Islands Of Polynesia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called
 Polynesia is characterized by a small amount of land spread over a very large portion of the mid- and southern Pacific Ocean. It comprises approximately of land, of which more than are within New Zealand. The Hawaiian archipelago comprises about half the remainder.
Most Polynesian islands and archipelagos, including the
Polynesia is characterized by a small amount of land spread over a very large portion of the mid- and southern Pacific Ocean. It comprises approximately of land, of which more than are within New Zealand. The Hawaiian archipelago comprises about half the remainder.
Most Polynesian islands and archipelagos, including the
 The Polynesian people are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, a subset of the sea-migrating
The Polynesian people are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, a subset of the sea-migrating  The results of research at the Teouma Lapita site (
The results of research at the Teouma Lapita site ( A complete mtDNA and genome-wide SNP comparison (Pugach ''et al.'', 2021) of the remains of early settlers of the
A complete mtDNA and genome-wide SNP comparison (Pugach ''et al.'', 2021) of the remains of early settlers of the

 In the 10th century, the Tuʻi Tonga Empire was established in Tonga, and most of the Western Pacific came within its sphere of influence, up to parts of the Solomon Islands. The Tongan influence brought Polynesian customs and language throughout most of Polynesia. The empire began to decline in the 13th century.
After a bloody civil war, political power in Tonga eventually fell under the
In the 10th century, the Tuʻi Tonga Empire was established in Tonga, and most of the Western Pacific came within its sphere of influence, up to parts of the Solomon Islands. The Tongan influence brought Polynesian customs and language throughout most of Polynesia. The empire began to decline in the 13th century.
After a bloody civil war, political power in Tonga eventually fell under the
 The reef islands and atolls of Tuvalu are identified as being part of West Polynesia. During pre-European-contact times there was frequent canoe voyaging between the islands as Polynesian navigation skills are recognised to have allowed deliberate journeys on double-hull sailing canoes or outrigger canoes. Eight of the nine islands of Tuvalu were inhabited; thus the name, Tuvalu, means "eight standing together" in Tuvaluan. The pattern of settlement that is believed to have occurred is that the Polynesians spread out from Samoa and Tonga into the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone for migration into the Polynesian outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia.
Stories as to the ancestors of the Tuvaluans vary from island to island. On Niutao, Funafuti and Vaitupu the founding ancestor is described as being from Samoa; whereas on
The reef islands and atolls of Tuvalu are identified as being part of West Polynesia. During pre-European-contact times there was frequent canoe voyaging between the islands as Polynesian navigation skills are recognised to have allowed deliberate journeys on double-hull sailing canoes or outrigger canoes. Eight of the nine islands of Tuvalu were inhabited; thus the name, Tuvalu, means "eight standing together" in Tuvaluan. The pattern of settlement that is believed to have occurred is that the Polynesians spread out from Samoa and Tonga into the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone for migration into the Polynesian outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia.
Stories as to the ancestors of the Tuvaluans vary from island to island. On Niutao, Funafuti and Vaitupu the founding ancestor is described as being from Samoa; whereas on
 Polynesia divides into two distinct cultural groups, East Polynesia and West Polynesia. The culture of West Polynesia is conditioned to high populations. It has strong institutions of marriage and well-developed judicial, monetary and trading traditions. West Polynesia comprises the groups of Tonga, Samoa and
Polynesia divides into two distinct cultural groups, East Polynesia and West Polynesia. The culture of West Polynesia is conditioned to high populations. It has strong institutions of marriage and well-developed judicial, monetary and trading traditions. West Polynesia comprises the groups of Tonga, Samoa and  Religion, farming, fishing, weather prediction, out-rigger canoe (similar to modern
Religion, farming, fishing, weather prediction, out-rigger canoe (similar to modern
Interstellar Migration and the Human Experience
'". University of California Press. p.176. Many low-lying islands could suffer severe famine if their gardens were poisoned by the salt from the storm surge of a tropical cyclone. In these cases fishing, the primary source of protein, would not ease the loss of food energy. Navigators, in particular, were highly respected and each island maintained a house of navigation with a canoe-building area. Settlements by the Polynesians were of two categories: the hamlet and the village. The size of the island inhabited determined whether or not a hamlet would be built. The larger
 Aside from New Zealand, another focus area of economic dependence regarding tourism is Hawaii. Hawaii is one of the most visited areas within the Polynesian Triangle, entertaining more than ten million visitors annually, excluding 2020. The economy of Hawaii, like that of New Zealand, is steadily dependent on annual tourists and financial counseling or aid from other countries or states. "The rate of tourist growth has made the economy overly dependent on this one sector, leaving Hawaii extremely vulnerable to external economic forces." By keeping this in mind, island states and nations similar to Hawaii are paying closer attention to other avenues that can positively affect their economy by practicing more independence and less emphasis on tourist entertainment.
Aside from New Zealand, another focus area of economic dependence regarding tourism is Hawaii. Hawaii is one of the most visited areas within the Polynesian Triangle, entertaining more than ten million visitors annually, excluding 2020. The economy of Hawaii, like that of New Zealand, is steadily dependent on annual tourists and financial counseling or aid from other countries or states. "The rate of tourist growth has made the economy overly dependent on this one sector, leaving Hawaii extremely vulnerable to external economic forces." By keeping this in mind, island states and nations similar to Hawaii are paying closer attention to other avenues that can positively affect their economy by practicing more independence and less emphasis on tourist entertainment.

 These wayfinding techniques, along with outrigger canoe construction methods, were kept as guild secrets. Generally, each island maintained a guild of navigators who had very high status; in times of famine or difficulty these navigators could trade for aid or evacuate people to neighboring islands. On his first voyage of Pacific exploration Cook had the services of a Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who drew a hand-drawn chart of the islands within radius (to the north and west) of his home island of
These wayfinding techniques, along with outrigger canoe construction methods, were kept as guild secrets. Generally, each island maintained a guild of navigators who had very high status; in times of famine or difficulty these navigators could trade for aid or evacuate people to neighboring islands. On his first voyage of Pacific exploration Cook had the services of a Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who drew a hand-drawn chart of the islands within radius (to the north and west) of his home island of
Interview with David Lewis
Useful introduction to Maori society, including canoe voyages
{{Authority control 1750s neologisms Asia-Pacific Islands of Oceania Regions of Oceania
 Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
. They have many things in common, including language relatedness, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays o ...
. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand.
The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the islands of the Pacific
Collectively called the Pacific Islands, the islands in the Pacific Ocean are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of se ...
. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Geographical Society of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the southern Pacific
The Southern Pacific (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the ...
have also often been called the South Sea Islands, and their inhabitants have been called South Sea Islanders. The Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
have often been considered to be part of the South Sea Islands because of their relative proximity to the southern Pacific islands, even though they are in fact located in the North Pacific. Another term in use, which avoids this inconsistency, is "the Polynesian Triangle
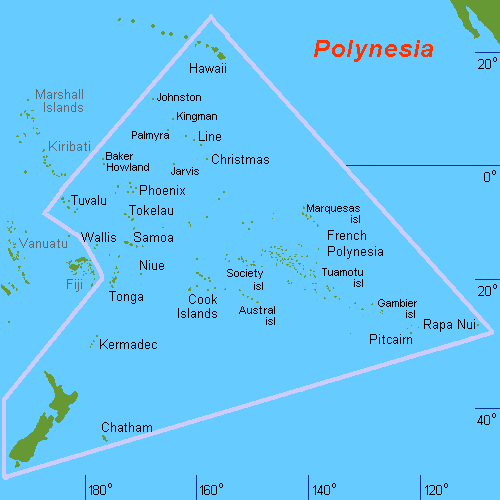
The Polynesian Triangle is a region of the Pacific Ocean with three island groups at its corners: Hawai‘i, Easter Island (''Rapa Nui'') and New Zealand (Aotearoa). It is often used as a simple way to define Polynesia.
Outside the triangle, th ...
" (from the shape created by the layout of the islands in the Pacific Ocean). This term makes clear that the grouping includes the Hawaiian Islands, which are located at the northern vertex
Vertex, vertices or vertexes may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics and computer science
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet
*Vertex (computer graphics), a data structure that describes the position ...
of the referenced "triangle".
Geography
Geology
 Polynesia is characterized by a small amount of land spread over a very large portion of the mid- and southern Pacific Ocean. It comprises approximately of land, of which more than are within New Zealand. The Hawaiian archipelago comprises about half the remainder.
Most Polynesian islands and archipelagos, including the
Polynesia is characterized by a small amount of land spread over a very large portion of the mid- and southern Pacific Ocean. It comprises approximately of land, of which more than are within New Zealand. The Hawaiian archipelago comprises about half the remainder.
Most Polynesian islands and archipelagos, including the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
and Samoa, are composed of volcanic islands built by hotspots
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tra ...
(volcanoes). The other land masses in Polynesia — New Zealand, Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together with ...
, and Ouvéa, the Polynesian outlier near New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
— are the unsubmerged portions of the largely sunken continent of Zealandia.
Zealandia is believed to have mostly sunk below sea level 23 million years ago, and recently partially resurfaced due to a change in the movements of the Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate.
The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Iza ...
in relation to the Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and the surrounding ocean and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and the adjacent waters. It was formed by the fusion of the Indian an ...
. The Pacific plate had previously been subducted under the Australian Plate. When that changed, it had the effect of uplifting the portion of the continent that is modern-day New Zealand.
The convergent plate boundary that runs northwards from New Zealand's North Island is called the Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone
The Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary that stretches from the North Island of New Zealand northward. The formation of the Kermadec and Tonga Plates started about 4–5 million years ago. Today, the eastern boundary ...
. This subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
zone is associated with the volcanism that gave rise to the Kermadec Kermadec or de Kermadec may refer to:
Geography
* Kermadec Islands, a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand
* Kermadec Plate, a long narrow tectonic plate located west of the Kermadec Trench
* Kermadec Trench, ...
and Tongan islands.
There is a transform fault that currently traverses New Zealand's South Island, known as the Alpine Fault.
Zealandia's continental shelf has a total area of approximately .
The oldest rocks in Polynesia are found in New Zealand and are believed to be about 510 million years old. The oldest Polynesian rocks outside Zealandia are to be found in the Hawaiian Emperor Seamount Chain and are 80 million years old.
Geographical area
Polynesia is generally defined as the islands within thePolynesian Triangle
The Polynesian Triangle is a region of the Pacific Ocean with three island groups at its corners: Hawai‘i, Easter Island (''Rapa Nui'') and New Zealand (Aotearoa). It is often used as a simple way to define Polynesia.
Outside the triangle, th ...
, although some islands inhabited by Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
are situated outside the Polynesian Triangle. Geographically, the Polynesian Triangle is drawn by connecting the points of Hawaii, New Zealand, and Easter Island. The other main island groups located within the Polynesian Triangle are Samoa, Tonga, the Cook Islands, Tuvalu, Tokelau, Niue, Wallis and Futuna, and French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of Frenc ...
.
Also, small Polynesian settlements are in Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, and Vanuatu. An island group with strong Polynesian cultural traits outside of this great triangle is Rotuma, situated north of Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
. The people of Rotuma have many common Polynesian traits, but speak a non- Polynesian language. Some of the Lau Islands to the southeast of Fiji have strong historic and cultural links with Tonga. However, in essence, Polynesia remains a cultural term referring to one of the three parts of Oceania (the others being Melanesia and Micronesia).
Island groups
The following are the islands and island groups, either nations or overseas territories of former colonial powers, that are of native Polynesian culture or where archaeological evidence indicates Polynesian settlement in the past. Some islands of Polynesian origin are outside the general triangle that geographically defines the region.Core area
TheLine Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands (in Gilbertese, ''Aono Raina'') are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawa ...
and the Phoenix Islands, most of which are parts of Kiribati, had no permanent settlements until European colonization, but are often considered to be parts of the Polynesian Triangle
The Polynesian Triangle is a region of the Pacific Ocean with three island groups at its corners: Hawai‘i, Easter Island (''Rapa Nui'') and New Zealand (Aotearoa). It is often used as a simple way to define Polynesia.
Outside the triangle, th ...
.
Polynesians once inhabited the Auckland Islands, the Kermadec Islands, and Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together with ...
in pre-colonial times, but these islands were uninhabited by the time European explorers arrived.
The oceanic islands beyond Easter Island, such as Clipperton Island, the Galápagos Islands, and the Juan Fernández Islands, have, on rare occasion, been categorized as being geographically within Polynesia. Some of these islands are still uninhabited, and they are believed to have had no prehistoric contact with either Polynesians or the indigenous peoples of the Americas.
Outliers
=Melanesia
= *Anuta
Anuta is a small high island in the southeastern part of the Solomon Islands province of Temotu, one of the smallest permanently inhabited Polynesian islands. It is one of the Polynesian Outlier communities in Melanesia.
Geography
The island ...
(in Solomon Islands)
* Bellona Island (in Solomon Islands)
* Emae (in Vanuatu)
* Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
(excluding Rotuma and the Lau Islands)
* Mele
Mele () is a ''Comune'' (Municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Genoa in the Italian region Liguria, located about west of Genoa.
Mele borders the following municipalities: Genoa, Masone
Masone ( or ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the ...
(in Vanuatu)
* Nuguria (in Papua New Guinea)
* Nukumanu
The Nukumanu Islands, formerly the Tasman Islands, is an atoll of Papua New Guinea, located in the south-western Pacific Ocean, 4 degrees south of the Equator.
Description
Comprising a ring of more than twenty islets on a reef surrounding a ...
(in Papua New Guinea)
* Ontong Java
Ontong Java Atoll or Luangiua, (formerly ''Lord Howe Atoll'', not to be confused with Lord Howe Island) is one of the largest atolls on earth.
Geographically it belongs to a scattered group of three atolls which includes nearby Nukumanu Atol ...
(in Solomon Islands)
* Pileni (in Solomon Islands)
* Rennell (in Solomon Islands)
* Sikaiana (in Solomon Islands)
* Takuu
Takuu, formerly known as Tauu and also known as Takuu Mortlock or Marqueen Islands, is a small, isolated atoll off the east coast of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea.
Geography
Takuu lies about 250 km to the northeast of Kieta, capital of ...
(in Papua New Guinea)
* Tikopia (in Solomon Islands)
=Micronesia
= * Kapingamarangi (in the Federated States of Micronesia) * Nukuoro (in the Federated States of Micronesia) * Wake Island (a part of the United States Minor Outlying Islands)=Sub-Antarctic islands
= * Auckland Islands (the most southerly known evidence of Polynesian settlement)History
Origins and expansion
 The Polynesian people are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, a subset of the sea-migrating
The Polynesian people are considered, by linguistic, archaeological, and human genetic evidence, a subset of the sea-migrating Austronesian people
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrones ...
. Tracing Polynesian languages places their prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
origins in Island Melanesia, Maritime Southeast Asia, and ultimately, in Taiwan.
Between about 3,000 and 1,000 BCE, speakers of Austronesian languages began spreading from Taiwan into Maritime Southeast Asia.
There are three theories regarding the spread of humans across the Pacific to Polynesia. These are outlined well by Kayser ''et al.'' (2000) and are as follows:
* Express Train model: A recent (c. 3,000–1,000 BCE) expansion out of Taiwan, via the Philippines and eastern Indonesia and from the northwest ("Bird's Head
The Bird's Head Peninsula ( Indonesian: ''Kepala Burung'', nl, Vogelkop) or Doberai Peninsula (''Semenanjung Doberai''), is a large peninsula that makes up the northwest portion of the island of New Guinea, comprising the Indonesian provinces ...
") of New Guinea, on to Island Melanesia by roughly 1400 BCE, reaching western Polynesian islands around 900 BCE followed by a roughly 1,000 year "pause" before continued settlement in central and eastern Polynesia. This theory is supported by the majority of current genetic, linguistic, and archaeological data.
* Entangled Bank model: Emphasizes the long history of Austronesian speakers' cultural and genetic interactions with indigenous Island Southeast Asians and Melanesians along the way to becoming the first Polynesians.
* Slow Boat model: Similar to the express-train model but with a longer hiatus in Melanesia along with admixture — genetically, culturally and linguistically — with the local population. This is supported by the Y-chromosome data of Kayser ''et al.'' (2000), which shows that all three haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA or ...
s of Polynesian Y chromosomes can be traced back to Melanesia.
In the archaeological record, there are well-defined traces of this expansion which allow the path it took to be followed and dated with some certainty. It is thought that by roughly 1,400 BCE, "Lapita
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
Peoples", so-named after their pottery tradition, appeared in the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
of northwest Melanesia. This culture is seen as having adapted and evolved through time and space since its emergence "Out of Taiwan". They had given up rice production, for instance, which required paddy field
A paddy field is a flooded field (agriculture), field of arable land used for growing Aquatic plant, semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in sout ...
agriculture unsuitable for small islands. However, they still cultivated other ancestral Austronesian staple cultigens like ''Dioscorea
''Dioscorea'' is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extending ...
'' yams and taro (the latter are still grown with smaller-scale paddy field technology), as well as adopting new ones like breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family (Moraceae) believed to be a domesticated descendant of ''Artocarpus camansi'' originating in New Guinea, the Maluku Islands, and the Philippi ...
and sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
.
Efate Island
Efate (french: Éfaté) is an island in the Pacific Ocean which is part of the Shefa Province in Vanuatu. It is also known as Île Vate.
Geography
It is the most populous (approx. 66,000) island in Vanuatu. Efate's land area of makes it Vanua ...
, Vanuatu) and the Talasiu Lapita site (near Nuku'alofa, Tonga) published in 2016 supports the Express Train model; although with the qualification that the migration bypassed New Guinea and Island Melanesia. The conclusion from research published in 2016 is that the initial population of those two sites appears to come directly from Taiwan or the northern Philippines and did not mix with the ‘ Australo-Papuans’ of New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. The preliminary analysis of skulls found at the Teouma
Teouma is a major archaeological site from Teouma Bay on the island of Éfaté in Vanuatu. The site contains the oldest known cemetery within the Pacific Islands, and has been important in the gathering of information relating to the Lapita pe ...
and Talasiu Lapita sites is that they lack Australian or Papuan affinities and instead have affinities to mainland Asian populations.
A 2017 DNA analysis of modern Polynesians indicates that there has been intermarriage resulting in a mixed Austronesian-Papuan ancestry of the Polynesians (as with other modern Austronesians, with the exception of Taiwanese aborigines). Research at the Teouma and Talasiu Lapita sites implies that the migration and intermarriage, which resulted in the mixed Austronesian-Papuan ancestry of the Polynesians, occurred after the first initial migration to Vanuatu and Tonga.
 A complete mtDNA and genome-wide SNP comparison (Pugach ''et al.'', 2021) of the remains of early settlers of the
A complete mtDNA and genome-wide SNP comparison (Pugach ''et al.'', 2021) of the remains of early settlers of the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
and early Lapita individuals from Vanuatu and Tonga also suggest that both migrations originated directly from the same ancient Austronesian source population from the Philippines. The complete absence of "Papuan" admixture in the early samples indicates that these early voyages bypassed eastern Indonesia and the rest of New Guinea. The authors have also suggested a possibility that the early Lapita Austronesians were direct descendants of the early colonists of the Marianas (which preceded them by about 150 years), which is also supported by pottery evidence.
The most eastern site for Lapita archaeological remains recovered so far is at Mulifanua on Upolu. The Mulifanua site, where 4,288 pottery shards have been found and studied, has a "true" age of based on radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
and is the oldest site yet discovered in Polynesia. This is mirrored by a 2010 study also placing the beginning of the human archaeological sequences of Polynesia in Tonga at 900 BCE.
Within a mere three or four centuries, between 1,300 and 900 BCE, the Lapita archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
spread 6,000 km further to the east from the Bismarck Archipelago, until reaching as far as Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, Tonga, and Samoa. A cultural divide began to develop between Fiji to the west, and the distinctive Polynesian language and culture emerging on Tonga and Samoa to the east. Where there was once faint evidence of uniquely shared developments in Fijian and Polynesian speech, most of this is now called "borrowing" and is thought to have occurred in those and later years more than as a result of continuing unity of their earliest dialects on those far-flung lands. Contacts were mediated especially through the Tovata confederacy of Fiji. This is where most Fijian-Polynesian linguistic interactions occurred.
In the chronology of the exploration and first populating of Polynesia, there is a gap commonly referred to as the long pause between the first populating of Western Polynesia including Fiji, Tonga, and Samoa among others and the settlement of the rest of the region. In general this gap is considered to have lasted roughly 1,000 years. The cause of this gap in voyaging is contentious among archaeologists with a number of competing theories presented including climate shifts, the need for the development of new voyaging techniques, and cultural shifts.
After the long pause, dispersion of populations into central and eastern Polynesia began. Although the exact timing of when each island group was settled is debated, it is widely accepted that the island groups in the geographic center of the region (i.e. the Cook Islands, Society Islands, Marquesas Islands, etc.) were settled initially between 1,000 and 1,150 CE, and ending with more far flung island groups such as Hawaii, New Zealand, and Easter Island settled between 1,200 and 1,300 CE.
Tiny populations may have been involved in the initial settlement of individual islands; although Professor Matisoo-Smith of the Otago study said that the founding Māori population of New Zealand must have been in the hundreds, much larger than previously thought. The Polynesian population experienced a founder effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
and genetic drift. The Polynesian may be distinctively different both genotypically
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
and phenotypically from the parent population from which it is derived. This is due to new population being established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population which also causes a loss of genetic variation.
Atholl Anderson wrote that analysis of mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
(mtDNA, female) and Y chromosome (male) concluded that the ancestors of Polynesian women were Austronesians while those of Polynesian men were Papuans. Subsequently, it was found that 96% (or 93.8%) of Polynesian mtDNA has an Asian origin, as does one-third of Polynesian Y chromosomes; the remaining two-thirds from New Guinea and nearby islands; this is consistent with matrilocal residence patterns. Polynesians existed from the intermixing of few ancient Austronesian-Melanesian founders, genetically they belong almost entirely to the Haplogroup B (mtDNA), which is the marker of Austronesian expansions. The high frequencies of mtDNA Haplogroup B in the Polynesians are the result of founder effect and represents the descendants of a few Austronesian females who intermixed with Papuan males.
A genomic analysis of modern populations in Polynesia, published in 2021, provides a model of the direction and timing of Polynesian migrations from Samoa to the islands to the east. This model presents consistencies and inconsistencies with models of Polynesian migration that are based on archaeology and linguistic analysis. The 2021 genomic model presents a migration pathway from Samoa to the Cook Islands (Rarotonga), then to the Society Islands (Tōtaiete mā) in the 11th century, the western Austral Islands (Tuha’a Pae) and the Tuāmotu Archipelago in the 12th century, with the migrant pathway branching to the north to the Marquesas (Te Henua ‘Enana), to Raivavae in the south, and to the easternmost destination on Easter Island (Rapa Nui), which was settled in approximately CE 1200 via Mangareva.
Culture
The Polynesians were matrilineal and matrilocalStone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
societies upon arrival in Fiji, Tonga and Samoa, after having been through at least some time in the Bismarck Archipelago. The modern Polynesians still show human genetic results of a Melanesian culture which allowed indigenous men, but not women, to "marry in" – useful evidence for matrilocality.
Although matrilocality and matrilineality receded at some early time, Polynesians and most other Austronesian speakers in the Pacific Islands, were/are still highly "matricentric" in their traditional jurisprudence. The Lapita pottery for which the general archaeological complex of the earliest "Oceanic" Austronesian speakers in the Pacific Islands are named also went away in Western Polynesia. Language, social life and material culture
Material culture is the aspect of social reality grounded in the objects and architecture that surround people. It includes the usage, consumption, creation, and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms, and rituals that the objects creat ...
were very distinctly "Polynesian" by 1000 BCE.
Linguistically, there are five sub-groups of the Polynesian language group. Each represents a region within Polynesia and the categorization of these language groups by Green in 1966 helped to confirm Polynesian settlement took place west to east. There is a very distinct "East Polynesian" subgroup with many shared innovations not seen in other Polynesian languages. The Marquesas dialects are perhaps the source of the oldest Hawaiian speech which is overlaid by Tahitian variety speech, as Hawaiian oral histories would suggest. The earliest varieties of New Zealand Maori speech may have had multiple sources from around central Eastern Polynesia as Maori oral histories would suggest.
Political history

Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is made up of 15 islands comprising the Northern and Southern groups. The islands are spread out across many kilometers of a vast ocean. The largest of these islands is called Rarotonga, which is also the political and economic capital of the nation. The Cook Islands were formerly known as the Hervey Islands, but this name refers only to the Northern Groups. It is unknown when this name was changed to reflect the current name. It is thought that the Cook Islands were settled in two periods: the Tahitian Period, when the country was settled between 900 and 1300 AD, and the Maui Settlement, which occurred in 1600 AD, when a large contingent from Tahiti settled in Rarotonga, in the Takitumu district. The first contact between Europeans and the native inhabitants of the Cook Islands took place in 1595 with the arrival of Spanish explorerÁlvaro de Mendaña Álvaro (, , ) is a Spanish, Galician and Portuguese male given name and surname (see Spanish naming customs) of Visigothic origin. Some claim it may be related to the Old Norse name Alfarr, formed of the elements ''alf'' "elf" and ''arr'' "warrior ...
in Pukapuka, who called it ''San Bernardo'' (Saint Bernard). A decade later, navigator Pedro Fernández de Quirós made the first European landing in the islands when he set foot on Rakahanga in 1606, calling it ''Gente Hermosa'' (Beautiful People).
Cook Islanders are ethnically Polynesians or Eastern Polynesia. They are culturally associated with Tahiti, Eastern Islands, NZ Maori and Hawaii. Early in the 17th century, they became the first race to settle in New Zealand.
Fiji
The Lau Islands were subject to periods of Tongan rulership and then Fijian control until their eventual conquest by Seru Epenisa Cakobau of the Kingdom of Fiji by 1871. In around 1855 a Tongan prince, Enele Ma'afu, proclaimed the Lau islands as his kingdom, and took the title Tui Lau. Fiji had been ruled by numerous divided chieftains until Cakobau unified the landmass. The Lapita culture, the ancestors of the Polynesians, existed in Fiji from about 3500 BCE until they were displaced by the Melanesians about a thousand years later. (Both Samoans and subsequent Polynesian cultures adopted Melanesian painting and tattoo methods.) In 1873, Cakobau ceded a Fiji heavily indebted to foreign creditors to the United Kingdom. It became independent on 10 October 1970 and a republic on 28 September 1987. Fiji is classified as Melanesian and (less commonly) Polynesian.Hawaii
New Zealand
Beginning in the late 13th and early 14th centuries, Polynesians began to migrate in waves to New Zealand via their canoes, settling on both the North andSouth
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
islands as well as the Chatham Islands. Over the course of several centuries, the Polynesian settlers formed distinct cultures that became known as the Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
on the New Zealand mainland , while those who settled in the Chatham Islands became the Moriori people. Beginning the 17th century, the arrival of Europeans to New Zealand drastically impacted Māori culture. Settlers from Europe (known as " Pākehā") began to colonize New Zealand in the 19th century, leading to tension with the indigenous Māori. On October 28, 1835, a group of Māori tribesmen issued a declaration of independence (drafted by Scottish businessman James Busby) as the " United Tribes of New Zealand", in order to resist potential efforts at colonizing New Zealand by the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and prevent merchant ships and their cargo which belonged to Māori merchants from being seized at foreign ports. The new state received recognition from the British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
in 1836.
In 1840, Royal Navy officer William Hobson and several Māori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which transformed New Zealand into a colony of the British Empire and granting all Māori the status of British subjects. However, tensions between Pākehā settlers and the Māori over settler encroachment on Māori lands and disputes over land sales led to the New Zealand Wars (1845-1872) between the colonial government and the Māori. In response to the conflict, the colonial government initiated a series of land confiscations from the Māori. This social upheavel, combined with epidemics of infectious diseases from Europe, devastated both the Māori population and their social standing in New Zealand. In the 20th and 21st centuries, the Maori population began to recover, and efforts were made to redress social, economic, political and economic issues facing the Māori in wider New Zealand society. Beginning in the 1960s, a protest movement
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration or remonstrance) is a public expression of objection, disapproval or dissent towards an idea or action, typically a political one.
Protests can be thought of as acts of cooper ...
emerged seeking redress for historical grievances. In the 2013 New Zealand census
The 2013 New Zealand census was the thirty-third national census. "The National Census Day" used for the census was on Tuesday, 5 March 2013. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,242,048, – an increase of 214,101 or 5.3% over the 20 ...
, roughly 600,000 people in New Zealand identified as being Māori.
Samoa
In the 9th century, theTui Manu'a
The title Tui Manuʻa was the title of the ruler or paramount chief of the Manuʻa Islands in present-day American Samoa.
The Tuʻi Manuʻa Confederacy, or Samoan Empire, are descriptions sometimes given to Samoan expansionism and projecte ...
controlled a vast maritime empire comprising most of the settled islands of Polynesia. The Tui Manu'a is one of the oldest Samoan titles in Samoa. Traditional oral literature
Oral literature, orature or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung as opposed to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used vary ...
of Samoa and Manu'a talks of a widespread Polynesian network or confederacy (or "empire") that was prehistorically ruled by the successive Tui Manu'a dynasties. Manuan genealogies and religious oral literature also suggest that the Tui Manu'a had long been one of the most prestigious and powerful paramount of Samoa. Oral history suggests that the Tui Manu'a kings governed a confederacy of far-flung islands which included Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, Tonga as well as smaller western Pacific chiefdoms and Polynesian outliers such as Uvea, Futuna, Tokelau, and Tuvalu. Commerce and exchange routes between the western Polynesian societies are well documented and it is speculated that the Tui Manu'a dynasty grew through its success in obtaining control over the oceanic trade of currency goods such as finely woven ceremonial mats, whale ivory " tabua", obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.
Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements s ...
and basalt tools, chiefly red feathers, and seashells reserved for royalty (such as polished nautilus and the egg cowry).
Samoa's long history of various ruling families continued until well after the decline of the Tui Manua's power, with the western isles of Savaii and Upolu rising to prominence in the post-Tongan occupation period and the establishment of the Tafa'ifa system that dominated Samoan politics well into the 20th century. This was disrupted in the early 1900s due to colonial intervention, with east–west division by Tripartite Convention (1899)
The Tripartite Convention of 1899 concluded the Second Samoan Civil War, resulting in the formal partition of the Samoan archipelago into a German colony and a United States territory.
Forerunners to the Tripartite Convention of 1899 were the W ...
and subsequent annexation by the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
and the United States. The German-controlled Western portion of Samoa (consisting of the bulk of Samoan territory – Savai'i, Apolima, Manono and Upolu) was occupied by New Zealand in WWI, and administered by it under a Class C League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
. After repeated efforts by the Samoan independence movement, the New Zealand Western Samoa Act 1961 of 24 November 1961 granted Samoa independence, effective on January 1, 1962, upon which the Trusteeship Agreement terminated. The new Independent State of Samoa was not a monarchy, though the Malietoa title-holder remained very influential. It officially ended, however with the death of Malietoa Tanumafili II on May 11, 2007.
Tahiti
Tonga
 In the 10th century, the Tuʻi Tonga Empire was established in Tonga, and most of the Western Pacific came within its sphere of influence, up to parts of the Solomon Islands. The Tongan influence brought Polynesian customs and language throughout most of Polynesia. The empire began to decline in the 13th century.
After a bloody civil war, political power in Tonga eventually fell under the
In the 10th century, the Tuʻi Tonga Empire was established in Tonga, and most of the Western Pacific came within its sphere of influence, up to parts of the Solomon Islands. The Tongan influence brought Polynesian customs and language throughout most of Polynesia. The empire began to decline in the 13th century.
After a bloody civil war, political power in Tonga eventually fell under the Tuʻi Kanokupolu
(chiefs) are a junior rank of the (king's lineage) in Tonga.
Terminology
The are described as . means 'side of the road' and means 'lower'. Thus, is the lower side of the road.
The term differentiates the from the who are the most sen ...
dynasty in the 16th century.
In 1845, the ambitious young warrior, strategist, and orator Tāufaʻāhau
George Tupou I (4 December 1797 – 18 February 1893), originally known as Tāufaʻāhau I, was the first king of modern Tonga. He adopted the name Siaosi (originally Jiaoji), the Tongan equivalent of ''George'', after King George III of the U ...
united Tonga into a more Western-style kingdom. He held the chiefly title of Tuʻi Kanokupolu, but had been baptised with the name Jiaoji ("George") in 1831. In 1875, with the help of the missionary Shirley Waldemar Baker
Shirley Waldemar Baker (1836 – 16 November 1903) was a Methodist missionary in Tonga. He was the founder of the Free Church of Tonga and enjoyed significant influence during the reign of George Tupou I, who made him prime minister.
Early life ...
, he declared Tonga a constitutional monarchy, formally adopted the western royal style, emancipated the "serfs", enshrined a code of law, land tenure, and freedom of the press, and limited the power of the chiefs.
Tonga became a British protectorate under a Treaty of Friendship on 18 May 1900, when European settlers and rival Tongan chiefs tried to oust the second king. Within the British Empire, which posted no higher permanent representative on Tonga than a British Consul (1901–1970), Tonga formed part of the British Western Pacific Territories
The British Western Pacific Territories (BWPT) was the name of a colonial entity, created in 1877, for the administration, under a single representative of the British Crown, styled High Commissioner for the Western Pacific, of a series of Paci ...
(under a High Commissioner who residing in Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
) from 1901 until 1952. Despite being under the protectorate, Tonga retained its monarchy without interruption. On June 4, 1970, the Kingdom of Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesia, Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has List of islands and towns in Tonga, 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its tota ...
became independent from the British Empire.
Tuvalu
 The reef islands and atolls of Tuvalu are identified as being part of West Polynesia. During pre-European-contact times there was frequent canoe voyaging between the islands as Polynesian navigation skills are recognised to have allowed deliberate journeys on double-hull sailing canoes or outrigger canoes. Eight of the nine islands of Tuvalu were inhabited; thus the name, Tuvalu, means "eight standing together" in Tuvaluan. The pattern of settlement that is believed to have occurred is that the Polynesians spread out from Samoa and Tonga into the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone for migration into the Polynesian outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia.
Stories as to the ancestors of the Tuvaluans vary from island to island. On Niutao, Funafuti and Vaitupu the founding ancestor is described as being from Samoa; whereas on
The reef islands and atolls of Tuvalu are identified as being part of West Polynesia. During pre-European-contact times there was frequent canoe voyaging between the islands as Polynesian navigation skills are recognised to have allowed deliberate journeys on double-hull sailing canoes or outrigger canoes. Eight of the nine islands of Tuvalu were inhabited; thus the name, Tuvalu, means "eight standing together" in Tuvaluan. The pattern of settlement that is believed to have occurred is that the Polynesians spread out from Samoa and Tonga into the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone for migration into the Polynesian outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia.
Stories as to the ancestors of the Tuvaluans vary from island to island. On Niutao, Funafuti and Vaitupu the founding ancestor is described as being from Samoa; whereas on Nanumea
Nanumea is the northwesternmost atoll in the Polynesian nation of Tuvalu, a group of nine coral atolls and islands spread over about of the Pacific Ocean just south of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Nanumea is with a popul ...
the founding ancestor is described as being from Tonga.
The extent of influence of the Tuʻi Tonga line of Tongan kings, which originated in the 10th century, is understood to have extended to some of the islands of Tuvalu in the 11th to mid-13th century. The oral history of Niutao recalls that in the 15th century Tongan warriors were defeated in a battle on the reef of Niutao. Tongan warriors also invaded Niutao later in the 15th century and again were repelled. A third and fourth Tongan invasion of Niutao occurred in the late 16th century, again with the Tongans being defeated.
Tuvalu was first sighted by Europeans in January 1568 during the voyage of Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira who sailed past the island of Nui, and charted it as ''Isla de Jesús'' (Spanish for "Island of Jesus") because the previous day was the feast of the Holy Name. Mendaña made contact with the islanders but did not land. During Mendaña's second voyage across the Pacific he passed Niulakita
Niulakita is the southernmost island of Tuvalu, and also the name of the only village on this island. Niulakita has a population of 34 (2017 Census). The residents of Niulakita have moved to the island from Niutao. Niulakita is represented in th ...
in August 1595, which he named ''La Solitaria'', meaning "the solitary one".
Fishing was the primary source of protein, with the Tuvaluan cuisine
The cuisine of Tuvalu, a state in the Central Pacific (Oceania), is based on the staple of coconut and the many species of fish found in the ocean and the lagoons of the atolls of Tuvalu. Pulaka, (cyrtosperma merkusii), or swamp taro, is an import ...
reflecting food that could be grown on low-lying atolls. Navigation between the islands of Tuvalu was carried out using outrigger canoes. The population levels of the low-lying islands of Tuvalu had to be managed because of the effects of periodic droughts and the risk of severe famine if the gardens were poisoned by salt from the storm surge of a tropical cyclone.
Links to the Americas
Thesweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
, called in Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
and in Quechua, is native to the Americas and was widespread in Polynesia when Europeans first reached the Pacific. Remains of the plant in the Cook Islands have been radiocarbon-dated to 1000, and the present scholarly consensus is that it was brought to central Polynesia by Polynesians who had traveled to South America and back, from where it spread across the region. Some genetic evidence suggests that sweet potatoes may have reached Polynesia via seeds at least 100,000 years ago, pre-dating human arrival; however, this hypothesis fails to account for the similarity of names.
There are also other possible material and cultural evidence of Pre-Columbian contact by Polynesia with the Americas with varying levels of plausibility. These include chickens, coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
s, and bottle gourds. The question of whether Polynesians reached the Americas and the extent of cultural and material influences resulting from such a contact remains highly contentious among anthropologists.
One of the most enduring misconceptions about Polynesians was that they originated from the Americas. This was due to Thor Heyerdahl's proposals in the mid-20th century that the Polynesians had migrated in two waves of migrations: one by Native Americans from the northwest coast of Canada by large whale-hunting dugouts; and the other from South America by "bearded white men" with "reddish to blond hair" and "blue-grey eyes" led by a high priest and sun-king named "Kon-Tiki" on balsa-log rafts. He claimed the "white men" then "civilized" the dark-skinned natives in Polynesia. He set out to prove this by embarking on a highly publicized ''Kon-Tiki'' expedition on a primitive raft with a Scandinavian crew. It captured the public's attention, making the ''Kon-Tiki'' a household name.Sharp, Andrew (1963). ''Ancient Voyagers in Polynesia'', Longman Paul Ltd. pp. 122–128.Finney, Ben R. (1976) "New, Non-Armchair Research". In Ben R. Finney, ''Pacific Navigation and Voyaging'', The Polynesian Society Inc. p. 5.
None of Heyerdahl's proposals have been accepted in the scientific community. The anthropologist Wade Davis in his book ''The Wayfinders'', criticized Heyerdahl as having "ignored the overwhelming body of linguistic, ethnographic, and ethnobotanical evidence, augmented today by genetic and archaeological data, indicating that he was patently wrong." Anthropologist Robert Carl Suggs included a chapter titled "The Kon-Tiki Myth" in his 1960 book on Polynesia, concluding that "The ''Kon-Tiki'' theory is about as plausible as the tales of Atlantis, Mu, and 'Children of the Sun'. Like most such theories, it makes exciting light reading, but as an example of scientific method it fares quite poorly." Other authors have also criticized Heyerdahl's hypothesis for its implicit racism in attributing advances in Polynesian society to "white people", at the same time ignoring relatively advanced Austronesian maritime technology in favor of a primitive balsa raft.
In July 2020, a novel high-density genome-wide DNA analysis of Polynesians and Native South Americans claimed that there has been intermingling between Polynesian people and pre-Columbian Zenú people in a period dated between 1150 and 1380 CE. Whether this happened because of indigenous American people reaching eastern Polynesia or because the northern coast of South America was visited by Polynesians is not clear yet.
Cultures
 Polynesia divides into two distinct cultural groups, East Polynesia and West Polynesia. The culture of West Polynesia is conditioned to high populations. It has strong institutions of marriage and well-developed judicial, monetary and trading traditions. West Polynesia comprises the groups of Tonga, Samoa and
Polynesia divides into two distinct cultural groups, East Polynesia and West Polynesia. The culture of West Polynesia is conditioned to high populations. It has strong institutions of marriage and well-developed judicial, monetary and trading traditions. West Polynesia comprises the groups of Tonga, Samoa and Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
. The pattern of settlement to East Polynesia began from Samoan Islands into the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone to migration into the Polynesian outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia.
Eastern Polynesian cultures are highly adapted to smaller islands and atolls, principally Niue, the Cook Islands, Tahiti, the Tuamotus, the Marquesas, Hawaii, Rapa Nui, and smaller central-pacific groups. The large islands of New Zealand were first settled by Eastern Polynesians who adapted their culture to a non-tropical environment.
Unlike western Melanesia, leaders were chosen in Polynesia based on their hereditary bloodline. Samoa, however, had another system of government that combines elements of heredity and real-world skills to choose leaders. This system is called Fa'amatai. According to Ben R. Finney and Eric M. Jones, "On Tahiti, for example, the 35,000 Polynesians living there at the time of European discovery were divided between high-status persons with full access to food and other resources, and low-status persons with limited access."
 Religion, farming, fishing, weather prediction, out-rigger canoe (similar to modern
Religion, farming, fishing, weather prediction, out-rigger canoe (similar to modern catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran
Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-stab ...
s) construction and navigation were highly developed skills because the population of an entire island depended on them. Trading of both luxuries and mundane items was important to all groups. Periodic droughts and subsequent famines often led to war.Finney, Ben R. and Jones, Eric M. (1986). "Interstellar Migration and the Human Experience
'". University of California Press. p.176. Many low-lying islands could suffer severe famine if their gardens were poisoned by the salt from the storm surge of a tropical cyclone. In these cases fishing, the primary source of protein, would not ease the loss of food energy. Navigators, in particular, were highly respected and each island maintained a house of navigation with a canoe-building area. Settlements by the Polynesians were of two categories: the hamlet and the village. The size of the island inhabited determined whether or not a hamlet would be built. The larger
volcanic islands
Geologically, a high island or volcanic island is an island of volcanic origin. The term can be used to distinguish such islands from low islands, which are formed from sedimentation or the uplifting of coral reefs (which have often formed ...
usually had hamlets because of the many zones that could be divided across the island. Food and resources were more plentiful. These settlements of four to five houses (usually with gardens) were established so that there would be no overlap between the zones. Villages, on the other hand, were built on the coasts of smaller islands and consisted of thirty or more houses—in the case of atolls, on only one of the group so that food cultivation was on the others. Usually, these villages were fortified with walls and palisades made of stone and wood.
However, New Zealand demonstrates the opposite: large volcanic islands with fortified villages.
As well as being great navigators, these people were artists and artisans of great skill. Simple objects, such as fish-hooks would be manufactured to exacting standards for different catches and decorated even when the decoration was not part of the function. Stone and wooden weapons were considered to be more powerful the better they were made and decorated. In some island groups weaving was a strong part of the culture and gifting woven articles was an ingrained practice. Dwellings were imbued with character by the skill of their building. Body decoration and jewelry is of an international standard to this day.
The religious attributes of Polynesians were common over the whole Pacific region. While there are some differences in their spoken languages they largely have the same explanation for the creation of the earth and sky, for the gods that rule aspects of life and for the religious practices of everyday life. People traveled thousands of miles to celebrations that they all owned communally.
Beginning in the 1820s large numbers of missionaries worked in the islands, converting many groups to Christianity. Polynesia, argues Ian Breward, is now "one of the most strongly Christian regions in the world....Christianity was rapidly and successfully incorporated into Polynesian culture. War and slavery disappeared."
Languages
Polynesian languages are all members of the family ofOceanic languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages ...
, a sub-branch of the Austronesian language family. Polynesian languages show a considerable degree of similarity. The vowels are generally the same—a, e, i, o, and u, pronounced as in Italian, Spanish, and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
—and the consonants are always followed by a vowel. The languages of various island groups show changes in consonants. ''R'' and ''v'' are used in central and eastern Polynesia whereas ''l'' and ''v'' are used in western Polynesia. The glottal stop
The glottal plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents thi ...
is increasingly represented by an inverted comma or ‘okina. In the Society Islands, the original Proto-Polynesian
Proto-Polynesian (abbreviated PPn) is the hypothetical proto-language from which all the modern Polynesian languages descend. It is a daughter language of the Proto-Austronesian language. Historical linguists have reconstructed the language using ...
*''k'' and *''ng'' have merged as glottal stop; so the name for the ancestral homeland, deriving from Proto-Nuclear Polynesian ''*sawaiki'', becomes Havai'i. In New Zealand, where the original *''w'' is used instead of ''v'', the ancient home is Hawaiki. In the Cook Islands, where the glottal stop replaces the original *''s'' (with a likely intermediate stage of *''h''), it is ‘Avaiki. In the Hawaiian islands, where the glottal stop replaces the original ''k'', the largest island of the group is named Hawai‘i. In Samoa, where the original ''s'' is used instead of ''h'', ''v'' replaces ''w'', and the glottal stop replaces the original ''k'', the largest island is called Savaiʻi.
Economy
With the exception of New Zealand, the majority of independent Polynesian islands derive much of their income from foreign aid and remittances from those who live in other countries. Some encourage their young people to go where they can earn good money to remit to their stay-at-home relatives. Many Polynesian locations, such as Easter Island, supplement this with tourism income. Some have more unusual sources of income, such as Tuvalu which marketed its '.tv
The domain name .tv is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Tuvalu.
Except for reserved names like com.tv, net.tv, org.tv and others, any person may register second-level domains under .tv. The domain name is popular, and thus ...
' internet top-level domain name or the Cooks that relied on postage stamp sales.
 Aside from New Zealand, another focus area of economic dependence regarding tourism is Hawaii. Hawaii is one of the most visited areas within the Polynesian Triangle, entertaining more than ten million visitors annually, excluding 2020. The economy of Hawaii, like that of New Zealand, is steadily dependent on annual tourists and financial counseling or aid from other countries or states. "The rate of tourist growth has made the economy overly dependent on this one sector, leaving Hawaii extremely vulnerable to external economic forces." By keeping this in mind, island states and nations similar to Hawaii are paying closer attention to other avenues that can positively affect their economy by practicing more independence and less emphasis on tourist entertainment.
Aside from New Zealand, another focus area of economic dependence regarding tourism is Hawaii. Hawaii is one of the most visited areas within the Polynesian Triangle, entertaining more than ten million visitors annually, excluding 2020. The economy of Hawaii, like that of New Zealand, is steadily dependent on annual tourists and financial counseling or aid from other countries or states. "The rate of tourist growth has made the economy overly dependent on this one sector, leaving Hawaii extremely vulnerable to external economic forces." By keeping this in mind, island states and nations similar to Hawaii are paying closer attention to other avenues that can positively affect their economy by practicing more independence and less emphasis on tourist entertainment.
Inter-Polynesian cooperation
The first major attempt at uniting the Polynesian islands was by Imperial Japan in the 1930s, when various theorists (chiefly Hachirō Arita) began promulgating the idea of what would soon become known as the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere. Under the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere, all nations stretching from Southeast Asia and Northeast Asia to Oceania would be united under one, large, cultural and economic bloc which would be free from Westernimperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
. The policy theorists who conceived it, along with the Japanese public, largely saw it as a pan-Asian movement driven by ideals of freedom and independence from Western colonial oppression. In practice, however, it was frequently corrupted by militarists who saw it as an effective policy vehicle through which to strengthen Japan's position and advance its dominance within Asia. At its greatest extent, it stretched from Japanese occupied Indochina in the west to the Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
in the east, although it was originally planned to stretch as far east as Hawaii and Easter Island and as far west as India. This never came to fruition, however, as Japan was defeated during World War II and subsequently lost all power and influence it had.Weinberg, L. Gerhard. (2005). ''Visions of Victory: The Hopes of Eight World War II Leaders'' p.62-65.
After several years of discussing a potential regional grouping, three sovereign states (Samoa, Tonga, and Tuvalu) and five self-governing but non-sovereign territories formally launched, in November 2011, the Polynesian Leaders Group, intended to cooperate on a variety of issues including culture and language, education, responses to climate change, and trade and investment. It does not, however, constitute a political or monetary union.
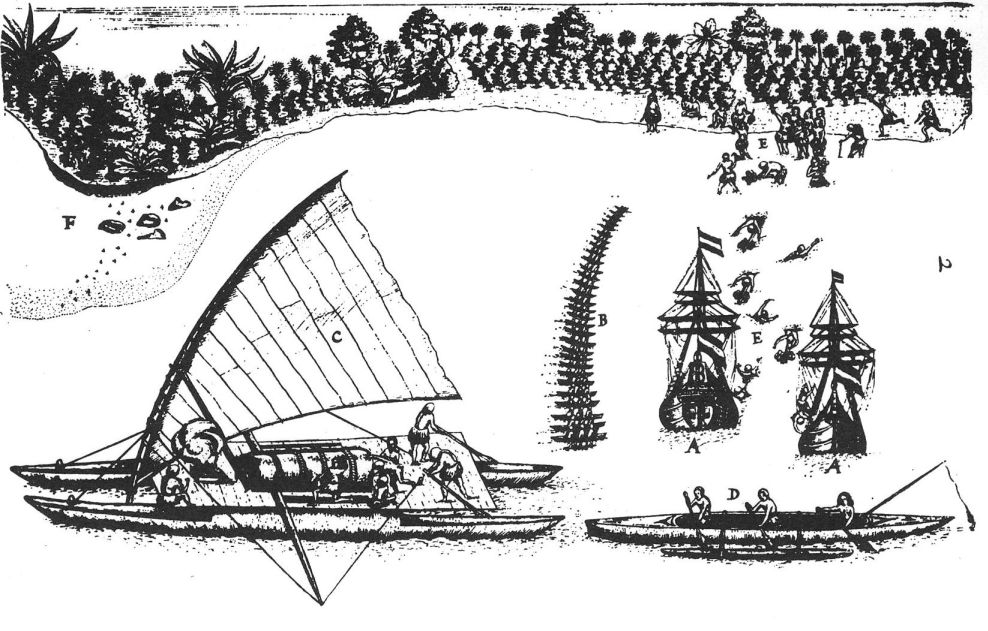
Navigation
Polynesia comprised islands diffused throughout a triangular area with sides of four thousand miles. The area from the Hawaiian Islands in the north, to Easter Island in the east and to New Zealand in the south were all settled by Polynesians. Navigators traveled to small inhabited islands using only their own senses and knowledge passed by oral tradition from navigator to apprentice. In order to locate directions at various times of day and year, navigators in Eastern Polynesia memorized important facts: the motion of specificstar
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s, and where they would rise on the horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
of the ocean; weather; times of travel; wildlife species (which congregate at particular positions); directions of swells on the ocean, and how the crew would feel their motion; colors of the sea and sky, especially how clouds would cluster at the locations of some islands; and angles for approaching harbors.

Ra'iatea
Raiatea or Ra'iatea ( Tahitian: ''Ra‘iātea'') is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the "centre" of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the ...
. Tupaia had knowledge of 130 islands and named 74 on his chart. Tupaia had navigated from Ra'iatea in short voyages to 13 islands. He had not visited western Polynesia, as since his grandfather's time the extent of voyaging by Raiateans has diminished to the islands of eastern Polynesia. His grandfather and father had passed to Tupaia the knowledge as to the location of the major islands of western Polynesia and the navigation information necessary to voyage to Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, Samoa and Tonga. As the Admiralty orders directed Cook to search for the "Great Southern Continent", Cook ignored Tupaia's chart and his skills as a navigator. To this day, original traditional methods of Polynesian Navigation are still taught in the Polynesian outlier of Taumako Island in the Solomon Islands.
From a single chicken bone recovered from the archaeological site of El Arenal-1, on the Arauco Peninsula, Chile, a 2007 research report looking at radiocarbon dating and an ancient DNA sequence indicate that Polynesian navigators may have reached the Americas at least 100 years before Columbus (who arrived 1492 AD), introducing chickens to South America. A later report looking at the same specimens concluded:
A published, apparently pre-Columbian, Chilean specimen and six pre-European Polynesian specimens also cluster with the same European/Indian subcontinental/Southeast Asian sequences, providing no support for a Polynesian introduction of chickens to South America. In contrast, sequences from two archaeological sites on Easter Island group with an uncommon haplogroup from Indonesia, Japan, and China and may represent a genetic signature of an early Polynesian dispersal. Modeling of the potential marine carbon contribution to the Chilean archaeological specimen casts further doubt on claims for pre-Columbian chickens, and definitive proof will require further analyses of ancient DNA sequences and radiocarbon and stable isotope data from archaeological excavations within both Chile and Polynesia.Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was largely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. This left the problem of accounting for the presence of the Polynesians in such isolated and scattered parts of the Pacific. By the late 19th century to the early 20th century, a more generous view of Polynesian navigation had come into favor, perhaps creating a romantic picture of their canoes, seamanship and navigational expertise. In the mid to late 1960s, scholars began testing sailing and paddling experiments related to Polynesian navigation: David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand using
stellar navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of ...
without instruments and Ben Finney
Ben Rudolph Finney was an American anthropologist known for his expertise in the history and the social and cultural anthropology of surfing, Polynesian navigation, and canoe sailing, as well as in the cultural and social anthropology of hum ...
built a 12-meter (40-foot) replica of a Hawaiian double canoe "Nalehia" and tested it in Hawaii. Meanwhile, Micronesian ethnographic research in the Caroline Islands revealed that traditional stellar navigational methods were still in everyday use. Recent re-creations of Polynesian voyaging have used methods based largely on Micronesian methods and the teachings of a Micronesian navigator, Mau Piailug.
It is probable that the Polynesian navigators employed a whole range of techniques including use of the stars, the movement of ocean currents and wave patterns, the air and sea interference patterns caused by islands and atolls, the flight of birds, the winds and the weather. Scientists think that long-distance Polynesian voyaging followed the seasonal paths of birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
. There are some references in their oral traditions to the flight of birds and some say that there were range marks onshore pointing to distant islands in line with these flyways. One theory is that they would have taken a frigatebird with them. These birds refuse to land on the water as their feathers will become waterlogged making it impossible to fly. When the voyagers thought they were close to land they may have released the bird, which would either fly towards land or else return to the canoe. It is likely that the Polynesians also used wave and swell formations to navigate. It is thought that the Polynesian navigators may have measured the time it took to sail between islands in "canoe-days’’ or a similar type of expression.
Another navigational technique may have involved following sea turtle migrations. While other navigational techniques may have been sufficient to reach known islands, some research finds only sea turtles could have helped Polynesian navigators reach new islands. Sea turtle migrations are feasible for canoes to follow, at shallow depths, slower speeds, and in large groups. This could explain how Polynesians were able to find and settle the majority of Pacific Islands.
Also, people of the Marshall Islands used special devices called stick charts, showing the places and directions of swells and wave-breaks, with tiny seashells affixed to them to mark the positions of islands along the way. Materials for these maps were readily available on beaches, and their making was simple; however, their effective use needed years and years of study.
See also
* Films set in Polynesia * Polynesian narrative * Polynesian Society * Polynesian Voyaging Society *Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
Interview with David Lewis
Useful introduction to Maori society, including canoe voyages
{{Authority control 1750s neologisms Asia-Pacific Islands of Oceania Regions of Oceania