Istrian Third League on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Istria ( ;
''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries''
John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas
''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe''
Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), Croatia encapsulates most of the Istrian peninsula with its Istria County.
 The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria mountain range; the rivers Dragonja/Dragogna, Mirna/Quieto, Pazinčica, and Raša; and the Lim/Canale di Leme bay and valley. Istria lies in three countries: Croatia, Slovenia and Italy. By far the largest portion (89%) lies in Croatia. "Croatian Istria" is divided into two counties, the larger being Istria County in western Croatia. Important towns in Istria County include
The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria mountain range; the rivers Dragonja/Dragogna, Mirna/Quieto, Pazinčica, and Raša; and the Lim/Canale di Leme bay and valley. Istria lies in three countries: Croatia, Slovenia and Italy. By far the largest portion (89%) lies in Croatia. "Croatian Istria" is divided into two counties, the larger being Istria County in western Croatia. Important towns in Istria County include
Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
and Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian, Italian and Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the largest peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Kvarner Gulf. It is shared by three countries: Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy.Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries''
John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas
''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe''
Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), Croatia encapsulates most of the Istrian peninsula with its Istria County.
Geography
Pula
Pula (; also known as Pola, it, Pola , hu, Pòla, Venetian language, Venetian; ''Pola''; Istriot language, Istriot: ''Puola'', Slovene language, Slovene: ''Pulj'') is the largest city in Istria County, Croatia, and the List of cities and town ...
/Pola, Poreč/Parenzo, Rovinj/Rovigno, Pazin/Pisino, Labin/Albona, Umag/Umago, Motovun/Montona, Buzet
Buzet (; la, Piquentum; it, Pinguente) is a town in Istria, west Croatia, population 6,133 (2011).
Demographics
In 2011 the total municipal population was 6,133 people, distributed in the following settlements (with population shown in parenth ...
/Pinguente, and Buje/Buie. Smaller towns in Istria County include Višnjan
Višnjan ( it, Visignano) is a village and municipality in Istria, Croatia. Višnjan is the site of Višnjan Observatory (an astronomical observatory). The observatory is home of several long-running international summer programs for youth in astr ...
/Visignano, Roč
Roč ( it, Rozzo, german: Rotz) is a village in Istria County, north-west Croatia. Administratively it belongs to the town of Buzet. Roč is considered a historic town rather than a village due to its rich cultural heritage.
Geography
It is si ...
/Rozzo, and Hum/Olmo.
The northwestern part of Istria lies in Slovenia: it is known as Slovenian Istria, and includes the coastal municipalities of Piran/ Pirano, Izola/Isola, and Koper
Koper (; it, Capodistria, hr, Kopar) is the fifth largest city in Slovenia. Located in the Istrian region in the southwestern part of the country, approximately five kilometres () south of the border with Italy and 20 kilometres () from Triest ...
/Capodistria. It also includes the Karstic municipality of Hrpelje-Kozina
The Municipality of Hrpelje-Kozina (; sl, Občina Hrpelje - Kozina) is a municipality in the Littoral region of Slovenia. This smallest portion of Istria consists of the '' comunes'' of Muggia/Milje and San Dorligo della Valle/Dolina with Santa Croce ( Trieste) lying farthest to the north.
The ancient region of ''Histria'' extended over a much wider area, including the whole Karst Plateau with the southern edges of the Vipava Valley/Vipacco Valley, the southwestern portions of modern Inner Carniola with
 * Central Istria (Pazin/Pisino) has a
* Central Istria (Pazin/Pisino) has a
 The name is derived from the Histri ( grc-gre, Ἱστρών έθνος) tribes, which
The name is derived from the Histri ( grc-gre, Ἱστρών έθνος) tribes, which
 The coastal areas and cities of Istria came under Venetian Influence in the 9th century. On 15 February 1267, Parenzo was formally incorporated with the Venetian state. Other coastal towns followed shortly thereafter. Bajamonte Tiepolo was sent away from Venice in 1310, to start a new life in Istria after his downfall. A description of the 16th-century Istria with a precise map was prepared by the Italian geographer Pietro Coppo. A copy of the map inscribed in stone can now be seen in the Pietro Coppo Park in the center of the town of Izola in southwestern Slovenia.
The coastal areas and cities of Istria came under Venetian Influence in the 9th century. On 15 February 1267, Parenzo was formally incorporated with the Venetian state. Other coastal towns followed shortly thereafter. Bajamonte Tiepolo was sent away from Venice in 1310, to start a new life in Istria after his downfall. A description of the 16th-century Istria with a precise map was prepared by the Italian geographer Pietro Coppo. A copy of the map inscribed in stone can now be seen in the Pietro Coppo Park in the center of the town of Izola in southwestern Slovenia.
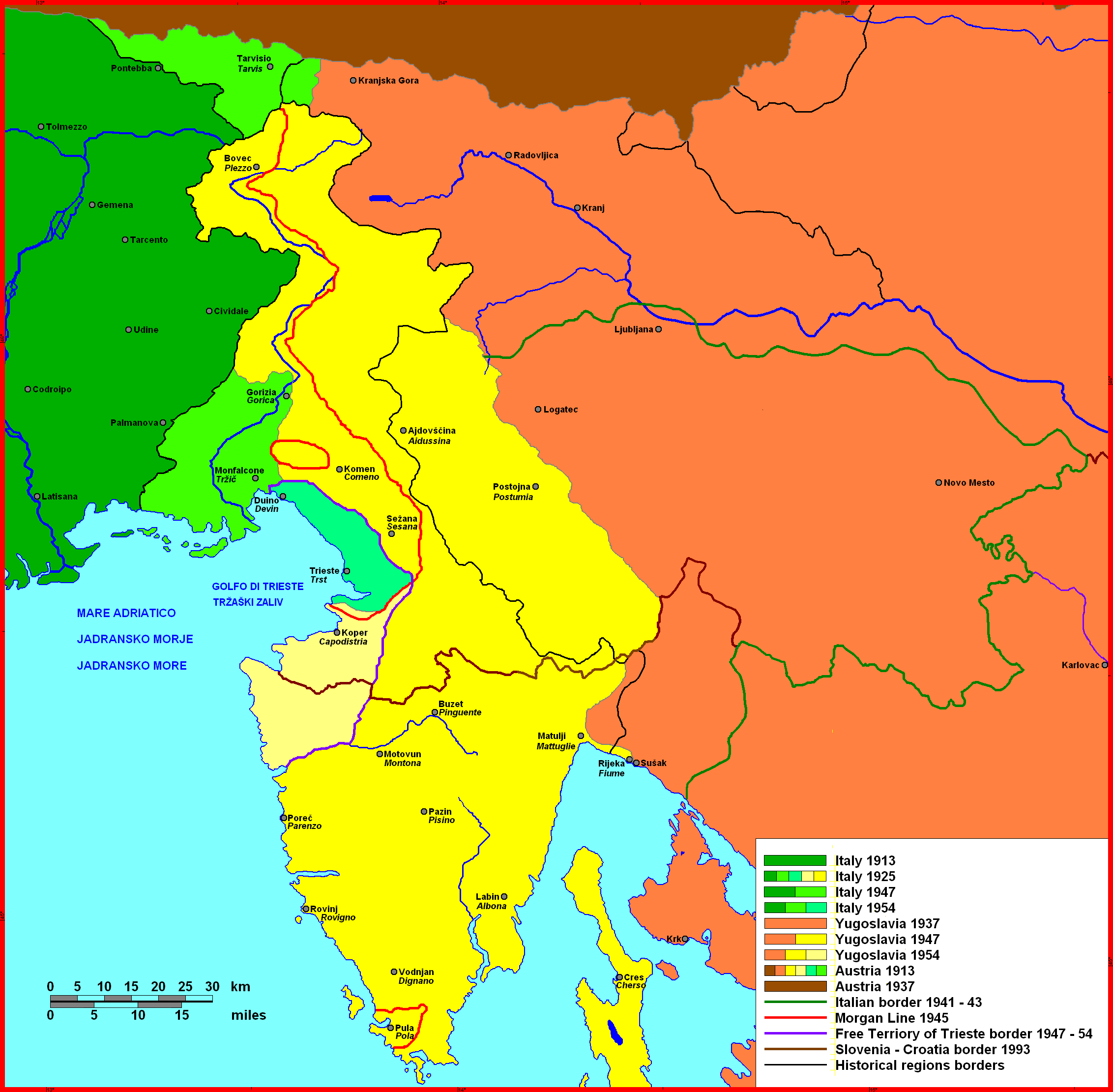 After this seven-year period, the Austrian Empire regained Istria, which became part of the constituent
After this seven-year period, the Austrian Empire regained Istria, which became part of the constituent
"Capitolo 1980-1918"
, Capodistria, 2000 During the meeting of the Council of Ministers of 12 November 1866, Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria outlined a wide-ranging project aimed at the Germanization or Slavization of the areas of the empire with an Italian presence: There are some claims, Istrian Italians were more than 50% of the total population for centuries, while making up about a third of the population in 1900. With its strategic position at the southern tip of the peninsula and good harbor Pula was the primary base of the Austrian Navy. A limited tension with the Austrian state did not in fact stop the rise of the use of the Italian language, in the second part of the 19th century, when the population of predominantly Italian-speaking towns in Istria had a significant rise: in the part of Istria that eventually became part of Croatia, the first Austrian census from 1846 found 34 thousand Italian speakers, alongside 120 thousand Croatian speakers (in the Austrian censuses, the ethnic composition of the population wasn't surveyed, only the main "language of use" of a person). Until 1910, the proportion changed significantly: there were 108 thousand Italian speakers and 134 thousand Croatian speakers. Vanni D'Alessio notes (2008), the Austrian surveys of the language of use "overestimated the diffusion of the socially dominant languages of the empire... The capacity of assimilation of the Italian language suggests that amongst those who declared themselves Italian speakers in Istria, there were people whose mother tongue was different." D'Alessio notes even members of the Austrian state bureaucracy and the members of their families with the German mother tongue tended to use Italian, after living in Istrian small towns long enough. The Poles, Czechs and Slovenes and Croats tended to join the "Slav" social group.
''A city in search of an author: the literacy identity of Trieste''
pg. 23, Sheffield Academic Press (2002), The events of the period are visible in
The events of the period are visible in
 Discussions about Istrian ethnicity often use the words "Italian", "Croatian", and "Slovene" to describe the character of the Istrian people. However these terms are best understood as "national affiliations" that may exist in combination with or independently of linguistic, cultural and historical attributes. In the Istrian context, for example, the word "Italian" can just as easily refer to autochthonous speakers of the Venetian language whose antecedents in the region extend before the inception of the Venetian Republic or to the
Discussions about Istrian ethnicity often use the words "Italian", "Croatian", and "Slovene" to describe the character of the Istrian people. However these terms are best understood as "national affiliations" that may exist in combination with or independently of linguistic, cultural and historical attributes. In the Istrian context, for example, the word "Italian" can just as easily refer to autochthonous speakers of the Venetian language whose antecedents in the region extend before the inception of the Venetian Republic or to the
File:Pula-avion.JPG, Aerial picture of
Istria on the Internet (a non-commercial, non-political, cultural site)
Old postcards of Istria
A Brief History of Istria / Darko Darovec
Istrian cultural heritage. Bukaleta Kazun, wall paintings
Travels in Istria and Dalmatia: drawn up from the itinerary of L. F. Cassas
on Google Books {{Authority control Peninsulas of Croatia Geography of Italy Geography of Southern Europe Geography of Central Europe Peninsulas of Slovenia Austrian Littoral Former states and territories in Slovenia
Postojna
Postojna (; german: Adelsberg, it, Postumia) is a town in the traditional region of Inner Carniola, from Trieste, in southwestern Slovenia. It is the seat of the Municipality of Postojna.
/Postumia and Ilirska Bistrica/Bisterza, and the Italian Province of Trieste, but not the Liburnian coast which was already part of Illyricum.
Climate
 * Central Istria (Pazin/Pisino) has a
* Central Istria (Pazin/Pisino) has a continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
.
* The northern (or Slovenian and Italian) coast of Istria (Ankaran/Ancarano, Koper/Capodistria, Izola/Isola, Muggia/Milje) has a sub-Mediterranean climate.
* The western and southern coast (Piran/Pirano, Portorož/Portorose, Novigrad/Cittanova, Rovinj/Rovigno, Pula/Pola) has a Mediterranean climate.
* The eastern coast (Rabac/Porto Albona, Labin/Albona, Opatija/Abbazia) has a sub-Mediterranean climate with oceanic influences.
* The warmest places are Pula/Pola and Rovinj/Rovigno, while the coldest is Pazin/Pisino.
* Precipitation is moderate, with between falling in the coastal areas, and up to in the hills.
History
Early history
 The name is derived from the Histri ( grc-gre, Ἱστρών έθνος) tribes, which
The name is derived from the Histri ( grc-gre, Ἱστρών έθνος) tribes, which Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
refers to as living in the region and who are credited as being the builders of the hillfort settlements (castellieri). The Histri are classified in some sources as a "Venetic" Illyrian tribe with certain linguistic differences from other Illyrians. The Romans described the Histri as a fierce tribe of pirates, protected by the difficult navigation of their rocky coasts. It took two military campaigns for the Romans to finally subdue them in 177 BC. The region was then called together with the Venetian part the X. Roman Region of "Venetia et Histria", the ancient definition of the northeastern border of Italy. Dante Alighieri refers to it as well, the eastern border of Italy per ancient definition is the river '' Arsia''. The eastern side of this river was settled by people whose culture was different than Histrians. Earlier influence of the Iapodes was attested there, while at some time between the 4th and 1st century BC the Liburnians extended their territory and it became a part of Liburnia. On the northern side, Histria extended much further north and included the Italian city of Trieste.
Some scholars speculate that the names Histri and Istria are related to the Latin name Hister, or Danube (especially its lower course). Ancient folktales reported —inaccurately— that the Danube split in two or "bifurcated" and came to the sea near Trieste as well as at the Black Sea. The story of the "bifurcation of the Danube" is part of the Argonaut legend. There is also a suspected link (but no historical documentation in support of it) to the commune of Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
in Constanța, Romania which is named after the ancient city Histria, named after River Hister.
In the Dark Ages, Istria was conquered and occupied by the Goths. Ostrogoth coins were found in Istria, as well as the remains of some buildings. South of Poreč there are the remains of the church of Sv. Petar, erected in the 5th century (with a baptistery added later), which reportedly served the Arian eastern Goths ruling Istria. Most notably, the Goths used Istrian stone
Istrian stone, ''pietra d'Istria'', the characteristic group of building stones in the architecture of Venice, Istria and Dalmatia, is a dense type of impermeable limestones that was quarried in Istria, nowadays Croatia; between Portorož and Pu ...
to build their best known monument, the Mausoleum of Theodoric in Ravenna. In the following centuries, the peninsula was attacked and conquered by the Lombards, often in conjunction with the Slavs, such as in 601. However, the extent to which the Lombards occupied Istria is a matter of debate. After the Goths, Istria became part of the Exarchate of Ravenna. Gulfaris, who served the Byzantines but was of Lombard descent, is reported as its dux in 599.
Pope Gregory I in 600 wrote to bishop of Salona Maximus in which he expresses concern about arrival of the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
, ''"Et quidem de Sclavorum gente, quae vobis valde imminet, et affligor vehementer et conturbor. Affligor in his quae jam in vobis patior; conturbor, quia per Istriae aditum jam ad Italiam intrare coeperunt"'' (And as for the people of the Slavs who are really approaching you, I am very depressed and confused. I am depressed because I sympathize with you, confused because they over the Istria began to enter the Italy)
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the region was pillaged by the Goths, the Eastern Roman Empire, and the Avars. It western part was subsequently annexed to the Lombard Kingdom in 751, and then annexed to the Frankish kingdom by Pepin of Italy
Pepin or Pippin (or ''Pepin Carloman'', ''Pepinno'', April 777 – 8 July 810), born Carloman, was the son of Charlemagne and King of the Lombards (781–810) under the authority of his father.
Pepin was the second son of Charlemagne by his th ...
in 789. In 804, the Placitum of Riziano
The Placitum of Riziano ( it, Placito del Risano; sl, Rižanski zbor) was a dispute that took place c. 804 around the river Riziano, probably at Rižana in modern Slovenia. The document is important for the history of Capodistria (Koper) and Tr ...
was held in the Parish of Rižan ( la, Risanum), which was a meeting between the representatives of Istrian towns and castles and the deputies of Charlemagne and his son Pepin. The report about this judicial diet illustrates the changes accompanying the transfer of power from the Eastern Roman Empire to the Carolingian Empire and the discontent of the local residents.
Afterwards it was successively controlled by the dukes of Carantania
Carantania, also known as Carentania ( sl, Karantanija, german: Karantanien, in Old Slavic '), was a Slavic principality that emerged in the second half of the 7th century, in the territory of present-day southern Austria and north-eastern ...
, Merania, Bavaria and by the patriarch of Aquileia, before it became the territory of the Republic of Venice in 1267. The medieval Croatian kingdom held only the far eastern part of Istria (the border was near the river Raša), but they lost it to the Holy Roman Empire in the late 11th century.
Venetian Republic
Habsburg Monarchy (1797–1805)
The Inner part of Istria around Mitterburg ( Pazin) had been part of the Holy Roman Empire for centuries, and more specifically part of the domains of the Austrian Habsburgs since the 14th century. In 1797, with the Treaty of Campo Formio, the Venetian parts of the peninsula also passed to the Habsburg monarchy which became the Austrian Empire in 1804.Napoleonic Era (1805–1814)
The French victory of 1809 compelled Austria to cede a portion of its South Slav lands to France. Napoleon combined Istira,Carniola
Carniola ( sl, Kranjska; , german: Krain; it, Carniola; hu, Krajna) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region sti ...
, western Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost States of Austria, Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German language, German. Its regional dialects belong to t ...
, Gorica ( Gorizia), Trieste. and parts of Croatia, Dalmatia, and Dubrovnik to form the Illyrian Provinces
The Illyrian Provinces sl, Ilirske province hr, Ilirske provincije sr, Илирске провинције it, Province illirichegerman: Illyrische Provinzen, group=note were an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province of France d ...
. The Code Napoléon was introduced, and roads and schools were constructed. Local citizens were given administrative posts, and native languages were used to conduct official business. This sparked the Illyrian Movement for the cultural and linguistic unification of South Slavic lands.
Austrian Empire (1814–1918)
 After this seven-year period, the Austrian Empire regained Istria, which became part of the constituent
After this seven-year period, the Austrian Empire regained Istria, which became part of the constituent Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
. This kingdom was broken up in 1849, after which Istria formed part of Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral (german: Österreichisches Küstenland, it, Litorale Austriaco, hr, Austrijsko primorje, sl, Avstrijsko primorje, hu, Osztrák Tengermellék) was a crown land (''Kronland'') of the Austrian Empire, established in 1849. ...
, also known as the "Küstenland", which also included the city of Trieste and the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca until 1918. At that time the borders of Istria included part of what is now Italian Venezia-Giulia and parts of modern-day Slovenia and Croatia, but not the city of Trieste.
Many Istrian Italians looked with sympathy towards the Risorgimento movement that fought for the unification of Italy. However, after the Third Italian War of Independence (1866), when the Veneto and Friuli regions were ceded by the Austrians to the newly formed Kingdom Italy, Istria remained part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, together with other Italian-speaking areas on the eastern Adriatic. This triggered the gradual rise of Italian irredentism among many Italians in Istria, who demanded the unification of Istria with Italy. The Italians in Istria supported the Italian Risorgimento: as a consequence, the Austrians saw the Italians as enemies and favored the Slav communities of Istria,''Die Protokolle des Österreichischen Ministerrates 1848/1867. V Abteilung: Die Ministerien Rainer und Mensdorff. VI Abteilung: Das Ministerium Belcredi'', Wien, Österreichischer Bundesverlag für Unterricht, Wissenschaft und Kunst 1971 fostering the nascent nationalism of Slovenes and Croats.Relazione della Commissione storico-culturale italo-slovena, Relazioni italo-slovene 1880-1956"Capitolo 1980-1918"
, Capodistria, 2000 During the meeting of the Council of Ministers of 12 November 1866, Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria outlined a wide-ranging project aimed at the Germanization or Slavization of the areas of the empire with an Italian presence: There are some claims, Istrian Italians were more than 50% of the total population for centuries, while making up about a third of the population in 1900. With its strategic position at the southern tip of the peninsula and good harbor Pula was the primary base of the Austrian Navy. A limited tension with the Austrian state did not in fact stop the rise of the use of the Italian language, in the second part of the 19th century, when the population of predominantly Italian-speaking towns in Istria had a significant rise: in the part of Istria that eventually became part of Croatia, the first Austrian census from 1846 found 34 thousand Italian speakers, alongside 120 thousand Croatian speakers (in the Austrian censuses, the ethnic composition of the population wasn't surveyed, only the main "language of use" of a person). Until 1910, the proportion changed significantly: there were 108 thousand Italian speakers and 134 thousand Croatian speakers. Vanni D'Alessio notes (2008), the Austrian surveys of the language of use "overestimated the diffusion of the socially dominant languages of the empire... The capacity of assimilation of the Italian language suggests that amongst those who declared themselves Italian speakers in Istria, there were people whose mother tongue was different." D'Alessio notes even members of the Austrian state bureaucracy and the members of their families with the German mother tongue tended to use Italian, after living in Istrian small towns long enough. The Poles, Czechs and Slovenes and Croats tended to join the "Slav" social group.
Italy (1919–1947)
Although a member of the Central Powers, Italy remained neutral at the start of WWI, and soon launched secret negotiations with the Triple Entente, bargaining to participate in the war on its side, in exchange for significant territorial gains. To get Italy to join the war, the secret 1915 Treaty of London the Entente promised Italy Istria and parts ofDalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
, South Tyrol, the Greek Dodecanese Islands, parts of Albania and Turkey, plus more territory for Italy's North Africa colonies.
After the war, Italy annexed Istria. Istria's political and economic importance declined under Italian rule, and after the fascist takeover of Italy in 1922 the Italian government began a campaign of forced Italianization
Italianization ( it, italianizzazione; hr, talijanizacija; french: italianisation; sl, poitaljančevanje; german: Italianisierung; el, Ιταλοποίηση) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or a ...
. In 1926, the use of Slavic languages in schools and government was banned, even Slavic family names were Italianized to suit the fascist authorities. Slavic newspapers and libraries were closed, all Slavic cultural, sporting, business and political associations were banned. As a result, 100,000 Slavic-speakers left Italian-annexed areas in an exodus, moving mostly to Yugoslavia.
The organization TIGR, founded in 1927 by young Slovene liberal nationalists from Gorizia region and Trieste and regarded as the first armed antifascist resistance group in Europe soon penetrated into Slovene and Croatian-speaking parts of Istria.
In World War II, Istria became a battleground of competing ethnic and political groups. Istrian nationalist groups which were pro-fascist and pro-Allied and Yugoslav-supported pro-communist groups fought with each other and the Italian army. After the German withdrawal in 1945, Yugoslav partisans gained the upper hand and began a violent purge of real or suspected opponents in an "orgy of revenge".
SFR Yugoslavia (1947–1991)
After the end of World War II, Istria was ceded to Yugoslavia, except for a small part in the northwest corner that formed Zone B of the provisionally independent Free Territory of Trieste; Zone B was under Yugoslav administration and after the '' de facto'' dissolution of the Free Territory in 1954 it was also incorporated into Yugoslavia. Only the small town of Muggia, near Trieste, being part of Zone A remained with Italy.Katia Pizzi''A city in search of an author: the literacy identity of Trieste''
pg. 23, Sheffield Academic Press (2002),
 The events of the period are visible in
The events of the period are visible in Pula
Pula (; also known as Pola, it, Pola , hu, Pòla, Venetian language, Venetian; ''Pola''; Istriot language, Istriot: ''Puola'', Slovene language, Slovene: ''Pulj'') is the largest city in Istria County, Croatia, and the List of cities and town ...
. The city had an Istrian Italians majority and is located on the southernmost tip of the Istrian peninsula. Between December 1946 and September 1947, a large proportion of the city's inhabitants were forced to emigrate to Italy. Most of them left in the immediate aftermath of the signing of the Paris Peace Treaty on February 10, 1947 which granted Pula and the greater part of Istria to Yugoslavia.
After the breakup of Yugoslavia (after 1991)
The division of Istria between Croatia and Slovenia runs on the former republic borders, which were not precisely defined in the former Yugoslavia. Various points of contention remain unresolved between the two countries regarding the precise line of the border. It became an international boundary with the independence of both countries from Yugoslavia in 1991. Since Croatia's first multi-party elections in 1990, the regionalist party Istrian Democratic Assembly (IDS-DDI, ''Istarski demokratski sabor'' or ''Dieta democratica istriana'') has consistently received a majority of the vote and maintained through the 1990s a position often contrary to the government in Zagreb, led by the then nationalistic partyCroatian Democratic Union
The Croatian Democratic Union ( hr, Hrvatska demokratska zajednica, lit=Croatian Democratic Community, HDZ) is the major conservative, centre-right political party in Croatia. It is one of the two major contemporary political parties in Croa ...
(HDZ, ''Hrvatska demokratska zajednica''), with regards to decentralization in Croatia and certain facets of regional autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
. The Istrian regionalist movement is known as Istrianism
Istrianism or Istrianness is the name given to the regionalist identity developed by the inhabitants of the part of Istria located in Croatia. Istria is the biggest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea and a multiethnic region divided between Croatia ...
.
However, that changed in 2000 when the IDS formed with five other parties a left-centre coalition government, led by the Social Democratic Party of Croatia
The Social Democratic Party of Croatia ( hr, Socijaldemokratska partija Hrvatske, SDP) is a social-democratic political party in Croatia. The SDP is anti-fascist, progressive, and strongly pro-European. The SDP was formed in 1990 as the succe ...
(SDP, ''Socijaldemokratska Partija Hrvatske''). After the reformed HDZ won the Croatian parliamentary elections in late 2003 and formed a minority government, the IDS has cooperated with the state government on many projects, both local (in Istria County) and national. Since Slovenia's accession to the European Union and the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
, customs and immigration checks have been abolished at the Italian-Slovenian border.
Demographic history
The region has traditionally been ethnically mixed. Under Austrian rule in the 19th century it included a large population of Italians, Croats, and Slovenes as well as someIstro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to sev ...
, Serbs, and Montenegrins; however, official statistics in those times did not show those nationalities as they do today.
In 1910, the ethnic and linguistic composition was completely mixed. According to the Austrian census results (Istria included here parts of the Karst and Liburnia which are not really part of Istria and excluded ancient Istrian parts, like Trieste), out of 404,309 inhabitants in Istria, 168,116 (41.6%) spoke Serbo-Croatian, 147,416 (36.5%) spoke Italian, 55,365 (13.7%) spoke Slovene, 13,279 (3.3%) spoke German, 882 (0.2%) spoke Istro-Romanian, 2,116 (0.5%) spoke other languages, and 17,135 (4.2%) were non-citizens, which had not been asked for their language of communication. During the last decades of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
dynasty the coast of Istria profited from tourism within the Empire. Generally speaking, Italians lived on the coast and in the inland cities of northern Istria, while Croats and Slovenes lived in the eastern and southeastern inland parts of the countryside.
In the second half of the 19th century a clash of new ideological movements, Italian irredentism (which claimed Trieste and Istria), Slovene nationalism, and Croatian nationalism (developing individual identities in some quarters while seeking to unite in a Southern Slav identity in others) resulted in growing ethnic conflict between Italians on one side and Slovenes and Croats on the other side. This was intertwined with class conflict, as inhabitants of Istrian towns were mostly Italian, while Croats and Slovenes largely lived out in the eastern countryside.
The Croatian word for the Istrians is ''Istrani'', or ''Istrijani'', the latter being in the local Chakavian dialect. The term ''Istrani'' is also used in Slovenia. The Italian word for the Istrians is ''Istriani'' and today the Italian minority is organized in many towns. The Istrian county in Croatia is bilingual, as are large parts of Slovenian Istria. Every citizen has the right to speak either Italian or Croatian (Slovene in Slovenian Istria and Italian in the town of Koper/Capodistria, Piran/Pirano, Portorož/Portorose, and Izola/Isola d'Istria) in public administration or in court. Furthermore, Istria is a supranational European Region that includes Italian, Slovenian and Croatian Istria.
Ethnicity
Istriot language
The Istriot language () is a Romance language of the Italo-Dalmatian branch spoken by about 400 people in the southwestern part of the Istrian peninsula in Croatia, particularly in Rovinj and Vodnjan. It should not be confused with the Istrian d ...
the oldest spoken language in Istria, dated back to the Romans, today spoken in the southwest of Istria. It can also refer to Istrian Croats who adopted the veneer of Italian culture
Italy is considered one of the birthplaces of Western civilization and a cultural superpower. Italian culture is the culture of the Italians, a Romance ethnic group, and is incredibly diverse spanning the entirety of the Italian peninsula ...
as they moved from rural to urban areas, or from the farms into the bourgeoisie.
Similarly, national powers claim Istrian Croats according to local language, so that speakers of Čakavian and Štokavian
Shtokavian or Štokavian (; sh-Latn, štokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, штокавски, ) is the prestige dialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. It ...
dialects of Croatian
Croatian may refer to:
* Croatia
*Croatian language
*Croatian people
*Croatians (demonym)
See also
*
*
* Croatan (disambiguation)
* Croatia (disambiguation)
* Croatoan (disambiguation)
* Hrvatski (disambiguation)
* Hrvatsko (disambiguation)
* S ...
are considered to be Croatians while speakers of other dialects may be considered to be Slovene. Croatian dialect speakers are descendants of the refugees of the Turkish invasion and Ottoman Empire of Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
in the 16th century.
The government of the Republic of Venice had settled them in Inner Istria, which had been devastated by wars and plague. As with other regions, the local dialects of the Croatian communities vary greatly across close distances. The Istrian Croatian and Italian vernaculars had both developed for many generations before being divided as they are today. This meant that Croats/Slovenes on the one side and Venetians/other Italians on the other side yielded to each other culturally while simultaneously distancing themselves from members of their ethnic groups living farther away.
Another important Istrian community are the Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to sev ...
in the south and north of the Učka mountain range of Istria. A small Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
community, which until the late 19th century spoke the Istrian Albanian dialect is also present in the peninsula.
Austro-Hungarian census
According to Austro-Hungarian censuses, the ethnic composition of Istria (i.e. the Habsburg Magraviate of Istria) was as follows:Recent census
The 2001 population census counted 23 languages spoken by the people of Istria. According to the 2011 Croatian census data for the Istria County, 68.33% of the inhabitants were Croats, 6.03% were Italians, 3.46% were Serbs, 2.95% wereBosniaks
The Bosniaks ( bs, Bošnjaci, Cyrillic: Бошњаци, ; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to the Southeast European historical region of Bosnia, which is today part of Bosnia and Herzegovina, who share a common Bosnian ancestry ...
, 1.15% were Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
, and 1.96% did not state their nationality. Those declaring themselves regionally as Istrians made up 12.11%. Other nationalities had less than 1% each. In 2021 Census show that 76.40% are Croats, Italians were 5.01%, 2.96% were Serbs, 2.48% Bosniaks, 1.05% were Albanians, while regionally declared were 5.13%.
The data for Slovenian Istria is not as neatly organized, but the 2002 Slovenian census indicates that the three Istrian municipalities ( Izola, Piran, Koper
Koper (; it, Capodistria, hr, Kopar) is the fifth largest city in Slovenia. Located in the Istrian region in the southwestern part of the country, approximately five kilometres () south of the border with Italy and 20 kilometres () from Triest ...
) had a total of 56,482 Slovenes, 6,426 Croats, and 1,840 Italians.
The small town of Peroj has had a unique history which exemplifies the multi-ethnic complexity of the history of the region, as do some villages on both sides of the Učka that are still identified with the Istro-Romanian people which the UNESCO Redbook of Endangered Languages calls "the smallest ethnic group in Europe".
Image gallery
Pula
Pula (; also known as Pola, it, Pola , hu, Pòla, Venetian language, Venetian; ''Pola''; Istriot language, Istriot: ''Puola'', Slovene language, Slovene: ''Pulj'') is the largest city in Istria County, Croatia, and the List of cities and town ...
/Pola (Croatia)
File:Porec riva.jpg, The promenade of Poreč/Parenzo (Croatia)
File:Rovinj.jpg, Rovinj/Rovigno, as seen from the bell tower of the church of Saint Eufemia (Croatia)
File:Motovun aerial view.jpg, Motovun/Montona (Croatia)
File:Lim canal.jpg, Lim canal (Croatia)
File:Koper Praetorian Palace.jpg, The Praetorian Palace/Palazzo Pretorio in Koper
Koper (; it, Capodistria, hr, Kopar) is the fifth largest city in Slovenia. Located in the Istrian region in the southwestern part of the country, approximately five kilometres () south of the border with Italy and 20 kilometres () from Triest ...
/Capodistria (Slovenia)
File:Piran - overview.jpg, Old town of Piran/Pirano (Slovenia)
File:Muggia z001.JPG, Port in Muggia (Italy)
File:Istarska narodna nošnja.2.jpg, Traditional folk costume of Istrian Croats
File:Vineyards of Istria (Croatia).jpg, Vineyards of Istria
Major towns and municipalities of Istria
This list includes towns and municipalities of Istria with populations estimated to be higher than 8,000 people. *Koper
Koper (; it, Capodistria, hr, Kopar) is the fifth largest city in Slovenia. Located in the Istrian region in the southwestern part of the country, approximately five kilometres () south of the border with Italy and 20 kilometres () from Triest ...
/Capodistria
* Pula
Pula (; also known as Pola, it, Pola , hu, Pòla, Venetian language, Venetian; ''Pola''; Istriot language, Istriot: ''Puola'', Slovene language, Slovene: ''Pulj'') is the largest city in Istria County, Croatia, and the List of cities and town ...
/Pola
* Poreč/Parenzo
* Rovinj/Rovigno
* Umag/Umago
* Muggia/Milje
* Labin/Albona
* Pazin/Pisino
See also
*List of Istrians
This is a list of notable Istrians. People of Istrian descent born outside the geographical region of Istria have their place of birth credited. The nationality and ethnicity of people included in this list are not mentioned.
Academic sciences ...
* March of Istria
* Istrian–Dalmatian exodus
* Istrian Italians
* ''Acta Histriae
''Acta Histriae'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the contemporary history. It is published by the Historical Society of Southern Primorska of Koper, based in Koper and the editor-in-chief is Darko Friš. The journal was establish ...
''
References
;NotesFurther reading
* * Luigi Tomaz, ''Il confine d'Italia in Istria e Dalmazia. Duemila anni di storia'', Presentazione di Arnaldo Mauri, Think ADV, Conselve 2008. * Luigi Tomaz, ''In Adriatico nel secondo millennio'', Presentazione di Arnaldo Mauri, Think ADV, Conselve, 2010. * Louis François Cassas "Travels in Istria and Dalmatia, drawn up from the itinerary of L. F. Cassas" Eng trans. from 1802 Fr pub.External links
*Istria on the Internet (a non-commercial, non-political, cultural site)
Old postcards of Istria
A Brief History of Istria / Darko Darovec
Istrian cultural heritage. Bukaleta Kazun, wall paintings
Travels in Istria and Dalmatia: drawn up from the itinerary of L. F. Cassas
on Google Books {{Authority control Peninsulas of Croatia Geography of Italy Geography of Southern Europe Geography of Central Europe Peninsulas of Slovenia Austrian Littoral Former states and territories in Slovenia