Imperial Free City of Trieste on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Imperial Free City of Trieste and its Territory (german: Reichsunmittelbare Stadt Triest und ihr Gebiet, it, Città Imperiale di Trieste e Dintorni) was a possession of the
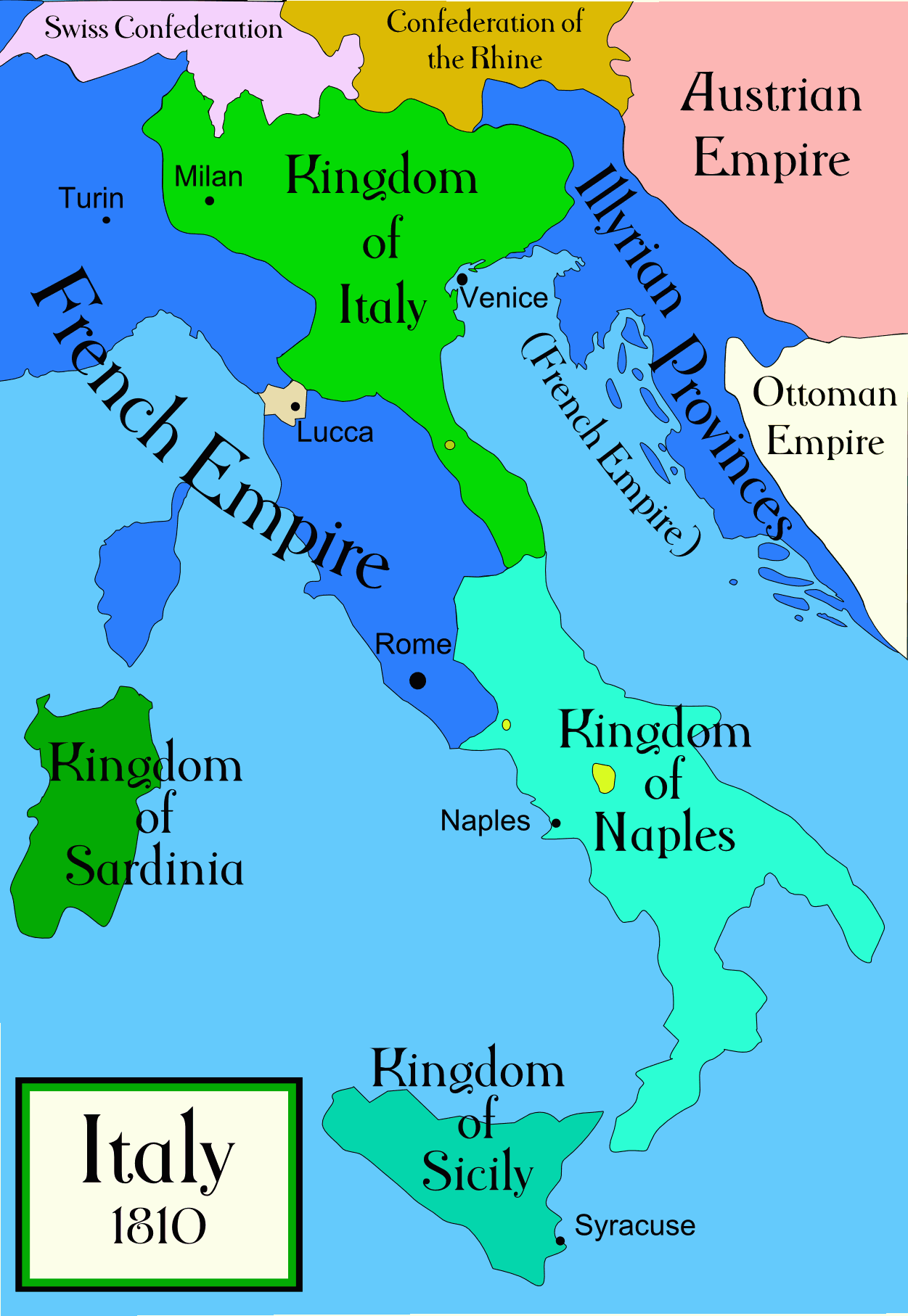 Trieste was occupied by
Trieste was occupied by
 Following the Napoleonic Wars, Trieste continued to prosper as the
Following the Napoleonic Wars, Trieste continued to prosper as the
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
from the 14th century to 1806, a constituent part of the German Confederation
The German Confederation (german: Deutscher Bund, ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, w ...
and the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
from 1849 to 1920, and part of the Italian Julian March
Venezia Giulia, traditionally called Julian March (Serbo-Croatian, Slovene: ''Julijska krajina'') or Julian Venetia ( it, Venezia Giulia; vec, Venesia Julia; fur, Vignesie Julie; german: Julisch Venetien) is an area of southeastern Europe wh ...
until 1922. In 1719 it was declared a free port
Free economic zones (FEZ), free economic territories (FETs) or free zones (FZ) are a class of special economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate areas in which com ...
by Emperor Charles VI
, house = Habsburg
, spouse =
, issue =
, issue-link = #Children
, issue-pipe =
, father = Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
, mother = Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg
, birth_date ...
; the construction of the Austrian Southern Railway
The Austrian Southern Railway (german: link=no, Österreichische Südbahn) is a long double track railway, which linked the capital Vienna with Trieste, former main seaport of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy, by railway for the first time. It now ...
(1841–57) turned it into a bustling seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
, through which much of the exports and imports of the Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
n Lands were channelled. The city administration and economy were dominated by the city's Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
population element; Italian was the language of administration and jurisdiction. In the later 19th and early 20th century, the city attracted the immigration of workers from the city's hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated ...
s, many of whom were speakers of Slovene.
History
Background
After thefall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
in 476, Trieste was a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
military outpost. In 567 AD the city was destroyed by the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
, in the course of their invasion of northern Italy. In 788 it became part of the Frankish kingdom
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
, under the authority of their count-bishop. From 1081 the city came loosely under the Patriarchate of Aquileia
The Patriarchate of Aquileia was an episcopal see in northeastern Italy, centred on the ancient city of Aquileia situated at the head of the Adriatic, on what is now the Italian seacoast. For many centuries it played an important part in histor ...
, developing into a free commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
by the end of the 12th century.
After two centuries of war, Trieste came with the signing of a peace treaty on 30 October 1370 in front of St. Bartholomew's Church in the village of Šiška () (now part of Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
) under the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
. The Venetians retained the town until 1378, when it became the property of the Patriarchate of Aquileia
The Patriarchate of Aquileia was an episcopal see in northeastern Italy, centred on the ancient city of Aquileia situated at the head of the Adriatic, on what is now the Italian seacoast. For many centuries it played an important part in histor ...
. (Digitalna Knjižnica Slovenije) Discontent with the patriarch's rule, the main citizens of Trieste in 1382 petitioned Leopold III of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
, Duke of Austria
This is a list of people who have ruled either the Margraviate of Austria, the Duchy of Austria or the Archduchy of Austria. From 976 until 1246, the margraviate and its successor, the duchy, was ruled by the House of Babenberg. At that time, t ...
to become part of his domains, in exchange for his defence. This united Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
's southern marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a national "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diff ...
under Habsburg rule, subsequently consolidated as the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
(german: Österreichisches Küstenland).
thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
Trieste in the Holy Roman Empire
Following an unsuccessful Habsburg invasion of Venice in the prelude to theWar of the League of Cambrai
The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was fought from February 1508 to December 1516 as part of the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fough ...
, the Venetians occupied Trieste again in 1508, and under the terms of the peace were allowed to keep the city. The Habsburg Empire recovered Trieste a little over a year later, however, when conflict resumed. With their acquisition by the Habsburgs, Carniola
Carniola ( sl, Kranjska; , german: Krain; it, Carniola; hu, Krajna) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region sti ...
and the Julian March ceased to act as an east-facing outpost of Italy against the unsettled peoples of the Danube basin, becoming a region of contact between the land-based Austrian domains and the maritime republic
The maritime republics ( it, repubbliche marinare), also called merchant republics ( it, repubbliche mercantili), were thalassocratic city-states of the Mediterranean Basin during the Middle Ages. Being a significant presence in Italy in the Mid ...
of Venice, whose foreign policy depended on control of the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ...
. Austro-Venetian rivalry over the Adriatic weakened each state's efforts to repel the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's expansion into the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
(which caused many Slavs to flee into the , sowing the seeds of future Yugoslav union), and paving the way for the success of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's invasion.
On the Habsburg's annexation, Trieste had a patriciate, a bishop and his chapter, two municipal chapters totalling 200 people, armed forces and institutions of higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
. Italian irredentism
Italian irredentism ( it, irredentismo italiano) was a nationalist movement during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries in Italy with irredentist goals which promoted the unification of geographic areas in which indigenous peoples ...
was continually popular — writing in 1917, the Italian nationalist Litta Visconti Arese described the city as:
Trieste became an important port and trade hub. In June 1717, it was made a free port
Free economic zones (FEZ), free economic territories (FETs) or free zones (FZ) are a class of special economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate areas in which com ...
within the Habsburg Empire by Emperor Charles VI
, house = Habsburg
, spouse =
, issue =
, issue-link = #Children
, issue-pipe =
, father = Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
, mother = Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg
, birth_date ...
(r. 1711–40), effective from his visit to the city on 10 September 1718, and remained a free port until 1 July 1891, when it was eclipsed by Fiume (now Rijeka
Rijeka ( , , ; also known as Fiume hu, Fiume, it, Fiume ; local Chakavian: ''Reka''; german: Sankt Veit am Flaum; sl, Reka) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia (after Zagreb and Split). It is located in Primor ...
). From June 1734, Charles VI began assembling a navy in the city. The reign of Charles VI's successor, Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position ''suo jure'' (in her own right). ...
(r. 1740–65), marked the beginning of a flourishing era for the city, starting with her order for the dismantling of the city walls
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
in 1749, in order to allow the freer expansion of the city, and ordering expansive building works and canal dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
.
In 1768, the German art historian Johann Joachim Winckelmann
Johann Joachim Winckelmann (; ; 9 December 17178 June 1768) was a German art historian and archaeologist. He was a pioneering Hellenist who first articulated the differences between Greek, Greco-Roman and Roman art. "The prophet and founding he ...
was murdered by a robber in Trieste, while on his way from Vienna to Italy.
French Revolution and Napoleonic Wars
 Trieste was occupied by
Trieste was occupied by French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
troops three times during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, in 1797, 1805 and in 1809. Between 1809 and 1813, it was annexed to the Illyrian Provinces
The Illyrian Provinces sl, Ilirske province hr, Ilirske provincije sr, Илирске провинције it, Province illirichegerman: Illyrische Provinzen, group=note were an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province of France d ...
, interrupting its status as a free port and causing a loss of the city's autonomy; the municipal autonomy was not restored after the return of the city to the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
in 1813. For the French, the Illyrian Provinces provided a military frontier against the remaining Austrian lands and a military base against the Turks, as well as providing distant endowments for Marshals of the Empire.
When Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
defeated the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
in 1797, he found that Istria was populated by Italians on the coast and in the main cities, but the interior was populated mainly by Croats and Slovenians; this dual ethnicity in the same peninsula created antagonism between Slavs and Italians for the supremacy of Istria, when nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
first started to rise after Napoleon's fall. The restoration of Istria to the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
was confirmed at the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
, but a nationalistic feud began to develop between the Slavs and the Italians.
Trieste in the Austrian Empire and Austria–Hungary
 Following the Napoleonic Wars, Trieste continued to prosper as the
Following the Napoleonic Wars, Trieste continued to prosper as the free imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
of Trieste (german: Reichsunmittelbare Stadt Triest), a status that granted economic freedom, but limited its political self-government. The city's role as main Austrian trading port and shipbuilding centre was later emphasised with the foundation of the merchant shipping line Austrian Lloyd in 1836, whose headquarters stood at the corner of the Piazza Grande and Sanità. By 1913, Austrian Lloyd had a fleet of 62 ships comprising a total of With the introduction of the constitutionalism
Constitutionalism is "a compound of ideas, attitudes, and patterns of behavior elaborating the principle that the authority of government derives from and is limited by a body of fundamental law".
Political organizations are constitutional ...
in the Austrian Empire in 1860, the municipal autonomy of the city was restored, with Trieste becoming capital of the ', the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
region.
In the later part of the 19th century, Pope Leo XIII
Pope Leo XIII ( it, Leone XIII; born Vincenzo Gioacchino Raffaele Luigi Pecci; 2 March 1810 – 20 July 1903) was the head of the Catholic Church from 20 February 1878 to his death in July 1903. Living until the age of 93, he was the second-old ...
considered moving his residence to Trieste (or to Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian) is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the ...
), due to what he considered a hostile anti-Catholic climate in Italy, following the capture of Rome
The Capture of Rome ( it, Presa di Roma) on 20 September 1870 was the final event of the unification of Italy (''Risorgimento''), marking both the final defeat of the Papal States under Pope Pius IX and the unification of the Italian Peninsula ...
by the newly founded Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
. However, the Austrian monarch Franz Josef I
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the Grand title of the Emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg m ...
gently rejected this idea.
The modern Austro-Hungarian Navy
The Austro-Hungarian Navy or Imperial and Royal War Navy (german: kaiserliche und königliche Kriegsmarine, in short ''k.u.k. Kriegsmarine'', hu, Császári és Királyi Haditengerészet) was the naval force of Austria-Hungary. Ships of the A ...
used Trieste's shipbuilding facilities for construction and as a base. The Austrian acquisition of Lombardy-Veneto (1815–66) meant that Trieste was no longer in a frontier zone, encouraging the construction of the first major trunk railway in the Empire, the Vienna–Trieste Austrian Southern Railway
The Austrian Southern Railway (german: link=no, Österreichische Südbahn) is a long double track railway, which linked the capital Vienna with Trieste, former main seaport of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy, by railway for the first time. It now ...
(german: Südbahn), was completed in 1857, a valuable asset for trade and the supply of coal. The importance of Trieste as a trading and shipbuilding city to the Empire is testified by the expenditure made. The construction of cost 29 million crowns
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
over 15 years (1868–83) and in the following decade another 10 million crowns were spent extending the port (roughly equivalent to 12 tons of gold). Up until 1914, over 14 million crowns of subsidies were paid to Austrian shipping companies using Trieste. This investment and railway-building resulted in a rapid expansion of Triestine trade, which peaked in 1913 at over 6 million tons of goods, with the port almost entirely reliant on Austro-Hungarian trade, as opposed to transshipment
Transshipment, trans-shipment or transhipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
One possible reason for transshipment is to change the means of transport during the journey (e.g. ...
; even after the Italian acquisition of the city, Trieste continued to be a port for central and southeastern Europe, rather than Italian trade, mainly for coffee, sugar and tropical fruits, wines, oils, cotton, iron, wood and machinery.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Trieste was a buzzing cosmopolitan city frequented by artists and philosophers such as James Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influential and important writers of ...
, Italo Svevo
Aron Hector Schmitz (19 December 186113 September 1928), better known by the pseudonym Italo Svevo (), was an Italian writer, businessman, novelist, playwright, and short story writer.
A close friend of Irish novelist and poet James Joyce, Svevo ...
, Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies explained as originatin ...
, Dragotin Kette
Dragotin Kette (19 January 1876 – 26 April 1899) was a Slovene Impressionist and Neo-Romantic poet. Together with Josip Murn, Ivan Cankar, and Oton Župančič, he is considered the founder of modernism in Slovene literature.
Life
Kette was ...
, Ivan Cankar
Ivan Cankar (, ) (10 May 1876 – 11 December 1918) was a Slovene writer, playwright, essayist, poet, and political activist. Together with Oton Župančič, Dragotin Kette, and Josip Murn, he is considered as the beginner of modernism in Slo ...
, Scipio Slataper
Scipio Slataper (14 July 1888 – 3 December 1915) was an Italian writer, most famous for his lyrical essay '' My Karst''. He is considered, alongside Italo Svevo, the initiator of the prolific tradition of Italian literature in Trieste.
Biogra ...
, and Umberto Saba
Umberto Saba (9 March 1883 – 26 August 1957) was an Italian poet and novelist, born Umberto Poli in the cosmopolitan Mediterranean port of Trieste when it was the fourth largest city of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Poli assumed the pen name " ...
. The city was the major port of the Austrian Riviera
The Austrian Riviera (German language, German: ''Österreichische Riviera'', Italian language, Italian: ''Riviera Austriaca'', Slovene language, Slovene: ''Avstrijska riviera'', Croatian language, Croatian: ''Austrijska rivijera'') was a term used ...
, and perhaps the only real enclave of ' south of the Alps. Viennese architecture and coffeehouse
A coffeehouse, coffee shop, or café is an establishment that primarily serves coffee of various types, notably espresso, latte, and cappuccino. Some coffeehouses may serve cold drinks, such as iced coffee and iced tea, as well as other non-ca ...
s still dominate the streets of Trieste to this day.
End of Austrian Trieste
Together withTrento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th centu ...
, Trieste was a main focus of the irredentist
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
movement, which aimed for the annexation to Italy of all the lands they claimed were inhabited by an Italian-speaking population. Many local Italians enrolled voluntarily in the Royal Italian Army
The Royal Italian Army ( it, Regio Esercito, , Royal Army) was the land force of the Kingdom of Italy, established with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy. During the 19th century Italy started to unify into one country, and in 1861 Manfre ...
(a notable example is the writer Scipio Slataper
Scipio Slataper (14 July 1888 – 3 December 1915) was an Italian writer, most famous for his lyrical essay '' My Karst''. He is considered, alongside Italo Svevo, the initiator of the prolific tradition of Italian literature in Trieste.
Biogra ...
).
After the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
dissolved, and many of its border areas, including the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
, were disputed among its successor states. On November 3, 1918, the Armistice of Villa Giusti
The Armistice of Villa Giusti or Padua ended warfare between Italy and Austria-Hungary on the Italian Front during World War I. The armistice was signed on 3 November 1918 in the Villa Giusti, outside Padua in the Veneto, Northern Italy, and too ...
was signed ending hostilities between Italy and Austria-Hungary. Trieste, with Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
and Gorizia
Gorizia (; sl, Gorica , colloquially 'old Gorizia' to distinguish it from Nova Gorica; fur, label= Standard Friulian, Gurize, fur, label= Southeastern Friulian, Guriza; vec, label= Bisiacco, Gorisia; german: Görz ; obsolete English ''Gorit ...
was occupied by the Italian Army
"The safeguard of the republic shall be the supreme law"
, colors =
, colors_labels =
, march = ''Parata d'Eroi'' ("Heroes's parade") by Francesco Pellegrino, ''4 Maggio'' (May 4) ...
after the Austro-Hungarian troops had been ordered to lay down their arms, a day before the Armistice was due to enter into effect, effectively allowing the Italians to claim the region had been taken before the cessation of hostilities (a similar situation occurred in South Tyrol
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol
, settlement_type = Autonomous province
, image_skyline =
, image_alt ...
). Trieste was lost to Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
at Saint-Germain-en-Laye
Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, from the centre of Paris.
Inhabitants are called ''Saint-Germanois'' or ''Saint-Ge ...
and officially annexed to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
at Rapallo
Rapallo ( , , ) is a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Genoa, located in the Liguria region of northern Italy.
As of 2017 it had 29,778 inhabitants. It lies on the Ligurian Sea coast, on the Tigullio Gulf, between Portofino and Chiavar ...
in 1920. If the Liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
governments ruling Italy at time granted Trieste of its ancient autonomy, maintained most of former Austrian laws, and simply gave a new name to the Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
as Julian March
Venezia Giulia, traditionally called Julian March (Serbo-Croatian, Slovene: ''Julijska krajina'') or Julian Venetia ( it, Venezia Giulia; vec, Venesia Julia; fur, Vignesie Julie; german: Julisch Venetien) is an area of southeastern Europe wh ...
( it, Venezia Giulia) without any other legal change, Fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
violence which occurred to Socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
s and Christian Democrat
Christian democracy (sometimes named Centrist democracy) is a political ideology that emerged in 19th-century Europe under the influence of Catholic social teaching and neo-Calvinism.
It was conceived as a combination of modern democratic ...
s in other parts of Italy, were suffered by Slovene organizations in Trieste.
The union to Italy brought a loss of importance to the city, as it was now a city on the margin of Italy's map, cut off from its economic hinterland. The Slovene ethnic group (around 25% of the population according to the 1910 census) suffered persecution by rising Italian Fascism. The period of violent persecution of Slovenes began with riots on 13 April 1920, which were organized as a retaliation for the assault on Italian occupying troops in Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enterta ...
by the local Croatian population. Many Slovene-owned shops and buildings were destroyed during the riots, which culminated when a group of Italian Fascists, led by Francesco Giunta
Francesco Giunta (21 March 1887 – 8 June 1971) was an Italian Fascist politician. A leading figure in the early years of fascism, he helped to build the movement in several regions of the country and was particularly active in Trieste. Duri ...
, burned down the ("National Hall
National Hall is a former venue in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, located at 1222–24 Market Street, between Twelfth and Thirteenth Streets. It was one of the most popular venues in the city, site of concerts, lectures, meetings, and political spee ...
"), the community hall of Trieste's Slovenes.
The end of Trieste autonomy was a consequence of the March on Rome
The March on Rome ( it, Marcia su Roma) was an organized mass demonstration and a coup d'état in October 1922 which resulted in Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party (PNF) ascending to power in the Kingdom of Italy. In late October 1922, Fa ...
in 1922. Immediately after their rose to power, the Fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
s abolished the Austrian administrative structure of the Julian March
Venezia Giulia, traditionally called Julian March (Serbo-Croatian, Slovene: ''Julijska krajina'') or Julian Venetia ( it, Venezia Giulia; vec, Venesia Julia; fur, Vignesie Julie; german: Julisch Venetien) is an area of southeastern Europe wh ...
, which was divided between the newly formed Province of Trieste
The Province of Trieste ( it, Provincia di Trieste, sl, Tržaška pokrajina; fur, provinzia di Triest) was a Provinces of Italy, province in the autonomous Friuli-Venezia Giulia region of Italy. Its capital was the city of Trieste.
It had an are ...
, of which Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into provi ...
became a mere municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
, and the Province of Pola
Province of Pola (in Italian ''Provincia di Pola'') was a province of the Kingdom of Italy created after World War I, that officially existed from 1923 until 1947. The capital ("Capoluogo" in Italian) was Pola. After the Second World War the Provi ...
; the remainder of the territory was annexed by the Province of Udine
The province of Udine ( it, provincia di Udine, fur, provincie di Udin, sl, videmska pokrajina, Resian dialect, Resian: , german: Provinz Weiden) was a Provinces of Italy, province in the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia of Italy, borderi ...
.Royal decree n°53 of January 18, 1923, by King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
Victor Emmanuel III
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French shor ...
and Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
.
Demographics
The particular Friulian dialect, called , spoken until the beginning of the 19th century, was gradually overcome by theTriestine dialect
The Triestine dialect ( it, triestino, Triestine: ) is a dialect of Venetian spoken in the city of Trieste.
Many words in Triestine are taken from other languages. As Trieste borders with Slovenia and was under the Habsburg monarchy for almost ...
(with a Venetian base, deriving directly from vulgar Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
) and other languages, including German grammar, Slovene and standard Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
languages. While Triestine was spoken by the largest part of the population, German was the language of the Austrian bureaucracy and Slovene was predominant in the surrounding villages. From the last decades of the 19th century, Slovene language speakers grew steadily, reaching 25% of the overall population of the municipality of Trieste in 1911 (30% of the Austro-Hungarian citizens in Trieste).
According to the 1911 census, the proportion of Slovene speakers amounted to 12.6% in the city centre, 47.6% in the suburbs, and 90.5% in the surroundings. They were the largest ethnic group in 9 of the 19 urban neighborhoods of Trieste, and represented an absolute majority in 7 of them. The Italian speakers, on the other hand, were 60.1% of the population in the city centre, 38.1% in the suburbs, and 6.0% in the surroundings. They were the largest linguistic group in 10 of the 19 urban neighborhoods and represented the majority in 7 of them (including all 6 in the city centre). Of the 11 villages included within the city limits, the Slovene speakers had an overwhelming majority in 10, and the German speakers in one (Miramare
Miramare Castle ( it, Castello di Miramare; es, Castillo de Miramar; german: Schloss Miramar; sl, Grad Miramar) is a 19th-century castle direct on the Gulf of Trieste between Barcola and Grignano in Trieste, northeastern Italy. It was built ...
).
German speakers amounted to 5% of the city's population, with the highest proportions in the city centre. A small number of the population spoke Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and ...
(around 1.3% in 1911), and the city also counted several other smaller ethnic communities: Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, c ...
, Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to se ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
and Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, which mostly assimilated either to the Italian or Slovene-speaking community.
See also
*Austrian Riviera
The Austrian Riviera (German language, German: ''Österreichische Riviera'', Italian language, Italian: ''Riviera Austriaca'', Slovene language, Slovene: ''Avstrijska riviera'', Croatian language, Croatian: ''Austrijska rivijera'') was a term used ...
* Battles of the Isonzo
The Battles of the Isonzo (known as the Isonzo Front by historians, sl, soška fronta) were a series of 12 battles between the Austro-Hungarian and Italian armies in World War I mostly on the territory of present-day Slovenia, and the remaind ...
* History of Trieste
The history of Trieste began with the formation of a town of modest size in pre-Roman times, which became an actual city only after Roman conquest in the second century BC and subsequent colonisation. After the imperial era, the city declined foll ...
* London Pact
The Treaty of London ( it, Trattato di Londra) or the Pact of London () was a secret agreement concluded on 26 April 1915 by the United Kingdom, France, and Russia on the one part, and Italy on the other, in order to entice the latter to enter ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Trieste, Imperial Free City Free imperial cities City-statesImperial Free City of Trieste
The Imperial Free City of Trieste and its Territory (german: Reichsunmittelbare Stadt Triest und ihr Gebiet, it, Città Imperiale di Trieste e Dintorni) was a possession of the Habsburg monarchy in the Holy Roman Empire from the 14th century to 1 ...
History of Austria-Hungary
1918 disestablishments in Austria-Hungary
Disestablishments in the Empire of Austria (1867–1918)
Lands of the Empire of Austria (1867–1918)
States and territories disestablished in 1918