Isin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Isin (, modern
 Ishan al-Bahriyat was visited by
Ishan al-Bahriyat was visited by
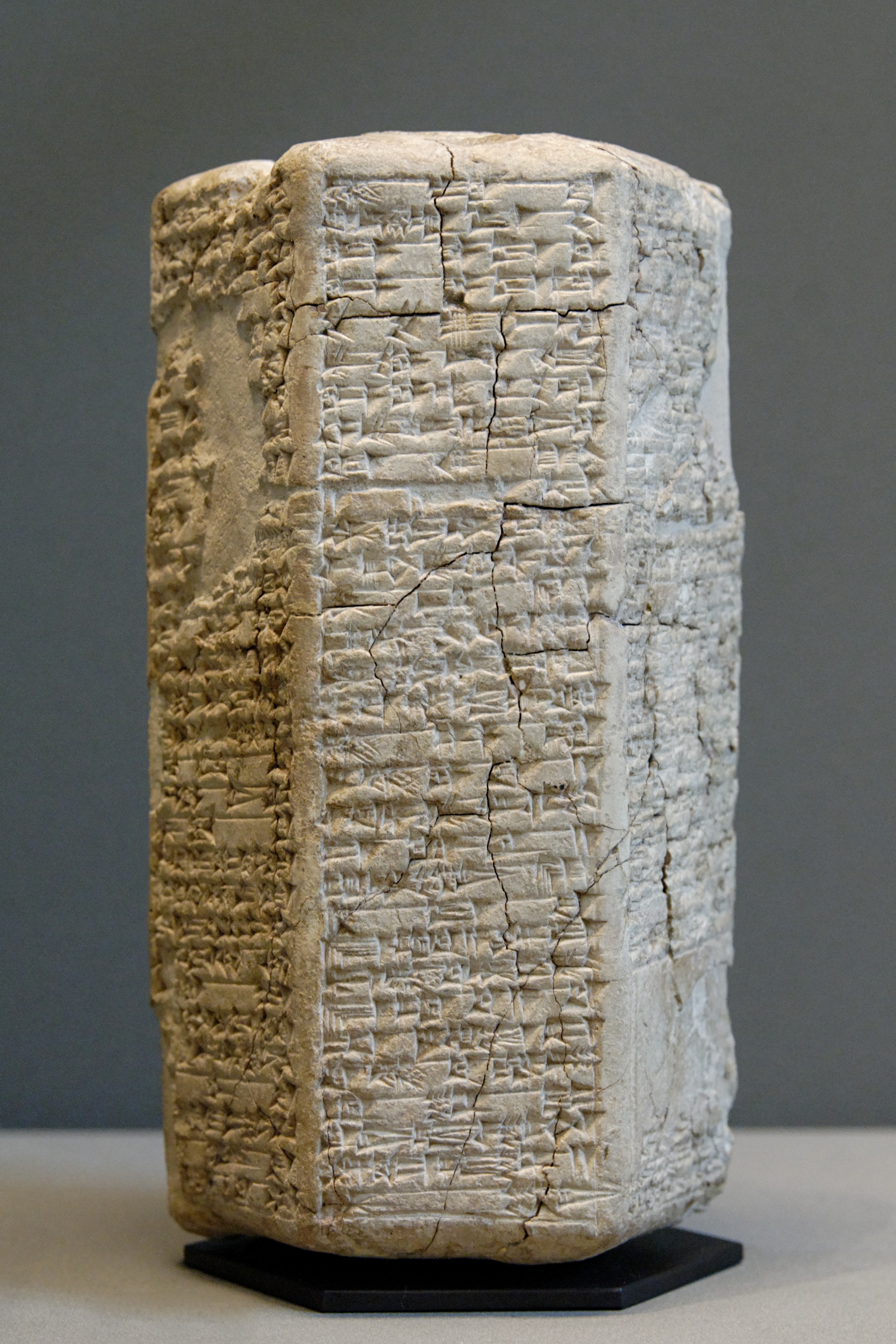 The site of Isin was occupied at least as early as the Early Dynastic period in the middle of the 3rd millennium BC, and possibly as far back as the Ubaid period. While cuneiform tablets from that time were found, the first epigraphic reference to Isin was not until the Ur III period.
When the deteriorating Third Dynasty of Ur ( Ur III) finally collapsed at the hands of the Elamites at the end of the third millennium BC, a power vacuum was left that other city-states scrambled to fill. The last king of the Ur Dynasty, Ibbi-Sin, had not the resources nor the organized government needed to expel the Elamite invaders. One of his governmental officials, Ishbi-Erra, relocated from Ur to Isin, another city in the south of
The site of Isin was occupied at least as early as the Early Dynastic period in the middle of the 3rd millennium BC, and possibly as far back as the Ubaid period. While cuneiform tablets from that time were found, the first epigraphic reference to Isin was not until the Ur III period.
When the deteriorating Third Dynasty of Ur ( Ur III) finally collapsed at the hands of the Elamites at the end of the third millennium BC, a power vacuum was left that other city-states scrambled to fill. The last king of the Ur Dynasty, Ibbi-Sin, had not the resources nor the organized government needed to expel the Elamite invaders. One of his governmental officials, Ishbi-Erra, relocated from Ur to Isin, another city in the south of

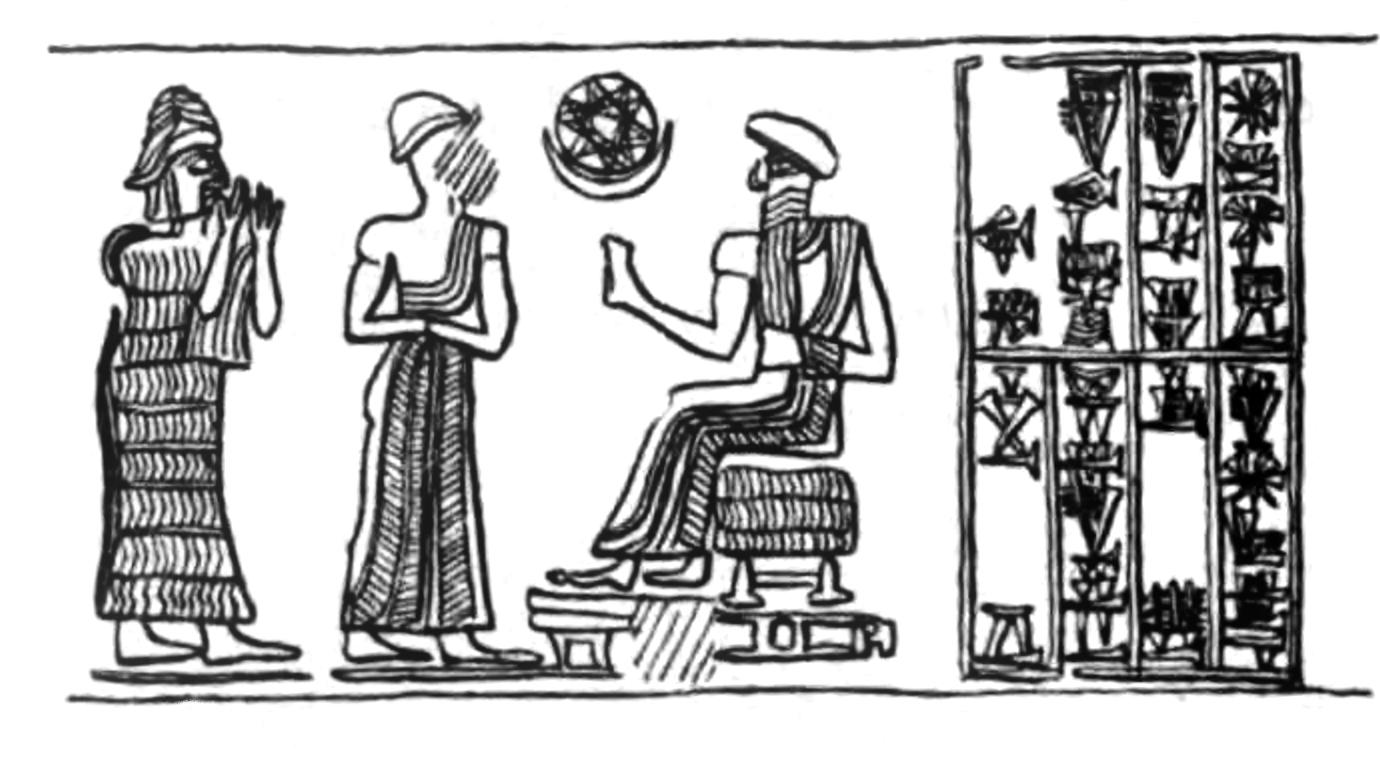 The city lay on the Isinnitum Canal, part of a set of waterways that connected the cities of Mesopotamia. The patron deity of Isin was Nintinuga (Gula) goddess of healing, and a temple to her was built there. The Isin king Enlil-bani reported building a temple to Gula named E-ni-dub-bi, a temple for Sud named E-dim-gal-an-na, a temple E-ur-gi-ra to Ninisina, as well as a temple for the god Ninbgal.William W. Hallo, The Last Years of the Kings of ISIN, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 54-72, 1959
Ishbi-Erra continued many of the cultic practices that had flourished in the preceding Ur III period. He continued acting out the
The city lay on the Isinnitum Canal, part of a set of waterways that connected the cities of Mesopotamia. The patron deity of Isin was Nintinuga (Gula) goddess of healing, and a temple to her was built there. The Isin king Enlil-bani reported building a temple to Gula named E-ni-dub-bi, a temple for Sud named E-dim-gal-an-na, a temple E-ur-gi-ra to Ninisina, as well as a temple for the god Ninbgal.William W. Hallo, The Last Years of the Kings of ISIN, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 54-72, 1959
Ishbi-Erra continued many of the cultic practices that had flourished in the preceding Ur III period. He continued acting out the
Archaeological Site Photographs of Isin at Oriental Institute
Edmund L. Andrews.
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
. Excavations have shown that it was an important city-state in the past.
History of archaeological research
 Ishan al-Bahriyat was visited by
Ishan al-Bahriyat was visited by Stephen Herbert Langdon
Stephen Herbert Langdon (1876May 19, 1937) was an American-born British Assyriologist. Born to George Knowles and Abigail Hassinger Langdon in Monroe, Michigan, Langdon studied at the University of Michigan, participating in Phi Beta Kappa and ...
for a day to conduct a sounding, while he was excavating at Kish in 1924. Most of the major archaeological work at Isin was accomplished in 11 seasons between 1973 and 1989 by a team of German archaeologists led by Barthel Hrouda. However, as was the case at many sites in Iraq, research was interrupted by the Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a Coalition of the Gulf War, 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Ba'athist Iraq, ...
(1990-1) and the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
(2003 to 2011). Since the end of excavations, extensive looting is reported to have occurred at the site. Even when the German team began their work, the site had already been heavily looted.
Isin and its environment
Isin is located approximately south of Nippur. It is a tell, or settlement mound, about across and with a maximum height of .History
 The site of Isin was occupied at least as early as the Early Dynastic period in the middle of the 3rd millennium BC, and possibly as far back as the Ubaid period. While cuneiform tablets from that time were found, the first epigraphic reference to Isin was not until the Ur III period.
When the deteriorating Third Dynasty of Ur ( Ur III) finally collapsed at the hands of the Elamites at the end of the third millennium BC, a power vacuum was left that other city-states scrambled to fill. The last king of the Ur Dynasty, Ibbi-Sin, had not the resources nor the organized government needed to expel the Elamite invaders. One of his governmental officials, Ishbi-Erra, relocated from Ur to Isin, another city in the south of
The site of Isin was occupied at least as early as the Early Dynastic period in the middle of the 3rd millennium BC, and possibly as far back as the Ubaid period. While cuneiform tablets from that time were found, the first epigraphic reference to Isin was not until the Ur III period.
When the deteriorating Third Dynasty of Ur ( Ur III) finally collapsed at the hands of the Elamites at the end of the third millennium BC, a power vacuum was left that other city-states scrambled to fill. The last king of the Ur Dynasty, Ibbi-Sin, had not the resources nor the organized government needed to expel the Elamite invaders. One of his governmental officials, Ishbi-Erra, relocated from Ur to Isin, another city in the south of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, and established himself as a ruler there. One of Ishbi-Erra's year names reports his defeating Ibbi-Sin in battle.Vaughn E. Crawford, An Ishbi-Irra Date Formula, Journal of Cuneiform Studies, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 13-19, 1948
Although he is not considered part of the Third Dynasty of Ur, Ishbi-Erra did make some attempts at continuing the trappings of that dynasty, most likely to justify his rule. Ishbi-Erra had ill luck expanding his kingdom, however, for other city-states in Mesopotamia rose to power as well. Eshnunna and Ashur Ashur, Assur, or Asur may refer to:
Places
* Assur, an Assyrian city and first capital of ancient Assyria
* Ashur, Iran, a village in Iran
* Asur, Thanjavur district, a village in the Kumbakonam taluk of Thanjavur district, Tamil Nadu, India
* Assu ...
were developing into powerful centers. However, he did succeed in repulsing the Elamites from the Ur region. This gave the Isin dynasty control over the culturally significant cities of Ur, Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.H ...
, and the spiritual center of Nippur.
For over 100 years, Isin flourished. Remains of large buildings projects, such as temples, have been excavated. Many royal edicts and law-codes from that period have been discovered. The centralized political structure of Ur-III was largely continued, with Isin's rulers appointing governors and other local officials to carry out their will in the provinces. Lucrative trade routes to the Persian Gulf remained a crucial source of income for Isin.
The exact events surrounding Isin's disintegration as a kingdom are mostly unknown, but some evidence can be pieced together. Documents indicate that access to water sources presented a huge problem for Isin. Isin also endured an internal coup of a sort when Gungunum the royally appointed governor of Larsa and Lagash province, seized the city of Ur. Ur had been the main center of the Gulf trade; thus this move economically crippled Isin. Additionally, Gungunum's two successors Abisare and Sumuel
Sumuel or Sumu-El (, ''su-mu-el3'') ruled the ancient Near East city-state
of Larsa from c. 1894 BC to 1866 BC (middle chronology). He was an Amorite.
Annals for his complete 29-year reign have survived; thus it is known that he campaigned again ...
(c. 1905 BC and 1894 BC) both sought to cut Isin off from its canals by rerouting them into Larsa. At some point, Nippur was also lost. Isin would never recover. Around 1860 BC, an outsider named Enlil-bani seized the throne of Isin, ending the hereditary dynasty established by Ishbi-Erra over 150 years earlier.
Although politically and economically weak, Isin maintained its independence from Larsa for at least another forty years, ultimately succumbing to Larsa's ruler Rim-Sin I.
After the First Dynasty of Babylon rose to power in the early 2nd millennium and captured Larsa, much significant construction occurred at Isin. This ended with a destruction dated to around the 27th year of the reign of Samsu-iluna, son of Hammurabi, based on tablets found there.
Later, the Kassites who took over in Babylon after its sack in 1531 BC, resumed building at Isin. The final significant stage of activity occurred during the Second Dynasty of Isin at the end of the 2nd millennium, most notably by king Adad-apla-iddina.
Of the at least 256 ruler year names about 75% have been found. Most have the standard format, aside from Bur-Sin who numbered his years. These year names combined with new tablet joins show that there were two additional rulers, Sumu-abum and Ikūn-pī-Išta, slotting in between Erra-imittī and Enlil-bān. The reign of Sumu-abum lasted less than a year.
Kings of Isin
First Dynasty of Isin ( short chronology)
Culture and literature
 The city lay on the Isinnitum Canal, part of a set of waterways that connected the cities of Mesopotamia. The patron deity of Isin was Nintinuga (Gula) goddess of healing, and a temple to her was built there. The Isin king Enlil-bani reported building a temple to Gula named E-ni-dub-bi, a temple for Sud named E-dim-gal-an-na, a temple E-ur-gi-ra to Ninisina, as well as a temple for the god Ninbgal.William W. Hallo, The Last Years of the Kings of ISIN, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 54-72, 1959
Ishbi-Erra continued many of the cultic practices that had flourished in the preceding Ur III period. He continued acting out the
The city lay on the Isinnitum Canal, part of a set of waterways that connected the cities of Mesopotamia. The patron deity of Isin was Nintinuga (Gula) goddess of healing, and a temple to her was built there. The Isin king Enlil-bani reported building a temple to Gula named E-ni-dub-bi, a temple for Sud named E-dim-gal-an-na, a temple E-ur-gi-ra to Ninisina, as well as a temple for the god Ninbgal.William W. Hallo, The Last Years of the Kings of ISIN, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 54-72, 1959
Ishbi-Erra continued many of the cultic practices that had flourished in the preceding Ur III period. He continued acting out the sacred marriage
''Hieros gamos'', hieros (ἱερός) meaning "holy" or "sacred" and gamos (γάμος) meaning marriage, or Hierogamy (Greek , "holy marriage"), is a sacred marriage that plays out between a god and a goddess, especially when enacted in a symb ...
ritual each year. During this ritual, the king played the part of the mortal Dumuzi, and he had sex with a priestess who represented the goddess of love and war, Inanna
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
(also known as Ishtar). This was thought to strengthen the king's relationship to the gods, which would then bring stability and prosperity on the entire country.
The Isin kings continued also the practice of appointing their daughters official priestesses of the moon god of Ur.
The literature of the period also continued in the line of the Ur III traditions when the Isin dynasty was first begun. For example, the royal hymn, a genre started in the preceding millennium, was continued. Many royal hymns written for the Isin rulers mirrored the themes, structure, and language of the Ur ones. Sometimes the hymns were written in the first person of a king's voice; other times, they were pleas of ordinary citizens meant for the ears of a king (sometimes an already dead one).
It was during this period that the Sumerian King List attained its final form, though it used many much earlier sources. The very compilation of the List seems to lead up to the Isin Dynasty itself, which would give it much legitimacy in the minds of the people because the dynasty would then be linked to earlier (albeit sometimes legendary) kings.M. B. Rowton, The Date of the Sumerian King List, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 156-162, 1960
See also
* Cities of the Ancient Near EastReferences
Further reading
*Vaughn Emerson Crawford, Sumerian economic texts from the first dynasty of Isin, Yale University Press, 1954 *Frayne, D. R, (1998): New light on the reign of Išme-Dagan, ZA 88, 6-44 *Goetze, A. (1965): Date formula of Iddin-Dagān of Isin, JCS 19, 56 *Barthel Hrouda, Isan Bahriyat I. D. Ergebnisse d. Ausgrabungen 1973–1974 (Veroffentlichungen der Kommission zur Erschliessung von Keilschrifttexten), In Kommission bei der C.H. Beck, 1977, *Barthel Hrouda, Isin, Isan Bahriyat II: Die Ergebnisse der Ausgrabungen 1975–1978 (Veroffentlichungen der Kommission zur Erschliessung von Keilschrifttexten), In Kommission bei der C.H. Beck, 1981, *Barthel Hrouda, Isin, Isan Bahriyat III: Die Ergebnisse der Ausgrabungen 1983–1984 (Veroffentlichungen der Kommission zur Erschliessung von Keilschrifttexten), In Kommission bei C.H. Beck, 1987, *Barthel Hrouda, Isin, Isan Bahriyat IV: Die Ergebnisse der Ausgrabungen, 1986–1989 (Veroffentlichungen der Kommission zur Erschliessung von Keilschrifttexten), In Kommission bei C.H. Beck, 1992, *Kaniuth, Kai. "18. Isin in the Kassite Period". Volume 2 Karduniaš. Babylonia under the Kassites 2, edited by Alexa Bartelmus and Katja Sternitzke, Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter, 2017, pp. 492-507 *M. van de Mieroop, Crafts in the Early Isin Period: A Study of the Isin Craft Archive from the Reigns of Isbi-Erra and Su-Illisu, Peeters Publishers, 1987, *Wilcke, C., Edzard, D. O., Walker, C., Odzuck, S., & Sommerfeld, W. (2018). Keilschrifttexte aus Isin-Išān Baḥrīyāt: Ergebnisse der Ausgrabungen der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft unter der Schirmherrschaft der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. Bayerische Akademie d. Wissenschaften.External links
Archaeological Site Photographs of Isin at Oriental Institute
Edmund L. Andrews.
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
, May 23, 2003.
{{Authority control
States and territories established in the 20th century BC
States and territories disestablished in the 18th century BC
1924 archaeological discoveries
Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate
Archaeological sites in Iraq
Former populated places in Iraq
Sumerian cities
Isin-Larsa period
City-states
Former kingdoms