Irsee Abbey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Irsee Abbey, also the Imperial Abbey of Irsee (german: Reichsabtei Irsee), was a
 According to tradition, the monastery, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, was founded in 1182 by Margrave Heinrich von Ursin-Ronsberg, to house a community that had grown up around a local hermit. The monastery was first established at the long-abandoned Burg Ursin, the margrave's ancestral castle, where St. Stephen Church's cemetery is now located. A few years later, the monks headed by their first abbot Cuomo, decided to build a new monastery in the valley below where water was more readily available. The original name Ursin or Ursinium was eventually changed to Irsee.
The small abbey's community averaged 6 monks during its first century of existence, but this number was reduced to a single monk at one time during the troubled 14th century when Irsee came close to collapse due to poor harvest, famine, war and excessive expenses by pleasure-loving abbots. It was saved only by the intervention in 1373 of Anna von Ellerbach, the second founder, sister of the Bishop of Augsburg, and her appointee, abbot Conrad III, known for his extreme frugality. Prosperity was restored within 20 years and during the late Middle Ages, Irsee Abbey had become one of the major abbeys in the diocese of Augsburg.
The abbey was nearly obliterated during the German Peasants' War and again during the
According to tradition, the monastery, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, was founded in 1182 by Margrave Heinrich von Ursin-Ronsberg, to house a community that had grown up around a local hermit. The monastery was first established at the long-abandoned Burg Ursin, the margrave's ancestral castle, where St. Stephen Church's cemetery is now located. A few years later, the monks headed by their first abbot Cuomo, decided to build a new monastery in the valley below where water was more readily available. The original name Ursin or Ursinium was eventually changed to Irsee.
The small abbey's community averaged 6 monks during its first century of existence, but this number was reduced to a single monk at one time during the troubled 14th century when Irsee came close to collapse due to poor harvest, famine, war and excessive expenses by pleasure-loving abbots. It was saved only by the intervention in 1373 of Anna von Ellerbach, the second founder, sister of the Bishop of Augsburg, and her appointee, abbot Conrad III, known for his extreme frugality. Prosperity was restored within 20 years and during the late Middle Ages, Irsee Abbey had become one of the major abbeys in the diocese of Augsburg.
The abbey was nearly obliterated during the German Peasants' War and again during the
 As an imperial abbey Irsee enjoyed
As an imperial abbey Irsee enjoyed 
 The abbey celebrated the 600th anniversary of its foundation in 1782 but its prosperity soon came to a brutal end in the aftermath of the French Revolution and Napoleonic campaigns. War refugees sought refuge and accommodation in the abbey, which also suffered heavily from military marches, billeting and heavy war contributions. Finally, in the course of the German mediatisation of 1802-1803, Irsee, like all the other Imperial abbeys, lost its independence and was dissolved. On 3 September 1802, soldiers of the
The abbey celebrated the 600th anniversary of its foundation in 1782 but its prosperity soon came to a brutal end in the aftermath of the French Revolution and Napoleonic campaigns. War refugees sought refuge and accommodation in the abbey, which also suffered heavily from military marches, billeting and heavy war contributions. Finally, in the course of the German mediatisation of 1802-1803, Irsee, like all the other Imperial abbeys, lost its independence and was dissolved. On 3 September 1802, soldiers of the
Kloster Irsee Training Centre
*
Irsee Abbey
in the ''Abbeys in Bavaria'' database
File:Abbey Irsee 101.JPG, Irsee Abbey
File:IKBLuftbild.jpg, Aerial overview
File:Abbey Irsee 102.JPG, Nave
File:Abbey Irsee 104.JPG, Main altar
File:Abbey Irsee 106.JPG, Decorations in front of the Main altar
File:Abbey Irsee 109.JPG, Statue of
{{Authority control
Benedictine monasteries in Germany
Monasteries in Bavaria
Imperial abbeys disestablished in 1802–03
1180s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1186 establishments in Europe
Religious organizations established in the 1180s
Psychiatric hospitals in Germany
Hospitals established in 1849
Christian monasteries established in the 12th century
1849 establishments in Bavaria
1694 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
Medical and health organisations based in Bavaria
Buildings and structures in Ostallgäu
Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
abbey located at Irsee
Irsee is a village and municipality in the district of Ostallgäu in Bavaria in Germany.
The centre of the village is dominated by a monastery (Klosterbau), dedicated to the Virgin Mary The monastery was founded in 1186 by Margrave Henry of Ron ...
near Kaufbeuren
Kaufbeuren (; Bavarian: ''Kaufbeiren'') is an independent town in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' of Swabia, Bavaria. The town is an enclave within the district of Ostallgäu.
Districts
Kaufbeuren consists of nine districts:
* Kaufbeuren (town core i ...
in Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
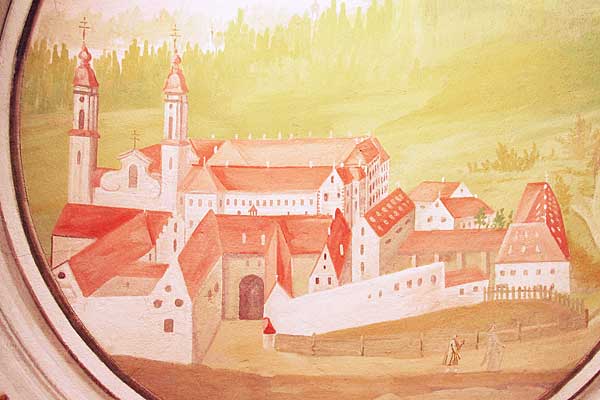
. The self-ruling imperial abbey was secularized in the course of the German mediatization of 1802–1803 and its territory annexed to Bavaria. The buildings of the former abbey now house a conference and training centre for Bavarian Swabia.
History
Abbey
 According to tradition, the monastery, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, was founded in 1182 by Margrave Heinrich von Ursin-Ronsberg, to house a community that had grown up around a local hermit. The monastery was first established at the long-abandoned Burg Ursin, the margrave's ancestral castle, where St. Stephen Church's cemetery is now located. A few years later, the monks headed by their first abbot Cuomo, decided to build a new monastery in the valley below where water was more readily available. The original name Ursin or Ursinium was eventually changed to Irsee.
The small abbey's community averaged 6 monks during its first century of existence, but this number was reduced to a single monk at one time during the troubled 14th century when Irsee came close to collapse due to poor harvest, famine, war and excessive expenses by pleasure-loving abbots. It was saved only by the intervention in 1373 of Anna von Ellerbach, the second founder, sister of the Bishop of Augsburg, and her appointee, abbot Conrad III, known for his extreme frugality. Prosperity was restored within 20 years and during the late Middle Ages, Irsee Abbey had become one of the major abbeys in the diocese of Augsburg.
The abbey was nearly obliterated during the German Peasants' War and again during the
According to tradition, the monastery, dedicated to the Virgin Mary, was founded in 1182 by Margrave Heinrich von Ursin-Ronsberg, to house a community that had grown up around a local hermit. The monastery was first established at the long-abandoned Burg Ursin, the margrave's ancestral castle, where St. Stephen Church's cemetery is now located. A few years later, the monks headed by their first abbot Cuomo, decided to build a new monastery in the valley below where water was more readily available. The original name Ursin or Ursinium was eventually changed to Irsee.
The small abbey's community averaged 6 monks during its first century of existence, but this number was reduced to a single monk at one time during the troubled 14th century when Irsee came close to collapse due to poor harvest, famine, war and excessive expenses by pleasure-loving abbots. It was saved only by the intervention in 1373 of Anna von Ellerbach, the second founder, sister of the Bishop of Augsburg, and her appointee, abbot Conrad III, known for his extreme frugality. Prosperity was restored within 20 years and during the late Middle Ages, Irsee Abbey had become one of the major abbeys in the diocese of Augsburg.
The abbey was nearly obliterated during the German Peasants' War and again during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
. It was ravaged no less than five times by Swedish troops and then devastated by Imperial Croat troops and French troops. Its library as well as its archives were destroyed. For many years the monastery was so destitute that it could not accommodate even half a dozen monks. The abbey was finally able to put itself back on a stable footing in the later 17th century.
Imperial Abbey
Irsee recuperated quickly but in 1662 the powerful prince-abbot ofKempten
Kempten (, (Swabian German: )) is the largest town of Allgäu, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. The population was about 68,000 in 2016. The area was possibly settled originally by Celts, but was later taken over by the Romans, who called the town ' ...
purchased the right of advocacy (German: ''Vogteirechte''), which limited the autonomy of the abbey. In 1694, following the election of the energetic Romanus Köpfle as the new abbot in 1692, Irsee succeeded in obtaining the status of an Imperial abbey
Princely abbeys (german: Fürstabtei, ''Fürststift'') and Imperial abbeys (german: Reichsabtei, ''Reichskloster'', ''Reichsstift'', ''Reichsgotthaus'') were religious establishments within the Holy Roman Empire which enjoyed the status of impe ...
, which it will keep until it was dissolved in 1802.
 As an imperial abbey Irsee enjoyed
As an imperial abbey Irsee enjoyed Imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
. While its small territory covered 118 square kilometers and 22 villages and hamlets, its abbot ruled over 3200 to 4200 subjects. The abbot had seat and voice on the Bench of the Swabian prelates at the Imperial Diet. In case of a declared war, the abbot was required by the Swabian Circle to supply a contingent of one officer and 61 infantrymen.
In 1699 the dilapidated church tower collapsed and damaged the choir of the old Romanesque church built in 1194, which prompted Abbot Romanus to undertake the revamping of the church and monastery buildings. The construction project was greatly expanded by its successor, abbot Willibald Grindl and the monastery buildings were completely rebuilt. The plans have been attributed to Magnus Remy, an Irsee monk, who also created many of the paintings in the church. During the long rule of Abbot Bernard Beck (1731-1765), Irsee became a center of intellectual and scientific life in Swabia and beyond. Irsee's natural history collection with its instruments of mathematics and physics were famous.

 The abbey celebrated the 600th anniversary of its foundation in 1782 but its prosperity soon came to a brutal end in the aftermath of the French Revolution and Napoleonic campaigns. War refugees sought refuge and accommodation in the abbey, which also suffered heavily from military marches, billeting and heavy war contributions. Finally, in the course of the German mediatisation of 1802-1803, Irsee, like all the other Imperial abbeys, lost its independence and was dissolved. On 3 September 1802, soldiers of the
The abbey celebrated the 600th anniversary of its foundation in 1782 but its prosperity soon came to a brutal end in the aftermath of the French Revolution and Napoleonic campaigns. War refugees sought refuge and accommodation in the abbey, which also suffered heavily from military marches, billeting and heavy war contributions. Finally, in the course of the German mediatisation of 1802-1803, Irsee, like all the other Imperial abbeys, lost its independence and was dissolved. On 3 September 1802, soldiers of the Electorate of Bavaria
The Electorate of Bavaria (german: Kurfürstentum Bayern) was an independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
The Wittelsbach dynasty which ruled the Duchy of Ba ...
launched a "provisional military occupation" of Irsee and in 1803 the territory of the former abbey, including the villages of Irsee, Romatsried, Eggenthal, Baisweil, Lauchdorf, Ingenried, Schlingen, Ketterschwang, Rieden, Pforzen, Leinau and Mauerstetten, was absorbed into the Electorate, as were its 3221 inhabitants. The monastery's inventory was auctioned off. In 1833, the greater part of the library was moved to Metten Abbey
Metten Abbey, or St. Michael's Abbey at Metten (in German Abtei Metten or Kloster Metten) is a house of the Benedictine Order in Metten near Deggendorf, situated between the fringes of the Bavarian Forest and the valley of the Danube, in Bavaria i ...
.http://www.sueddeutscher-barock.ch/PDF_Bau/Irsee.pdf
Hospital
For many years the Bavarian authorities found no use for the former monastery complex. After 1849, the buildings served as an asylum and hospital for the mentally ill. Between 1939 and 1945 more than 2,000 patients, both adults and children, were transported by the then regime from Irsee and Kaufbeuren to death camps.Conference centre
In 1972 the hospital was wound up. The local authority of the district of Schwaben began the restoration of the buildings in 1974, which opened as the ''Schwäbische Tagungs- und Bildungszentrum Kloster Irsee'' ("Kloster Irsee Swabian Conference and Training Centre") in 1984.References
External links
* * *Kloster Irsee Training Centre
*
Irsee Abbey
in the ''Abbeys in Bavaria'' database
Images
Exterior
Interiors
Saint Roch
Roch (lived c. 1348 – 15/16 August 1376/79 (traditionally c. 1295 – 16 August 1327, also called Rock in English, is a Catholic saint, a confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he is especially invoked a ...
File:Abbey Irsee 130.JPG, Decoration on the vault
File:Abbey Irsee 132.JPG, Frescos on the vault
File:Abbey Irsee 120.JPG, Pulpit in the shape of a ship
File:Abbey Irsee 122.JPG, Decorations on the pulpit
File:Abbey Irsee 124.JPG, Decorations on the sounding board above the pulpit
File:Irsee Abbey. Carved side of Baroque church bench (c. 1725).jpg, Carved side of church bench