Irish round tower on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Irish round towers ( ga, Cloigtheach (singular), (plural);
Irish round towers ( ga, Cloigtheach (singular), (plural);
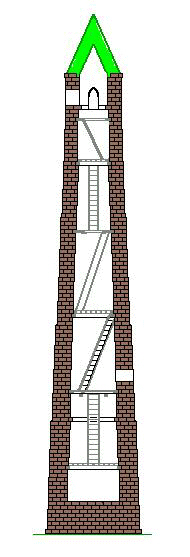 It is likely that the primary reason for the round tower was—as the name ''cloigtheach'' indicates—to act as a belfry. The
It is likely that the primary reason for the round tower was—as the name ''cloigtheach'' indicates—to act as a belfry. The

 Another "revival" round tower was built in 1997 in the
Another "revival" round tower was built in 1997 in the
roundtowers.org
Irish Round Towers
— detailed photographic archive and information for fifty-two Irish round towers. *
— articles and photos about Kinneigh Round Tower {{DEFAULTSORT:Irish Round Tower Archaeology of Ireland Buildings and structures in Ireland Towers in Ireland Christian bell towers !
 Irish round towers ( ga, Cloigtheach (singular), (plural);
Irish round towers ( ga, Cloigtheach (singular), (plural); literally
''Literally'' is an English adverb. It has been controversially used as an intensifier for figurative statements.
History
The first known use of the word ''literally'' was in the 15th century, or the 1530s, when it was used in the sense of "in ...
'bell house') are early mediaeval stone towers of a type found mainly in Ireland, with two in Scotland and one on the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
. As their name indicates, they were originally bell towers, though they may have been later used for additional purposes.
A tower of this kind is generally found in the vicinity of a church or monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
, with the door of the tower facing the west doorway of the church. Knowledge of this fact has made it possible, where towers still exist, to determine without excavation the approximate sites of lost churches that once stood nearby.
Construction and distribution
Surviving towers range in height from to , and to in circumference; that atKilmacduagh
Kilmacduagh () is a small village in south County Galway, near Gort, in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is the site of Kilmacduagh monastery, seat of the Diocese of that name. The diocese is now part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Galway, Ki ...
being the highest surviving in Ireland (and leaning out of perpendicular). The masonry differs according to date, the earliest examples being uncut rubble, while the later ones are of neatly joined stonework (ashlar
Ashlar () is finely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruv ...
). The lower portion is solid masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
with a single door raised two to three metres above, often accessible only by a ladder. Within, in some, are two or more floors (or signs of where such floors existed), usually of wood, and it is thought that there were ladders in between. The windows, which are high up, are slits in the stone. The cap (roof), is of stone, usually conical in shape, although some of the towers are now crowned by a later circle of battlement
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at interv ...
s.
The main reason for the entrance-way being built above ground level was to maintain the structural integrity of the building rather than for defence. The towers were generally built with very little foundation. The tower at Monasterboice
The Monasterboice ( ga, Mainistir Bhuithe) ruins are the remains of an early Christian monastic settlement in County Louth in Ireland, north of Drogheda. The ruins are a National monument of Ireland and also give their name to the local villag ...
has an underground foundation of only sixty centimetres. Building the door at ground level would weaken the tower. The buildings still stand today because their round shape is gale
A gale is a strong wind; the word is typically used as a descriptor in nautical contexts. The U.S. National Weather Service defines a gale as sustained surface winds moving at a speed of between 34 and 47 knots (, or ).posthole
In archaeology a posthole or post-hole is a cut feature used to hold a surface timber or stone. They are usually much deeper than they are wide; however, truncation may not make this apparent. Although the remains of the timber may survive, most ...
s, confirm that wooden steps were built. However, the use of ladders prior to the construction of such steps
cannot be ruled out.
The towers were probably built between the 9th and 12th centuries. In Ireland about 120 examples are thought once to have existed; most are in ruins, while eighteen to twenty are almost perfect. There are three examples outside Ireland. Two are in eastern Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
: the Brechin
Brechin (; gd, Breichin) is a city and former Royal burgh in Angus, Scotland. Traditionally Brechin was described as a city because of its cathedral and its status as the seat of a pre-Reformation Roman Catholic diocese (which continues today ...
Round Tower and the Abernethy
Abernethy may refer to:
Places Scotland
* Abernethy, Perth and Kinross, a village
** Abernethy (NBR) railway station, a former railway station in this village
* Nethy Bridge, Highland, a village formerly known as Abernethy
* Abernethy Forest, ...
Round Tower, and the other is in Peel Castle
Peel Castle (''Cashtal Phurt ny h-Inshey'' in Manx Gaelic) is a castle in Peel on the Isle of Man, originally constructed by Vikings. The castle stands on St Patrick's Isle which is connected to the town by a causeway. It is now owned by Man ...
on St. Patrick's Isle, now linked to the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
.
Famous examples are to be found at Devenish Island
Devenish or Devinish () is an island in Lower Lough Erne, County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland. Aligned roughly north–south, it is about one and a quarter miles (2 km) long and two-thirds of a mile (1 km) wide. The main place to catch a ferry ...
, and Glendalough
Glendalough (; ) is a glacial valley in County Wicklow, Ireland, renowned for an Early Medieval monastic settlement founded in the 6th century by St Kevin. From 1825 to 1957, the head of the Glendalough Valley was the site of a galena lead min ...
, while that at Clondalkin
Clondalkin ( ; ) is a suburban town situated 10 km south-west of Dublin city centre, Ireland, under the administrative jurisdiction of South Dublin. It features an 8th-century round tower that acts as a focal point for the area. Clondal ...
is the only Round Tower in Ireland to still retain its original cap. With five towers each, County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the Taxus baccata, yew trees") is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. In the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Conn ...
, County Kilkenny
County Kilkenny ( gle, Contae Chill Chainnigh) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the South-East Region. It is named after the city of Kilkenny. Kilkenny County Council is the local authority for the cou ...
and County Kildare
County Kildare ( ga, Contae Chill Dara) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is named after the town of Kildare. Kildare County Council is the local authority for the county, ...
have the most. Mayo's round towers are at Aughagower
Aughagower or Aghagower () is a small village in rural County Mayo in western Ireland. It is located about 6 km from Westport. Aughagower has around 40 houses, 1 pub and a shop, with a clear view of Croagh Patrick from Reek View. It also ...
, Balla, Killala
Killala () is a village in County Mayo in Ireland, north of Ballina. The railway line from Dublin to Ballina once extended to Killala. To the west of Killala is a Townsplots West (known locally as Enagh Beg), which contains a number of ancient ...
, Meelick and Turlough, while Kildare's are located at Kildare Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of St. Brigid, Kildare, in Kildare, County Kildare, is one of two cathedrals in the United Dioceses of Meath and Kildare of the Church of Ireland in Ireland. It is in the ecclesiastical province of Dublin.
History Early hi ...
(which is high), and also at Castledermot
Castledermot () is an inland village in the south-east of Ireland in County Kildare, about from Dublin, and from the town of Carlow. The N9 road from Dublin to Waterford previously passed through the village but upon completion of a motorway ...
, Oughter Ard
Oughterard (, “a high place”) is an ecclesiastical hilltop site, graveyard, townland, and formerly a parish, borough and royal manor in County Kildare, nowadays part of the community of Ardclough, close to the Dublin border. It is the buria ...
, Taghadoe (near Maynooth
Maynooth (; ga, Maigh Nuad) is a university town in north County Kildare, Ireland. It is home to Maynooth University (part of the National University of Ireland and also known as the National University of Ireland, Maynooth) and St Patrick's ...
) and Old Kilcullen
''Old Kilcullen'', formerly ''Kilcullen'' (''Cill Chuilinn'', "the Church of the Holly" in Irish), is a townland in County Kildare, Ireland, which includes a noted religious archaeological site within its boundary. As a townland it is rel ...
. The only known round tower with a hexagonal base is at Kinneigh in County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are ...
, built in 1014. The round tower at Ardmore, County Waterford, believed to be the latest built in Ireland (c. 12th century), has the unique feature of three string courses around the exterior.
Purpose
 It is likely that the primary reason for the round tower was—as the name ''cloigtheach'' indicates—to act as a belfry. The
It is likely that the primary reason for the round tower was—as the name ''cloigtheach'' indicates—to act as a belfry. The Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
wordPatrick S. Dinneen, ''An Irish English Dictionary'', The Educational Company of Ireland, Dublin, 1927 for round tower, ''cloigtheach'', literally meaning ''bellhouse'' indicates this, as noted by George Petrie in 1845. The Irish language has greatly evolved over the last millennium. Dinneen notes the alternate pronunciations, ''cluiceach'' and ''cuilceach'' for ''cloigtheach''. The closely pronounced ''cloichtheach'' means stone-house or stone-building. The round tower seems to be the only significant stone building in Ireland before the advent of the Normans in 1169–1171 CE.
UCD Professor of Archaeology Tadhg O'Keeffe has suggested that the towers were originally high-status royal chapels, citing how two of them (Kells and Duleek) were scenes of regicide. He also suggested that the windows were arranged clockwise to imitate the order of relic-carrying procession from the elevated door to the very top.
Another possible purpose would be for taking shelter during raids. The mostly enclosed top floors and stone rooftops would make for terrible belltowers. The elevated doorway could have had a ladder that would be drawn up during raids, and the thick stone walls could withstand most attacks. Since the doors always face where a church stood, this also adds weight to the theory they were where monks would evacuate to.
Modern symbolic towers

In Ireland
Daniel O'Connell
Daniel O'Connell (I) ( ga, Dónall Ó Conaill; 6 August 1775 – 15 May 1847), hailed in his time as The Liberator, was the acknowledged political leader of Ireland's Roman Catholic majority in the first half of the 19th century. His mobilizat ...
's tomb at Glasnevin Cemetery
Glasnevin Cemetery ( ga, Reilig Ghlas Naíon) is a large cemetery in Glasnevin, Dublin, Ireland which opened in 1832. It holds the graves and memorials of several notable figures, and has a museum.
Location
The cemetery is located in Glasne ...
in Dublin had a round tower built above it after his burial in 1847.
At what is now the Irish National Heritage Park at Ferrycarrig in County Wexford
County Wexford ( ga, Contae Loch Garman) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic territory of Hy Kinsella (''Uí Ceinns ...
, there is a 19th-century copy of a round tower. It was erected to the memory of the Wexford men who fell in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
.
At St. Ita's Hospital in Portrane, County Dublin, there is a replica round tower built in 1844 as a memorial to George Hampden Evans
The Rt.Hon. George Hampden Evans (died 2 July 1842) was an Irish politician.
Biography
George was the eldest son of Captain Hampden Evans and his wife Margaret née Davis of Portrane, County Dublin. in 1805 he married Sophia Parnell, only daugh ...
by his wife.
In the Knockmealdown Mountains
The Knockmealdown Mountains ( ga, Sléibhte Chnoc Mhaoldomhnaigh) are a mountain range located on the border of counties Tipperary and Waterford in Ireland, running east and west between the two counties. The highest peak of the range is Knockmea ...
in County Waterford is another memorial in the form of an 18m high round tower. It was erected in 1935 on the spot where Liam Lynch, military leader of the anti-treaty Irish Republican Army during the Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War ( ga, Cogadh Cathartha na hÉireann; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United ...
is thought to have fallen in 1923.
The Ulster History Park in County Tyrone
County Tyrone (; ) is one of the six Counties of Northern Ireland, counties of Northern Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the thirty-two traditional Counties of Ireland, counties of Ireland. It is no longer used as an admini ...
has a replica of a round tower.
St Patrick's Church of Ireland church in Saul, County Down has a round tower, built in 1933.
The Chaine Memorial
The Chaine Memorial Tower in Larne, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, is a memorial to James Chaine, a former Member of Parliament for Antrim, who died in 1885. It is a cylindrical stone tower lighthouse with a conical roof, situated on the wes ...
Tower in Larne County Antrim is a lighthouse done in the style of a round tower. It was built to commemorate James Chaine
James Chaine (1841 – 4 May 1885) was an Irish shipping businessman and a Conservative PartyWalker, p. 249. politician from County Antrim in Ulster.
The son of James Chaine of Ballycraigy and his wife, Maria (née Whittle), from Antrim, he was ...
, a former MP for Antrim.
Outside Ireland
 Another "revival" round tower was built in 1997 in the
Another "revival" round tower was built in 1997 in the Island of Ireland Peace Park
The Island of Ireland Peace Park and its surrounding park ( ga, Páirc Síochána d'Oileán na hÉireann), also called the Irish Peace Park or Irish Peace Tower in Messines, near Ypres in Flanders, Belgium, is a war memorial to the soldiers of ...
in Belgium, as a war memorial
A war memorial is a building, monument, statue, or other edifice to celebrate a war or victory, or (predominating in modern times) to commemorate those who died or were injured in a war.
Symbolism
Historical usage
It has ...
to the soldiers of the island of Ireland who died, were wounded or are missing from World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The tower is in the traditional design of an Irish round tower and is partially built with stone from a former army barracks in Tipperary
Tipperary is the name of:
Places
*County Tipperary, a county in Ireland
**North Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Nenagh
**South Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Clonmel
*Tipperary (town), County Tipperary's na ...
.
At Saint Mary's Cemetery in Milford, Massachusetts
Milford is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 30,379 according to the 2020 census. First settled in 1662 and incorporated in 1780, Milford became a booming industrial and quarrying community in the 19th c ...
a round tower was built of Milford granite in the late 19th century as a memorial to central Massachusetts' Irish immigrants, of whom thousands are buried there.
In 2003 Tony Ryan
Thomas Anthony Ryan (2 February 1936 – 3 October 2007) was an Irish billionaire, philanthropist and businessman who co-founded the Ryanair airline.
Through his establishment of Guinness Peat Aviation in 1975 he began a course of events which ...
, a native of Thurles
Thurles (; ''Durlas Éile'') is a town in County Tipperary, Ireland. It is located in the civil parish of the same name in the barony of Eliogarty and in the ecclesiastical parish of Thurles. The cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Arc ...
, County Tipperary, built a round tower at his Castleton Lyons Stud in Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
.
The second church to be built on the site of St John the Evangelist Catholic Church in East Melbourne, Victoria
East Melbourne is an inner-city suburb in Melbourne, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia, east of Melbourne's Melbourne central business district, Central Business District, located within the City of Melbourne Local government areas of ...
, Australia, completed in December 1900, features a 13-metre Irish round tower on its eastern side. The tower is based on the entrance to King Cormac's Chapel on the Rock of Cashel
The Rock of Cashel ( ga, Carraig Phádraig ), also known as Cashel of the Kings and St. Patrick's Rock, is a historic site located at Cashel, County Tipperary, Ireland.
History
According to local legends, the Rock of Cashel originated in the ...
in Tipperary
Tipperary is the name of:
Places
*County Tipperary, a county in Ireland
**North Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Nenagh
**South Tipperary, a former administrative county based in Clonmel
*Tipperary (town), County Tipperary's na ...
, built in 1137. The structure is now part of the Catholic Leadership Centre, operated by the Catholic Education Office Melbourne.
List of Irish round towers
The following is a list of surviving Irish round towers, excluding modern reconstructions. Sourceroundtowers.org
List of missing towers
This is a list of Irish round towers known to have existed, but no trace now remains.See also
*Broch
A broch is an Iron Age drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland. Brochs belong to the classification "complex Atlantic roundhouse" devised by Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s. Their origin is a matter of some controversy.
Origin ...
*Chaine Memorial
The Chaine Memorial Tower in Larne, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, is a memorial to James Chaine, a former Member of Parliament for Antrim, who died in 1885. It is a cylindrical stone tower lighthouse with a conical roof, situated on the wes ...
, a relatively modern tower lighthouse at Larne
Larne (, , the name of a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic territory) is a town on the east coast of County Antrim, Northern Ireland, with a population of 18,755 at the United Kingdom census, 2011, 2011 Census. It is a major passenger and freight Roll-on/ro ...
, in the style of a round tower.
*Pele tower
Peel towers (also spelt pele) are small fortified keeps or tower houses, built along the English and Scottish borders in the Scottish Marches and North of England, mainly between the mid-14th century and about 1600. They were free-standing ...
*Rock of Cashel
The Rock of Cashel ( ga, Carraig Phádraig ), also known as Cashel of the Kings and St. Patrick's Rock, is a historic site located at Cashel, County Tipperary, Ireland.
History
According to local legends, the Rock of Cashel originated in the ...
References
Sources
* * * * *External links
Irish Round Towers
— detailed photographic archive and information for fifty-two Irish round towers. *
— articles and photos about Kinneigh Round Tower {{DEFAULTSORT:Irish Round Tower Archaeology of Ireland Buildings and structures in Ireland Towers in Ireland Christian bell towers !