Insurgent Privateer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
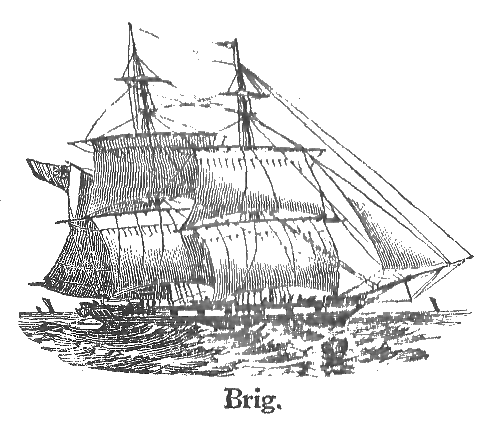
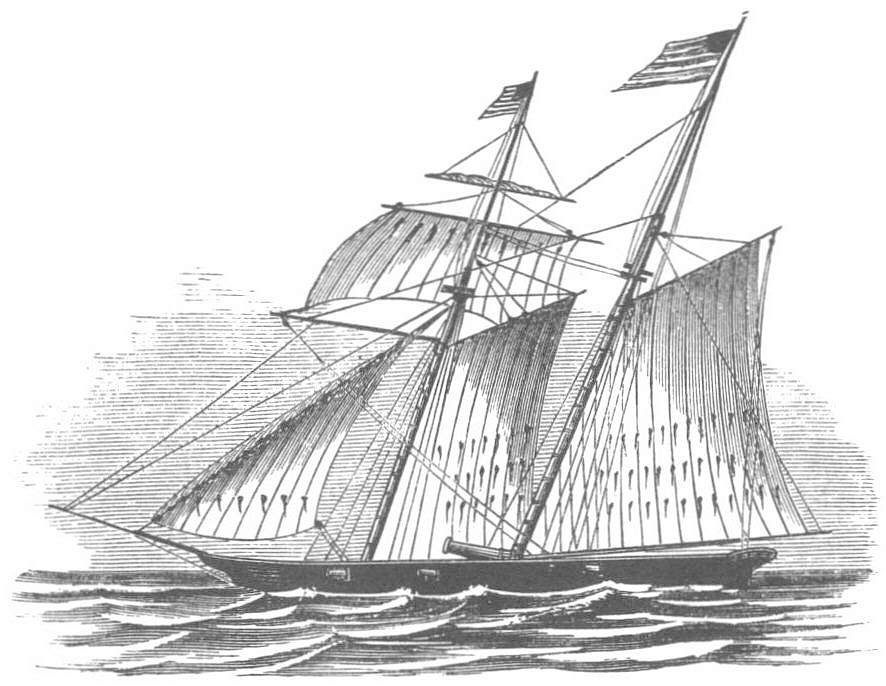 Insurgent privateers ( es, corsarios insurgentes) were private armed vessels recruited by the insurgent governments during the
Insurgent privateers ( es, corsarios insurgentes) were private armed vessels recruited by the insurgent governments during the

 Insurgent privateers ( es, corsarios insurgentes) were private armed vessels recruited by the insurgent governments during the
Insurgent privateers ( es, corsarios insurgentes) were private armed vessels recruited by the insurgent governments during the Spanish American wars of independence
The Spanish American wars of independence (25 September 1808 – 29 September 1833; es, Guerras de independencia hispanoamericanas) were numerous wars in Spanish America with the aim of political independence from Spanish rule during the early ...
to destroy Spanish trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
and capture Spanish merchant vessels.
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
ing started early in the war in 1812, but large scale deployment of warships started between 1816 and 1821, most notably under the flag of Buenos Aires and flag of Artigas. Between 1821 and 1829 these privateers sailed under the flags of Mexico and Colombia (privateers coming from Cartagena, Colombia, were referred to as "Carthaginians"). The main motivation of these insurgent privateers were to earn money but their political motivation was scant. They captured merchant vessels and slave ships to seize loot but they refused to fight against the Spanish Navy.
After the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
privately armed vessels came from North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, mostly from Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
. More than one hundred ships set sail from the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, with more than three thousand American sailors and captains to fight as insurgent privateers. ''In the 1810s, privateers from different regions of the United States (from New York to Louisiana, from Boston to Charleston) manned more than one hundred ships under the flags of Latin American revolutionary governments.'' There were also shipowners of other nationalities involved, such as French and British. These vessels were fast namely schooners or brigs
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part ...
, typically armed with twelve to sixteen guns, consisting of either twelve or twenty four lb caliber.
Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ...
was the principal port targeted, but there were other ports in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
and the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
that were also threatened. The second most important port was La Habana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
, in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
where Spanish trade with the Americas suffered considerable damage. The most important factor for reduction of Spanish commerce was not privateer attacks but loss of ports and new territories gained by republican countries.
The UK merchant fleet arrived from the Americas amounted to the fifteen percent of the total of their global commerce. British trade with Latin America was not totally legal but it was tolerated as they were an allied power in the Napoleonic Wars and later, with the mediation of the UK, in the Latin American wars. The Royal Navy tried to protect their trade without interfering in the local conflicts of independence. The US Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
turned a blind eye to North American privateers, and tried to force Spain to accelerate the cession of Florida ( Adams–Onís Treaty), nevertheless they took firm measures to terminate privateering after the end of the war, in 1829.
See also
* List of ships under Chilean Letter of marqueReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * {{cite book , first=Nicolas , last=Terrien , title="Des patriotes sans patrie", Histoire des corsaires insurgés de l'Amérique espagnole (1810-1825) , location=Rennes , publisher=Les Perséides , date=May 2015 , pages=384 Naval warfare Privateering Spanish American wars of independence