Incremental Games on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
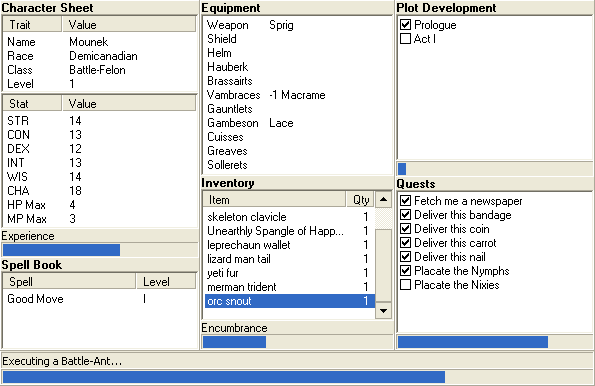 Incremental games, also known as clicker games, clicking games (on PCs) or tap games (in mobile games), are
Incremental games, also known as clicker games, clicking games (on PCs) or tap games (in mobile games), are
 According to Anthony Pecorella in his Game Developers Conference, GDC summit talks, the first idle game was attributed to ''Progress Quest'' (2002) by Eric Fredriksen, which is a parody of MMORPG's stats and auto-attack. He argued that Kongregate was an early breeding ground for the genre, as some people just want to chat, so, the first game of the genre was aptly titled ''Kongregate Chat'' (July 24, 2007, by John Cooney (video game developer), John Cooney),
where the game just run by itself, and people are just chatting in the chat section of the game. While one of the first visual idle games ("rudimentary RPG" according to Pecorella) was ''Ayumilove's HackerStory v1'' (2008, by Ayumilove), which was a parody of bot Grinding (video games), grinding in a ''Maple Story'' game, a famous MMORPG from Korea at that time.
The early pioneers of idle games also saw some games parodying idle games, such as ''Anti-Idle'' (2009, by tukkun) which has both elements of active and idle games, and is extremely complicated, content-rich, and constantly updated; it helped popularize the genre. An idle game in Facebook platform, called ''Cow Clicker'' (2010, by Ian Bogost), which according to the author, "a satire and playable theory of ''Farmville, social games circa that era'', ... Facebook games distilled to their essence.", was the first to receive mainstream media attention. Another parody of idle games (and parody of capitalism) called ''AdVenture Capitalist'' (2015, by Cody Vigue / Hyper Hippo Games) also saw success as a browser game and was subsequently made available in many platforms. It was one of the first games to implement monetization, as well as ''offline earning'' which calculates the progress of a player during the time they are offline, unlike previous browser-based idle games which only run when open in a browser window.
Some idle games did not follow the infinite ending, and instead opt for finite ending, more like puzzle-like and exploration based, for example ''A Dark Room'' (2013, by Doublespeak Games), and ''Candy Box!'' (2013, by aniwey).
Incremental games gained popularity in 2013 after the success of ''Cookie Clicker'', although earlier games such as ''Cow Clicker'' and ''Candy Box!'' were based on the same principles. ''Make It Rain: The Love of Money, Make It Rain'' (2014, by Space Inch) was the first major mobile idle game success, although the idle elements in the game were heavily limited, requiring check-ins to progress. In 2015, the gaming press observed such games proliferating on the Steam (service), Steam distribution platform with titles such as ''Clicker Heroes'' (2014, by Playsaurus).
Other idle games that have become classic includes ''Sandcastle Builder'' (2013, by Eternal Density) which was based on the xkcd comic 1190: Time (xkcd), ''Time'', ''Sharky Clicker'' (2014, by Cirr), ''Crank'' (by FaeDine), and ''Kittens Game'' (2014, by Bloodrizer)
During the evolution of the genre, monetization (through ads or other venues), premium contents, and other game mechanics are slowly being added in.
According to Anthony Pecorella in his Game Developers Conference, GDC summit talks, the first idle game was attributed to ''Progress Quest'' (2002) by Eric Fredriksen, which is a parody of MMORPG's stats and auto-attack. He argued that Kongregate was an early breeding ground for the genre, as some people just want to chat, so, the first game of the genre was aptly titled ''Kongregate Chat'' (July 24, 2007, by John Cooney (video game developer), John Cooney),
where the game just run by itself, and people are just chatting in the chat section of the game. While one of the first visual idle games ("rudimentary RPG" according to Pecorella) was ''Ayumilove's HackerStory v1'' (2008, by Ayumilove), which was a parody of bot Grinding (video games), grinding in a ''Maple Story'' game, a famous MMORPG from Korea at that time.
The early pioneers of idle games also saw some games parodying idle games, such as ''Anti-Idle'' (2009, by tukkun) which has both elements of active and idle games, and is extremely complicated, content-rich, and constantly updated; it helped popularize the genre. An idle game in Facebook platform, called ''Cow Clicker'' (2010, by Ian Bogost), which according to the author, "a satire and playable theory of ''Farmville, social games circa that era'', ... Facebook games distilled to their essence.", was the first to receive mainstream media attention. Another parody of idle games (and parody of capitalism) called ''AdVenture Capitalist'' (2015, by Cody Vigue / Hyper Hippo Games) also saw success as a browser game and was subsequently made available in many platforms. It was one of the first games to implement monetization, as well as ''offline earning'' which calculates the progress of a player during the time they are offline, unlike previous browser-based idle games which only run when open in a browser window.
Some idle games did not follow the infinite ending, and instead opt for finite ending, more like puzzle-like and exploration based, for example ''A Dark Room'' (2013, by Doublespeak Games), and ''Candy Box!'' (2013, by aniwey).
Incremental games gained popularity in 2013 after the success of ''Cookie Clicker'', although earlier games such as ''Cow Clicker'' and ''Candy Box!'' were based on the same principles. ''Make It Rain: The Love of Money, Make It Rain'' (2014, by Space Inch) was the first major mobile idle game success, although the idle elements in the game were heavily limited, requiring check-ins to progress. In 2015, the gaming press observed such games proliferating on the Steam (service), Steam distribution platform with titles such as ''Clicker Heroes'' (2014, by Playsaurus).
Other idle games that have become classic includes ''Sandcastle Builder'' (2013, by Eternal Density) which was based on the xkcd comic 1190: Time (xkcd), ''Time'', ''Sharky Clicker'' (2014, by Cirr), ''Crank'' (by FaeDine), and ''Kittens Game'' (2014, by Bloodrizer)
During the evolution of the genre, monetization (through ads or other venues), premium contents, and other game mechanics are slowly being added in.
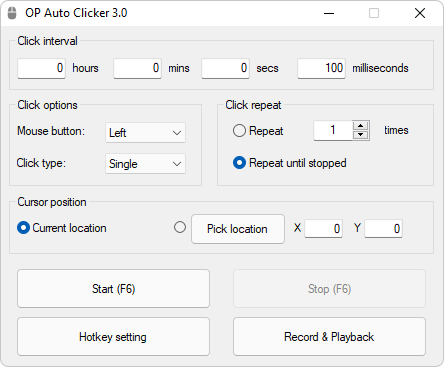 An auto clicker is automation software or a macro that is generally used to automate the clicking (or tapping) process in idle games. A number of idle games employ clicking as a method to gain currency while active (to complement to the idle element), and players may sometimes employ an auto clicker to automate this part, thus getting resources/currency much faster. Pecorella, in his 2016 GDC summit talk, argues that auto clickers are considered necessary by any "serious" idle game players, and that it's not cheating, but rather an exploration of an ''error in design''.
An auto clicker is automation software or a macro that is generally used to automate the clicking (or tapping) process in idle games. A number of idle games employ clicking as a method to gain currency while active (to complement to the idle element), and players may sometimes employ an auto clicker to automate this part, thus getting resources/currency much faster. Pecorella, in his 2016 GDC summit talk, argues that auto clickers are considered necessary by any "serious" idle game players, and that it's not cheating, but rather an exploration of an ''error in design''.
 Incremental games, also known as clicker games, clicking games (on PCs) or tap games (in mobile games), are
Incremental games, also known as clicker games, clicking games (on PCs) or tap games (in mobile games), are video game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This fee ...
s whose gameplay
Gameplay is the specific way in which players interact with a game, and in particular with video games. Gameplay is the pattern defined through the game rules, connection between player and the game, challenges and overcoming them, plot and pla ...
consists of the player performing simple actions such as clicking on the screen repeatedly. This "grinding
Grind is the cross-sectional shape of a blade.
Grind, grinds, or grinding may also refer to:
Grinding action
* Grinding (abrasive cutting), a method of crafting
* Grinding (dance), suggestive club dancing
* Grinding (video gaming), repetitive and ...
" earns the player in-game currency
A virtual economy (or sometimes synthetic economy) is an emergent economy existing in a virtual world, usually exchanging virtual goods in the context of an online game, particularly in massively multiplayer online games (MMOs). People enter th ...
which can be used to increase the rate of currency acquisition. In some games, even the clicking becomes unnecessary at some point, as the game plays itself, including in the player's absence, hence the moniker idle game.
Mechanics
Progress without interaction, or very limited interaction
In an incremental game, players perform simple actions – usually clicking a button or object – which rewards the player with currency. The player may spend the currency to purchase items or abilities that allow the player to earn the currency faster or automatically, without needing to perform the initial action. A common theme is offering the player sources of income displayed as buildings such as factories or farms. These sources increase the currency production rate, but higher tier sources usually have an exponentially higher cost, so upgrading between tiers takes usually about the same time or even increasingly longer. This mechanism offers a low-pressure experience (one does not have to be constantly playing), no loss condition, and constant growth and feedback, which is ideal for social or mobile play patterns, and often result in a very high player retention. It often relies onexponential growth
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a q ...
(or perhaps high-degree polynomial growth), which is countered by diminishing returns
In economics, diminishing returns are the decrease in marginal (incremental) output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, holding all other factors of production equal ( ceteris paribu ...
.
Rapid growth
The rapid growth of cost, power and rewards is what makes incremental games fun and satisfying. They often incorporate verylarge numbers
Large numbers are numbers significantly larger than those typically used in everyday life (for instance in simple counting or in monetary transactions), appearing frequently in fields such as mathematics, cosmology, cryptography, and statistical ...
in their calculation of rewards/power, either using scientific notations (1x1034), shorthands (1M, 1T, etc.), shorthand (1a, 1b, 1aa, 1ab), or invented words (e.g. "duoquadragintillion"), which sometimes make recording high scores a problem for the server.
This mechanism, in its core, involves a loop: the player logs in, spends all their currency, and logs out for a few hours. This is similar to (or even derived from) the "Glossary of video game terms#energy, energy currency" concept in social games, where a player gets one energy per hour, for example. The difference being that in idle games this mechanism is natural, whereas in other social games, it is a construct intended to constrain the players.
This mechanism may be more palatable to core gamers who dislike social games. It resonates with real world dialog (e.g., "I'm out of cash; I need to come back when I have more.") and gives players more control over their decision.
Many goals and achievements
This mechanism provides moments of joy spread out throughout the gameplay, to counter boredom and grinding feeling. The mechanism could also be tied to the previous mechanism of giving more power/rewards upon achieving a goal or achievement, which lead to optimization decision and meaningful direction.New Game Plus
As a late-game or advanced mechanism, some games feature a reset-based system or "New Game Plus", a term coined by ''Chrono Trigger'' (1995), where the player resets the progress of their game and gains another form of currency (prestige). This new currency is normally used to gain global bonuses that do not disappear after a reset, allowing the player to go further than the previous reset, or let the player replay the game with a greater power, often with several choices upon restart. This eventually would create an infinite game replays and various strategy of playing. It creates another layer of loop: players play from the start. ''Tap Titans'' (2014, by Game Hive) is a pioneer of the prestige mechanics in mobile games. This mechanism is mostly optional; player could choose to "prestige" once they feel they hit the wall and felt their progress is getting slower (compared to the cost). This mechanism gives players a sense of a rush of progress, which feels very rewarding. Some games include prestiging within prestiging within prestiging, thereby making new content, meta-currencies or gameplay available. ''Realm Grinder'' by Divine Games (2015), introduced abdicating, reincarnating, and ascending.Open-ended or closed gameplay loops
Incremental games vary as to whether they have a Game mechanics#Victory condition mechanics, victory condition: games like ''Cookie Clicker'' allow the players to play indefinitely, while games like ''Candy Box!'' or ''Universal Paperclips'' feature endings that can be reached after a certain amount of progress is made.Monetization
Pioneered by AdVenture Capitalist, developer may sell premium boost such as instant currency infusion (usually a percentage of current rate of income) or sometimes wrapped as a "time-warp" (instantly gain x-hours of future income), permanent boost multiplier that persist after each prestiging, instant prestige (claiming prestige without starting over), protection against negative events, ''gacha'' system (random draws of a character or a permanent bonus), and event currencies. On the other side, they may also deliver advertisements for players to receive minor rewards, such as short burst of cash, doubling offline earnings, small amount of premium currency, brief powerful boost/medium-length small boost, relief of a negative status, etc.History
 According to Anthony Pecorella in his Game Developers Conference, GDC summit talks, the first idle game was attributed to ''Progress Quest'' (2002) by Eric Fredriksen, which is a parody of MMORPG's stats and auto-attack. He argued that Kongregate was an early breeding ground for the genre, as some people just want to chat, so, the first game of the genre was aptly titled ''Kongregate Chat'' (July 24, 2007, by John Cooney (video game developer), John Cooney),
where the game just run by itself, and people are just chatting in the chat section of the game. While one of the first visual idle games ("rudimentary RPG" according to Pecorella) was ''Ayumilove's HackerStory v1'' (2008, by Ayumilove), which was a parody of bot Grinding (video games), grinding in a ''Maple Story'' game, a famous MMORPG from Korea at that time.
The early pioneers of idle games also saw some games parodying idle games, such as ''Anti-Idle'' (2009, by tukkun) which has both elements of active and idle games, and is extremely complicated, content-rich, and constantly updated; it helped popularize the genre. An idle game in Facebook platform, called ''Cow Clicker'' (2010, by Ian Bogost), which according to the author, "a satire and playable theory of ''Farmville, social games circa that era'', ... Facebook games distilled to their essence.", was the first to receive mainstream media attention. Another parody of idle games (and parody of capitalism) called ''AdVenture Capitalist'' (2015, by Cody Vigue / Hyper Hippo Games) also saw success as a browser game and was subsequently made available in many platforms. It was one of the first games to implement monetization, as well as ''offline earning'' which calculates the progress of a player during the time they are offline, unlike previous browser-based idle games which only run when open in a browser window.
Some idle games did not follow the infinite ending, and instead opt for finite ending, more like puzzle-like and exploration based, for example ''A Dark Room'' (2013, by Doublespeak Games), and ''Candy Box!'' (2013, by aniwey).
Incremental games gained popularity in 2013 after the success of ''Cookie Clicker'', although earlier games such as ''Cow Clicker'' and ''Candy Box!'' were based on the same principles. ''Make It Rain: The Love of Money, Make It Rain'' (2014, by Space Inch) was the first major mobile idle game success, although the idle elements in the game were heavily limited, requiring check-ins to progress. In 2015, the gaming press observed such games proliferating on the Steam (service), Steam distribution platform with titles such as ''Clicker Heroes'' (2014, by Playsaurus).
Other idle games that have become classic includes ''Sandcastle Builder'' (2013, by Eternal Density) which was based on the xkcd comic 1190: Time (xkcd), ''Time'', ''Sharky Clicker'' (2014, by Cirr), ''Crank'' (by FaeDine), and ''Kittens Game'' (2014, by Bloodrizer)
During the evolution of the genre, monetization (through ads or other venues), premium contents, and other game mechanics are slowly being added in.
According to Anthony Pecorella in his Game Developers Conference, GDC summit talks, the first idle game was attributed to ''Progress Quest'' (2002) by Eric Fredriksen, which is a parody of MMORPG's stats and auto-attack. He argued that Kongregate was an early breeding ground for the genre, as some people just want to chat, so, the first game of the genre was aptly titled ''Kongregate Chat'' (July 24, 2007, by John Cooney (video game developer), John Cooney),
where the game just run by itself, and people are just chatting in the chat section of the game. While one of the first visual idle games ("rudimentary RPG" according to Pecorella) was ''Ayumilove's HackerStory v1'' (2008, by Ayumilove), which was a parody of bot Grinding (video games), grinding in a ''Maple Story'' game, a famous MMORPG from Korea at that time.
The early pioneers of idle games also saw some games parodying idle games, such as ''Anti-Idle'' (2009, by tukkun) which has both elements of active and idle games, and is extremely complicated, content-rich, and constantly updated; it helped popularize the genre. An idle game in Facebook platform, called ''Cow Clicker'' (2010, by Ian Bogost), which according to the author, "a satire and playable theory of ''Farmville, social games circa that era'', ... Facebook games distilled to their essence.", was the first to receive mainstream media attention. Another parody of idle games (and parody of capitalism) called ''AdVenture Capitalist'' (2015, by Cody Vigue / Hyper Hippo Games) also saw success as a browser game and was subsequently made available in many platforms. It was one of the first games to implement monetization, as well as ''offline earning'' which calculates the progress of a player during the time they are offline, unlike previous browser-based idle games which only run when open in a browser window.
Some idle games did not follow the infinite ending, and instead opt for finite ending, more like puzzle-like and exploration based, for example ''A Dark Room'' (2013, by Doublespeak Games), and ''Candy Box!'' (2013, by aniwey).
Incremental games gained popularity in 2013 after the success of ''Cookie Clicker'', although earlier games such as ''Cow Clicker'' and ''Candy Box!'' were based on the same principles. ''Make It Rain: The Love of Money, Make It Rain'' (2014, by Space Inch) was the first major mobile idle game success, although the idle elements in the game were heavily limited, requiring check-ins to progress. In 2015, the gaming press observed such games proliferating on the Steam (service), Steam distribution platform with titles such as ''Clicker Heroes'' (2014, by Playsaurus).
Other idle games that have become classic includes ''Sandcastle Builder'' (2013, by Eternal Density) which was based on the xkcd comic 1190: Time (xkcd), ''Time'', ''Sharky Clicker'' (2014, by Cirr), ''Crank'' (by FaeDine), and ''Kittens Game'' (2014, by Bloodrizer)
During the evolution of the genre, monetization (through ads or other venues), premium contents, and other game mechanics are slowly being added in.
Reception
Nathan Grayson of ''Kotaku'' attributed the popularity of idle games to their ability to provide unchallenging distractions that fit easily into a person's daily routine, while using themes and aesthetics of more sophisticated games so as to be appealing to a "core gamer" audience. Grayson also noted that the genre allowed for a wide variety of game mechanics and themes, such as fantasy, sci-fi and erotica, to provide sufficient perceived depth to avoid boring players. IGN's Justin Davis describes the genre as being tuned for a never-ending sense of escalation, as expensive upgrades and items rapidly become available, only to become trivial and replaced by more. This leads to the player feeling powerful and weak at the same time in pursuit of exponential progress. Julien "Orteil" Thiennot (creator of games such as ''Cookie Clicker'') described his own works as "non-games". In early 2014, Orteil released an early version of ''Idle Game Maker'', a tool allowing customized idle games to be made without coding knowledge. Commenting on the parodic nature of the genre, Pecorella commented that "[idle games is] a genre that's almost doesn't want to exist; it's a joke, but despite itself, keeps being really successful", and on popular idle-games in general, "a lot of these are just glorified spreadsheet with some really neat mechanics in it."Influence
The idle games genre has in many ways influenced other genres. Pecorella (2015) identified several genres that includes idle elements in their mechanics: * Real-time social and strategy games: ''Hay Day'', ''Mafia Wars'', ''Game of War'' * Chinese MMORPGs (skipping the early games through "Glossary of video game terms#AFK, AFK mode" and going straight to end-game): ''Mythborne'' using auto-path mode, ''Wartune'', among others * Launch games (tight-loop prestige/newgame+ mechanic, not the idling one ''per se''): ''Curl Up and Fly'', among others. Shooting games, RPGs, and other genres also starts to introduce short prestige loop or mini idle games within, while some introduces offline progress to entice players to return, allowing for genre blends, from idle rhythm games to RPGs, to puzzle and dating sims.Auto clicker
 An auto clicker is automation software or a macro that is generally used to automate the clicking (or tapping) process in idle games. A number of idle games employ clicking as a method to gain currency while active (to complement to the idle element), and players may sometimes employ an auto clicker to automate this part, thus getting resources/currency much faster. Pecorella, in his 2016 GDC summit talk, argues that auto clickers are considered necessary by any "serious" idle game players, and that it's not cheating, but rather an exploration of an ''error in design''.
An auto clicker is automation software or a macro that is generally used to automate the clicking (or tapping) process in idle games. A number of idle games employ clicking as a method to gain currency while active (to complement to the idle element), and players may sometimes employ an auto clicker to automate this part, thus getting resources/currency much faster. Pecorella, in his 2016 GDC summit talk, argues that auto clickers are considered necessary by any "serious" idle game players, and that it's not cheating, but rather an exploration of an ''error in design''.
References
Further reading
* * {{Video game genre Video game genres Incremental games,