Intermontane Islands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
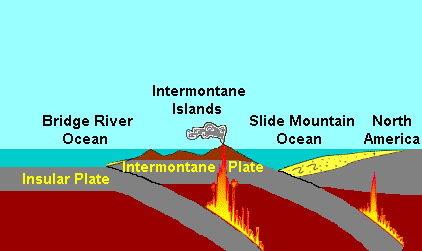 The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active
The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active
Burke Museum - University of Washington
Former islands of Canada Volcanic arc islands Natural history of British Columbia Geology of British Columbia Triassic paleogeography Jurassic paleogeography {{palaeo-geo-stub
 The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active
The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active volcanic island
Geologically, a high island or volcanic island is an island of volcanic origin. The term can be used to distinguish such islands from low islands, which are formed from sedimentation or the uplifting of coral reefs (which have often formed ...
s somewhere in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
during the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
time beginning around 245 million years ago. They were 600 to long and rode atop a microplate known as the Intermontane Plate
The Intermontane Plate was an ancient oceanic tectonic plate that lay on the west coast of North America about 195 million years ago. The Intermontane Plate was surrounded by a chain of volcanic islands called the Intermontane Islands, which had b ...
. Over early Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
time the Intermontane Islands and the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
drew closer together as the continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
moved west and the Intermontane Plate subduct
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
ed. About 180 million years ago in the Mid-Jurassic time the last of the Intermontane Plate subducted and the Intermontane Islands collided with the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
, forming parts of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
. The Intermontane Islands were too big to sink beneath the continent, and welded onto the continent, forming the Intermontane Belt
The Intermontane Belt is a physiogeological region in the Pacific Northwest of North America, stretching from northern Washington into British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska. It comprises rolling hills, high plateaus and deeply cut valleys. The roc ...
. Geologists call the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America the Slide Mountain Ocean
The Slide Mountain Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America beginning around 245 million years ago in the Triassic period. It is named after the Slide Mountain Terrane, which is composed of rocks f ...
.
See also
*Island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
* Insular Islands
*Intermontane Plate
The Intermontane Plate was an ancient oceanic tectonic plate that lay on the west coast of North America about 195 million years ago. The Intermontane Plate was surrounded by a chain of volcanic islands called the Intermontane Islands, which had b ...
*Intermontane Belt
The Intermontane Belt is a physiogeological region in the Pacific Northwest of North America, stretching from northern Washington into British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska. It comprises rolling hills, high plateaus and deeply cut valleys. The roc ...
External links
Burke Museum - University of Washington
Former islands of Canada Volcanic arc islands Natural history of British Columbia Geology of British Columbia Triassic paleogeography Jurassic paleogeography {{palaeo-geo-stub