Insular India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The term Insular India refers to the isolated landmass which became the 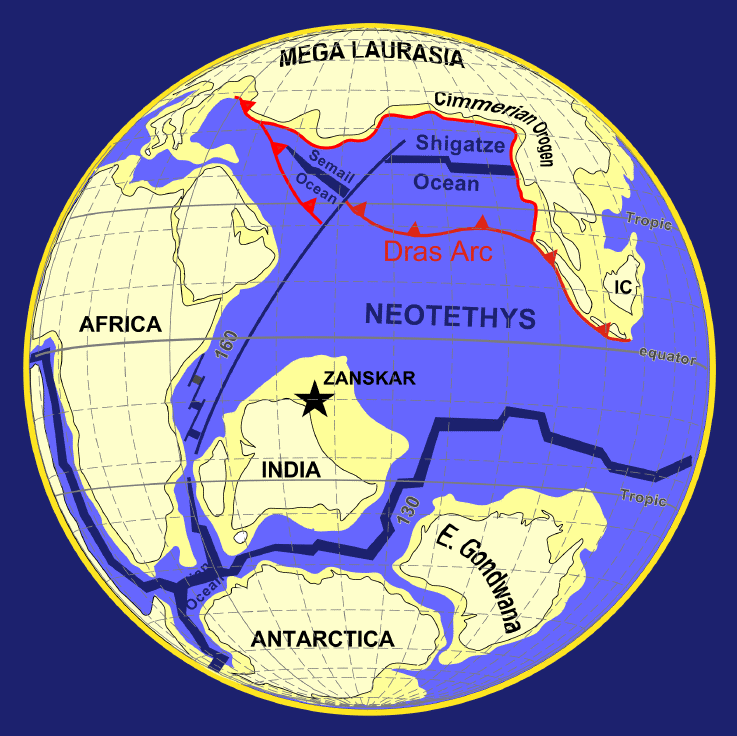 Thus, for a period of 53 million years India has retained a degree of isolation, 11 of which it has been a complete island continent. This has allowed for its local biota to follow the typical patterns seen in islands and diversify in unique ways, much like in modern Madagascar, its sister landmass. Faunal interchanges with other landmasses, like
Thus, for a period of 53 million years India has retained a degree of isolation, 11 of which it has been a complete island continent. This has allowed for its local biota to follow the typical patterns seen in islands and diversify in unique ways, much like in modern Madagascar, its sister landmass. Faunal interchanges with other landmasses, like
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. Across the latter stages of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
and most of the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), E ...
, following the breakup of Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
, the Indian subcontinent remained an isolated landmass as the Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began mov ...
drifted across the Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents ...
, forming the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
. The process of India's separation from Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
first began 88 million years ago, but complete isolation only occurred towards the end of the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
, a process that has been suggested to be the creation of the Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flood ...
. Soon after, the land mass moved northward rather quickly, until contact with Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
was established 55 million years ago. Even then, both landmasses did not become fully united until around 35 million years ago, and periods of isolation occurred as recently as 24 million years ago.
 Thus, for a period of 53 million years India has retained a degree of isolation, 11 of which it has been a complete island continent. This has allowed for its local biota to follow the typical patterns seen in islands and diversify in unique ways, much like in modern Madagascar, its sister landmass. Faunal interchanges with other landmasses, like
Thus, for a period of 53 million years India has retained a degree of isolation, 11 of which it has been a complete island continent. This has allowed for its local biota to follow the typical patterns seen in islands and diversify in unique ways, much like in modern Madagascar, its sister landmass. Faunal interchanges with other landmasses, like Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
(then an archipelago of islands across the Tethys) have occurred during this period, and a considerable Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
influence can already been seen long before contact was made. This rendered India rather peculiar as not just an isolated continent but also a "stepping stone" in the dispersal of many animal and plant clades across Africa, Europe, Madagascar, Asia and possibly even Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
. Still, several "archaic" clades managed to survive. However, the vast majority of India's terrestrial vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
life was wiped out in the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event; only 3 extant tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct theraps ...
lineages can trace their ancestry to Cretaceous India. Most of India's few other surviving Gondwanan lineages were outcompeted during the Paleogene by newly-arriving lineages. However, plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
and invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
fauna were less affected.
During the Paleogene, dispersing tetrapod lineages from Asia repopulated India, with some such as lagomorphs evolving on the continent. By the time full contact was established, a large percentage of India's old and new indigenous fauna was outcompeted by Eurasian species. However, several groups like lagomorph
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae (hares and rabbits) and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek ''lagos'' (λαγ� ...
sRose K.D., Deleon V.B., Mmissian P., Rana R.S., Sahni A., Singh L. & Smith T. (2008). – Early Eocene lagomorph (Mammalia) from western India and the early diversification of Lagomorpha. – Proc. Royal Society B, RSPB 2007.1661.R1 have become widespread, becoming dominant clades across the world's faunas, in addition to floral groups such as dipterocarps, which went on to become dominant tree species throughout much of tropical Asia. A significant diversity of Asian mantises
Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They ha ...
also originated on Insular India.The islands of the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, V ...
still retain an indigenous herpetofauna
Herpetology (from Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is the branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians (gymnophiona)) and rept ...
, presumably an echo of the amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
and reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
species seen in India as an island.
Geology
The Burma Terrane, an isolated island arc that was present in the Tethys Sea during the Cretaceous, collided with Insular India during the Paleocene and was pushed northwards, eventually colliding with mainland Asia independent of Insular India's own collision. Much of western Myanmar consists of the former Burma Terrane.Cretaceous fauna
The Cretaceous fauna of India is well attested in bothConiacian
The Coniacian is an age or stage in the geologic timescale. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series and spans the time between 89.8 ± 1 Ma and 86.3 ± 0.7 Ma (million years ago). The Coniacian is preceded by t ...
and Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
aged sites such as the Lameta Formation
The Lameta Formation, also known as the Infratrappean Beds, is a sedimentary geological formation found in Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, India, associated with the Deccan Traps. It is of Maastrichtian age (Late Cretaceous), and is nota ...
. Generally speaking, the local dinosaurian
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutiona ...
and crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
fauna is almost identical to that of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, with clades like abelisaurids
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are found ...
, titanosaurs
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thr ...
, noasaurids and notosuchians
Notosuchia is a suborder of primarily Gondwanan mesoeucrocodylian crocodylomorphs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Some phylogenies recover Sebecosuchia as a clade within Notosuchia, others as a sister group (see below); if S ...
being well represented here. A possible deviation is the presence of stegosaurs
Stegosauria is a group of Herbivore, herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and early Cretaceous Period (geology), periods. Stegosaurian fossils have been found mostly in the Northern Hemisphere, predominantly in what i ...
, the last remaining members of this lineage; if these aren't misidentified remains of herbivorous notosuchians and sauropods, then these relics would be the only indigenous ornithischians
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek s ...
in the entire Indo-Malagasy landmass. Another possible deviation is the presence of a troodontid
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discov ...
, a lineage more typically associated with Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
and thus possibly indicating interchange with Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
or even mainland Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
, but these remains are controversial and could belong either other theropods or notosuchians.
The mammalian fauna of India also bears similarities with that of Madagascar, with the gondwanathere
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaffia ...
''Bharattherium
''Bharattherium'' is a mammal that lived in India during the Maastrichtian (latest Cretaceous) and possibly the Paleocene. The genus has a single species, ''Bharattherium bonapartei''. It is part of the gondwanathere family Sudamericidae, which i ...
'', one of the most common mammals, being extremely similar to the malagasy ''Lavanify
''Lavanify'' is a mammalian genus from the late Cretaceous (probably Maastrichtian, about 71 to 66 million years ago) of Madagascar. The only species, ''L. miolaka'', is known from two isolated teeth, one of which is damaged. The teeth were ...
''. The most diverse mammals in the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
of India are eutherians, a clade normally associated with northern continents and also found in Madagascar in this epoch, which combined with their ambiguous phylogenetic positions renders them extremely important in the understanding of placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsup ...
evolution. Some like ''Deccanolestes
''Deccanolestes'' is a scansorial, basal Euarchontan from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and Paleocene Intertrappean Beds of Andhra Pradesh, India. It may be closely related to '' Sahnitherium''. ''Deccanolestes'' has been referred to Palae ...
'' have been variously interpreted as euarchonta
The Euarchonta are a proposed grandorder of mammals: the order Scandentia (treeshrews), and its sister Primatomorpha mirorder, containing the Dermoptera or colugos and the primates (Plesiadapiformes and descendents).
The term "Euarchonta" (mea ...
ns, adapisoriculids, or stem-afrotherian
Afrotheria ( from Latin ''Afro-'' "of Africa" + ''theria'' "wild beast") is a clade of mammals, the living members of which belong to groups that are either currently living in Africa or of African origin: golden moles, elephant shrews (also know ...
s, though the general consensus appears to be that they are non-placental eutherians and that there are non known Cretaceous placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsup ...
s. '' Kharmerungulatum'', formerly interpreted as a stem-ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, cam ...
, is now known to be a representative of Zhelestidae
Zhelestidae is a lineage of extinct eutherian mammals. Occurring in the Late Cretaceous from the Turonian to the Maastrichtian, they were an extremely successful group, with representatives present in Europe, Asia, India (and subsequently in Mad ...
, a herbivorous non-placental eutherian clade. Regardless of the phylogenetics of these eutherians, they almost certainly reached India and Madagascar through either Europe, Africa or mainland Asia; later they would propagate across Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
as far west as Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
.
Probably the most spectacular representative of India's Cretaceous fauna is '' Avashishta'', a late surviving haramiyid and the last known non-mammalian synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ...
. Non-gondwanathere multituberculates
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, ...
and meridiolestida
Meridiolestida is an extinct clade of mammals known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic of South America and possibly Antarctica. They represented the dominant group of mammals in South America during the Late Cretaceous. Meridiolestidans were morp ...
ns can probably also be inferred as having lived in India during this epoch, due to the former's presence in all landmasses including Madagascar and the latter being the dominant mammals in other known Gondwannan sites.
The herpetofauna
Herpetology (from Greek ἑρπετόν ''herpetón'', meaning "reptile" or "creeping animal") is the branch of zoology concerned with the study of amphibians (including frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians (gymnophiona)) and rept ...
of India in the Cretaceous is a mosaic of indigenous groups and forms that rafted their way from Asia. Neobatrachians are an indigenous clade and locally well represented as they are in Madagascar in the form of ranids, hylids, leptodactylids, pelobatids and discoglossids, as are madtsoiid snakes
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joi ...
like ''Sanajeh
''Sanajeh'' (meaning "ancient gape" in Sanskrit) is a genus of late Cretaceous Madtsoiidae, madtsoiid snake from western India. A fossil described in 2010 in paleontology, 2010 from the Lameta Formation was found coiled around an egg and an adjac ...
'' and possibly '' Indophis'' and iguanian lizards, while anguids are from Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
. Caecillians are an indigenous Gondwanan clade, but their absence in Madagascar suggests that the Asian species have descended from African species that colonized India as it drifted north. The divergence between African and Asian groups has been estimated at 120 million years ago, indicating that this likely happened during the Cretaceous.
Several fish taxa are known from estuarine locales; most are marine species, but there are also forms like lepisosteids, which do also occur in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
but are otherwise rare in Gondwanan landmasses. Cichlids
Cichlids are fish from the family (biology), family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses (Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have c ...
and other forms suspected of having had an Indian Gondwanan origin were most likely present.
Effects of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event had a particularly catastrophic effect in India, wiping out almost all terrestrialvertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
lineages on the continent. It is thought that the effects of the Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flood ...
volcanism may have compounded the extinction event's impacts, making it especially devastating there. Only three extant tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct theraps ...
groups have representatives that can be verified as descending from Gondwanan endemics of Insular India: one family of frogs
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
( Nasikabatrachidae), several families of caecilians (Grandisoniidae
The Grandisoniidae are a family of common caecilians found in Africa, Seychelles and India. Like other caecilians, they superficially resemble worms or snakes. The family was formerly known as Indotyphlidae.
Taxonomy
The genera in this fami ...
, Chikilidae
Chikilidae is a family of Indian caecilians, the 10th and most recent (2012) family of caecilians (legless amphibians) to be identified, although the type species, ''Chikila fulleri'' (formerly ''Herpele fulleri'') was first described in 1904. Th ...
and Ichthyophiidae
The Ichthyophiidae are the family of Asiatic tailed caecilians or fish caecilians found in South and Southeast Asia as well as southernmost China.
They are primitive caecilians, lacking many of the derived characters found in the other families ...
), and 1 family of blindsnakes (Gerrhopilidae
The Gerrhopilidae (Indo-Malayan blindsnakes) are a family of blindsnakes that contains at least 16 species in the genus '' Gerrhopilus'', and possibly others (the genus '' Cathetorhinus'' and the species known as either ''Malayotyphlops manilae' ...
). Notably, all three lineages have a fossorial
A fossorial () animal is one adapted to digging which lives primarily, but not solely, underground. Some examples are badgers, naked mole-rats, clams, meerkats, and mole salamanders, as well as many beetles, wasps, and bees.
Prehistoric eviden ...
mode of life, indicating that this lifestyle may have saved them from the extinction's impacts. Several mammal genera also survived the event, although they went extinct during the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), E ...
.
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
fauna, especially soil invertebrates such as centipedes
Centipedes (from New Latin , "hundred", and Latin , "foot") are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda (Ancient Greek , ''kheilos'', lip, and New Latin suffix , "foot", describing the forcipules) of the subphylum Myriapoda, an a ...
, were likely less affected by the extinction, and several lineages that persist today are thought to have Gondwanan ancestry. The Parreysiinae, a subfamily of the freshwater mussel
Freshwater bivalves are one kind of freshwater mollusc, along with freshwater snails. They are bivalves that live in fresh water as opposed to salt water, which is the main habitat type for bivalves.
The majority of species of bivalve molluscs ...
family Unionidae
The Unionidae are a family of freshwater mussels, the largest in the order Unionida, the bivalve molluscs sometimes known as river mussels, or simply as unionids.
The range of distribution for this family is world-wide. It is at its most diverse ...
, are thought to have originated in East Gondwana
The South Polar region of the Cretaceous comprised the continent of East Gondwana–modern day Australia and Antarctica–a product of the break-up of Gondwana in the Cretaceous Period. The southern region, during this time, was much warmer than i ...
during the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
, and survived on both Africa and Insular India throughout the Cretaceous. Several different tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
( Indochinellini, Lamellidentini, and Parreysiini) of the Parreysiinae evolved in isolation on Insular India. These endemic tribes managed to survive the K-Pg extinction, and colonized mainland Asia via both Insular India and the Burma Terrane, the latter of which collided with and was pushed north by Insular India during the Paleogene. They are now found throughout much of India and Southeast Asia. Similarly, numerous lineages of mantises
Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They ha ...
(clade Cernomantodea) are thought to have originated on the Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and other ...
-Indian landmass after the breakup of Gondwana, and persisted on Insular India after it broke away. This massive diversity of mantises survived the K-Pg extinction and invaded mainland Asia following the collision of Insular India with Asia.
Paleogene fauna
Following the near-total extirpation of vertebrate life from India during the K-Pg extinction, India's vertebrate fauna was successively rebuilt by dispersing lineages primarily from Asia, first over water during its period of isolation, and later via land when it collided with Asia. Some of India's surviving tetrapod Gondwanan vertebrate lineages were outcompeted by these new arrivals. It was previously thought that several major families of Neobatrachia ( Ranidae,Dicroglossidae
The frog family Dicroglossidae occurs in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia and Africa, with most genera and species being found in Asia. The common name of the family is fork-tongued frogs.
The Dicroglossidae were previously considered to ...
, Rhacophoridae
The Rhacophoridae are a family of frogs that occur in tropical sub-Saharan Africa, South India and Sri Lanka, Japan, northeastern India to eastern China and Taiwan, south through the Philippines and Greater Sundas, and Sulawesi. They are commonly ...
) originated in India from an ancestor that colonized the continent from Africa during the Cretaceous. This was supported by closely related families ( Nyctibatrachidae, Ranixalidae
Ranixalidae is a family of frogs commonly known as the leaping frogs or Indian frogs. They are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or oth ...
, Micrixalidae) being endemic to India. However, more recent studies hypothesize that these families have a mainland Asian origin and colonized India during the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
.
Paleocene fauna
The fossil record of the Paleocene of India, when the continent was a fully isolated landmass, is dubious and thus most inferrals about its fauna are somewhat speculative. It is known for certain that ''Deccanolestes
''Deccanolestes'' is a scansorial, basal Euarchontan from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and Paleocene Intertrappean Beds of Andhra Pradesh, India. It may be closely related to '' Sahnitherium''. ''Deccanolestes'' has been referred to Palae ...
'' and ''Bharattherium
''Bharattherium'' is a mammal that lived in India during the Maastrichtian (latest Cretaceous) and possibly the Paleocene. The genus has a single species, ''Bharattherium bonapartei''. It is part of the gondwanathere family Sudamericidae, which i ...
'' survived the K-Pg event,WILSON, Gregory P, NEW MAMMALIAN FOSSILS FROM THE INTERTRAPPEAN BEDS OF THE SOUTHERN PART OF THE DECCAN VOLCANIC PROVINCE AND THE CRETACEOUS–PALEOGENE TRANSITION IN INDIA, October 27, 2016 though for how further long did non-placental eutherians and gondwanatheres live in India is unknown, and by the time the landmass makes contact with Asia they are most likely extinct.
During this epoch, unambiguous placental mammals make their way into India in spite of its isolation, probably by rafting like the many placental groups in Madagascar, or perhaps brief connections with Africa and Europe (the latter still an archipelago). Hyaenodonts
Hyaenodontidae ("hyena teeth") is a family of extinct predatory mammals from extinct superfamily Hyaenodontoidea within extinct order Hyaenodonta. Hyaenodontids arose during the early Eocene and persisted well into the early Miocene. Fossils of t ...
are an endemic African clade, first showing outside of the continent in the Paleocene of India and Europe. Glires
Glires (, Latin ''glīrēs'' 'dormice') is a clade (sometimes ranked as a grandorder) consisting of rodents and lagomorphs (rabbits, hares, and pikas). The hypothesis that these form a monophyletic group has been long debated based on morphologic ...
evolved in Asia, but a lineage became isolated in India, where it gave rise to the lagomorphs.
For a while it was theorised that ostriches
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There are ...
evolved in India during this epoch, under the assumption that European ratites like ''Palaeotis
''Palaeotis'' is a genus of paleognath birds from the middle Eocene epoch of central Europe. One species is known, ''Palaeotis weigelti''. The holotype specimen is a fossil tarsometatarsus and phalanx. Lambrect (1928) described it as an extinct ...
'' represented recent Asiatic migrations. However, the first unambiguous ostriches are now thought to have evolved in Africa, with eogruiids
Eogruidae (also spelled Eogruiidae in some publications) is a family of large, flightless birds that inhabited Asia from the Eocene to Pliocene epochs. Related to modern ostriches, it was formerly thought to be related to cranes, limpkins and tr ...
having occupied their ecological niche in Asia; likewise, European ratites are now thought to be among the oldest known, and probably evolved independently there, being unrelated to ostriches. Still, India probably had a thriving paleognath
Palaeognathae (; ) is a infraclass of birds, called paleognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contain ...
fauna; the volant ancestors of kiwis and elephant birds
Elephant birds are members of the Extinction, extinct ratite family (biology), family Aepyornithidae, made up of flightless birds that once lived on the island of Madagascar. They are thought to have become extinct around 1000-1200 CE, probably ...
presumably flew from there to Oceania and Madagascar respectively, while the mysterious ''Hypselornis
''Hypselornis'' is an extinct genus of fossil reptile, most likely a crocodilian, from the late Pliocene of India. Known only from a single toe bone, ''Hypselornis'' was originally mistakenly identified as a ratite bird related to the living cass ...
'' may represent an indigenous clade.
Eocene fauna
By this time India already has an extensive placental fauna (as well asmetatherians
Metatheria is a mammalian clade that includes all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. First proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1880, it is a more inclusive group than the marsupials; it contains all marsupials as wel ...
like '' Indodelphis''), but in its isolation there are still high degrees of endemism, with some clades like anthracobunids not being found elsewhere. A study on ''Cambaytherium
''Cambaytherium'' is an extinct genus of placental mammals in the family Cambaytheriidae whose fossils were found in an open pit coal mine located in Gujarat, India. The mine was a treasure trove full of teeth and bones, over 200 of which were id ...
'' suggests that Perissodactyla might have had an insular origin in India. The most notorious endemic mammals are cetaceans
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
, which are in fact restricted to the Indian Subcontinent until the evolution of the marine " protocetids". Eocene India is also rich in bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most bi ...
remains, including many representatives of modern groups, though its unclear if this Indian chiropteran fauna represents an adaptive radiation or simply that bat fossils elsewhere are rare.
During this time, lagomorphs
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae ( hares and rabbits) and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek ''lagos'' (λα� ...
and hyaenodonts
Hyaenodontidae ("hyena teeth") is a family of extinct predatory mammals from extinct superfamily Hyaenodontoidea within extinct order Hyaenodonta. Hyaenodontids arose during the early Eocene and persisted well into the early Miocene. Fossils of t ...
disperse out of India, establishing their cosmopolitan ranges.
The Gecarcinucidae
The Gecarcinucidae are a family of true freshwater crabs. The family Parathelphusidae is now demoted to the rank of subfamily, as the Parathelphusinae, within the Gecarcinucidae. "Family" Parathelphusidae is now considered as a junior synonym.
...
, a family of freshwater crabs
Around 1,300 species of freshwater crabs are distributed throughout the tropics and subtropics, divided among eight families. They show direct development and maternal care of a small number of offspring, in contrast to marine crabs, which relea ...
widespread throughout much of tropical Asia, is thought to have originated in India, despite not being of ancient Gondwanan origins themselves. Divergence estimates indicate that the Gecarcinucidae originate from Southeast Asian
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
ancestors that dispersed to Insular India and diverged there during the middle Eocene, before India collided with Asia. As India drifted northwards, it may have come into close enough proximity to Southeast Asia to allow for dispersing lineages to colonize it. Notably, as the Gecarcinucidae are a freshwater group that could not disperse via marine habitats, this indicates that temporary land bridges
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea leve ...
may have formed in the Eocene between India and Southeast Asia, allowing for the dispersal of freshwater organisms to India while it was still isolated. Following the India-Asia collision, the Gecarcinucidae dispersed back into mainland Asia.
Flora
TheDipterocarpoideae
Dipterocarpaceae is a family (biology), family of 16 genera and about 695 known species of mainly tropical lowland rainforest trees. The family name, from the type genus ''Dipterocarpus'', is derived from Greek language, Greek (''di'' = two, ''pt ...
, the largest subfamily of the Dipterocarpaceae
Dipterocarpaceae is a family of 16 genera and about 695 known species of mainly tropical lowland rainforest trees. The family name, from the type genus ''Dipterocarpus'', is derived from Greek (''di'' = two, ''pteron'' = wing and ''karpos'' = fru ...
, is thought to originate from ancestors that dispersed from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
to India during the Late Cretaceous. Surviving the K-Pg extinction event, the Dipterocarpoideae were isolated on Insular India (aside from some representatives in the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, V ...
) until India's collision with Asia, after which they migrated out of the continent and diversified. The Dipterocarpaceae are now among the most widespread and dominant tree groups in tropical Asia. Fossil evidence indicates that the other subfamily of Dipterocarpaceae, the Monotoideae
Monotoideae is a subfamily of the plant family Dipterocarpaceae, with 3 genera and 30 species. It is native to the rainforest habitat of Africa and Madagascar, as well as South America. The geographical discontinuity can be traced back to a date ...
(presently found in Africa, Madagasar, and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
), also colonized India and was present until the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
, but ultimately went extinct in India and thus did not disperse to other parts of Asia.
References
{{reflist Historical continents