The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting
international labour standards
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work (human activity) and the workplace. The Interna ...
.
Founded in October 1919 under the
League of Nations, it is the first and oldest
specialised agency of the UN. The ILO has
187 member states: 186 out of 193
UN member states plus the
Cook Islands. It is headquartered in
Geneva, Switzerland
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situa ...
, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.
The ILO's standards are aimed at ensuring accessible, productive, and sustainable
work
Work may refer to:
* Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community
** Manual labour, physical work done by humans
** House work, housework, or homemaking
** Working animal, an animal t ...
worldwide in conditions of freedom, equity, security and dignity.
They are set forth in
189 conventions and treaties, of which eight are classified as fundamental according to the 1998
Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work
The Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work was adopted in 1998, at the 86th International Labour Conference. It is a statement made by the International Labour Organization "that all Members, even if they have not ratified the C ...
; together they protect freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to
collective bargaining, the elimination of forced or compulsory labour, the abolition of
child labour, and the elimination of
discrimination in respect of
employment and occupation. The ILO is a major contributor to
international labour law
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work (human activity) and the workplace. The Inte ...
.
Within the UN system the organization has a unique tripartite structure: all standards, policies, and programmes require discussion and approval from the representatives of governments, employers, and workers. This framework is maintained in the ILO's three main bodies: The International Labour Conference, which meets annually to formulate international labour standards; the Governing Body, which serves as the executive council and decides the agency's policy and budget; and the International Labour Office, the permanent secretariat that administers the organization and implements activities. The secretariat is led by the Director-General,
Guy Ryder
Guy Bernard Ryder (born 3 January 1956) is a British international civil servant who currently serves as Under-Secretary-General for Policy at the United Nations.
He was previously Director-General of the International Labour Organization from ...
of the United Kingdom, who was elected by the Governing Body in 2012.
In 1969, the ILO received the
Nobel Peace Prize for improving
fraternity and peace among nations, pursuing
decent work
Decent work is employment that "respects the fundamental rights of the human person as well as the rights of workers in terms of conditions of work safety and remuneration. ... respect for the physical and mental integrity of the worker in the ...
and
justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to other developing nations.
In 2019, the organization convened the Global Commission on the Future of Work, whose report made ten recommendations for governments to meet the challenges of the 21st century labour environment; these include a universal labour guarantee, social protection from birth to old age and an entitlement to lifelong learning. With its focus on international development, it is a member of the United Nations Development Group, a coalition of UN organizations aimed at helping meet the
Sustainable Development Goals.
Governance, organization, and membership

Unlike other United Nations specialized agencies, the International Labour Organization (ILO) has a
tripartite governing structure that brings together governments, employers, and workers of 187 member States, to set labour standards, develop policies and devise programmes promoting decent work for all women and men. The structure is intended to ensure the views of all three groups are reflected in ILO labour standards, policies, and programmes, though governments have twice as many representatives as the other two groups.
Governing body
The Governing Body is the
executive body
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state.
In political systems ba ...
of the International Labour Organization. It meets three times a year, in March, June and November. It takes decisions on ILO policy, decides the agenda of the International Labour Conference, adopts the draft Programme and Budget of the Organization for submission to the Conference, elects the Director-General, requests information from the member states concerning labour matters, appoints commissions of inquiry and supervises the work of the International Labour Office.
The Governing Body is composed of 56 titular members (28 governments, 14 employers and 14 workers) and 66 deputy members (28 governments, 19 employers and 19 workers).
Ten of the titular government seats are permanently held by States of chief industrial importance:
Brazil,
China,
France,
Germany,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
,
Italy,
Japan, the
Russian Federation, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. The other Government members are elected by the Conference every three years (the last elections were held in June 2017). The Employer and Worker members are elected in their individual capacity.
India assumed the Chairmanship of the Governing Body of International Labour Organization in 2020. Apurva Chandra, Secretary (Labour and Employment) has been elected as the Chairperson of the Governing Body of the ILO for the period October 2020-June 2021.
Director-General
On 25 March 2022
Gilbert Fossoun Houngbo was elected Director-General of ILO. On 1 October 2022 he will succeed
Guy Ryder
Guy Bernard Ryder (born 3 January 1956) is a British international civil servant who currently serves as Under-Secretary-General for Policy at the United Nations.
He was previously Director-General of the International Labour Organization from ...
, who was elected by the ILO Governing Body in October 2012, and re-elected for a second five-year-term in November 2016. He will be the organization's first African Director-General.
The list of the Directors-General of ILO since its establishment in 1919 is as follows:
International Labour Conference
Once a year, the ILO organises the International Labour Conference in Geneva to set the broad policies of the ILO, including conventions and recommendations. Also known as the "international parliament of labour", the conference makes decisions about the ILO's general policy, work programme and budget and also elects the Governing Body.
Each member state is represented by a delegation: two government delegates, an employer delegate, a worker delegate and their respective advisers. All of them have individual voting rights and all votes are equal, regardless of the population of the delegate's member State. The employer and worker delegates are normally chosen in agreement with the most representative national organizations of employers and workers. Usually, the workers and employers' delegates coordinate their voting. All delegates have the same rights and are not required to vote in blocs.
Delegates have the same rights, they can express themselves freely and vote as they wish. This diversity of viewpoints does not prevent decisions from being adopted by very large majorities or unanimously.
Heads of State and prime ministers also participate in the Conference. International organizations, both governmental and others, also attend but as observers.
The 109th session of the International Labour Conference was delayed from 2020 to May 2021 and was held online because of the
COVID-19 pandemic. The first meeting was on 20 May 2021 in
Geneva for the election of its officers. Further sittings were held in June, November and December. The 110th session took place from 27 May to 11 June 2022.
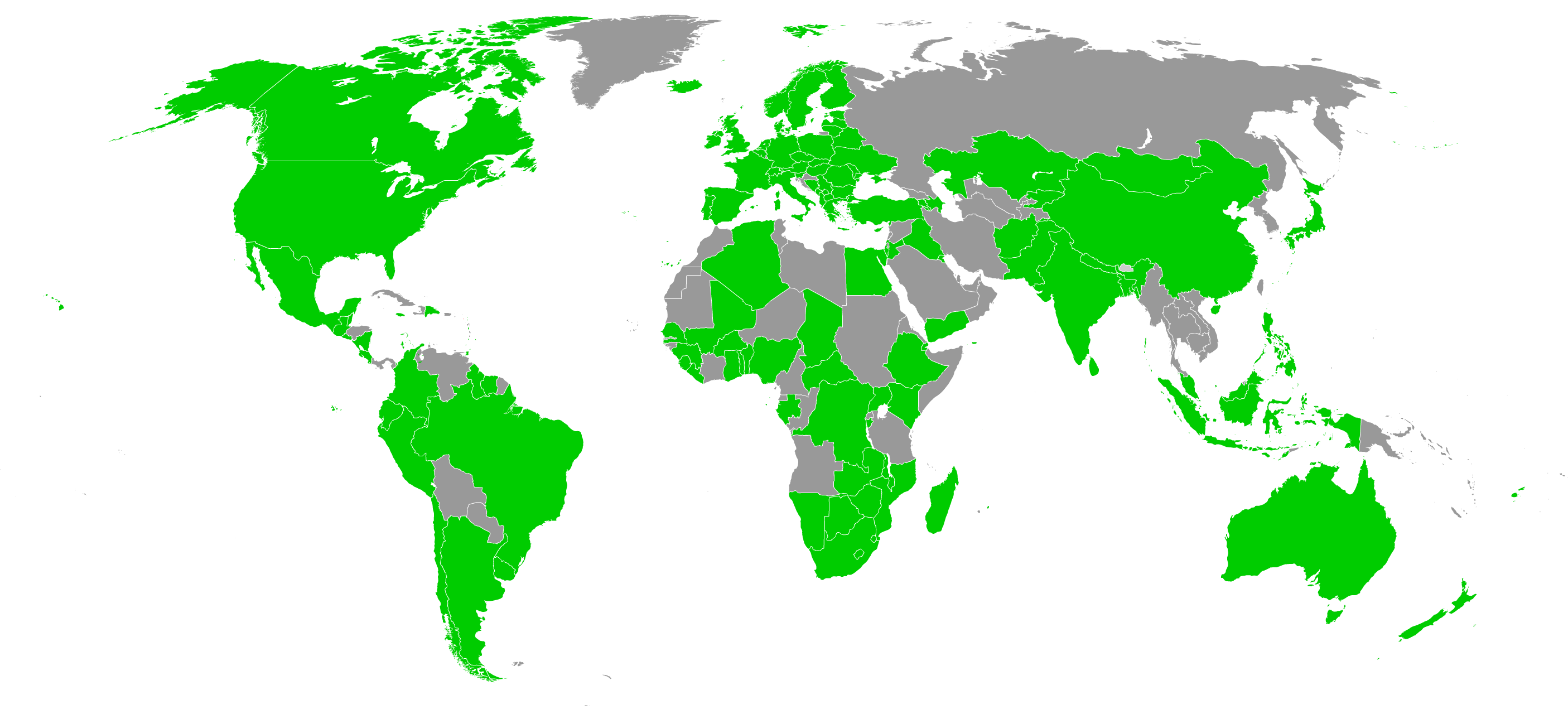
Membership

The ILO has 187 state members. 186 of the 193
member states of the United Nations plus the
Cook Islands are members of the ILO. The UN member states which are not members of the ILO are
Andorra,
Bhutan,
Liechtenstein,
Micronesia,
Monaco,
Nauru, and
North Korea.
The ILO constitution permits any member of the UN to become a member of the ILO. To gain membership, a nation must inform the director-general that it accepts all the obligations of the ILO constitution.
Other states can be admitted by a two-thirds vote of all delegates, including a two-thirds vote of government delegates, at any ILO General Conference. The Cook Islands, a non-UN state, joined in June 2015.
Members of the ILO under the League of Nations automatically became members when the organization's new constitution came into effect after World War II.
Position within the UN
The ILO is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN). As with other UN specialized agencies (or programmes) working on
international development, the ILO is also a member of the
United Nations Development Group.
Normative function
Conventions
Through July 2018, the ILO had adopted 189 conventions. If these conventions are ratified by enough governments, they come in force. However, ILO conventions are considered
international labour standards
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work (human activity) and the workplace. The Interna ...
regardless of ratification. When a convention comes into force, it creates a legal obligation for ratifying nations to apply its provisions.
Every year the International Labour Conference's Committee on the Application of Standards examines a number of alleged breaches of international labour standards. Governments are required to submit reports detailing their compliance with the obligations of the conventions they have ratified. Conventions that have not been ratified by member states have the same legal force as recommendations.
In 1998, the 86th International Labour Conference adopted the ''
Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work
The Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work was adopted in 1998, at the 86th International Labour Conference. It is a statement made by the International Labour Organization "that all Members, even if they have not ratified the C ...
''. This declaration contains four fundamental policies:
* The right of workers to associate freely and
bargain collectively
* The end of
forced and compulsory labour
* The end of
child labour
* The end of
unfair discrimination among workers
The ILO asserts that its members have an obligation to work towards fully respecting these principles, embodied in relevant ILO conventions. The ILO conventions that embody the fundamental principles have now been ratified by most member states.
Protocols
This device is employed for making conventions more flexible or for amplifying obligations by amending or adding provisions on different points.
Protocols are always linked to Convention, even though they are international treaties they do not exist on their own. As with Conventions, Protocols can be ratified.
Recommendations
Recommendations do not have the binding force of conventions and are not subject to ratification. Recommendations may be adopted at the same time as conventions to supplement the latter with additional or more detailed provisions. In other cases recommendations may be adopted separately and may address issues separate from particular conventions.
History
Origins
While the ILO was established as an agency of the
League of Nations following
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, its founders had made great strides in social thought and action before 1919. The core members all knew one another from earlier private professional and ideological networks, in which they exchanged knowledge, experiences, and ideas on social policy. Prewar "
epistemic communities", such as the
International Association for Labour Legislation (IALL), founded in 1900, and political networks, such as the
socialist Second International, were a decisive factor in the institutionalization of international labour politics.
In the post–World War I euphoria, the idea of a "makeable society" was an important catalyst behind the social engineering of the ILO architects. As a new discipline, international labour law became a useful instrument for putting social reforms into practice. The utopian ideals of the founding members—social justice and the right to decent work—were changed by diplomatic and political compromises made at the
Paris Peace Conference of 1919, showing the ILO's balance between idealism and pragmatism.
Over the course of the First World War, the international
labour movement proposed a comprehensive programme of protection for the working classes, conceived as compensation for labour's support during the war. Post-war reconstruction and the protection of labour unions occupied the attention of many nations during and immediately after World War I. In Great Britain, the
Whitley Commission, a subcommittee of the Reconstruction Commission, recommended in its July 1918 Final Report that "industrial councils" be established throughout the world. The
British Labour Party had issued its own reconstruction programme in the document titled ''Labour and the New Social Order''. In February 1918, the third
Inter-Allied Labour and Socialist Conference (representing delegates from Great Britain, France, Belgium and Italy) issued its report, advocating an international labour rights body, an end to secret diplomacy, and other goals. And in December 1918, the
American Federation of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutu ...
(AFL) issued its own distinctively apolitical report, which called for the achievement of numerous incremental improvements via the
collective bargaining process.
[Foner, Philip S. ''History of the Labor Movement in the United States. Vol. 7: Labor and World War I, 1914–1918.'' New York: International Publishers, 1987. ]
IFTU Bern Conference
As the war drew to a close, two competing visions for the post-war world emerged. The first was offered by the
International Federation of Trade Unions
The International Federation of Trade Unions (also known as the Amsterdam International) was an international organization of trade unions, existing between 1919 and 1945. IFTU had its roots in the pre-war IFTU.
IFTU had close links to the Labou ...
(IFTU), which called for a meeting in
Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
,
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, in July 1919. The Bern meeting would consider both the future of the IFTU and the various proposals which had been made in the previous few years. The IFTU also proposed including delegates from the
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
as equals.
Samuel Gompers
Samuel Gompers (; January 27, 1850December 13, 1924) was a British-born American cigar maker, labor union leader and a key figure in American labor history. Gompers founded the American Federation of Labor (AFL) and served as the organization's ...
, president of the AFL, boycotted the meeting, wanting the Central Powers delegates in a subservient role as an admission of guilt for their countries' role in bringing about war. Instead, Gompers favoured a meeting in Paris which would consider President
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
's
Fourteen Points
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms ...
only as a platform. Despite the American boycott, the Bern meeting went ahead as scheduled. In its final report, the Bern Conference demanded an end to wage labour and the establishment of socialism. If these ends could not be immediately achieved, then an international body attached to the League of Nations should enact and enforce legislation to protect workers and trade unions.
Commission on International Labour Legislation
Meanwhile, the
Paris Peace Conference sought to dampen public support for communism. Subsequently, the
Allied Powers agreed that clauses should be inserted into the emerging peace treaty protecting labour unions and workers' rights, and that an international labour body be established to help guide international labour relations in the future. The advisory Commission on International Labour Legislation was established by the Peace Conference to draft these proposals. The Commission met for the first time on 1 February 1919, and Gompers was elected as the chairman.

Two competing proposals for an international body emerged during the Commission's meetings. The British proposed establishing an international parliament to enact labour laws which each member of the League would be required to implement. Each nation would have two delegates to the parliament, one each from labour and management.
An international labour office would collect statistics on labour issues and enforce the new international laws. Philosophically opposed to the concept of an international parliament and convinced that international standards would lower the few protections achieved in the United States, Gompers proposed that the international labour body be authorized only to make recommendations and that enforcement be left up to the League of Nations. Despite vigorous opposition from the British, the American proposal was adopted.
Gompers also set the agenda for the draft charter protecting workers' rights. The Americans made 10 proposals. Three were adopted without change: That labour should not be treated as a commodity; that all workers had the right to a wage sufficient to live on; and that women should receive equal pay for equal work. A proposal protecting the freedom of speech, press, assembly, and association was amended to include only freedom of association. A proposed ban on the international shipment of goods made by children under the age of 16 was amended to ban goods made by children under the age of 14. A proposal to require an
eight-hour work day was amended to require the eight-hour work day ''or'' the 40-hour work week (an exception was made for countries where productivity was low). Four other American proposals were rejected. Meanwhile, international delegates proposed three additional clauses, which were adopted: One or more days for weekly rest; equality of laws for foreign workers; and regular and frequent inspection of factory conditions.
The Commission issued its final report on 4 March 1919, and the Peace Conference adopted it without amendment on 11 April. The report became Part XIII of the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
.
Interwar period

The first annual
International Labour Conference (ILC) began on 29 October 1919 at the
Pan American Union Building
The Pan American Union Building is the headquarters for the Organization of American States. It is located at 17th Street N.W. between C Street N.W. and Constitution Avenue, Northwest, Washington, D.C.
History
On the former site of the John P ...
in Washington, D.C. and adopted the first six International Labour Conventions, which dealt with hours of work in industry, unemployment, maternity protection, night work for women, minimum age, and night work for young persons in industry. The prominent French socialist
Albert Thomas became its first director-general.
Despite open disappointment and sharp critique, the revived
International Federation of Trade Unions
The International Federation of Trade Unions (also known as the Amsterdam International) was an international organization of trade unions, existing between 1919 and 1945. IFTU had its roots in the pre-war IFTU.
IFTU had close links to the Labou ...
(IFTU) quickly adapted itself to this mechanism. The IFTU increasingly oriented its international activities around the lobby work of the ILO.
At the time of establishment, the U.S. government was not a member of ILO, as the US Senate rejected the covenant of the League of Nations, and the United States could not join any of its agencies. Following the election of
Franklin Delano Roosevelt to the U.S. presidency, the new administration made renewed efforts to join the ILO without league membership. On 19 June 1934, the U.S. Congress passed a joint resolution authorizing the president to join ILO without joining the League of Nations as a whole. On 22 June 1934, the ILO adopted a resolution inviting the U.S. government to join the organization. On 20 August 1934, the U.S. government responded positively and took its seat at the ILO.
Wartime and the United Nations
During the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, when Switzerland was surrounded by German troops, ILO director
John G. Winant made the decision to leave Geneva. In August 1940, the
government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown ...
officially invited the ILO to be housed at
McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 by royal charter granted by King George IV,Frost, Stanley Brice. ''McGill Universit ...
in Montreal. Forty staff members were transferred to the temporary offices and continued to work from McGill until 1948.
The ILO became the first specialized agency of the United Nations system after the demise of the league in 1946.
Its constitution, as amended, includes the
Declaration of Philadelphia
The Declaration of Philadelphia (10 May 1944) restated the traditional objectives of the International Labour Organization (ILO) and then branched out in two new directions: the centrality of human rights to social policy, and the need for intern ...
(1944) on the aims and purposes of the organization.
Cold War era

Beginning in the late 1950s the organization was under pressure to make provisions for the potential membership of ex-colonies which had become independent; in the Director General's report of 1963 the needs of the potential new members were first recognized. The tensions produced by these changes in the world environment negatively affected the established politics within the organization and they were the precursor to the eventual problems of the organization with the USA
In July 1970, the United States withdrew 50% of its financial support to the ILO following the appointment of an assistant director-general from the Soviet Union. This appointment (by the ILO's British director-general,
C. Wilfred Jenks
C. Wilfred Jenks (7 March 1909 – 9 October 1973) was an international lawyer and director-general of the International Labour Organization (1970–1973).Elihu Lauterpacht, "Jenks, Clarence Wilfred (1909–1973)", Oxford Dictionary of Nat ...
) drew particular criticism from
AFL–CIO
The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL–CIO) is the largest federation of unions in the United States. It is made up of 56 national and international unions, together representing more than 12 million ac ...
president
George Meany
William George Meany (August 16, 1894 – January 10, 1980) was an American labor union leader for 57 years. He was the key figure in the creation of the AFL–CIO and served as the AFL–CIO's first president, from 1955 to 1979.
Meany, the son ...
and from Congressman
John E. Rooney. However, the funds were eventually paid.
On 12 June 1975, the ILO voted to grant the
Palestinian Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, منظمة التحرير الفلسطينية, ') is a Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establishing Arab unity and ...
observer status at its meetings. Representatives of the United States and Israel walked out of the meeting. The
U.S. House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
subsequently decided to withhold funds. The United States gave notice of full withdrawal on 6 November 1975, stating that the organization had become politicized. The United States also suggested that representation from communist countries was not truly "
tripartite"—including government, workers, and employers—because of the structure of these economies. The withdrawal became effective on 1 November 1977.
The United States returned to the organization in 1980 after extracting some concession from the organization. It was partly responsible for the ILO's shift away from a human rights approach and towards support for the
Washington Consensus. Economist
Guy Standing wrote "the ILO quietly ceased to be an international body attempting to redress structural inequality and became one promoting employment equity".
In 1981, the government of
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
declared
martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Marti ...
. It interrupted the activities of
Solidarność
Solidarity ( pl, „Solidarność”, ), full name Independent Self-Governing Trade Union "Solidarity" (, abbreviated ''NSZZ „Solidarność”'' ), is a Polish trade union founded in August 1980 at the Lenin Shipyard in Gdańsk, Poland. Subseq ...
detained many of its leaders and members. The ILO Committee on Freedom of Association filed a complaint against Poland at the 1982 International Labour Conference. A Commission of Inquiry established to investigate found Poland had violated ILO Conventions No. 87 on freedom of association and No. 98 on trade union rights, which the country had ratified in 1957. The ILO and many other countries and organizations put pressure on the Polish government, which finally gave legal status to Solidarność in 1989. During that same year, there was a roundtable discussion between the government and Solidarnoc which agreed on terms of relegalization of the organization under ILO principles. The government also agreed to hold the first free elections in Poland since the Second World War.
Offices
ILO headquarters

The ILO is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. In its first months of existence in 1919, it offices were located in London, only to move to Geneva in the summer 1920. The first seat in Geneva was on the Pregny hill in the ''Ariana'' estate, in the building that used to host the Thudicum boarding school and currently the headquarters of the
International Committee of the Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signato ...
. As the office grew, the Office relocated to a purpose-built headquarters by the shores of
lake Leman
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
, designed by
Georges Epitaux and inaugurated in 1926 (currently the sear of the
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
). During the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
the Office was temporarily relocated to
McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 by royal charter granted by King George IV,Frost, Stanley Brice. ''McGill Universit ...
in
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
,
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.
The current seat of the ILO's headquarters is located on the Pregny hill, not far from its initial seat. The building, a biconcave rectangular block designed by
Eugène Beaudoin,
Pier Luigi Nervi
Pier Luigi Nervi (21 June 1891 – 9 January 1979) was an Italian engineer and architect. He studied at the University of Bologna graduating in 1913. Nervi taught as a professor of engineering at Rome University from 1946 to 1961 and is known wor ...
and
Alberto Camenzind, was purpose-built between 1969-1974 in a severe rationalist style and, at the time of construction, constituted the largest administrative building in Switzerland.
Regional offices
* Regional Office for
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, in
Abidjan
Abidjan ( , ; N'Ko script, N’ko: ߊߓߌߖߊ߲߬) is the economic capital of the Ivory Coast. As of the Demographics of Ivory Coast, 2021 census, Abidjan's population was 6.3 million, which is 21.5 percent of overall population of the country, ...
,
Côte d'Ivoire
* Regional Office for
Asia and the Pacific, in
Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estima ...
,
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
* Regional Office for
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and Central Asia, in
Geneva,
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
* Regional Office for Latin America and the Caribbean, in Lima, Peru
* Regional Office for the Arab States, in Beirut, Lebanon
Sub-regional offices
Called "Decent Work Technical Support Teams (DWT)", they provide technical support to the work of a number of countries under their area of competence.

* DWT for North Africa, in Cairo, Egypt
* DWT for West Africa, in Dakar, Senegal
* DWT for Eastern and Southern Africa, in Pretoria, South Africa
* DWT for Central Africa, in Yaoundé, Cameroon
* DWT for the Arab States, in Beirut, Lebanon
* DWT for South Asia, in New Delhi,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
* DWT for East and South-East Asia and the Pacific, in Bangkok, Thailand
* DWT for Central and Eastern Europe, in Budapest, Hungary
* DWT for Eastern Europe and Central Asia, in Moscow, Russia
* DWT for the Andean Countries, in Lima, Peru
* DWT for the Caribbean Countries, in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago
* DWT for Central American Countries, in San José, Costa Rica, San José, Costa Rica
* DWT for Countries of the South Cone of Latin America, in Santiago, Chile
Country and liaison offices
* In Africa:
Abidjan
Abidjan ( , ; N'Ko script, N’ko: ߊߓߌߖߊ߲߬) is the economic capital of the Ivory Coast. As of the Demographics of Ivory Coast, 2021 census, Abidjan's population was 6.3 million, which is 21.5 percent of overall population of the country, ...
, Abuja, Addis Ababa, Algiers, Antananarivo, Cairo, Dakar, Dar es Salaam, Harare, Kinshasa, Lusaka, Pretoria, Yaoundé
* In the Arab States: Beirut, Doha, Jerusalem
* In Asia and the Pacific: Bangkok, Beijing, Colombo, Dhaka, Hanoi, Islamabad, Jakarta, Kabul, Kathmandu, Manila, New Delhi, Suva, Tokyo, Yangon
* In Europe and Central Asia: Ankara, Berlin, Brussels, Budapest, Lisbon, Madrid, Moscow, Paris, Rome
* In the Americas: Brasilia, Buenos Aires, Mexico City, New York City, New York, Lima, Port-of-Spain, San José, Santiago, Washington, D.C., Washington
Programmes
Labour statistics
The ILO is a major provider of labour statistics. Labour statistics are an important tool for its member states to monitor their progress toward improving labour standards. As part of their statistical work, ILO maintains several databases. This database covers 11 major data series for over 200 countries. In addition, ILO publishes a number of compilations of labour statistics, such as the Key Indicators of Labour Markets (KILM). KILM covers 20 main indicators on labour participation rates, employment, unemployment, educational attainment, labour cost, and economic performance. Many of these indicators have been prepared by other organizations. For example, the Division of international labor comparisons, Division of International Labour Comparisons of the Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics prepares the hourly compensation in manufacturing indicator.
The United States Department of Labor, U.S. Department of Labor also publishes a yearly report containing a ''List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor'' issued by the Bureau of International Labor Affairs. The December 2014 updated edition of the report listed a total of 74 countries and 136 goods.
Training and teaching units
The International Training Centre of the International Labour Organization (ITCILO) is based in Turin, Italy. Together with the University of Turin Department of Law, the ITC offers training for ILO officers and secretariat members, as well as offering educational programmes. The ITC offers more than 450 training and educational programmes and projects every year for some 11,000 people around the world.
For instance, the ITCILO offers a Master of Laws programme in management of development, which aims specialize professionals in the field of cooperation and development.
Child labour
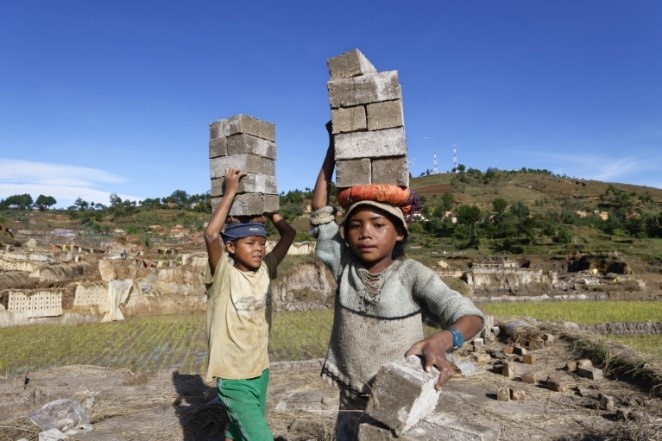

The term ''
child labour'' is often defined as work that deprives children of their childhood, potential, dignity, and is harmful to their physical and mental development.
''Child labour'' refers to work that is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children. Further, it can involve interfering with their schooling by depriving them of the opportunity to attend school, obliging them to leave school prematurely, or requiring them to attempt to combine school attendance with excessively long and heavy work.
In its most extreme forms, child labour involves children being enslaved, separated from their families, exposed to serious hazards and illnesses and left to fend for themselves on the streets of large cities – often at a very early age. Whether or not particular forms of "work" can be called ''child labour'' depends on the child's age, the type and hours of work performed, the conditions under which it is performed and the objectives pursued by individual countries. The answer varies from country to country, as well as among sectors within countries.
ILO's response to child labour

The ILO's International Programme on the Elimination of Child Labour (IPEC) was created in 1992 with the overall goal of the progressive elimination of child labour, which was to be achieved through strengthening the capacity of countries to deal with the problem and promoting a worldwide movement to combat child labour. The IPEC currently has operations in 88 countries, with an annual expenditure on technical cooperation projects that reached over US$61 million in 2008. It is the largest programme of its kind globally and the biggest single operational programme of the ILO.
The number and range of the IPEC's partners have expanded over the years and now include employers' and workers' organizations, other international and government agencies, private businesses, community-based organizations, NGOs, the media, parliamentarians, the judiciary, universities, religious groups and children and their families.
The IPEC's work to eliminate child labour is an important facet of the ILO's Decent Work Agenda. Child labour prevents children from acquiring the skills and education they need for a better future.
The ILO also hosts a Global Conference on the Elimination of Child Labour every four years. The most recent conference was held in Durban, South Africa from 15 to 20 May 2022.
Exceptions in indigenous communities
Because of different cultural views involving labour, the ILO developed a series of culturally sensitive mandates, including convention Nos. 169, 107, 138, and 182, to protect indigenous culture, traditions, and identities. Convention Nos. 138 and 182 lead in the fight against
child labour, while Nos. 107 and 169 promote the rights of indigenous people, indigenous and tribal peoples and protect their right to define their own developmental priorities.
In many indigenous communities, parents believe children learn important life lessons through the act of work and through the participation in daily life. Working is seen as a learning process preparing children of the future tasks they will eventually have to do as an adult. It is a belief that the family's and child well-being and survival is a shared responsibility between members of the whole family. They also see work as an intrinsic part of their child's Indigenous peoples of the Americas#Child Development, developmental process. While these attitudes toward Child work in indigenous American cultures, child work remain, many children and parents from indigenous communities still highly value education.
Issues
Forced labour

The ILO has considered the fight against forced labour to be one of its main priorities. During the interwar years, the issue was mainly considered a colonial phenomenon, and the ILO's concern was to establish minimum standards protecting the inhabitants of colonies from the worst abuses committed by economic interests. After 1945, the goal became to set a uniform and universal standard, determined by the higher awareness gained during World War II of politically and economically motivated systems of forced labour, but debates were hampered by the Cold War and by exemptions claimed by colonial powers. Since the 1960s, declarations of labour standards as a component of human rights have been weakened by government of postcolonial countries claiming a need to exercise extraordinary powers over labour in their role as emergency regimes promoting rapid economic development.

In June 1998 the International Labour Conference adopted a
Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work
The Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work was adopted in 1998, at the 86th International Labour Conference. It is a statement made by the International Labour Organization "that all Members, even if they have not ratified the C ...
and its follow-up that obligates member states to respect, promote and realize freedom of association and the right to collective bargaining, the elimination of all forms of forced or compulsory labour, the effective abolition of child labour, and the elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation.
With the adoption of the declaration, the ILO created the InFocus Programme on Promoting the Declaration which is responsible for the reporting processes and technical cooperation activities associated with the declaration; and it carries out awareness raising, advocacy and knowledge functions.
In November 2001, following the publication of the InFocus Programme's first global report on forced labour, the ILO's governing body created a special action programme to combat forced labour (SAP-FL), as part of broader efforts to promote the 1998 Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work and its follow-up.
Since its inception, the SAP-FL has focused on raising global awareness of forced labour in its different forms, and mobilizing action against its manifestation. Several thematic and country-specific studies and surveys have since been undertaken, on such diverse aspects of forced labour as bonded labour, human trafficking, forced domestic work, rural servitude, and forced prisoner labour.
In 2013, the SAP-FL was integrated into the ILO's Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work Branch (FUNDAMENTALS) bringing together the fight against forced and child labour and working in the context of Alliance 8.7.
One major tool to fight forced labour was the adoption of the ILO Forced Labour Protocol by the International Labour Conference in 2014. It was ratified for the second time in 2015 and on 9 November 2016 it entered into force. The new protocol brings the existing ILO Convention 29 on Forced Labour, adopted in 1930, into the modern era to address practices such as human trafficking. The accompanying Recommendation 203 provides technical guidance on its implementation.
In 2015, the ILO launched a global campaign to end modern slavery, in partnership with the International Organization of Employers (IOE) and the International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC). The 50 for Freedom campaign aims to mobilize public support and encourage countries to ratify the ILO's Forced Labour Protocol.
Minimum wage law
To protect the right of labours for fixing minimum wage, ILO has created Minimum Wage-Fixing Machinery Convention, 1928, Minimum Wage Fixing Machinery (Agriculture) Convention, 1951 and Minimum Wage Fixing Convention, 1970 as minimum wage law.
Commercialized sex
'White Slavery'
Before the creation of the ILO in 1919, legislation and preconceived notions about commercialized sex already existed around the globe. The first example of this legislation was passed by the British parliament in 1885 in response to local citizens in Britain who demanded parliament abolish "white slavery" and raise the age of consent for girls.
The term 'White Slavery (prostitution), white slavery' was used in the 19th century to describe girls and women who had been taken advantage of by professional seducers who manipulated them into being prostitutes.
After the turn of the twentieth century, the focus of laws in England shifted to protecting the country's borders from the threat of foreign girls.
The Alien Acts of 1905 focused on preventing Jewish immigration, but it created the foundation for future legislation that would be used to crack down on foreign prostitutes.
This law enhanced British power to repatriate foreign women suspected of prostitution.
Inter-War Period
From the moment its creation in the Treaty of Versailles, 1919 Treaty of Versailles, the ILO has been concerned with the controversial issue of commercial sex. Prior to the creation of the ILO and
League of Nations, the issue of sex work had been exclusively under the jurisdiction of the state, now, the ILO and League of Nations believed the issue transcended borders and within their jurisdiction.
In the early twentieth, commercialized sex was considered both immoral and criminal activity. Initially, the ILO strongly believed prostitution was linked to vulnerable single working women emigrating to other nations without being under the paternal supervision of a man.
After the widespread destruction caused by
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the ILO saw prostitution as spreading contagion requiring regulation.
Under the leadership of the French socialist Albert Thomas, the ILO created a medical division whose primary focus was on male sailors whose lives were viewed as "nomadic" and "promiscuous," which made these men susceptible to infection of STD's.
After the conclusion of the Genoa maritime conference in 1920, the ILO proclaimed itself as the critical leader of the prevention and treatment of STD's in sailors. In the interwar years, the ILO also sought to protect female workers in dangers trades, but delegates to ILO Conferences did not consider the sex trade to be "work," which was conceived of as industrial labor. The ILO believed that if women worked industrial jobs, this would be a deterrent from them living immoral lives. In order to make these industrial jobs more attractive, the ILO promoted better wages and safer working conditions, both intended to prevent women from falling victim to the temptation of the sex trades.
Postwar Period
After the surrender of the Japanese military and the end of World War II, a new inter-governmental governing body, the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, was formed, while the ILO continued to be the primary international body governing labor. Following the creation of the United Nations, the ILO took a back seat to the newly formed organization on the issue of commercialized sex.The UN Commission on the Status of Women called for abolishing both sex trafficking and prostitution.
Socialist countries proclaimed they had eliminated the issue of prostitution through the economic empowerment of their citizens. This claim linked prostitution to economic causes.
In the 1950s, the UN Economic and Social Council and the International Police Organization sought to end any activity that resembled slavery, classifying sex trafficking and prostitution as criminal rather than labor issues.
These new initiatives by the United Nations would lead to later debates at the World Conference on Women, 1975, World Conference on Women in Mexico City during International Women's Year in 1975.
Coming out of the Conference in Mexico City, delegates pleaded with governments all over the globe to take action to prevent the forced prostitution of both women and children.
= Post 1975 Conference
=
Beginning in 1976, the ILO and other organizations began to examine the working and living conditions of rural women in Third World countries.
One example the ILO investigated was the "go-go" bars and the growing phenomenon of "hired wives" in Thailand, which both thrived because the development of U.S. military bases in the region.
In the late 1970s, the ILO established the "Programme on Rural Women," which investigated the involvement of young masseuses in the sex trade in Bangkok.
As part of this investigation, Pasuk Phongpaichit, a Thai doctor who received their degree from Cambridge University, interviewed fifty masseuses and explored why these rural women were migrating from the countryside to Bangkok and why they chose to become prostitutes.
Phongpaichit also investigated the women's experiences after migrating and the impact on the women's families after leaving the countryside.
This report exposed the wide income gap between rural and urban families and emphasized economic motives.
It was critical because it was the first time in the history of the ILO or any of its branches that prostitution was described as a form of labor.
In the decades that followed, the increase in sexual tourism and the exploding AIDS epidemic strengthened ILO interest in the commercial sex trade.
An ILO Senior Specialist on Women Workers' Questions for Asia and the Pacific, Lin Lim, published another study directly influenced by Phongpaichit's findings. Lim's study detailed the different social and economic factors that directly contributed to the growth of the sex industry in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand.
The findings emphasized the economic reasons for and advantages of entering into the commercial sex trade, including increased wages, flexibility between work and home life and the ability to migrate.
The authors of this report argued the sex industry should be recognized as a legitimate economic sector.
It would take another decade until the ILO discussed commercialized sex, this time, it would be under the shadow of the exploding AIDS epidemic.
HIV/AIDS
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is the lead UN-agency on HIV workplace policies and programmes and private sector mobilization. ILOAIDS is the branch of the ILO dedicated to this issue.
The ILO has been involved with the HIV response since 1998, attempting to prevent potentially devastating impact on Contract labour, labour and productivity and that it says can be an enormous burden for working people, their families and communities. In June 2001, the ILO's governing body adopted a pioneering code of practice on HIV/AIDS and the world of work, which was launched during a special session of the UN General Assembly.
The same year, ILO became a cosponsor of the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS).
In 2010, the 99th International Labour Conference adopted the ILO's recommendation concerning HIV and AIDS and the world of work, 2010 (No. 200), the first international labour standard on HIV and AIDS. The recommendation lays out a comprehensive set of principles to protect the rights of HIV-positive workers and their families, while scaling up prevention in the workplace. Working under the theme of ''Preventing HIV, Protecting Human Rights at Work'', ILOAIDS undertakes a range of policy advisory, research and technical support functions in the area of HIV and AIDS and the world of work. The ILO also works on promoting social protection as a means of reducing vulnerability to HIV and mitigating its impact on those living with or affected by HIV.
ILOAIDS ran a "Getting to Zero" campaign to arrive at zero new infections, zero AIDS-related deaths and zero-discrimination by 2015. Building on this campaign, ILOAIDS is executing a programme of voluntary and confidential counselling and testing at work, known as VCT@WORK.
Migrant workers
As the word "migrant" suggests, migrant workers refer to those who moves from one country to another to do their job. For the rights of migrant workers, ILO has adopted conventions, including Migrant Workers (Supplementary Provisions) Convention, 1975 and United Nations Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families in 1990.
Domestic workers
Domestic workers are those who perform a variety of tasks for and in other peoples' homes. For example, they may cook, clean the house, and look after children. Yet they are often the ones with the least consideration, excluded from labour and social protection. This is mainly due to the fact that women have traditionally carried out the tasks without pay. For the rights and
decent work
Decent work is employment that "respects the fundamental rights of the human person as well as the rights of workers in terms of conditions of work safety and remuneration. ... respect for the physical and mental integrity of the worker in the ...
of domestic workers including migrant domestic workers, ILO has adopted the Convention on Domestic Workers on 16 June 2011.
ILO and globalization
Seeking a process of globalization that is inclusive, democratically governed and provides opportunities and tangible benefits for all countries and people. The World Commission on the Social Dimension of Globalization was established by the ILO's governing body in February 2002 at the initiative of the director-general in response to the fact that there did not appear to be a space within the multilateral system that would cover adequately and comprehensively the social dimension of the various aspects of globalization. The World Commission Report, A Fair Globalization: Creating Opportunities for All, is the first attempt at structured dialogue among representatives of constituencies with different interests and opinions on the social dimension of globalization.
Future of work
The ILO launched the Future of Work Initiative in order to gain understanding on the transformations that occur in the world of work and thus be able to develop ways of responding to these challenges. The initiative begun in 2016 by gathering the views of government representatives, workers, employers, academics and other relevant figures around the world. About 110 countries participated in dialogues at the regional and national level. These dialogues were structured around "four centenary conversations: work and society, decent jobs for all, the organization of work and production, and the governance of work." The second step took place in 2017 with the establishment of the Global Commission on the Future of Work dealing with the same "four centenary conversations". A report was published for the 2019 Centenary International Labour Conference. ILO also assessed the impact of technological disruptions on employments worldwide. The agency was worried about the global economic and health impact of technology, like industrial and process automation, artificial intelligence (AI), Robots and robotic process of automation on human labour and was increasingly being considered by commentators, but in widely divergent ways. Among the salient views technology was going to bring less work, make workers redundant or end work by replacing the human labour. The other fold of view was technological creativity and abundant opportunities for economy boosts. In the modern era, technology has changed the way we think, design, and deploy the system solutions, but no doubt there are threats to human jobs. Paul Schulte (Director of the Education and Information Division, and Co-Manager of the Nanotechnology Research Center, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Centers for Disease Control) and D. P. Sharma, (International Consultant, Information Technology and Scientist) clearly articulated such disruptions and warned that it will be worse than ever before if appropriate, timely actions are not taken. They said that human generation needs to reinvent in terms of competitive accuracy, speed, capacity and honesty. Machines are more honest than human labours and pose a crystal clear threat to this generation. The science and technology have no reverse gear and accepting the challenge "Human vs. Machine" is the only remedy for survival.
The ILO has also looked at the transition to a green economy, and the Green growth#Employment, impact thereof on employment. It came to the conclusion a shift to a greener economy could create 24 million Employment, new jobs globally by 2030, if Environmental policy, the right policies are put in place. Also, if a transition to a green economy were not to take place, 72 million full-time jobs may be lost by 2030 due to heat stress, and temperature increases will lead to shorter available work hours, particularly in agriculture
Greening with jobs – World Employment and Social Outlook 2018
/ref>
See also
* Administrative Tribunal of the International Labour Organization
* Centre William Rappard, first permanent home of the ILO on the north bank of Lake Geneva
*League of Nations archives
* Seoul Declaration on Safety and Health at Work, 2008
* Social clause, the integration of seven core ILO labour rights conventions into trade agreements
*Total Digital Access to the League of Nations Archives Project (LONTAD)
* United Nations Global Compact, 1999–2000, encouraging businesses to adopt sustainable and socially responsible policies
References
Further reading
* Alcock, A. ''History of the International Labour Organization'' (London, 1971)
*
* Chisholm, A. ''Labour's Magna Charta: A Critical Study of the Labour Clauses of the Peace Treaty and of the Draft Conventions and Recommendations of the Washington International Labour Conference'' (London, 1925)
* Dufty, N.F. "Organizational Growth and Goal Structure: The Case of the ILO," ''International Organization'' 1972 Vol. 26, pp 479–49
in JSTOR
* Endres, A.; Fleming, G. ''International Organizations and the Analysis of Economic Policy, 1919–1950'' (Cambridge, 2002)
* Evans, A.A. ''My Life as an International Civil Servant in the International Labour Organization'' (Geneva, 1995)
* Ewing, K. ''Britain and the ILO'' (London, 1994)
Fried, John H. E. "Relations Between the United Nations and the International Labor Organization," ''American Political Science Review'', Vol. 41, No. 5 (October 1947), pp. 963–977 in JSTOR
* Galenson, Walter. ''The International Labor Organization: An American View'' (Madison, 1981)
* Ghebali, Victor-Yves. "The International Labour Organisation : A Case Study on the Evolution of U.N. Specialised Agencies" ''Dordrecht, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers'', (1989)
Guthrie, Jason. "The international labor organization and the social politics of development, 1938–1969." (PhD Dissertation, University of Maryland, 2015).
* Haas, Ernst B. "Beyond the nation-state: functionalism and international organization" ''Colchester, ECPR Press'', (2008)
* Heldal, H. "Norway in the International Labour Organization, 1919–1939" ''Scandinavian Journal of History'' 1996 Vol. 21, pp 255–283,
* Imber, M.F. ''The USA, ILO, UNESCO and IAEA: politicization and withdrawal in the Specialized Agencies'' (1989)
* Johnston, G.A. ''The International Labour Organization: Its Work for Social and Economic Progress'' (London, 1970)
* McGaughey, E. 'The International Labour Organization's Next Century: Economic Democracy, and the Undemocratic Third' (2021
32(2) King's Law Journal 287
and on SSRN
* Manwaring, J. ''International Labour Organization: A Canadian View'' (Ottawa, 1986)
* Morse, David. ''The Origin and Evolution of the ILO and its Role in the World Community'' (Ithaca, 1969)
Morse, David. "International Labour Organization – Nobel Lecture: ILO and the Social Infrastructure of Peace"
* Ostrower, Gary B. "The American decision to join the international labor organization", ''Labor History'', Volume 16, Issue 4 Autumn 1975, pp 495–504 The U.S. joined in 1934
* Silva, Vicente. "The ILO and the future of work: The politics of global labour policy". Global Social Policy. March 2021. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/14680181211004853
* VanDaele, Jasmien. "The International Labour Organization (ILO) In Past and Present Research," ''International Review of Social History'' 2008 53(3): 485–511, historiography
External links
*
The International Training Centre of the ILO
Nobel Peace Prize 1969 for the ILO
* with the Nobel Lecture 11 December 1969 ''ILO and the Social Infrastructure of Peace''
Contains electronic copies of ILO reports published from 1919 onwards
YouTube channel
{{Authority control
International Labour Organization,
United Nations specialized agencies
United Nations Development Group
Global workforce and labor organizations
Workers' rights organizations
Organizations awarded Nobel Peace Prizes
Organizations established in 1919
United Nations organizations based in Geneva
Swiss Nobel laureates
 The ILO has 187 state members. 186 of the 193 member states of the United Nations plus the Cook Islands are members of the ILO. The UN member states which are not members of the ILO are Andorra, Bhutan, Liechtenstein, Micronesia, Monaco, Nauru, and North Korea.
The ILO constitution permits any member of the UN to become a member of the ILO. To gain membership, a nation must inform the director-general that it accepts all the obligations of the ILO constitution. Other states can be admitted by a two-thirds vote of all delegates, including a two-thirds vote of government delegates, at any ILO General Conference. The Cook Islands, a non-UN state, joined in June 2015.
Members of the ILO under the League of Nations automatically became members when the organization's new constitution came into effect after World War II.
The ILO has 187 state members. 186 of the 193 member states of the United Nations plus the Cook Islands are members of the ILO. The UN member states which are not members of the ILO are Andorra, Bhutan, Liechtenstein, Micronesia, Monaco, Nauru, and North Korea.
The ILO constitution permits any member of the UN to become a member of the ILO. To gain membership, a nation must inform the director-general that it accepts all the obligations of the ILO constitution. Other states can be admitted by a two-thirds vote of all delegates, including a two-thirds vote of government delegates, at any ILO General Conference. The Cook Islands, a non-UN state, joined in June 2015.
Members of the ILO under the League of Nations automatically became members when the organization's new constitution came into effect after World War II.
 Two competing proposals for an international body emerged during the Commission's meetings. The British proposed establishing an international parliament to enact labour laws which each member of the League would be required to implement. Each nation would have two delegates to the parliament, one each from labour and management. An international labour office would collect statistics on labour issues and enforce the new international laws. Philosophically opposed to the concept of an international parliament and convinced that international standards would lower the few protections achieved in the United States, Gompers proposed that the international labour body be authorized only to make recommendations and that enforcement be left up to the League of Nations. Despite vigorous opposition from the British, the American proposal was adopted.
Gompers also set the agenda for the draft charter protecting workers' rights. The Americans made 10 proposals. Three were adopted without change: That labour should not be treated as a commodity; that all workers had the right to a wage sufficient to live on; and that women should receive equal pay for equal work. A proposal protecting the freedom of speech, press, assembly, and association was amended to include only freedom of association. A proposed ban on the international shipment of goods made by children under the age of 16 was amended to ban goods made by children under the age of 14. A proposal to require an eight-hour work day was amended to require the eight-hour work day ''or'' the 40-hour work week (an exception was made for countries where productivity was low). Four other American proposals were rejected. Meanwhile, international delegates proposed three additional clauses, which were adopted: One or more days for weekly rest; equality of laws for foreign workers; and regular and frequent inspection of factory conditions.
The Commission issued its final report on 4 March 1919, and the Peace Conference adopted it without amendment on 11 April. The report became Part XIII of the
Two competing proposals for an international body emerged during the Commission's meetings. The British proposed establishing an international parliament to enact labour laws which each member of the League would be required to implement. Each nation would have two delegates to the parliament, one each from labour and management. An international labour office would collect statistics on labour issues and enforce the new international laws. Philosophically opposed to the concept of an international parliament and convinced that international standards would lower the few protections achieved in the United States, Gompers proposed that the international labour body be authorized only to make recommendations and that enforcement be left up to the League of Nations. Despite vigorous opposition from the British, the American proposal was adopted.
Gompers also set the agenda for the draft charter protecting workers' rights. The Americans made 10 proposals. Three were adopted without change: That labour should not be treated as a commodity; that all workers had the right to a wage sufficient to live on; and that women should receive equal pay for equal work. A proposal protecting the freedom of speech, press, assembly, and association was amended to include only freedom of association. A proposed ban on the international shipment of goods made by children under the age of 16 was amended to ban goods made by children under the age of 14. A proposal to require an eight-hour work day was amended to require the eight-hour work day ''or'' the 40-hour work week (an exception was made for countries where productivity was low). Four other American proposals were rejected. Meanwhile, international delegates proposed three additional clauses, which were adopted: One or more days for weekly rest; equality of laws for foreign workers; and regular and frequent inspection of factory conditions.
The Commission issued its final report on 4 March 1919, and the Peace Conference adopted it without amendment on 11 April. The report became Part XIII of the  The first annual International Labour Conference (ILC) began on 29 October 1919 at the
The first annual International Labour Conference (ILC) began on 29 October 1919 at the  Beginning in the late 1950s the organization was under pressure to make provisions for the potential membership of ex-colonies which had become independent; in the Director General's report of 1963 the needs of the potential new members were first recognized. The tensions produced by these changes in the world environment negatively affected the established politics within the organization and they were the precursor to the eventual problems of the organization with the USA
In July 1970, the United States withdrew 50% of its financial support to the ILO following the appointment of an assistant director-general from the Soviet Union. This appointment (by the ILO's British director-general,
Beginning in the late 1950s the organization was under pressure to make provisions for the potential membership of ex-colonies which had become independent; in the Director General's report of 1963 the needs of the potential new members were first recognized. The tensions produced by these changes in the world environment negatively affected the established politics within the organization and they were the precursor to the eventual problems of the organization with the USA
In July 1970, the United States withdrew 50% of its financial support to the ILO following the appointment of an assistant director-general from the Soviet Union. This appointment (by the ILO's British director-general,  On 12 June 1975, the ILO voted to grant the
On 12 June 1975, the ILO voted to grant the  The ILO is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. In its first months of existence in 1919, it offices were located in London, only to move to Geneva in the summer 1920. The first seat in Geneva was on the Pregny hill in the ''Ariana'' estate, in the building that used to host the Thudicum boarding school and currently the headquarters of the
The ILO is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. In its first months of existence in 1919, it offices were located in London, only to move to Geneva in the summer 1920. The first seat in Geneva was on the Pregny hill in the ''Ariana'' estate, in the building that used to host the Thudicum boarding school and currently the headquarters of the  * DWT for North Africa, in Cairo, Egypt
* DWT for West Africa, in Dakar, Senegal
* DWT for Eastern and Southern Africa, in Pretoria, South Africa
* DWT for Central Africa, in Yaoundé, Cameroon
* DWT for the Arab States, in Beirut, Lebanon
* DWT for South Asia, in New Delhi,
* DWT for North Africa, in Cairo, Egypt
* DWT for West Africa, in Dakar, Senegal
* DWT for Eastern and Southern Africa, in Pretoria, South Africa
* DWT for Central Africa, in Yaoundé, Cameroon
* DWT for the Arab States, in Beirut, Lebanon
* DWT for South Asia, in New Delhi,  The term '' child labour'' is often defined as work that deprives children of their childhood, potential, dignity, and is harmful to their physical and mental development.
''Child labour'' refers to work that is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children. Further, it can involve interfering with their schooling by depriving them of the opportunity to attend school, obliging them to leave school prematurely, or requiring them to attempt to combine school attendance with excessively long and heavy work.
In its most extreme forms, child labour involves children being enslaved, separated from their families, exposed to serious hazards and illnesses and left to fend for themselves on the streets of large cities – often at a very early age. Whether or not particular forms of "work" can be called ''child labour'' depends on the child's age, the type and hours of work performed, the conditions under which it is performed and the objectives pursued by individual countries. The answer varies from country to country, as well as among sectors within countries.
The term '' child labour'' is often defined as work that deprives children of their childhood, potential, dignity, and is harmful to their physical and mental development.
''Child labour'' refers to work that is mentally, physically, socially or morally dangerous and harmful to children. Further, it can involve interfering with their schooling by depriving them of the opportunity to attend school, obliging them to leave school prematurely, or requiring them to attempt to combine school attendance with excessively long and heavy work.
In its most extreme forms, child labour involves children being enslaved, separated from their families, exposed to serious hazards and illnesses and left to fend for themselves on the streets of large cities – often at a very early age. Whether or not particular forms of "work" can be called ''child labour'' depends on the child's age, the type and hours of work performed, the conditions under which it is performed and the objectives pursued by individual countries. The answer varies from country to country, as well as among sectors within countries.
 The ILO's International Programme on the Elimination of Child Labour (IPEC) was created in 1992 with the overall goal of the progressive elimination of child labour, which was to be achieved through strengthening the capacity of countries to deal with the problem and promoting a worldwide movement to combat child labour. The IPEC currently has operations in 88 countries, with an annual expenditure on technical cooperation projects that reached over US$61 million in 2008. It is the largest programme of its kind globally and the biggest single operational programme of the ILO.
The number and range of the IPEC's partners have expanded over the years and now include employers' and workers' organizations, other international and government agencies, private businesses, community-based organizations, NGOs, the media, parliamentarians, the judiciary, universities, religious groups and children and their families.
The IPEC's work to eliminate child labour is an important facet of the ILO's Decent Work Agenda. Child labour prevents children from acquiring the skills and education they need for a better future.
The ILO also hosts a Global Conference on the Elimination of Child Labour every four years. The most recent conference was held in Durban, South Africa from 15 to 20 May 2022.
The ILO's International Programme on the Elimination of Child Labour (IPEC) was created in 1992 with the overall goal of the progressive elimination of child labour, which was to be achieved through strengthening the capacity of countries to deal with the problem and promoting a worldwide movement to combat child labour. The IPEC currently has operations in 88 countries, with an annual expenditure on technical cooperation projects that reached over US$61 million in 2008. It is the largest programme of its kind globally and the biggest single operational programme of the ILO.
The number and range of the IPEC's partners have expanded over the years and now include employers' and workers' organizations, other international and government agencies, private businesses, community-based organizations, NGOs, the media, parliamentarians, the judiciary, universities, religious groups and children and their families.
The IPEC's work to eliminate child labour is an important facet of the ILO's Decent Work Agenda. Child labour prevents children from acquiring the skills and education they need for a better future.
The ILO also hosts a Global Conference on the Elimination of Child Labour every four years. The most recent conference was held in Durban, South Africa from 15 to 20 May 2022.
 The ILO has considered the fight against forced labour to be one of its main priorities. During the interwar years, the issue was mainly considered a colonial phenomenon, and the ILO's concern was to establish minimum standards protecting the inhabitants of colonies from the worst abuses committed by economic interests. After 1945, the goal became to set a uniform and universal standard, determined by the higher awareness gained during World War II of politically and economically motivated systems of forced labour, but debates were hampered by the Cold War and by exemptions claimed by colonial powers. Since the 1960s, declarations of labour standards as a component of human rights have been weakened by government of postcolonial countries claiming a need to exercise extraordinary powers over labour in their role as emergency regimes promoting rapid economic development.
The ILO has considered the fight against forced labour to be one of its main priorities. During the interwar years, the issue was mainly considered a colonial phenomenon, and the ILO's concern was to establish minimum standards protecting the inhabitants of colonies from the worst abuses committed by economic interests. After 1945, the goal became to set a uniform and universal standard, determined by the higher awareness gained during World War II of politically and economically motivated systems of forced labour, but debates were hampered by the Cold War and by exemptions claimed by colonial powers. Since the 1960s, declarations of labour standards as a component of human rights have been weakened by government of postcolonial countries claiming a need to exercise extraordinary powers over labour in their role as emergency regimes promoting rapid economic development.
 Since its inception, the SAP-FL has focused on raising global awareness of forced labour in its different forms, and mobilizing action against its manifestation. Several thematic and country-specific studies and surveys have since been undertaken, on such diverse aspects of forced labour as bonded labour, human trafficking, forced domestic work, rural servitude, and forced prisoner labour.
In 2013, the SAP-FL was integrated into the ILO's Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work Branch (FUNDAMENTALS) bringing together the fight against forced and child labour and working in the context of Alliance 8.7.
One major tool to fight forced labour was the adoption of the ILO Forced Labour Protocol by the International Labour Conference in 2014. It was ratified for the second time in 2015 and on 9 November 2016 it entered into force. The new protocol brings the existing ILO Convention 29 on Forced Labour, adopted in 1930, into the modern era to address practices such as human trafficking. The accompanying Recommendation 203 provides technical guidance on its implementation.
In 2015, the ILO launched a global campaign to end modern slavery, in partnership with the International Organization of Employers (IOE) and the International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC). The 50 for Freedom campaign aims to mobilize public support and encourage countries to ratify the ILO's Forced Labour Protocol.
Since its inception, the SAP-FL has focused on raising global awareness of forced labour in its different forms, and mobilizing action against its manifestation. Several thematic and country-specific studies and surveys have since been undertaken, on such diverse aspects of forced labour as bonded labour, human trafficking, forced domestic work, rural servitude, and forced prisoner labour.
In 2013, the SAP-FL was integrated into the ILO's Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work Branch (FUNDAMENTALS) bringing together the fight against forced and child labour and working in the context of Alliance 8.7.
One major tool to fight forced labour was the adoption of the ILO Forced Labour Protocol by the International Labour Conference in 2014. It was ratified for the second time in 2015 and on 9 November 2016 it entered into force. The new protocol brings the existing ILO Convention 29 on Forced Labour, adopted in 1930, into the modern era to address practices such as human trafficking. The accompanying Recommendation 203 provides technical guidance on its implementation.
In 2015, the ILO launched a global campaign to end modern slavery, in partnership with the International Organization of Employers (IOE) and the International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC). The 50 for Freedom campaign aims to mobilize public support and encourage countries to ratify the ILO's Forced Labour Protocol.