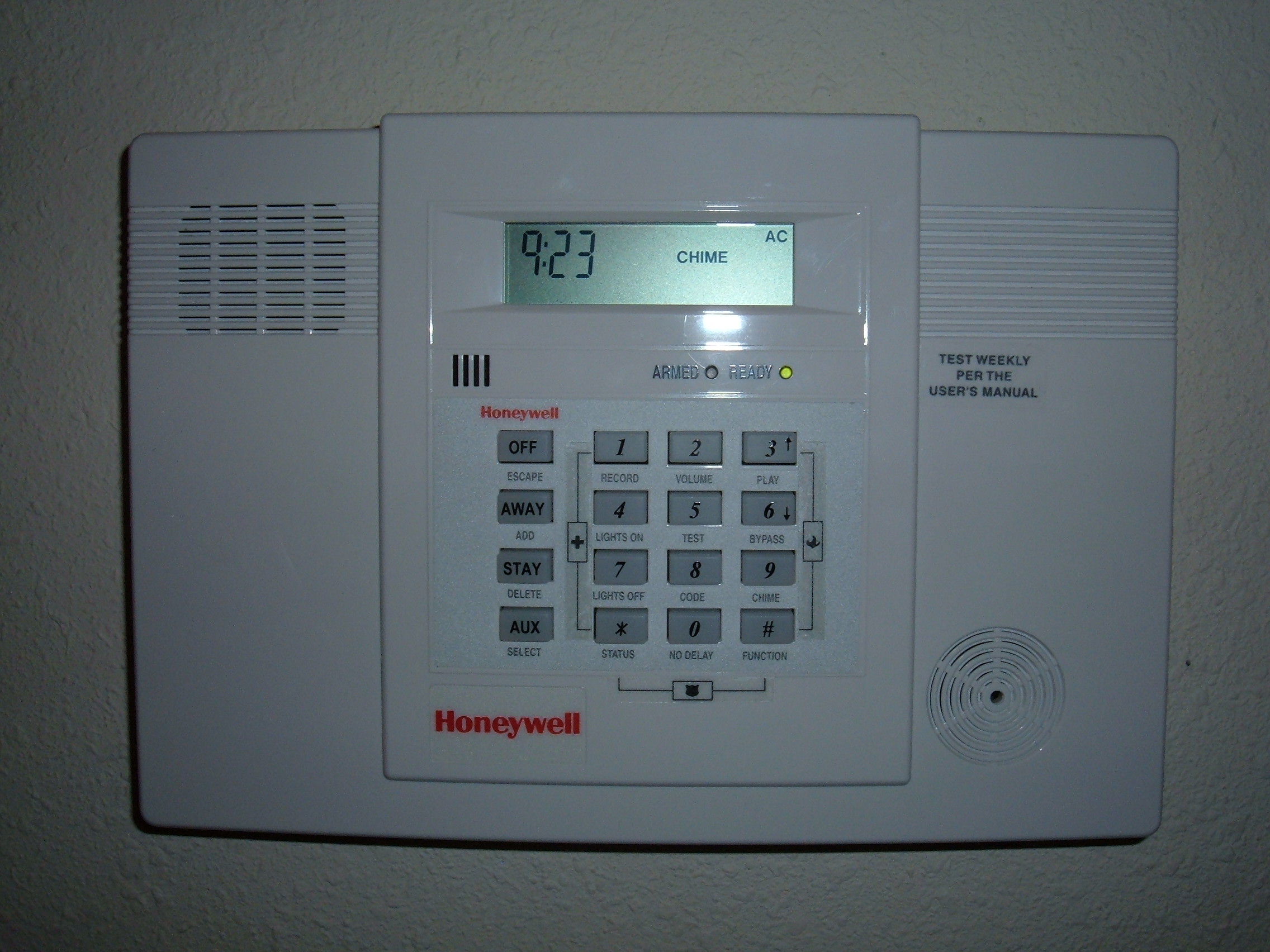


A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusions, such as unauthorized entry, into a building or other areas, such as a home or school. Security alarms protect against
burglary
Burglary, also called breaking and entering (B&E) or housebreaking, is a property crime involving the illegal entry into a building or other area without permission, typically with the intention of committing a further criminal offence. Usually ...
(
theft
Theft (, cognate to ) is the act of taking another person's property or services without that person's permission or consent with the intent to deprive the rightful owner of it. The word ''theft'' is also used as a synonym or informal shor ...
) or
property damage
Property damage (sometimes called damage to property) is the damage or destruction of real or tangible personal property, caused by negligence, willful destruction, or an act of nature. Destruction of property (sometimes called property de ...
, as well as against intruders. Examples include personal systems, neighborhood security alerts,
car alarm
A car alarm is an electronic device installed in a vehicle in an attempt to discourage theft of the vehicle itself, its contents, or both. Car alarms work by emitting high-volume sound (often a vehicle-mounted siren, klaxon, pre-recorded verba ...
s, and
prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol, penitentiary, detention center, correction center, correctional facility, or remand center, is a facility where Prisoner, people are Imprisonment, imprisoned under the authority of the State (polity), state ...
alarms.
Some alarm systems serve a single purpose of burglary protection; combination systems provide
fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion re ...
and intrusion protection. Intrusion-alarm systems are combined with
closed-circuit television
Closed-circuit television (CCTV), also known as video surveillance, is the use of closed-circuit television cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place on a limited set of monitors. It differs from broadcast television in that the signa ...
surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing, or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as ...
(CCTV) systems to record intruders' activities and interface to
access control
In physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the action of deciding whether a subject should be granted or denied access to an object (for example, a place or a resource). The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming ...
systems for electrically locked doors. There are many types of security systems. Homeowners typically have small, self-contained noisemakers. These devices can also be complicated, multirole systems with
computer monitoring and control. It may even include a two-way voice which allows communication between the panel and monitoring station.
Components
The most basic alarm consists of at least one sensor to detect trespassers and an alerting device to indicate the intrusion. However, a typical premises security alarm employs the following components:
* Alarm control panel (ACP), or simply panel: The panel reads sensor inputs, tracks arm/disarm status, and signals intrusions. In a modern device, there are typically one or more computer
circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) ...
s inside a metal enclosure. Many newer networks often use sealed plastic boxes. Some also have their control units built-into the keypad or other
human-machine interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
.
* Sensors: In a security alarm, some sensors detect intrusions. Sensors' locations are at the perimeter of the protected area, within it, or both. Sensors can detect intruders by different methods.
* Alerting devices indicate an alarm condition. Most commonly, these are
bell
A bell /ˈbɛl/ () is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be m ...
s, sirens, also and or flashing lights. Alerting devices serve the dual purpose of warning occupants of intrusion and potentially scaring off burglars.
* Keypads: Keypads are devices that function as the
human-machine interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
to the system. In addition to buttons, keypads typically feature indicator lights, a small multi-character display, or both.
In addition to the system itself, security alarms often offer a monitoring service. In the event of an alarm, the premises control unit contacts a central monitoring station. Operators at the station take appropriate action, such as contacting property owners, notifying the police, or dispatching private security forces. Such alerts transmit via dedicated alarm circuits, telephone lines, or the internet.
Sensor types
Hermetically sealed reed switches

The hermetically sealed
reed switch
The reed switch is an Electromechanics, electromechanical switch operated by an applied magnetic field. It was invented in 1922 by professor Valentin Kovalenkov at the Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University#Soviet era, Petrogra ...
is a common type of two-piece sensor. This switch operates with an electrically conductive switch that is either normally open or normally closed when under the influence of a magnetic field in respect to proximity to the second piece, which contains a
magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
. When the magnet moves away from the reed switch, the reed switch either closes or opens, based on the normally closed or open design. This action, coupled with an electric current, allows an alarm control panel to detect a fault on that zone or circuit. These sensors are common, are found wired directly to an alarm control panel, or are typically found in wireless door or window contacts as sub-components.
Passive infrared detectors
The
passive infrared (PIR) motion detector is one of the most common sensors found in household and small business environments. This sensor does not generate or radiate energy; it works entirely by detecting the heat energy given off by other objects.
PIR sensors identify abrupt changes in temperature at a given point. As an intruder walks in front of the sensor, the temperature at that point will rise from
room temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and ...
to
body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
and then back again. This quick change triggers the detection.
PIR sensors designed to be wall- or ceiling-mounted come in various
fields of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angular extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation. It ...
. PIRs require a power supply in addition to the detection signaling circuit.
Infrasound detectors
The
infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
detector works by detecting infrasound, or sound waves at frequencies below 20Hz. Sounds at those frequencies are inaudible to the human ear. Due to its inherent properties, infrasound can travel distances of many hundreds of kilometers.
The entire infrasound detection system consists of the following components: a speaker (infrasound sensor) as a microphone input, an order-frequency filter, an analog-to-digital (A/D) converter, and an microcomputer to analyze the recorded signal.

If a potential intruder tries to enter into a house, they test whether it is closed and locked, uses tools on openings, or/and applies pressure, creating low-frequency sound vibrations. Before the intruder breaks in, the infrasound detector automatically detects the intruder's actions.
The purpose of such a system is to detect burglars before they enter the house to avoid both theft and vandalism. The sensitivity is dependent on the size of a home and the presence of animals.
Ultrasonic detectors
These active detectors transmit ultrasonic sound waves that are inaudible to humans using frequencies between 15 kHz and 75 kHz.
The Doppler shift principle is the underlying method of operation which detects a change in frequency due to object motion. This detection occurs when the object must cause a change in the ultrasonic frequency to the receiver relative to the transmitting frequency.
The ultrasonic detector operates by the transmitter emitting an ultrasonic signal into the area to be protected. Solid objects (such as the surrounding floor, walls, and ceiling) reflect sound waves, which the receiver will detect. Because ultrasonic waves are transmitted through air, hard-surfaced objects tend to reflect most of the ultrasonic energy, while soft surfaces tend to absorb the most energy.
When the surfaces are stationary, the frequency of the waves detected by the receiver will be equal to the transmitted frequency. However, a change in frequency will occur as a result of the Doppler principle when a person or object is moving towards or away from the detector. Such an event initiates an alarm signal. This technology is not active in many properties as many consider this obsolete.
Microwave detectors
This device emits microwaves from a transmitter and detects any reflected microwaves or reduction in beam intensity using a receiver. The transmitter and receiver are usually combined inside a single housing (monostatic) for indoor applications and separate housings (bistatic) for the protection of outdoor perimeters high-risk sites and critical infrastructures such as
fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work (physics), work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chem ...
storage,
petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable s ...
facilities,
military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
sites, civil and military
airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial Aviation, air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surf ...
s,
nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
facilities and more. To reduce false alarms this type of detector is usually combined with a passive infrared detector or similar alarm. Compared to the monostatic, the bistatic units work over longer distances: typical distances for transmitter-receivers up to 200m for
X-band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequency, frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is set at approximately 7.0� ...
frequencies and up to 500m for
K-band frequencies.

Microwave detectors respond to a
Doppler shift
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described t ...
in the frequency of the reflected energy, by a phase shift, or by a sudden reduction of the level of received energy. Any of these effects may indicate motion of an intruder. Microwave detectors are low cost, easy to install, have an invisible perimeter barrier. and is not affected by fog, rain, snow, sand storms, or wind. May be affected by the presence of water dripping on the ground. Typically need a sterile clearance area to prevent partial blocking of the detection field.
Functioning
The microwave generator is equipped with an
antenna that allows it to concentrate the beam of electromagnetic waves in one preferred location and the beam is intercepted by the receiver, equipped with a similar antenna to the transmitter.
The graphical representation of the beam is similar to a cigar, and, when not disturbed, it runs between the transmitter and the receiver and generates a continuous signal. When an individual tries to cross this beam, it produces a disturbance that is caught by the receiver as a variation of amplitude of the received signal.
These barriers are immune to harsh weather, such as
fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus and is heavily influenc ...
, heavy
rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
,
snow
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
and
sandstorms
A dust storm, also called a sandstorm, is a meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi-arid regions. Dust storms arise when a gust front or other strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface. Fine particles are transport ...
: none of these atmospheric phenomena affect in any way the behaviour and the reliability of the microwave detection. Furthermore, the working
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
range of this technology goes from -35 °C to +70 °C.
Digital analysis of the signal
The more recent and higher performance models of these detectors generate a detection whether the intruder is rolling, crossing, crawling or moving very slow within the
electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
reducing false alarms. The
ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional Scaling (geometry), scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a Surface (mathemat ...
al shape of the longitudinal section however does not allow a good detection capability close to the receiver or transmitter heads, and those areas are commonly referred to as "dead zones". A solution to avoid this problem, when installing 2 or more barriers, is to cross the respective transmitter and receiver heads some meters from the respective heads or to use mono-head sensor to cover the dead zones.
Compact surveillance radar
Compact surveillance radar
Compact surveillance radar are small lightweight radar systems that have a wide coverage area and are able to track people and vehicles in range and azimuth
An azimuth (; from ) is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonl ...
emits microwaves from a transmitter and detects any reflected microwaves. They are similar to microwave detectors but can detect the precise location and a GPS coordinate of intruders in areas extending over hundreds of acres. It has the capability of measuring the range, angle, velocity, direction, and size of the target. This target information is typically displayed on a map, user interface or situational awareness software that defines geographical alert zones or geofences with different types of actions initiated depending on time of day and other factors. CSR is commonly used to protect outside the fence line of critical facilities such as
electrical substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station an ...
s, power plants, dams, and bridges.
Photoelectric beams
Photoelectric beam systems detect the presence of an intruder by transmitting invisible infrared light beams across an area, where these beams may be obstructed. To improve the detection surface area, the beams are often employed in stacks of two or more. However, if an intruder is aware of the technology's presence, it can be avoided. The technology can be an effective long-range detection system, if installed in stacks of three or more where the transmitters and receivers are staggered to create a fence-like barrier. To prevent a clandestine attack using a secondary light source being used to hold the detector in a sealed condition whilst an intruder passes through, most systems use and detect a modulated light source. These sensors are low cost, easy to install, and require very little sterile clearance area to operate. However, it may be affected by fog or very high luminosity, and the position of the transmitter can be located with cameras.
Glass-break detection
A
glass-break detector may be used for internal perimeter building protection. Glass-break acoustic detectors are mounted in close proximity to the glass panes and listen for sound frequencies associated with glass breaking.
Seismic glass-break detectors, generally referred to as shock sensors, are different in that they are installed on the glass pane. When glass breaks it produces specific shock frequencies which travel through the glass and often through the window frame and the surrounding walls and ceiling. Typically, the most intense frequencies generated are between 3 and 5 kHz, depending on the type of glass and the presence of a plastic interlayer. Seismic glass-break detectors feel these shock frequencies and in turn generate an alarm condition.
Window foil is a less advanced detection method that involves gluing a thin strip of conducting foil on the inside of the glass and putting low-power electric current through it. Breaking the glass will tear the foil and break the circuit.
Smoke, heat, and carbon monoxide detectors
Most systems can also be equipped with smoke, heat, and/or
carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
detectors. These are also known as 24-hour zones (which are on at all times). Smoke and heat detectors protect from the risk of fire using different detection methods. Carbon monoxide detectors help protect from the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Although an intruder alarm panel may also have these detectors connected, it may not meet all the local
fire code
Fire safety is the set of practices intended to reduce destruction caused by fire. Fire safety measures include those that are intended to prevent wikt:ignition, the ignition of an uncontrolled fire and those that are used to limit the spread a ...
requirements of a fire alarm system.
Traditional smoke detectors are ionization smoke detectors which create an electric current between two metal plates, which sound an alarm when disrupted by smoke entering the chamber. Ionization smoke alarms can quickly detect the small amounts of particles produced by fast-flaming fires, such as cooking fires or those fueled by paper or flammable liquids. A newer type of the smoke detector is the photoelectric smoke detector. It contains a light source, which is positioned indirectly to the light sensitive electric sensor. Normally, light from the light source shoots straight across and misses the sensor. When smoke enters the chamber, it scatters the light, which then hits the sensor and triggers the alarm. Photoelectric smoke detectors typically respond faster to a fire in its early, smoldering stage, before the source of the fire bursts into flames.
Motion sensors
Motion sensors are devices that use various forms of technology to detect movement. The technology typically found in motion sensors to trigger an alarm includes infrared, ultrasonic, vibration and contact. Dual technology sensors combine two or more forms of detection in order to reduce false alarms as each method has its advantages and disadvantages. Traditionally motion sensors are an integral part of a home security system. These devices are typically installed to cover a large area as they commonly cover up to , with a 135° field of vision.
A type of motion sensor was used by the Japanese since ancient times. In the past, "(m)any people in Japan kept singing crickets and used them like watch dogs." Although a dog would bark when it senses an intruder, a cricket stops singing when approached by an intruder. The crickets are kept in decorative cages resembling bird cages, and these cages are placed in contact with the floor. During the day, the house is busy with normal daytime tasks. When activity reduces at night, the crickets start singing. If someone comes into the house at night, the floor starts to vibrate. "The vibration frightens the crickets and they stop singing. Then everyone wakes up --- from the silence. The family is used to hearing crickets at night and knows something is wrong if the crickets aren't singing. A similar observation was made in England about millers who lived in their mills. A mill wheel makes a great deal of noise, but the miller only awakens when the mill wheel stops turning.
Driveway alarms
Driveway alarm systems can be combined with most security and automation systems. They are designed to alert residents to unexpected visitors, intruders, or deliveries arriving at the property. Types of driveway sensors include magnetic and infrared motion sensors. Driveway alarms can be found in both hard-wired and wireless systems. They are common in rural security systems as well as for commercial applications.
Electro-mechanical (shaker) sensors
These
electro-mechanical
Electromechanics combine processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focus on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each ...
devices are mounted on barriers and are used primarily to detect an attack on the structure itself. The technology relies on an unstable mechanical configuration that forms part of the electrical circuit. When movement or vibration occurs, the unstable portion of the circuit moves and breaks the current flow, which produces an alarm. The medium transmitting the vibration must be correctly selected for the specific sensor as they are best suited to different types of structures and configurations. These systems are low cost and easily installed on existing fences, but can only be fence mounted and are unable to analyze differences in the pattern of vibrations (for example, the difference between gusts of wind and a person climbing the fence). For this reason, this technology is gradually being replaced by digital
accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (tha ...
-based systems.
MEMS Accelerometer
MEMS technology is an electromagnetic device that is created using
photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
The process begins with a photosensiti ...
, incision and ionian implantation. This produces a very compact and small device. In this device, in addition to the mechanical system, there are electronic circuits for control, acquisition and conditioning of the signal able to sense the environment.
MEMS accelerometer can be divided into two groups, piezoresistive and capacitive-based accelerometers. The former consists of a single-degree-of-freedom system of a mass suspended by a spring. They also have a beam with a proof mass at the beam’s tip and a Piezoresistive patch on the beam web.
On the contrary, capacitive-based accelerometers, also known as vibration sensors, rely on a change in electrical capacitance in response to acceleration.
Operating principle
The current technology allows to realize suspended silicon structures that are attached to the substrate in some points called anchors, and that constitute the sensitive mass of the accelerometer MEMS. These structures are free to move in the direction of the acceleration detected. They constitute the mobile reinforcement of a pair of capacitors connected to the ''half bridge''.
In this way, the acquired signals are amplified, filtered and converted in digital signals with the supervision of specific control circuits. MEMS' incorporations evolved from a single, stand-alone device to the integrated inertial motion units that are available today.
This technology uses a variety of transduction mechanisms to detect the displacement. They include capacitive, piezoresistive, thermal, optical, piezoelectric and tunneling.
Applications

In the last decades, many technological progresses have been made in this area and MEMS accelerometers are used in high-reliability environments and are starting to replace other established technologies.
MEMS accelerometer can be applied as a sensor in the earthquake disaster prevention, since one of the main characteristics of MEMS accelerometers is the linear frequency response to DC to about 500 Hz, and this capability offers an improvement in measuring
ground motion
Ground motion is the movement of the Earth’s surface from earthquakes or explosions. Ground motion is produced by seismic waves that are generated by sudden slip on a fault or sudden pressure at the explosive source and travel through the Eart ...
at lower-frequency band.
Another practical application of MEMS accelerometers is in machine condition monitoring to reduce machines’ maintenance. Wireless and embedded technologies such as Micro-electro Mechanical system sensors offer a wireless smart vibration measurement of machine’s condition.
Moving to the
defence
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indust ...
field, it can be applied in fence-mounted intrusion
detection
{{Unreferenced, date=March 2018
In general, detection is the action of accessing information without specific cooperation from with the sender.
In the history of radio communications, the term "detector" was first used for a device that detected ...
systems. Since MEMS sensors are able to work in a wide temperature range, they can prevent intrusions in outdoors and very spread-off perimeters.
Properties
An advantage offered by MEMS Accelerometers is the ability to measure static accelerations, such as acceleration due to gravity. This enables them to constantly verify that the positioning of the sensor, based on MEMS accelerometer, remains unaltered from the installation one.
MEMS accelerometers’ significant advantages also stem from their small size and high measurement frequency; additionally, they can be integrated with multiple sensors with different functions.
Ferrous metal detectors
Change in the local magnetic field due to the presence of
ferrous
In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the chemical element, element iron in its +2 oxidation number, oxidation state. The adjective ''ferrous'' or the prefix ''ferro-'' is often used to specify such compounds, as in ''ferrous chloride'' for iron(II ...
metals induces a current in the buried sensors (buried cables or discrete sensors) which are analyzed by the system. If the change exceeds a predetermined threshold, an alarm is generated.
This type of sensor can be used to detect intruders carrying substantial amounts of metal, such as a firearm, making it ideally suited for
anti-poaching
Anti-poaching is the organised act to counter the poaching of wildlife. However, it is generally used to describe an overall effort against the illegal wildlife trade. The act of anti-poaching is normally carried out by national parks on public ...
applications.
Electrostatic field
Sometimes referred to as E-field, this volumetric sensor uses
Electric field proximity sensing and can be installed on buildings, perimeters, fences, and walls. It also has the ability to be installed free-standing on dedicated poles. The system uses an electromagnetic field generator powering one wire, with another sensing wire running parallel to it. The sensing wire is connected to a signal processor that analyses amplitude change (mass of intruder), rate change (movement of intruder), and preset disturbance time (time the intruder is in the pattern). These items define the characteristics of an intruder and when all three are detected simultaneously, an alarm signal is generated.
The barrier can provide vertical protection from the ground to the height of the mounting posts (typically 4–6meters of height), depending on the number of sensor wires installed. It is usually configured in zones of about 200 metre lengths. Electrostatic field sensors are high-security and difficult to defeat, and have high vertical detection field. However, these sensors are expensive and have short zones, which contributes to more electronics (and thus a higher cost).
Microphonic systems

Microphonic systems vary in design (for example,
time-domain reflectrometer or
piezo-electric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress.
The piezoel ...
) but each is generally based on the detection of an intruder attempting to cut or climb over a fence. Usually the microphonic detection systems are installed as sensor cables attached to rigid chain-wire fences, however, some specialized versions of these systems can also be installed buried underground. Depending on the type, it can be sensitive to different frequencies or levels of noise or vibration. The system is based on coaxial or electro-magnetic sensor cable with the controller having the ability to differentiate between signals from the cable or chain-wire being cut, an intruder climbing the fence, or bad weather conditions.
The systems are designed to detect and analyze incoming electronic signals received from the sensor cable, and then to generate alarms from signals which exceed pre-set conditions. The systems have adjustable electronics to permit installers to change the sensitivity of the alarm detectors to the suit specific environmental conditions. The tuning of the system is usually done during commissioning of the detection devices.
Microphonic systems are relatively inexpensive compared to other systems and easy to install, but older systems may have a high rate of false alarms caused by wind and other distances. Some newer systems use
DSP to process the signal and reduce false alarms.
Taut wire fence systems
A taut wire perimeter security system is an independent screen of tensioned tripwires usually mounted on a fence or wall. Alternatively, the screen can be made thicker to avoid the need for a supporting chain-wire fence. These systems are designed to detect any physical attempt to penetrate the barrier. Taut wire systems can operate with a variety of switches or detectors that sense movement at each end of the tense wires. These switches or detectors can be a simple mechanical contact, static force transducer or an electronic strain gauge. Unwanted alarms caused by birds and other animals can be avoided by adjusting the sensors to ignore objects that exert small amounts of pressure on the wires. This type of system is vulnerable to intruders digging under the fence. A concrete footing directly below the fence is installed to prevent this type of attack.
Taut wire fence systems have low false alarm rates, reliable sensors, and high detection rates, but is expensive and complicated to install.
Fiber optic cable
A fiber-optic cable can be used to detect intruders by measuring the difference in the amount of light sent through the fiber core. A variety of fiber optic sensing technologies may be used, including
Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ) is the scattering or deflection of light, or other electromagnetic radiation, by particles with a size much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scat ...
or
interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important inves ...
. If the cable is disturbed, the light will change and the intrusion is detected. The cable can be attached directly to a chain-wire fence or bonded into a barbed steel tape that is used to protect the tops of walls and fences. This type of barbed tape provides a good physical deterrent as well as giving an immediate alarm if the tape is cut or severely distorted.
Being cable-based, fiber optic cables are very similar to the microphonic system and easy to install and can cover large perimeters. However, despite performing in a similar manner to microphonic-based systems, fiber optic cables have higher cost and is more complex due to the use of fiber-optic technology.
Ported coaxial cable

This system employs an electro-magnetic field disturbance principle based on two unshielded coaxial cables. The transmitter emits continuous radio frequency (RF) energy along one cable and the energy is received by the other cable. When the change in field strength weakens due to the presence of an object and reaches a pre-set lower threshold, an alarm condition is generated. The system is covert after installation. The surrounding soil must offer good drainage in order to avoid nuisance alarms. Ported coaxial cables are concealed as a buried form but can be affected by RF noise and is difficult to install.
Security electric fence
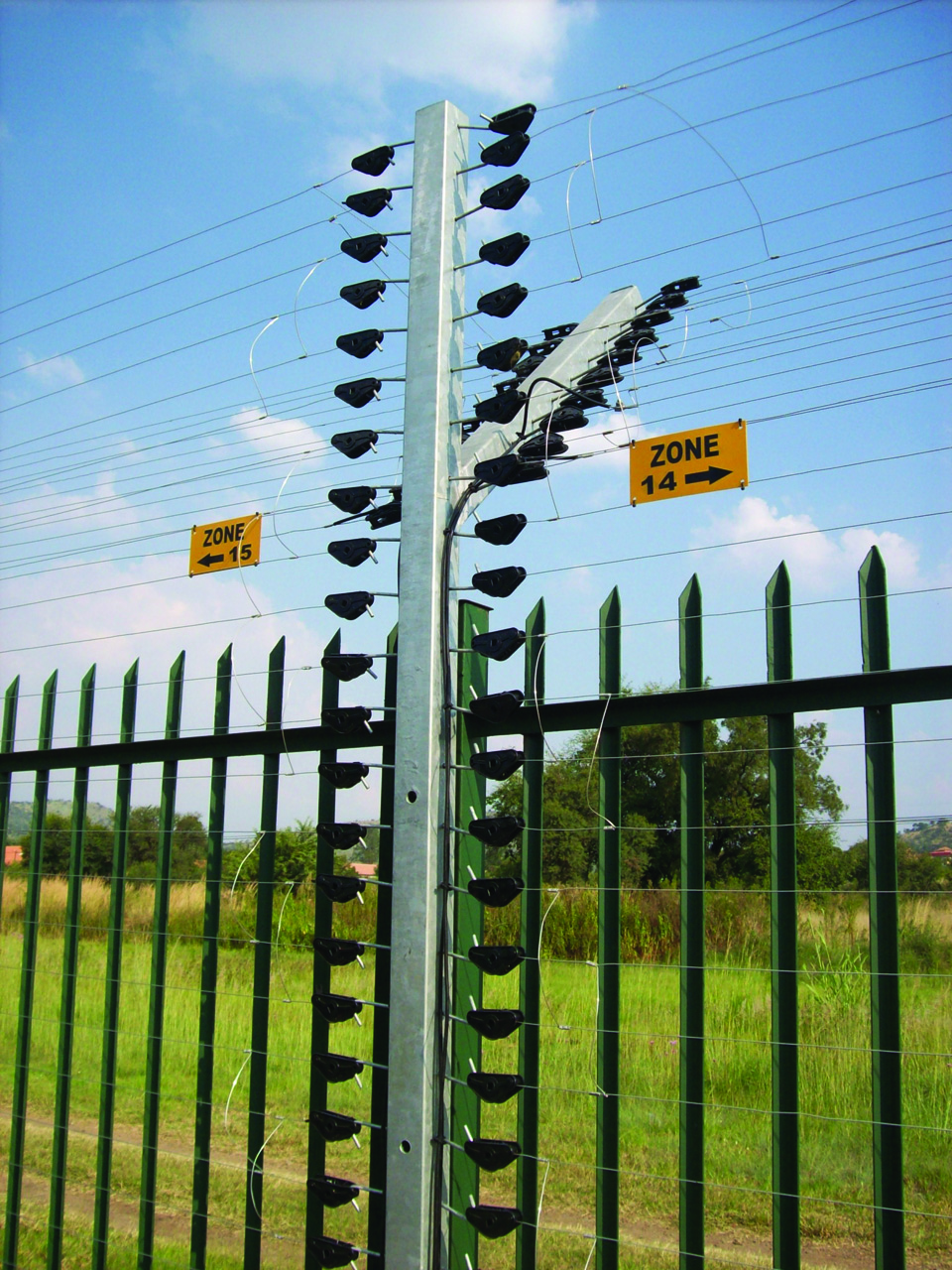

Security electric fences consist of wires that carry pulses of electric current to provide a non-lethal shock to deter potential intruders. Tampering with the fence also results in an alarm that is logged by the security electric fence energiser, and can also trigger a siren, strobe, and/or notifications to a control room or directly to the owner via email or phone. In practical terms, security electric fences are a type of
sensor array
A sensor array is a group of sensors, usually deployed in a certain geometry pattern, used for collecting and processing electromagnetic or acoustic signals. The advantage of using a sensor array over using a single sensor lies in the fact that an ...
that acts as a (or part of a) physical barrier, a psychological deterrent to potential intruders, and as part of a security alarm system.
Electric fences are less expensive than many other methods, less likely to give false alarms than many other alternative perimeter security methods, and have highest psychological deterrent of all methods, but there is a potential for unintended shock.
Wired, wireless, and hybrid systems
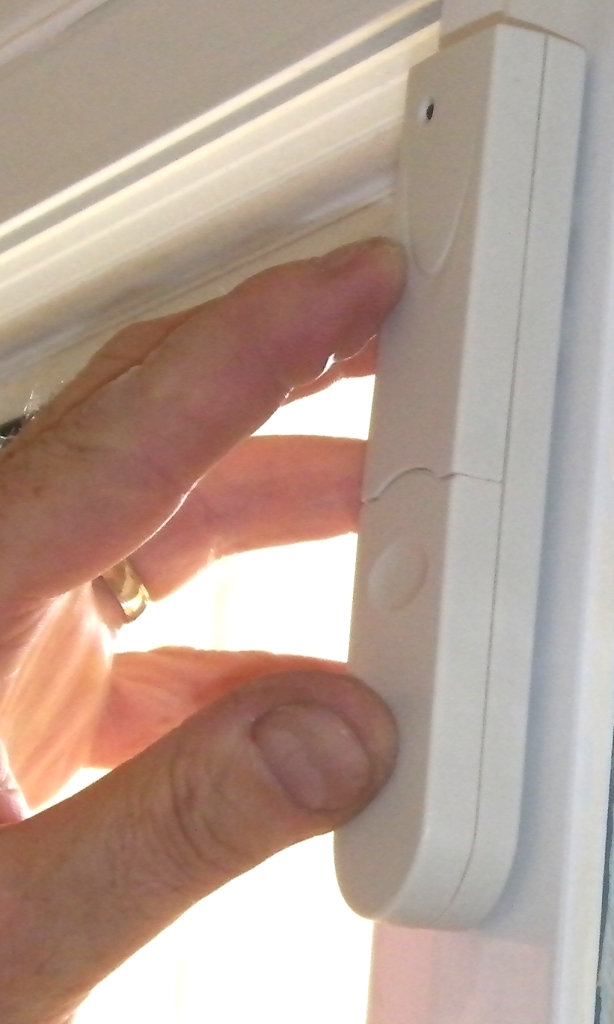

The trigger signal from sensors are transmitted to one or more control units either through wires or wireless means, such as radio, line carrier, and infrared.
Wired systems are convenient when sensors, such as passive infrared motion sensors and smoke detectors require external power to operate correctly; however, they may be more costly to install. Basic wired systems utilize a
star network
A star network is an implementation of a spoke–hub distribution paradigm in computer networks. In a star network, every host is connected to a central hub. In its simplest form, one central hub acts as a conduit to transmit messages. The ...
topology, where the panel is at the center logically, and all devices home run their line wires back to the panel. More complex panels use a
Bus network
A bus network is a network topology in which Node (networking), nodes are directly connected to a common half-duplex link called a bus (computing), bus.
A Host (network), host on a bus network is called a ''station''. In a bus network, every ...
topology where the wire basically is a
data loop around the perimeter of the facility, and has drops for the sensor devices which must include a unique device identifier integrated into the sensor device itself. Wired systems also have the advantage, if wired properly for example by dual loop, of being
tamper-evident
Tamper-evident describes a device or process that makes unauthorized access to the protected object easily detected. Seals, markings, or other techniques may be tamper indicating.
Tampering
Tampering involves the deliberate altering or adulterat ...
.
Wireless systems, on the other hand, often use battery-powered
transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
s which are easier to install and have less expensive start-up costs, but may fail if the batteries are not maintained. Depending on distance and construction materials, one or more wireless
repeater
In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it. Repeaters are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction. Some ...
s may be required to bring the signal to the alarm panel reliably. A wireless system can be moved to a new property easily. An important wireless connection for security is between the control panel and the monitoring station. Wireless monitoring of the alarm system protects against a burglar cutting cables or from failures of an internet provider. This setup is commonly referred to as fully wireless.
Hybrid systems use both wired and wireless sensors to achieve the benefits of both. Transmitters can also be connected through the premises' electrical circuits to transmit coded signals to the control unit (line carrier). The control unit usually has a separate channel or zone for burglar and fire sensors, and more advanced systems have a separate zone for every different sensor, as well as internal trouble indicators, such as mains power loss, low battery, and broken wires.
Alarm connection and monitoring
Depending upon the application, the alarm output may be local, remote or a combination of both. Local alarms do not include monitoring, but may include indoor and/or outdoor sounders, such as motorized bells or electronic sirens and lights, such
strobe light
A strobe light or stroboscopic lamp, commonly called a strobe, is a device used to produce regular flashes of light. It is one of a number of devices that can be used as a stroboscope. The word originated from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning ...
s which may be useful for signaling an evacuation notice during fire emergencies, or to scare off an amateur burglar quickly. However, with the widespread use of alarm systems, especially in cars, false alarms are very frequent and many urbanites tend to ignore alarms rather than investigating, and not contacting the necessary authorities. In rural areas where not many may hear the fire bell or burglar siren, lights or sounds may not make much difference, as the nearest emergency responders may arrive too late to avoid losses.
Remote alarm systems are used to connect the control unit to a predetermined monitor of some sort, and they are available in many different configurations. Advanced systems connect to a
central station
Central stations or central railway stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century as railway stations that had initially been built on the edge of city centres were enveloped by urban expansion and became an integral part of the ...
or first responder (e.g. police/fire/medical) via a direct phone wire, a cellular network, a radio network, or an IP path. In the case of a dual signaling system two of these options are utilized simultaneously. The alarm monitoring includes not only the sensors, but also the communication transmitter itself. While direct phone circuits are still available in some areas from phone companies, because of their high cost and the advent of dual signaling with its comparatively lower cost, their use is being phased out. Direct connections are now most usually seen only in federal, state, and local government buildings, or on a school campus that has a dedicated security, police, fire, or emergency medical department. In the United Kingdom, communication is only possible to an alarm receiving centre, and communication directly to the emergency services is not permitted.
More typical systems incorporate a digital cellular communication unit that will contact the central station or a monitoring station via the
Public Switched Telephone Network
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators. It provides infrastructure and services for public telephony. The PSTN consists o ...
(PSTN) and raise the alarm, either with a synthesized voice or increasingly via an encoded message string that the central station decodes. These may connect to the regular phone system on the system side of the
demarcation point
In telephony, the demarcation point is the point at which the public switched telephone network ends and connects with the customer's on-premises wiring. It is the dividing line which determines who is responsible for installation and mainte ...
, but typically connect on the customer side ahead of all phones within the monitored premises so that the alarm system can seize the line by cutting-off any active calls and call the monitoring company if needed. A dual signaling system would raise the alarm wirelessly via a radio path or cellular path using the phone line or broadband line as a backup overcoming any compromise to the phone line. Encoders can be programmed to indicate which specific sensor was triggered, and monitors can show the physical location of the sensor on a list or even a map of the protected premises, which can make the resulting response more effective.
Many alarm panels are equipped with a backup communication path for use when the primary PSTN circuit is not functioning. The redundant dialer may be connected to a second communication path, or a specialized encoded
cellular phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This radi ...
, radio, or internet interface device to bypass the PSTN entirely, to thwart intentional tampering with the phone lines. Tampering with the line could trigger a supervisory alarm via the radio network, giving early warning of an imminent problem. In some cases a remote building may not have PSTN phone service, and the cost of trenching and running a direct line may be prohibitive. It is possible to use a wireless cellular or radio device as the primary communication method.
In the UK, the most popular solution of this kind is similar in principle to the above but with the primary and backup paths reversed. Utilizing a radio path as the primary signaling path is not only quicker than PSTN but also allows significant cost savings as unlimited amounts of data can be sent at no extra expense.
Broadband alarm monitoring
Increasing deployment of voice over IP technology (VoIP) is driving the adoption of broadband signaling for alarm reporting. Many sites requiring alarm installations no longer have conventional telephone lines (POTS), and alarm panels with conventional telephone dialer capability do not work reliably over some types of VoIP service.
Dial-up analogue alarm panels or systems with serial/parallel data ports may be migrated to broadband through the addition of an alarm server device which converts telephone signaling signals or data port traffic to IP messages suitable for broadband transmission. However, the direct use of VoIP to transport analogue alarms without an alarm server device is problematic as the audio codecs used throughout the entire network transmission path cannot guarantee a suitable level of reliability or quality of service acceptable for the application.
In response to the changing public communications network, new alarm systems often use broadband signaling as a method of alarm transmission, and manufacturers are including IP reporting capability directly in their alarm panel products. When the Internet is used as a primary signaling method for critical security and life safety applications, frequent supervision messages are configured to overcome concerns about backup power for network equipment and signal delivery time. But for typical applications, connectivity concerns are controlled by normal supervision messages.
Radio alarm dual signaling
Dual signaling is a method of alarm transmission that uses a mobile phone network and a telephone and/or IP path to transmit intruder, fire and personal attack signals at high speed from the protected premises to an Alarm Receiving Centre (ARC). It most commonly uses GPRS or GSM, a high-speed signaling technology used to send and receive ‘packets’ of data, with a telephone line in addition. IP is not used as frequently due to issues with installation and configuration as high levels of expertise is often required in addition to alarm installation knowledge.
A dual signaling communication device is attached to a control panel on a security installation and is the component that transmits the alarm to the ARC. It can do this in a number of different ways, via the GPRS radio path, via the GSM radio path or via the telephone line/or IP. These multiple signaling paths are all present and live at the same time backing each other up to minimize exposure of the property to intruders. Should one fail, there is always a back up and depending on the manufacturer chosen up to three paths working simultaneously at any one time.
Dual paths allow distinction between hardware failures and a genuine attack on the alarm. This helps eliminate false alarms and unnecessary responses. Dual signaling has helped considerably with the restoration of police response as in an instance where a phone line is cut as the dual signaling device can continue to send alarm calls via one of its alternative paths either confirming or denying the alarm from the initial path.
In the UK,
CSL DualCom Ltd pioneered dual signaling in 1996. The company offered an alternative to existing alarm signaling while setting the current standard for professional dual path security monitoring. Dual signaling is now firmly regarded as the standard format for alarm signaling and is duly specified by all of the leading insurance companies.
Listen-in alarm monitoring
Monitored alarms and speaker phones allow for the central station to speak with the homeowner or intruder. This may be beneficial to the owner for medical emergencies. For actual break-ins, the speaker phones allow the central station to urge the intruder to cease and desist as response units have been dispatched. Listen-in alarm monitoring is also known as Immediate Audio-Response monitoring or Speaking Alarm Systems in the UK.
Alarm response
In the United States,
police
The police are Law enforcement organization, a constituted body of Law enforcement officer, people empowered by a State (polity), state with the aim of Law enforcement, enforcing the law and protecting the Public order policing, public order ...
respond to at least 36million alarm activations each year, at an estimated annual cost of $1.8billion.
Depending upon the zone triggered, number and sequence of zones, time of day, and other factors, the alarm monitoring center may automatically initiate various actions. Central station operators might be instructed to call emergency services immediately, or to first call the protected premises or
property manager
A property manager or estate manager is a person or firm charged with operating a real estate property for a fee. The property may be individual title owned or owned under the sectional title, share block company owned, and may be registered for ...
to try to determine if the alarm is genuine. Operators could also start calling a list of phone numbers provided by the customer to contact someone to go check on the protected premises. Some zones may trigger a call to the local heating oil company to check on the system, or a call to the owner with details of which room may be flooded. Some alarm systems are tied to
video surveillance
Closed-circuit television (CCTV), also known as video surveillance, is the use of closed-circuit television cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place on a limited set of monitors. It differs from broadcast television in that the signal ...
systems so that current video of the intrusion area can be instantly displayed on a remote monitor and recorded.
Some alarm systems use real-time audio and video
monitoring technology to verify the legitimacy of an alarm. In some
municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
around the United States, this type of alarm verification allows the property it is protecting to be placed on a "verified response" list, allowing for quicker and safer police responses.
Access control and bypass codes
To be useful, an intrusion alarm system is deactivated or reconfigured when authorized personnel are present. Authorization may be indicated in any number of ways, often with keys or codes used at the control panel or a remote panel near an entry. High-security alarms may require multiple codes, or a fingerprint, badge,
hand-geometry, retinal scan, encrypted-response generator, and other means that are deemed sufficiently secure for the purpose.
Failed authorizations would result in an alarm or a timed lockout to prevent experimenting with possible codes. Some systems can be configured to permit deactivation of individual sensors or groups. Others can also be programmed to bypass or ignore individual sensors and leave the remainder of the system armed. This feature is useful for permitting a single door to be opened and closed before the alarm is armed, or to permit a person to leave, but not return. High-end systems allow multiple access codes, and may only permit them to be used once, or on particular days, or only in combination with other users' codes (i.e., escorted). In any case, a remote monitoring center should arrange an oral code to be provided by an authorized person in case of false alarms, so the monitoring center can be assured that a further alarm response is unnecessary. As with access codes, there can also be a hierarchy of oral codes, for example, for furnace repairperson to enter the kitchen and basement sensor areas but not the silver vault in the pantry. There are also systems that permit a
duress code to be entered and silence the local alarm, but still trigger the remote alarm to summon the police to a robbery.
Fire sensors can be isolated, meaning that when triggered, they will not trigger the main alarm network. This is important when smoke and heat is intentionally produced. The owners of buildings can be fined for generating false alarms that waste the time of emergency personnel.
False and absent alarms
The
United States Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a United States federal executive departments, federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of Law of the Unite ...
estimates that between 94% and 98% of all alarm calls to law enforcement are
false alarm
A false alarm, also called a nuisance alarm, is the deceptive or erroneous report of an emergency, causing unnecessary panic and/or bringing resources (such as emergency services) to a place where they are not needed. False alarms may occur with ...
s.
System reliability and user error are the cause of most false alarms, sometimes called "nuisance alarms." False alarms can be very costly to local governments, local law enforcement, security system users and members of local communities. In 2007, the Department of Justice reported that in just one year, false alarms cost local municipalities and their constituents at least $1.8 billion.
In many municipalities across the United States, policies have been adopted to fine home and business owners for multiple false alarm activations from their security system. If multiple false alarms from the same property persist, that property could be added to a "no response" list, which prevents police dispatch to the property except in the event of verified emergency. Approximately 1% of police alarm calls actually involve a crime.
Nuisance alarms occur when an unintended event evokes an alarm status by an otherwise properly working alarm system. A false alarm also occurs when there is an alarm system malfunction that results in an alarm state. In all three circumstances, the source of the problem should be immediately found and fixed, so that responders will not lose confidence in the alarm reports. It is easier to know when there are false alarms, because the system is designed to react to that condition. Failure alarms are more troublesome because they usually require periodic testing to make sure the sensors are working and that the correct signals are getting through to the monitor. Some systems are designed to detect problems internally, such as low or dead batteries, loose connections, phone circuit trouble, etc. While earlier nuisance alarms could be set off by small disturbances, like insects or pets, newer model alarms have technology to measure the size/weight of the object causing the disturbance, and thus are able to decide how serious the threat is, which is especially useful in burglar alarms.
Some municipalities across the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
require alarm verification before police are dispatched. Under this approach, alarm monitoring companies must verify the legitimacy of alarms (except holdup, duress, and
panic alarms) before calling the police. Verified response typically involves visual on-scene verification of a break-in, or remote audio or video verification.
Audio and video verification
Alarms that utilize audio, video, or combination of both audio and video verification technology give security companies, dispatchers, police officers, and property managers more reliable data to assess the threat level of a triggered alarm.
Audio and video verification techniques use microphones and cameras to record audio frequencies, video signals, or image snapshots. The source audio and video streams are sent over a communication link, usually an Internet protocol (IP) network, to the
central station
Central stations or central railway stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century as railway stations that had initially been built on the edge of city centres were enveloped by urban expansion and became an integral part of the ...
where monitors retrieve the images through proprietary software. The information is then relayed to law enforcement and recorded to an event file, which can be used to plan a more strategic and tactical approach of a property, and later as prosecution evidence.
An example of this system is when a passive infrared or other sensor is triggered a designated number of video frames from before and after the event is sent to the central station.
A second video solution can be incorporated into a standard panel, which sends the central station an alarm. When a signal is received, a trained monitoring professional accesses the on-site digital video recorder (DVR) through an IP link to determine the cause of the activation. For this type of system, the camera input to the DVR reflects the alarm panel's zones and partitioning, which allows personnel to look for an alarm source in multiple areas.
The United States Department of Justice states that legislation requiring alarm companies to verify the legitimacy of an alarm, before contacting law enforcement (commonly known as "verified response") is the most effective way to reduce false burglar alarms. The Department of Justice considers audio, video, or an eye-witness account as verification for the legitimacy of a burglar alarm.
Cross-zoning
Cross-zoning is a strategy that uses multiple sensors to monitor activity in one area and software analyses input from all the sources. For example, if a motion detector trips in one area, the signal is recorded and the central-station monitor notifies the customer. A second alarm signal—received in an adjacent zone within a short time—is the confirmation the central-station monitor needs to request a dispatch immediately. This method builds increased protection.
Enhanced call verification
Enhanced call verification (ECV) helps reduce false dispatches while still protecting citizens, and is mandated in several US jurisdictions, although the alarm industry has successfully opposed it in others.
ECV requires central station personnel to attempt to verify the alarm activation by making a minimum of two phone calls to two different responsible party telephone numbers before dispatching law enforcement to the scene.
The first alarm-verification call goes to the location the alarm originated. If contact with a person is not made, a second call is placed to a different number. The secondary number, best practices dictate, should be to a telephone that is answered even after hours, preferably a cellular phone of a decision maker authorized to request or bypass emergency response.
ECV, as it cannot confirm an actual intrusion event and will not prompt a priority law enforcement dispatch, is not considered true alarm verification by the security industry.
Independent certification
Some insurance companies and local agencies require that alarm systems be installed to code or be certified by an independent third party. The alarm system is required to have a maintenance check carried out every 6 – 12 months. In the UK, 'Audible Only' intruder alarm systems require a routine service visit once every 12 months and monitored intruder alarm systems require a check twice in every 12-month period. This is to ensure all internal components, sensors and PSUs are functioning correctly. In the past, this would require an alarm service engineer to attend site and carry the checks out. With the use of the Internet or radio path and a compatible IP/radio transmitting device (at the alarmed premises), some checks can now be carried out remotely from the central station.
See also
*
Access control
In physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the action of deciding whether a subject should be granted or denied access to an object (for example, a place or a resource). The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming ...
*
Alarm management
Alarm management is the application of human factors and ergonomics along with instrumentation engineering and systems thinking to manage the design of an alarm system to increase its usability. Most often the major usability problem is that ...
*
Door security
*
Dual loop
*
Emergency service
Emergency services and rescue services are organizations that ensure public safety, security, and health by addressing and resolving different emergencies. Some of these agencies exist solely for addressing certain types of emergencies, while oth ...
*
Environmental design
Environmental design is the process of addressing surrounding environmental parameters when devising plans, programs, policies, buildings, or products. It seeks to create spaces that will enhance the natural, social, cultural and physical environm ...
*
Fire alarm system
A fire alarm system is a building system designed to detect, alert occupants, and alert emergency forces of the presence of fire, smoke, carbon monoxide, or other fire-related emergencies. Fire alarm systems are required in most commercial buil ...
*
Glass-break detector
*
IoT Security Devices Internet of Things (IoT) security devices are electronic tools connected via Internet to a common network and are used to provide security measures. These devices can be controlled remotely through a mobile application, web-based interface or any pr ...
*
Perimeter intrusion detection
A perimeter intrusion detection system (PIDS) is a device or sensor that detects the presence of an intruder attempting to breach the physical perimeter of a property, building, or other secured area. A PIDS is typically deployed as part of an ...
*
Physical security
Physical security describes security measures that are designed to deny unauthorized access to facilities, equipment, and resources and to protect personnel and property from damage or harm (such as espionage, theft, or terrorist attacks). Physi ...
*
Security lighting In the field of physical security, security lighting is lighting that intended to deter or detect intrusions or other criminal activity occurring on a property or site. It can also be used to increase a feeling of safety. Lighting is integral to cri ...
*
Vandal-resistant switch
*
Voice-activated radio-dispatched alarm
References
Sources
*
*
*
Further reading
*Aii, N. Clifton. "Broadband CSV, XML Alarm data Standards" Auckland NZ, (2002)
*
*
*
*
*"Wolf guard alarm system" China CN, (1998)
External links
How a burglar alarm works
{{DEFAULTSORT:Burglar Alarm
Security technology
Electrical systems
Alarms
 A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusions, such as unauthorized entry, into a building or other areas, such as a home or school. Security alarms protect against
A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusions, such as unauthorized entry, into a building or other areas, such as a home or school. Security alarms protect against  The most basic alarm consists of at least one sensor to detect trespassers and an alerting device to indicate the intrusion. However, a typical premises security alarm employs the following components:
* Alarm control panel (ACP), or simply panel: The panel reads sensor inputs, tracks arm/disarm status, and signals intrusions. In a modern device, there are typically one or more computer
The most basic alarm consists of at least one sensor to detect trespassers and an alerting device to indicate the intrusion. However, a typical premises security alarm employs the following components:
* Alarm control panel (ACP), or simply panel: The panel reads sensor inputs, tracks arm/disarm status, and signals intrusions. In a modern device, there are typically one or more computer  The hermetically sealed
The hermetically sealed  Microwave detectors respond to a
Microwave detectors respond to a  In the last decades, many technological progresses have been made in this area and MEMS accelerometers are used in high-reliability environments and are starting to replace other established technologies.
MEMS accelerometer can be applied as a sensor in the earthquake disaster prevention, since one of the main characteristics of MEMS accelerometers is the linear frequency response to DC to about 500 Hz, and this capability offers an improvement in measuring
In the last decades, many technological progresses have been made in this area and MEMS accelerometers are used in high-reliability environments and are starting to replace other established technologies.
MEMS accelerometer can be applied as a sensor in the earthquake disaster prevention, since one of the main characteristics of MEMS accelerometers is the linear frequency response to DC to about 500 Hz, and this capability offers an improvement in measuring  Microphonic systems vary in design (for example, time-domain reflectrometer or
Microphonic systems vary in design (for example, time-domain reflectrometer or  This system employs an electro-magnetic field disturbance principle based on two unshielded coaxial cables. The transmitter emits continuous radio frequency (RF) energy along one cable and the energy is received by the other cable. When the change in field strength weakens due to the presence of an object and reaches a pre-set lower threshold, an alarm condition is generated. The system is covert after installation. The surrounding soil must offer good drainage in order to avoid nuisance alarms. Ported coaxial cables are concealed as a buried form but can be affected by RF noise and is difficult to install.
This system employs an electro-magnetic field disturbance principle based on two unshielded coaxial cables. The transmitter emits continuous radio frequency (RF) energy along one cable and the energy is received by the other cable. When the change in field strength weakens due to the presence of an object and reaches a pre-set lower threshold, an alarm condition is generated. The system is covert after installation. The surrounding soil must offer good drainage in order to avoid nuisance alarms. Ported coaxial cables are concealed as a buried form but can be affected by RF noise and is difficult to install.