Injection (medicine) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in
An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in
 Injections are classified in multiple ways, including the type of tissue being injected into, the location in the body the injection is designed to produce effects, and the duration of the effects. Regardless of classification, injections require a puncture to be made, thus requiring
Injections are classified in multiple ways, including the type of tissue being injected into, the location in the body the injection is designed to produce effects, and the duration of the effects. Regardless of classification, injections require a puncture to be made, thus requiring
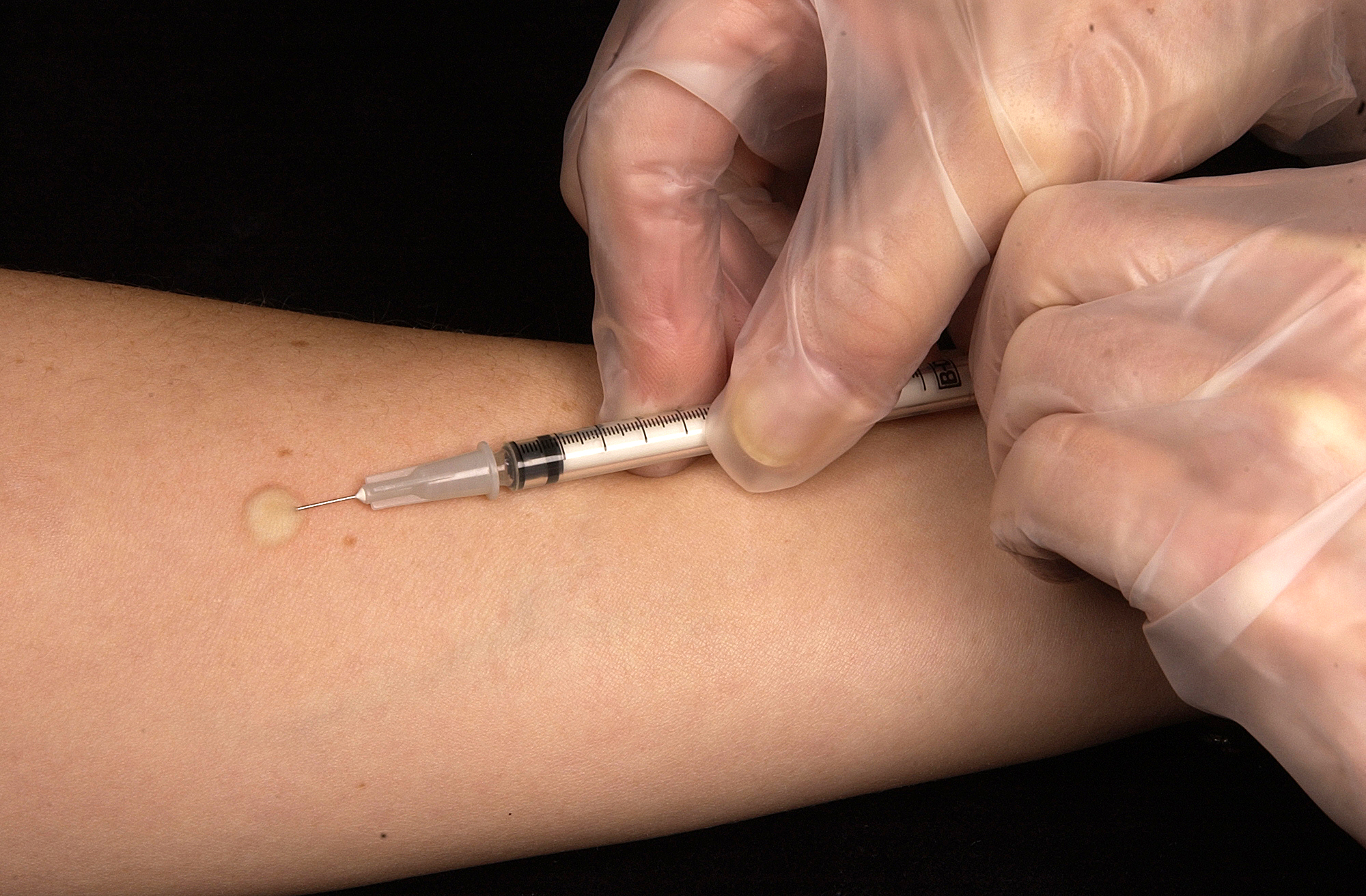 Intradermal injections, abbreviated as ID, consist of a substance delivered into the
Intradermal injections, abbreviated as ID, consist of a substance delivered into the
Information about injections
from the '' Merck Manual''
FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Data Standards Manual: Route of Administration
{{DEFAULTSORT:Injection (Medicine)
 An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in
An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in UK English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, ...
, or a "jag" in Scottish English
Scottish English ( gd, Beurla Albannach) is the set of varieties of the English language spoken in Scotland. The transregional, standardised variety is called Scottish Standard English or Standard Scottish English (SSE). Scottish Standa ...
and Scots) is the act of administering a liquid, especially a drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhala ...
, into a person's body using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)), one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used ...
) and a syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside ...
. An injection is considered a form of parenteral
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
drug administration; it does not involve absorption in the digestive tract. This allows the medication to be absorbed more rapidly and avoid the first pass effect. There are many types of injection, which are generally named after the body tissue the injection is administered into. This includes common injections such as subcutaneous, intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles ha ...
, and intravenous injections, as well as less common injections such as intraperitoneal, intraosseous, intracardiac, intraarticular, and intracavernous injections.
Injections are among the most common health care procedures, with at least 16 billion administered in developing and transitional countries each year. Of these, 95% are used in curative care or as treatment for a condition, 3% are to provide immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen).
When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-s ...
s/ vaccinations, and the rest are used for other purposes, including blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
s. The term ''injection'' is sometimes used synonymously with inoculation
Inoculation is the act of implanting a pathogen or other microorganism. It may refer to methods of artificially inducing immunity against various infectious diseases, or it may be used to describe the spreading of disease, as in "self-inoculati ...
, but injection does not only refer to the act of inoculation. Injections generally administer a medication as a bolus (or one-time) dose, but can also be used for continuous drug administration. After injection, a medication may be designed to be released slowly, called a depot injection, which can produce long-lasting effects.
An injection necessarily causes a small puncture wound
Penetrating trauma is an open wound injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating a deep but relatively narrow entry wound. In contrast, a blunt or ''non-penetrating'' trauma may have some deep d ...
to the body, and thus may cause localized pain or infection. The occurrence of these side effects varies based on injection location, the substance injected, needle gauge, procedure, and individual sensitivity. Rarely, more serious side effects including gangrene, sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, and nerve damage may occur. Fear of needles, also called needle phobia, is also common and may result in anxiety and fainting before, during, or after an injection. To prevent the localized pain that occurs with injections the injection site may be numbed or cooled before injection and the person receiving the injection may be distracted by a conversation or similar means. To reduce the risk of infection from injections, proper aseptic technique should be followed to clean the injection site before administration. If needles or syringes are reused between people, or if an accidental needlestick occurs, there is a risk of transmission of bloodborne diseases such as HIV and hepatitis.
Unsafe injection practices contribute to the spread of bloodborne diseases, especially in less-developed countries. To combat this, safety syringes exist which contain features to prevent accidental needlestick injury and reuse of the syringe after it is used once. Furthermore, recreational drug users who use injections to administer the drugs commonly share or reuse needles after an injection. This has led to the development of needle exchange programs and safe injection sites as a public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
measure, which may provide new, sterile syringes and needles to discourage the reuse of syringes and needles. Used needles should ideally be placed in a purpose-made sharps container which is safe and resistant to puncture. Some locations provide free disposal programs for such containers for their citizens.
Types
 Injections are classified in multiple ways, including the type of tissue being injected into, the location in the body the injection is designed to produce effects, and the duration of the effects. Regardless of classification, injections require a puncture to be made, thus requiring
Injections are classified in multiple ways, including the type of tissue being injected into, the location in the body the injection is designed to produce effects, and the duration of the effects. Regardless of classification, injections require a puncture to be made, thus requiring sterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgi ...
environments and procedures to minimize the risk of introducing pathogens into the body. All injections are considered forms of parenteral administration, which avoids the first pass metabolism which would potentially affect a medication absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract.
Systemic
Many injections are designed to administer a medication which has an effect throughout the body. Systemic injections may be used when a person cannot take medicine by mouth, or when the medication itself would not be absorbed into circulation from the gastrointestinal tract. Medications administered via a systemic injection will enter into blood circulation, either directly or indirectly, and thus will have an effect on the entire body.Intravenous
Intravenous injections, abbreviated as IV, involve inserting a needle into avein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
, allowing a substance to be delivered directly into the bloodstream. An intravenous injection provides the quickest onset of the desired effects because the substance immediately enters the blood, and is quickly circulated to the rest of the body. Because the substance is administered directly into the bloodstream, there is no delay in the onset of effects due to the absorption of the substance into the bloodstream. This type of injection is the most common and is used frequently for administration of medications in an inpatient setting.
Another use for intravenous injections includes for the administration of nutrition to people who cannot get nutrition through the digestive tract. This is termed parenteral nutrition and may provide all or only part of a person's nutritional requirements. Parenteral nutrition may be pre-mixed or customized for a person's specific needs. Intravenous injections may also be used for recreational drugs when a rapid onset of effects is desired.
Intramuscular
Intramuscular injections, abbreviated as IM, deliver a substance deep into amuscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
, where they are quickly absorbed by the blood vessels into systemic circulation. Common injection sites include the deltoid Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to:
* The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder
* Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral
* A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid
* A leaf shape
* The deltoid tuberosity, a part o ...
, vastus lateralis, and ventrogluteal
The gluteal muscles, often called glutes are a group of three muscles which make up the gluteal region commonly known as the buttocks: the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. The three muscles originate from the ilium and sacr ...
muscles. Medical professionals are trained to give IM injections, but people who are not medical professionals can also be trained to administer medications like epinephrine using an autoinjector
An autoinjector (or auto-injector) is a medical device designed to deliver a dose of a particular drug. The injectors were initially designed to overcome the hesitation associated with self-administration of the needle-based drug delivery devic ...
in an emergency. Some depot injections are also administered intramuscularly, including medroxyprogesterone acetate among others. In addition to medications, most inactivated vaccines, including the influenza vaccine, are given as an IM injection.
Subcutaneous
Subcutaneous injections, abbreviated as SC or sub-Q, consist of injecting a substance into the fat tissue between the skin and the muscle. Absorption of the medicine from this tissue is slower than in an intramuscular injection. Since the needle does not need to penetrate to the level of the muscle, a thinner and shorter needle can be used. Subcutaneous injections may be administered in the fatty tissue behind the upper arm, in the abdomen, or in the thigh. Certain medications, including epinephrine, may be used either intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Others, such asinsulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
, are almost exclusively injected subcutaneously. Live or attenuated vaccines, including the MMR vaccine
The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (German measles), abbreviated as ''MMR''. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, ...
(measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, mumps, rubella), varicella vaccine ( chickenpox), and zoster vaccine
A zoster vaccine is a vaccine that reduces the incidence of herpes zoster (shingles), a disease caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus, which is also responsible for chickenpox. Shingles provokes a painful rash with blisters, and ...
(shingles
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or fac ...
) are also injected subcutaneously.
Intradermal
 Intradermal injections, abbreviated as ID, consist of a substance delivered into the
Intradermal injections, abbreviated as ID, consist of a substance delivered into the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
, the layer of skin above the subcutaneous fat layer, but below the epidermis or top layer. An intradermal injection is administered with the needle placed almost flat against the skin, at a 5 to 15 degree angle. Absorption from an intradermal injection takes longer than when the injection is given intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously. For this reason, few medications are administered intradermally. Intradermal injections are most commonly used for sensitivity tests, including tuberculin skin tests and allergy tests, as well as sensitivity tests to medications a person has never had before. The reactions caused by tests which use intradermal injection are more easily seen due to the location of the injection, and when positive will present as a red or swollen area. Common sites of intradermal injections include the forearm and lower back.
Intraosseous
An intraosseous injection or infusion is the act of administering medication through a needle inserted into the bone marrow of a large bone. This method of administration is only used when it is not possible to maintain access through a less invasive method such as an intravenous line, either due to frequent loss of access due to a collapsed vessel, or due to the difficulty of finding a suitable vein to use in the first place. Intraosseous access is commonly obtained by inserting a needle into the bone marrow of the humerus ortibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
, and is generally only considered once multiple attempts at intravenous access have failed, as it is a more invasive method of administration than an IV. With the exception of occasional differences in the accuracy of blood tests when drawn from an intraosseous line, it is considered to be equivalent in efficacy to IV access. It is most commonly used in emergency situations where there is not ample time to repeatedly attempt to obtain IV access, or in younger people for whom obtaining IV access is more difficult.
Localized
Injections may be performed into specific parts of the body when the medication's effects are desired to be limited to a specific location, or where systemic administration would produce undesirable side effects which may be avoided by a more directed injection. Injections to the corpus cavernosum of the penis, termed intracavernous injections, may be used to treat conditions which are localized to the penis. They can be self-administered for erectile dysfunction prior to intercourse or used in a healthcare setting for emergency treatment for a prolonged erection with an injection to either remove blood from the penis or to administer asympathomimetic
Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of sympathomimetic effects include increases in hea ...
medication to reduce the erection. Intracavernosal injections of alprostadil
Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), also known as alprostadil, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin which is used as a medication. In infants with congenital heart defects, it is delivered by slow injection into a vein to open the ductus arteriosus unti ...
may be used by people for whom other treatments such as PDE5 inhibitors are ineffective or contraindicated. Other medications may also be administered in this way, including papaverine, phentolamine, and aviptadil
Aviptadil is an injectable synthetic formulation of human vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP).
VIP was discovered in 1970, and has been used to treat various inflammatory conditions, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), asthma, ...
. The most common adverse effects of intercavernosal injections include fibrosis and pain, as well as hematomas or bruising around the injection site.
Medications may also be administered by injecting them directly into the vitreous humor of the eye. This is termed an intravitreal injection, and may be used to treat endophthalmitis (an infection of the inner eye), macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, so ...
, and macular edema. An intravitreal injection is performed by injecting a medication through the pupil into the vitreous humor core of the eye after applying a local anesthetic drop to numb the eye and a mydriatic drop to dilate the pupil. They are commonly used in lieu of systemic administration to both increase the concentrations present in the eye, as well as avoid systemic side effects of medications.
When an effect is only required in one joint, a joint injection (or intra-articular injection) may be administered into the articular space surrounding the joint. These injections can range from a one-time dose of a steroid to help with pain and inflammation to complete replacement of the synovial fluid
Synovial fluid, also called synovia, elp 1/sup> is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articul ...
with a compound such as hyaluronic acid. The injection of a steroid into a joint is used to reduce inflammation associated with conditions such as osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
, and the effects may last for up to 6 months following a single injection. Hyaluronic acid injection is used to supplement the body's natural synovial fluid and decrease the friction and stiffness of the joint. Administering a joint injection generally involves the use of an ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
or other live imaging technique to ensure the injection is administered in the desired location, as well as to reduce the risk of damaging surrounding tissues.
Long-acting
Long-acting injectable (LAI) formulations of medications are not intended to have a rapid effect, but instead release a medication at a predictable rate continuously over a period of time. Both depot injections and solid injectable implants are used to increase adherence to therapy by reducing the frequency at which a person must take a medication.Depot
A depot injection is an injection, usually subcutaneous,intradermal
Intradermal injection, often abbreviated ID, is a shallow or superficial injection of a substance into the dermis, which is located between the epidermis and the hypodermis. For certain substances, administration via an ID route can result in a ...
, or intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles ha ...
, that deposits a drug in a localized mass, called a depot, from which it is gradually absorbed by surrounding tissue. Such injection allows the active compound to be released in a consistent way over a long period. Depot injections are usually either oil-based or an aqueous suspension. Depot injections may be available as certain salt forms of a drug, such as decanoate
Capric acid, also known as decanoic acid or decylic acid, is a saturated fatty acid, medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA), and carboxylic acid. Its formula is CH3(CH2)8COOH. Salts and esters of decanoic acid are called caprates or decanoates. The ter ...
salts or esters. Examples of depot injections include haloperidol decanoate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, and naltrexone.
Implant
Injections may also be used to insert a solid or semi-solid into the body which releases a medication slowly over time. These implants are generally designed to be temporary, replaceable, and ultimately removed at the end of their use or when replaced. There are multiple contraceptive implants marketed for different active ingredients, as well as differing duration of action - most of these are injected under the skin. A form of buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence is also available as an injectable implant. Various materials can be used to manufacture implants including biodegradable polymers, osmotic release systems, and small spheres which dissolve in the body.Adverse effects
Pain
The act of piercing the skin with a needle, while necessary for an injection, also may cause localized pain. The most common technique to reduce the pain of an injection is simply to distract the person receiving the injection. Pain may be dampened by prior application of ice or topical anesthetic, or pinching of the skin while giving the injection. Some studies also suggest that forced coughing during an injection stimulates a transient rise in blood pressure which inhibits the perception of pain. For some injections, especially deeper injections, a local anesthetic is given. When giving an injection to young children or infants, they may be distracted by giving them a small amount of sweet liquid, such assugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
solution, or be comforted by breastfeeding during the injection, which reduces crying.
Infection
A needle tract infection, also called a needlestick infection, is aninfection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
that occurs when pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
s are inadvertently introduced into the tissues of the body during an injection. Contamination of the needle used for injection, or reuse of needles for injections in multiple people, can lead to transmission of hepatitis B and C, HIV, and other bloodstream infections. Injection drug users have high rates of unsafe needle use including sharing needles between people. The spread of HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C from injection drug use is a common health problem, in particular contributing to over half of new HIV cases in North America in 1994.
Other infections may occur when pathogens enter the body through the injection site, most commonly due to improper cleaning of the site before injection. Infections occurring in this way are mainly localized infections, including skin infections, skin structure infections, abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
es, or gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the gan ...
. An intravenous injection may also result in a bloodstream infection (termed sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
) if the injection site is not cleaned properly prior to insertion. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition which requires immediate treatment.
Others
Injections into the skin and soft tissue generally do not cause any permanent damage, and the puncture heals within a few days. However, in some cases, injections can cause long-term adverse effects. Intravenous and intramuscular injections may cause damage to a nerve, leading topalsy Palsy is a medical term which refers to various types of paralysisDan Agin, ''More Than Genes: What Science Can Tell Us About Toxic Chemicals, Development, and the Risk to Our Children;; (2009), p. 172. or paresis, often accompanied by weakness a ...
or paralysis. Intramuscular injections may cause fibrosis or contracture. Injections also cause localized bleeding, which may lead to a hematoma. Intravenous injections may also cause phlebitis, especially when multiple injections are given in a vein over a short period of time. Infiltration
Infiltration may refer to:
Science, medicine, and engineering
*Infiltration (hydrology), downward movement of water into soil
*Infiltration (HVAC), a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning term for air leakage into buildings
*Infiltration (me ...
and extravasation may also occur when a medication intended to be injected into a vein is inadvertently injected into surrounding tissues. Those who are afraid of needles may also experience fainting at the sight of a needle, or before or after an injection.
Technique
Proper needle use is important to perform injections safely, which includes the use of a new, sterile needle for each injection. This is partly because needles get duller with each use and partly because reusing needles increases risk of infection. Needles should not be shared between people, as this increases risk of transmittingblood-borne
A blood-borne disease is a disease that can be spread through contamination by blood and other body fluids. Blood can contain pathogens of various types, chief among which are microorganisms, like bacteria and parasites, and non-living infecti ...
pathogens. The practice of using the same needle for multiple people increases the risk of disease transmission between people sharing the same medication. In addition, it is not recommended to reuse a used needle to pierce a medication bag, bottle, or ampule designed to provide multiple doses of a medication, instead a new needle should be used each time the container must be pierced. Aseptic technique should always be practiced when administering injections. This includes the use of barriers including gloves, gowns, and masks for health care providers. It also requires the use of a new, sterile needle, syringe and other equipment for each injection, as well as proper training to avoid touching non-sterile surfaces with sterile items.
To help prevent accidental needlestick injury to the person administering the injection, and prevent reuse of the syringe for another injection, a safety syringe
A safety syringe is a syringe with a built-in safety mechanism to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries to healthcare workers and others. The needle on a safety syringe can be detachable or permanently attached. On some models, a sheath is pla ...
and needle may be used. The most basic reuse prevention device is an "auto-disable" plunger, which once pressed past a certain point will no longer retract. Another common safety feature is an auto-retractable needle, where the needle is spring-loaded and either retracts into the syringe after injection, or into a plastic sheath on the side of the syringe. Other safety syringes have an attached sheath which may be moved to cover the end of the needle after the injection is given. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
recommends the use of single-use syringes with both reuse prevention devices and a needlestick injury prevention mechanism for all injections to prevent accidental injury and disease transmission.
Novel injection techniques include drug diffusion within the skin using needle-free micro-jet injection (NFI) technology.
Disposal of used needles
Used needles should be disposed of in specifically designed sharps containers to reduce the risk of accidental needle sticks and exposure to other people. In addition, a new sharps container should be begun once it is full. A sharps container which is filled should be sealed properly to prevent re-opening or accidental opening during transportation. Some locations offer publicly accessible "sharps take-back" programs where a sharps container may be dropped off to a public location for safe disposal at no fee to the person. In addition, some pharmaceutical and independent companies provide mail-back sharps programs, sometimes for an additional fee. In the United States, there are 39 states that offer programs to provide needle or syringe exchange. Over half of non- industrialized countries report open burning of disposed or used syringes. This practice is considered unsafe by theWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
.
Aspiration
The aspiration is the technique of pulling back on the plunger of a syringe prior to the actual injection. If blood flows into the syringe it signals that a blood vessel has been hit.Society and culture
Due to the prevalence of unsafe injection practices, especially among injection drug users, many locations have begun offering supervised injection sites and needle exchange programs, which may be offered separately or colocated. These programs may provide new sterile needles upon request to mitigate infection risk, and some also provide access to on-site clinicians and emergency medical care if it becomes required. In the event of an overdose, a site may also provide medications such as naloxone, used as an antidote in opioid overdose situations, or other antidotes or emergency care. Safe injection site have been associated with lower rates of death from overdose, less ambulance calls, and lower rates of new HIV infections from unsafe needle practices. As of 2019, at least ten countries currently offer safe injection sites, including Australia, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, Norway, Spain and Switzerland. In total, there are at least 120 sites operating. Although the United States does not currently have any safe injection sites, some cities such San Francisco, Philadelphia, and Denver are considering opening them, and some localities offer needle exchange programs. In 2018, the California State Assembly passed Assembly Bill 186 to launch a three-year pilot program in San Francisco for California's first safe injection sites, but this bill was not signed by the governor. Colorado and Pennsylvania have also expressed interest in offering safe injection sites. Court rulings in Pennsylvania have determined that safe injection sites are not illegal under federal law.Plants and animals
Many species of animals use injections for self-defence or catching prey. This includes venomous snakes which inject venom when they bite into the skin with their fangs. Common substances present in snake venom include neurotoxins, toxic proteins, and cytotoxic enzymes. Different species of snakes inject different formulations ofvenom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a st ...
, which may cause severe pain and necrosis before progressing into neurotoxicity and potentially death. The weever
Weevers (or weeverfish) are nine extant species of fishes of family Trachinidae, order Trachiniformes, part of the Percomorpha clade. They are long (up to 37 cm), mainly brown in color, and have venomous spines on their first dorsal fin ...
is a type of fish which has venomous spines covering its fins and gills and injects a venom consisting of proteins which cause a severe local reaction which is not life-threatening. Sting rays use their spinal blade to inject a protein-based venom which causes localized cell death but is not generally life-threatening.
Some types of insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
s also utilize injection for various purposes. Bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfami ...
s use a stinger located in their hind region to inject a venom consisting of proteins such as melittin, which causes a localized painful and itching reaction. Leeches can inject an anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where t ...
peptide called hirudin
Hirudin is a naturally occurring peptide in the salivary glands of blood-sucking leeches (such as '' Hirudo medicinalis'') that has a blood anticoagulant property. This is fundamental for the leeches’ habit of feeding on blood, since it keeps ...
after attaching to prevent blood from clotting during feeding. This property of leeches has been used historically as a natural form of anticoagulation therapy, as well as for the use of bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily f ...
as a treatment for various ailments. Some species of ants inject forms of venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a st ...
which include compounds which produce minor pain such as the formic acid, which is injected by members of the Formicinae
The Formicinae are a subfamily within the Formicidae containing ants of moderate evolutionary development.
Formicines retain some primitive features, such as the presence of cocoons around pupae, the presence of ocelli in workers, and lit ...
subfamily. Other species of ants, including '' Dinoponera'' species, inject protein-based venom which causes severe pain but is still not life-threatening. The bullet ant ('' Paraponera clavata'') injects a venom which contains a neurotoxin named poneratoxin which causes extreme pain, fever, and cold sweats, and may cause arrhythmias.
Plants may use a form of injection which is passive, where the injectee pushes themselves against the stationary needle. The stinging nettle plant has many trichomes, or stinging hairs, over its leaves and stems which are used to inject a mix of irritating chemicals which includes histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discover ...
, serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and va ...
, and acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
. This sting produces a form of dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
which is characterized by a stinging, burning, and itching sensation in the area. '' Dendrocnide'' species, also called stinging trees, use their trichomes to inject a mix of neurotoxic peptides which causes a reaction similar to the stinging nettle, but also may result in recurring flares for a much longer period after the injection. While some plants have thorns, spines, and prickles, these generally are not used for injection of any substance, but instead it is the act of piercing the skin which causes them to be a deterrent.
See also
* Dart injection * Jet injector * Injection port *Lethal injection
Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person (typically a barbiturate, paralytic, and potassium solution) for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital puni ...
* Needlestick injury
* Needle remover
* Safety syringe
A safety syringe is a syringe with a built-in safety mechanism to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries to healthcare workers and others. The needle on a safety syringe can be detachable or permanently attached. On some models, a sheath is pla ...
References
External links
Information about injections
from the '' Merck Manual''
FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Data Standards Manual: Route of Administration
{{DEFAULTSORT:Injection (Medicine)