Ipomovirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Ipomovirus'' is a genus of
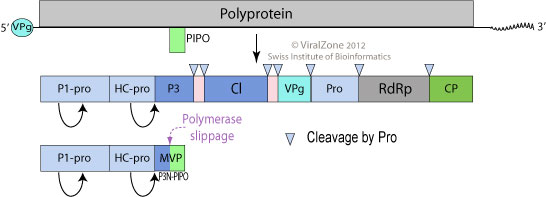 The genome is either monpartite or bipartite depending on the species. Member viruses have linear, single stranded RNA genome of positive polarity about 10-11 kilobases in length. The 3’ terminus has a poly (A) tract and the 5’ terminus has a genome linked protein (VPg).
Member viruses encode a single polypeptide with a predicted molecular weight of 390 kilo
The genome is either monpartite or bipartite depending on the species. Member viruses have linear, single stranded RNA genome of positive polarity about 10-11 kilobases in length. The 3’ terminus has a poly (A) tract and the 5’ terminus has a genome linked protein (VPg).
Member viruses encode a single polypeptide with a predicted molecular weight of 390 kilo
Viralzone: Ipomovirus
ICTV
{{Taxonbar, from=Q6065310 Virus genera Ipomoviruses
positive-strand RNA viruses
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated in ...
in the family ''Potyviridae
''Potyviridae'' is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to ...
''. Member viruses infect plants and are transmitted by whiteflies (''Bemisia tabaci
The silverleaf whitefly (''Bemisia tabaci'', also informally referred to as the sweet potato whitefly) is one of several species of whitefly that are currently important agriculture, agricultural pest (animal), pests. A review in 2011 concluded t ...
''). The name of the genus is derived from ''Ipomoea
''Ipomoea'' () is the largest genus in the plant family Convolvulaceae, with over 600 species. It is a large and diverse group, with common names including morning glory, water convolvulus or water spinach, sweet potato, bindweed, moonfl ...
'' – the generic name of sweet potato. There are seven species in this genus.
Structure
Viruses in genus ''Ipomovirus'' are non-enveloped, with flexuous and filamentous geometries. The diameter is around 12–15 nm, and may have a variety of lengths depending on the species (for single segmented species lengths of around 650–900 nm, or for double segmented species 200–300 nm and 500–600 nm). The capsid has helical symmetry with a pitch of 3.4 nm. They induce characteristic inclusion bodies (pinwheels) within infected plant cells.Genome
 The genome is either monpartite or bipartite depending on the species. Member viruses have linear, single stranded RNA genome of positive polarity about 10-11 kilobases in length. The 3’ terminus has a poly (A) tract and the 5’ terminus has a genome linked protein (VPg).
Member viruses encode a single polypeptide with a predicted molecular weight of 390 kilo
The genome is either monpartite or bipartite depending on the species. Member viruses have linear, single stranded RNA genome of positive polarity about 10-11 kilobases in length. The 3’ terminus has a poly (A) tract and the 5’ terminus has a genome linked protein (VPg).
Member viruses encode a single polypeptide with a predicted molecular weight of 390 kiloDalton
Dalton may refer to:
Science
* Dalton (crater), a lunar crater
* Dalton (program), chemistry software
* Dalton (unit) (Da), the atomic mass unit
* John Dalton, chemist, physicist and meteorologist
Entertainment
* Dalton (Buffyverse), minor ch ...
s (kDa) which is cleaved into ~10 protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s. In 5'–3' order these proteins are
*P1 (a serine protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
): 83 kDa
*HC (a protease): 51 kDa
*P3: 34 kDa
*6K1: 5 kDa
*Cl (helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separatin ...
): 71 kDa
*6K2: 6 kDa
*VPg (the 5' binding protein): 20 kDa
*NIa-Pro (a protease): 27 kDa
*NIb (RNA dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to ...
): 57 kDa
*Capsid protein: 34 kDa
There may be some variation in the number of the proteins depending on the species, for instance some ipomoviruses lack HC and have a P1 tandem. Inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (known as ITPase or HAM1) is an atypical protein domain identified in some ipomoviruses.
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by tubule-guided viral movement. Plants serve as the natural host. The virus is transmitted via a vector (white fly). Transmission routes are vector and mechanical.Taxonomy
The genus contains the following species: *'' Cassava brown streak virus'' *'' Coccinia mottle virus'' *'' Cucumber vein yellowing virus'' *'' Squash vein yellowing virus'' *'' Sweet potato mild mottle virus'' *'' Tomato mild mottle virus'' *'' Ugandan cassava brown streak virus''References
External links
Viralzone: Ipomovirus
ICTV
{{Taxonbar, from=Q6065310 Virus genera Ipomoviruses