the P6 and S6 trusses, respectively. The P3/P4 and S3/S4 truss assemblies' length was limited by the cargo bay capacity of the
The P5 and S5 trusses are connectors that support the P6 and S6 trusses, respectively. The P3/P4 and S3/S4 truss assemblies' length was limited by the cargo bay capacity of the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
, so these small (3.37 m long) connectors are needed to extend the truss. The P5 truss was installed on December 12, 2006, during the first EVA of mission STS-116. The S5 truss was brought into orbit by mission STS-118 and installed on August 11, 2007.
P6, S6 trusses


 The P6 truss was the second truss segment to be added because it contains a large Solar Array Wing (SAW) that generated essential electricity for the station, prior to activation of the SAW on the P4 truss. It was originally mounted to the Z1 truss and had its SAW extended during
The P6 truss was the second truss segment to be added because it contains a large Solar Array Wing (SAW) that generated essential electricity for the station, prior to activation of the SAW on the P4 truss. It was originally mounted to the Z1 truss and had its SAW extended during STS-97
STS-97 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. The crew installed the first set of solar arrays to the ISS, prepared a docking port for arrival of the Destiny Laboratory Modul ...
, but the SAW was folded, one half at a time, to make room for the SAWs on the P4 and S4 trusses, during STS-116 and STS-117 respectively. Shuttle mission STS-120 (assembly mission 10A) detached the P6 truss from Z1, remounted it on the P5 truss, redeployed its radiator panels, and attempted to redeploy its SAWs. One SAW (2B) was deployed successfully but the second SAW (4B) developed a significant tear that temporarily stopped deployment at around 80%. This was subsequently fixed and the array is now fully deployed. A later assembly mission (the out of sequence STS-119
STS-119 ( ISS assembly flight 15A) was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was flown by space shuttle Discovery during March 2009. It delivered and assembled the fourth starboard Integrated Truss Segment (S ...
) mounted the S6 truss on the S5 truss, which provided a fourth and final set of solar arrays and radiators.
Gallery of Trusses
Truss subsystems
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
on November 5, 2007 after relocation of the P6 truss assembly (far right) by STS-120
File:ISS March 2009.jpg, The space station, showing the completed truss assembly (as of March 2009)
Solar arrays
TheInternational Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
's main source of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
is from the four large U.S.-made photovoltaic arrays currently on the station, sometimes referred to as the ''Solar Array Wings'' (SAW). The first pair of arrays are attached to the P6 truss segment, which was launched and installed on top of Z1 in late 2000 during STS-97
STS-97 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. The crew installed the first set of solar arrays to the ISS, prepared a docking port for arrival of the Destiny Laboratory Modul ...
. The P6 segment was relocated to its final position, bolted to the P5 truss segment, in November 2007 during STS-120. The second pair of arrays was launched and installed in September 2006 during STS-115, but they didn't provide electricity until STS-116 in December 2006 when the station got an electrical rewiring. The third pair of arrays was installed during STS-117 in June 2007. A final pair arrived in March 2009 on STS-119
STS-119 ( ISS assembly flight 15A) was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was flown by space shuttle Discovery during March 2009. It delivered and assembled the fourth starboard Integrated Truss Segment (S ...
. More solar power was to have been available via the Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
n-built Science Power Platform
The Science Power Platform (SPP; russian: Научно-Энергетическая Платформа, ''Sci-Energy Platform'', also known by Russian initialism NEP) was a planned Russian element of the International Space Station (ISS) that wa ...
, but it was canceled.
Each of the Solar Array Wings are 34 m (112 ft) long by 12 m (39 ft) wide, have roughly of mass, and are capable of generating nearly 30 kW of DC power. They are split into two photovoltaic blankets, with the deployment mast in between. Each blanket has 16,400 silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
photovoltaic cells, each cell measuring 8 cm x 8 cm, grouped into 82 active panels, each consisting of 200 cells, with 4,100 diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diod ...
s.
Each pair of blankets was folded like an accordion
Accordions (from 19th-century German ''Akkordeon'', from ''Akkord''—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free-reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a ree ...
for compact delivery to space. Once in orbit, the deployment mast between each pair of blankets unfolds the array to its full length. Gimbals, known as the ''Beta Gimbal Assembly'' (BGA) are used to rotate
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
the arrays so that they face the Sun to provide maximum power to the International Space Station.
Over time, the photovoltaic cells on the wings have degraded gradually, having been designed for a 15-year service life. This is especially noticeable with the first arrays to launch, with the P6 and P4 Trusses in 2000 and 2006. To augment the P6 truss' wings, in June 2021, NASA launched two scaled-up versions of the Roll Out Solar Array
The Roll Out Solar Array (ROSA) and its larger version ISS Roll Out Solar Array (iROSA) are lightweight, flexible power sources for spacecraft designed and developed by Redwire.
This new type of solar array provides much more energy than tra ...
aboard the SpaceX Dragon 2
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed and manufactured by American aerospace manufacturer SpaceX, primarily for flights to the International Space Station (ISS). SpaceX has also launched private missions such as Ins ...
mission SpaceX CRS-22, and is set to launch four more on SpaceX CRS-25
SpaceX CRS-25, also known as SpX-25, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission (CRS) to the International Space Station (ISS) that was launched on 15 July 2022. The mission was contracted by NASA and was flown by SpaceX using their reusable s ...
, and SpaceX CRS-26
SpaceX CRS-26, also known as SpX-26, is a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS) launched on 26 November 2022. The mission is contracted by NASA and is flown by SpaceX using a . This is the sixth flight fo ...
. These arrays are more lightweight and generate more energy than the existing arrays. They are intended to be deployed along the central part of the wings up to two thirds of their length. Work to install support brackets for the new arrays on the P6 truss mast cans was initiated by the members of Expedition 64. Work to install and deploy the first two arrays themselves on the P6 brackets was successfully conducted over three spacewalks by Shane Kimbrough
Robert Shane Kimbrough (born June 4, 1967) is a retired United States Army officer and NASA astronaut. He was part of the first group of candidates selected for NASA astronaut training following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster. Kimbrou ...
and Thomas Pesquet of Expedition 65
Expedition 65 was the 65th long duration expedition to the International Space Station. The mission began on 17 April 2021, with the departure of Soyuz MS-17, and was initially commanded by NASA astronaut Shannon Walker serving as the third fe ...
.
Solar alpha rotary joint
The Alpha joint is the main rotary joint allowing the solar arrays to track the sun; in nominal operation the alpha joint rotates by 360° each orbit (however, see also Night Glider mode). One Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) is located between the P3 and P4 truss segments and the other is located between the S3 and S4 truss segments. When in operation, these joints continuously rotate to keep the solar array wings on the outboard truss segments oriented towards the Sun. Each SARJ is 10 feet in diameter, weighs approximately 2,500 pounds and can be rotated continuously using bearing assemblies and a servo control system. On both the port and starboard sides, all of the power flows through the Utility Transfer Assembly (UTA) in the SARJ. Roll ring assemblies allow transmission of data and power across the rotating interface so it never has to unwind. The SARJ was designed, built, and tested byLockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
and its subcontractors.
The Solar Alpha Rotary Joints contain Drive Lock Assemblies which allow the outer segments of the ITS to rotate and track the Sun. A component of the DLA is a pinion
A pinion is a round gear—usually the smaller of two meshed gears—used in several applications, including drivetrain and rack and pinion systems.
Applications
Drivetrain
Drivetrains usually feature a gear known as the pinion, which may ...
which engages with the race ring that serves as a bull gear
This page lists the standard US nomenclature used in the description of mechanical gear construction and function, together with definitions of the terms. The terminology was established by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), unde ...
. There are two race rings and two DLAs in each SARJ providing on-orbit redundancy, however a series of space walks would be required to reposition the DLAs and the Trundle Bearing Assemblies (TBAs) to utilize the alternate race ring. A spare DLA was brought to the ISS on STS-122.
In 2007, a problem was detected in the starboard SARJ and in one of the two beta gimbal assemblies (BGA). Damage had occurred due to excessive and premature wear of a track in the joint mechanism. The SARJ was frozen during problem diagnosis, and in 2008 lubrication was applied to the track to address the issue.
Power conditioning and storage
The sequential shunt unit (SSU) is designed to coarsely regulate the solar power collected during periods of insolation—when the arrays collect power during sun-pointing periods. A sequence of 82 separate strings, or power lines, leads from the solar array to the SSU. Shunting, or controlling, the output of each string regulates the amount of power transferred. The regulated voltage setpoint is controlled by a computer located on the IEA and is normally set to around 140 volts. The SSU has an overvoltage protection feature to maintain the output voltage below 200 V DC maximum for all operating conditions. This power is then passed through the BMRRM to the DCSU located in the IEA. The SSU measures and weighs . Each battery assembly, situated on the S4, P4, S6, and P6 Trusses, consists of 24 lightweightlithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also s ...
cells and associated electrical and mechanical equipment. Each battery assembly has a nameplate capacity of 110 Ah ( C) (originally 81 Ah) and . This power is fed to the ISS via the BCDU and DCSU respectively.
The batteries ensure that the station is never without power to sustain life-support systems and experiments. During the sunlight part of the orbit, the batteries are recharged. The nickel-hydrogen batteries had a design life of 6.5 years which means that they were replaced multiple times during the expected 30-year life of the station. The batteries and the battery charge/discharge units are manufactured by Space Systems/Loral
SSL, formerly Space Systems/Loral, LLC (SS/L), of Palo Alto, California, is a wholly owned manufacturing subsidiary of Maxar Technologies.
SSL designs and builds satellites and space systems for a wide variety of government and commercial cust ...
(SS/L), under contract to Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and ...
. Ni-H2 batteries on the P6 truss were replaced in 2009 and 2010 with more Ni-H2 batteries brought by Space Shuttle missions. The nickel-hydrogen batteries had a design life of 6.5 years and could exceed 38,000 charge/discharge cycles at 35% depth of discharge. Each battery measured and weighed .
From 2017 to 2021, the nickel-hydrogen batteries were replaced by lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
. On January 6, 2017, Expedition 50 members Shane Kimbrough
Robert Shane Kimbrough (born June 4, 1967) is a retired United States Army officer and NASA astronaut. He was part of the first group of candidates selected for NASA astronaut training following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster. Kimbrou ...
and Peggy Whitson began the process of converting some of the oldest batteries on the ISS to the new lithium-ion batteries. Expedition 64 members Victor J. Glover
Victor Jerome Glover (born April 30, 1976) is a NASA astronaut of the class of 2013 and Pilot on the first operational flight of the SpaceX Crew Dragon to the International Space Station. Glover is a captain in the U.S. Navy where he pilots ...
and Michael S. Hopkins concluded the campaign on February 1, 2021. There is a number of differences between the two battery technologies. One difference is that the lithium-ion batteries can handle twice the charge, so only half as many lithium-ion batteries were needed during replacement. Also, the lithium-ion batteries are smaller than the older nickel-hydrogen batteries. Although Li-Ion batteries typically have shorter lifetimes than Ni-H2 batteries as they cannot sustain as many charge/discharge cycles before suffering notable degradation, the ISS Li-Ion batteries have been designed for 60,000 cycles and ten years of lifetime, much longer than the original Ni-H2 batteries' design life span of 6.5 years.
Mobile Base System
The Mobile Base System (MBS) is a platform (mounted on the Mobile Transporter) for the robotic armsCanadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, su ...
and Dextre
Dextre, also known as the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM), is a two armed robot, or telemanipulator, which is part of the Mobile Servicing System on the International Space Station (ISS), and does repairs that would otherwise r ...
carrying them 108 metres down rails between the S3 and P3 truss. Beyond the rails Canadarm2 can step over the alpha rotary joint and relocate to grapple fixtures on the S6 and P6 truss. During STS-120 Astronaut Scott Parazynski rode the Orbiter Boom Sensor to repair a tear in the 4B solar array.
Truss and solar array assembly sequence

Technical blueprints
See also
* * * *References
{{ISS modules Components of the International Space Station Spacecraft components Articles containing video clips