Italian Irredentism In Dalmatia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Italian irredentism in Dalmatia was the political movement supporting the unification to
Italian irredentism in Dalmatia was the political movement supporting the unification to
"Capitolo 1980-1918"
, Capodistria, 2000 During the meeting of the Council of Ministers on 12 November 1866, Emperor The Italian linguist
The Italian linguist  Not only Italian irredentists (like Gabriele D'Annunzio), but also Italian prominent scholars (like Angelo Vivante), alleged that Joseph Fölch did not include the Dalmatian islands of
Not only Italian irredentists (like Gabriele D'Annunzio), but also Italian prominent scholars (like Angelo Vivante), alleged that Joseph Fölch did not include the Dalmatian islands of

 In 1909, the
In 1909, the
 Italian irredentism in Dalmatia was the political movement supporting the unification to
Italian irredentism in Dalmatia was the political movement supporting the unification to Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, during the 19th and 20th centuries, of Adriatic Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stre ...
.
History
19th century
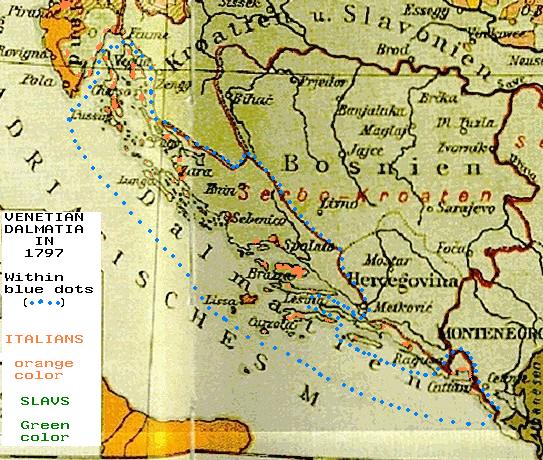
TheRepublic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
, between the 9th century
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar.
The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abb ...
and 1797, extended its dominion to Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian and Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian, Italian and Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic betwee ...
, the islands of Kvarner
The Kvarner Gulf (, or , la, Sinus Flanaticus or ), sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal wa ...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stre ...
, when it was conquered by Napoleon. After the fall of Napoleon (1814) Istria, the islands of Kvarner and Dalmatia were annexed to the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
. Many Istrian Italians
Istrian Italians are an ethnic group from the Adriatic region of Istria in modern northwestern Croatia and southwestern Slovenia. Istrian Italians descend from the original Latinized population of Roman Histria, from the Venetian-speaking sett ...
and Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Dalm ...
looked with sympathy towards the Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single s ...
movement that fought for the unification of Italy. The first events that involved the Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Dalm ...
in the unification of Italy were the revolutions of 1848
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in Euro ...
, during which they took part in the constitution of the Republic of San Marco
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
in Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
. The most notable Dalmatian Italians exponents who intervened were Niccolò Tommaseo
Niccolò Tommaseo (; 9 October 1802 – 1 May 1874) was a Dalmatian linguist, journalist and essayist, the editor of a ''Dizionario della Lingua Italiana'' in eight volumes (1861–74), of a dictionary of synonyms (1830) and other works. He is ...
and Federico Seismit-Doda
Federico Seismit-Doda (1825–1893) was an Italian politician who gained prominence during the Revolutions of 1848 in the Italian states.
Frederico Seismit-Doda was born in Ragusa ( Dubrovnik) in the Kingdom of Dalmatia (today's Croat ...
.''Dizionario Enciclopedico Italiano'' (Vol. III, pag. 729-730), Roma, Ed. Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana, founded by Giovanni Treccani, 1970 (In Italian)
After the Third Italian War of Independence
The Third Italian War of Independence ( it, Terza Guerra d'Indipendenza Italiana) was a war between the Kingdom of Italy and the Austrian Empire fought between June and August 1866. The conflict paralleled the Austro-Prussian War and resulted in ...
(1866), when the Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 = ...
and Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giul ...
regions were ceded by the Austrians
, pop = 8–8.5 million
, regions = 7,427,759
, region1 =
, pop1 = 684,184
, ref1 =
, region2 =
, pop2 = 345,620
, ref2 =
, region3 =
, pop3 = 197,990
, ref3 ...
to the newly formed Kingdom Italy, Istria and Dalmatia remained part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with t ...
, together with other Italian-speaking areas on the eastern Adriatic. This triggered the gradual rise of Italian irredentism
Italian irredentism ( it, irredentismo italiano) was a nationalist movement during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries in Italy with irredentist goals which promoted the unification of geographic areas in which indigenous peoples ...
among many Italians in Istria, Kvarner and Dalmatia, who demanded the unification of the Julian March
Venezia Giulia, traditionally called Julian March (Serbo-Croatian, Slovene: ''Julijska krajina'') or Julian Venetia ( it, Venezia Giulia; vec, Venesia Julia; fur, Vignesie Julie; german: Julisch Venetien) is an area of southeastern Europe wh ...
, Kvarner
The Kvarner Gulf (, or , la, Sinus Flanaticus or ), sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal wa ...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stre ...
with Italy. The Italians in Istria, Kvarner and Dalmatia supported the Italian Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single s ...
; as a consequence, the Austrians saw the Italians as enemies and favored the Slav communities of Istria, Kvarner and Dalmatia,''Die Protokolle des Österreichischen Ministerrates 1848/1867. V Abteilung: Die Ministerien Rainer und Mensdorff. VI Abteilung: Das Ministerium Belcredi'', Wien, Österreichischer Bundesverlag für Unterricht, Wissenschaft und Kunst 1971 fostering the nascent nationalism of Slovenes and Croats.Relazione della Commissione storico-culturale italo-slovena, Relazioni italo-slovene 1880-1956"Capitolo 1980-1918"
, Capodistria, 2000 During the meeting of the Council of Ministers on 12 November 1866, Emperor
Franz Joseph I of Austria
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until hi ...
outlined a wide-ranging project aimed at the Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
or Slavization
Slavicisation or Slavicization, is the acculturation of something Slavic into a non-Slavic culture, cuisine, region, or nation. To a lesser degree, it also means acculturation or adoption of something non-Slavic into Slavic culture or terms. Th ...
of the areas of the empire with an Italian presence:
 The Italian linguist
The Italian linguist Matteo Bartoli
Matteo Giulio Bartoli (22 November 1873 in Labin/Albona – 23 January 1946 in Turin) was an Italian linguist from Istria (then a part of Austria-Hungary, today part of modern Croatia).
He obtained a doctorate at the University of Vienna, wher ...
calculated that Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
was the primary spoken language by 33% of the Dalmatian population in 1803. Bartoli's evaluation was followed by other claims that Auguste de Marmont
Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont (20 July 1774 – 22 March 1852) was a French general and nobleman who rose to the rank of Marshal of the Empire and was awarded the title (french: duc de Raguse). In the Peninsular War Marmont succeede ...
, the French Governor General of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces
The Illyrian Provinces sl, Ilirske province hr, Ilirske provincije sr, Илирске провинције it, Province illirichegerman: Illyrische Provinzen, group=note were an autonomous province of France during the First French Empire that e ...
commissioned a census in 1809 which found that Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Dalm ...
comprised 29% of the total population of Dalmatia.
With the development of Croatian nationalism, critics such as Croatian historian Duško Večerina alleged that these evaluations were not conducted by modern scientific standards and that they took spoken language as the criterion, rather than blood, origin and ethnicity. They pointed out that according to a report by Imperial court councillor Joseph Fölch in 1827, the Italian language was spoken by noblemen and some citizens of middle and lower classes exclusively in the coastal cities of Zadar
Zadar ( , ; historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian: ); see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar serv ...
, Šibenik
Šibenik () is a historic city in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is a political, educational, transport, industrial and tourist center of Šibenik-Knin County, and is also the ...
and Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertain ...
. Since only around 20,000 people populated these towns and not all were Italian speakers, they claim that the real number was rather smaller, probably around seven percent of the total population, as is asserted by the Department of Historical Studies of the Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts
The Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts ( la, Academia Scientiarum et Artium Croatica, hr, Hrvatska akademija znanosti i umjetnosti, abbrev. HAZU) is the national academy of Croatia.
HAZU was founded under patronage of the Croatian bishop Jo ...
(HAZU).
 Not only Italian irredentists (like Gabriele D'Annunzio), but also Italian prominent scholars (like Angelo Vivante), alleged that Joseph Fölch did not include the Dalmatian islands of
Not only Italian irredentists (like Gabriele D'Annunzio), but also Italian prominent scholars (like Angelo Vivante), alleged that Joseph Fölch did not include the Dalmatian islands of Cres
Cres (; dlm, Crepsa, vec, Cherso, it, Cherso, la, Crepsa, Greek: Χέρσος, ''Chersos'') is an Adriatic island in Croatia. It is one of the northern islands in the Kvarner Gulf and can be reached via ferry from Rijeka, the island Krk o ...
(Cherso), Lošinj
Lošinj (; it, Lussino; vec, Lusin, earlier ''Osero''; german: Lötzing; la, Apsorrus; grc, Ἄψορρος) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, in the Kvarner Gulf. It is almost due south of the city of Rijeka and part of the ...
(Lussino), Krk
Krk (; it, Veglia; ruo, Krk; dlm, label= Vegliot Dalmatian, Vikla; la, Curicta; grc-gre, Κύρικον, Kyrikon) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of Primorje-Gorski Kot ...
(Veglia), Vis
Vis, ViS, VIS, and other capitalizations may refer to:
Places
* Vis (island), a Croatian island in the Adriatic sea
** Vis (town), on the island of Vis
* Vis (river), in south-central France
* Vis, Bulgaria, a village in Haskovo Province
* V ...
(Lissa), Hvar (Lesina), Korcula (Curzola) and many other islands with significant Italian communities. They reasserted that the only official evidence about the Dalmatian population comes from the 1857 Austro-Hungarian census, which showed that in this year there were 369,310 indigenous Croatians and 45,000 Italians in Dalmatia, making Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Dalm ...
10.8 percent of the total population of Dalmatia in the mid-19th century.
Two nationalist movements were born in Dalmatia, the Italian and the Slav. The political instances of the Dalmatian Italians were promoted to the Autonomist Party
The Autonomist Party ( it, Partito Autonomista; hr, Autonomaška stranka) was an Italian-Dalmatianist political party in the Dalmatian political scene, that existed for around 70 years of the 19th century and until World War I. Its goal was ...
, founded in 1878 and dissolved in 1915: a prominent member was Antonio Bajamonti
Antonio Baiamonti (19February 182213January 1891) was an Austrian and Dalmatian Italian politician and longtime mayor of Split. He is remembered as one of the most successful mayors of the city, occupying the post almost continuously for twenty ...
, who from 1860 to 1880 was mayor of Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertain ...
. The party, which originally also had the favour of part of the Slavic population, gradually replaced an autonomous program for the region with an irredentist project for the region, given the hostility of the Austrian authorities and the disagreements with the Slavic element.Maura Hametz. ''In the Name of Italy: Nation, Family, and Patriotism in a Fascist Court: Nation, Family, and Patriotism in a Fascist Court.'' Fordham University Press, 2012.
In 1889, the foundation of the Dante Alighieri Society
The Dante Alighieri Society ( Italian: ''Società Dante Alighieri'') is a society that promotes Italian culture and language around the world. Today this society is present in more than 60 countries.
It was formed in Italy in July 1889. The ...
, with the aim of protecting and promoting the Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 8 ...
, made it possible to give support to the initiatives for the preservation of the Italian-speaking linguistic element. In this period Roberto Ghiglianovich
Roberto Ghiglianovich (17 July 1863 – 2 September 1930) was an Italian politician.
Biography
He was grown up in a liberal family in Zara, Austria-Hungary (today Zadar, Croatia). As a child, two of his greatest friends were the Croat Petar Kla ...
, as trustee of the company establishes the '' La Lega'' in Zadar and promoted the enhancement of Italian culture in the area. The same year the irredentist Luigi Ziliotto
Luigi Ziliotto (8 February 1863 – 6 February 1922) was an Italian politician and irredentist. Ziliotto was an Italian senator. He was ''podestà'' of Zara (Zadar) several times.
Bibliography
* L.Monzali, Italiani di Dalmazia. Dal Risorgime ...
becomes mayor of Zara, a position he would hold until the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, was accused of treason and declared forfeited by the Austrian authorities. The policy of collaboration with the local Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their ...
, inaugurated by Roberto Ghiglianovich and by Giovanni Avoscani, then allowed the Italians to conquer the municipal administration of Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranea ...
in 1899.
20th century

 In 1909, the
In 1909, the Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 8 ...
lost its status
Status (Latin plural: ''statūs''), is a state, condition, or situation, and may refer to:
* Status (law)
** City status
** Legal status, in law
** Political status, in international law
** Small entity status, in patent law
** Status conference ...
as the official language of Dalmatia in favour of Croatian only (previously both languages were recognized), thus Italian could no longer be used in the public and administrative sphere.
For the Austrian Kingdom of Dalmatia
The Kingdom of Dalmatia ( hr, Kraljevina Dalmacija; german: Königreich Dalmatien; it, Regno di Dalmazia) was a crown land of the Austrian Empire (1815–1867) and the Cisleithanian half of Austria-Hungary (1867–1918). It encompassed the entir ...
, (Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stre ...
), the 1910 numbers were 96.2 percent Slavic speakers and 2.8 percent Italian speakers, recording a drastic decline in the number of Dalmatian Italians, who in 1845 amounted to 20 percent of the total population of Dalmatia. Another evidence about the Dalmatian population comes from the 1857 Austro-Hungarian census, which showed that in this year there were 369,310 indigenous Croatians and 45,000 Italians in Dalmatia, making Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Dalm ...
10.8 percent of the total population of Dalmatia in the mid-19th century.
Dalmatia was a strategic region during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
that both Italy and Serbia intended to seize from Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Triple Entente
The Triple Entente (from French ''entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well as ...
Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in 1915 upon agreeing to the London Pact
The Treaty of London ( it, Trattato di Londra) or the Pact of London () was a secret agreement concluded on 26 April 1915 by the United Kingdom, France, and Russia on the one part, and Italy on the other, in order to entice the latter to e ...
that guaranteed Italy the right to annex a large portion of Dalmatia in exchange for Italy's participation on the Allied side. From 5–6 November 1918, Italian forces were reported to have reached Vis
Vis, ViS, VIS, and other capitalizations may refer to:
Places
* Vis (island), a Croatian island in the Adriatic sea
** Vis (town), on the island of Vis
* Vis (river), in south-central France
* Vis, Bulgaria, a village in Haskovo Province
* V ...
, Lastovo
Lastovo (; it, Lagosta, german: Augusta, la, Augusta Insula, el, Ladestanos, Illyrian: ''Ladest'') is an island municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County in Croatia. The municipality consists of 46 islands with a total population of 792 p ...
, Šibenik
Šibenik () is a historic city in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is a political, educational, transport, industrial and tourist center of Šibenik-Knin County, and is also the ...
, and other localities on the Dalmatian coast. By the end of the hostilities in November 1918, the Italian military had seized control of the entire portion of Dalmatia that had been guaranteed to Italy by the London Pact and by 17 November had seized Fiume as well.Paul O'Brien. ''Mussolini in the First World War: the Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist''. Oxford, England, UK; New York, New York, USA: Berg, 2005. Pp. 17. In 1918, Admiral Enrico Millo
Enrico Millo (12 February 1865 – 14 June 1930) was an Italian admiral and politician. As a military commander, he led the raid against the Ottoman Navy in the Dardanelles.http://www.marina.difesa.it/palazzo/personaggi/millo.asp, Italian Navy we ...
declared himself Italy's Governor of Dalmatia. Italian nationalist
Italian nationalism is a movement which believes that the Italians are a nation with a single homogeneous identity, and therefrom seeks to promote the cultural unity of Italy as a country. From an Italian nationalist perspective, Italianness is ...
Gabriele d'Annunzio supported the seizure of Dalmatia, and proceeded to occupy some areas in an Italian warship in December 1918.
The last city with a significant Italian presence in Dalmatia was the city of Zara (now called Zadar
Zadar ( , ; historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian: ); see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar serv ...
). In the Austro-Hungarian census of 1910, the city of Zara had an Italian population of 9,318 out of 13,438 inhabitants (69.3 percent). In 1921, the population grew to 17,075 inhabitants, of which 12,075 Italians (70.8 percent). In 1941, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
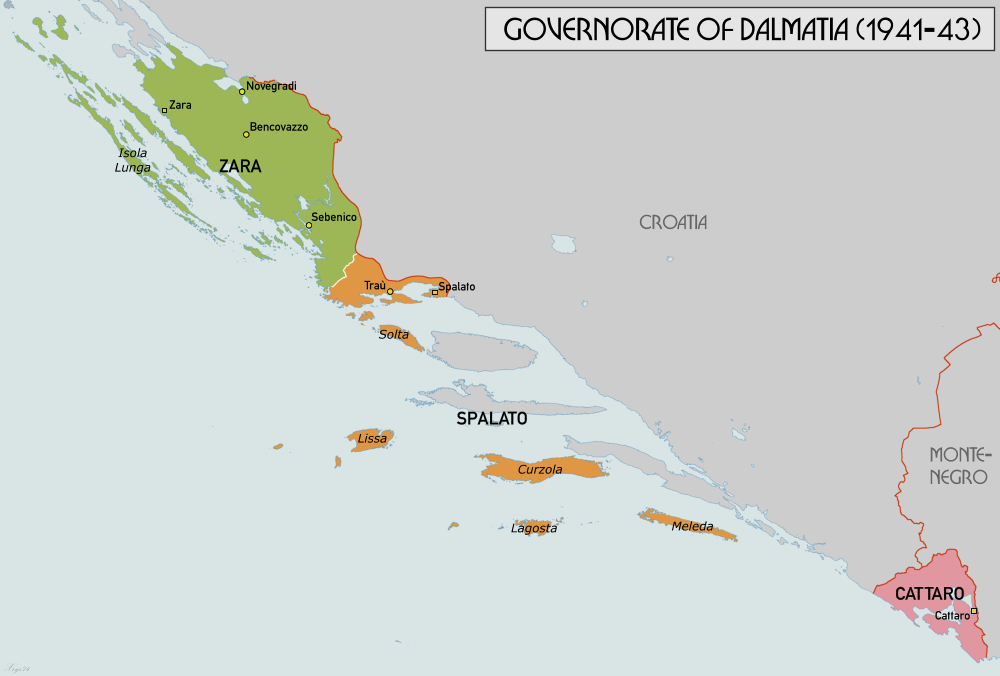
was occupied by Italy and Germany. Dalmatia was divided between Italy, which constituted the Governorate of Dalmatia
The Governorate of Dalmatia ( it, Governatorato di Dalmazia) was a territory divided into three provinces of Italy during the Italian Kingdom and Italian Empire epoch. It was created later as an entity in April 1941 at the start of World War II ...
, and the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
, which annexed Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranea ...
and Morlachia
Morlachia ( la, Morlachia; it, Morlacchia; hr, Morlakija; ro, Morlachia) was a vaguely defined region, named after the Morlachs, used on European maps between the 16th and the 19th centuries. Morlachia was located in modern-day Croatia between ...
. After the Italian surrender
The Armistice of Cassibile was an armistice signed on 3 September 1943 and made public on 8 September between the Kingdom of Italy and the Allies during World War II.
It was signed by Major General Walter Bedell Smith for the Allies and Briga ...
on 8 September 1943, the Independent State of Croatia annexed the Governorate of Dalmatia, except for the territories that had been Italian before the start of the conflict, such as Zara.
In 1943, Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz ( sh-Cyrl, Јосип Броз, ; 7 May 1892 – 4 May 1980), commonly known as Tito (; sh-Cyrl, Тито, links=no, ), was a Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman, serving in various positions from 1943 until his deat ...
informed the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
that Zara was a chief logistic centre for German forces in Yugoslavia. By overstating its importance, he persuaded them of its military significance. Italy surrendered in September 1943 and over the following year, specifically between 2 November 1943 and 31 October 1944, Allied Forces bombarded the town 54 times. Nearly 2,000 people were buried beneath rubble; 10–12,000 people escaped and took refuge in Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
and just over 1,000 people reached Apulia. Tito's partisans entered the city on 31 October 1944, and 138 people were killed.Lovrovici, don Giovanni Eleuterio. ''Zara dai bombardamenti all'esodo (1943-1947)'' Tipografia Santa Lucia - Marino. Roma, 1974. pag.66 With the Peace Treaty of 1947, Italians still living in the city and in Dalmatia followed the Italian exodus from Istria and Dalmatia and only about 100 Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Dalm ...
now remain in Zadar.
See also
*Italian irredentism in Istria
The Italian irredentism in Istria was the political movement supporting the unification to Italy, during the 19th and 20th centuries, of the peninsula of Istria. It is considered closely related to the Italian irredentism in Trieste and Fiume, tw ...
*Governorate of Dalmatia
The Governorate of Dalmatia ( it, Governatorato di Dalmazia) was a territory divided into three provinces of Italy during the Italian Kingdom and Italian Empire epoch. It was created later as an entity in April 1941 at the start of World War II ...
Notes
Bibliography
*Bartoli, Matteo. ''Le parlate italiane della Venezia Giulia e della Dalmazia''. Tipografia italo-orientale. Grottaferrata, 1919. *Barzilai, Salvatose. ''L'irredentismo: ecco il nemico!'' Editore Il Circolo Garibaldi, 1890. Harvard University, 2002 *Lovrovici, Giovanni Eleuterio. ''Zara dai bombardamenti all'esodo (1943–1947)''. Tipografia Santa Lucia - Marino. Roma, 1974. *Monzali, Vitale. ''The Italians of Dalmatia: from Italian unification to World War I''. University of Toronto Press. Toronto, 2009. *Petacco, Arrigo. ''A tragedy revealed: the story of Italians from Istria, Dalmatia, Venezia Giulia (1943–1953)''. University of Toronto Press. Toronto, 1998 *Rodogno, Davide. ''Fascism's European empire: Italian occupation during the Second World War''. Publisher Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, 2006 *Tommaseo, Niccolo. ''La questione dalmatica riguardata ne'suoi nuovi aspetti: osservazioni''. (Tipografia Fratelli Battara, 1861). Harvard University Press. Harvard, 2007 *Večerina, Duško. ''Talijanski Iredentizam''. Zagreb, 2001. *Vignoli, Giulio. ''I territori italofoni non appartenenti alla Repubblica Italiana''. Giuffrè Editoriale. Milano, 1995. *Vivante, Angelo. ''Irredentismo adriatico''. Venezia, 1984. {{Irredentism Italian irredentism Dalmatia Political controversies in Italy Adriatic question