Intradermal injection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Intradermal injection (also intracutaneous or intradermic, abbreviated as ID) is a shallow or superficial
EMA and FDA promote
the use of ID route of administration in case of possible vaccine shortage, for example during the Monkeypox outbreak in 2022 where 1/5th intradermal (fractional) dosing was advised, due to a risk of vaccine shortage.
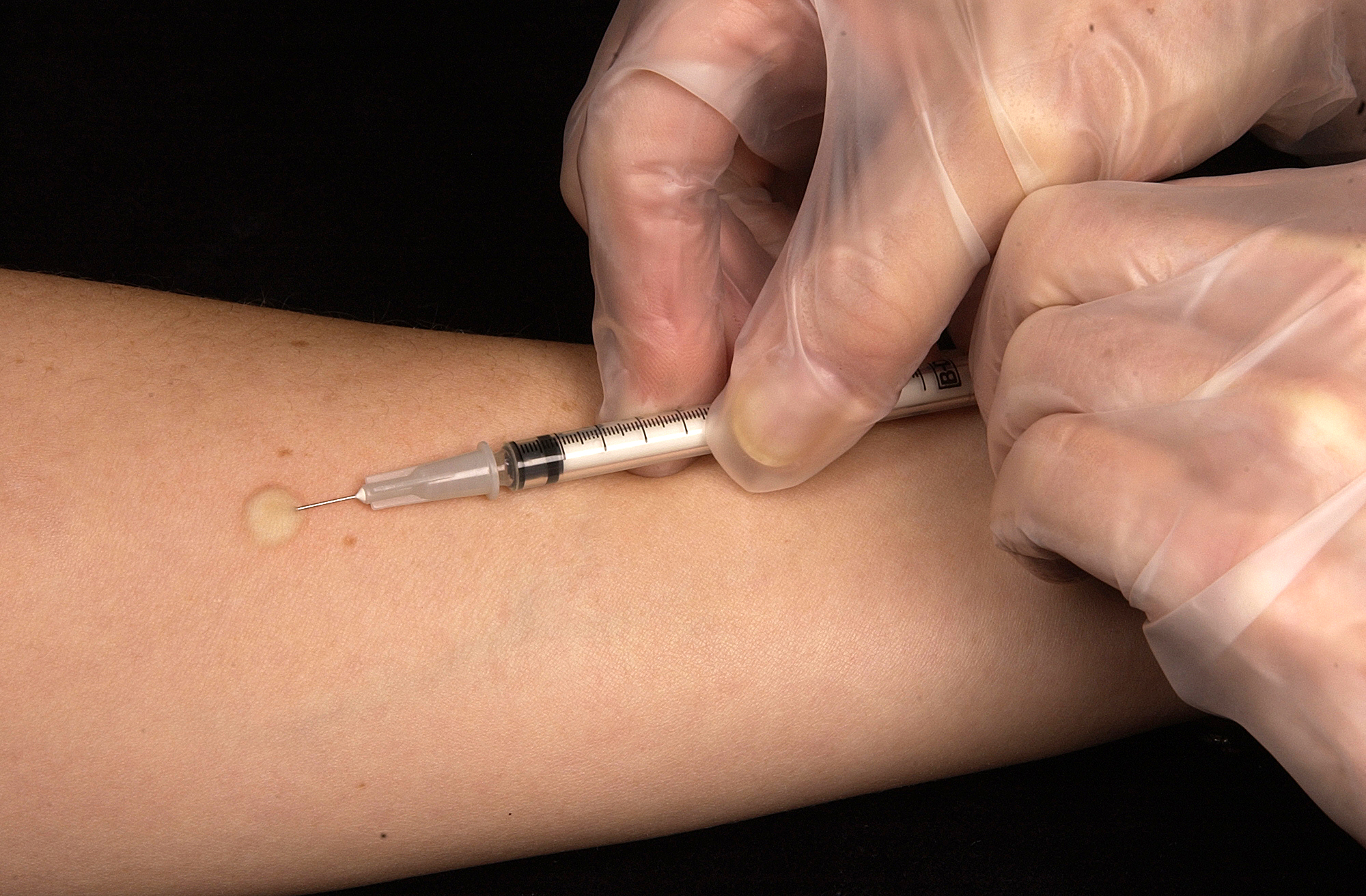 The traditional procedure of ID injection known as the Mantoux procedure (as used in the
The traditional procedure of ID injection known as the Mantoux procedure (as used in the
injection
Injection or injected may refer to:
Science and technology
* Injective function, a mathematical function mapping distinct arguments to distinct values
* Injection (medicine), insertion of liquid into the body with a syringe
* Injection, in broadca ...
of a substance into the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
, which is located between the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
and the hypodermis
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and ...
. For certain substances, administration
Administration may refer to:
Management of organizations
* Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal: the process of dealing with or controlling things or people.
** Administrative assistant, traditionally known as a se ...
via an ID route can result in a faster systemic uptake compared with subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and ...
s, leading to a stronger immune response to vaccinations, immunology and novel cancer treatments, and faster drug uptake. Additionally, since administration is closer to the surface of the skin, the body's reaction to substances is more easily visible. However, due to complexity of the procedure compared to subcutaneous injection and intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be ...
, administration via ID is relatively rare, and is only used for tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
and allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
tests, monkeypox vaccination, and certain therapies.
Vaccine dose sparing
For vaccination many clinical studies have proven efficacy of ID administration over subcutaneous (SC), intramuscular (IM) or other routes of administration. Since the COVID19 pandemic (2020EMA and FDA promote
the use of ID route of administration in case of possible vaccine shortage, for example during the Monkeypox outbreak in 2022 where 1/5th intradermal (fractional) dosing was advised, due to a risk of vaccine shortage.
Injection sites
Common injection sites include the inner surface of theforearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
, the upper back, deltoid, thigh, and under the shoulder blade
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
. Injections sites are often chosen for skin thickness, preferring thicker skin.
Equipment
Equipment includesyringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside ...
s calibrated in tenths and hundredths of a milliliter
The litre (Commonwealth English, Commonwealth spelling) or liter (American English, American spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric units, metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic c ...
. The dosage given is usually less than 0.5 mL, less than given subcutaneously or intramuscularly. A and 26 or 27 gauge
Gauge ( ) may refer to:
Measurement
* Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments
* Gauge (firearms)
* Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire
** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, especia ...
thick hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek Language, Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug admini ...
is used.
Mantoux procedure
 The traditional procedure of ID injection known as the Mantoux procedure (as used in the
The traditional procedure of ID injection known as the Mantoux procedure (as used in the Mantoux test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening (medicine), screening for tuberculosis, tuberculo ...
) involves injecting at angle of administration of 5 to 15 degrees angle, almost against the skin. With bevel
A bevelled edge (UK) or beveled edge (US) is an edge of a structure that is not perpendicular to the faces of the piece. The words bevel and chamfer overlap in usage; in general usage, they are often interchanged, while in technical usage, they ...
(opening) side up, the needle is inserted about with the entire bevel inside and injected while watching for a small wheal or blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled ...
to appear.
Intradermic needles
Traditionallyhypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek Language, Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug admini ...
s are used for intradermal injections, instead of intradermic needles. Various microneedle technology researchers worldwide develop new devices and therapies to overcome typical usability issues associated with the traditional Mantoux procedure. Most intradermic needles require a change in injection technique or instruction to use, for example a perpendicular intradermal injection.
Immune reaction tests sometimes use a set of non-hollow needles for scarification, shallowly abrading the skin. The inoculation is limited to the dermis.
See also
*Subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and ...
* Intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be ...
* Intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
References
{{Authority control Medical procedures Injection (medicine)