Irrigation In Israel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow
 In year 2000, the total fertile land was 2,788,000 km2 (689 million acres) and it was equipped with irrigation infrastructure worldwide. About 68% of this area is in Asia, 17% in the Americas, 9% in Europe, 5% in Africa and 1% in Oceania. The largest contiguous areas of high irrigation density are found in Northern and Eastern India and Pakistan along the Ganges and Indus rivers; in the Hai He, Huang He and Yangtze basins in China; along the Nile river in Egypt and Sudan; and in the Mississippi-Missouri river basin, the Southern Great Plains, and in parts of California in the United States. Smaller irrigation areas are spread across almost all populated parts of the world.
By 2012, the area of irrigated land had increased to an estimated total of 3,242,917 km2 (801 million acres), which is nearly the size of India. The irrigation of 20% of farming land accounts for the production of 40% of food production.
In year 2000, the total fertile land was 2,788,000 km2 (689 million acres) and it was equipped with irrigation infrastructure worldwide. About 68% of this area is in Asia, 17% in the Americas, 9% in Europe, 5% in Africa and 1% in Oceania. The largest contiguous areas of high irrigation density are found in Northern and Eastern India and Pakistan along the Ganges and Indus rivers; in the Hai He, Huang He and Yangtze basins in China; along the Nile river in Egypt and Sudan; and in the Mississippi-Missouri river basin, the Southern Great Plains, and in parts of California in the United States. Smaller irrigation areas are spread across almost all populated parts of the world.
By 2012, the area of irrigated land had increased to an estimated total of 3,242,917 km2 (801 million acres), which is nearly the size of India. The irrigation of 20% of farming land accounts for the production of 40% of food production.
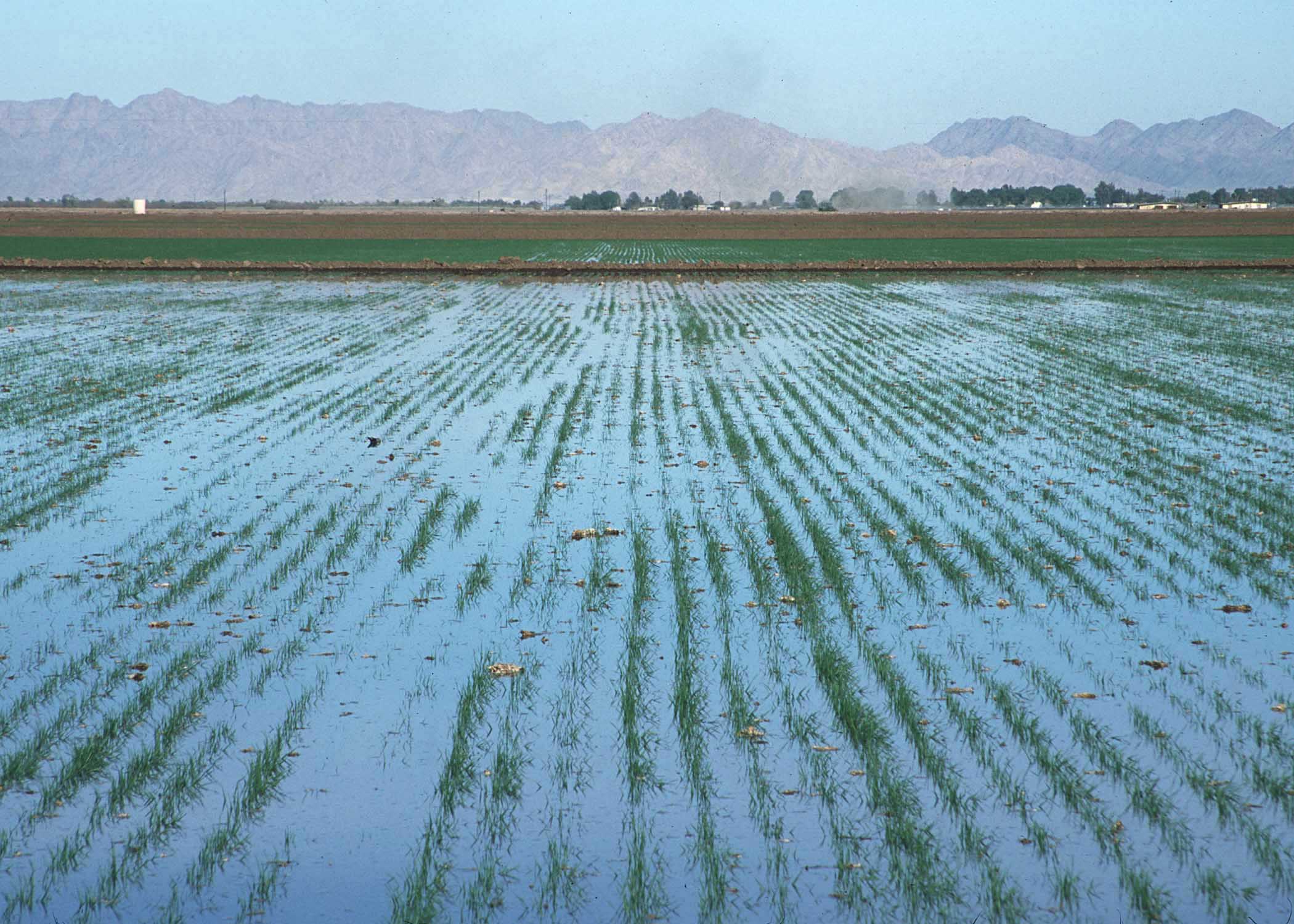 Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irrigation, is the oldest form of irrigation and has been in use for thousands of years. In ''surface'' (''furrow,'' ''flood'', or ''level basin'') irrigation systems, water moves across the surface of agricultural lands, in order to wet it and infiltrate into the soil. Water moves by following gravity or the slope of the land. Surface irrigation can be subdivided into furrow,'' border strip or basin irrigation''. It is often called ''flood irrigation'' when the irrigation results in flooding or near flooding of the cultivated land. Historically, surface irrigation is the most common method of irrigating agricultural land across most parts of the world. The water application efficiency of surface irrigation is typically lower than other forms of irrigation, due in part to the lack of control of applied depths. Surface irrigation involves a significantly lower capital cost and energy requirement than pressurised irrigation systems. Hence it is often the irrigation choice for developing nations, for low value crops and for large fields. Where water levels from the irrigation source permit, the levels are controlled by dikes, usually plugged by soil. This is often seen in terraced rice fields (rice paddies), where the method is used to flood or control the level of water in each distinct field. In some cases, the water is pumped, or lifted by human or animal power to the level of the land.
Surface irrigation is even used to water urban gardens in certain areas, for example, in and around Phoenix, Arizona. The irrigated area is surrounded by a berm and the water is delivered according to a schedule set by a local irrigation district.
A special form of irrigation using surface water is
Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irrigation, is the oldest form of irrigation and has been in use for thousands of years. In ''surface'' (''furrow,'' ''flood'', or ''level basin'') irrigation systems, water moves across the surface of agricultural lands, in order to wet it and infiltrate into the soil. Water moves by following gravity or the slope of the land. Surface irrigation can be subdivided into furrow,'' border strip or basin irrigation''. It is often called ''flood irrigation'' when the irrigation results in flooding or near flooding of the cultivated land. Historically, surface irrigation is the most common method of irrigating agricultural land across most parts of the world. The water application efficiency of surface irrigation is typically lower than other forms of irrigation, due in part to the lack of control of applied depths. Surface irrigation involves a significantly lower capital cost and energy requirement than pressurised irrigation systems. Hence it is often the irrigation choice for developing nations, for low value crops and for large fields. Where water levels from the irrigation source permit, the levels are controlled by dikes, usually plugged by soil. This is often seen in terraced rice fields (rice paddies), where the method is used to flood or control the level of water in each distinct field. In some cases, the water is pumped, or lifted by human or animal power to the level of the land.
Surface irrigation is even used to water urban gardens in certain areas, for example, in and around Phoenix, Arizona. The irrigated area is surrounded by a berm and the water is delivered according to a schedule set by a local irrigation district.
A special form of irrigation using surface water is
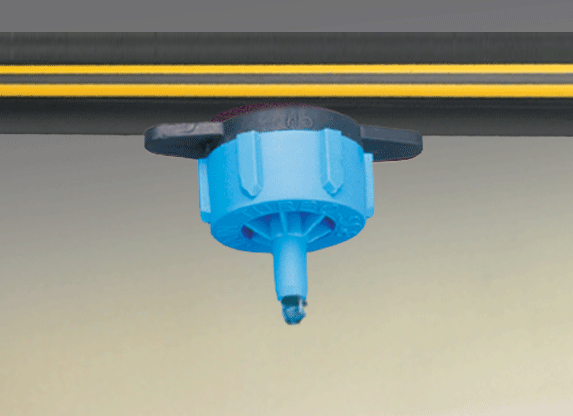 ''Micro-irrigation'', sometimes called localized irrigation, low volume irrigation, or trickle irrigation is a system where water is distributed under low pressure through a piped network, in a pre-determined pattern, and applied as a small discharge to each plant or adjacent to it. Traditional drip irrigation use individual emitters, subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), micro-spray or micro-sprinklers, and mini-bubbler irrigation all belong to this category of irrigation methods.
''Micro-irrigation'', sometimes called localized irrigation, low volume irrigation, or trickle irrigation is a system where water is distributed under low pressure through a piped network, in a pre-determined pattern, and applied as a small discharge to each plant or adjacent to it. Traditional drip irrigation use individual emitters, subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), micro-spray or micro-sprinklers, and mini-bubbler irrigation all belong to this category of irrigation methods.
 Drip (or micro) irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation, functions as its name suggests. In this system, water is delivered at or near the root zone of plants, one drop at a time. This method can be the most water-efficient method of irrigation, if managed properly; evaporation and runoff are minimized. The field water efficiency of drip irrigation is typically in the range of 80 to 90 percent when managed correctly.
In modern agriculture, drip irrigation is often combined with plastic mulch, further reducing evaporation, and is also the means of delivery of fertilizer. The process is known as ''
Drip (or micro) irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation, functions as its name suggests. In this system, water is delivered at or near the root zone of plants, one drop at a time. This method can be the most water-efficient method of irrigation, if managed properly; evaporation and runoff are minimized. The field water efficiency of drip irrigation is typically in the range of 80 to 90 percent when managed correctly.
In modern agriculture, drip irrigation is often combined with plastic mulch, further reducing evaporation, and is also the means of delivery of fertilizer. The process is known as ''

 In ''sprinkler'' or overhead irrigation, water is piped to one or more central locations within the field and distributed by overhead high-pressure sprinklers or guns. A system using sprinklers, sprays, or guns mounted overhead on permanently installed risers is often referred to as a ''solid-set'' irrigation system. Higher pressure sprinklers that rotate are called ''rotors'' and are driven by a ball drive, gear drive, or impact mechanism. Rotors can be designed to rotate in a full or partial circle. Guns are similar to rotors, except that they generally operate at very high pressures of 275 to 900 kPa (40 to 130 psi) and flows of 3 to 76 L/s (50 to 1200 US gal/min), usually with nozzle diameters in the range of 10 to 50 mm (0.5 to 1.9 in). Guns are used not only for irrigation, but also for industrial applications such as dust suppression and
In ''sprinkler'' or overhead irrigation, water is piped to one or more central locations within the field and distributed by overhead high-pressure sprinklers or guns. A system using sprinklers, sprays, or guns mounted overhead on permanently installed risers is often referred to as a ''solid-set'' irrigation system. Higher pressure sprinklers that rotate are called ''rotors'' and are driven by a ball drive, gear drive, or impact mechanism. Rotors can be designed to rotate in a full or partial circle. Guns are similar to rotors, except that they generally operate at very high pressures of 275 to 900 kPa (40 to 130 psi) and flows of 3 to 76 L/s (50 to 1200 US gal/min), usually with nozzle diameters in the range of 10 to 50 mm (0.5 to 1.9 in). Guns are used not only for irrigation, but also for industrial applications such as dust suppression and
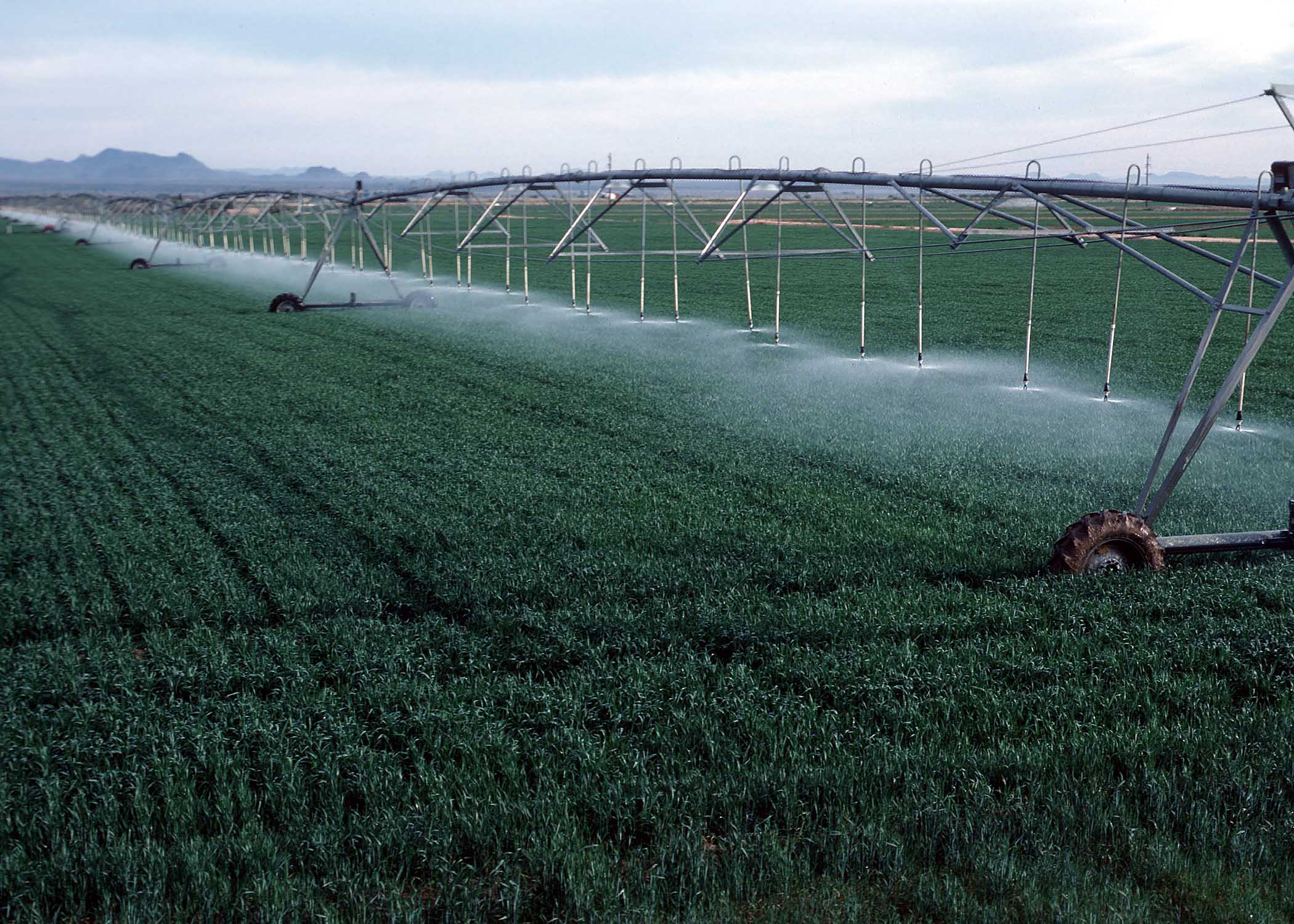




 Center pivot irrigation is a form of sprinkler irrigation utilising several segments of pipe (usually galvanized steel or aluminium) joined and supported by trusses, mounted on wheeled towers with sprinklers positioned along its length.
The system moves in a circular pattern and is fed with water from the pivot point at the center of the arc. These systems are found and used in all parts of the world and allow irrigation of all types of terrain. Newer systems have drop sprinkler heads as shown in the image that follows.
most center pivot systems have drops hanging from a U-shaped pipe attached at the top of the pipe with sprinkler heads that are positioned a few feet (at most) above the crop, thus limiting evaporative losses. Drops can also be used with drag hoses or bubblers that deposit the water directly on the ground between crops. Crops are often planted in a circle to conform to the center pivot. This type of system is known as LEPA (Low Energy Precision Application). Originally, most center pivots were water-powered. These were replaced by hydraulic systems ('' T-L Irrigation'') and electric-motor-driven systems (Reinke, Valley, Zimmatic). Many modern pivots feature
Center pivot irrigation is a form of sprinkler irrigation utilising several segments of pipe (usually galvanized steel or aluminium) joined and supported by trusses, mounted on wheeled towers with sprinklers positioned along its length.
The system moves in a circular pattern and is fed with water from the pivot point at the center of the arc. These systems are found and used in all parts of the world and allow irrigation of all types of terrain. Newer systems have drop sprinkler heads as shown in the image that follows.
most center pivot systems have drops hanging from a U-shaped pipe attached at the top of the pipe with sprinkler heads that are positioned a few feet (at most) above the crop, thus limiting evaporative losses. Drops can also be used with drag hoses or bubblers that deposit the water directly on the ground between crops. Crops are often planted in a circle to conform to the center pivot. This type of system is known as LEPA (Low Energy Precision Application). Originally, most center pivots were water-powered. These were replaced by hydraulic systems ('' T-L Irrigation'') and electric-motor-driven systems (Reinke, Valley, Zimmatic). Many modern pivots feature

/ref> Such problems include: * Ground
 Archaeological investigation has found evidence of irrigation in areas lacking sufficient natural rainfall to support crops for rainfed agriculture. Some of the earliest known use of the technology dates to the 6th millennium BC in Khuzistan in the south-west of present-day Iran. The site of
Archaeological investigation has found evidence of irrigation in areas lacking sufficient natural rainfall to support crops for rainfed agriculture. Some of the earliest known use of the technology dates to the 6th millennium BC in Khuzistan in the south-west of present-day Iran. The site of  The
The
 The oldest known hydraulic engineers of
The oldest known hydraulic engineers of
Center-pivot irrigation.jpg, upThe hub of a center-pivot irrigation system
Irrigation drip leaks.jpg, Leaks in micro-irrigation drip lines
Irrigated blueberries4046.jpg, Sprinkler irrigation of
International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID)
Irrigation
at the Water Quality Information Center, U.S. Department of Agriculture
AQUASTAT
FAO's global information system on water and agriculture {{Authority control Agricultural soil science Agronomy Environmental issues with water Land management Water management
 Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponics ...
, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
, suppress weed growth in grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residenc ...
, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation.
There are several methods of irrigation that differ in how water is supplied to plants. Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irrigation, is the oldest form of irrigation and has been in use for thousands of years. In sprinkler irrigation
Sprinkler may refer to:
* Irrigation sprinkler, a device for watering lawns or crops
* Fire sprinkler, a device for fire suppression
* Sprinkler (dance), a dance move
See also
*
* Feynman sprinkler, an experimental device and problem of physics ...
, water is piped to one or more central locations within the field and distributed by overhead high-pressure water devices. Micro-irrigation is a system that distributes water under low pressure through a piped network and applies it as a small discharge to each plant. Micro-irrigation uses less pressure and water flow than sprinkler irrigation. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone of plants. Subirrigation has been used in field crops in areas with high water tables for many years. It involves artificially raising the water table to moisten the soil below the root zone of plants.
Irrigation water can come from groundwater (extracted from springs
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
or by using wells), from surface water (withdrawn from rivers, lakes or reservoirs) or from non-conventional sources like treated wastewater
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environmen ...
, desalinated water, drainage water, or fog collection. Irrigation can be supplementary to rainfall, which is common in many parts of the world as rainfed agriculture, or it can be full irrigation, where crops rarely rely on any contribution from rainfall. Full irrigation is less common and only occurs in arid landscapes with very low rainfall or when crops are grown in semi-arid areas outside of rainy seasons.
The environmental effects of irrigation relate to the changes in quantity and quality of soil and water as a result of irrigation and the subsequent effects on natural and social conditions in river basins and downstream of an irrigation scheme. The effects stem from the altered hydrological conditions caused by the installation and operation of the irrigation scheme. Amongst some of these problems is depletion of underground aquifers through overdrafting. Soil can be over-irrigated due to poor distribution uniformity or management wastes
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor Value (economics), economic v ...
water, chemicals, and may lead to water pollution. Over-irrigation can cause deep drainage from rising water tables that can lead to problems of irrigation salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
requiring watertable control by some form of subsurface land drainage.
Extent
Global overview
The scale of irrigation increased dramatically over the 20th century. In 1800, 8 million hectares globally were irrigated, in 1950, 94 million hectares, and in 1990, 235 million hectares. By 1990, 30% of the global food production came from irrigated land. Irrigation techniques across the globe includes canals redirecting surface water, Peterson 2016 groundwater pumping, and diverting water from dams. National governments lead most irrigation schemes within their borders, but private investors and other nations, especially the United States,China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and European countries like the United Kingdom, McNeill 2000 pp.169-170. also fund and organize some schemes within other nations.
Irrigation enables the production of more crops, especially commodity crops in areas which otherwise could not support them. Countries frequently invested in irrigation to increase wheat, rice, or cotton production, often with the overarching goal of increasing self-sufficiency.Water sources
Groundwater and surface water
Irrigation water can come from groundwater (extracted fromsprings
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
or by using wells), from surface water (withdrawn from rivers, lakes or reservoirs) or from non-conventional sources like treated wastewater
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environmen ...
, desalinated water, drainage water, or fog collection.
While floodwater
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrolog ...
harvesting belongs to the accepted irrigation methods, rainwater harvesting is usually not considered as a form of irrigation. Rainwater harvesting is the collection of runoff water from roofs or unused land and the concentration of this.
Treated or untreated wastewater
Other sources
Irrigation water can also come from non-conventional sources liketreated wastewater
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environmen ...
, desalinated water, drainage water, or fog collection.
In countries where humid air sweeps through at night, water can be obtained by condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
onto cold surfaces. This is practiced in the vineyards at Lanzarote
Lanzarote (, , ) is a Spanish island, the easternmost of the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean. It is located approximately off the north coast of Africa and from the Iberian Peninsula. Covering , Lanzarote is the fourth-largest of the i ...
using stones to condense water. Fog collectors are also made of canvas or foil sheets. Using condensate from air conditioning units as a water source is also becoming more popular in large urban areas.
a Glasgow-based startup has helped a farmer in Scotland to establish edible saltmarsh crops irrigated with sea water. An acre of previously marginal land has been put under cultivation to grow samphire, sea blite
__NOTOC__
''Suaeda'' is a genus of plants also known as seepweeds and sea-blites. Most species are confined to saline or alkaline soil habitats, such as coastal salt-flats and tidal wetlands. Many species have thick, succulent leaves, a character ...
, and sea aster
''Tripolium pannonicum'', called sea aster or seashore aster and often known by the synonyms ''Aster tripolium'' or ''Aster pannonicus'', is a flowering plant, native to Eurasia and northern Africa, that is confined in its distribution to salt ma ...
; these plants yield a higher profit than potatoes. The land is flood irrigated twice a day to simulate tidal flooding; the water is pumped from the sea using wind power. Additional benefits are soil remediation and carbon sequestration.
Competition for water resources
Until 1960s, there were fewer than half the current number of people on the planet. People were not as wealthy as today, consumed fewer calories and ate less meat, so less water was needed to produce their food. They required a third of the volume of water we presently take from rivers. Today, the competition forwater resources
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slight ...
is much more intense. This is because there are now more than seven billion people on the planet, increasing the likelihood of overconsumption of food produced by water-thirsty animal agriculture and intensive farming practices, and there is increasing competition for water from industry, urbanisation and biofuel crops
Energy crops are low-cost and low-maintenance crops grown solely for energy production by combustion (not for food). The crops are processed into solid, liquid or gaseous fuels, such as pellets, bioethanol or biogas. The fuels are burned to g ...
. Farmers will have to strive to increase productivity to meet growing demands for food, while industry and cities find ways to use water more efficiently.
Successful agriculture is dependent upon farmers having sufficient access to water. However, water scarcity is already a critical constraint to farming in many parts of the world.
Irrigation methods
There are several methods of irrigation. They vary in how the water is supplied to the plants. The goal is to apply the water to the plants as uniformly as possible, so that each plant has the amount of water it needs, neither too much nor too little. Irrigation can also be understood whether it is ''supplementary'' to rainfall as happens in many parts of the world, or whether it is full'' irrigation' whereby crops rarely depend on any contribution from rainfall. Full irrigation is less common and only happens in arid landscapes experiencing very low rainfall or when crops are grown in semi-arid areas outside of any rainy seasons.Surface irrigation
spate irrigation
Surface irrigation is where water is applied and distributed over the soil surface by gravity. It is by far the most common form of irrigation throughout the world and has been practiced in many areas virtually unchanged for thousands of years.
S ...
, also called floodwater harvesting. In case of a flood (spate), water is diverted to normally dry river beds (wadis) using a network of dams, gates and channels and spread over large areas. The moisture stored in the soil will be used thereafter to grow crops. Spate irrigation areas are in particular located in semi-arid or arid, mountainous regions.
Micro-irrigation
 ''Micro-irrigation'', sometimes called localized irrigation, low volume irrigation, or trickle irrigation is a system where water is distributed under low pressure through a piped network, in a pre-determined pattern, and applied as a small discharge to each plant or adjacent to it. Traditional drip irrigation use individual emitters, subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), micro-spray or micro-sprinklers, and mini-bubbler irrigation all belong to this category of irrigation methods.
''Micro-irrigation'', sometimes called localized irrigation, low volume irrigation, or trickle irrigation is a system where water is distributed under low pressure through a piped network, in a pre-determined pattern, and applied as a small discharge to each plant or adjacent to it. Traditional drip irrigation use individual emitters, subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), micro-spray or micro-sprinklers, and mini-bubbler irrigation all belong to this category of irrigation methods.
Drip irrigation
 Drip (or micro) irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation, functions as its name suggests. In this system, water is delivered at or near the root zone of plants, one drop at a time. This method can be the most water-efficient method of irrigation, if managed properly; evaporation and runoff are minimized. The field water efficiency of drip irrigation is typically in the range of 80 to 90 percent when managed correctly.
In modern agriculture, drip irrigation is often combined with plastic mulch, further reducing evaporation, and is also the means of delivery of fertilizer. The process is known as ''
Drip (or micro) irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation, functions as its name suggests. In this system, water is delivered at or near the root zone of plants, one drop at a time. This method can be the most water-efficient method of irrigation, if managed properly; evaporation and runoff are minimized. The field water efficiency of drip irrigation is typically in the range of 80 to 90 percent when managed correctly.
In modern agriculture, drip irrigation is often combined with plastic mulch, further reducing evaporation, and is also the means of delivery of fertilizer. The process is known as ''fertigation
Fertigation is the injection of fertilizers, used for soil amendments, water amendments and other water-soluble products into an irrigation system.
Fertigation is related to chemigation, the injection of chemicals into an irrigation system. The ...
''.
Deep percolation, where water moves below the root zone, can occur if a drip system is operated for too long or if the delivery rate is too high. Drip irrigation methods range from very high-tech and computerized to low-tech and labor-intensive. Lower water pressures are usually needed than for most other types of systems, with the exception of low energy center pivot systems and surface irrigation systems, and the system can be designed for uniformity throughout a field or for precise water delivery to individual plants in a landscape containing a mix of plant species. Although it is difficult to regulate pressure on steep slopes, pressure compensating emitters are available, so the field does not have to be level. High-tech solutions involve precisely calibrated emitters located along lines of tubing that extend from a computerized set of valves.
Sprinkler irrigation

logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply chain ...
.
Sprinklers can also be mounted on moving platforms connected to the water source by a hose. Automatically moving wheeled systems known as ''traveling sprinklers'' may irrigate areas such as small farms, sports fields, parks, pastures, and cemeteries unattended. Most of these use a length of polyethylene tubing wound on a steel drum. As the tubing is wound on the drum powered by the irrigation water or a small gas engine, the sprinkler is pulled across the field. When the sprinkler arrives back at the reel the system shuts off. This type of system is known to most people as a "waterreel" traveling irrigation sprinkler and they are used extensively for dust suppression, irrigation, and land application of waste water.
Other travelers use a flat rubber hose that is dragged along behind while the sprinkler platform is pulled by a cable.
Center pivot


 Center pivot irrigation is a form of sprinkler irrigation utilising several segments of pipe (usually galvanized steel or aluminium) joined and supported by trusses, mounted on wheeled towers with sprinklers positioned along its length.
The system moves in a circular pattern and is fed with water from the pivot point at the center of the arc. These systems are found and used in all parts of the world and allow irrigation of all types of terrain. Newer systems have drop sprinkler heads as shown in the image that follows.
most center pivot systems have drops hanging from a U-shaped pipe attached at the top of the pipe with sprinkler heads that are positioned a few feet (at most) above the crop, thus limiting evaporative losses. Drops can also be used with drag hoses or bubblers that deposit the water directly on the ground between crops. Crops are often planted in a circle to conform to the center pivot. This type of system is known as LEPA (Low Energy Precision Application). Originally, most center pivots were water-powered. These were replaced by hydraulic systems ('' T-L Irrigation'') and electric-motor-driven systems (Reinke, Valley, Zimmatic). Many modern pivots feature
Center pivot irrigation is a form of sprinkler irrigation utilising several segments of pipe (usually galvanized steel or aluminium) joined and supported by trusses, mounted on wheeled towers with sprinklers positioned along its length.
The system moves in a circular pattern and is fed with water from the pivot point at the center of the arc. These systems are found and used in all parts of the world and allow irrigation of all types of terrain. Newer systems have drop sprinkler heads as shown in the image that follows.
most center pivot systems have drops hanging from a U-shaped pipe attached at the top of the pipe with sprinkler heads that are positioned a few feet (at most) above the crop, thus limiting evaporative losses. Drops can also be used with drag hoses or bubblers that deposit the water directly on the ground between crops. Crops are often planted in a circle to conform to the center pivot. This type of system is known as LEPA (Low Energy Precision Application). Originally, most center pivots were water-powered. These were replaced by hydraulic systems ('' T-L Irrigation'') and electric-motor-driven systems (Reinke, Valley, Zimmatic). Many modern pivots feature GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
devices.
Irrigation by lateral move (side roll, wheel line, wheelmove)
A ''series of pipes, each with a wheel'' of about 1.5 m diameter permanently affixed to its midpoint, and sprinklers along its length, are coupled together. Water is supplied at one end using a large hose. After sufficient irrigation has been applied to one strip of the field, the hose is removed, the water drained from the system, and the assembly rolled either by hand or with a purpose-built mechanism, so that the sprinklers are moved to a different position across the field. The hose is reconnected. The process is repeated in a pattern until the whole field has been irrigated. This system is less expensive to install than a center pivot, but much more labor-intensive to operate – it does not travel automatically across the field: it applies water in a stationary strip, must be drained, and then rolled to a new strip. Most systems use 100 or 130 mm (4 or 5 inch) diameter aluminum pipe. The pipe doubles both as water transport and as an axle for rotating all the wheels. A drive system (often found near the centre of the wheel line) rotates the clamped-together pipe sections as a single axle, rolling the whole wheel line. Manual adjustment of individual wheel positions may be necessary if the system becomes misaligned. Wheel line systems are limited in the amount of water they can carry, and limited in the height of crops that can be irrigated. One useful feature of a lateral move system is that it consists of sections that can be easily disconnected, adapting to field shape as the line is moved. They are most often used for small, rectilinear, or oddly-shaped fields, hilly or mountainous regions, or in regions where labor is inexpensive.Lawn sprinkler systems
A lawn sprinkler system is permanently installed, as opposed to a hose-end sprinkler, which is portable. Sprinkler systems are installed in residential lawns, in commercial landscapes, for churches and schools, in public parks and cemeteries, and on golf courses. Most of the components of these irrigation systems are hidden under ground, since aesthetics are important in a landscape. A typical lawn sprinkler system will consist of one or more zones, limited in size by the capacity of the water source. Each zone will cover a designated portion of the landscape. Sections of the landscape will usually be divided by microclimate, type of plant material, and type of irrigation equipment. A landscape irrigation system may also include zones containing drip irrigation, bubblers, or other types of equipment besides sprinklers. Although manual systems are still used, most lawn sprinkler systems may be operated automatically using anirrigation controller
An irrigation controller is a device to operate automatic irrigation systems such as lawn sprinklers and drip irrigation systems. Most controllers have a means of setting the frequency of irrigation, the start time, and the duration of watering. ...
, sometimes called a clock or timer. Most automatic systems employ electric solenoid valves. Each zone has one or more of these valves that are wired to the controller. When the controller sends power to the valve, the valve opens, allowing water to flow to the sprinklers in that zone.
There are two main types of sprinklers used in lawn irrigation, pop-up spray heads and rotors. Spray heads have a fixed spray pattern, while rotors have one or more streams that rotate. Spray heads are used to cover smaller areas, while rotors are used for larger areas. Golf course rotors are sometimes so large that a single sprinkler is combined with a valve and called a 'valve in head'. When used in a turf area, the sprinklers are installed with the top of the head flush with the ground surface. When the system is pressurized, the head will pop up out of the ground and water the desired area until the valve closes and shuts off that zone. Once there is no more pressure in the lateral line, the sprinkler head will retract back into the ground. In flower beds or shrub areas, sprinklers may be mounted on above ground risers or even taller pop-up sprinklers may be used and installed flush as in a lawn area.

Hose-end sprinklers
There are many types of hose-end sprinklers. Many of them are smaller versions of larger agricultural and landscape sprinklers, sized to work with a typical garden hose. Some have a spiked base allowing them to be temporarily stuck in the ground, while others have a sled base designed to be dragged while attached to the hose.Subirrigation
Subirrigation has been used for many years in field crops in areas with high water tables. It is a method of artificially raising the water table to allow the soil to be moistened from below the plants' root zone. Often those systems are located on permanent grasslands in lowlands or river valleys and combined with drainage infrastructure. A system of pumping stations, canals, weirs and gates allows it to increase or decrease the water level in a network of ditches and thereby control the water table. Subirrigation is also used in the commercialgreenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
production, usually for potted plants. Water is delivered from below, absorbed by upwards, and the excess collected for recycling. Typically, a solution of water and nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s floods a container or flows through a trough for a short period of time, 10–20 minutes, and is then pumped back into a holding tank for reuse. Sub-irrigation in greenhouses requires fairly sophisticated, expensive equipment and management. Advantages are water and nutrient conservation, and labor savings through reduced system maintenance and automation. It is similar in principle and action to subsurface basin irrigation.
Another type of subirrigation is the self-watering container, also known as a sub-irrigated planter. This consists of a planter suspended over a reservoir with some type of wicking material such as a polyester rope. The water is drawn up the wick through capillary action. A similar technique is the wicking bed; this too uses capillary action.
Efficiency
Modern irrigation methods are efficient enough to supply the entire field uniformly with water, so that each plant has the amount of water it needs, neither too much nor too little. Water use efficiency in the field can be determined as follows: * Field Water Efficiency (%) = (Water Transpired by Crop ÷ Water Applied to Field) x 100 Increased irrigation efficiency has a number of positive outcomes for the farmer, the community and the wider environment. Low application efficiency infers that the amount of water applied to the field is in excess of the crop or field requirements. Increasing the application efficiency means that the amount of crop produced per unit of water increases. Improved efficiency may either be achieved by applying less water to an existing field or by using water more wisely thereby achieving higher yields in the same area of land. In some parts of the world, farmers are charged for irrigation water hence over-application has a direct financial cost to the farmer. Irrigation often requires pumping energy (either electricity or fossil fuel) to deliver water to the field or supply the correct operating pressure. Hence increased efficiency will reduce both the water cost and energy cost per unit of agricultural production. A reduction of water use on one field may mean that the farmer is able to irrigate a larger area of land, increasing total agricultural production. Low efficiency usually means that excess water is lost through seepage or runoff, both of which can result in loss of crop nutrients or pesticides with potential adverse impacts on the surrounding environment. Improving the efficiency of irrigation is usually achieved in one of two ways, either by improving the system design or by optimising the irrigation management. Improving system design includes conversion from one form of irrigation to another (e.g. from furrow to drip irrigation) and also through small changes in the current system (for example changing flowrates and operating pressures). Irrigation management refers to the scheduling of irrigation events and decisions around how much water is applied.Challenges
Environmental impacts
Negative impacts frequently accompany extensive irrigation. Some projects which diverted surface water for irrigation dried up the water sources, which led to a more extreme regional climate. McNeill 2000 pp.164-165. Projects that relied on groundwater and pumped too much from underground aquifers createdsubsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
and salinization. Salinization of irrigation water in turn damaged the crops and seeped into drinking water. Pests and pathogens also thrived in the irrigation canals or ponds full of still water, which created regional outbreaks of diseases like malaria and schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody s ...
. Governments also used irrigation schemes to encourage migration, especially of more desirable populations into an area. Visser 2018 Additionally, some of these large nationwide schemes failed to pay off at all, costing more than any benefit gained from increased crop yields. McNeill 2000
Overdrafting (depletion) of underground aquifers: In the mid-20th century, the advent of diesel and electric motors led to systems that could pump groundwater out of major aquifers faster than drainage basins could refill them. This can lead to permanent loss of aquifer capacity, decreased water quality, ground subsidence, and other problems. The future of food production in such areas as the North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is bord ...
, the Punjab region in India and Pakistan, and the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
of the US is threatened by this phenomenon.
Technical challenges
Irrigation schemes involve solving numerous engineering and economic problems while minimizing negative environmental consequences.ILRI, 1989, Effectiveness and Social/Environmental Impacts of Irrigation Projects: a Review. In: Annual Report 1988, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp. 18 – 34 . On line/ref> Such problems include: * Ground
subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
(e.g. New Orleans, Louisiana)
* Underirrigation or irrigation giving only just enough water for the plant (e.g. in drip line irrigation) gives poor soil salinity control which leads to increased soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the ...
with consequent buildup of toxic salts on soil surface in areas with high evaporation. This requires either leaching to remove these salts and a method of drainage to carry the salts away. When using drip lines, the leaching is best done regularly at certain intervals (with only a slight excess of water), so that the salt is flushed back under the plant's roots.
* Drainage front instability, also known as viscous fingering, where an unstable drainage front results in a pattern of fingers and viscous entrapped saturated zones.
* Overirrigation because of poor distribution uniformity or management wastes water, chemicals, and may lead to water pollution.
* Deep drainage (from over-irrigation) may result in rising water tables which in some instances will lead to problems of irrigation salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
requiring watertable control by some form of subsurface land drainage.
* Irrigation with saline
Saline may refer to:
* Saline (medicine), a liquid with salt content to match the human body
* Saline water, non-medicinal salt water
* Saline, a historical term (especially US) for a salt works or saltern
Places
* Saline, Calvados, a commune in ...
or high-sodium water may damage soil structure owing to the formation of alkaline soil.
* Clogging of filters: algae can clog filters, drip installations, and nozzles. Chlorination, algaecide, UV and ultrasonic methods can be used for algae control in irrigation systems.
*Complications in accurately measuring irrigation performance which changes over time and space using measures such as productivity, efficiency, equity and adequacy.
Social aspects
* Competition for surface water rights. * Assisting smallholders in sustainably and collectively managing irrigation technology and changes in technology.History
Ancient history
 Archaeological investigation has found evidence of irrigation in areas lacking sufficient natural rainfall to support crops for rainfed agriculture. Some of the earliest known use of the technology dates to the 6th millennium BC in Khuzistan in the south-west of present-day Iran. The site of
Archaeological investigation has found evidence of irrigation in areas lacking sufficient natural rainfall to support crops for rainfed agriculture. Some of the earliest known use of the technology dates to the 6th millennium BC in Khuzistan in the south-west of present-day Iran. The site of Choga Mami
Choga Mami is a Samarran settlement site in Diyala province in Eastern Iraq in the Mandali region. It shows the first canal irrigation in operation at about 6000 BCE.
The site, about 70 miles northeast of Baghdad, has been dated to the late 6th m ...
, in Iraq on the border with Iran, is believed to be the earliest to show the first canal irrigation in operation at about 6000 BCE.
Irrigation was used as a means of manipulation of water in the alluvial plains of the Indus valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
, the application of which is estimated to have begun around 4500 BC and drastically increased the size and prosperity of their agricultural settlements. The Indus Valley Civilization developed sophisticated irrigation and water-storage systems, including artificial reservoirs at Girnar dated to 3000 BCE, and an early canal irrigation system from 2600 BCE. Large-scale agriculture was practiced, with an extensive network of canals used for the purpose of irrigation.
Farmers in the Mesopotamian plain used irrigation from at least the third millennium BCE.
They developed ''perennial irrigation'', regularly watering crops throughout the growing season
A season is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology, and the amount of daylight. The growing season is that portion of the year in which local conditions (i.e. rainfall, temperature, daylight) permit normal plant growth. Whil ...
by coaxing water through a matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
of small channels formed in the field.
Ancient Egyptians practiced ''basin irrigation'' using the flooding of the Nile to inundate land plots which had been surrounded by dykes. The flood water remained until the fertile sediment had settled before the engineers returned the surplus to the watercourse.''p19'' Hill There is evidence of the ancient Egyptian pharaoh Amenemhet III in the twelfth dynasty (about 1800 BCE) using the natural lake of the Faiyum Oasis as a reservoir to store surpluses of water for use during dry seasons. The lake swelled annually from the flooding of the Nile.
 The
The Ancient Nubians
Nubians () (Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of the earliest cradles of c ...
developed a form of irrigation by using a waterwheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
-like device called a '' sakia''. Irrigation began in Nubia some time between the third and second millennia BCE. It largely depended upon the flood waters that would flow through the Nile River
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
and other rivers in what is now the Sudan.
In sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
irrigation reached the Niger River region cultures and civilizations by the first or second millennium BCE and was based on wet-season flooding and water harvesting.
Evidence of ''terrace irrigation'' occurs in pre-Columbian America, early Syria, India, and China. In the Zana Valley of the Andes Mountains
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the List of mountain ranges#Mountain ranges by length, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range i ...
in Peru, archaeologists have found remains of three irrigation canals radiocarbon-dated from the 4th millennium BCE
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
, the 3rd millennium BCE and the 9th century CE. These canals provide the earliest record of irrigation in the New World. Traces of a canal possibly dating from the 5th millennium BCE
The 5th millennium BC spanned the years 5000 BC to 4001 BC (c. 7 ka to c. 6 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological an ...
were found under the 4th-millennium canal.
Ancient Persia (modern day Iran) used irrigation as far back as the 6th millennium BCE
The 6th millennium BC spanned the years 6000 BC to 5001 BC (c. 8 ka to c. 7 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological an ...
to grow barley in areas with insufficient natural rainfall. The Qanats, developed in ancient Persia about 800 BCE, are among the oldest known irrigation methods still in use today. They are now found in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa. The system comprises a network of vertical wells and gently sloping tunnels driven into the sides of cliffs and of steep hills to tap groundwater. The noria, a water wheel with clay pots around the rim powered by the flow of the stream (or by animals where the water source was still), first came into use at about this time among Roman settlers in North Africa. By 150 BCE the pots were fitted with valves to allow smoother filling as they were forced into the water.
Sri Lanka
The irrigation works of ancientSri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, the earliest dating from about 300 BCE in the reign of King Pandukabhaya, and under continuous development for the next thousand years, were one of the most complex irrigation systems of the ancient world. In addition to underground canals, the Sinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language prima ...
were the first to build completely artificial reservoirs to store water. These reservoirs and canal systems were used primarily to irrigate paddy field
A paddy field is a flooded field (agriculture), field of arable land used for growing Aquatic plant, semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in sout ...
s, which require a lot of water to cultivate. Most of these irrigation systems still exist undamaged up to now, in Anuradhapura and Polonnaruwa, because of the advanced and precise engineering. The system was extensively restored and further extended during the reign of King Parakrama Bahu (1153–1186 CE).
China
 The oldest known hydraulic engineers of
The oldest known hydraulic engineers of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
were Sunshu Ao
Sunshu Ao (孫叔敖, c. 630 – c. 593 BCE) was a Chinese hydraulic engineer and politician. He was a court minister serving the administration of King Zhuang of Chu during the Eastern Zhou Dynasty. During his governmental career, Sunshu Ao was ...
(6th century BCE) of the Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
and Ximen Bao
Ximen Bao was a Chinese hydraulic engineer, philosopher, and politician. He was a government minister and court advisor to Marquis Wen of Wei (reigned 445–396 BC) during the Warring States period of ancient China. He was known as an early ratio ...
(5th century BCE) of the Warring States period, both of whom worked on large irrigation project
A project is any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular goal.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of even ...
s. In the Sichuan region belonging to the state of Qin
Qin () was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Traditionally dated to 897 BC, it took its origin in a reconquest of western lands previously lost to the Rong; its position at the western edge of Chinese civilization permitted ex ...
of ancient China, the Dujiangyan Irrigation System devised by the Qin Chinese hydrologist and irrigation engineer Li Bing was built in 256 BCE to irrigate a vast area of farmland that today still supplies water. By the 2nd century AD, during the Han Dynasty, the Chinese also used chain pump
The chain pump is type of a water pump in which several circular discs are positioned on an endless chain. One part of the chain dips into the water, and the chain runs through a tube, slightly bigger than the diameter of the discs. As the chain is ...
s which lifted water from a lower elevation to a higher one.Needham, Joseph (1986). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology, Part 2, Mechanical Engineering''. Taipei: Caves Books Ltd. Pages 344–346. These were powered by manual foot-pedal, hydraulic waterwheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
s, or rotating mechanical wheels pulled by oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 340–343. The water was used for public works, providing water for urban residential quarters and palace gardens, but mostly for irrigation of farmland canals and channels in the fields.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 33, 110.
Korea
Korea, Jang Yeong-sil, a Korean engineer of the Joseon Dynasty, under the active direction of the king,Sejong the Great
Sejong of Joseon (15 May 1397 – 8 April 1450), personal name Yi Do (Korean: 이도; Hanja: 李祹), widely known as Sejong the Great (Korean: 세종대왕; Hanja: 世宗大王), was the fourth ruler of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. Initial ...
, invented the world's first rain-gauge, ''uryanggye'' ( Korean: 우량계) in 1441. It was installed in irrigation tanks as part of a nationwide system to measure and collect rainfall for agricultural applications. With this instrument, planners and farmers could make better use of the information gathered in the survey.
North America
The earliest agricultural irrigation canal system known in the area of the present-day United States dates to between 1200 B.C. and 800 B.C. and was discovered by Desert Archaeology, Inc. in Marana, Arizona (adjacent to Tucson) in 2009. The irrigation-canal system predates the Hohokam culture by two thousand years and belongs to an unidentified culture. In North America, the Hohokam were the only culture known to rely on irrigation canals to water their crops, and their irrigation systems supported the largest population in the Southwest by AD 1300. The Hohokam constructed an assortment of simple canals combined with weirs in their various agricultural pursuits. Between the 7th and 14th centuries they built and maintained extensive irrigation networks along the lower Salt and middleGila River
The Gila River (; O'odham ima Keli Akimel or simply Akimel, Quechan: Haa Siʼil, Maricopa language: Xiil) is a tributary of the Colorado River flowing through New Mexico and Arizona in the United States. The river drains an arid watershed of n ...
s that rivaled the complexity of those used in the ancient Near East, Egypt, and China. These were constructed using relatively simple excavation tools, without the benefit of advanced engineering technologies, and achieved drops of a few feet per mile, balancing erosion and siltation. The Hohokam cultivated varieties of cotton, tobacco, maize, beans and squash, as well as harvesting an assortment of wild plants. Late in the Hohokam Chronological Sequence, they also used extensive dry-farming systems, primarily to grow agave for food and fiber. Their reliance on agricultural strategies based on canal irrigation, vital in their less-than-hospitable desert environment and arid climate, provided the basis for the aggregation of rural populations into stable urban centers.
South America
The oldest known irrigation canals in the Americas are in the desert of northern Peru in the Zaña valley near the hamlet of Nanchoc. The canals have been radiocarbon dated to at least 3400 B.C. and possibly as old as 4700 B.C. The canals at that time irrigated crops such as peanuts, squash, manioc, chenopods, a relative of Quinoa, and later maize.Modern history
In the 20th century, global anxiety specifically about the American cotton monopoly fueled many empirical irrigation projects: Britain began developing irrigation in India, theOttomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in Egypt, the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
in Algeria, the Portuguese in Angola, the Germans in Togo, and Soviets in Central Asia.
American West
Irrigated land in the United States increased from 300,000 acres in 1880 to 4.1 million in 1890, then to 7.3 million in 1900. Two thirds of this irrigation sources from groundwater or small ponds and reservoirs, while the other one third comes from large dams. One of the main attractions of irrigation in the West was its increased dependability compared to rainfall-watered agriculture in the East. Proponents argued that farmers with a dependable water supply could more easily get loans from bankers interested in this more predictable farming model. Most irrigation in theGreat Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
region derived from underground aquifers. Euro-American farmers who colonized the region in the 19th century tried to grow the commodity crops that they were used to, like wheat, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, and alfalfa
Alfalfa () (''Medicago sativa''), also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as w ...
, but rainfall stifled their growing capacity. Between the late 1800s and the 1930s, farmers used wind-powered pumps to draw groundwater. These windpumps had limited power, but the development of gas-powered pumps in the mid-1930s pushed wells deep into the Ogallala Aquifer. Farmers irrigated fields by laying pipes across the field with sprinklers at intervals, a labor-intensive process, until the advent of the center-pivot sprinkler after WWII, which made irrigation significantly easier. By the 1970s farmers drained the aquifer ten times faster than it could recharge, and by 1993 they had removed half of the accessible water.
Large-scale federal funding and intervention pushed through the majority of irrigation projects in the West, especially in California, Colorado, Arizona, and Nevada. At first, plans to increase irrigated farmland, largely by giving land to farmers and asking them to find water, failed across the board. Congress passed the Desert Land Act
The Desert Land Act is a United States federal law which was passed by the United States Congress on March 3, 1877, to encourage and promote the economic development of the arid and semiarid public lands within certain states of the Western states. ...
in 1877 and the Carey Act in 1894, which only marginally increased irrigation. Only in 1902 Congress passed the National Reclamation Act, which channeled money from the sale of western public lands, in parcels up to 160 acres large, into irrigation projects on public or private land in the arid West. The Congressmen who passed the law, as well as their wealthy supporters, supported Western irrigation because it would increase American exports, ‘reclaim’ the West, and push the Eastern poor out West in search of a better life.
While the National Reclamation Act was the most successful piece of federal irrigation legislation, the implementation of the act did not go as planned. Originally, the Reclamation Service planned to construct a small number of projects that would allow engineers to learn from the process, but President Roosevelt chose instead push as many irrigation projects through as fast as possible. The Reclamation Service also chose to push most of the Act’s money toward construction rather than settlement, so the Service overwhelmingly prioritized building large dams like the Hoover Dam
Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression and was dedicated on Se ...
. Over the 20th century Congress and state governments grew more frustrated with the Reclamation Service and the irrigation schemes in general. Frederick Newell, head of the Reclamation Service, proving uncompromising and difficult to work with, falling crop prices, resistance to delay debt payments, and refusal to begin new projects until the completion of old ones all contributed. The Reclamation Extension Act of 1914, transferring a significant amount of irrigation decision-making power regarding irrigation projects from the Reclamation Service to Congress, was in many ways a result of an increasing political unpopularity of the Reclamation Service.
In the lower Colorado Basin of Arizona, Colorado, and Nevada, the states derive irrigation water largely from rivers, especially the Colorado River, which irrigates more than 4.5 million acres of land, with a less significant amount coming from groundwater. In the 1952 case Arizona v. California
''Arizona v. California'' is a set of United States Supreme Court cases, all dealing with disputes over water distribution from the Colorado River between the states of Arizona and California. It also covers the amount of water that the State of ...
, Arizona sued California for increased access to the Colorado, under the grounds that their groundwater supply could not sustain their almost entirely irrigation-based agricultural economy, which they won. California, which began irrigating in earnest in the 1870s in San Joaquin Valley, had passed the Wright Act of 1887 permitting agricultural communities to construct and operate needed irrigation works. The Colorado also irrigates large fields in California’s Imperial Valley, fed by the National Reclamation Act-built All-American Canal.
Soviet Central Asia
When the Bolsheviks conquered Central Asia in 1917, the nativeKazakhs
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also parts o ...
, Uzbeks, and Turkmens used minimal irrigation. The Slavic immigrants pushed into the area by the Tsarist government brought their own irrigation methods, including waterwheels, the use of rice paddies to restore salted land, and underground irrigation channels. Russians dismissed these techniques as crude and inefficient. Despite this, in absence of other solutions, tsarist officials maintained these systems through the late 19th century. Peterson 2016.
Before conquering the area, the Russian government accepted a 1911 American proposal to send hydraulic experts to Central Asia to investigate the potential for large-scale irrigation. A 1918 decree by Lenin then encouraged irrigation development in the region, and development began in the 1930s. When it did, Stalin and other Soviet leaders prioritized large-scale, ambitious hydraulic projects, especially along the Volga River. The Soviet irrigation push stemmed largely from their late 19th century fears of the American cotton monopoly and subsequent desire to achieve cotton self-sufficiency. They had built up their textile manufacturing industry in the 19th century, requiring increased cotton and irrigation, as the region did not receive enough rainfall to support cotton farming.
The Russians built dams on the Don and Kuban
Kuban (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian: Кубань; ady, Пшызэ) is a historical and geographical region of Southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Pontic–Caspian steppe, ...
Rivers for irrigation, removing freshwater flow from the Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, ...
and making it much saltier. Depletion and salinization scourged other areas of the Russian irrigation project. In the 1950s Soviet officials began also diverting the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
and the Amu Darya, which fed the Aral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic basin, endorheic lake lyi ...
. Before diversion, the rivers delivered 55km3 of water to the Aral Sea per year, but after they only delivered 6km3 to the Sea. Because of its reduced inflow, the Aral Sea covered less than half of its original seabed, which made the regional climate more extreme and created airborne salinization, lowering nearby crop yields.
By 1975, the USSR used eight times as much water as they had in 1913, mostly for irrigation. Russia’s expansion of irrigation began to decrease in the late 1980s, and irrigated hectares in Central Asia capped out at 7 million. Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
killed a proposed plan to reverse the Ob and Yenisei for irrigation in 1986, and the breakup of the USSR in 1991 ended Russian investment in Central Asian cotton irrigation.
Africa
Different irrigation schemes with a variety of goals and success rates have been implemented across Africa in the 20th century, but have all been influenced by colonial forces. The Tana River Irrigation Scheme in eastern Kenya, completed between 1948 and 1963, opened up new lands for agriculture, and the Kenyan government attempted to resettle the area with detainees from theMau Mau uprising
The Mau Mau rebellion (1952–1960), also known as the Mau Mau uprising, Mau Mau revolt or Kenya Emergency, was a war in the British Kenya Colony (1920–1963) between the Kenya Land and Freedom Army (KLFA), also known as the ''Mau Mau'', an ...
. Libya’s underground water resources were discovered by Italian oil drillers during the Italian colonization of Libya. This water lay dormant until 1969, when Muammar al-Gaddafi and American Armand Hammer built the Great Man-Made River to deliver the Saharan water to the coast. The water largely contributed to irrigation but cost four to ten times more than the crops it produced were worth.
In 1912, the Union of South Africa created an irrigation department and began investing in water storage infrastructure and irrigation. The government used irrigation and dam-building to further social goals like poverty relief, both by creating construction jobs for poor whites and by creating irrigation schemes to increase white farming. One of their first major irrigation projects was the Hartbeespoort Dam, begun in 1916 as a mechanism to elevate the living conditions of the ‘poor whites’ in the region and eventually completed as a ‘whites only’ employment opportunity. The Pretoria irrigation scheme, Kammanassie project, and Buchuberg irrigation scheme on the Orange River all followed in the same vein in the 1920s and 30s.
In Egypt, modern irrigation began with Muhammad Ali Pasha in the mid-1800s, who sought to achieve Egyptian independence from the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
through increased trade with Europe—specifically cotton exportation. His administration proposed replacing the traditional Nile basin irrigation, which took advantage of the annual ebb and flow of the Nile, with irrigation barrages in the lower Nile which better suited cotton production. Egypt devoted 105,000 ha to cotton in 1861, which increased fivefold by 1865. The majority of their exports were shipped to England, and the United-States-Civil-War-induced cotton scarcity in the 1860s cemented Egypt as England’s cotton producer. As the Egyptian economy became more dependent on cotton in the 20th century, it became more important to control even small Nile floods. Cotton production was more at risk of destruction than more common crops like barley or wheat. After the British occupation of Egypt in 1882, the British intensified the conversion to perennial irrigation with the construction of the Delta Barrage, the Assiut Barrage, and the first Aswan Dam. Perennial irrigation decreased local control over water and made traditional subsistence farming or the farming of other crops incredibly difficult, eventually contributing to widespread peasant bankruptcy and the 1879-1882 ‘Urabi revolt. Ross 2017 p. 37-38.
Examples by country
Gallery
blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
in Plainville, New York, United States
Peanuts irrigation.jpg, Irrigation in Tamil Nadu, India
Irrigation ditch in Montour County, Pennsylvania.JPG, upIrrigation ditch in Montour County
Montour County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in Northeastern Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 18,136. Its county seat is Danville. The county is named for Andrew Montour, a prominent Mét ...
, Pennsylvania, USA
Sigiriya WaterGardens.JPG, Water gardens in Sigiriya, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
Sprinkler Irrigation - Sprinkler head.JPG, Micro-sprinkler
See also
* Deficit irrigation * Gezira Scheme * Irrigation management *Irrigation statistics This page shows statistical data on irrigation of agricultural lands worldwide.
Irrigation is the artificial ''abstraction'' of water from a source followed by the ''distribution'' of it at scheme level aiming at ''application'' at field level to en ...
* Leaf Sensor
* Lift irrigation scheme
* List of countries by irrigated land area
This is a list of countries by irrigated land area based on ''The World Factbook'' of the Central Intelligence Agency . The two countries with the largest irrigated land area are China and India, which make up 21.3% and 20.6% of worldwide irrigat ...
* Surface irrigation
* Tidal irrigation
* Water use in alluvial fans {{Multiple issues, {{cleanup, date=April 2021, reason=Rephrase to remove journal-style arguments based on individual illustrations, condense excessive technical detail{{primary sources, date=April 2021{{overly detailed, date=April 2021
Water use i ...
*
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID)
Irrigation
at the Water Quality Information Center, U.S. Department of Agriculture
AQUASTAT
FAO's global information system on water and agriculture {{Authority control Agricultural soil science Agronomy Environmental issues with water Land management Water management