Imamah (Shi'a doctrine) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
4:165
of
5:3
of
Quran, 2:124
Shias believe that Imamah is a divine position always Imamah is accompanied by the word guidance, of course a guidance by God's Command. A kind of guidance which brings humanity to the goal. Regardin
17:71
no age can be without an Imam. So, according to the upper verse, 1. Imamah is a position which is appointed by God and must be specified by Him; 2. Imam is protected by a divine protection and no one excels him in nobility; 3. No age can be without an Imam and finally Imam knows everything which is needed for human being to get to the truth and goal.
corrupt rulers
''Islamic Dynasties of the Arab East: State and Civilization during the Later Medieval Times'' by Abdul Ali, M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd., 1996, p97 The renowned Muslim jurist Abu Hanifa who is credited for the

Al-imamah (emamah) pageShia Islam: History and Doctrines
a chapter of Shi'ite Islam (book) by Allameh Tabatabaei
"The Twelve Imams"
��Taken from ''A Shi'ite Anthology'' by Allameh Tabatabaei
A Short History of the Lives of The Twelve ImamsImamah in the Qur'an"Imam"
��An article by ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Online
by Maria Dakake, an entry in the '' Encyclopædia Iranica''
Shia Islam – Ask ImamShia Network Ahlulbayt Discussion ForumsBay Area Shiite-Muslims Association
(basma.us)
Imamia Mission BuryThe Shia Islamic Guide
(shiacode.com)
Imamah according to Sunnis
{{Authority control Shia belief and doctrine Islamic states by type Islamic terminology Imamate
Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, m ...
, the Imamah ( ar, إمامة) is a doctrine
Doctrine (from la, doctrina, meaning "teaching, instruction") is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a belief syste ...
which asserts that certain individuals from the lineage of the Islamic prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
are to be accepted as leaders and guides of the ummah after the death of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mono ...
. Imamah further says that Imams possess divine knowledge and authority ( Ismah) as well as being part of the Ahl al-Bayt, the family of Muhammad. These Imams have the role of providing commentary and interpretation of the Quran as well as guidance.
Etymology
The word "Imām" denotes a person who stands or walks "in front". For Sunni Islam, the word is commonly used to mean a person who leads the course of prayer in themosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
. It also means the head of a '' madhhab'' ("school of thought"). However, from the Shia point of view this is merely the ''basic'' understanding of the word in the Arabic language and, for its proper religious usage, the word "Imam" is applicable ''only'' to those members of the house of Muhammad designated as infallible by the preceding Imam.
Introduction
The Shia further believe only these A'immah have the right to be Caliphs, meaning that all other caliphs, whether elected by consensus ('' Ijma'') or not, are usurpers of theCaliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
as those were political positions not divine positions.
All Muslims believe that Muhammad had said: "To whomsoever I am Mawla
Mawlā ( ar, مَوْلَى, plural ''mawālī'' ()), is a polysemous Arabic word, whose meaning varied in different periods and contexts.A.J. Wensinck, Encyclopedia of Islam 2nd ed, Brill. "Mawlā", vol. 6, p. 874.
Before the Islamic prophet ...
, Ali is his Mawla." This hadith has been narrated in different ways by many different sources in no less than 45 hadith books of both Sunni and Shia collections. This hadith has also been narrated by the collector of hadiths, al-Tirmidhi, 3713; as well as Ibn Maajah, 121; etc. The major point of conflict between the Sunni and the Shia is in the interpretation of the word 'Mawla'. For the Shia the word means 'Master' and has the same elevated significance as when the term had been used to address Muhammad himself during his lifetime. Thus, when Muhammad actually (by speech) and physically (by way of having his closest companions including Abu Bakr, Umar and Uthman he three future Caliphs who had preceded Ali as Caliph''publicly'' accept Ali as their Master by taking Ali's hand in both of theirs as token of their allegiance to Ali) ''transferred'' this title and manner of addressing Ali as the Mawla for all Muslims at Ghadiri Khum Oasis just a few months before his death, the people that came to look upon Ali as Muhammad's ''immediate successor'' even before Muhammad's death came to be known as the Shia. However, for Sunnis the word simply means the 'beloved' or the 'revered' and has no other significance at all.
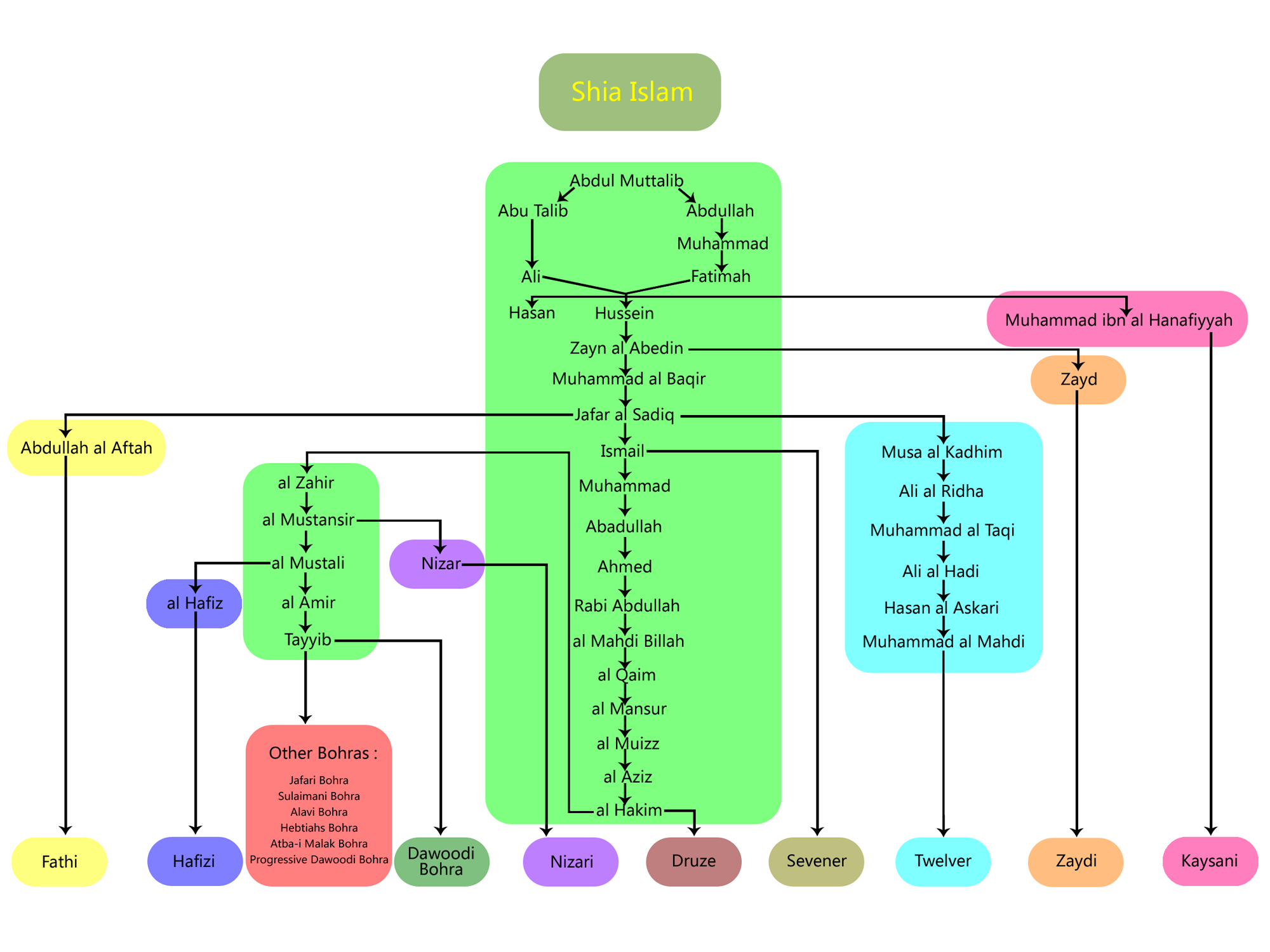
Sects
Within Shia Islam (Shiism), the various sects came into being because they differed over their Imams' successions, just as the Shia – Sunni separation within Islam itself came into being from the dispute that had arisen over the succession toMuhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
. Each succession dispute brought forth a different tariqah (literal meaning 'path'; extended meaning 'sect') within Shiism. Each Shia tariqah followed its own particular Imam's dynasty, resulting in different numbers of Imams for each particular Shia tariqah. When the dynastic line of the separating successor Imam ended with no heir to succeed him, then either he (the last Imam) or his unborn successor was believed to have gone into a concealment known as The Occultation
Occultation ( ar, غَيْبَة, ') in Shia Islam refers to the eschatological belief that Mahdi, a descendant of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, has already been born and subsequently concealed, but will reemerge to establish justice and peace ...
.
The Shia tariqah with a majority of adherents are the Twelvers
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
who are commonly known as "Shia". After that come the Nizari
The Nizaris ( ar, النزاريون, al-Nizāriyyūn, fa, نزاریان, Nezāriyān) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent ...
Ismailis commonly known as the Ismailis, then the Mustalian Ismailis also called the "Bohras", and there are further schisms within their Bohri tariqah. The Druze tariqah initially were part of the Fatimid Ismailis but separated from them after the death of the Fatimid Imam and Caliph Al Hakim Bi Amrillah. The Shia Sevener tariqah no longer exists. Another small tariqah is that of the Zaidi Shias, or the "Fivers;" they do not believe in the Occultation of their last Imam.
Although all these different Shia tariqahs belong to the Shia (as opposed to the Sunni) sect in Islam, there are major doctrinal differences between the main Shia tariqahs. After that there is the complete doctrinal break between all the different Shia tariqahs whose last Imams have gone into Occultation and the Shia Nizari Ismailis, who deny the concept of Occultation and so have to have a present and living Imam until the end of time.
Twelver view
Shias believe that Imamah is of the Principles of Faith (Usul al-Din). As the vers4:165
of
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
expresses the necessity to the appointment of the prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
; so after the demise of the prophet who will play the role of the prophet; until the people have not any plea against Allah. The same logic that necessitated the assignment of prophets also is applied for Imamah. That is Allah must assign someone similar to prophet in his attributes and Ismah as his successor to guide the people without any deviation in religion.
They refer to the verse ("...This day I have perfected for you your religion and completed My favor upon you and have approved for you Islam as religion..."5:3
of
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
which was revealed to the prophet when he appointed Ali as his successor
Successor may refer to:
* An entity that comes after another (see Succession (disambiguation))
Film and TV
* ''The Successor'' (film), a 1996 film including Laura Girling
* ''The Successor'' (TV program), a 2007 Israeli television program Musi ...
at the day of Ghadir Khumm
The Ghadīr Khumm ( ar, غَدِير خُم) refers to a gathering of Muslims to attend a sermon delivered by the Islamic prophet Muhammad on 16 March 632 CE (18 Dhu al-Hijjah 10 AH). The gathering is said to have taken place at the Ghadir K ...
.
By the versQuran, 2:124
Shias believe that Imamah is a divine position always Imamah is accompanied by the word guidance, of course a guidance by God's Command. A kind of guidance which brings humanity to the goal. Regardin
17:71
no age can be without an Imam. So, according to the upper verse, 1. Imamah is a position which is appointed by God and must be specified by Him; 2. Imam is protected by a divine protection and no one excels him in nobility; 3. No age can be without an Imam and finally Imam knows everything which is needed for human being to get to the truth and goal.
Why only specific members of Muhammad's family?
Sunnis reject the doctrine of Imamate on the basis of their interpretation of verse 33:40 of theQur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
which says that Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
, as the , "is not the father of any of your men"; and that is why God let Muhammad's sons die in infancy. This is why Muhammad did not nominate a successor, as he wanted to leave the succession to be resolved "by the Muslim Community on the basis of the Qur’anic principle of consultation ()". The question Madelung proposes here is why the family members of Muhammad should not inherit aspects of Muhammad's character, apart from prophethood, such as rule (), wisdom (), and leadership (). Since the Sunni concept of the "true caliphate" itself defines it as a "succession of the Prophet in every respect except his prophethood", Madelung further asks, "If God really wanted to indicate that he should not be succeeded by any of his family, why did He not let his grandsons and other kin die like his sons?"
It is narrated that it is forbidden for the Divine Leader not to be from the family of Muhammad. According to Ali al-Ridha, since it is obligatory to obey him, there should be a sign to clearly indicate the Divine Leader. That sign is his well-known ties of kinship with Muhammad and his clear appointment so that the people could distinguish him from others, and be clearly guided toward him. Otherwise others are nobler than Muhammad's offspring and they are to be followed and obeyed; and the offspring of Muhammad are obedient and subject to the offspring of Muhammad's enemies such as Abi Jahl or Ibn Abi Ma’eet.However, Muhammad is much nobler than others to be in charge and to be obeyed.
Moreover, once the prophethood of Muhammad is testified they would obey him, no one would hesitate to follow his offspring and this would not be hard for anyone. While to follow the offspring of the corrupted families is difficult. And that is maybe why the basic characteristic of Muhammad and other prophets was their nobility. For none of them, it is said, were originated from a disgraced family. It is believed that all Muhammad's ancestors up to Adam were true Muslims. Jesus was also from a pious family, as it is mentioned in Quran that after his birth, people said to Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religious contexts
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also calle ...
: "O sister of Aaron, your father was not a man of evil, nor was your mother unchaste."
The Ismā'īlī view
The doctrine of the Imamate in Isma'ilism differs from that of the Twelvers because the Isma'ilis had living Imams for centuries after the last Twelver Imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi went into hiding. They followed Isma'il ibn Jafar, elder brother of Musa al-Kadhim, as the rightful Imam after his father,Ja'far al-Sadiq
Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī al-Ṣādiq ( ar, جعفر بن محمد الصادق; 702 – 765 CE), commonly known as Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq (), was an 8th-century Shia Muslim scholar, jurist, and theologian.. He was the founder of th ...
. The Ismailis believe that whether Imam Ismail did or did not die before Imam Ja'far, he had passed on the mantle of the imamate to his son Muhammad ibn Isma'il as the next imam.
According to Isma'ilism, God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
has sent seven great prophets known as ''Nātiq''s "Speaker" in order to disseminate and improve his dīn
Dīn ( ar, دين, Dīn, also anglicized as Deen) is an Arabic word with three general senses: judgment, custom, and religion. It is used by both Muslims and Arab Christians.
In Islamic terminology, the word refers to the way of life Muslims ...
of '' Islam''. All of these great prophets has also one assistant known as ''Sāmad'' "Silent" Imām. At the end of each seven ''Sāmad'' silsilas, one great ''Nātiq'' has been sent in order to improve the faith. After Adam and his son Seth, and after six ''Nātiq–Sāmad'' silsila ( Noah–Shem
Shem (; he, שֵׁם ''Šēm''; ar, سَام, Sām) ''Sḗm''; Ge'ez: ሴም, ''Sēm'' was one of the sons of Noah in the book of Genesis and in the book of Chronicles, and the Quran.
The children of Shem were Elam, Ashur, Arphaxad, Lu ...
), ( Abraham– Ishmael), ( Moses– Aaron), (Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
– Simeon, son of Jacob), (Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
– Ali); the silsila of ''Nātiq''s and ''Sāmad''s have been completed with Muhammad ibn Isma'il
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Ismāʿīl (), also known in his own time as al-Maymūn and hence sometimes incorrectly identified as Maymūn al-Qaddāḥ, was the son of Isma'il ibn Ja'far; he was an Ismāʿīlī Imam. The majority of Ism� ...
.
Why Imams from only (specific) family members
Ismailis view Imams as the true representative of God. God has made all prophets his representative. Individual prophets era are distinct. After one prophets God created next prophet. Islam view that Mohammed is last prophet. Mohammed appointed his specific representative Ali. Ali made imams as his next representative and one imam appointed another until date. The Isma'ili view that these Imam are only from their hereditary chain and their appointment is a must, and Earth cannot remain vacant, without presence of Imam.Zaidi view
Zaidiyyah or Zaidi is a Shia madhhab (sect, school) named after the imam Zayd ibn Ali. Followers of the Zaidi fiqh are called Zaidis (or are occasionally called Fivers in the West). However, there is also a group called the Zaidi ''Wasītī''s who are Twelvers. In the context of the Shi'a Muslim belief in spiritual leadership or Imamate, Zaydis believe that the leader of the Ummah or Muslim community must be ''Fatimids'': descendants of Muhammad through his only surviving daughterFatimah
Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, ...
, whose sons were Hasan ibn ʻAlī and Husayn ibn ʻAlī. These Shi'a called themselves Zaydi so they could differentiate themselves from other Shi'is who refused to take up arms with Zayd ibn Ali.
Zaydis believe Zayd ibn Ali was the rightful successor to the Imamate because he led a rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
, who he believed were tyrannical and corrupt. Muhammad al-Baqir
Muḥammad al-Bāqir ( ar, مُحَمَّد ٱلْبَاقِر), with the full name Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib, also known as Abū Jaʿfar or simply al-Bāqir () was the fifth Imam in Shia Islam, succee ...
did not engage in political action and the followers of Zayd believed that a true Imām must fight againscorrupt rulers
''Islamic Dynasties of the Arab East: State and Civilization during the Later Medieval Times'' by Abdul Ali, M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd., 1996, p97 The renowned Muslim jurist Abu Hanifa who is credited for the
Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named a ...
school of Sunni Islam, delivered a fatwā
A fatwā ( ; ar, فتوى; plural ''fatāwā'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist ...
or legal statement in favour of Zayd in his rebellion against the Umayyad ruler. He also urged people in secret to join the uprising and delivered funds to Zayd.
Unlike Twelver Shi'ites, Zaydis do not believe in the infallibility of Imāms Francis Robinson, ''Atlas of the Islamic World Since 1500'', pg. 47. New York: Facts on File
Infobase Publishing is an American publisher of reference book titles and textbooks geared towards the North American library, secondary school, and university-level curriculum markets. Infobase operates a number of prominent imprints, including ...
, 1984. The Imamate can be passed down to anyone of the household of Muhammad.
The period of occultation
Twelver view
The period of occultation (''ghaybah'') is divided into two parts: * ''Ghaybah al-Sughra'' or Minor Occultation (874–941), consists of the first few decades after the Imam's disappearance when communication with him was maintained through deputies of the Imam. * ''Ghaybah al-Kubra'' or Major Occultation began in 941 and is believed to continue until a time decided byGod
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
, when the Mahdi will reappear to bring absolute justice to the world.
During the Minor Occultation (''Ghaybah al-Sughrá''), it is believed that al-Mahdi maintained contact with his followers via deputies ( Arab. ''an-nuwāb al-arbaʻa'' or "the Four Leaders"). They represented him and acted as agents between him and his followers. Whenever the believers faced a problem, they would write their concerns and send them to his deputy. The deputy would ascertain his verdict, endorse it with his seal and signature and return it to the relevant parties. The deputies also collected zakat and khums on his behalf.
For the Shia, the idea of consulting a hidden Imam was not something new because the two prior Twelver Imams had, on occasion, met with their followers from behind a curtain. Also, during the oppressive rule of the later Abbasid caliphs, the Shia Imams were heavily persecuted and held prisoners, thus their followers were forced to consult their Imams via messengers or secretly.
Shia Tradition hold that four deputies acted in succession to one another:
# Uthman ibn Sa’id al-Asadi
# Abu Jafar Muhammad ibn Uthman
# Abul Qasim Husayn ibn Ruh al-Nawbakhti
# Abul Hasan Ali ibn Muhammad al-Samarri
Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn Muhammad al-Samarri ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن مُحَمَّد ٱلسَّمَّرِيّ, ') was the last of the Four Deputies, who are believed by the Twelvers to have successively represented th ...
In 941 (329 AH), the fourth deputy announced an order by al-Mahdi, that the deputy would soon die and that the deputyship would end and the period of the Major Occultation would begin.
The fourth deputy died six days later and the Shia Muslims continue to await the reappearance of the Mahdi. In the same year, many notable Shia scholars such as Ali ibn Babawayh Qummi and Muhammad ibn Ya'qub Kulayni, the learned compiler of '' Kitab al-Kafi'', also died.
One view is that the Hidden Imam is on earth "among the body of the Shia" but "incognito". "Numerous stories" exist of the Hidden Imam "manifesting himself to prominent members of the ulama."
The Ismā'īlī view
The Ismailis differ from Twelvers because they had living imams for centuries after the last Twelver Imam went into concealment. They followed Isma'il ibn Jafar, elder brother of Musa al-Kadhim, as the rightful Imam after his fatherJa'far al-Sadiq
Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī al-Ṣādiq ( ar, جعفر بن محمد الصادق; 702 – 765 CE), commonly known as Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq (), was an 8th-century Shia Muslim scholar, jurist, and theologian.. He was the founder of th ...
. The Ismailis believe that whether Imam Ismail did or did not die before Imam Ja'far, he had passed on the mantle of the imamate to his son Muḥammad ibn Ismail as the next imam. Thus, their line of imams is as follows (the years of their individual imamats during the Common Era are given in brackets):
First phase
The eighth Imam, Abd Allah al-Akbar of the Ismaili Shia remained hidden but continued the Ismaili movement in the 9th century in Salamiyah, Syria. The eighth to tenth Imams ( Abadullah, Ahmed and Husain), remained hidden and worked for the movement against the period's time's rulers. First phase of seclusion ends with 10th Imam. The 11th Imam Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah, under the guise of being a merchant, and his son had made their way to Sijilmasa, fleeing persecution by the Abbasids. Imam Abdullah founded Fatimid Caliphate. The Fatimid Ismaili Imams continued until 20th Imam holding the post of caliph also, ruling a vast part of Arabian peninsula.Second phase
Upon the death of the twentieth Imam, al-Amir bi-Ahkami'l-Lah (d. ), his two-year-old childat-Tayyib Abu'l-Qasim
Al-Ṭayyib Abūʾl-Qāsim ibn Al-Manṣūr ( ar, ٱلطَّيِّب أَبُو ٱلْقَاسِم ابْن ٱلْمَنْصُوْر) was, according to the Tayyibi Isma'ili- Musta'li sect of Isma'ilism, the twenty-first Imam and the last Ca ...
(b. ) was appointed twenty-first Imam. The supporters of Tayyeb became the Tayyibi
Tayyibi Isma'ilism is the only surviving sect of the Musta'li branch of Isma'ilism, the other being the extinct Hafizi branch. Followers of Tayyibi Isma'ilism are found in various Bohra communities: Dawoodi, Sulaymani, and Alavi.
The Tayyibi ...
Ismāʿīlī
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-S ...
. As Tayyeb was not in position to run the dawah, Queen Arwa al-Sulayhi
)
, name = Arwā bint Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn Jaʿfar ibn Mūsā Aṣ-Ṣulayḥī
, other_names = ''As-Sayyidah Al-Ḥurrah'' () ''Al-Malikah Al-Ḥurrah'' ( ar, ٱلْمَلِكَة ٱلْحُرَّة or ...
, the Da'i al-Mutlaq, acted as his regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
. Imam Tayyeb was hidden, and the second phase of seclusion started. The Da'i had now been given absolute authority and made independent from political activity. With the period of time the Tayyibi divided further into several sects headed by different Dais. These Da'i al-Mutlaq continued acting on behalf of the hidden Tayyibi Ismāʿīlī Imams until date. Dawoodi Bohra
The Dawoodi Bohras are a religious denomination within the Ismā'īlī branch of Shia Islam. Their largest numbers reside in India, Pakistan, Yemen, East Africa, and the Middle East, with a growing presence across Europe, North America, South ...
is the biggest sub-sect amongst the Tayyibi Ismāʿīlī with a population spread over many countries.
Imams
Twelver Imams
According to the majority of Shī'a, namely the Twelvers (''Ithnā'ashariyya''), the following is a listing of the rightful successors to Muḥammad. Each Imam was the son of the previous Imam except for Hussayn ibn 'Alī, who was the brother of Hassan ibn 'Alī.The belief in this succession to Muḥammad stems from various Quranic verses which include: 75:36, 13:7, 35:24, 2:30, 2:124, 36:26, 7:142, 42:23. They support their discussion by citing Genesis 17:19–20 and Sunni hadith:Sahih Muslim, Hadith number 4478, English translation by Abdul Hamid Siddiqui.List of The Twelve Imams
According to Twelvers, there is always an Imam of the era, who is the divinely appointed authority on all matters of faith and law in the Muslim community. Ali was the first of the Twelve Imams, and, in the Twelvers and Sufis' view, the rightful successor to Muhammad, followed by male descendants of Muhammad through his daughterFatimah
Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, ...
. Each Imam was the son of the previous Imam, with the exception of Husayn ibn Ali, who was the brother of Hasan ibn Ali
Hasan ibn Ali ( ar, الحسن بن علي, translit=Al-Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī; ) was a prominent early Islamic figure. He was the eldest son of Ali and Fatima and a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He briefly ruled as caliph from Jan ...
. The twelfth and final Imam is Muhammad al-Mahdi, who is believed by the Twelvers to be currently alive, and hidden in the Major Occultation until he returns to bring justice to the world. It is believed by Twelver and Alevi
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, w ...
Muslims that the Twelve Imams have been foretold in the Hadith of the Twelve Successors. All of the Imams met unnatural deaths, with the exception of the last Imam, who according to Twelver and Alevi belief, is living in occultation.
Ismaili Imams
The Ismaili line of imams for both sects (theNizari
The Nizaris ( ar, النزاريون, al-Nizāriyyūn, fa, نزاریان, Nezāriyān) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent ...
and Musta'li) continues undivided until al-Mustansir Billah (d. 1094). After his death the line of the imamat separates into the Nizari and Musta'li dynasties.
The line of imams of the Musta'li Muslims (also known as the Bohras/Dawoodi Bohra
The Dawoodi Bohras are a religious denomination within the Ismā'īlī branch of Shia Islam. Their largest numbers reside in India, Pakistan, Yemen, East Africa, and the Middle East, with a growing presence across Europe, North America, South ...
) continued up to Aamir ibn Mustali. After his death, they believe their 21st Imam, at-Tayyib Abu'l-Qasim
Al-Ṭayyib Abūʾl-Qāsim ibn Al-Manṣūr ( ar, ٱلطَّيِّب أَبُو ٱلْقَاسِم ابْن ٱلْمَنْصُوْر) was, according to the Tayyibi Isma'ili- Musta'li sect of Isma'ilism, the twenty-first Imam and the last Ca ...
went into a Dawr-e Satr (period of concealment) that continues to this day. In the absence of an imam they are led by a Da'i al-Mutlaq (absolute missionary) who manages the affairs of the Imam-in-Concealment until re-emergence of the Imam from concealment.
The line of imams of the Nizari Ismaili Shia Muslims (also known as the Agha-khani Ismailis in South and Central Asia) continues to their present living 49th hereditary imam, Aga Khan IV
Shāh Karim al-Husayni (born 13 December 1936), known by the religious title Mawlānā Hazar Imam by his Ismaili followers and elsewhere as Aga Khan IV, is the 49th and current Imam of Nizari Ismailis, a denomination within Shia Islam. He ha ...
(son of Prince Aly Khan). They are the only Shia Muslim community today led by a present and living (Hazir wa Mawjud) imam.

Zaidi Imams
The Zaidi branch of Shi'ism established its own line of Imams starting in the year 897; the line continued without interruption until 1962 when theNorth Yemen Civil War
The North Yemen Civil War ( ar, ثورة 26 سبتمبر, Thawra 26 Sabtambar, 26 September Revolution) was fought in North Yemen from 1962 to 1970 between partisans of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom and supporters of the Yemen Arab Republic. The ...
brought the Imamate to an end and established a republic.
Sunni view of the Shia Imamate
Ibn Taymiyyah (d. 728 AH/1328 AD) composed a long refutation of the notion of the Imamate in his '' Minhaj as-Sunnah an-Nabawiyyah''. The belief of the Twelver Imamah with the consideration of the sacred status of the four Rashidun Caliphs is shared in Sunni Islam, due to the following hadith of Muhammad:I heard the Prophet of Allah say 'Islam shall not cease to be glorious up to twelve Caliphs, every one of them being from theQuraish The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qu ...'". (And in a narration) "The affairs of men will not cease to decline so long as twelve men will rule over them, every one of them coming from Quraish. And in a narration: The religion will continue to be established till the hour comes as there are twelve Caliphs over them, everyone of them coming from the Quraish
The affairs of the people will continue to be conducted as long as they are governed by twelve men, he then added from Quraish
I will be followed by twelve Khalifas all will be QurayshSunan Tirmidhi Volume 1 page 813
Succession
See also
*Imams of Yemen
The Imams of Yemen, later also titled the Kings of Yemen, were religiously consecrated leaders belonging to the Zaidiyyah branch of Shia Islam. They established a blend of religious and temporal-political rule in parts of Yemen from 897. Their i ...
*Imamzadeh
An imamzadeh () is a Persian term with two related meanings: a type of holy person in Shia Islam, and the shrine-tomb of such a person.
Firstly, it means an immediate descendant of a Shi'i Imam. The term is also used in Urdu and Azeri. Imamzad ...
* Ismah
* Mahdi
* Succession to Muhammad
Footnotes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Al-imamah (emamah) page
a chapter of Shi'ite Islam (book) by Allameh Tabatabaei
"The Twelve Imams"
��Taken from ''A Shi'ite Anthology'' by Allameh Tabatabaei
A Short History of the Lives of The Twelve Imams
��An article by ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Online
by Maria Dakake, an entry in the '' Encyclopædia Iranica''
Shia Islam – Ask Imam
(basma.us)
Imamia Mission Bury
(shiacode.com)
{{Authority control Shia belief and doctrine Islamic states by type Islamic terminology Imamate