International Settlement In Shanghai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Shanghai International Settlement () originated from the merger in the year 1863 of the British and
The Shanghai International Settlement () originated from the merger in the year 1863 of the British and
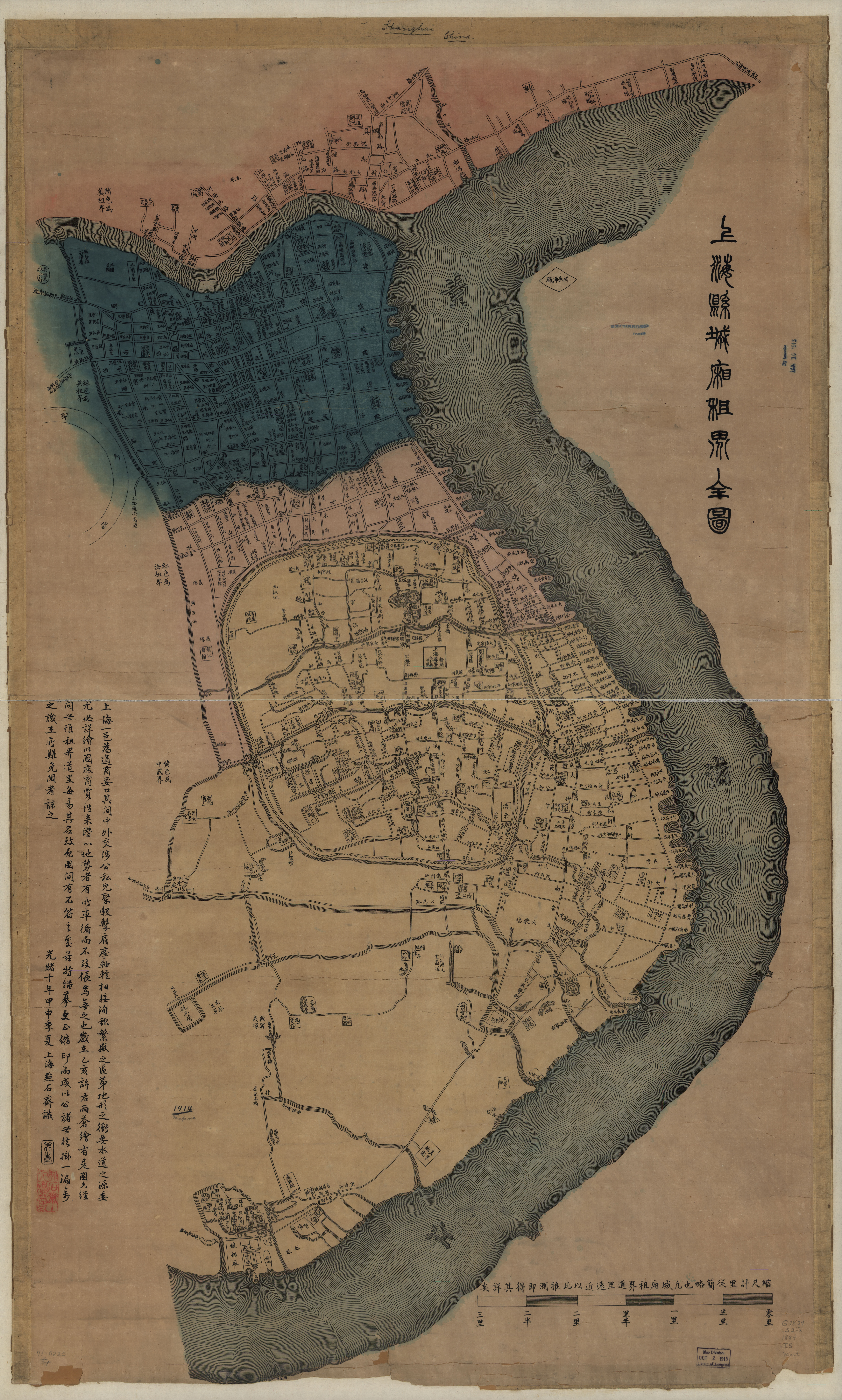 Although Europeans had shown more interest in Canton than Shanghai early on for commercial advantages, the port's strategic position was key to British interests as the island nation declared war against China in 1839, starting the first Anglo-Chinese Opium War. The first settlement in Shanghai for foreigners was the British settlement, opened in 1843 under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking.Darwent, Charles Ewart. ''Shanghai; a handbook for travelers and residents to the chief objects of interest in and around the foreign settlements and native city.'' Shanghai, Hongkong: Kelly and Walsh ate of publication not identified This treaty forced the Qing Dynasty to make punitive territorial and economic concessions and would become the first of the unequal treaties imposed upon China by its fellow great powers. To the north, the settlement was bordered by the right bank of the Suzhou River before its inflow into the Huangpu River, which delineated the concession's eastern boundaries. To the south, the Yang-King-Pang channel marked the concession's southern limits which would later become the boundary between the British and French concessions.
On the orders of Sir Henry Pottinger, first Governor of Hong Kong, Captain George Balfour of the East India Company's Madras Artillery arrived as Britain's first consul in Shanghai on 8November 1843 aboard the steamer ''Medusa''. The next morning Balfour sent word to the circuit intendant of Shanghai,
Although Europeans had shown more interest in Canton than Shanghai early on for commercial advantages, the port's strategic position was key to British interests as the island nation declared war against China in 1839, starting the first Anglo-Chinese Opium War. The first settlement in Shanghai for foreigners was the British settlement, opened in 1843 under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking.Darwent, Charles Ewart. ''Shanghai; a handbook for travelers and residents to the chief objects of interest in and around the foreign settlements and native city.'' Shanghai, Hongkong: Kelly and Walsh ate of publication not identified This treaty forced the Qing Dynasty to make punitive territorial and economic concessions and would become the first of the unequal treaties imposed upon China by its fellow great powers. To the north, the settlement was bordered by the right bank of the Suzhou River before its inflow into the Huangpu River, which delineated the concession's eastern boundaries. To the south, the Yang-King-Pang channel marked the concession's southern limits which would later become the boundary between the British and French concessions.
On the orders of Sir Henry Pottinger, first Governor of Hong Kong, Captain George Balfour of the East India Company's Madras Artillery arrived as Britain's first consul in Shanghai on 8November 1843 aboard the steamer ''Medusa''. The next morning Balfour sent word to the circuit intendant of Shanghai,  The Sino-American Treaty of Wanghia was signed in July 1844 by Chinese and American officials, under orders to "save the Chinese from the condition of being an exclusive monopoly in the hands of England" as a consequence of the 1842 Treaty of Nanking. Under the Treaty of Wanghia, the Americans gained the same rights as those enjoyed by the British in China's treaty ports. It also contained a clause that effectively carved out Shanghai as an extraterritorial zone, though it did not actually give the American government a true legal concession.
It was only in 1845 that Britain followed in the United States' footsteps and signed a land-deal to allow Britons to rent land in Shanghai in perpetuity. The American consular presence did not create a problem for the British because it was never intended to have a post in person. Since American traders in China were prohibited from engaging in the opium trade, their business transactions were conducted under the auspices of British firms. The only serious incident of political complaint against the Americans was in 1845, when the Stars and Stripes was raised by the acting US Consul, Henry G. Wolcott, who had just arrived in the city. Neither the British nor the Chinese governor approved of the display. In 1848, the French established its own French concession under French consular jurisdiction, squeezed between the British settlement to the north and the Chinese walled city to the south.
Towards the end of the 19th century, Shanghai Russians also arrived, with Russia's construction of the Chinese Eastern Railway and acquisition of
The Sino-American Treaty of Wanghia was signed in July 1844 by Chinese and American officials, under orders to "save the Chinese from the condition of being an exclusive monopoly in the hands of England" as a consequence of the 1842 Treaty of Nanking. Under the Treaty of Wanghia, the Americans gained the same rights as those enjoyed by the British in China's treaty ports. It also contained a clause that effectively carved out Shanghai as an extraterritorial zone, though it did not actually give the American government a true legal concession.
It was only in 1845 that Britain followed in the United States' footsteps and signed a land-deal to allow Britons to rent land in Shanghai in perpetuity. The American consular presence did not create a problem for the British because it was never intended to have a post in person. Since American traders in China were prohibited from engaging in the opium trade, their business transactions were conducted under the auspices of British firms. The only serious incident of political complaint against the Americans was in 1845, when the Stars and Stripes was raised by the acting US Consul, Henry G. Wolcott, who had just arrived in the city. Neither the British nor the Chinese governor approved of the display. In 1848, the French established its own French concession under French consular jurisdiction, squeezed between the British settlement to the north and the Chinese walled city to the south.
Towards the end of the 19th century, Shanghai Russians also arrived, with Russia's construction of the Chinese Eastern Railway and acquisition of

 On 11July 1854 a committee of Western businessmen met and held the first annual meeting of the Shanghai Municipal Council (SMC, formally the Council for the Foreign Settlement North of the Yang-king-pang), ignoring protests of consular officials, and laid down the Land Regulations which established the principles of self-government. The aims of this first Council were simply to assist in the formation of roads, refuse collection, and taxation across the disparate Concessions.
In 1863 the American concession—land fronting the
On 11July 1854 a committee of Western businessmen met and held the first annual meeting of the Shanghai Municipal Council (SMC, formally the Council for the Foreign Settlement North of the Yang-king-pang), ignoring protests of consular officials, and laid down the Land Regulations which established the principles of self-government. The aims of this first Council were simply to assist in the formation of roads, refuse collection, and taxation across the disparate Concessions.
In 1863 the American concession—land fronting the  By the late-1860s Shanghai's official governing body had been practically transferred from the individual concessions to the Shanghai Municipal Council (工部局, literally "Works Department", from the standard English local government title of 'Board of works'). The British Consul was the ''de jure'' authority in the Settlement, but he had no actual power unless the ratepayers (who voted for the council) agreed. Instead, he and the other consulates deferred to the council.
By the late-1860s Shanghai's official governing body had been practically transferred from the individual concessions to the Shanghai Municipal Council (工部局, literally "Works Department", from the standard English local government title of 'Board of works'). The British Consul was the ''de jure'' authority in the Settlement, but he had no actual power unless the ratepayers (who voted for the council) agreed. Instead, he and the other consulates deferred to the council.
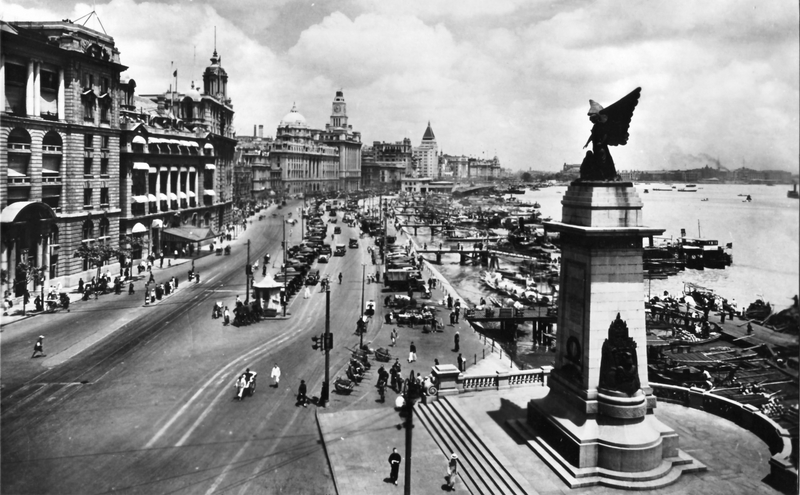 The council had become a practical monopoly over the city's businesses by the mid-1880s. It bought up all the local gas-suppliers, electricity producers and water-companies, then — during the 20th-century — took control over all non-private rickshaws and the Settlement tramways. It also regulated opium sales and prostitution until their banning in 1918 and 1920 respectively.
Until the late-1920s, therefore, the SMC and its subsidiaries, including the police, power station, and public works, were British dominated (though not controlled, since Britain itself had no authority over the council). Some of the Settlement's actions during this period, such as the
The council had become a practical monopoly over the city's businesses by the mid-1880s. It bought up all the local gas-suppliers, electricity producers and water-companies, then — during the 20th-century — took control over all non-private rickshaws and the Settlement tramways. It also regulated opium sales and prostitution until their banning in 1918 and 1920 respectively.
Until the late-1920s, therefore, the SMC and its subsidiaries, including the police, power station, and public works, were British dominated (though not controlled, since Britain itself had no authority over the council). Some of the Settlement's actions during this period, such as the  No Chinese residing in the International Settlement were permitted to join the council until 1928. Amongst the many members who served on the council, its chairman during the 1920s,
No Chinese residing in the International Settlement were permitted to join the council until 1928. Amongst the many members who served on the council, its chairman during the 1920s,
 In the 19th century, Europeans possessed treaty ports in Japan in the same way they held those in China. However, Japan rapidly developed into a modern nation, and by the turn of the 20th century the Japanese had successfully negotiated with all powers to abrogate all unequal treaties with it. Japan stood alongside the European powers as part of the
In the 19th century, Europeans possessed treaty ports in Japan in the same way they held those in China. However, Japan rapidly developed into a modern nation, and by the turn of the 20th century the Japanese had successfully negotiated with all powers to abrogate all unequal treaties with it. Japan stood alongside the European powers as part of the
 In 1932 there were 1,040,780 Chinese living within the International Settlement, with another 400,000 fleeing into the area after the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out in 1937. For the next five years, the International Settlement and the French Concession were surrounded by Japanese occupiers and Chinese revolutionaries, with conflict often spilling into the Settlement's borders. In 1941, the Japanese launched an abortive political bid to take over the SMC: during a mass meeting of ratepayers at the Settlement Race Grounds, a Japanese official leaped up and shot William Keswick, then chairman of the council. While Keswick was only wounded, a near riot broke out.
In 1932 there were 1,040,780 Chinese living within the International Settlement, with another 400,000 fleeing into the area after the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out in 1937. For the next five years, the International Settlement and the French Concession were surrounded by Japanese occupiers and Chinese revolutionaries, with conflict often spilling into the Settlement's borders. In 1941, the Japanese launched an abortive political bid to take over the SMC: during a mass meeting of ratepayers at the Settlement Race Grounds, a Japanese official leaped up and shot William Keswick, then chairman of the council. While Keswick was only wounded, a near riot broke out.

 The International Settlement did not have a unified legal system. The Municipal Council issued Land Regulations and regulations under this, that were binding on all people in the settlement. Other than this, citizens and subjects of powers that had treaties with China that provided for extraterritorial rights were subject to the laws of their own countries and civil and criminal complaints against them were required to be brought against them to their consular courts (courts overseen by consular officials) under the laws of their own countries.
The number of treaty powers had climbed to a high of 19 by 1918 but was down to 14 by the 1930s: the United Kingdom, the United States, Japan, France, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, Peru, Mexico, and Switzerland. Germany and Austria-Hungary lost their treaty rights after WWI, and Russia gave up her rights as a matter of political expediency. Belgium was declared by China to have lost her rights in 1927. Furthermore, the Chinese government adamantly refused to grant treaty power status to any of the new nations born in the wake of WWI, such as Austria and Hungary (formerly Austria-Hungary), Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, the Baltic states, or Finland.
Chinese citizens and citizens of non-treaty powers were subject to Chinese law. Inside the Settlement, cases against them would be brought to the Mixed Court, a court established in the Settlement in the 1864 which existed until 1926. In cases involving foreigners, a foreign
The International Settlement did not have a unified legal system. The Municipal Council issued Land Regulations and regulations under this, that were binding on all people in the settlement. Other than this, citizens and subjects of powers that had treaties with China that provided for extraterritorial rights were subject to the laws of their own countries and civil and criminal complaints against them were required to be brought against them to their consular courts (courts overseen by consular officials) under the laws of their own countries.
The number of treaty powers had climbed to a high of 19 by 1918 but was down to 14 by the 1930s: the United Kingdom, the United States, Japan, France, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, Peru, Mexico, and Switzerland. Germany and Austria-Hungary lost their treaty rights after WWI, and Russia gave up her rights as a matter of political expediency. Belgium was declared by China to have lost her rights in 1927. Furthermore, the Chinese government adamantly refused to grant treaty power status to any of the new nations born in the wake of WWI, such as Austria and Hungary (formerly Austria-Hungary), Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, the Baltic states, or Finland.
Chinese citizens and citizens of non-treaty powers were subject to Chinese law. Inside the Settlement, cases against them would be brought to the Mixed Court, a court established in the Settlement in the 1864 which existed until 1926. In cases involving foreigners, a foreign
 The currency situation in China was very complicated in the 19th century, as there was no unified monetary system. Different parts of China operated different systems, and the Spanish pieces of eight that had been coming from Mexico for a few hundred years on Manila Galleons were current along the China coast. Until the 1840s these silver dollar coins were Spanish coins minted mainly in Mexico City, but from the 1840s these gave way to Mexican republican dollars.
In Shanghai, this complexity represented a microcosm of the complicated economy existing elsewhere along the China coast. The Chinese reckoned in weights of silver, which did not necessarily correspond to circulating coins. One important unit was a tael, a measurement of weight with several different definitions. These included: Customs Taels (for foreign trade), Cotton Taels (for cotton trade), etc. Shanghai had its own tael, which was very similar in weight to the Customs Tael and therefore popular for international business. China also had a mixture of coins, including Chinese Copper Cash coins and Mexican dollars. Paper money was first issued by European and North American colonial banks (one British colonial bank known as the
The currency situation in China was very complicated in the 19th century, as there was no unified monetary system. Different parts of China operated different systems, and the Spanish pieces of eight that had been coming from Mexico for a few hundred years on Manila Galleons were current along the China coast. Until the 1840s these silver dollar coins were Spanish coins minted mainly in Mexico City, but from the 1840s these gave way to Mexican republican dollars.
In Shanghai, this complexity represented a microcosm of the complicated economy existing elsewhere along the China coast. The Chinese reckoned in weights of silver, which did not necessarily correspond to circulating coins. One important unit was a tael, a measurement of weight with several different definitions. These included: Customs Taels (for foreign trade), Cotton Taels (for cotton trade), etc. Shanghai had its own tael, which was very similar in weight to the Customs Tael and therefore popular for international business. China also had a mixture of coins, including Chinese Copper Cash coins and Mexican dollars. Paper money was first issued by European and North American colonial banks (one British colonial bank known as the
 Shanghai had developed a
Shanghai had developed a
James Lawrence Man
(11.7.1854 - 1855) #
James Lawrence Man
(1.1856 - 31.1.1857) #
George Basil Dixwell
(2.4.1870 - 4.4.1871) # John Dent (4.4.1871 - 1.1873) # Robert Inglis Fearon (1.1873 - 16.4.1874) #
John Graeme Purdon
(16.4.1874 - 1876) #
John Graeme Purdon
(5.1891 - 1.1893) #
James Lidderdale Scott
(11.1893 - 26.1.1897) # Edward Albert Probst (26.1.1897 - 21.4.1897) # Albert Robson Burkill (12.5.1897 - 1.1898) # James S. Fearon (1.1898 - 8.1899) #*
online
* * Bickers, Robert, '' Empire Made Me: An Englishman Adrift in Shanghai'' (Allen Lane History, 2003). * Bickers, Robert. "Shanghailanders: The formation and identity of the British settler community in Shanghai 1843–1937." ''Past & Present'' 159.1 (1998): 161–211
online
* Cheng, Hu. "Quarantine, Race and Politics in the International Settlement: Clashes between Chinese and Foreigners after the Outbreak of Plague in Shanghai in 1910." ''Modern Chinese History Studies'' 4 (2007): 5+. * * * * * Hao, Yen-p'ing. ''The Commercial Revolution of Nineteenth-Century China: The Rise of Sino-Western Mercantile Competition'' (U of California Press, 1984), * Henriot, Christian, and Wen-Hsin Yeh, eds. ''In the shadow of the rising sun: Shanghai under Japanese occupation'' (Cambridge UP, 2004). * Hudson, Manley O. "The Rendition of the International Mixed Court at Shanghai." ''American Journal of International Law'' 21.3 (1927): 451–471. * Lockwood, William W. "The International Settlement at Shanghai, 1924–34." ''American Political Science Review'' 28.6 (1934): 1030–1046
online
* MacPherson, Kerrie L. "Designing China's urban future: The Greater Shanghai Plan, 1927–1937." ''Planning Perspective'' 5.1 (1990): 39–62. * Ristaino, Marcia Reynders. ''Port of last resort: The diaspora communities of Shanghai'' (Stanford University Press, 2003). * Wakeman, Frederic E., and Wen-Hsin Yeh, eds. ''Shanghai sojourners'' (Institute of East Asian Studies, University of California, 1992.
excerpt
* Wakeman, Frederick. "Licensing Leisure: The Chinese Nationalists' Attempt to Regulate Shanghai, 1927–49." ''Journal of Asian Studies'' 54.1 (1995): 19–42.
 The Shanghai International Settlement () originated from the merger in the year 1863 of the British and
The Shanghai International Settlement () originated from the merger in the year 1863 of the British and American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
enclaves in Shanghai, in which British subjects and American citizens would enjoy extraterritoriality and consular jurisdiction under the terms of treaties agreed by both parties. These treaties were abrogated in 1943.
The British settlements were established following the victory of the British in the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
(18391842). Under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking, the five treaty ports including Shanghai were opened to foreign merchants, overturning the monopoly then held by the southern port of Canton ( Guangzhou) under the Canton System. The British also established a base on Hong Kong. American and French involvement followed closely on the heels of the British and their enclaves were established north and south, respectively, of the British area.
Unlike the colonies of Hong Kong and Macau, where the United Kingdom and Portugal enjoyed full sovereignty in perpetuity, the foreign concessions in China remained under Chinese sovereignty. In 1854, the three countries created the Shanghai Municipal Council to serve all their interests, but, in 1862, the French concession dropped out of the arrangement. The following year the British and American settlements formally united to create the Shanghai International Settlement. As more foreign powers entered into treaty relations with China, their nationals also became part of the administration of the settlement. The number of treaty powers had climbed to a high of 19 by 1918 but was down to 14 by the 1930s: the United Kingdom, the United States, Japan, France, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, Peru, Mexico, and Switzerland.
Nonetheless, the SMC remained a predominantly British affair until the growth of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
's involvement in the late 1930s. The international character of the Settlement was reflected in the flag and seal of the Municipal Council, which featured the flags of several countries.
The international settlement came to an abrupt end in December 1941 when Japanese troops stormed in immediately following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. In early 1943, new treaties signed formally ended the extraterritorial privileges of Americans and Britons, although its terms were not met until the recovery of Shanghai following Japan's 1945 surrender. The French later surrendered their privileges in a separate agreement in February 1946.
It was one of two Chinese international settlements, along with Gulangyu International Settlement.
History
Arrival of the Americans, British and other Europeans
 Although Europeans had shown more interest in Canton than Shanghai early on for commercial advantages, the port's strategic position was key to British interests as the island nation declared war against China in 1839, starting the first Anglo-Chinese Opium War. The first settlement in Shanghai for foreigners was the British settlement, opened in 1843 under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking.Darwent, Charles Ewart. ''Shanghai; a handbook for travelers and residents to the chief objects of interest in and around the foreign settlements and native city.'' Shanghai, Hongkong: Kelly and Walsh ate of publication not identified This treaty forced the Qing Dynasty to make punitive territorial and economic concessions and would become the first of the unequal treaties imposed upon China by its fellow great powers. To the north, the settlement was bordered by the right bank of the Suzhou River before its inflow into the Huangpu River, which delineated the concession's eastern boundaries. To the south, the Yang-King-Pang channel marked the concession's southern limits which would later become the boundary between the British and French concessions.
On the orders of Sir Henry Pottinger, first Governor of Hong Kong, Captain George Balfour of the East India Company's Madras Artillery arrived as Britain's first consul in Shanghai on 8November 1843 aboard the steamer ''Medusa''. The next morning Balfour sent word to the circuit intendant of Shanghai,
Although Europeans had shown more interest in Canton than Shanghai early on for commercial advantages, the port's strategic position was key to British interests as the island nation declared war against China in 1839, starting the first Anglo-Chinese Opium War. The first settlement in Shanghai for foreigners was the British settlement, opened in 1843 under the terms of the Treaty of Nanking.Darwent, Charles Ewart. ''Shanghai; a handbook for travelers and residents to the chief objects of interest in and around the foreign settlements and native city.'' Shanghai, Hongkong: Kelly and Walsh ate of publication not identified This treaty forced the Qing Dynasty to make punitive territorial and economic concessions and would become the first of the unequal treaties imposed upon China by its fellow great powers. To the north, the settlement was bordered by the right bank of the Suzhou River before its inflow into the Huangpu River, which delineated the concession's eastern boundaries. To the south, the Yang-King-Pang channel marked the concession's southern limits which would later become the boundary between the British and French concessions.
On the orders of Sir Henry Pottinger, first Governor of Hong Kong, Captain George Balfour of the East India Company's Madras Artillery arrived as Britain's first consul in Shanghai on 8November 1843 aboard the steamer ''Medusa''. The next morning Balfour sent word to the circuit intendant of Shanghai, Gong Mujiu
A gongFrom Indonesian and ms, gong; jv, ꦒꦺꦴꦁ ; zh, c=鑼, p=luó; ja, , dora; km, គង ; th, ฆ้อง ; vi, cồng chiêng; as, কাঁহ is a percussion instrument originating in East Asia and Southeast Asia. Gongs ...
(then romanized Kung Moo-yun), requesting a meeting, at which he indicated his desire to find a house to live in. Initially Balfour was told no such properties were available, but on leaving the meeting, he received an offer from a pro-British Cantonese named Yao to rent a large house within the city walls for four hundred dollars per annum. Balfour, his interpreter Walter Henry Medhurst, surgeon Dr. Hale and clerk A. F. Strachan moved into the luxuriously furnished 52-room house immediately.
It served as the consulate during construction of a Western-style buildings within the official Settlement boundaries just to the south of Suzhou Creek. This soon became the epicenter of the British settlement. Afterward both the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and the Americans signed treaties with China that gave their citizens extraterritorial rights similar to those granted to the British, but initially their respective nationals accepted that the foreign settlement came under British consular jurisdiction. However, it must be clearly understood that Shanghai has been from the beginning a settlement, not a possession. The British Government annexed Hong Kong, which became British territory, and subject to British law. The land on which the Foreign Settlement of Shanghai was created was, on the other hand, only leased to the British Government. That is proved by the fact that all the landowners still pay ground rent to the Chinese Government.
Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
and Port Arthur.
Municipal Council

 On 11July 1854 a committee of Western businessmen met and held the first annual meeting of the Shanghai Municipal Council (SMC, formally the Council for the Foreign Settlement North of the Yang-king-pang), ignoring protests of consular officials, and laid down the Land Regulations which established the principles of self-government. The aims of this first Council were simply to assist in the formation of roads, refuse collection, and taxation across the disparate Concessions.
In 1863 the American concession—land fronting the
On 11July 1854 a committee of Western businessmen met and held the first annual meeting of the Shanghai Municipal Council (SMC, formally the Council for the Foreign Settlement North of the Yang-king-pang), ignoring protests of consular officials, and laid down the Land Regulations which established the principles of self-government. The aims of this first Council were simply to assist in the formation of roads, refuse collection, and taxation across the disparate Concessions.
In 1863 the American concession—land fronting the Huangpu River
The Huangpu (), formerly romanized as Whangpoo, is a river flowing north through Shanghai. The Bund and Lujiazui are located along the Huangpu River.
The Huangpu is the biggest river in central Shanghai, with the Suzhou Creek being its maj ...
to the north-east of Soochow Creek (Suzhou Creek
Suzhou Creek (or Soochow Creek), also called the Wusong (Woosung) River, is a river that passes through the Shanghai city center. It is named after the neighboring city of Suzhou (Soochow), Jiangsu, the predominant settlement in this area prior ...
)—officially joined the British Settlement (stretching from Yang-ching-pang Creek
Yan'an Road (; Shanghainese: Yi'ue Lu) is a road in Shanghai, a major east–west thoroughfare through the centre of the city. The modern Yan'an Road is in three sections, reflecting three connected streets which existed pre-1945: Avenue Edward ...
to Suzhou Creek) to become the Shanghai International Settlement. The French concession remained independent and the Chinese retained control over the original walled city and the area surrounding the foreign enclaves. This would later result in sometimes absurd administrative outcomes, such as needing three drivers' licenses to travel through the complete city.
 By the late-1860s Shanghai's official governing body had been practically transferred from the individual concessions to the Shanghai Municipal Council (工部局, literally "Works Department", from the standard English local government title of 'Board of works'). The British Consul was the ''de jure'' authority in the Settlement, but he had no actual power unless the ratepayers (who voted for the council) agreed. Instead, he and the other consulates deferred to the council.
By the late-1860s Shanghai's official governing body had been practically transferred from the individual concessions to the Shanghai Municipal Council (工部局, literally "Works Department", from the standard English local government title of 'Board of works'). The British Consul was the ''de jure'' authority in the Settlement, but he had no actual power unless the ratepayers (who voted for the council) agreed. Instead, he and the other consulates deferred to the council.
 The council had become a practical monopoly over the city's businesses by the mid-1880s. It bought up all the local gas-suppliers, electricity producers and water-companies, then — during the 20th-century — took control over all non-private rickshaws and the Settlement tramways. It also regulated opium sales and prostitution until their banning in 1918 and 1920 respectively.
Until the late-1920s, therefore, the SMC and its subsidiaries, including the police, power station, and public works, were British dominated (though not controlled, since Britain itself had no authority over the council). Some of the Settlement's actions during this period, such as the
The council had become a practical monopoly over the city's businesses by the mid-1880s. It bought up all the local gas-suppliers, electricity producers and water-companies, then — during the 20th-century — took control over all non-private rickshaws and the Settlement tramways. It also regulated opium sales and prostitution until their banning in 1918 and 1920 respectively.
Until the late-1920s, therefore, the SMC and its subsidiaries, including the police, power station, and public works, were British dominated (though not controlled, since Britain itself had no authority over the council). Some of the Settlement's actions during this period, such as the May 30th Movement
The May Thirtieth Movement () was a major labor and anti-imperialist movement during the middle-period of the Republic of China era. It began when the Shanghai Municipal Police opened fire on Chinese protesters in Shanghai's International Settl ...
, in which Chinese demonstrators were shot by members of the Shanghai Municipal Police (leading to anti-Western protests), did embarrass and threaten the British Empire's position in China.
 No Chinese residing in the International Settlement were permitted to join the council until 1928. Amongst the many members who served on the council, its chairman during the 1920s,
No Chinese residing in the International Settlement were permitted to join the council until 1928. Amongst the many members who served on the council, its chairman during the 1920s, Stirling Fessenden
Stirling Fessenden (29 September 1875 – 1 February 1944), an American lawyer who practised in Shanghai, was the chairman of the Shanghai Municipal Council from 1923 to 1929 and then Secretary-General of the Council from 1929 to 1939.
Early lif ...
, is possibly the most notable. An American, he served as the settlement's main administrator during Shanghai's most turbulent era, and was considered more "British" than the council's British members. He oversaw many of the major incidents of the decade, including the May 30th Movement and the White Terror
White Terror is the name of several episodes of mass violence in history, carried out against anarchists, communists, socialists, liberals, revolutionaries, or other opponents by conservative or nationalist groups. It is sometimes contrasted wit ...
that came with the Shanghai massacre of 1927
The Shanghai massacre of 12 April 1927, the April 12 Purge or the April 12 Incident as it is commonly known in China, was the violent suppression of Chinese Communist Party (CCP) organizations and leftist elements in Shanghai by forces supportin ...
.
By the early 1930s, the British and the Chinese each had five members on the council, the Japanese two and the Americans and others two. At the 1936 Council election, because of their increasing interests in the Settlement, the Japanese nominated three candidates. Only two were elected, which led to a Japanese protest after 323 uncounted votes were discovered. As a result, the election was declared invalid and a new poll held on April20-21, 1936, at which the Japanese nominated only two candidates. In the case of the Chinese members, in 1926 the Ratepayers' Meeting adopted a resolution approving the addition of three Chinese members to the council and they took their seats for the first time in April, 1928; while in May, 1930, their number was increased to five.
The International Settlement was wholly foreign-controlled, with staff of all nationalities, including British, Americans, Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
Danes generally regard t ...
, Italians and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
s. In reality, the British held the largest number of seats on the council and headed all the Municipal departments (British included Australians, New Zealanders, Canadians, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
ers, and South Africans whose extraterritorial rights were established by the United Kingdom treaty).
The only department not chaired by a Briton was the Municipal Orchestra, which was controlled by an Italian.
The Settlement maintained its own fire-service, police force (the Shanghai Municipal Police), and even possessed its own military reserve
A military reserve, active reserve, reserve formation, or simply reserve, is a group of military personnel or units that is initially not committed to a battle by its commander, so that it remains available to address unforeseen situations or ex ...
in the Shanghai Volunteer Corps
The Shanghai Volunteer Corps (SVC) (1853−1942) was a multinational, mostly volunteer force controlled by the Shanghai Municipal Council which governed the Shanghai International Settlement.
History
The Shanghai Volunteer Corps was created on 1 ...
(). Following some disturbances at the British concession in Hankow in 1927, the defences at Shanghai were augmented by a permanent battalion of the British Army, which was referred to as the Shanghai Defence Force The Shanghai Defence Force was a tri-service military formation established by the British Government to protect European nationals and their property in Shanghai from Chinese nationalist forces during a period of tension in 1927.
History
Following ...
(SDF or SHAF), and a contingent of US Marines. Other armed forces would arrive in Shanghai; the French Concession had a defensive force of Troupes de marine and Annamite
The Vietnamese people ( vi, người Việt, lit=Viet people) or Kinh people ( vi, người Kinh) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to modern-day Northern Vietnam and Dongxing, Guangxi, Southern China (Jing Islands, Dongxing, Guangxi ...
suppletive troops from French Indochina, the Italians also introduced their own marines, as did the Japanese (whose troops eventually outnumbered the other countries' many times over).
Extra-settlement roads
From the 1860s, the Municipal Council began building roads beyond the concession boundaries, ostensibly to connect the concession with other properties or facilities which required the protection of Britain and other treaty powers during the unrest of the Taiping Rebellion. The Municipal Council obtained limited administrative powers over the areas adjacent to these "extra-settlement roads", making the area a "quasi-concession". The expansion of the International Settlement in 1899 took in most of the extra-settlement roads area, but from 1901 the Municipal Council began building further roads beyond the new boundary with a view to expanding the concession to cover those areas as well. However, a request to further expand the concession (inspired by a similar expansion of the French concession in 1914) was turned down by the Chinese government due to anti-imperialist sentiments. Britain, pre-occupied with World War I, did not press the issue and the extra-settlement roads area retained the "quasi-concession" status until the demise of the concession. Parts of the northern extra-settlement roads area was allocated to Japan for defence purposes in 1927, which the Japanese used as a base for military operations during the 1932 January 28th Incident and the 1937 Battle of Shanghai. After that battle, Japan took full control over the northern extra-settlement roads area and expelled International Settlement police. The neutrality of the western extra-settlement roads area survived in some form until the withdrawal of British troops in 1940.Legal Status of the International Settlement
Article 28 of the International Settlement's ''Land Regulations'' stated unequivocally that "the land encompassed in the territory remains Chinese territory, subject to China's sovereign rights." As expressed by legal experts, "the self-governing International Settlement possesses no more power than the mere delegation of purely local and municipal powers and functions. Control of police, sanitation, roads, and other problems of local administration are granted to the Municipal Council simply because that body happens to be the one best equipped to deal with these matters in an area where the large majority of foreigners dwell. But the Municipal Council is in no sense a political body. Its powers, being delegated and hence limited, are subject to strict construction. What foreigners acquire is simply the delegated power of municipal administration, while the reserve powers remain in the sovereign grantor, the Chinese Government. Although under the control of the Consular Council, the area is still Chinese territory, over which China's sovereignty remains unsurrendered".Rise of Imperial Japan (20th century)
Eight-Nation Alliance
The Eight-Nation Alliance was a multinational military coalition that invaded northern China in 1900 with the stated aim of relieving the foreign legations in Beijing, then besieged by the popular Boxer militia, who were determined to remove fo ...
during the infamous fifty-five-day siege of the foreign embassy compound in Peking. Japan entered the 20th century as a rising world power, and with its unequal treaties with the European powers now abrogated, it actually joined in, obtaining an unequal treaty with China granting extraterritorial rights under the Treaty of Shimonoseki signed in 1895.
In 1915, during the First World War, Japan overtook Britain as the country with the largest number of foreign residents in Shanghai. In 1914, Japan sided with Britain and France in the war and conquered all German possessions in China. By the beginning of the 1930s, Japan was swiftly becoming the most powerful national group in Shanghai and accounted for some 80% of all extraterritorial foreigners in China. Much of Hongkew
, formerly spelled Hongkew, is a district of Shanghai, forming part of the northern urban core. It has a land area of and a population of 852,476 as of 2010.
It is the location of the Astor House Hotel, Broadway Mansions, Lu Xun Park, and Hon ...
, which had become an unofficial Japanese settlement, was known as ''Little Tokyo''.
In 1931, supposed "protection of Japanese colonists from Chinese aggression" in Hongkew was used as a pretext for the Shanghai Incident, when Japanese troops invaded Shanghai. From then until the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) Hongkew was almost entirely outside of the SMC's hands, with law and protection enforced to varying degrees by the Japanese Consular Police
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
and Japanese members of the Shanghai Municipal Police.
Japanese take over rest of Shanghai (1937)
 In 1932 there were 1,040,780 Chinese living within the International Settlement, with another 400,000 fleeing into the area after the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out in 1937. For the next five years, the International Settlement and the French Concession were surrounded by Japanese occupiers and Chinese revolutionaries, with conflict often spilling into the Settlement's borders. In 1941, the Japanese launched an abortive political bid to take over the SMC: during a mass meeting of ratepayers at the Settlement Race Grounds, a Japanese official leaped up and shot William Keswick, then chairman of the council. While Keswick was only wounded, a near riot broke out.
In 1932 there were 1,040,780 Chinese living within the International Settlement, with another 400,000 fleeing into the area after the Second Sino-Japanese War broke out in 1937. For the next five years, the International Settlement and the French Concession were surrounded by Japanese occupiers and Chinese revolutionaries, with conflict often spilling into the Settlement's borders. In 1941, the Japanese launched an abortive political bid to take over the SMC: during a mass meeting of ratepayers at the Settlement Race Grounds, a Japanese official leaped up and shot William Keswick, then chairman of the council. While Keswick was only wounded, a near riot broke out.
Evacuation of British garrison
Britain evacuated its garrisons from mainland Chinese cities, particularly Shanghai, in August 1940.
Japanese occupy the International Settlement (1941)
Anglo-American influence effectively ended after 8 December 1941, when the Imperial Japanese Army entered and occupied the British and American controlled parts of the city in the wake of the attack on Pearl Harbor. The British and American troops, taken by surprise, surrendered without a shot, with the exception of the only British riverboat in Shanghai, HMS ''Peterel'', which refused to surrender; six of the 18 British crew on board at the time were killed when the ship was sunk after the Japanese opened fire at almost point-blank range. The French troops did not move from the preserved French Concession, as the French Vichy government considered itself neutral. European residents of the International Settlement were forced to wear armbands to differentiate them, were evicted from their homes, and — just like Chinese citizens — were liable to maltreatment. All were liable for punitive punishments, torture and even death during the period of Japanese occupation. The Japanese sent European and American citizens to be interned at theLunghua Civilian Assembly Center
Lunghua Civil Assembly Centre was one of the internment camps eventually established by the Empire of Japan in Shanghai for European and American citizens, who had been resident under Japanese occupation since December 1941. Many had formerly live ...
, a work camp on what was then the outskirts of Shanghai. Survivors of Lunghua were released in August 1945.
Shanghai was notable for a long period as the only place in the world that unconditionally offered refuge for Jews escaping from the Nazis. These refugees often lived in squalid conditions in an area known as the Shanghai Ghetto in Hongkew. On 21 August 1941 the Japanese government closed Hongkew to Jewish immigration.
Return to Chinese rule
In February 1943, the International Settlement was ''de jure'' returned to the Chinese as part of the British–Chinese Treaty for the Relinquishment of Extra-Territorial Rights in China and American–Chinese Treaty for Relinquishment of Extraterritorial Rights in China with the Nationalist Government of theRepublic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
under Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
. However, because Shanghai was under Japanese control, this was unenforceable. In reply, in July 1943, the Japanese retroceded the SMC to the City Government of Shanghai, which was then in the hands of the pro-Japanese Wang Jingwei Government.
After the war and the liberation of the city from the Japanese, a Liquidation Commission fitfully met to discuss the remaining details of the handover. By the end of 1945, most Westerners not actively involved in the Chinese Civil War (such as intelligence agents, soldiers, journalists, etc.) or in Shanghai's remaining foreign businesses, had left the city. With the defeat of the Kuomintang in 1949, the city was occupied by Communist People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
and came under the control of the Mayor of Shanghai This is a list of Mayor, mayors of Shanghai, China. In the People's Republic of China, the mayor is subordinate to the Chinese Communist Party Shanghai Committee, Communist Party Secretary of Shanghai.
Republic of China
Mayor of the Shanghai Sp ...
.
The foreign architecture of the International Settlement era can still be seen today along the Bund and in many locations around the city.
Legal system
 The International Settlement did not have a unified legal system. The Municipal Council issued Land Regulations and regulations under this, that were binding on all people in the settlement. Other than this, citizens and subjects of powers that had treaties with China that provided for extraterritorial rights were subject to the laws of their own countries and civil and criminal complaints against them were required to be brought against them to their consular courts (courts overseen by consular officials) under the laws of their own countries.
The number of treaty powers had climbed to a high of 19 by 1918 but was down to 14 by the 1930s: the United Kingdom, the United States, Japan, France, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, Peru, Mexico, and Switzerland. Germany and Austria-Hungary lost their treaty rights after WWI, and Russia gave up her rights as a matter of political expediency. Belgium was declared by China to have lost her rights in 1927. Furthermore, the Chinese government adamantly refused to grant treaty power status to any of the new nations born in the wake of WWI, such as Austria and Hungary (formerly Austria-Hungary), Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, the Baltic states, or Finland.
Chinese citizens and citizens of non-treaty powers were subject to Chinese law. Inside the Settlement, cases against them would be brought to the Mixed Court, a court established in the Settlement in the 1864 which existed until 1926. In cases involving foreigners, a foreign
The International Settlement did not have a unified legal system. The Municipal Council issued Land Regulations and regulations under this, that were binding on all people in the settlement. Other than this, citizens and subjects of powers that had treaties with China that provided for extraterritorial rights were subject to the laws of their own countries and civil and criminal complaints against them were required to be brought against them to their consular courts (courts overseen by consular officials) under the laws of their own countries.
The number of treaty powers had climbed to a high of 19 by 1918 but was down to 14 by the 1930s: the United Kingdom, the United States, Japan, France, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, Peru, Mexico, and Switzerland. Germany and Austria-Hungary lost their treaty rights after WWI, and Russia gave up her rights as a matter of political expediency. Belgium was declared by China to have lost her rights in 1927. Furthermore, the Chinese government adamantly refused to grant treaty power status to any of the new nations born in the wake of WWI, such as Austria and Hungary (formerly Austria-Hungary), Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, the Baltic states, or Finland.
Chinese citizens and citizens of non-treaty powers were subject to Chinese law. Inside the Settlement, cases against them would be brought to the Mixed Court, a court established in the Settlement in the 1864 which existed until 1926. In cases involving foreigners, a foreign assessor
An assessor may be:
* ''Assessor'' (fish), a genus of fishes
* Assessor (law), the assistant to a judge or magistrate
* Assessor (Oxford), a senior officer of the University of Oxford
* Assessor (property), an expert who calculates the value of pr ...
, usually a consular officer, would sit with the Chinese magistrate and in many cases acted like a judge. In 1927, a Provisional Court was established with a sole Chinese judge presiding. In 1930, Chinese Special Courts were established which had jurisdiction over all non-treaty power individuals and companies in the Settlement.
Two countries, Britain and the United States established formal court systems in China to try cases. The British Supreme Court for China and Japan
The British Supreme Court for China (originally the British Supreme Court for China and Japan) was a court established in the Shanghai International Settlement to try cases against British subjects in China, Japan and Korea under the principles ...
was established in 1865 and located in its own building in the British Consulate compound, and the United States Court for China was established in the US Consulate in 1906. Both courts were occupied by the Japanese on 8 December 1941 and effectively ceased to function from that date.
Currency
 The currency situation in China was very complicated in the 19th century, as there was no unified monetary system. Different parts of China operated different systems, and the Spanish pieces of eight that had been coming from Mexico for a few hundred years on Manila Galleons were current along the China coast. Until the 1840s these silver dollar coins were Spanish coins minted mainly in Mexico City, but from the 1840s these gave way to Mexican republican dollars.
In Shanghai, this complexity represented a microcosm of the complicated economy existing elsewhere along the China coast. The Chinese reckoned in weights of silver, which did not necessarily correspond to circulating coins. One important unit was a tael, a measurement of weight with several different definitions. These included: Customs Taels (for foreign trade), Cotton Taels (for cotton trade), etc. Shanghai had its own tael, which was very similar in weight to the Customs Tael and therefore popular for international business. China also had a mixture of coins, including Chinese Copper Cash coins and Mexican dollars. Paper money was first issued by European and North American colonial banks (one British colonial bank known as the
The currency situation in China was very complicated in the 19th century, as there was no unified monetary system. Different parts of China operated different systems, and the Spanish pieces of eight that had been coming from Mexico for a few hundred years on Manila Galleons were current along the China coast. Until the 1840s these silver dollar coins were Spanish coins minted mainly in Mexico City, but from the 1840s these gave way to Mexican republican dollars.
In Shanghai, this complexity represented a microcosm of the complicated economy existing elsewhere along the China coast. The Chinese reckoned in weights of silver, which did not necessarily correspond to circulating coins. One important unit was a tael, a measurement of weight with several different definitions. These included: Customs Taels (for foreign trade), Cotton Taels (for cotton trade), etc. Shanghai had its own tael, which was very similar in weight to the Customs Tael and therefore popular for international business. China also had a mixture of coins, including Chinese Copper Cash coins and Mexican dollars. Paper money was first issued by European and North American colonial banks (one British colonial bank known as the Chartered Bank of India, Australia, and China
The Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China (informally The Chartered Bank) was a bank incorporated in London in 1853 by Scotsman James Wilson, under a Royal Charter from Queen Victoria.
at one time issued banknotes in Shanghai that were denominated in Mexican dollars).
European and North American currencies did not officially circulate in the International Settlement, except Yen in the Japanese district of "Little Tokyo". Until the year 1873, however, US dollar coins would have reasonably corresponded in size, shape and value to Mexican dollars. Between 1873 and 1900, all silver standard dollars had depreciated to about 50% of the value of the gold standard dollars of the United States and Canada, leading to a rising economic depression.
The Chinese themselves officially adopted the dollar unit as their national currency in 1889, and the first Chinese dollar coins, known as yuan, contained an inscription which related their value to an already existing Chinese system of accounts. On the earliest Chinese dollar (yuan) coins it states the words 7 mace and 2 candareens. The mace and candareen were sub-divisions of the tael unit of weight. Banknotes tended to be issued in dollars, either worded as such or as yuan.
Despite the complications arising from a mixture of Chinese and Spanish coinages, there was one overwhelming unifying factor binding all the systems in use: silver. The Chinese reckoned purely in terms of silver, and value was always compared against a weight of silver (hence, the reason large prices were given in tael). It was the strict adherence of the Chinese to silver that caused China and even the British colonies of Hong Kong and Weihaiwei to remain on the silver standard after the rest of the world had changed over to the gold standard. When China began producing official Republican yuan coins in 1934, they were minted in Shanghai and shipped to Nanking for distribution.
Postal services
 Shanghai had developed a
Shanghai had developed a postal service
The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal syst ...
as early as the Ming Dynasty, but during the treaty port era foreign postal services were organised through their respective consulates. For example, the United States Post Office Department maintained a United States Postal Agency at the Shanghai consulate through which Americans could use the US Post Office to send mail to and from the US mainland and US territories. Starting in 1919 the 16 current regular US stamps were overprinted for use in Shanghai with the city's name, "China", and amounts double their printed face values. In 1922 texts for two of the overprints were changed, thereby completing the Scott catalogue
The Scott catalogue of postage stamps, published by Scott Publishing Company, now a subsidiary of Amos Media, is updated annually and lists all the stamps of the world that its editors recognize as issued for postal purposes. It is published in f ...
set of K1-18, "Offices in China".
The British originally used British postage stamps overprinted with the local currency amount, but from 1868, the British changed to Hong Kong postage stamps already denominated in dollars. However, in the special case of Shanghai, in the year 1865 the International settlement began to issue its own postage stamps, denominated in the local Shanghai tael unit.
The Shanghai Post Office controlled all post within the Settlement, but post entering or leaving the treaty port was required to go through the Chinese Imperial Post Office. In 1922 the various foreign postal services, the Shanghai Post Office, and the Chinese Post Office were all brought together into a single Chinese Post Office, thus extending the 1914 membership of the Chinese Post Office to the Universal Postal Union to the Shanghai Post Office. Some other foreign countries refused to fall under this new postal service's remit, however; for many years, Japan notably sent almost all its mail to Shanghai in diplomatic bag
A diplomatic bag, also known as a diplomatic pouch, is a container with certain legal protections used for carrying official correspondence or other items between a diplomatic mission and its home government or other diplomatic, consular, or other ...
s, which could not be opened by postal staff.
The General Shanghai Post Office was first located on Beijing Road and moved to the location on Sichuan North Road of the General Post Office Building, Shanghai that is today the Shanghai Post Museum.
Music
International merchants brought with them amateur musical talent that manifested in the creation of the Shanghai Philharmonic Society in 1868. From here, theShanghai Municipal Orchestra
The Shanghai Symphony Orchestra () is a symphony orchestra in Shanghai, China. Its music director is Yu Long.
Founded in 1879, the SSO is the oldest Chinese symphony orchestra. Originally, it was known as the Shanghai Public Band, expanding in ...
was officially formed in 1879.
In 1938, the Shanghai Municipal Orchestra faced disbandment as the ratepayers in the annual Municipal Council meeting considered reallocating budgets away from the orchestra, since it was "western and unnecessary." However, after much discussion, they decided to keep the orchestra, acknowledging that its educational value was much greater than the cost of keeping it up. The Shanghai Municipal Orchestra had the financial and verbal backing of many other larger countries, including Italy, who donated 50,000 lire to the orchestra, the France Council, who acted as a defending argument for the maintenance of the orchestra, and Japan, whose Viscount Konoye encouraged the Japanese people to support the orchestra and the culture that it brought to the East.
In addition to the string orchestra, opera and choral music were favored forms of entertainment. Often, the orchestra would accompany singers as a part of orchestra concerts, in addition to the symphonies and other pieces that they played, or just in choral or opera concerts.
List of chairmen of the Shanghai Municipal Council
# Edward Cunningham (25.5.1852 - 21.7.1853, as Chairman of the Committee on Roads and Jetties, the Municipal Council's predecessor) #William Shepard Wetmore
William Shepard Wetmore (January 26, 1801 – June 16, 1862) was an Americans, American Businessperson, businessman and Philanthropy, philanthropist who was an Old China Trade merchant.
Early life
He was born on January 26, 1801 to Nancy Shepar ...
(21.7.1853 - 11.7.1854, as Chairman of the Committee on Roads and Jetties)
#James Lawrence Man
(11.7.1854 - 1855) #
Christopher Augustus Fearon
Christopher is the English version of a Europe-wide name derived from the Greek name Χριστόφορος (''Christophoros'' or '' Christoforos''). The constituent parts are Χριστός (''Christós''), "Christ" or "Anointed", and φέρει� ...
(1855)
# William Shepard Wetmore
William Shepard Wetmore (January 26, 1801 – June 16, 1862) was an Americans, American Businessperson, businessman and Philanthropy, philanthropist who was an Old China Trade merchant.
Early life
He was born on January 26, 1801 to Nancy Shepar ...
(3.1855 - 1855)
# William Thorbun (1855 - 1856)
#James Lawrence Man
(1.1856 - 31.1.1857) #
George Watson Coutts
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd President ...
(31.1.1857 - 1.1858)
# John Thorne John Thorne may refer to:
* John Thorne (American football) (born 1957), American football coach
* John Thorne (colonial administrator) (1888–1964), civil servant in the Indian Civil Service
* John Thorne (MP) in 1388, MP for Guildford
* John T ...
(1.1858 - 1.1859)
# Robert Reid (31.1.1859 - 15.2.1860)
# Rowland Hamilton Rowland may refer to:
Places
;in the United States
*Rowland Heights, California, an unincorporated community in Los Angeles County
*Rowland, Kentucky, an unincorporated community
* Rowland Township, Michigan
* Rowland, Missouri, an unincorporated c ...
(15.2.1860 - 2.2.1861)
# William Howard (2.2.1861 - 31.3.1862)
# Henry Turner (31.3.1862 - 4.4.1863)
# Henry William Dent
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
*Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal ...
(4.4.1863 - 25.4.1865)
# William Keswick (25.4.1865 - 18.4.1866)
# F.B. Johnson
FB, Fb, or fb may refer to:
Arts and media
* F♭ (musical note)
* FB (band), an electronic music collaboration of Benny Benassi and Ferry Corsten
* Facebook, a social networking website, also known as FB.com
** Meta Platforms, formerly Facebook ...
(18.4.1866 - 3.1868)
# Edward Cunningham (3.1868 - 2.4.1870)
#George Basil Dixwell
(2.4.1870 - 4.4.1871) # John Dent (4.4.1871 - 1.1873) # Robert Inglis Fearon (1.1873 - 16.4.1874) #
John Graeme Purdon
(16.4.1874 - 1876) #
Alfred Adolphus Krauss
Alfred may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*''Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series
* ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne
* ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák
*"Alfred (Interlu ...
(1876 - 1.1877)
# J. Hart
''J. The Jewish News of Northern California'', formerly known as ''Jweekly'', is a weekly print newspaper in Northern California, with its online edition updated daily. It is owned and operated by San Francisco Jewish Community Publications In ...
(1.1877 - 16.1.1879)
# Robert "Bob" W. Little (16.1.1879 - 30.1.1882)
# H.R. Hearn
Paul D. Hudson (born February 11, 1956), known professionally as H.R. (Human Rights), is an American musician who leads the hardcore punk band Bad Brains, and is an instrumental figure in the development of the genre. His vocal delivery has b ...
(30.1.1882 - 1882)
# Walter Cyril Ward (1882 - 1883)
# Alexander Myburgh
Alexander Myburgh (1848–1889) was a South African barrister who served as the chairman of the Shanghai Shanghai International Settlement, Municipal Council from 1883 to 1884.
Early life
Myburgh was born in 1848. He was the fifth surviving son ...
(1883 - 22.1.1884)
# James Johnstone Keswick (22.1.1884 - 22.1.1886)
# A.G. Wood
A&G, AG, Ag or ag may refer to
Businesses and organizations
* A&G Railroad (former reporting mark AG)
* Action Group (Nigeria), a political party during the Nigerian First Republic
* Aktiengesellschaft, a German type of corporation
* Assembli ...
(22.1.1886 - 1889)
# John Macgregor John MacGregor, John Macgregor or John McGregor may refer to:
Sportsmen
* John McGregor (footballer, born 1851), Scottish international football player
* John McGregor (footballer, born 1900) (1900–1993), English football player
* John McGrego ...
(1889 - 5.1891)
#John Graeme Purdon
(5.1891 - 1.1893) #
John Macgregor John MacGregor, John Macgregor or John McGregor may refer to:
Sportsmen
* John McGregor (footballer, born 1851), Scottish international football player
* John McGregor (footballer, born 1900) (1900–1993), English football player
* John McGrego ...
(1.1893 - 7.11.1893)
#James Lidderdale Scott
(11.1893 - 26.1.1897) # Edward Albert Probst (26.1.1897 - 21.4.1897) # Albert Robson Burkill (12.5.1897 - 1.1898) # James S. Fearon (1.1898 - 8.1899) #*
Joseph Welch
Joseph Nye Welch (October 22, 1890 – October 6, 1960) was an American lawyer and actor who served as the chief counsel for the United States Army while it was under investigation for Communist activities by Senator Joseph McCarthy's Senate Perm ...
, ''acting'' (3.8.1898 - 30.11.1898)
# Frederick Anderson (8.1899 – 1.1900)
# Edbert Ansgar Hewett
Edbert Ansgar Hewett, (5 September 1860 – 24 November 1915) was a prominent British merchant in Hong Kong and China and member of the Executive Council and Legislative Council of Hong Kong.
Family and early life
Hewett was born on 5 Septem ...
(8.1900 - 25.1.1901)
# John Prentice (26.1.1901 - 25.1.1902)
# William George Bayne (25.1.1902 - 1904)
# Frederick Anderson (1904 - 25.1.1906)
# Cecil Holliday
Cecil Holliday was the Chairman of the Shanghai International Settlement, Shanghai Municipal Council in 1906. He also served as commandant of the Shanghai Volunteer Corps.
Biography
Holliday was born in Kersemoor, Manchester in 1857, the younges ...
(25.1.1906 - 24.8.1906)
# Henry Keswick (24.8.1906 - 5.1907)
# David Landale
David Landale (6 August 1868 – 6 September 1935) was the 13th Tai-pan of the Jardine Matheson & Co. and member of the Executive Council and Legislative Council of Hong Kong.
Early life
Born on 6 August 1868, Landale was the son of Rev. Da ...
(5.1907 – 17.1.1911)
# Harry De Gray
Harry De Gray (1866–1952) was the Chairman of the Shanghai Municipal Council for 2 years from 1911 to 1913.
Biography
De Gray was born in Paterson, New Jersey on 31 October 1866, the son of William M. De Gary.
De Gray moved to Shanghai 1900. ...
(17.1.1911 - 24.1.1913)
# Edward Charles Pearce
Sir Edward Charles Pearce was the Chairman of the Shanghai Municipal Council for 7 years, serving throughout World War I.
Biography
Pearce was born 1862 in London the son of John Swayne Pearce. He was educated at the Charterhouse School.
Pearce ...
(24.1.1913 - 17.2.1920)
# Alfred Brooke-Smith
Alfred Brooke-Smith (1874–1938) was the Chairman of the Shanghai Municipal Council for 2 years from 1920 to 1922. He also served as Managing Director of Jardine Matheson & Co.
Biography
Brooke-Smith was born on 3 November 1874 in Yokohama, Jap ...
(17.2.1920 - 17.3.1922)
# H.G. Simms
H. G. Simms was the Chairman of Shanghai International Settlement's Municipal Council from 1922 to 1923. He was also Chairman of the Shanghai Club from 1914 to 1920.
Biography
Simms was born in Strabane, County Tyrone, Ireland. After leaving ...
(17.3.1922 - 12.10.1923)
# Stirling Fessenden
Stirling Fessenden (29 September 1875 – 1 February 1944), an American lawyer who practised in Shanghai, was the chairman of the Shanghai Municipal Council from 1923 to 1929 and then Secretary-General of the Council from 1929 to 1939.
Early lif ...
(12.10.1923 - 5.3.1929)
# Harry Edward Arnhold (5.3.1929 - 1930)
# Ernest Brander Macnaghten (1930 - 22.3.1932)
# A.D. Bell (22.3.1932 - 27.3.1934)
# Harry Edward Arnhold (27.3.1934 - 4.1937)
# Cornell Franklin (4.1937 - 4.1940)
# William Johnstone "Tony" Keswick (4.1940 - 1.5.1941)
# John Hellyer Liddell
John Hellyer Liddell CBE (29 June 1899 – 24 January 1984) was businessman who served as the last British chairman of the Shanghai Municipal Council from 1941 to 1942.
Life
Liddell was born on 29 June 1899 in Shanghai. He was the son of John and ...
(1.5.1941 - 5.1.1942)
# Katsuo Okazaki (5.1.1942 - 1.8.1943)
Notable people born in the International Settlement
* J. G. Ballard, writer. His acclaimed novel '' Empire of the Sun'' is set in the International Settlement and other parts of Shanghai. * Mary Hayley Bell, English actress * Pat Carney, Canadian politician * Eileen Chang, Chinese-American writer * Eunice Crowther, dancer and choreographer * Edmond H. Fischer, Swiss-American Nobel Prize winner *Thierry Jordan
Thierry Romain Camille Jordan (born 31 August 1943) is a French prelate of the Catholic Church who was Archbishop of Reims from 1999 to 2018. He was previously Bishop of Pontoise for more than a decade.
Personal life
Thierry Jordan was born to ...
, French clergyman and Archbishop of Reims
* China Machado
Noelie Dasouza Machado (25 December 1929 – 18 December 2016), known as China Machado, was a Chinese-born American fashion model, editor, and television producer. She was the first model of color to appear in a major American fashion magazin ...
, Portuguese-Macanese model, ''Harpers Bazaar'' editor, TV producer, designer
* Jane Scott, Duchess of Buccleuch
Jane Montagu Douglas Scott, Duchess of Buccleuch and Queensberry (''née'' McNeill; 19 December 1929 – 18 April 2011) was a British duchess and model. She was a fashion model for Norman Hartnell before marrying John Scott, Earl of Dalkeith, th ...
, British duchess and fashion model
* Qian Xuesen, Chinese aerospace engineer and father of China's missile and space program
* Hu Hesheng
Hu Hesheng (; born 20 June 1928) is a Chinese mathematician. She served as vice-president of Chinese Mathematical Society, president of the Shanghai Mathematical Society, and is an academician of Chinese Academy of Science. She held the Noether ...
, Chinese mathematician
Relation with the French Concession
The French Concession was governed by a separate municipal council, under the direction of the Consul General. The French Concession was not part of the International Settlement, but had economical interests in it as evidenced by the presence of the French flag on the seal and the flag of the Municipal Council.Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* Altman, Avraham, and Irene Eber. "Flight to Shanghai, 1938-1940: the larger setting." ''Yad Vashem Studies'' 28 (2000): 51–86. Jews fleeing Europonline
* * Bickers, Robert, '' Empire Made Me: An Englishman Adrift in Shanghai'' (Allen Lane History, 2003). * Bickers, Robert. "Shanghailanders: The formation and identity of the British settler community in Shanghai 1843–1937." ''Past & Present'' 159.1 (1998): 161–211
online
* Cheng, Hu. "Quarantine, Race and Politics in the International Settlement: Clashes between Chinese and Foreigners after the Outbreak of Plague in Shanghai in 1910." ''Modern Chinese History Studies'' 4 (2007): 5+. * * * * * Hao, Yen-p'ing. ''The Commercial Revolution of Nineteenth-Century China: The Rise of Sino-Western Mercantile Competition'' (U of California Press, 1984), * Henriot, Christian, and Wen-Hsin Yeh, eds. ''In the shadow of the rising sun: Shanghai under Japanese occupation'' (Cambridge UP, 2004). * Hudson, Manley O. "The Rendition of the International Mixed Court at Shanghai." ''American Journal of International Law'' 21.3 (1927): 451–471. * Lockwood, William W. "The International Settlement at Shanghai, 1924–34." ''American Political Science Review'' 28.6 (1934): 1030–1046
online
* MacPherson, Kerrie L. "Designing China's urban future: The Greater Shanghai Plan, 1927–1937." ''Planning Perspective'' 5.1 (1990): 39–62. * Ristaino, Marcia Reynders. ''Port of last resort: The diaspora communities of Shanghai'' (Stanford University Press, 2003). * Wakeman, Frederic E., and Wen-Hsin Yeh, eds. ''Shanghai sojourners'' (Institute of East Asian Studies, University of California, 1992.
excerpt
* Wakeman, Frederick. "Licensing Leisure: The Chinese Nationalists' Attempt to Regulate Shanghai, 1927–49." ''Journal of Asian Studies'' 54.1 (1995): 19–42.
External links
*See also
* American Concession (Shanghai) * Shanghai French Concession * List of former foreign enclaves in China * Astor House Hotel (Shanghai) *British Supreme Court for China and Japan
The British Supreme Court for China (originally the British Supreme Court for China and Japan) was a court established in the Shanghai International Settlement to try cases against British subjects in China, Japan and Korea under the principles ...
* The Bund
* China Marines
* Former Consulate-General of the United Kingdom, Shanghai
The Former Consulate-General of the United Kingdom (英国驻上海总领事馆) building located in Shanghai, China, is one of the oldest buildings on the Bund.
It is housed in a compound that housed a number of buildings used by the British C ...
* Klaus Mehnert
Klaus Mehnert (October 10, 1906, Moscow, Russia – January 2, 1984, Freudenstadt, Germany) was a German writer, journalist and academic. He was a correspondent in the Soviet Union; a professor in the United States; a publisher of a German-funded ...
* List of historic buildings in Shanghai
* Richard Sorge
* Shanghai Club
* Shanghai Municipal Police
* Tilanqiao Prison
The Tilanqiao Prison (), formerly known as the Ward Road Gaol or Shanghai Municipal Gaol, is a former prison in Hongkou District of Shanghai, China. Originally built in the foreign-controlled Shanghai International Settlement, following the Chin ...
(formerly Ward Road Gaol)
* United States Court for China
* ''When We Were Orphans
''When We Were Orphans'' is the fifth novel by Nobel Prize-winning British author Kazuo Ishiguro, published in 2000. It is loosely categorised as a detective novel. ''When We Were Orphans'' was shortlisted for the 2000 Booker Prize.
Plot sum ...
''
* '' The Blue Lotus''
* '' Empire of the Sun''
{{Shanghai
1943 disestablishments in Asia
Concessions in China
European colonisation in Asia
History of Shanghai
China–United Kingdom relations
China–United States relations
United Kingdom–United States relations
City-states
Foreign affairs in Shanghai