Irish Priests on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, native_name_lang = ga
, image = Armagh, St Patricks RC cathedral.jpg
, imagewidth = 200px
, alt =
, caption =
Irish Bishops' Conference
, slogan = , logo = , footnotes = The Catholic Church in Ireland ( ga, Eaglais Chaitliceach in Éireann) or Irish Catholic Church, is part of the worldwide Catholic Church in communion with the Holy See. With 3.7 million members (in the Republic of Ireland), it is the largest Christian church in Ireland. In the Republic of Ireland's 2016 census, 78% of the population identified as Catholic; this was 6% lower than the 2011 figure. By contrast, 41% of people in Northern Ireland identified as Catholic at the 2011 census; it is expected that this proportion will increase in the coming years. The
 During classical antiquity, the Roman Empire conquered most of Western Europe but never reached Ireland. So when the Edict of Milan in 313 AD allowed tolerance for the Mediterranean-originated religion of Christianity and then the Edict of Thessalonica in 380 AD enforced it as the
During classical antiquity, the Roman Empire conquered most of Western Europe but never reached Ireland. So when the Edict of Milan in 313 AD allowed tolerance for the Mediterranean-originated religion of Christianity and then the Edict of Thessalonica in 380 AD enforced it as the  The influence of the Irish Church spread back across the Irish Sea to Great Britain. Dál Riata in what is now Argyll was geopolitically continuous with Ireland and
The influence of the Irish Church spread back across the Irish Sea to Great Britain. Dál Riata in what is now Argyll was geopolitically continuous with Ireland and  The oldest surviving liturgical text of the Church in Ireland is the '' Antiphonary of Bangor'' from the 7th century. Indeed, at Bangor, a saint by the name of
The oldest surviving liturgical text of the Church in Ireland is the '' Antiphonary of Bangor'' from the 7th century. Indeed, at Bangor, a saint by the name of
 One of the major figures associated with the Gregorian Reform in Ireland was Máel Máedóc Ó Morgair, also known as Malachy, who was an Archbishop of Armagh and the first Gaelic Irish saint to undergo a formal canonisation process and official proclamation. Máel Máedóc was closely associated with Bernard of Clairvaux and introduced his
One of the major figures associated with the Gregorian Reform in Ireland was Máel Máedóc Ó Morgair, also known as Malachy, who was an Archbishop of Armagh and the first Gaelic Irish saint to undergo a formal canonisation process and official proclamation. Máel Máedóc was closely associated with Bernard of Clairvaux and introduced his  Crusading military orders, such as the
Crusading military orders, such as the
"Monastic Ireland: The Mendicant Orders"
History Ireland The first of these to arrive were the Order of Preachers (also known as the Dominicans), they first established a branch at Dublin in 1224, shortly followed by one at Drogheda the same year, before spreading further. Prominent examples of Dominican establishments from this era are
Richard II and the Wider Gaelic World: A Reassessment
Cambridge University Press This was not a doctrinal dispute, but a political one. The Plantagenet-controlled Lordship of Ireland followed the Kingdom of England in backing the Pope in Rome. Meanwhile, there were two main power blocs among the Gaelic kingdoms and Gaelicised-lordships supporting different contenders. The "''Donn''" faction, led by the

 A confusing but defining period arose during the
A confusing but defining period arose during the
 From the time that Ireland achieved independence, the church came to play an increasingly significant social and political role in the Irish Free State and following that, the Republic of Ireland. For many decades, Catholic influence (coupled with the rural nature of Irish society) meant that Ireland was able to uphold family-orientated social policies for longer than most of the West, contrary to the '' laissez-faire''-associated cultural liberalism of the British and Americans. This cultural direction was particularly prominent under Éamon de Valera. For example, from 1937 until 1995, divorce and remarriage was not permitted (in line with
From the time that Ireland achieved independence, the church came to play an increasingly significant social and political role in the Irish Free State and following that, the Republic of Ireland. For many decades, Catholic influence (coupled with the rural nature of Irish society) meant that Ireland was able to uphold family-orientated social policies for longer than most of the West, contrary to the '' laissez-faire''-associated cultural liberalism of the British and Americans. This cultural direction was particularly prominent under Éamon de Valera. For example, from 1937 until 1995, divorce and remarriage was not permitted (in line with
Other outlets issued them freely, accepting donations and, as this was not selling, it was legal; see
. also helped to uphold Catholic hegemony. In both parts of Ireland, church policy and practice changed markedly after the Vatican II reforms of 1962. Probably the largest change was that Mass could be said in vernacular languages instead of Latin, and in 1981 the church commissioned its first edition of the Bible in the
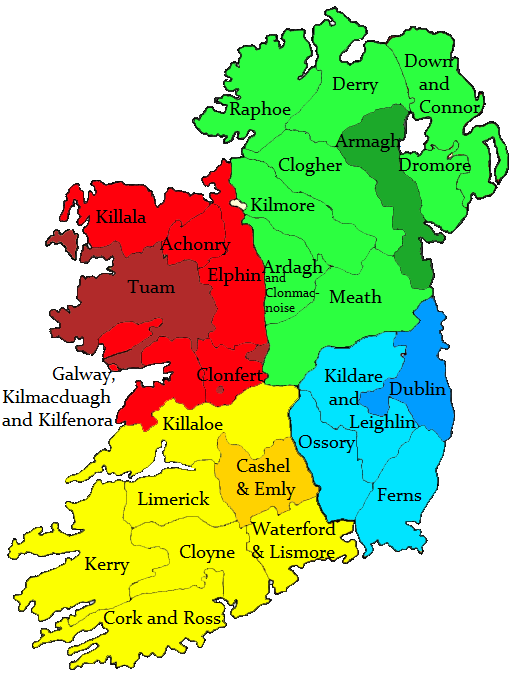 The church is organised into four ecclesiastical provinces. While these may have coincided with contemporary 12th century civil provinces or petty kingdoms, they are not now coterminous with the modern civil provincial divisions. The church is led by four
The church is organised into four ecclesiastical provinces. While these may have coincided with contemporary 12th century civil provinces or petty kingdoms, they are not now coterminous with the modern civil provincial divisions. The church is led by four
Catholic Church in Ireland
Irish Bishops' ConferenceCatholicIreland.netCatholic Parish Registers
{{DEFAULTSORT:Catholic Church in Ireland All-Ireland organisations Irish culture
St Patrick's Cathedral, Armagh There are two St Patrick's Cathedrals in Armagh, Northern Ireland:
* St Patrick's Cathedral, Armagh (Church of Ireland), the Anglican cathedral (and the Catholic cathedral prior to the Protestant Reformation)
* St Patrick's Cathedral, Armagh (Roma ...
.
, abbreviation =
, type = National polity
, main_classification = Catholic
, orientation = Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
, scripture = Bible
, theology = Catholic theology
Catholic theology is the understanding of Catholic doctrine or teachings, and results from the studies of theologians. It is based on canonical scripture, and sacred tradition, as interpreted authoritatively by the magisterium of the Catholic ...
, polity =
, governance = Episcopal
Episcopal may refer to:
*Of or relating to a bishop, an overseer in the Christian church
*Episcopate, the see of a bishop – a diocese
*Episcopal Church (disambiguation), any church with "Episcopal" in its name
** Episcopal Church (United State ...
, structure =
, leader_title = Pope
, leader_name = Francis
Francis may refer to:
People
*Pope Francis, the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State and Bishop of Rome
*Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
*Francis (surname)
Places
* Rural M ...
, leader_title1 = Primate of All Ireland
The Primacy of Ireland was historically disputed between the Archbishop of Armagh and the Archbishop of Dublin until finally settled by Pope Innocent VI. ''Primate'' is a title of honour denoting ceremonial precedence in the Church, and in t ...
, leader_name1 = Eamon Martin
Eamon Martin KC*HS (born 30 October 1961) is a prelate of the Catholic Church from Northern Ireland who has been Archbishop of Armagh and the Primate of All Ireland since 2014.
Early life and education
Martin was born in Derry, Northern Irela ...
, leader_title2 = Apostolic Nuncio
, leader_name2 = Jude Thaddeus Okolo
Jude Thaddeus Okolo KC*HS (born 18 December 1956) is a prelate of the Catholic Church who has worked in the diplomatic service of the Holy See since 1990. He has been an archbishop since 2008 and held the post of Apostolic Nuncio in several count ...
, leader_title3 =
, leader_name3 =
, fellowships_type =
, fellowships =
, fellowships_type1 =
, fellowships1 =
, division_type =
, division =
, division_type1 =
, division1 =
, division_type2 =
, division2 =
, division_type3 =
, division3 =
, associations =
, area = Ireland
, language = Irish, English, Latin
, headquarters = Ara Coeli, Armagh
Armagh ( ; ga, Ard Mhacha, , "Macha's height") is the county town of County Armagh and a city in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Pri ...
, Northern Ireland
, origin_link =
, founder = St. Patrick
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy an ...
, founded_date = Claims continuity with Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
. Roman diocesan structure introduced at Synod of Ráth Breasail.
, founded_place = Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland ( ga, Éire Ghaelach) was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the early 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans co ...
, separated_from =
, parent =
, merger =
, absorbed =
, separations = Church of Ireland (1536/1871)
, merged_into =
, defunct =
, congregations_type =
, congregations =
, members = 3,729,000 (2016)
, ministers_type =
, ministers =
, missionaries =
, churches =
, hospitals =
, nursing_homes =
, aid =
, primary_schools =
, secondary_schools =
, tax_status =
, tertiary =
, other_names =
, publications =
, website Irish Bishops' Conference
, slogan = , logo = , footnotes = The Catholic Church in Ireland ( ga, Eaglais Chaitliceach in Éireann) or Irish Catholic Church, is part of the worldwide Catholic Church in communion with the Holy See. With 3.7 million members (in the Republic of Ireland), it is the largest Christian church in Ireland. In the Republic of Ireland's 2016 census, 78% of the population identified as Catholic; this was 6% lower than the 2011 figure. By contrast, 41% of people in Northern Ireland identified as Catholic at the 2011 census; it is expected that this proportion will increase in the coming years. The
Archbishop of Armagh
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdio ...
, as the Primate of All Ireland
The Primacy of Ireland was historically disputed between the Archbishop of Armagh and the Archbishop of Dublin until finally settled by Pope Innocent VI. ''Primate'' is a title of honour denoting ceremonial precedence in the Church, and in t ...
, has ceremonial precedence in the church. The church is administered on an all-Ireland basis. The Irish Catholic Bishops' Conference is a consultative body for ordinaries in Ireland.
Christianity has existed in Ireland since the 5th century and arrived from Roman Britain (most famously associated with Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick ( la, Patricius; ga, Pádraig ; cy, Padrig) was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints be ...
), forming what is today known as Gaelic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
. It gradually gained ground and replaced the old pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
traditions. The Catholic Church in Ireland cites its origin to this period and considers Palladius as the first bishop sent to the Gaels by Pope Celestine I. However, during the 12th century a stricter uniformity in the Western Church was enforced, with the diocesan structure introduced with the Synod of Ráth Breasail in 1111 and culminating with the Gregorian Reform which coincided with the Norman invasion of Ireland.
After the Tudor conquest of Ireland, the English Crown
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself King of the Anglo-Sax ...
attempted to import the Protestant Reformation into Ireland. The Catholic Church was outlawed and adherents endured oppression and severe legal penalties
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. ...
for refusing to conform to the religion established by law — the Church of Ireland. By the 16th century, Irish national identity coalesced around Irish Catholicism. For several centuries, the Irish Catholic majority were suppressed. In the 19th century, the church and the British Empire came to a '' rapprochement''. Funding for Maynooth College
St Patrick's Pontifical University, Maynooth ( ga, Coláiste Naoimh Phádraig, Maigh Nuad), is the "National Seminary for Ireland" (a Roman Catholic college), and a pontifical university, located in the town of Maynooth, from Dublin, Ireland. ...
was agreed as was Catholic Emancipation to ward off revolutionary republicanism. Following the Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the a ...
of 1916 and the creation of the Irish Free State, the church gained significant social and political influence. During the late 20th century, a number of sexual abuse scandals involving clerics emerged.History
Gaels and early Christianity
 During classical antiquity, the Roman Empire conquered most of Western Europe but never reached Ireland. So when the Edict of Milan in 313 AD allowed tolerance for the Mediterranean-originated religion of Christianity and then the Edict of Thessalonica in 380 AD enforced it as the
During classical antiquity, the Roman Empire conquered most of Western Europe but never reached Ireland. So when the Edict of Milan in 313 AD allowed tolerance for the Mediterranean-originated religion of Christianity and then the Edict of Thessalonica in 380 AD enforced it as the state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular state, secular, is not n ...
of the Empire; covering much of Europe (including within the British Isles itself, Roman Britain); the indigenous Indo-European pagan traditions of the Gaels in Ireland remained normative. Aside from this independence, Gaelic Ireland was a highly decentralised tribal society, so mass conversion to a new system would prove a drawn out process even as the Christian religion began to gradually move into the island.
There is no tradition of a New Testament figure visiting the island. Joseph of Arimathea was said to have come to Britain, Mary Magdalene
Mary Magdalene (sometimes called Mary of Magdala, or simply the Magdalene or the Madeleine) was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to crucifixion of Jesus, his cru ...
, Martha and Lazarus of Bethany to France, but none were reputed to have seen Ireland itself. Instead, medieval Gaelic historians in works such as the '' Lebor Gabála Érenn'' attempted to link the historical narrative of their people (represented by the proto-Gaelic Scythians) to Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
in Egypt. Specifically, works such as the '' Lebor Gabála Érenn'', '' Book of Ballymote'' and '' Great Book of Lecan'', say that, during the time of Moses, Goídel Glas
In medieval Irish and Scottish legend, Goídel Glas (Latinised as Gaithelus) is the creator of the Goidelic languages and eponymous ancestor of the Gaels. The tradition can be traced to the 11th-century ''Lebor Gabála Érenn''. A Scottish varia ...
(the reputed progenitor of the Irish) was bitten in the neck by a snake while in Egypt as a youth. His father, the Scythian prince Níul (husband of Egyptian princess Scota) brought Goídel to the noted wonder-worker, Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
, who healed the boy immediately upon applying his rod to the wound. Moses made a prophecy that no serpent would live in the land of his progeny, and that God promised his descendants a "northern island of the world"; he claimed that “kings and lords, saints and righteous” would come from the seed of Goídel. In some ways, the Gaelic authors of these works sought to present themselves as a kind of "chosen people" while approaching the Biblical narrative, mirroring the Israelites. Furthermore, according to the ''Lebor Gabála Érenn'', the lifetime of Jesus Christ was syncronised with the reigns of Eterscél, Nuadu Necht
Nuadu Necht ("the pure"), son of Sétna Sithbac, a descendant of Crimthann Coscrach, of the Laigin, was, according to medieval Irish legend and historical tradition, a High King of Ireland. He came to power after killing his predecessor, Etersc� ...
and Conaire Mór as High Kings of Ireland. In medieval tellings, Conchobar mac Nessa, a King of Ulster, was born at the same hour as Christ. Later in life, upon seeing an unexplained " darkening of the skies", Conchobar mac Nessa found out from a ''druí
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celts, Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accoun ...
'' that Christ had been crucified. He fled into a rage, and died himself on the spot
Regardless, the earliest stages of Christianity in Ireland, during its 5th century arrival, are somewhat obscure. Native Christian "pre-Patrician" figures, however, including Ailbe, Abbán, Ciarán
Ciarán (Irish spelling) or Ciaran (Scottish Gaelic spelling) is a traditionally male given name of Irish origin. It means "little dark one" or "little dark-haired one", produced by appending a diminutive suffix to ''ciar'' ("black", "dark"). ...
and Declán, later venerated as saints
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual res ...
, are known. These were typically in Leinster and Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the ...
. The early stories of these people mention journeys to Roman Britain, Roman Gaul and even Rome itself. Indeed, Pope Celestine I is held to have sent Palladius to evangelise the Gaels in 431, though success was limited. Apart from these, the figure most associated with the Christianisation of Ireland is Patrick Patrick may refer to:
* Patrick (given name), list of people and fictional characters with this name
* Patrick (surname), list of people with this name
People
* Saint Patrick (c. 385–c. 461), Christian saint
*Gilla Pátraic (died 1084), Patrick ...
(Maewyn Succat), a Romano-British nobleman, who was captured by the Gaels during a raid, when the Roman rule in Britain was in decline. Patrick contested with the ''druí'', targeted the local royalty for conversion, and re-orientated Irish Christianity to having Armagh
Armagh ( ; ga, Ard Mhacha, , "Macha's height") is the county town of County Armagh and a city in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Pri ...
, an ancient royal site associated with the goddess Macha (an aspect of An Morríghan
An, AN, aN, or an may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
* Airlinair (IATA airline code AN)
* Alleanza Nazionale, a former political party in Italy
* AnimeNEXT, an annual anime convention located in New Jersey
* Anime North, a Canadian an ...
), as the preeminent seat of power. Much of what is known about Patrick is to be gleaned from the two Latin works attributed to him: ''Confessio'' and ''Epistola ad Coroticum''. The two earliest lives of Ireland's patron saint emerged in the 7th century, authored by Tírechán
Tírechán was a 7th-century Irish bishop from north Connacht, specifically the Killala Bay area, in what is now County Mayo.
Background
Based on a knowledge of Irish customs of the times, historian Terry O’Hagan has concluded that Tírechán ...
and Muirchú. Both of these are contained within the '' Book of Armagh''.
From its inception in the Early Middle Ages, the Gaelic Church was organised around powerful local monasteries. The lands which monasteries were based on were known as '' termonn'' lands, holding a special tax exempt status, and were places of sanctuary. The spiritual heirs and successors of the saintly founders of these monasteries were known as '' Coarbs'', who held the right to provide Abbots. For example: the Abbot of Armagh
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The fem ...
was the '' Comharba Phádraig'', the Abbot of Iona
The Abbot of Iona was the head of Iona Abbey during the Middle Ages and the leader of the monastic community of Iona, as well as the overlord of scores of monasteries in both Scotland and Ireland, including Durrow, Kells and, until the Synod of ...
was the '' Comharba Cholm Cille'', the Abbot of Clonmacnoise was the '' Comharba Chiarán'', the Abbot of Glendalough was the '' Comharba Chaoimhín'' and so on. The larger monasteries had various subordinate monasteries within a particular "family". The position of ''Coarb'', like others in Gaelic culture, was hereditary, held by a particular ecclesiastical '' clann'' with the same paternal bloodline and elected from within a family through tanistry (usually protected by the local Gaelic king). This was the same system used for the selection of kings, standard bearers, bardic poets and other hereditary roles. '' Erenagh'' were the hereditary stewards of the ''termonn'' lands of a monastery. Monks also founded monasteries on smaller islands around Ireland, for instance Finnian at Skellig Michael, Senán at Inis Cathaigh
Inis Cathaigh or Scattery Island is an island in the Shannon Estuary, Ireland, off the coast of Kilrush, County Clare. The island is home to a lighthouse, a ruined monastery associated with Saint Senan, an Irish round tower and the remains of a ...
and Columba at Iona
Iona (; gd, Ì Chaluim Chille (IPA: �iːˈxaɫ̪ɯimˈçiʎə, sometimes simply ''Ì''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there ...
. As well as this, Brendan was known for his offshore "voyage" journeys and the mysterious Saint Brendan's Island
Saint Brendan's Island, also known as Saint Brendan's Isle, is a phantom island or mythical island, supposedly situated in the North Atlantic somewhere west of Northern Africa. It is named after Saint Brendan of Clonfert. He and his followers ar ...
.
 The influence of the Irish Church spread back across the Irish Sea to Great Britain. Dál Riata in what is now Argyll was geopolitically continuous with Ireland and
The influence of the Irish Church spread back across the Irish Sea to Great Britain. Dál Riata in what is now Argyll was geopolitically continuous with Ireland and Iona
Iona (; gd, Ì Chaluim Chille (IPA: �iːˈxaɫ̪ɯimˈçiʎə, sometimes simply ''Ì''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there ...
held an important place in Irish Christianity, with Columban monastic activities either side of the North Channel North Channel may refer to:
*North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland)
*North Channel (Ontario), body of water along the north shore of Lake Huron, Canada
*North Channel, Hong Kong
*Canal du Nord, France
{{geodis ...
. From here, Irish missionaries converted the pagan northern Picts of Fortriu. They were also esteemed at the court of the premier Angle-kingdom of the time, Northumbria, with Aidan
Aidan or Aiden is a modern version of a number of Celtic language names, including the Irish male given name ''Aodhán'', the Scottish Gaelic given name Aodhan and the Welsh name Aeddan. Phonetic variants, such as spelled with an "e" instead of ...
from Iona founding a monastery at Lindisfarne
Lindisfarne, also called Holy Island, is a tidal island off the northeast coast of England, which constitutes the civil parish of Holy Island in Northumberland. Holy Island has a recorded history from the 6th century AD; it was an important ...
, converting them to Christianity (the Northumbrians in turn converted Mercia). Surviving artifacts such as the '' Lindisfarne Gospels'', share the same insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style dif ...
-style with the ''Stowe Missal
The Stowe Missal (sometimes known as the Lorrha Missal), which is, strictly speaking, a sacramentary rather than a missal, is a small Irish illuminated manuscript written mainly in Latin with some Old Irish in the late eighth or early ninth cen ...
'' and ''Book of Kells
The Book of Kells ( la, Codex Cenannensis; ga, Leabhar Cheanannais; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New ...
''. By the 7th century, rivalries between Hibernocentric-Lindisfarne and Kentish- Canterbury emerged within the Heptarchy, with the latter established by the mission of Roman-born Augustine of Canterbury
Augustine of Canterbury (early 6th century – probably 26 May 604) was a monk who became the first Archbishop of Canterbury in the year 597. He is considered the "Apostle to the English" and a founder of the English Church.Delaney '' ...
. Customs of the Irish Church which differed, such as the date which Easter was calculated and the Gaelic monks' manner of tonsure was highlighted. The issue was resolved in southern Ireland with Clonfert replying to Pope Honorius I with the ''Letter of Cumméne Fota'', around 626-628. After a separate dialogue with Rome, Armagh followed in 692. The Columbans of Iona were the most resistant of the Irish, holding out until the early 700s, though their satellite Lindisfarne was pressured into changing at the Synod of Whitby in 664, partly due to an internal political struggle.Retroactively, Protestants would point to this controversy to suggest the existence of a proto-Protestant " Celtic Church" or "British Church" independent from Rome in the Early Middle Ages as part of their historiography. However, during the dispute over the dating of Easter, the Primacy of the Bishop of Rome, Catholic doctrine, liturgical practice (see Hiberno-Latin
Hiberno-Latin, also called Hisperic Latin, was a learned style of literary Latin first used and subsequently spread by Irish monks during the period from the sixth century to the tenth century.
Vocabulary and influence
Hiberno-Latin was notab ...
) or the sacraments—issues of importance to Protestants—were not under question. The longest holdouts were the Cornish Britons of Dumnonia, as part of their conflict with Wessex. Indeed, the Cornish had been converted by Irish missionaries: patron saint Piran (also known as Ciarán
Ciarán (Irish spelling) or Ciaran (Scottish Gaelic spelling) is a traditionally male given name of Irish origin. It means "little dark one" or "little dark-haired one", produced by appending a diminutive suffix to ''ciar'' ("black", "dark"). ...
) and a nun princess Ia; who gave her name to St. Ives; were foremost. As well as Ia, there were also female saints in Ireland during the early period, such as Brigid of Kildare and Íte of Killeedy.
 The oldest surviving liturgical text of the Church in Ireland is the '' Antiphonary of Bangor'' from the 7th century. Indeed, at Bangor, a saint by the name of
The oldest surviving liturgical text of the Church in Ireland is the '' Antiphonary of Bangor'' from the 7th century. Indeed, at Bangor, a saint by the name of Columbanus
Columbanus ( ga, Columbán; 543 – 21 November 615) was an Irish missionary notable for founding a number of monasteries after 590 in the Frankish and Lombard kingdoms, most notably Luxeuil Abbey in present-day France and Bobbio Abbey in pr ...
developed his ''Rule of St. Columbanus''. Strongly penetential
A penitential is a book or set of church rules concerning the Christian sacrament of penance, a "new manner of reconciliation with God" that was first developed by Celtic monks in Ireland in the sixth century AD. It consisted of a list of sins a ...
in nature, this Rule played a seminal role in the formalisation of the Sacrament of Confession
Confession, in many religions, is the acknowledgment of one's sins (sinfulness) or wrongs.
Christianity Catholicism
In Catholic teaching, the Sacrament of Penance is the method of the Church by which individual men and women confess sins ...
in the Catholic Church. The zeal and piety of the Church in Ireland during the 6th and 7th centuries was such that many monks, including Columbanus and his companions, went as missionaries to Continental Europe, especially to the Merovingian and Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippin ...
Frankish Empire. Notable establishments founded by the Irish Christians were Luxeuil Abbey in Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
, Bobbio Abbey in Lombardy
Lombardy ( it, Lombardia, Lombard language, Lombard: ''Lombardia'' or ''Lumbardia' '') is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in the northern-central part of the country and has a population of about 10 ...
, Abbey of Saint Gall in modern Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
and Disibodenberg Abbey Disibodenberg today
Disibodenberg ruins
Disibodenberg ruins
Disibodenberg picture
Disibodenberg is a monastery ruin in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It was founded by Saint Disibod. Hildegard of Bingen, who wrote Disibod's biography "Vita Sa ...
near Odernheim am Glan. These Columbanian monasteries were great places of learning, with substantial libraries; these became centres of resistance to the heresy of Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
. Later, the ''Rule of St. Columbanus'' was supplanted by the "softer" ''Rule of St. Benedict
The ''Rule of Saint Benedict'' ( la, Regula Sancti Benedicti) is a book of precepts written in Latin in 516 by St Benedict of Nursia ( AD 480–550) for monks living communally under the authority of an abbot.
The spirit of Saint Benedict's Ru ...
''. The ascetic nature of Gaelic monasticism
There is archaeological evidence of insular monasticism as early as the mid 5th century, influenced by establishments in Gaul such as the monastery of Martin of Tours at Marmoutier Abbey, Tours, Marmoutier, the abbey established by Honoratus at Lé ...
has been compared to the Desert Fathers of Egypt. Martin of Tours
Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 – 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the ...
and John Cassian were significant influences.
Gregorian Reform and Norman influence
Within the Catholic Church, the Gregorian Reform took place during the 11th century, which reformed the administration of theRoman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while dist ...
to a more centralised model and closely enforced disciplines such as the struggle against simony
Simony () is the act of selling church offices and roles or sacred things. It is named after Simon Magus, who is described in the Acts of the Apostles as having offered two disciples of Jesus payment in exchange for their empowering him to imp ...
, marriage irregularities and in favour of clerical celibacy
Clerical celibacy is the requirement in certain religions that some or all members of the clergy be unmarried. Clerical celibacy also requires abstention from deliberately indulging in sexual thoughts and behavior outside of marriage, because the ...
. This was in the aftermath of the East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, a ...
between the Catholic Church in the West and the Orthodox Church
Orthodox Church may refer to:
* Eastern Orthodox Church
* Oriental Orthodox Churches
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church of New Zealand
* State church of the Roman Empire
* True Orthodox church
See also
* Orthodox (dis ...
in the East. These Roman Reforms reached Ireland with three or four significant Synods: the First Synod of Cashel (1101) was called by Muirchertach Ó Briain
Muirchertach (modern spelling: Muircheartach, anglicised as Murtagh) is an Irish language male given name meaning "mariner". The name was sometimes Anglicised as "Mortimer." The Old Norse name Kjartan is derived from this name. Ásgeir Blöndal M ...
, the High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ga, Ardrí na hÉireann ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and later sometimes assigned ana ...
and King of Munster, held at the Rock of Cashel with Máel Muire Ó Dúnáin as papal legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title ''legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic ...
, affirming many of these disciplines. This was followed by the Synod of Ráth Breasail (1111), called by the High King with Giolla Easpaig as the papal legate (he had been an associate of Anselm of Aosta
Anselm of Canterbury, OSB (; 1033/4–1109), also called ( it, Anselmo d'Aosta, link=no) after his birthplace and (french: Anselme du Bec, link=no) after his monastery, was an Italian Benedictine monk, abbot, philosopher and theologian of the ...
), which moved the administration of the Church in Ireland from a monastic-centered model to diocesian-centered one, with two Provinces at Armagh and Cashel established, with twelve territorial diocese under the Archbishop of Armagh
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdio ...
and Archbishop of Cashel respectively. It also brought Waterford under Cashel, as the Norsemen had previously looked to the Province of Canterbury
The Province of Canterbury, or less formally the Southern Province, is one of two ecclesiastical provinces which constitute the Church of England. The other is the Province of York (which consists of 12 dioceses).
Overview
The Province consist ...
. Cellach of Armagh, the " Coarb Pádraig", was present and recognised with the new title as Archbishop of Armagh, which was given the Primacy of Ireland.
 One of the major figures associated with the Gregorian Reform in Ireland was Máel Máedóc Ó Morgair, also known as Malachy, who was an Archbishop of Armagh and the first Gaelic Irish saint to undergo a formal canonisation process and official proclamation. Máel Máedóc was closely associated with Bernard of Clairvaux and introduced his
One of the major figures associated with the Gregorian Reform in Ireland was Máel Máedóc Ó Morgair, also known as Malachy, who was an Archbishop of Armagh and the first Gaelic Irish saint to undergo a formal canonisation process and official proclamation. Máel Máedóc was closely associated with Bernard of Clairvaux and introduced his Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint ...
order from France into Ireland with the foundation of Mellifont Abbey in 1142. He had visited Pope Innocent II
Pope Innocent II ( la, Innocentius II; died 24 September 1143), born Gregorio Papareschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 14 February 1130 to his death in 1143. His election as pope was controversial and the fi ...
in Rome to discuss implementing reforms. It was in association with these foundations that the Synod of Kells-Mellifont
The Synod of Kells (, ) took place in 1152, under the presidency of Giovanni Cardinal Paparoni, and continued the process begun at the Synod of Ráth Breasail (1111) of reforming the Irish church. The sessions were divided between the abbeys of ...
(1152) took place. Malachy had died a few years previously and so Cardinal Giovanni Paparoni Giovanni Cardinal Paparoni (sometimes known in English as John Cardinal Paparo; died ca. 1153/1154) was an Italian Cardinal and prominent papal legate in dealings with Ireland and Scotland.
He was created Cardinal by Pope Celestine II in 1143. He p ...
was present as papal legate for Pope Eugene III. It rejected Canterbury's pretentions of primacy over the Irish Church. This created two more Provinces and Archbishops, with an Archbishop of Dublin
The Archbishop of Dublin is an archepiscopal title which takes its name after Dublin, Ireland. Since the Reformation, there have been parallel apostolic successions to the title: one in the Catholic Church and the other in the Church of Irelan ...
and an Archbishop of Tuam added. Tuam was established in acknowledgement of the political rise of Connacht, with the High King being Toirdhealbhach Ó Conchobhair. Another major figure associated with this Reform was Lorcán Ó Tuathail, Archbishop of Dublin who founded Christ Church at Dublin under the Reformed Augustinians.
Due to the influential hagiography, the ''Life of Saint Malachy'', authored by Bernard of Clairvaux, with a strongly Reformist Cistercian zeal, the view that the Gaelic Irish Christians were "savages", "barbarian" or "semi-pagan"; due to their difference in church discipline and organisation and despite a reform already underway under the native High Kings; found a wide footing in Western Europe. In 1155, John of Salisbury
John of Salisbury (late 1110s – 25 October 1180), who described himself as Johannes Parvus ("John the Little"), was an English author, philosopher, educationalist, diplomat and bishop of Chartres.
Early life and education
Born at Salisbury, En ...
, Secretary to the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justi ...
(then Theobald of Bec), visited Benevento
Benevento (, , ; la, Beneventum) is a city and ''comune'' of Campania, Italy, capital of the province of Benevento, northeast of Naples. It is situated on a hill above sea level at the confluence of the Calore Irpino (or Beneventano) and the ...
where the first English Pontiff, Pope Adrian IV
Pope Adrian IV ( la, Adrianus IV; born Nicholas Breakspear (or Brekespear); 1 September 1159, also Hadrian IV), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 4 December 1154 to his death in 1159. He is the only Englishman t ...
(Nicholas Breakspear) was reigning. Here, he spoke of the need for Reform for the Church in Ireland, requesting that this be overseen by the King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ...
, then Henry II Plantagenet
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin king ...
, who would have the right to invade and rule Ireland. Adrian IV published the Papal bull '' Laudabiliter'' giving permission for this proposal. This was not acted on immediately or made public, partly due to the King's own problems with the church (i.e. — murder of Thomas Becket) and his mother Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as ...
being opposed to him acting on it. The Normans had conquered England around century earlier and now due to internal political rivalries within Gaelic Ireland, began to invade Ireland in 1169, under Strongbow, ostensibly to restore the King of Leinster. Fearful that the Norman barons would set up their own rival Kingdom and wanting Ireland himself, Henry II landed at Waterford in 1171, under the authority of ''Laudabiliter'' (ratified by Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland ( it, Rolando), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181.
A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a con ...
). Once established, he held the Second Synod of Cashel (1172). The Synod, ignored in the Irish annals
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over t ...
, is known from the writings of Gerald of Wales, the anti-Gaelic Norman who authored ''Expugnatio Hibernica'' (1189). Three of the four Irish Archbishops are said to have attended, with Armagh not present due to infirmity but supportive. It relisted most of the Reforms already approached before and included a tithe to be paid to the parish and that "divine matters" in the Irish Church should be conducted along the lines observed by the English Church. In the following years, Norman-descended churchmen would now play a direct role within the Irish Church as the political Lordship of Ireland was established, though many Gaelic kingdoms and their dioceses remained too.
Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
and Knights Hospitaller had a presence in Ireland, mostly, though not exclusively, in the Norman areas. The Templars had their Principal at Clontarf Castle
Clontarf Castle ( ga, Caisleán Chluain Tarbh) is a much-modernised castle, dating to 1837, in Clontarf, Dublin, Ireland, an area famous as a key location of the Battle of Clontarf in 1014. There has been a castle on the site since 1172. In mod ...
until their suppression in 1308 and received land grants from various patrons; from the de Laceys, Butlers, Taffes, FitzGeralds and even O'Mores. Their Master in Ireland was part of the administration of the Lordship of Ireland. The Hospitallers (later known as the Knights of Malta
The Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), officially the Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem, of Rhodes and of Malta ( it, Sovrano Militare Ordine Ospedaliero di San Giovanni di Gerusalemme, di Rodi e di Malta; ...
) had their Priory at Kilmainham and various preceptories in Ireland. They took over Templar properties and continued throughout the Medieval period. During the 13th century, the mendicant orders began to operate within Ireland and 89 friaries were established during this period.Gandharva, Joshi. (2021)"Monastic Ireland: The Mendicant Orders"
History Ireland The first of these to arrive were the Order of Preachers (also known as the Dominicans), they first established a branch at Dublin in 1224, shortly followed by one at Drogheda the same year, before spreading further. Prominent examples of Dominican establishments from this era are
Black Abbey
The Black Abbey of Kilkenny, Ireland, is a Catholic priory of the Dominican Order, dedicated to the Holy and Undivided Trinity. Black Abbey was established in 1225 as one of the first houses of the Dominican Order in Ireland.
The history of the ...
in Kilkenny
Kilkenny (). is a city in County Kilkenny, Ireland. It is located in the South-East Region and in the province of Leinster. It is built on both banks of the River Nore. The 2016 census gave the total population of Kilkenny as 26,512.
Kilken ...
and Sligo Abbey
Sligo Abbey () was a Dominican convent in Sligo, Ireland, founded in 1253. It was built in the Romanesque style with some later additions and alterations. Extensive ruins remain, mainly of the church and the cloister.
Name and location
The n ...
. Their biggest rivals, the Order of Friars Minor (also known as the Franciscans) arrived at around the same time, either 1224 or 1226, with their first establishment at Youghal. The Ennis Friary
Ennis Friary (Irish: ''Mainistir na hInse'') (colloquially also known as Ennis Abbey) was a Franciscan friary in the town of Ennis, County Clare, Ireland. It was established in the middle of the 13th century by the ruling O'Brien dynasty who s ...
and Roscrea Friary
Roscrea Friary () is a ruined medieval Franciscan friary and National Monument located in Roscrea, County Tipperary, Ireland. It is on Abbey Street, in the west end of Roscrea, on the north bank of the River Bunnow. The Friary was founded in the ...
in Thomond founded by the O'Briens are other prominent Franciscan examples. The Carmelites arrived next in 1271, followed by the Augustinians
Augustinians are members of Christian religious orders that follow the Rule of Saint Augustine, written in about 400 AD by Augustine of Hippo. There are two distinct types of Augustinians in Catholic religious orders dating back to the 12th–13 ...
. Within these orders, as demonstrated by the Franciscans in particular, there was often a strong ethnic conflict between the native Irish Gaels and the Normans.
During the Western Schism which lasted from 1378 to 1417, within which there were at least two claimants to the Papacy (one in Rome and one in Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
), different factions within Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland ( ga, Éire Ghaelach) was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the early 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans co ...
disagreed on whom to support.Egan, Simon. (2018)Richard II and the Wider Gaelic World: A Reassessment
Cambridge University Press This was not a doctrinal dispute, but a political one. The Plantagenet-controlled Lordship of Ireland followed the Kingdom of England in backing the Pope in Rome. Meanwhile, there were two main power blocs among the Gaelic kingdoms and Gaelicised-lordships supporting different contenders. The "''Donn''" faction, led by the
O'Neill of Tyrone
The O'Neill dynasty (Irish: ''Ó Néill'') are a lineage of Irish Gaelic origin, that held prominent positions and titles in Ireland and elsewhere. As kings of Cenél nEógain, they were historically the most prominent family of the Northern ...
, O'Brien of Thomond
The O'Brien dynasty ( ga, label=Classical Irish, Ua Briain; ga, label=Modern Irish, Ó Briain ; genitive ''Uí Bhriain'' ) is a noble house of Munster, founded in the 10th century by Brian Boru of the Dál gCais (Dalcassians). After becoming ...
, Burke of Clanrickard
Clanricarde (; ), also known as Mac William Uachtar (Upper Mac William) or the Galway Burkes, were a fully Gaelicised branch of the Hiberno-Norman House of Burgh who were important landowners in Ireland from the 13th to the 20th centuries.
Ter ...
and O'Connor Donn of Roscommon O'Connor or O'Conor may refer to:
People
* O'Connor or O'Conor, an Irish clan
* O'Connor Sligo, a royal dynasty ruling the northern part of the Kingdom of Connacht
* O'Connor (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Places
*Burnet O' ...
supported Rome. Through the agency of the Earl of Ormond, they had been loosely allied to Richard II of England
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father die ...
when he made an expedition to Ireland in 1394–95. Secondly, there was the ''"Ruadh"'' faction, led by the O'Donnell of Tyrconnell
The O'Donnell dynasty ( ga, Ó Dónaill or ''Ó Domhnaill,'' ''Ó Doṁnaill'' ''or Ua Domaill;'' meaning "descendant of Dónal") were the dominant Irish clan of the kingdom of Tyrconnell, Ulster, in medieval Ireland. Naming conventions
Or ...
, Burke of Mayo
Burke is an Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman Monarchy of Ireland, Irish surname, deriving from the ancient Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman and Hiberno-Norman noble dynasty, the House of Burgh. In Ireland, the descendants of William de Burgh (–1206) had ...
and O'Connor Ruadh of Roscommon
The O'Conor family (Middle Irish: ''Ó Conchubhair''; Modern ga, Ó Conchúir) are an Irish noble house and were one of the most influential and distinguished royal houses in Ireland. The O'Conor family held the throne of the Kingdom of Co ...
; from 1406, they were joined by the O'Neill of Clannaboy. This alternative power faction backed the Avignon Antipapacy and were more closely allied to the Stewart-controlled Kingdom of Scotland. The situation was finally resolved by the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance was a 15th-century ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance in present-day Germany. The council ended the Western Schism by deposing or accepting the res ...
of 1414–1418 with full reunification of the Church.
Counter-Reformation and suppression

 A confusing but defining period arose during the
A confusing but defining period arose during the English Reformation
The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Protestant Reformation, a religious and poli ...
in the 16th century, with monarchs alternately for or against papal supremacy
Papal supremacy is the doctrine of the Catholic Church that the Pope, by reason of his office as Vicar of Christ, the visible source and foundation of the unity both of the bishops and of the whole company of the faithful, and as pastor of the ...
. When on the death of Queen Mary in 1558, the church in England and Ireland broke away completely from the papacy, all but two of the bishops of the church in Ireland followed the decision. Very few of the local clergy led their congregations to follow. The new body became the established state church
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
, which was grandfathered in the possession of most church property. This allowed the Church of Ireland to retain a great repository of religious architecture and other religious items, some of which were later destroyed in subsequent wars. A substantial majority of the population remained Catholic, despite the political and economic advantages of membership in the state church. Despite its numerical minority, however, the Church of Ireland remained the official state church for almost 300 years until it was disestablished on 1 January 1871 by the Irish Church Act 1869 that was passed by Gladstone's Liberal government.
The effect of the Act of Supremacy 1558 and the papal bull of 1570 ( Regnans in Excelsis) legislated that the majority population of both kingdoms to be governed by an Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
ascendancy. After the defeat of King James II of The Three Kingdoms in 1690, the Test Acts were introduced which began a long era of discrimination against the recusant Catholics of the kingdoms.
Between emancipation and the revolution
The slow process of reform from 1778 on led to Catholic Emancipation in 1829. By then Ireland was a part of the newly created United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. As part of this,St. Patrick's College, Maynooth
St Patrick's Pontifical University, Maynooth ( ga, Coláiste Naoimh Phádraig, Maigh Nuad), is the "National Seminary for Ireland" (a Roman Catholic college), and a pontifical university, located in the town of Maynooth, from Dublin, Ireland ...
was founded as a national seminary for Ireland with the Maynooth College Act 1795
The Maynooth College Act 1795 (35 Geo. 3 c. 21) was an Act of the Parliament of Ireland that established and arranged the funding for St Patrick's College, Maynooth as Ireland's Catholic seminary.
Irish Catholic priests had traditionally been ...
(prior to this, from the time of Protestant persecutions beginning until around the time of the French Revolution, Irish priests underwent formation in Continental Europe). The Maynooth Grant of 1845, whereby the British government attempted to engender good will to Catholic Ireland became a political controversy with the Anti-Maynooth Conference
Anti-Maynooth Conference was a conference hosted in London in May 1845 by Conservatives, evangelical Anglicans and the Protestant Association to campaign against the Maynooth Grant and British State funding of the Roman Catholic Maynooth College. ...
group founded by anti-Catholics.
In 1835, Fr. John Spratt, an Irish Carmelite
, image =
, caption = Coat of arms of the Carmelites
, abbreviation = OCarm
, formation = Late 12th century
, founder = Early hermits of Mount Carmel
, founding_location = Mount Car ...
visited Rome and was given by Pope Gregory XVI, the relics and the remains of St. Valentine
Saint Valentine ( it, San Valentino; la, Valentinus) was a 3rd-century Roman saint, commemorated in Western Christianity on February 14 and in Eastern Orthodoxy on July 6. From the High Middle Ages, his Saints' Day has been associated with ...
(whose feast is St. Valentine's Day
Valentine's Day, also called Saint Valentine's Day or the Feast of Saint Valentine, is celebrated annually on February 14. It originated as a Christian feast day honoring one or two early Christian martyrs named Saint Valentine and, throu ...
), a Roman 3rd century Christian martyr, which Spratt brought back to Whitefriar Street Carmelite Church
Whitefriar Street Carmelite Church is a Roman Catholic church in Dublin, Ireland maintained by the Carmelite order. The church is noted for having the relics of Saint Valentine, which were donated to the church in the 19th century by Pope Gre ...
, Dublin. The faith was beginning to be legalised in Ireland again but the relics of most of the old Irish saints had been destroyed, so Pope Gregory XVI gifted these to the Irish nation. In the aftermath of the Great Hunger, Cardinal Paul Cullen became the first Irish cardinal of the Catholic Church. He played a significant role in shaping 19th century Irish Catholicism and also played a leading role at the First Vatican Council
The First Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the First Vatican Council or Vatican I was convoked by Pope Pius IX on 29 June 1868, after a period of planning and preparation that began on 6 December 1864. This, the twentieth ecu ...
as an ultramontanist involved in crafting the formula for papal infallibility. Cullen called the Synod of Thurles in 1850, the first formal synod of the Irish Catholic episcopacy and clergy since 1642 and then the Synod of Maynooth
Synod of Maynooth (1875) was the second national synod of the Catholic Church in Ireland since the passing of the Catholic Emancipation Act, the first was the 1850 Synod of Thurles. It was the first synod to be held in Maynooth College. The synod ...
.
In 1879, there was a significant Marian apparition in Ireland, that of Our Lady of Knock in County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the Taxus baccata, yew trees") is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. In the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Conn ...
. Here the Blessed Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother o ...
is said to have appeared, with St. Joseph and St. John the Evangelist either side (along with the '' Agnus Dei'') and she remained silent throughout. Statements were taken from 15 lay people who claimed to have witnessed the apparition. The Knock Shrine
The Sanctuary of Our Lady of Knock, commonly referred to as Knock Shrine, is a Roman Catholic pilgrimage site and national shrine in the village of Knock, County Mayo, Ireland, where locals claimed to have seen an apparition in 1879 of the Ble ...
became a major place of pilgrimage and later in 1932, Pope Pius XI
Pope Pius XI ( it, Pio XI), born Ambrogio Damiano Achille Ratti (; 31 May 1857 – 10 February 1939), was head of the Catholic Church from 6 February 1922 to his death in February 1939. He was the first sovereign of Vatican City fro ...
declared Our Lady of Knock to be "Queen of Heaven and of Ireland" at the closing of the Eucharistic Congress of Dublin
The 31st International Eucharistic Congress, held in Dublin 22–26 June 1932, was one of the largest eucharistic congresses of the 20th century. Ireland was then home to over three million Catholics and It was selected to host the congress as ...
.
Following the partition of Ireland
 From the time that Ireland achieved independence, the church came to play an increasingly significant social and political role in the Irish Free State and following that, the Republic of Ireland. For many decades, Catholic influence (coupled with the rural nature of Irish society) meant that Ireland was able to uphold family-orientated social policies for longer than most of the West, contrary to the '' laissez-faire''-associated cultural liberalism of the British and Americans. This cultural direction was particularly prominent under Éamon de Valera. For example, from 1937 until 1995, divorce and remarriage was not permitted (in line with
From the time that Ireland achieved independence, the church came to play an increasingly significant social and political role in the Irish Free State and following that, the Republic of Ireland. For many decades, Catholic influence (coupled with the rural nature of Irish society) meant that Ireland was able to uphold family-orientated social policies for longer than most of the West, contrary to the '' laissez-faire''-associated cultural liberalism of the British and Americans. This cultural direction was particularly prominent under Éamon de Valera. For example, from 1937 until 1995, divorce and remarriage was not permitted (in line with Catholic views of marriage
Marriage in the Catholic Church, also known as holy matrimony, is the "covenant by which a man and woman establish between themselves a partnership of the whole of life and which is ordered by its nature to the good of the spouses and the procre ...
).Divorce was permitted under the Constitution of the Irish Free State. The ban on divorce was introduced with the 1937 constitution. The ban was repealed in 1995. While the ban forbade remarriage, it provided for separation. Similarly, pornography, abortion, and contraceptionThe sale of contraceptives was banned until 1978. They were regarded as medical items thereafter, and were only available from pharmacies; seOther outlets issued them freely, accepting donations and, as this was not selling, it was legal; see
Contraception in the Republic of Ireland
Contraception was illegal in Ireland from 1935 until 1980, when it was legalised with strong restrictions, later loosened. The ban reflected Catholic teachings on sexual morality.
History Papal encyclicals
The encyclical (1930) followed the in ...
. For comparison, some other countries had a total ban: in the United States, for example, laws in some states prohibited contraception to married couples until the '' Griswold v. Connecticut'' decision in 1965; unmarried couples had to wait until the 1972 ruling ''Eisenstadt v. Baird
''Eisenstadt v. Baird'', 405 U.S. 438 (1972), was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court that established the right of unmarried people to possess contraception on the same basis as married couples.
The Court struck down a Massachusetts la ...
''. were also resisted; media depictions perceived to be detrimental to public morality were also opposed by Catholics. In addition, the church largely controlled many of the state's hospitals, and most schools, and remained the largest provider of many other social services.
At the partition of Ireland in 1922, 92.6% of the south's population were Catholic while 7.4% were Protestant. By the 1960s, the Anglican and Nonconformist Protestant population had fallen by half, mostly due to emigration in the early years of Irish independence, with some Anglicans preferring to live within the UK. However, in the early 21st century the percentage of Protestants in the Republic has risen slightly, to 4.2%, and the absolute numbers to over 200,000, almost equal to the number in 1920, due to immigration and a modest flow of conversions from Catholicism. The Catholic Church's policy of '' Ne Temere'', whereby the children of marriages between Catholics and Protestants had to be brought up as Catholics,The ''Ne Temere'' decree was issued in 1908. In one Irish instance, a court ruled, in 1957, that a pre-nuptial agreement based on this was legally binding. This led to the Fethard-on-Sea boycott
The Fethard-on-Sea boycott was a controversy in 1957 involving Sean and Sheila Cloney (née Kelly), a married couple from the village of Fethard-on-Sea, County Wexford, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It led to a sectarian boycott led by the local R ...
. Many, including Éamon de Valera condemned the incident. ''Ne Temere'' was criticised by the Second Vatican Council and repealed by Pope Paul VI in 1970, declaring: "The penalties decreed by canon 2319 of the Code of Canon Law are all abrogated. For those who have already incurred them the effects of those penalties cease" (se. also helped to uphold Catholic hegemony. In both parts of Ireland, church policy and practice changed markedly after the Vatican II reforms of 1962. Probably the largest change was that Mass could be said in vernacular languages instead of Latin, and in 1981 the church commissioned its first edition of the Bible in the
Irish language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was ...
, but the church overwhelmingly uses English. Archbishop John Charles McQuaid was uneasy about the introduction of an English liturgy and ecumenical revisions, finding it offensive to Catholic sensibilities; he wished to uphold the liturgy in Latin, while also offering Irish as the vernacular (he promoted an Irish language provision more than other Bishops).
Since the Celtic Tiger and the furtherance of cosmopolitanism
Cosmopolitanism is the idea that all human beings are members of a single community. Its adherents are known as cosmopolitan or cosmopolite. Cosmopolitanism is both prescriptive and aspirational, believing humans can and should be " world citizens ...
in Ireland, Catholicism has been one of the traditional elements of Ireland to fall into decline; particularly in urban areas. Fewer than one in five Catholics attend Mass on any given Sunday in Dublin with many young people only retaining a marginal interest in religion the Archbishop of Dublin, Diarmuid Martin
Diarmuid Martin (born 8 April 1945) is the retired Roman Catholic Archbishop of Dublin and Primate of Ireland. Martin was ordained a priest in 1969 and represented the Holy See at major United Nations International Conferences before becoming th ...
, said in May 2011. According to an Ipsos MRBI poll by the Irish Times, the majority of Irish Catholics do not attend mass weekly, with almost 62% rejecting key parts of Catholicism such as transubstantiation. After the results of both the 2015 same-sex marriage and the 2018 abortion referendums, Úna Mullally, a liberal journalist who writes for '' The Guardian'' claimed that "the fiction of Ireland as a conservative, dogmatically Catholic country has been shattered".
Northern Ireland
The Government of Ireland Act of 1920 acted as the constitution of Northern Ireland, in which was enshrined freedom of religion for all of Northern Ireland's citizens. Here Catholics formed a minority of some 35 percent of the population, which had mostly supported Irish nationalism and was therefore historically opposed to the creation of Northern Ireland. Many commentators have suggested that the separate education systems in Northern Ireland after 1921 prolonged the sectarian divisions in that community. Cases of gerrymandering and preference in public services for Protestants led on to the need for a Civil Rights Movement in 1967. This was in response to continuing discrimination against Catholics in Northern Ireland.Organization
 The church is organised into four ecclesiastical provinces. While these may have coincided with contemporary 12th century civil provinces or petty kingdoms, they are not now coterminous with the modern civil provincial divisions. The church is led by four
The church is organised into four ecclesiastical provinces. While these may have coincided with contemporary 12th century civil provinces or petty kingdoms, they are not now coterminous with the modern civil provincial divisions. The church is led by four archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
s and twenty-three bishops; however, because there have been amalgamations and absorptions, there are more than twenty-seven dioceses. For instance, the diocese of Cashel has been joined with the diocese of Emly, Waterford merged with Lismore, Ardagh merged with Clonmacnoise among others. The bishop of the Diocese of Galway
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Galway, Kilmacduagh and Kilfenora ( ga, Deoise na Gaillimhe, Chill Mhic Duaich agus Chill Fhionnúrach) is a Roman Catholic diocese in the west of Ireland. It is in the ecclesiastical province of Tuam and is subject ...
is also the Apostolic Administrator of Kilfenora. There are 1,087 parishes, a few of which are governed by administrators, the remainder by parish priests. There are about 3,000 secular clergy—parish priests, administrators, curate
A curate () is a person who is invested with the ''care'' or ''cure'' (''cura'') ''of souls'' of a parish. In this sense, "curate" means a parish priest; but in English-speaking countries the term ''curate'' is commonly used to describe clergy w ...
s, chaplains, and professors in colleges. The Association of Catholic Priests
The Association of Catholic Priests (ACP) is a liberal, independent and voluntary association of Catholic clergy in Ireland. The association was established on 1 September 2010 with the claimed objective of having "a forum, and a voice to reflec ...
is a voluntary association of clergy in Ireland that claims to have 800 members.
There are also many religious orders, which include: Augustinians
Augustinians are members of Christian religious orders that follow the Rule of Saint Augustine, written in about 400 AD by Augustine of Hippo. There are two distinct types of Augustinians in Catholic religious orders dating back to the 12th–13 ...
, Capuchins, Carmelites, Fathers of the Holy Ghost
The Congregation of the Holy Spirit ( la, Congregatio Sancti Spiritus) abbreviated CSSp), in full the Congregation of the Holy Spirit under the protection of the Immaculate Heart of the Virgin Mary () is a male religious congregation of the Catho ...
, Dominicans, Franciscans, Jesuits, Marists, Missionaries of Charity, Oblates, Passionists, Redemptorists, and Vincentians Vincentian can refer to:
*A citizen of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
*A person from Saint Vincent (island), the largest island in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
*A member of one of the orders or societies in the Vincentian Family, both Roman ...
. The total number of the regular clergy
Regular clergy, or just regulars, are clerics in the Catholic Church who follow a rule () of life, and are therefore also members of religious institutes. Secular clergy are clerics who are not bound by a rule of life.
Terminology and history
The ...
is about 700. They are engaged either in teaching or in giving missions
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
* Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
, and occasionally charged with the government of parishes.
Two societies of priests were founded in Ireland, namely St Patrick's Missionary Society
St. Patrick's Society for the Foreign Missions (Latin ''Societas Sancti Patritii pro Missionibus ad Exteros''; also known as the Kiltegan Fathers) is a Catholic society of apostolic life of pontifical right for men composed of missionary priests ...
, with its headquarters in County Wicklow
County Wicklow ( ; ga, Contae Chill Mhantáin ) is a county in Ireland. The last of the traditional 32 counties, having been formed as late as 1606, it is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is bordered by t ...
, and the Missionary Society of St. Columban
The Missionary Society of St. Columban ( la, Societas Sancti Columbani pro Missionibus ad Exteros) (abbreviated as S.S.C.M.E. or SSC), commonly known as the Columbans, is a missionary Catholic society of apostolic life of Pontifical Right foun ...
based in County Meath.
Affiliated groups
Besides numerousreligious institute
A religious institute is a type of institute of consecrated life in the Catholic Church whose members take religious vows and lead a life in community with fellow members. Religious institutes are one of the two types of institutes of consecrate ...
s such as the Dominicans, there are many groups more focused on Catholic laity in Ireland, such as:
*Society of Saint Vincent de Paul
The Society of St Vincent de Paul (SVP or SVdP or SSVP) is an international voluntary organization in the Catholic Church, founded in 1833 for the sanctification of its members by personal service of the poor.
Innumerable Catholic parishes have ...
(1844)
* Ancient Order of Hibernians (1890s)
* Knights of Columbanus (1915)
* Legion of Mary (1921)
Other organisations with Irish branches:
* Sovereign Military Order of Malta
* Order of the Holy Sepulchre
Missionary activity
In the years surrounding the Great Famine in Ireland, the Catholic Church was doing much work to evangelise other nations in the world. As a consequence of the famine, the Parish Mission's Movement commenced that would lead to a stricter observance of Catholicism in Ireland as well as the push for reform of healthcare and education which would later be expanded into the overseas missionary work. Initially inspired largely byCardinal Newman
John Henry Newman (21 February 1801 – 11 August 1890) was an English theologian, academic, intellectual, philosopher, polymath, historian, writer, scholar and poet, first as an Anglican priest and later as a Catholic priest and cardi ...
to convert the colonised peoples of the British Empire, after 1922 the church continued to work in healthcare and education what is now the Third World through its bodies such as Trócaire
Trócaire (, meaning "compassion") is the official overseas development agency of the Catholic Church in Ireland.
History
The roots of the charity lie in Pope Paul VI's 1967 encyclical ''Populorum Progressio'',
. Along with the Irish Catholic diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
in countries like the US and Australia, this has created a worldwide network, though affected by falling numbers of priests. For a large part of the 20th century, the number of men entering the priesthood in Ireland was so overwhelming that many were sent to the United States, Britain, Canada and Australia.
Statistics
In the 2016 Irish census 78.3% of the population identified as Catholic in Ireland; numbering approximately 3.7 million people. Ireland has seen a significant decline from the 84.2% who identified as Catholic in the 2011 census. In October 2019 the Association of Catholic Priests (ACP) announced that reform is urgently required to prevent parishes from closing across Ireland. The number of clerics dying or retiring continues to exceed the number of new priests. The ACP has long promoted church reform, including relaxing celibacy rules, ordaining married men, and ordaining women to the diaconate. 65% of Irish Catholics support same-sex marriage and 30% oppose it.Society
Politics
In Ireland the church had significant influence on public opinion. The introduction of the Irish Education Act (1831) of Lord Stanley placed Irish primary school education under it. It was associated with theJacobite
Jacobite means follower of Jacob or James. Jacobite may refer to:
Religion
* Jacobites, followers of Saint Jacob Baradaeus (died 578). Churches in the Jacobite tradition and sometimes called Jacobite include:
** Syriac Orthodox Church, sometimes ...
movement until 1766, and with Catholic emancipation until 1829. The church was resurgent between 1829 and the disestablishment of the Church of Ireland in 1869–71, when its most significant leaders included Bishop James Doyle
James Warren Doyle, O.E.S.A. (1786–1834) was a Roman Catholic Bishop of Kildare and Leighlin in Ireland, who used the signature "JKL", an acronym from "James Kildare and Leighlin." Doyle was active in the Anti-Tithe movement. A campaigner for C ...
, Cardinal Cullen
Paul Cardinal Cullen (29 April 1803 – 24 October 1878) was Roman Catholic Archbishop of Dublin and previously of Armagh, and the first Irish cardinal. His Ultramontanism spearheaded the Romanisation of the Catholic Church in Ireland and ...
and Archbishop MacHale. The relationship to Irish nationalism was complex; most of the bishops and high clergy supported the British Empire, but a considerable number of local priests were more sympathetic to Irish independence. While the church hierarchy was willing to work with Parliamentary Irish nationalism, it was mostly critical of " Fenianism"; i.e. – Irish republicanism. This continued right up until it was clear that the British-side was losing, then the church partly switched sides. It supported the Anglo-Irish Treaty and therefore were formally pro-treaty in the Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War ( ga, Cogadh Cathartha na hÉireann; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United ...
, excommunicating anti-treaty followers. Despite this, some Protestants in Ireland stated that they were opposing Irish self-government, because it would result in "Rome Rule
"Rome Rule" was a term used by Irish unionists to describe their belief that with the passage of a Home Rule Bill, the Roman Catholic Church would gain political power over their interests in Ireland. The slogan was popularised by the Radical MP ...
" instead of home rule, and this became an element in (or an excuse for) the creation of Northern Ireland.
The church continued to have great influence in Ireland. Éamon de Valera's 1937 constitution, while granting freedom of religion, recognised the "special position of the Holy Catholic Apostolic and Roman Church". Major popular church events attended by the political world have included the Eucharistic Congress in 1932 and the Papal Visit in 1979. The last prelate with strong social and political interests was Archbishop McQuaid
John Charles McQuaid, C.S.Sp. (28 July 1895 – 7 April 1973), was the Catholic Primate of Ireland and Archbishop of Dublin between December 1940 and January 1972. He was known for the unusual amount of influence he had over successive governme ...
, who retired in 1972.
Pope Francis visited Ireland in 2018 upon invitation extended to the Supreme Pontiff by Ireland's Catholic bishops to visit the country in August 2018 for the World Meeting of Families. This was only the second visit of a pope to the country, the first one having taken place in 1979 with John Paul II.
Education
After independence in 1922, the Church became more heavily involved inhealth care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profe ...
and education, raising money and managing institutions which were staffed by Catholic religious institute
A religious institute is a type of institute of consecrated life in the Catholic Church whose members take religious vows and lead a life in community with fellow members. Religious institutes are one of the two types of institutes of consecrate ...
s, paid largely by government intervention and public donations and bequests. Its main political effect was to continue to gain power in the national primary schools where religious proselytisation in education was a major element. The hierarchy opposed the free public secondary schools service introduced in 1968 by Donogh O'Malley, in part because they ran almost all such schools. The church's strong efforts since the 1830s to continue the control of Catholic education was primarily an effort to guarantee a continuing source of candidates for the priesthood, as they would have years of training before entering a seminary.
As Irish society has become more diverse and secular, Catholic control over primary education has become controversial, especially with regard to preference given to baptized Catholics when schools are oversubscribed. Virtually all state-funded primary schools – almost 97 percent – are under church control. Irish law allows schools under church control to consider religion the main factor in admissions. Oversubscribed schools often choose to admit Catholics over non-Catholics, a situation that has created difficulty for non-Catholic families. The United Nations Committee on the Rights of the Child
The Committee on the Rights of the Child (CRC) is a body of experts that monitor and report on the implementation of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child.
The Committee also monitors the Convention's three optional protoco ...
in Geneva asked Ireland's minister for children, James Reilly, to explain the continuation of preferential access to state-funded schools on the basis of religion. He said that the laws probably needed to change, but noted it may take a referendum because the Irish constitution gives protections to religious institutions. The issue is most problematic in the Dublin area. A petition initiated by a Dublin barrister
A barrister is a type of lawyer in common law jurisdictions. Barristers mostly specialise in courtroom advocacy and litigation. Their tasks include taking cases in superior courts and tribunals, drafting legal pleadings, researching law and ...
, Paddy Monahan, has received almost 20,000 signatures in favor of overturning the preference given to Catholic children. A recently formed advocacy group, Education Equality, is planning a legal challenge.
Health care
From 1930, hospitals were funded by a sweepstake (lottery) with tickets frequently distributed or sold by nuns or priests. In 1950, the church opposed the Mother and Child Scheme. Less hospitals in Ireland are still run by Catholic religious institutes. For example, the Mater Misericordiae University Hospital, Dublin is run by the Sisters of Mercy. In 2005, the hospital deferred trials of a lung cancer medication because female patients in the trial would be required to practise contraception contrary to Catholic teaching. Mater Hospital responded that its objection was that some pharmaceutical companies mandated that women of childbearing years use contraceptives during the drug trials: "The hospital said it was committed to meeting all of its legal requirements regarding clinical trials while at the same time upholding the principles and ethos of the hospital's mission", and "that individuals and couples have the right to decide themselves about how they avoid pregnancy."Public morality
Divorce allowing remarriage was banned in 1924 (though it had been rare), and selling artificial contraception was made illegal. The church's influence slipped somewhat after 1970, impacted partly by the media and the growingfeminist
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes. Feminism incorporates the position that society prioritizes the male po ...
movement as well as the sexual revolution. For instance, the Health (Family Planning) Act, 1979 showed the ability of the Catholic Church to influence the government to compromise over artificial contraception, though the church was unable to get the result it wanted—contraception could now be bought, but only with a prescription from a doctor and supplied only by registered chemists. A 1983 Amendment to the constitution introduced the constitutional prohibition of abortion, which the church supported, though abortion for social reasons had already been illegal under Irish statutory law. However, the church failed to influence the June 1996 removal of the constitutional prohibition of divorce. While the church opposed divorce allowing remarriage in civil law, its canon law allowed for a law of nullity and a limited divorce "''a mensa et thoro''", effectively a form of marital separation. The church helped reinforce public censorship and maintained its own list of banned literature until 1966, which influenced the State's list.
In spite of objections from the Catholic hierarchy, voters in Ireland approved a referendum to legalise same-sex marriage in 2015 and abortion in 2018. In September 2010, an Irish Times/Behaviour Attitudes survey of 1,006 people showed that 67% felt that same-sex couples should be allowed to marry. This majority extended across all age groups, with the exception of the over-65s, while 66% of Catholics were in favour of same-sex marriage. Only 25% disagreed that same-sex couples should be allowed to marry, opposition that was concentrated among older people and those in rural areas. In terms of same-sex adoption, 46% were in support of it and 38% opposed. However, a majority of females, 18- to 44-year-olds, and urban dwellers supported the idea. The survey also showed that 91% of people would not think less of someone who came out as homosexual, while 60% felt the recent civil partnership legislation was not an attack on marriage.
War-time censorship by the government for security was strict and included the church; when bishops spoke on aspects of the war, they were censored and treated "with no more ceremony than any other citizen". While statements and pastoral letters issued from the pulpit were not interfered with, the quoting of them in the press was subject to the censor.
Abuse scandals
Several reports detailing cases ofemotional
Emotions are mental states brought on by neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or displeasure. There is currently no scientific consensus on a definition. E ...
, physical
Physical may refer to:
*Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally co ...
and sexual abuse of thousands of children while in the pastoral care of dozens of priests have been published in 2005–2009. These include the Ferns Report and the Commission to Inquire into Child Abuse, and have led on to much discussion in Ireland about what changes may be needed in the future within the church.
Popular traditions
Alongside the church itself, many Irish devotional traditions have continued for centuries as a part of the church's local culture. One such tradition, unbroken since ancient times, is of annual pilgrimages to sacred Celtic Christian places such asSt Patrick's Purgatory
St Patrick's Purgatory is an ancient pilgrimage site on Station Island in Lough Derg (Donegal), Lough Derg, County Donegal, Ireland. According to legend, the site dates from the fifth century, when Christ showed Saint Patrick a cave, sometime ...
and Croagh Patrick
Croagh Patrick (), nicknamed 'the Reek', is a mountain with a height of and an important site of pilgrimage in County Mayo, Ireland. The mountain has a pyramid-shaped peak and overlooks Clew Bay, rising above the village of Murrisk, several mil ...
. Particular emphasis on mortification and offerings of sacrifices and prayers for the Holy Souls of Purgatory is another strong, long time cultural practice. The Leonine Prayers were said at the end of Low Mass for the deceased of the penal times. " Patterns" (processions) in honour of local saints also continue to this day. Marian Devotion is an element, focused on the shrine at Knock, an approved apparition of the Virgin Mary who appeared in 1879. Feasts and devotions such as the Immaculate Conception of Mary (1854) and the Sacred Heart
The Most Sacred Heart of Jesus ( la, Cor Jesu Sacratissimum) is one of the most widely practised and well-known Catholic devotions, wherein the heart of Jesus is viewed as a symbol of "God's boundless and passionate love for mankind". This devo ...
of Jesus (1642), and the concepts of martyrology are very prominent elements. Respect for mortification of the flesh
Mortification of the flesh is an act by which an individual or group seeks to mortify or deaden their sinful nature, as a part of the process of sanctification.
In Christianity, mortification of the flesh is undertaken in order to repent for s ...
has led on to the veneration of Matt Talbot
Matt Talbot (2 May 1856 – 7 June 1925) was an Irish ascetic revered by many Catholics for his piety, charity and mortification of the flesh.
Talbot was a manual labourer. Though he lived alone for most of his life, Talbot did live with hi ...
and Padre Pio.
See also
* Irish Catholic * Christianity in Ireland *Apostolic Nuncio to Ireland
The Apostolic Nunciature to Ireland the diplomatic mission of the Holy See to Ireland. It is located in Dublin. The position of Apostolic Nuncio is currently vacant.
The Apostolic Nunciature to Ireland is an ecclesiastical office of the Cathol ...
* List of Catholic churches in Ireland
A list of Catholic churches in Ireland, notable current and former individual church buildings and congregations and administration of the Catholic Church in Ireland. These churches are listed buildings or have been recognised for their historica ...
Footnotes
References
Further reading
* * * ''Contemporary Catholicism in Ireland: A Critical Appraisal'', ed. by John Littleton, Eamon Maher, Columbia Press 2008, *Brian Girvin: "Church, State, and Society in Ireland since 1960" In: ''Éire-Ireland'' – Volume 43:1&2, Earrach/Samhradh / Spring/Summer 2008, pp. 74–98 * Tom Inglis: ''Moral Monopoly: The Rise and Fall of the Catholic Church in Modern Ireland'', Univ College Dublin Press, 2nd Revised edition, 1998, *Moira J. Maguire: "The changing face of catholic Ireland: Conservatism and Liberalism in the Ann Lovett and Kerry Babies Scandal" In: ''feminist studies''. fs, ISSN 0046-3663, j. 27 (2001), n. 2, p. 335–359 * *Report on abuse by thCatholic Church in Ireland
External links
Irish Bishops' Conference
{{DEFAULTSORT:Catholic Church in Ireland All-Ireland organisations Irish culture