Intel Rapid Storage Technology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver
-
Intel VROC is a technology from the Intel Xeon Scalable processors series and is used to provide hot-plug, surprise-removal, and LED management of NVMe SSD's for server usage. For client PC's Intel RST is still the advised software package to use.https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/technology-briefs/client-raid-and-dc-raid-solutions-technology-brief.pdf
Intel VMD is targeted for Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems.
 Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver SATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) ...
AHCI and a firmware-based RAID solution built into a wide range of Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in one or more integrated circuits known as a "Data Flow Management System" that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on t ...
s.
Currently also is installed as a driver for Intel Optane
3D XPoint (pronounced ''three-D cross point'') is a discontinued non-volatile memory (NVM) technology developed jointly by Intel and Micron Technology. It was announced in July 2015 and is available on the open market under the brand name Optane ...
temporary storage units.
It contains two operation modes that do not follow the SATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) ...
standard, it follows two Intel specific modes.
The name modes and the application that contains them have been renamed since the first version.
Until 2010 it contains AHCI and Matrix RAID modes. The first mode is the Intel driver SATA normal and the latter mode is a fake RAID.
Up to version 4 it is included on Intel Application Accelerator RAID Edition, between versions 5 and 8.9 it is included on Intel Matrix Storage Manager (IMSM), since version 9 it is included on Intel Rapid Storage Technology (IRST) preferring the driver modes to be named RST AHCI and RST AHCI RAID instead of Matrix RAID. The latter is also known as RST RAID mode, since it is the mode that Intel recommends to use, even if you are not working with a RAID
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to:
Attack
* Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground
* Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeover in business
* Panty raid, a prankish raid by male colleg ...
configuration.
The purpose of the program, after installing the drivers, is to configure the operation in this mode.
Both modes work with SATA drives. The boot mode choice, with one mode or the other, is chosen in modern BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the ...
/UEFI
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a set of specifications written by the UEFI Forum. They define the architecture of the platform firmware used for booting and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples ...
after driver installation. Once one or the other driver is installed, it is not possible for the Windows operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
to boot again with the BIOS/UEFI set to RAID/IDE, producing BSOD in case of trying.
As of 2020, it includes a RAID
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to:
Attack
* Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground
* Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeover in business
* Panty raid, a prankish raid by male colleg ...
system capable of RAID level A RAID level is any of the possible configurations of a RAID
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to:
Attack
* Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground
* Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeo ...
s 0, 1, 5, and 10, a block level SSD
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is ...
caching accelerator ("Smart Response Technology
In computer data storage, Smart Response Technology (SRT, also called SSD Caching before it was launched) is a proprietary caching mechanism introduced in 2011 by Intel for their Z68 chipset (for the Sandy Bridge–series processors), which ...
") with support for write-back
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewher ...
and write-through
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewher ...
modes for speed or data protection of any disk or RAID array, and support for intelligent caching, speedy recovery from certain issues, and for PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common m ...
based drives. Intel RST came in two variants, RST for desktops, and RSTe for enterprise scenarios, although for many chipsets, the user could choose as both variants will operate correctly. VROC was a part of Intel RSTe. The SATA RAID portion of the product family was called Intel RSTe and the NVMe* RAID portion was called Intel VROC. However, starting in Q1 2019, with the launch of Intel VROC 6.0, the Intel RSTe name was removed, and all RAID solutions in this product family were branded as Intel VROC. The SATA functionality remains, but is now branded as Intel VROC (SATA RAID). Intel RSTe is no longer a referenced product by Intel. The name may still appear in some legacy products, but all new references will solely use the Intel VROC nomenclature.Intel® VROC vs. Previous Intel® RSTe: Name Change Explained-
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
article).
Intel RST is provided by a combination of firmware
In computing, firmware is a specific class of computer software that provides the low-level control for a device's specific hardware. Firmware, such as the BIOS of a personal computer, may contain basic functions of a device, and may provide ...
, chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in one or more integrated circuits known as a "Data Flow Management System" that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found on t ...
and CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, an ...
capabilities, and software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
...
. As such, the chipset, the firmware included in the BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the ...
, and the software installed by the user, must be compatible versions. Online forum
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are often longer than one line of text, and are at least temporar ...
s and communities exist which compare the benefits of different versions of these, advise as to best compatibility for specified hardware, and modify existing firmware and software to allow optimal combinations or updates beyond those provided by the hardware manufacturers.
Like all RAID
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to:
Attack
* Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground
* Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeover in business
* Panty raid, a prankish raid by male colleg ...
(Redundant Array of Independent Disks), Intel RST RAID employs two or more physical hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with mag ...
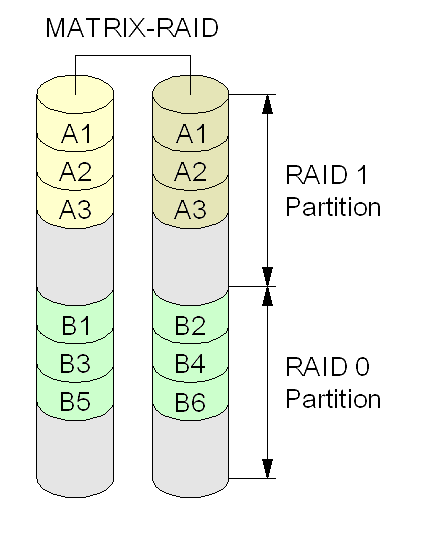
s which the operating system will treat as a single disk, in order to increase redundancy which avoids data loss (except RAID 0), and/or to increase the speed at which data is written to and/or read from a disk. Intel RST RAID does not provide new RAID levels. It allows different areas (e.g. partitions or logical volumes) on the same disk to be assigned to different RAID devices, unlike some other RAID controllers. Intel recommends to put any critical applications and data on a RAID 1, 5, or 10 volume, with redundancy to protect against data loss. The RAID 0 volume in Matrix RAID provides fast access to large files where data loss is not a critical issue but speed is; examples include video editing, swap files, and files that are backed up. Intel Matrix RAID, Intel Rapid RAID, and Intel Smart Response Technology
In computer data storage, Smart Response Technology (SRT, also called SSD Caching before it was launched) is a proprietary caching mechanism introduced in 2011 by Intel for their Z68 chipset (for the Sandy Bridge–series processors), which ...
are together described as Intel Rapid Storage Technology.
Operating system support
"Rapid Storage Technology" (RST), including creation of RAID volumes, works underWindows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009. It is the successor to Windows Vista, released nearl ...
and newer versions of Microsoft Windows. The older "Intel Matrix RAID" is supported under Microsoft Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and ...
.
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which i ...
supports Matrix RAID and Rapid Storage Technology (RST) through device mapper, with tool, for RAID 0, 1 and 10. And Linux MD RAID
mdadm is a Linux utility used to manage and monitor software RAID devices. It is used in modern Linux distributions in place of older software RAID utilities such as raidtools2 or raidtools.
mdadm is free software originally maintained by, an ...
, with tool, for RAID 0, 1, 10, and 5. Set up of the RAID volumes must be done by using the ROM option in the Matrix Storage Manager, then further configuration can be done in DM-RAID or MD-RAID.
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular ...
and MidnightBSD
MidnightBSD is a free Unix, desktop-oriented operating system originally forked from FreeBSD 6.1, and periodically updated with code and drivers from later FreeBSD releases. Its default desktop environment, Xfce, is a lightweight user friendl ...
support Intel Matrix RAID using the "ataraid" driver, managed through the atacontrol command. However, with older versions of FreeBSD there were critical reliability issues which include array device renaming when a disk in an array is replaced, an array being considered healthy if the machine reboot/crashes during an array rebuild, and kernel panics when a disk is lost or is removed from the bus. Some of these problems, when experienced in combination, could result in the loss of an entire array (even in the case of RAID 1).
VMware ESXi
VMware ESXi (formerly ESX) is an enterprise-class, type-1 hypervisor developed by VMware for deploying and serving virtual computers. As a type-1 hypervisor, ESXi is not a software application that is installed on an operating system (OS); ...
4 does not support any RAID function nor Intel Matrix RAID based on Intel ICHxR controllers.
PGPDisk does not support Intel Matrix RAID based on Intel ICHxR, and does not support standalone drives if the "RAID" mode is enabled on the motherboard.
Matrix Storage Manager option ROM
The Intel Matrix Storage Manager (IMSM)option ROM
An Option ROM for the PC platform (i.e. the IBM PC and derived successor computer systems) is a piece of firmware that resides in ROM on an expansion card (or stored along with the main system BIOS), which gets executed to initialize the device an ...
is a part of Matrix RAID that has to be used in the BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the ...
to create new RAID arrays.
Intel uses "Rapid Storage Technology" -"Option Rom"- on its new chipsets, dropping the "Matrix" name.
An Intel document notes that Intel Matrix Storage Manager storage changed to Intel Rapid Storage Technology beginning with version 9.5.
There have been several driver versions:
Since release 11.2.0.0000, TRIM commands can be read by Windows RAID drivers made for 7 series chipsets. There is no RAID mode TRIM support on drivers for older chipsets.
Intel states that RST support was added for the X79 chipset in RST version 11.6.0.0000 and after.
On some 6 series chipsets there is a modification for the ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
in the BIOS, which will allow TRIM support on the 6 series chipset.
For the X79 chipset, certain motherboard manufacturers have added both RAID ROMs in the BIOS, the RST and RST-E ROM. X79 is the Enterprise version, called RST-E. With the RST ROM added to the BIOS, this allows TRIM function to pass through the controller and TRIM SSD drives when RAID is enabled. This workaround was needed before RST-E driver version 3.8 was shipped which passed through TRIM commands to a RAID array without modifications to the RST-E ROM. There is no support for TRIM in the RST-E version of the ROM when RAID is enabled and the RST-E driver version is less than 3.8. It is possible to add an RST ROM to the BIOS to enable TRIM passthrough in RAID mode by using the RST ROM and driver.
The newest Option ROM version is a 13 series ROM, this ROM will not be used by motherboard manufacturers for the X79 chipset BIOS, and it can be injected into a BIOS to use on the X79 with modded code, for those MFG's who have added a ROM switch, this is where the MFG has added both RST and RSTe to the RAID option of a BIOS, but there needs to be a code added for TRIM commands to be sent, when you inject the RST and replace the RSTe with RST option ROM in X79 boards that do not contain the ROM switch, TRIM can be dysfunctional.
There are modded RST 13 series Option ROMs (legacy) available at certain BIOS modding sites that have been made functional for use in the X79 chipsets.
When booting in a BIOS environment (legacy) and some / EFI, the RST option ROM is used. When booting in a true UEFI environment the Option ROM is not used as a SataDriver with the RST version takes over. In BIOS mode the legacy/BIOS booting is under CSMCORE. In true UEFI mode the RST is controlled under SataDriver in BIOS.
The Intel RAID ROM is the firmware in the motherboard BIOS that is used to create the RAID array.
Note: The RST drivers can be used for RAID and also on a single drive as it contains an AHCI driver. There is a bug in the version 12.5.0.1066 RST driver, which cause TRIM commands not to pass through the RAID driver to the drives. TRIM is disabled using this driver.
Rapid Storage Technology enterprise (Intel RSTe)
Intel Rapid Storage Technology enterprise (Intel RSTe) provides performance and reliability for supported systems equipped with Serial ATA (SATA) devices, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) devices, and/or solid state drives (SSDs) to enable an optimal enterprise storage solution. The main difference between RST and RSTe is that the RST is used for desktop systems and the RSTe is mostly used for server systems. RST supports regular SATA controllers from desktop systems. If the BIOS of the motherboard has RSTe feature then the user cannot install Intel Rapid Storage Technology software (error message: This platform is not supported). The user has to install RSTe software. There have been several Option ROM versions: In 2019,Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
announced that the RTSe branding would be replaced, with RSTe consolidated into Intel's VROC (Virtual RAID on CPU) product line.
Intel VROC (Virtual RAID on CPU)
Intel VROC is a part of Intel RSTe. This was mostly designed withNVMe
NVM Express (NVMe) or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMHCIS) is an open, logical-device interface specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media usually attached via PCI Express (PCIe) bus. The ...
SSD's in mind and it is directly attached to the Intel Xeon
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the sa ...
Scalable processors. For the full functionality it uses a newer Intel technology called Intel VMD (Intel Volume Management Device). Intel VROC is a technology from the Intel Xeon Scalable processors series and is used to provide hot-plug, surprise-removal, and LED management of NVMe SSD's for server usage. For client PC's Intel RST is still the advised software package to use.https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/technology-briefs/client-raid-and-dc-raid-solutions-technology-brief.pdf
Intel VMD is targeted for Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems.
Criticism on Intel RST technology
The software created by Intel to manage the RAID configuration is under par. E.g. when using a RAID 1 configuration, Windows shall show a temporary message when one of the disk are down, however if this is not noticed (because the user is not at the computer), the user might not notice the disk failure in time. Furthermore the Intel RST software does not consistently log status changes (repair/rebuilds) in the Windows Eventlog, making it difficult for 3rd party monitoring software to warn users when the RAID status changes and the data might be in jeopardy. Other strange decision Intel has made, is to remove the e-mail warning from the latest version (v19.x) of the software. On earlier versions (18.x) the e-mail warning can be configured, but lacks the modern fields like password and SSL/TLS authentication to be used with modern e-mail providers like Gmail, Microsoft's Outlook and e-mail accounts from other providers. Also when field tested (with an older mail server *without authentication*), no warnings were e-mailed. This e-mail service was also inconsistent because the disk degradation was not e-mailed, but consequently the finished rebuild of the RAID was e-mailed, without the user ever being warned the computer was rebuilding the RAID drive. Intel also used to have a command line software (CLI) for their RST RAID, which one could use to request the status of the RAID drives, however this software was deprecated. The conclusion might be made that Intel is deliberately undermining the reliability of the RAID, by crippling the methods to warn the user before data is lost.See also
* Non-standard RAID levels * mdadmReferences
*External links
* *https://win-raid.com - forum specializing in Intel RST and similar soft raid, choice of driver/rom/orom, and modification of roms. {{Intel technology RAID AT Attachment Matrix RAID Matrix RAID