Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an

 After
After

 * "Outer Mongolia": This region corresponds to the modern state of
* "Outer Mongolia": This region corresponds to the modern state of
 Outer Mongolia gained independence from the Qing dynasty in 1911, when the Jebtsundamba Khutugtu of the Khalkha was declared the Bogd Khan of Mongolia. Although almost all banners of Inner Mongolia recognised the Bogd Khan as the supreme ruler of Mongols, the internal strife within the region prevented a full reunification. The Mongol rebellions in Inner Mongolia were counterbalanced by princes who hoped to see a restored Qing dynasty in Manchuria and Mongolia, as they considered the theocratic rule of the Bogd Khan would be against their modernising objectives for Mongolia. Eventually, the newly formed
Outer Mongolia gained independence from the Qing dynasty in 1911, when the Jebtsundamba Khutugtu of the Khalkha was declared the Bogd Khan of Mongolia. Although almost all banners of Inner Mongolia recognised the Bogd Khan as the supreme ruler of Mongols, the internal strife within the region prevented a full reunification. The Mongol rebellions in Inner Mongolia were counterbalanced by princes who hoped to see a restored Qing dynasty in Manchuria and Mongolia, as they considered the theocratic rule of the Bogd Khan would be against their modernising objectives for Mongolia. Eventually, the newly formed  Ethnic Mongolian guerrilla units were created by the Kuomintang Nationalists to fight against the Japanese during the war in the late 30s and early 40s. These Mongol militias were created by the Ejine and Alashaa based commissioner's offices created by the Kuomintang. Prince Demchugdongrob's Mongols were targeted by Kuomintang Mongols to defect to the Republic of China. The Nationalists recruited 1,700 ethnic minority fighters in Inner Mongolia and created war zones in the Tumet Banner, Ulanchab League, and Ordos Yekejuu League.
The Inner Mongolian People's Republic was founded shortly after the Second World War. It existed from 9 September 1945 until 6 November 1945.
Ethnic Mongolian guerrilla units were created by the Kuomintang Nationalists to fight against the Japanese during the war in the late 30s and early 40s. These Mongol militias were created by the Ejine and Alashaa based commissioner's offices created by the Kuomintang. Prince Demchugdongrob's Mongols were targeted by Kuomintang Mongols to defect to the Republic of China. The Nationalists recruited 1,700 ethnic minority fighters in Inner Mongolia and created war zones in the Tumet Banner, Ulanchab League, and Ordos Yekejuu League.
The Inner Mongolian People's Republic was founded shortly after the Second World War. It existed from 9 September 1945 until 6 November 1945.

 Officially Inner Mongolia is classified as one of the provincial-level divisions of
Officially Inner Mongolia is classified as one of the provincial-level divisions of
"Quaternary glacier development and the relationship between the climate change and tectonic uplift in the Helan Mountains"
; in ''Chinese Science Bulletin''; December 2012, Volume 57, Issue 34, pp. 4491–4504. Most of Inner Mongolia is a plateau averaging around in altitude and covered by extensive loess and sand deposits. The northern part consists of the Mesozoic era Khingan Mountains, and is owing to the cooler climate more forested, chiefly with Ulmus laciniata, Manchurian elm, Ash (Fraxinus), ash, birch, Quercus mongolica, Mongolian oak and a number of Pinus, pine and Picea, spruce species. Where discontinuous permafrost is present north of Hailar District, forests are almost exclusively coniferous. In the south, the natural vegetation is grassland in the east and very sparse in the arid west, and grazing is the dominant economic activity. Owing to the ancient, weathered rocks lying under its deep sedimentary cover, Inner Mongolia is a major mining district, possessing large reserves of coal, iron ore and rare-earth minerals, which have made it a major industrial region today.
 Inner Mongolia has an abundance of resources especially coal, Cashmere wool, cashmere, natural gas, rare-earth elements, and has more deposits of naturally occurring niobium, zirconium and beryllium than any other province-level region in China. However, in the past, the exploitation and utilisation of resources were rather inefficient, which resulted in poor returns from rich resources. Inner Mongolia is also an important coal production base, with more than a quarter of the world's coal reserves located in the province. It plans to double annual coal output by 2010 (from the 2005 volume of 260 million tons) to 500 million tons of coal a year.
Inner Mongolia has an abundance of resources especially coal, Cashmere wool, cashmere, natural gas, rare-earth elements, and has more deposits of naturally occurring niobium, zirconium and beryllium than any other province-level region in China. However, in the past, the exploitation and utilisation of resources were rather inefficient, which resulted in poor returns from rich resources. Inner Mongolia is also an important coal production base, with more than a quarter of the world's coal reserves located in the province. It plans to double annual coal output by 2010 (from the 2005 volume of 260 million tons) to 500 million tons of coal a year.
 Industry in Inner Mongolia has grown up mainly around coal, power generation, forestry-related industries, and related industries.
Inner Mongolia now encourages six competitive industries: energy, chemicals, metallurgy, equipment manufacturing, processing of farm (including dairy) produce, and high technology. Well-known Inner Mongolian enterprises include companies such as ERDOS, Yili Group, Yili, and Mengniu.
The nominal GDP of Inner Mongolia in 2015 was 1.8 trillion yuan (US$272.1 billion), with an average annual increase of 10% from the period 2010–2015. Its per capita GDP reached US$11,500 in 2015, ranking No.4th among all the 31 provinces of China, only after Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin.
As with much of China, economic growth has led to a boom in construction, including new commercial development and large apartment complexes.
In addition to its large reserves of natural resources, Inner Mongolia also has the largest usable wind power capacity in China thanks to strong winds which develop in the province's grasslands. Some private companies have set up Wind power in China, wind parks in parts of Inner Mongolia such as Bailingmiao, Hutengliang and Zhouzi.
East of Jilantai, Inner Mongolia, there is a ballistic missile training area used by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF) to train missile crews for mobile missile launchers, their support vehicles, and silo-based ballistic missiles.
Industry in Inner Mongolia has grown up mainly around coal, power generation, forestry-related industries, and related industries.
Inner Mongolia now encourages six competitive industries: energy, chemicals, metallurgy, equipment manufacturing, processing of farm (including dairy) produce, and high technology. Well-known Inner Mongolian enterprises include companies such as ERDOS, Yili Group, Yili, and Mengniu.
The nominal GDP of Inner Mongolia in 2015 was 1.8 trillion yuan (US$272.1 billion), with an average annual increase of 10% from the period 2010–2015. Its per capita GDP reached US$11,500 in 2015, ranking No.4th among all the 31 provinces of China, only after Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin.
As with much of China, economic growth has led to a boom in construction, including new commercial development and large apartment complexes.
In addition to its large reserves of natural resources, Inner Mongolia also has the largest usable wind power capacity in China thanks to strong winds which develop in the province's grasslands. Some private companies have set up Wind power in China, wind parks in parts of Inner Mongolia such as Bailingmiao, Hutengliang and Zhouzi.
East of Jilantai, Inner Mongolia, there is a ballistic missile training area used by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF) to train missile crews for mobile missile launchers, their support vehicles, and silo-based ballistic missiles.
 When the autonomous region was established in 1947, Han Chinese comprised 83.6% of the population, while the Mongols comprised 14.8% of the population. By 2010, the percentage of Han Chinese had dropped to 79.5%. While the Hetao region along the Yellow River has always alternated between farmers from the south and nomads from the north, the most recent wave of Han Chinese migration began in the early 18th century with encouragement from the
When the autonomous region was established in 1947, Han Chinese comprised 83.6% of the population, while the Mongols comprised 14.8% of the population. By 2010, the percentage of Han Chinese had dropped to 79.5%. While the Hetao region along the Yellow River has always alternated between farmers from the south and nomads from the north, the most recent wave of Han Chinese migration began in the early 18th century with encouragement from the

 Alongside Chinese, Mongolian is the official provincial language of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, where there are at least 4.1 million ethnic Mongols. Across the whole of China, the language is spoken by roughly half of the country's 5.8 million ethnic Mongols (2005 estimate) However, the exact number of Mongolian speakers in China is unknown, as there is no data available on the language proficiency of that country's citizens. The use of Mongolian in China, specifically in Inner Mongolia, has witnessed periods of decline and revival over the last few hundred years. The language experienced a decline during the late Qing period, a revival between 1947 and 1965, a second decline between 1966 and 1976, a second revival between 1977 and 1992, and a third decline between 1995 and 2012. However, in spite of the decline of the Mongolian language in some of Inner Mongolia's urban areas and educational spheres, the ethnic identity of the urbanised Chinese-speaking Mongols is most likely going to survive due to the presence of urban ethnic communities. The multilingual situation in Inner Mongolia does not appear to obstruct efforts by ethnic Mongols to preserve their language. Although an unknown number of Mongols in China, such as the Tumets, may have completely or partially lost the ability to speak their language, they are still registered as ethnic Mongols and continue to identify themselves as ethnic Mongols. The children of inter-ethnic Mongol-Chinese marriages also claim to be and are registered as ethnic Mongols.
By law, all street signs, commercial outlets, and government documents must be bilingual, written in both Mongolian and Chinese. There are three Mongolian TV channels in the Inner Mongolia Satellite TV network. In public transportation, all announcements are to be bilingual.
Mongols in Inner Mongolia speak Mongolian language, Mongolian dialects such as Chakhar Mongolian, Chakhar, Xilingol, Baarin Mongolian, Baarin, Khorchin Mongolian, Khorchin and Kharchin Mongolian and, depending on definition and analysis, further dialects or closely related independent Central Mongolic languages such as Ordos Mongolian, Ordos, Khamnigan Mongol, Khamnigan, Barghu Buryat language, Buryat and the arguably Oirat language, Oirat dialect Alasha dialect, Alasha. The standard pronunciation of Mongolian in China is based on the Chakhar dialect of the Plain Blue Banner, Inner Mongolia, Plain Blue Banner, located in central Inner Mongolia, while the grammar is based on all Southern Mongolian, Southern Mongolian dialects. This is different from the Mongolian state, where the standard pronunciation is based on the closely related Khalkha Mongolian, Khalkha dialect. There are a number of independent languages spoken in Hulunbuir such as the somewhat more distant Mongolic language Daur language, Dagur and the Tungusic languages, Tungusic language Evenki language, Evenki. Officially, even the Evenki dialect Oroqen language, Oroqin is considered a language.
The
Alongside Chinese, Mongolian is the official provincial language of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, where there are at least 4.1 million ethnic Mongols. Across the whole of China, the language is spoken by roughly half of the country's 5.8 million ethnic Mongols (2005 estimate) However, the exact number of Mongolian speakers in China is unknown, as there is no data available on the language proficiency of that country's citizens. The use of Mongolian in China, specifically in Inner Mongolia, has witnessed periods of decline and revival over the last few hundred years. The language experienced a decline during the late Qing period, a revival between 1947 and 1965, a second decline between 1966 and 1976, a second revival between 1977 and 1992, and a third decline between 1995 and 2012. However, in spite of the decline of the Mongolian language in some of Inner Mongolia's urban areas and educational spheres, the ethnic identity of the urbanised Chinese-speaking Mongols is most likely going to survive due to the presence of urban ethnic communities. The multilingual situation in Inner Mongolia does not appear to obstruct efforts by ethnic Mongols to preserve their language. Although an unknown number of Mongols in China, such as the Tumets, may have completely or partially lost the ability to speak their language, they are still registered as ethnic Mongols and continue to identify themselves as ethnic Mongols. The children of inter-ethnic Mongol-Chinese marriages also claim to be and are registered as ethnic Mongols.
By law, all street signs, commercial outlets, and government documents must be bilingual, written in both Mongolian and Chinese. There are three Mongolian TV channels in the Inner Mongolia Satellite TV network. In public transportation, all announcements are to be bilingual.
Mongols in Inner Mongolia speak Mongolian language, Mongolian dialects such as Chakhar Mongolian, Chakhar, Xilingol, Baarin Mongolian, Baarin, Khorchin Mongolian, Khorchin and Kharchin Mongolian and, depending on definition and analysis, further dialects or closely related independent Central Mongolic languages such as Ordos Mongolian, Ordos, Khamnigan Mongol, Khamnigan, Barghu Buryat language, Buryat and the arguably Oirat language, Oirat dialect Alasha dialect, Alasha. The standard pronunciation of Mongolian in China is based on the Chakhar dialect of the Plain Blue Banner, Inner Mongolia, Plain Blue Banner, located in central Inner Mongolia, while the grammar is based on all Southern Mongolian, Southern Mongolian dialects. This is different from the Mongolian state, where the standard pronunciation is based on the closely related Khalkha Mongolian, Khalkha dialect. There are a number of independent languages spoken in Hulunbuir such as the somewhat more distant Mongolic language Daur language, Dagur and the Tungusic languages, Tungusic language Evenki language, Evenki. Officially, even the Evenki dialect Oroqen language, Oroqin is considered a language.
The
Study on the Protection of the Lama Temple Heritage in Inner Mongolia as a Cultural Landscape
''. ''Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering'', v. 15 n. 1, January 2016. Note that the article, in an evident mistranslation from Chinese, reports 30 million Tibetan Buddhists in Inner Mongolia instead of 3 million. According to the Chinese Spiritual Life Survey of 2007 and the Chinese General Social Survey of 2009, Christianity is the religious identity of 3.2% of the population of the region; and Chinese ancestral religion the professed belonging of 2.36%,Chinese Spiritual Life Survey (CSLS) 2007, China General Social Survey (CGSS) 2009. Results reported by
Xiuhua Wang (2015, p. 15)
while a demographic analysis of the year 2010 reported that Muslims comprise the 0.91%.Min Junqing. ''The Present Situation and Characteristics of Contemporary Islam in China''. JISMOR, 8
2010 Islam by province, page 29
. Data from: Yang Zongde, ''Study on Current Muslim Population in China'', Jinan Muslim, 2, 2010. The cult (religious practice), cult of
 One of China's space vehicle launch facilities, Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, is located in the Alxa League's Ejin Banner, in the west of Inner Mongolia. It was founded in 1958, making it the PRC's first launch facility. As of 2021, Jiuquan has documented more launches than any other launch facilities in China, and is still the only launch site for manned space missions (Shenzhou program). While geologically located inside Inner Mongolia, the launch center is named after Jiuquan, which is the nearest urban center in the nearby province of Gansu.
As military facilities, the core areas at Jiuquan Center are highly restricted and can only be visited by tourist buses operated by the center, while the visitor center is open to the public and can be accessed from the south gate.
Inner Mongolia is also home to the two (and only two) space vehicles landing sites in China, the Siziwang Banner Landing Site in Ulanqab and the Dongfeng Landing Site in Alxa.
One of China's space vehicle launch facilities, Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, is located in the Alxa League's Ejin Banner, in the west of Inner Mongolia. It was founded in 1958, making it the PRC's first launch facility. As of 2021, Jiuquan has documented more launches than any other launch facilities in China, and is still the only launch site for manned space missions (Shenzhou program). While geologically located inside Inner Mongolia, the launch center is named after Jiuquan, which is the nearest urban center in the nearby province of Gansu.
As military facilities, the core areas at Jiuquan Center are highly restricted and can only be visited by tourist buses operated by the center, while the visitor center is open to the public and can be accessed from the south gate.
Inner Mongolia is also home to the two (and only two) space vehicles landing sites in China, the Siziwang Banner Landing Site in Ulanqab and the Dongfeng Landing Site in Alxa.
File:C-shaped jade dragon.jpg, Jade dragon of the Hongshan culture (4700 BC – 2900 BC) found in Ongniud Banner,
Online
* Borjigin, Monkbat.
A case study of Language education in the Inner Mongolia
Archive
Japanese title: ). ''Journal of Chiba University Eurasian Society'' () 16, 261–266, 2014-09-25. Chiba University Eurasian Society ()
See profile at
Chiba University Repository
See profile at
CiNii. – In English with a Japanese abstract. *
Inner Mongolia Government website
*
Welcome to Inner Mongolia-Mongolia Tours with Samar Magic Tours
* {{Authority control Inner Mongolia, Autonomous regions of China Mongols in China 1947 establishments in China States and territories established in 1947 Inner Asia Historical regions
autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
of the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Its border includes most of the length of China's border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
with the country of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
with Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
(Zabaykalsky Krai
Zabaykalsky Krai ( rus, Забайкальский край, r=Zabaikal'skii krai, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲskʲɪj kraj, lit. "Transbaikal krai"; bua, Yбэр Байгалай хизаар, Uber Baigalai Xizaar) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) t ...
). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou
Baotou (; mn, Buɣutu qota, Бугат хот) is the largest city by urban population in Inner Mongolia, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, as of the 2020 census, its built-up (''or metro'') area made up of its 5 urban districts is h ...
, Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to the ...
, Tongliao
Tongliao (; mn, ''Tüŋliyou qota'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Байшинт хот) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. The area is and as of the 2020 census, its population was 2,873,168 (3,139,153 i ...
, and Ordos Ordos may refer to:
Inner Mongolia
* Ordos City, Inner Mongolia, China
**Ordos Ejin Horo Airport
* Ordos Loop of the Yellow River, a region of China
**Ordos Plateau or "the Ordos", land enclosed by Ordos Loop
*Ordos Desert, in Inner Mongolia
*Ordos ...
.
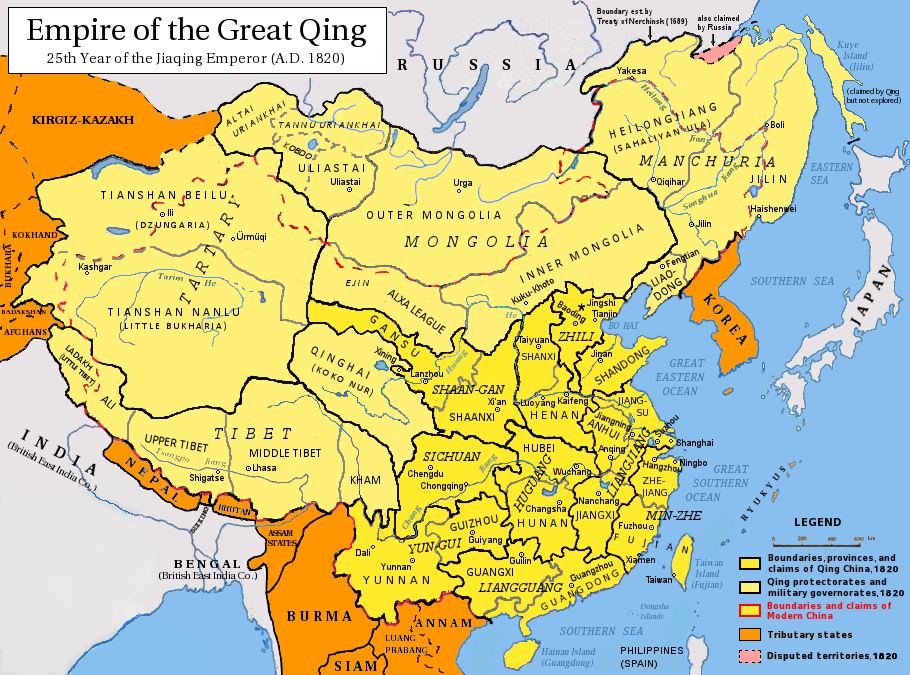
The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
provinces of Suiyuan
Suiyuan () is a ''de jure'' province of the Republic of China according to the ROC law, as the ROC government formally claims to be the legitimate government of China, with its capital located Guisui (now Hohhot). The abbreviation was (pinyi ...
, Chahar, Rehe, Liaobei
Liaobei ( Wade-Giles: Liaopei) also known as Liaopeh is a ''de jure'' province of the Republic of China under ROC law as the government of the Republic of China formally claims to be the sole legitimate government of China. Located in Manchuria ...
, and Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
and Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
.
Its area makes it the third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inner Mongolia is geographically divided into eastern and western divisions. The eastern division is often included in Northeastern China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
(Dongbei) with major cities including Tongliao
Tongliao (; mn, ''Tüŋliyou qota'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Байшинт хот) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. The area is and as of the 2020 census, its population was 2,873,168 (3,139,153 i ...
, Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to the ...
, Hailar
Hailar District, formerly a county-level city, is an urban district that serves as the seat of the prefecture-level city Hulunbuir in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Hulunbuir, due to its massive size, is a city in administrative terms only ...
, and Ulanhot
Ulanhot ( mn, ; ), formerly known as Wangin Süm, alternatively Wang-un Süme, Ulaγanqota (Red City) in Classical Mongolian, is a county-level cities, county-level city and the administrative center of Hinggan League in the east of the Inner ...
. The western division is included in North China
North China, or Huabei () is a List of regions of China, geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north ...
, with major cities including Baotou and Hohhot. It recorded a population of 24,706,321 in the 2010 census, accounting for 1.84% of Mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
's total population. Inner Mongolia is the country's 23rd most populous province-level division. The majority of the population in the region are Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
, with a sizeable Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
minority close to 5,000,000 (2019) which is the largest Mongolian population in the world (bigger than that of the country Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
). Inner Mongolia is one of the most economically developed provinces in China with annual GDP per capita close to US$13,000 (2019), often ranked 5th in the nation. The official languages are Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
and Mongolian, the latter of which is written in the traditional Mongolian script
The classical or traditional Mongolian script, also known as the , was the first writing system created specifically for the Mongolian language, and was the most widespread until the introduction of Cyrillic in 1946. It is traditionally writte ...
, as opposed to the Mongolian Cyrillic alphabet, which is used in the state of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
(formerly often described as Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
).
Etymology
In Chinese, the region is known as "Inner Mongolia", where the terms of "Inner/Outer" are derived fromManchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
''dorgi''/''tulergi'' (cf. Mongolian ''dotugadu''/''gadagadu''). Inner Mongolia is distinct from Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
, which was a term used by the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
and previous governments to refer to what is now the independent state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
plus the Republic of Tuva
Tuva (; russian: Тува́) or Tyva ( tyv, Тыва), officially the Republic of Tuva (russian: Респу́блика Тыва́, r=Respublika Tyva, p=rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə tɨˈva; tyv, Тыва Республика, translit=Tyva Respublika ...
in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The term Inner (Nei) referred to the Nei Fan (Inner Tributary), i.e., those descendants of Genghis Khan who were granted the title khan (king) in the Ming and Qing dynasties and lived in part of southern Mongolia. The region is sometimes called Southern Mongolia by local separatists and Mongolian irredentists.
History
Much of what is known about the history ofGreater Mongolia Greater Mongolia may refer to:
* In Pan-Mongolism, idea that advocates cultural and political solidarity of Mongols
* The Mongol heartland, the contiguous geographical area in which the Mongols primarily live
See also
* Mongolia (disambiguation)
...
, including Inner Mongolia, is known through Chinese chronicles and historians. Before the rise of the Mongols in the 13th century, what is now central and western Inner Mongolia, especially the Hetao
Hetao () is a C-shaped region in northwestern China consisting of a collection of flood plains stretching from the banks of the northern half of the Ordos Loop, a large northerly rectangular bend of the Yellow River that forms the river's entir ...
region, alternated in control between Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
agriculturalists in the south, and Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
, Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the ...
, Khitan, Jurchen, Tujue, and nomadic Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
of the north. The historical narrative of what is now Eastern Inner Mongolia mostly consists of alternations between different Tungusic and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
tribes, rather than the struggle between nomads and Chinese agriculturalists.
Early history
Slab Grave cultural monuments are found in Northern, Central and EasternMongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, Inner Mongolia, North-Western China, Southern, Central-Eastern and Southern Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Rep ...
territory. Mongolian scholars prove that this culture related to the Proto-Mongols
The proto-Mongols emerged from an area that had been inhabited by humans and predecessor hominin species as far back as 45,000 years ago during the Upper Paleolithic. The people there went through the Bronze and Iron Ages, forming tribal allianc ...
.
During the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
, Central and Western Inner Mongolia (the Hetao
Hetao () is a C-shaped region in northwestern China consisting of a collection of flood plains stretching from the banks of the northern half of the Ordos Loop, a large northerly rectangular bend of the Yellow River that forms the river's entir ...
region and surrounding areas) were inhabited by nomadic peoples such as the Loufan Loufan may refer to:
* Loufan (tribe) (樓煩), a Xiongnu-associated nomadic tribe; see Loufan County, Shanxi Province, China
* Loufan Commandery (樓煩郡, part of modern Xinzhou), former commandery in what is now Xinzhou Prefecture, Shanxi, Chi ...
, Linhu and Dí, while Eastern Inner Mongolia was inhabited by the Donghu. During the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
, King Wuling (340–295 BC) of the state of Zhao
Zhao () was one of the seven major State (Ancient China), states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han (state), Han and Wei (state), Wei, in the 5th century BC. ...
based in what is now Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
and Shanxi Provinces pursued an expansionist policy towards the region. After destroying the Dí state of Zhongshan
Zhongshan () was a small state that existed during the Warring States period, which managed to survive for almost 120 years despite its small size. Its origins of its founder are a matter of contention between scholars.
Origins
The origin of ...
in what is now Hebei province, he defeated the Linhu and Loufan Loufan may refer to:
* Loufan (tribe) (樓煩), a Xiongnu-associated nomadic tribe; see Loufan County, Shanxi Province, China
* Loufan Commandery (樓煩郡, part of modern Xinzhou), former commandery in what is now Xinzhou Prefecture, Shanxi, Chi ...
and created the Yunzhong Commandery
Yunzhong Commandery ( zh, 雲中郡) was a historical commandery of China. Its territories were located between the Great Wall and Yin Mountains, and correspond to part of modern-day Hohhot, Baotou and Ulanqab prefectures in Inner Mongolia.
The ...
near modern Hohhot. King Wuling of Zhao also built a long wall stretching through the Hetao region. After Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor ( ...
created the first unified Chinese empire in 221 BC, he sent the general Meng Tian
Meng Tian (c. 250 BC – 210 BC) was a Chinese inventor and military general of the Qin dynasty who distinguished himself in campaigns against the Xiongnu and in the construction of the Great Wall of China. He was the elder brother of Meng Yi. ...
to drive the Xiongnu from the region and incorporated the old Zhao wall into the Qin dynasty Great Wall of China. He also maintained two commanderies in the region: Jiuyuan
Jiuyuan District ( Mongolian: ''Jiü yuvan toɣoriɣ''; ) is a district of Baotou, the largest city of Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China ...
and Yunzhong and moved 30,000 households there to solidify the region. After the Qin dynasty collapsed in 206 BC, these efforts were abandoned.
During the Western Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
, Emperor Wu sent the general Wei Qing
Wei Qing (died 106 BC), courtesy name Zhongqing, born Zheng Qing in Linfen, Shanxi, was a Chinese military general and politician of the Western Han dynasty who was acclaimed for his campaigns against the Xiongnu, and his rags to riches life ...
to reconquer the Hetao region from the Xiongnu in 127 BC. After the conquest, Emperor Wu continued the policy of building settlements in Hetao to defend against the Xiong-Nu. In that same year, he established the commanderies of Shuofang
Shuofang () was an ancient Chinese commandery, situated in the Hetao region in modern-day Inner Mongolia near Baotou. First founded by Emperor Wu of Han in the wake of the successful reconquest of the area from Xiongnu tribes, it was dissolved ...
and Wuyuan in Hetao. At the same time, what is now Eastern Inner Mongolia was controlled by the Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the ...
, who would, later on, eclipse the Xiongnu in power and influence.
During the Eastern Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
(25–220 AD), Xiongnu who surrendered to the Han dynasty began to be settled in Hetao and intermingled with the Han immigrants in the area. Later on, during the Western Jin dynasty
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
, it was a Xiongnu noble from Hetao, Liu Yuan, who established the Han Zhao
The Han Zhao (; 304–329 AD), or Former Zhao (), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xiongnu people during the Sixteen Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In Chinese historiography, it was given two conditional state titles, the Northern ...
kingdom in the region, thereby beginning the Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by ...
period that saw the disintegration of northern China under a variety of Han and non-Han (including Xiongnu and Xianbei) regimes.
The Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and layi ...
(581–618) and Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
(618–907) re-established a unified Chinese empire and like their predecessors, they conquered and settled people into Hetao, though once again these efforts were aborted when the Tang empire began to collapse. Hetao (along with the rest of what now consists Inner Mongolia) was then taken over by the Khitan Empire
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
(Liao dynasty), founded by the Khitans
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
As a people desce ...
, a nomadic people originally from what is now the southern part of Manchuria and Eastern Inner Mongolia. They were followed by the Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China tha ...
of the Tanguts, who took control of what is now the western part of Inner Mongolia (including Western Hetao). The Khitans were later replaced by the Jurchens
Jurchen (Manchu language, Manchu: ''Jušen'', ; zh, 女真, ''Nǚzhēn'', ) is a term used to collectively describe a number of East Asian people, East Asian Tungusic languages, Tungusic-speaking peoples, descended from the Donghu people. They ...
, precursors to the modern Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
, who established the Jin dynasty over Manchuria and Northern China.
Mongol and Ming periods

 After
After Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
unified the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
tribes in 1206 and founded the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, the Tangut Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China tha ...
empire was ultimately conquered in 1227, and the Jurchen Jin dynasty fell in 1234. In 1271, Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of th ...
, the grandson of Genghis Khan established the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth ...
. Kublai Khan's summer capital Shangdu
Shangdu (, ), also known as Xanadu (; Mongolian: ''Šandu''), was the summer capital of the Yuan dynasty of China before Kublai decided to move his throne to the former Jin dynasty capital of Zhōngdū () which was renamed Khanbaliq ( presen ...
(aka Xanadu) was located near present-day Dolonnor. During that time Ongud
The Ongud (also spelled Ongut or Öngüt; Mongolian: Онгуд, Онход; Chinese: 汪古, ''Wanggu''; from Old Turkic ''öng'' "desolate, uninhabited; desert" plus ''güt'' "class marker") were a Turkic tribe that later became Mongolized ac ...
and Khunggirad
The Khongirad ( Mongolian: ᠬᠣᠩᠭᠢᠷᠠᠳ; Хонгирад; Khonghirad; ), also known as Qongirat (Qoŋğırat/Қоңғырат), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Q ...
peoples dominated the area of what is now Inner Mongolia. After the Yuan dynasty was overthrown by the Han-led Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
in 1368, the Ming captured parts of Inner Mongolia including Shangdu and Yingchang
Yingchang () was one of the important cities in the Yuan dynasty. It was situated on Lake Taal Nor in modern Heshigten Banner, Inner Mongolia, China.
The city of Yingchang was built by the Khongirad Mongols in 1271, the same year that Kublai (Em ...
. The Ming rebuilt the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic grou ...
at its present location, which roughly follows the southern border of the modern Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (though it deviates significantly at the Hebei-Inner Mongolia border). The Ming established the Three Guards composed of the Mongols there. Soon after the Tumu incident
The Crisis of the Tumu Fortress (), also known as the Tumu Crisis (; mn, Тумугийн тулалдаан), or the Jisi Incident (), was a frontier conflict between the Northern Yuan and Ming dynasties. The Oirat ruler of the Northern Yuan, ...
in 1449, when the Oirat ruler Esen taishi
Esen ( mn, Эсэн; Mongol script: ; ), (?–1454) was a powerful Oirat taishi and the ''de facto'' ruler of the Northern Yuan dynasty between 12 September 1453 and 1454. He is best known for capturing the Emperor Yingzong of Ming in 1450 in t ...
captured the Chinese emperor, Mongols flooded south from Outer Mongolia to Inner Mongolia. Thus from then on until 1635, Inner Mongolia was the political and cultural center of the Mongols during the Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later Jin ...
.
Qing period
The eastern Mongol tribes near and in Manchuria, particularly theKhorchin
The Khorchin ( mn, Хорчин, ''Horçin''; ''Qorčin''; ) are a subgroup of the Mongols that speak the Khorchin dialect of Mongolian and predominantly live in northeastern Inner Mongolia of China.
History
The Ming dynasty gave Borjigin p ...
and Southern Khalkha
The Khalkha (Mongolian script, Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongols, Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos Mongols, Ordos and Tum ...
in today's Inner Mongolia intermarried, formed alliances with, and fought against the Jurchen tribes until Nurhaci
Nurhaci (14 May 1559 – 30 September 1626), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Qing (), was a Jurchen chieftain who rose to prominence in the late 16th century in Manchuria. A member of the House of Aisin-Gioro, he reigned ...
, the founder of the new Jin dynasty, consolidated his control over all groups in the area in 1593. The Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
gained far-reaching control of the Inner Mongolian tribes in 1635, when Ligden Khan
Khutugtu Khan ( mn, Хутагт Хаан; ), born Ligdan ( mn, Лигдэн; ), (1588–1634) was a khagan of the Northern Yuan dynasty, reigning from 1604 to 1634. During his reign, he vigorously attempted to reunify the divided Mongol Empire, a ...
's son surrendered the Chakhar Mongol tribes to the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
. The Manchus subsequently invaded Ming China in 1644, bringing it under the control of their newly established Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. Under the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), Greater Mongolia Greater Mongolia may refer to:
* In Pan-Mongolism, idea that advocates cultural and political solidarity of Mongols
* The Mongol heartland, the contiguous geographical area in which the Mongols primarily live
See also
* Mongolia (disambiguation)
...
was administered in a different way for each region:

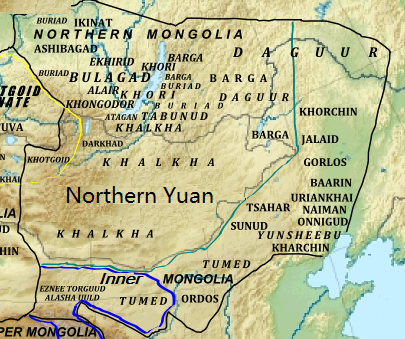
 * "Outer Mongolia": This region corresponds to the modern state of
* "Outer Mongolia": This region corresponds to the modern state of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, plus the Russian-administered region of Tannu Uriankhai
Tannu Uriankhai ( tyv, Таңды Урянхай, ; mn, Тагна Урианхай, Tagna Urianhai, ; ) is a historical region of the Mongol Empire (and its principal successor, the Yuan dynasty) and, later, the Qing dynasty. The territory of ...
, and a part of northern Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
. It included the four leagues (''aimag'') of the Khalkha Mongols
The Khalkha ( Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin khan ...
north of the Gobi
The Gobi Desert ( Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast ...
, as well as the Tannu Uriankhai
Tannu Uriankhai ( tyv, Таңды Урянхай, ; mn, Тагна Урианхай, Tagna Urianhai, ; ) is a historical region of the Mongol Empire (and its principal successor, the Yuan dynasty) and, later, the Qing dynasty. The territory of ...
and Khovd regions in northwestern Mongolia, which were overseen by the General of Uliastai from the city of Uliastai
Uliastai ( mn, Улиастай; ), also spelled Uliyasutai or Oulia-Sontai, and sometimes known as Javkhlant, is a city in Mongolia located in the western part of the country and from the capital Ulaanbaatar. Uliastai is the capital of Zavkhan P ...
.
* "Inner Mongolia": This region corresponded to most of modern Inner Mongolia and some neighbouring areas in Liaoning and Jilin provinces. The Banners of Inner Mongolia, banners and tribes in this region came under six Leagues of China, leagues (''chuulghan''): Tongliao, Jirim, Juuuda, Josutu, Xilingol, Ulanqab, and Yekejuu.
* "Taoxi Mongolia": The Alashan Öölüd and Ejine Torghuud banners were separate from the aimags of Outer Mongolia and the chuulghans of Inner Mongolia. This territory is equivalent to modern-day Alxa League, the westernmost part of what is now Inner Mongolia.
* The Chahar Banners of Inner Mongolia, Banners were controlled by the military commander of Chahar (now Zhangjiakou). Their extent corresponded to southern Ulanqab and Bayannur in modern Inner Mongolia, plus the region around Zhangjiakou in Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
province. At the same time, the jurisdiction of some border departments of Zhili Province, Zhili and Shanxi provinces also belonged to this region.
* The Guihua Tümed banner was controlled by the military commander of Suiyuan (now Hohhot). This corresponds to the vicinities of the modern city of Hohhot. At the same time, the jurisdiction of some border departments of modern Shanxi province also belonged to this region.
* The Hulunbuir region in what is now northeastern Inner Mongolia was part of the jurisdiction of the General of Heilongjiang, one of the three generals of Manchuria.
The Inner Mongolian Chahar Mongols, Chahar leader Ligdan Khan, a descendant of Genghis Khan, opposed and fought against the Qing until he died of smallpox in 1634. Thereafter, the Inner Mongols under his son Ejei Khan surrendered to the Qing and was given the title of Prince (), and Inner Mongolian nobility became closely tied to the Qing royal family and intermarried with them extensively. Ejei Khan died in 1661 and was succeeded by his brother Abunai. After Abunai showed disaffection with Manchu Qing rule, he was placed under house arrest in 1669 in Shenyang and the Kangxi Emperor gave his title to his son Borni. Abunai then bid his time and then he and his brother Lubuzung revolted against the Qing in 1675 during the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, with 3,000 Chahar Mongol followers joining in on the revolt. The revolt was put down within two months, the Qing then crushed the rebels in a battle on 20 April 1675, killing Abunai and all his followers. Their title was abolished, all Chahar Mongol royal males were executed even if they were born to Manchu Qing princesses, and all Chahar Mongol royal females were sold into slavery except the Manchu Qing princesses. The Chahar Mongols were then put under the direct control of the Qing Emperor, unlike the other Inner Mongol leagues which maintained their autonomy.
Despite officially prohibiting Han Chinese settlement on the Manchu and Mongol lands, by the 18th century the Qing decided to settle Han refugees from northern China who were suffering from famine, floods, and drought into Manchuria and Inner Mongolia. As a result, the Han Chinese farmed 500,000 hectares in Manchuria and tens of thousands of hectares in Inner Mongolia by the 1780s.
Ordinary Mongols were not allowed to travel outside their own leagues. Mongols were forbidden by the Qing from crossing the borders of their banners, even into other Mongol Banners and from crossing into neidi (the Han Chinese 18 provinces) and were given serious punishments if they did in order to keep the Mongols divided against each other to benefit the Qing. Mongol pilgrims wanting to leave their banner's borders for religious reasons such as pilgrimage had to apply for passports to give them permission.
During the eighteenth century, growing numbers of Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
settlers had illegally begun to move into the Inner Mongolian steppe. By 1791, there had been so many Han Chinese settlers in the Qian Gorlos Mongol Autonomous County, Front Gorlos Banner that the jasak had petitioned the Qing government to legalise the status of the peasants who had already settled there.
During the nineteenth century, the Manchus were becoming increasingly sinicised and faced with the Russian threat, they began to encourage Han Chinese farmers to settle in both Mongolia and Manchuria. This policy was followed by subsequent governments. The railroads that were being built in these regions were especially useful to the Han Chinese settlers. Land was either sold by Mongol Princes, or leased to Han Chinese farmers, or simply taken away from the nomads and given to Han Chinese farmers.
A group of Han Chinese during the Qing dynasty called "Mongol followers" immigrated to Inner Mongolia who worked as servants for Mongols and Mongol princes and married Mongol women. Their descendants continued to marry Mongol women and changed their ethnicity to Mongol as they assimilated into the Mongol people, an example of this were the ancestors of Li Shouxin. They distinguished themselves apart from "true Mongols" 真蒙古.
Republic of China and the Second World War periods
 Outer Mongolia gained independence from the Qing dynasty in 1911, when the Jebtsundamba Khutugtu of the Khalkha was declared the Bogd Khan of Mongolia. Although almost all banners of Inner Mongolia recognised the Bogd Khan as the supreme ruler of Mongols, the internal strife within the region prevented a full reunification. The Mongol rebellions in Inner Mongolia were counterbalanced by princes who hoped to see a restored Qing dynasty in Manchuria and Mongolia, as they considered the theocratic rule of the Bogd Khan would be against their modernising objectives for Mongolia. Eventually, the newly formed
Outer Mongolia gained independence from the Qing dynasty in 1911, when the Jebtsundamba Khutugtu of the Khalkha was declared the Bogd Khan of Mongolia. Although almost all banners of Inner Mongolia recognised the Bogd Khan as the supreme ruler of Mongols, the internal strife within the region prevented a full reunification. The Mongol rebellions in Inner Mongolia were counterbalanced by princes who hoped to see a restored Qing dynasty in Manchuria and Mongolia, as they considered the theocratic rule of the Bogd Khan would be against their modernising objectives for Mongolia. Eventually, the newly formed Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
promised a new nation of five races (Han Chinese, Han, Manchu, Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
, Tibetan people, Tibetan and Uyghur people, Uyghur). and suppressed the Mongol rebellions in the area.
The Republic of China reorganised Inner Mongolia into provinces:
* Rehe (province), Rehe province was created to include the Juuuda and Josutu leagues, plus the Chengde area in what is now northern Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
.
* Chahar (province), Chahar province was created to include Xilingol league as well as much of the former territory of the Eight Banners.
* Suiyuan
Suiyuan () is a ''de jure'' province of the Republic of China according to the ROC law, as the ROC government formally claims to be the legitimate government of China, with its capital located Guisui (now Hohhot). The abbreviation was (pinyi ...
province was created to include Ulanqab league, Yekejuu league, and the Hetao region (former Guihua Tümed territory).
* Hulunbuir stayed within Heilongjiang in Manchuria, which had become a province.
* Most of Jirim league came under the new province of Liaoning, Fengtian in southern Manchuria.
* Taoxi Mongolia, i.e., Alashan and Ejine leagues, was incorporated into neighbouring Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
province. Later on Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
province was split out of northern Gansu, and Taoxi Mongolia became part of Ningxia.
Some Republic of China maps still show this structure.
The history of Inner Mongolia during the Second World War is complicated, with Japanese invasion and different kinds of resistance movements. In 1931, Manchuria came under the control of the Japanese puppet state Manchukuo, taking some Mongol areas in the Manchurian provinces (i.e., Hulunbuir and Jirim leagues) along. Rehe was also incorporated into Manchukuo in 1933, taking Juu Uda and Josutu leagues along with it. These areas were occupied by Manchukuo until the end of World War II in 1945.
In 1937, the Empire of Japan openly and fully invaded Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
. On 8 December 1937, Mongolian Prince Demchugdongrub (also known as "De Wang") declared independence for the remaining parts of Inner Mongolia (i.e., the Suiyuan and Chahar provinces) as Mengjiang, and signed agreements with Manchukuo and Japan. Its capital was established at Zhangbei Town, Zhangbei (now in Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
province), with the Japanese puppet government's control extending as far west as the Hohhot region. The Japanese advance was defeated by Hui Muslim General Ma Hongbin at the Battle of West Suiyuan and Battle of Wuyuan. Since 1945, Inner Mongolia has remained part of China.
The Mongol Ulanhu fought against the Japanese.
 Ethnic Mongolian guerrilla units were created by the Kuomintang Nationalists to fight against the Japanese during the war in the late 30s and early 40s. These Mongol militias were created by the Ejine and Alashaa based commissioner's offices created by the Kuomintang. Prince Demchugdongrob's Mongols were targeted by Kuomintang Mongols to defect to the Republic of China. The Nationalists recruited 1,700 ethnic minority fighters in Inner Mongolia and created war zones in the Tumet Banner, Ulanchab League, and Ordos Yekejuu League.
The Inner Mongolian People's Republic was founded shortly after the Second World War. It existed from 9 September 1945 until 6 November 1945.
Ethnic Mongolian guerrilla units were created by the Kuomintang Nationalists to fight against the Japanese during the war in the late 30s and early 40s. These Mongol militias were created by the Ejine and Alashaa based commissioner's offices created by the Kuomintang. Prince Demchugdongrob's Mongols were targeted by Kuomintang Mongols to defect to the Republic of China. The Nationalists recruited 1,700 ethnic minority fighters in Inner Mongolia and created war zones in the Tumet Banner, Ulanchab League, and Ordos Yekejuu League.
The Inner Mongolian People's Republic was founded shortly after the Second World War. It existed from 9 September 1945 until 6 November 1945.
People's Republic of China
The Communist movement gradually gained momentum as part of the Third Communist International in Inner Mongolia during the Japanese period. By the end of WWII, the Inner Mongolian faction of the ComIntern had a functional militia and actively opposed the attempts at independence by De Wang's Chinggisid princes on the grounds of fighting feudalism. Following the end of World War II, the Communist Party of China, Chinese Communists gained control of Manchuria as well as the Inner Mongolian Communists with decisive Soviet support and established the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in 1947. The Comintern army was absorbed into the People's Liberation Army. Initially, the autonomous region included just the Hulunbuir region. Over the next decade, as the communists established the People's Republic of China and consolidated control over mainland China, Inner Mongolia was expanded westwards to include five of the six original leagues (except Josutu League, which remains in Liaoning province), the northern part of the Chahar region, by then a league as well (southern Chahar remains inHebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
province), the Hetao region, and the Alashan and Ejine banners. Eventually, nearly all areas with sizeable Mongol populations were incorporated into the region, giving present-day Inner Mongolia its elongated shape. The leader of Inner Mongolia during that time, as both regional CPC secretary and head of regional government, was Ulanhu.
During the Cultural Revolution, the administration of Ulanhu was purged, and a wave of repressions was initiated against the Mongol population of the autonomous region. Among the victims in Inner Mongolia, 75 per cent were Mongols, even though they only constituted 10 per cent of the population. In 1969, much of Inner Mongolia was distributed among surrounding provinces, with Hulunbuir divided between Heilongjiang and Jilin, Jirim going to Jilin, Juu Uda to Liaoning, and the Alashan and Ejine region divided among Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
and Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
. This decision was reversed in 1979.
Inner Mongolia has seen considerable development since Deng Xiaoping instituted Chinese economic reform in 1978. For about ten years since 2000, Inner Mongolia's GDP growth has been the highest in the country, (along with Guangdong) largely owing to the success of natural resource industries in the region. GDP growth has continually been over 10%, even 15% and connections with the Wolf Economy to the north has helped development. However, growth has come at a cost with huge amounts of pollution and degradation to the grasslands. Attempts to attract Han Chinese, ethnic Chinese to migrate from other regions, as well as urbanise those rural nomads and peasants has led to huge amounts of corruption and waste in public spending, such as Ordos City. Acute uneven wealth distribution has further exacerbated ethnic tensions, many indigenous Mongolians feeling they are increasingly marginalised in their own homeland, leading to 2011 Inner Mongolia unrest, riots in 2011 and 2013.
On 31 August 2020, 2020 Inner Mongolia protests, large protests broke out in ethnic Mongol communities due to unannounced plans by the Chinese government to phase out Mongolian-medium teaching.
Geography

 Officially Inner Mongolia is classified as one of the provincial-level divisions of
Officially Inner Mongolia is classified as one of the provincial-level divisions of North China
North China, or Huabei () is a List of regions of China, geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north ...
, but its great stretch means that parts of it belong to Northeast China and Northwest China as well. It borders eight provincial-level divisions in all three of the aforementioned regions (Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, an ...
, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in ...
, and Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibet ...
), tying with Shaanxi for the greatest number of bordering provincial-level divisions. Most of its international border is with Mongolia, which, in Chinese, is sometimes called "Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
", while a small portion is with Russia's Zabaykalsky Krai
Zabaykalsky Krai ( rus, Забайкальский край, r=Zabaikal'skii krai, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲskʲɪj kraj, lit. "Transbaikal krai"; bua, Yбэр Байгалай хизаар, Uber Baigalai Xizaar) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) t ...
.
Inner Mongolia largely consists of the northern side of the North China Craton, a tilted and sedimented Precambrian block. In the extreme southwest is the edge of the Tibetan Plateau where the autonomous region's highest peak, Main Peak, Helan Mountains, Main Peak in the Helan Mountains reaches , and is still being pushed up today in short bursts.Wei Zhang, Mingyue He, Yonghua Li, Zhijiu Cui, Zhilin Wang and Yang Yu"Quaternary glacier development and the relationship between the climate change and tectonic uplift in the Helan Mountains"
; in ''Chinese Science Bulletin''; December 2012, Volume 57, Issue 34, pp. 4491–4504. Most of Inner Mongolia is a plateau averaging around in altitude and covered by extensive loess and sand deposits. The northern part consists of the Mesozoic era Khingan Mountains, and is owing to the cooler climate more forested, chiefly with Ulmus laciniata, Manchurian elm, Ash (Fraxinus), ash, birch, Quercus mongolica, Mongolian oak and a number of Pinus, pine and Picea, spruce species. Where discontinuous permafrost is present north of Hailar District, forests are almost exclusively coniferous. In the south, the natural vegetation is grassland in the east and very sparse in the arid west, and grazing is the dominant economic activity. Owing to the ancient, weathered rocks lying under its deep sedimentary cover, Inner Mongolia is a major mining district, possessing large reserves of coal, iron ore and rare-earth minerals, which have made it a major industrial region today.
Climate
Due to its elongated shape, Inner Mongolia has a four-season monsoon climate with regional variations. The winters in Inner Mongolia are very long, cold, and dry with frequent blizzards, though snowfall is so light that Inner Mongolia has no modern glaciers even on the highest Helan peaks. The spring is short, mild and arid, with large, dangerous sandstorms, whilst the summer is very warm to hot and relatively humid except in the west where it remains dry. Autumn is brief and sees a steady cooling, with temperatures below reached in October in the north and November in the south. Officially, most of Inner Mongolia is classified as either a cold arid or Steppe climate, steppe regime (Köppen climate classification, Köppen ''BWk, BSk'', respectively). The small portion besides these are classified as humid continental (Köppen ''Dwa/Dwb'') in the northeast, or Subarctic climate, subarctic (Köppen ''Dwc'') in the far north near Hulunbuir.Administrative divisions
Inner Mongolia is divided into twelve Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level, prefecture-level divisions. Until the late 1990s, most of Inner Mongolia's prefectural regions were known as ''Leagues of China, Leagues'' (), a usage retained from Mongol divisions of theQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. Similarly, county-level divisions are often known as ''Banners'' (). Since the 1990s, numerous Leagues have converted into Prefecture-level city, prefecture-level cities, although Banners remain. The restructuring led to the conversion of primate cities in most leagues to convert to districts administratively (i.e.: Hailar
Hailar District, formerly a county-level city, is an urban district that serves as the seat of the prefecture-level city Hulunbuir in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Hulunbuir, due to its massive size, is a city in administrative terms only ...
, Jining District, Jining and Dongsheng). Some newly founded prefecture-level cities have chosen to retain the original name of League (i.e.: Hulunbuir, Bayannur and Ulanqab), some have adopted the Chinese name of their primate city (Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to the ...
, Tongliao
Tongliao (; mn, ''Tüŋliyou qota'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Байшинт хот) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. The area is and as of the 2020 census, its population was 2,873,168 (3,139,153 i ...
), and one League (Yekejuu) simply renamed itself Ordos Ordos may refer to:
Inner Mongolia
* Ordos City, Inner Mongolia, China
**Ordos Ejin Horo Airport
* Ordos Loop of the Yellow River, a region of China
**Ordos Plateau or "the Ordos", land enclosed by Ordos Loop
*Ordos Desert, in Inner Mongolia
*Ordos ...
. Despite these recent administrative changes, there is no indication that the Alxa, Hinggan, and Xilingol Leagues will convert to prefecture-level cities in the near future.
These prefecture-level divisions are in turn subdivided into 102 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#County level, county-level divisions, including 22 District of China, districts, 11 county-level cities, 17 County (People's Republic of China), counties, 49 Banners of Inner Mongolia, banners, and 3 autonomous banners. Those are in turn divided into 1425 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions, including 532 town of China, towns, 407 Townships of the People's Republic of China, townships, 277 sum (Inner Mongolia), sums, eighteen ethnic townships, one ethnic sum, and 190 Subdistricts of China, subdistricts. At the end of 2017, the total population of Inner-Mongolia is 25.29 million.
Urban areas
Economy
Farming of crops such as wheat takes precedence along the river valleys. In the more arid grasslands, herding of goats, sheep and so on is a traditional method of subsistence. Forestry and hunting are somewhat important in the Greater Khingan ranges in the east. Reindeer herding is carried out by Evenks in the Evenk Autonomous Banner. More recently, growing grapes and winemaking have become an economic factor in the Wuhai area. Inner Mongolia has an abundance of resources especially coal, Cashmere wool, cashmere, natural gas, rare-earth elements, and has more deposits of naturally occurring niobium, zirconium and beryllium than any other province-level region in China. However, in the past, the exploitation and utilisation of resources were rather inefficient, which resulted in poor returns from rich resources. Inner Mongolia is also an important coal production base, with more than a quarter of the world's coal reserves located in the province. It plans to double annual coal output by 2010 (from the 2005 volume of 260 million tons) to 500 million tons of coal a year.
Inner Mongolia has an abundance of resources especially coal, Cashmere wool, cashmere, natural gas, rare-earth elements, and has more deposits of naturally occurring niobium, zirconium and beryllium than any other province-level region in China. However, in the past, the exploitation and utilisation of resources were rather inefficient, which resulted in poor returns from rich resources. Inner Mongolia is also an important coal production base, with more than a quarter of the world's coal reserves located in the province. It plans to double annual coal output by 2010 (from the 2005 volume of 260 million tons) to 500 million tons of coal a year.
 Industry in Inner Mongolia has grown up mainly around coal, power generation, forestry-related industries, and related industries.
Inner Mongolia now encourages six competitive industries: energy, chemicals, metallurgy, equipment manufacturing, processing of farm (including dairy) produce, and high technology. Well-known Inner Mongolian enterprises include companies such as ERDOS, Yili Group, Yili, and Mengniu.
The nominal GDP of Inner Mongolia in 2015 was 1.8 trillion yuan (US$272.1 billion), with an average annual increase of 10% from the period 2010–2015. Its per capita GDP reached US$11,500 in 2015, ranking No.4th among all the 31 provinces of China, only after Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin.
As with much of China, economic growth has led to a boom in construction, including new commercial development and large apartment complexes.
In addition to its large reserves of natural resources, Inner Mongolia also has the largest usable wind power capacity in China thanks to strong winds which develop in the province's grasslands. Some private companies have set up Wind power in China, wind parks in parts of Inner Mongolia such as Bailingmiao, Hutengliang and Zhouzi.
East of Jilantai, Inner Mongolia, there is a ballistic missile training area used by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF) to train missile crews for mobile missile launchers, their support vehicles, and silo-based ballistic missiles.
Industry in Inner Mongolia has grown up mainly around coal, power generation, forestry-related industries, and related industries.
Inner Mongolia now encourages six competitive industries: energy, chemicals, metallurgy, equipment manufacturing, processing of farm (including dairy) produce, and high technology. Well-known Inner Mongolian enterprises include companies such as ERDOS, Yili Group, Yili, and Mengniu.
The nominal GDP of Inner Mongolia in 2015 was 1.8 trillion yuan (US$272.1 billion), with an average annual increase of 10% from the period 2010–2015. Its per capita GDP reached US$11,500 in 2015, ranking No.4th among all the 31 provinces of China, only after Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin.
As with much of China, economic growth has led to a boom in construction, including new commercial development and large apartment complexes.
In addition to its large reserves of natural resources, Inner Mongolia also has the largest usable wind power capacity in China thanks to strong winds which develop in the province's grasslands. Some private companies have set up Wind power in China, wind parks in parts of Inner Mongolia such as Bailingmiao, Hutengliang and Zhouzi.
East of Jilantai, Inner Mongolia, there is a ballistic missile training area used by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF) to train missile crews for mobile missile launchers, their support vehicles, and silo-based ballistic missiles.
Economic and Technological Development Zones
*Baotou
Baotou (; mn, Buɣutu qota, Бугат хот) is the largest city by urban population in Inner Mongolia, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, as of the 2020 census, its built-up (''or metro'') area made up of its 5 urban districts is h ...
National Rare-earth, Rare-Earth Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
* Erenhot Border Economic Cooperation Area
* Hohhot Export Processing Zone
Hohhot Export Processing Zone was established 21 June 2002 by the State Council, which is located in the west of the Hohhot, with a planning area of . Industries encouraged in the export processing zone include Electronics Assembly & Manufacturing, Telecommunications Equipment, Garment and Textiles Production, Trading and Distribution, Biotechnology/Pharmaceuticals, Food/Beverage Processing, Instruments & Industrial Equipment Production, Medical Equipment and Supplies, Shipping/Warehousing/Logistics, Heavy Industry.
* Hohhot Economic and Technological Development Zone
* Hohhot Export Processing Zone
* Manzhouli Border Economic Cooperation Area
Government and politics
Under the Constitution of the People's Republic of China, articles 112–122, autonomous regions have limited autonomy in both the political and economic arena. Autonomous regions have more discretion in administering economic policy in the region in accordance with national guidelines. Structurally, the Chairman—who legally must be an ethnic minority and is usually ethnic Mongolian—is always kept in check by the Communist Party of China, Communist Party Regional Committee Secretary, who is usually from a different part of China (to reduce corruption) and Han Chinese. , the current party secretary is Shi Taifeng. The Inner Mongolian government and its subsidiaries follow roughly the same structure as that of a Chinese province. With regards to economic policy, as a part of increased Chinese federalism, federalism characteristics in China, Inner Mongolia has become more independent in implementing its own economic roadmap. The position of Chairman of Inner Mongolia alternates between Khorchin Mongols in the east and the Tumed Mongols in the west. Since the end of the Cultural Revolution, this convention has not been broken. The family of Ulanhu has retained influence in regional politics ever since the founding the People's Republic. His son Buhe (politician), Buhe and granddaughter Bu Xiaolin both served as Chairman of the region.Demographics
 When the autonomous region was established in 1947, Han Chinese comprised 83.6% of the population, while the Mongols comprised 14.8% of the population. By 2010, the percentage of Han Chinese had dropped to 79.5%. While the Hetao region along the Yellow River has always alternated between farmers from the south and nomads from the north, the most recent wave of Han Chinese migration began in the early 18th century with encouragement from the
When the autonomous region was established in 1947, Han Chinese comprised 83.6% of the population, while the Mongols comprised 14.8% of the population. By 2010, the percentage of Han Chinese had dropped to 79.5%. While the Hetao region along the Yellow River has always alternated between farmers from the south and nomads from the north, the most recent wave of Han Chinese migration began in the early 18th century with encouragement from the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
, and continued into the 20th century. Han Chinese live mostly in the Hetao region as well as various population centres in central and eastern Inner Mongolia. Over 70% of Mongols are concentrated in less than 18% of Inner Mongolia's territory (Hinggan League, and the prefectures of Tongliao
Tongliao (; mn, ''Tüŋliyou qota'', Mongolian Cyrillic: Байшинт хот) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. The area is and as of the 2020 census, its population was 2,873,168 (3,139,153 i ...
and Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to the ...
).
Mongols are the second largest ethnic group, comprising 17.11% of the population as of the 2010 census. They include many diverse Mongolian-speaking groups; groups such as the Buryats and the Oirats are also officially considered to be Mongols in China. In addition to the Manchus, other Tungusic ethnic groups, the Oroqen people, Oroqen, and the Evenks also populate parts of northeastern Inner Mongolia.
Many of the traditionally nomadic Mongols have settled in permanent homes as their pastoral economy was collectivised during the Mao era, and some have taken jobs in cities as migrant labourers; however, some Mongols continue in their nomadic tradition. In practice, highly educated Mongols tend to migrate to big urban centers after which they become essentially indistinct with ethnic Han Chinese populations.
Inter-marriage between Mongol and non-Mongol populations is very common, particularly in areas where Mongols are in regular contact with other groups. There was little cultural stigma within Mongol families for marrying outside the ethnic group, and in urban centers in particular, Mongol men and women married non-Mongols at relatively similar rates. The rates of intermarriage stands in very sharp contrast to ethnic Tibetans and Uyghurs in their respective autonomous regions. By the 1980s, for instance, in Tongliao, the former Jirim League, nearly 40% of marriages with at least one Mongol spouse was a mixed Mongol-Han Chinese marriage. However, anecdotal reports have also demonstrated an increase in Mongol-female, Han Chinese-male pairings in which the woman is of a rural background, ostensibly shutting rural Mongol males from the marriage market as the sex ratio in China becomes more skewed with a much higher proportion of men.
There is also a significant number of Hui people, Hui and Koreans in China, Koreans.
''Population numbers exclude members of the People's Liberation Army in active service based in Inner Mongolia.''
Language and culture

 Alongside Chinese, Mongolian is the official provincial language of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, where there are at least 4.1 million ethnic Mongols. Across the whole of China, the language is spoken by roughly half of the country's 5.8 million ethnic Mongols (2005 estimate) However, the exact number of Mongolian speakers in China is unknown, as there is no data available on the language proficiency of that country's citizens. The use of Mongolian in China, specifically in Inner Mongolia, has witnessed periods of decline and revival over the last few hundred years. The language experienced a decline during the late Qing period, a revival between 1947 and 1965, a second decline between 1966 and 1976, a second revival between 1977 and 1992, and a third decline between 1995 and 2012. However, in spite of the decline of the Mongolian language in some of Inner Mongolia's urban areas and educational spheres, the ethnic identity of the urbanised Chinese-speaking Mongols is most likely going to survive due to the presence of urban ethnic communities. The multilingual situation in Inner Mongolia does not appear to obstruct efforts by ethnic Mongols to preserve their language. Although an unknown number of Mongols in China, such as the Tumets, may have completely or partially lost the ability to speak their language, they are still registered as ethnic Mongols and continue to identify themselves as ethnic Mongols. The children of inter-ethnic Mongol-Chinese marriages also claim to be and are registered as ethnic Mongols.
By law, all street signs, commercial outlets, and government documents must be bilingual, written in both Mongolian and Chinese. There are three Mongolian TV channels in the Inner Mongolia Satellite TV network. In public transportation, all announcements are to be bilingual.
Mongols in Inner Mongolia speak Mongolian language, Mongolian dialects such as Chakhar Mongolian, Chakhar, Xilingol, Baarin Mongolian, Baarin, Khorchin Mongolian, Khorchin and Kharchin Mongolian and, depending on definition and analysis, further dialects or closely related independent Central Mongolic languages such as Ordos Mongolian, Ordos, Khamnigan Mongol, Khamnigan, Barghu Buryat language, Buryat and the arguably Oirat language, Oirat dialect Alasha dialect, Alasha. The standard pronunciation of Mongolian in China is based on the Chakhar dialect of the Plain Blue Banner, Inner Mongolia, Plain Blue Banner, located in central Inner Mongolia, while the grammar is based on all Southern Mongolian, Southern Mongolian dialects. This is different from the Mongolian state, where the standard pronunciation is based on the closely related Khalkha Mongolian, Khalkha dialect. There are a number of independent languages spoken in Hulunbuir such as the somewhat more distant Mongolic language Daur language, Dagur and the Tungusic languages, Tungusic language Evenki language, Evenki. Officially, even the Evenki dialect Oroqen language, Oroqin is considered a language.
The
Alongside Chinese, Mongolian is the official provincial language of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, where there are at least 4.1 million ethnic Mongols. Across the whole of China, the language is spoken by roughly half of the country's 5.8 million ethnic Mongols (2005 estimate) However, the exact number of Mongolian speakers in China is unknown, as there is no data available on the language proficiency of that country's citizens. The use of Mongolian in China, specifically in Inner Mongolia, has witnessed periods of decline and revival over the last few hundred years. The language experienced a decline during the late Qing period, a revival between 1947 and 1965, a second decline between 1966 and 1976, a second revival between 1977 and 1992, and a third decline between 1995 and 2012. However, in spite of the decline of the Mongolian language in some of Inner Mongolia's urban areas and educational spheres, the ethnic identity of the urbanised Chinese-speaking Mongols is most likely going to survive due to the presence of urban ethnic communities. The multilingual situation in Inner Mongolia does not appear to obstruct efforts by ethnic Mongols to preserve their language. Although an unknown number of Mongols in China, such as the Tumets, may have completely or partially lost the ability to speak their language, they are still registered as ethnic Mongols and continue to identify themselves as ethnic Mongols. The children of inter-ethnic Mongol-Chinese marriages also claim to be and are registered as ethnic Mongols.
By law, all street signs, commercial outlets, and government documents must be bilingual, written in both Mongolian and Chinese. There are three Mongolian TV channels in the Inner Mongolia Satellite TV network. In public transportation, all announcements are to be bilingual.
Mongols in Inner Mongolia speak Mongolian language, Mongolian dialects such as Chakhar Mongolian, Chakhar, Xilingol, Baarin Mongolian, Baarin, Khorchin Mongolian, Khorchin and Kharchin Mongolian and, depending on definition and analysis, further dialects or closely related independent Central Mongolic languages such as Ordos Mongolian, Ordos, Khamnigan Mongol, Khamnigan, Barghu Buryat language, Buryat and the arguably Oirat language, Oirat dialect Alasha dialect, Alasha. The standard pronunciation of Mongolian in China is based on the Chakhar dialect of the Plain Blue Banner, Inner Mongolia, Plain Blue Banner, located in central Inner Mongolia, while the grammar is based on all Southern Mongolian, Southern Mongolian dialects. This is different from the Mongolian state, where the standard pronunciation is based on the closely related Khalkha Mongolian, Khalkha dialect. There are a number of independent languages spoken in Hulunbuir such as the somewhat more distant Mongolic language Daur language, Dagur and the Tungusic languages, Tungusic language Evenki language, Evenki. Officially, even the Evenki dialect Oroqen language, Oroqin is considered a language.
The Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
of Inner Mongolia speak a variety of dialects, depending on the region. Those in the eastern parts tend to speak Northeastern Mandarin, which belongs to the Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin group of dialects; those in the central parts, such as the Yellow River valley, speak varieties of Jin Chinese, Jin, another subdivision of Chinese, due to its proximity to other Jin-speaking areas in China such as the Shanxi province. Cities such as Hohhot and Baotou both have their unique brand of Jin Chinese such as the Zhangjiakou–Hohhot dialect which are sometimes incomprehensible with dialects spoken in northeastern regions such as Hailar
Hailar District, formerly a county-level city, is an urban district that serves as the seat of the prefecture-level city Hulunbuir in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Hulunbuir, due to its massive size, is a city in administrative terms only ...
.
The vast grasslands have long symbolised Inner Mongolia. Mongolian art often depicts the grassland in an uplifting fashion and emphasises Mongolian nomadic traditions. The Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
s of Inner Mongolia still practice their traditional arts. Inner Mongolian cuisine has Mongol roots and consists of dairy-related products and ''hand-held lamb'' (). In recent years, franchises based on hot pot have appeared in Inner Mongolia, the best known of which is Little Sheep Group, Little Sheep. Notable Inner Mongolian commercial brand names include Mengniu and Yili Group, Yili, both of which began as dairy product and ice cream producers.
Among the Han Chinese of Inner Mongolia, Shanxi opera is a popular traditional form of entertainment. See also: Shanxi. A popular career in Inner Mongolia is circus acrobatics. The internationally known Inner Mongolia Acrobatic Troupe travels and performs with the renowned Ringling Bros. and Barnum & Bailey Circus.
Religion
According to a survey held in 2004 by the Minzu University of China, about 80% of the population of the region practice the worship of Heaven (that is named ''Tian'' in the Chinese tradition and ''Tengri, Tenger'' in the Mongolian tradition) and of ''ovoo, ovoo/aobao''.Fenggang Yang, Graeme Lang. ''Social Scientific Studies of Religion in China''. BRILL, 2012. . pp. 184–185, reporting the results of surveys held in 2004 by the Minzu University of China. Quote from page 185: «[...] ''the registered adherents of the five official religions comprise only 3.7% of those [populations] in Inner Mongolia. When we compare this final statistic with Minzu University research team's finding that 80% of the inhabitants of Inner Mongolia worship ''Tian'' (loosely translated "Heaven") and ''aobao'' (traditional stone structures that serve as altars for sacrifice), it is evident that the official calculations of registered religious believers are markedly low, and the policy decisions based on these numbers lack the necessary grounding in reality.'' [...] ''Foreign religions can be transformed into indigenous ethnic religions, and the traditional folk religions of China's ethnic minorities can integrate and neutralize non-native religions. Thus, China's ethnic religions should not be regarded as social burdens or challenges, but rather as valuable cultural assets.''» Official statistics report that 10.9% of the population (3 million people) are members of Tibetan Buddhist groups.Jiayu Wu, Yong Fang (2016).Study on the Protection of the Lama Temple Heritage in Inner Mongolia as a Cultural Landscape
''. ''Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering'', v. 15 n. 1, January 2016. Note that the article, in an evident mistranslation from Chinese, reports 30 million Tibetan Buddhists in Inner Mongolia instead of 3 million. According to the Chinese Spiritual Life Survey of 2007 and the Chinese General Social Survey of 2009, Christianity is the religious identity of 3.2% of the population of the region; and Chinese ancestral religion the professed belonging of 2.36%,Chinese Spiritual Life Survey (CSLS) 2007, China General Social Survey (CGSS) 2009. Results reported by
Xiuhua Wang (2015, p. 15)
while a demographic analysis of the year 2010 reported that Muslims comprise the 0.91%.Min Junqing. ''The Present Situation and Characteristics of Contemporary Islam in China''. JISMOR, 8
2010 Islam by province, page 29
. Data from: Yang Zongde, ''Study on Current Muslim Population in China'', Jinan Muslim, 2, 2010. The cult (religious practice), cult of
Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
, present in the form of various Genghis Khan temples, is a tradition of Mongolian shamanism, in which he is considered a cultural hero and divine ancestor, an embodiment of the ''Tengri, Tenger'' (Heaven, God of Heaven). His worship in special temples, greatly developed in Inner Mongolia since the 1980s, is also shared by the Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
, claiming his spirit as the founding principle of the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth ...
.
Tibetan Buddhism (Buddhism in Mongolia, Mongolian Buddhism, locally also known as "Yellow Buddhism") is the dominant form of Buddhism in Inner Mongolia, also practised by many Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
. Another form of Buddhism, practised by the Chinese, are the schools of Chinese Buddhism.
Tourism
In the capital city Hohhot: * Dazhao Temple (Hohhot), Da Zhao Temple is a Tibetan Buddhism, Buddhist temple built in 1580. Dazhao Temple is known for three sites: a statue of Gautama Buddha, Buddha made from silver, elaborate carvings of dragons, and murals. * Five-pagoda Temple is located in the capital of Inner Mongolia Hohhot. It is also called Jingangzuo Dagoba, used to be one building of the Cideng Temple (Temple of Merciful Light) built in 1727. * Residence of Gurun Princess Kejing is a mansion typical ofQing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
architectural style that was built in 1705 by the Kangxi Emperor for his daughter.
* Wanbu-Huayanjing Pagoda () in Hohhot. It was built during the reign of Emperor Shengzong (983–1031) of the Khitan Liao dynasty (907–1125) and is still well preserved.
* Xiaozhao Temple, also known as Chongfu temple, is a Tibetan Buddhism, Buddhist temple built in 1697 and favoured by the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
.
* Xilitu Zhao, Xilitu Zhao / Siregtu juu Temple is the largest Buddhist temple in the Höhhot area, and once the center of power of Tibetan Buddhism in the region.
* Zhaojun Tomb is the tomb of Wang Zhaojun, a Han dynasty palace lady-in-waiting who became the consort of the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
ruler Huhanye Shanyu in 33BC.
Elsewhere in Inner Mongolia:
* The Mausoleum of Genghis Khan, the cenotaph of Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
, is located in Ordos City.
* Bashang Grasslands, on the border close to Beijing, is a popular retreat for urban residents wanting to get a taste of grasslands life.
* The Arshihaty Stone Forest in Hexigten Global Geopark has magnificent granite rock formations formed from natural erosion.
* Xiangshawan, or "singing sands gorge", is located in the Gobi Desert and contains numerous tourist attractions including sand sledding and camel rides.
* Remains of Zhongjing (Central Capital) built in 1003 by Emperor Shengzong of the Khitan Liao dynasty (907–1125) in Ningcheng County.
* Remains of Shangjing (Upper Capital) built in 918 by Yelu Abaoji the 1st emperor of the Khitan Liao dynasty (907–1125). Also called Huangdu it was one of the five capitals of the Liao dynasty.
* Zuling Mausoleum of Abaoji Khan. It was built in 926 for Abaoji the 1st Emperor of the Liao dynasty. Located north-west of Shifangzi village.
* Tablets of Juyan. Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) inscriptions on wood and bamboo. In 1930 Folke Bergman of the Sino-Swedish expedition first discovered 10,000 tablets at Ejin Banner, Ejin Khoshuu in the Gobi Desert.
* Ruins of Shangdu (Xanadu) the Summer Capital of the Mongol Yuan dynasty built in 1256 by Kublai Khan.
* White pagoda of the Mongol Yuan dynasty (1279–1368) in Kailu County, Tongliao. It is still well preserved.
* Ruins of Chagan Khoto () capital of the last Mongol Great Khan Ligdan Khan, Ligden (1588–1634). Located in Ar Horqin Banner.
 One of China's space vehicle launch facilities, Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, is located in the Alxa League's Ejin Banner, in the west of Inner Mongolia. It was founded in 1958, making it the PRC's first launch facility. As of 2021, Jiuquan has documented more launches than any other launch facilities in China, and is still the only launch site for manned space missions (Shenzhou program). While geologically located inside Inner Mongolia, the launch center is named after Jiuquan, which is the nearest urban center in the nearby province of Gansu.
As military facilities, the core areas at Jiuquan Center are highly restricted and can only be visited by tourist buses operated by the center, while the visitor center is open to the public and can be accessed from the south gate.
Inner Mongolia is also home to the two (and only two) space vehicles landing sites in China, the Siziwang Banner Landing Site in Ulanqab and the Dongfeng Landing Site in Alxa.
One of China's space vehicle launch facilities, Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, is located in the Alxa League's Ejin Banner, in the west of Inner Mongolia. It was founded in 1958, making it the PRC's first launch facility. As of 2021, Jiuquan has documented more launches than any other launch facilities in China, and is still the only launch site for manned space missions (Shenzhou program). While geologically located inside Inner Mongolia, the launch center is named after Jiuquan, which is the nearest urban center in the nearby province of Gansu.
As military facilities, the core areas at Jiuquan Center are highly restricted and can only be visited by tourist buses operated by the center, while the visitor center is open to the public and can be accessed from the south gate.
Inner Mongolia is also home to the two (and only two) space vehicles landing sites in China, the Siziwang Banner Landing Site in Ulanqab and the Dongfeng Landing Site in Alxa.
Education
Colleges and universities
Language policy and protest
Inner Mongolia under the People's Republic of China has historically allowed the Mongolian language as a medium of instruction. An 1979 article from the ''People's Daily'' praises the re-establishment of Mongolian-language education after "interference and vandalism by the Gang of Four" during the Cultural Revolution. It was reported by ''The New York Times'' on 31 August 2020 that in the summer 2020, the Chinese government announced a new education policy, which called for Chinese to gradually replace Mongolian as the language of instruction in three subjects, including language and literature, politics, and history, in elementary and middle schools around the Inner Mongolia region. Thousands of ethnic Mongolians in northern China gathered to protest the policy.Image gallery
Chifeng
Chifeng ( zh, s=赤峰市), also known as Ulanhad ( mn, (Улаанхад хот), ''Ulaɣanqada qota'', , "red cliff"), is a prefecture-level city in Southeastern Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China. It borders Xilin Gol League to the ...
File:乌兰布统3.jpg, Ulaanbutan grassland
File:Inner Mongolia grassland (2005).jpg, Inner Mongolian grassland
File:Statue at the Wang Zhaojun Tomb.jpg, Honorary tomb of Wang Zhaojun (born c. 50BC) in Hohhot
File:Fresco Songjingtu, Liao Dynasty Tomb at Baoshan.jpg, Fresco from the Liao dynasty (907–1125) tomb at Baoshan, Ar Horqin Banner
File:Cooking, mural from Tomb in Aohan, Liao Dynasty.jpg, Khitan people cooking. Fresco from the Liao dynasty (907–1125) tomb in Aohan Banner
File:Khara-khoto.jpg, Remains of the city Khara-Khoto built in 1032. Located in Ejin Banner, Alxa League
File:美岱召古城全景沙盘.jpg, Maidari Juu temple fortress () built by Altan Khan in 1575 near Baotou
Baotou (; mn, Buɣutu qota, Бугат хот) is the largest city by urban population in Inner Mongolia, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, as of the 2020 census, its built-up (''or metro'') area made up of its 5 urban districts is h ...
File:美岱召new stone arch.png, Newly built arch in front of the Maidari Juu temple fortress (1575)
File:Da Zhao Temple in Hohhot3.JPG, Dazhao Temple (Hohhot), Dazhao temple (also called Ikh Zuu) built by Altan Khan in 1579
File:InnerMongoliaBuddhistTemple.jpg, Badekar Monastery (1749) near Baotou, Inner Mongolia. Called Badgar Zuu in Mongolian
File:Five Pagoda Temple, Huhhot, Inner Mongolia.JPG, Five Pagoda temple (1727) in Hohhot
File:Badain Jaran Temple Reflection.JPG, Badain Jaran temple (1868) in Alxa Right Banner, western Inner Mongolia
File:Genghis khan mausoleum.jpg, Genghis Khan Mausoleum (1954) in Ejin Horo Banner
File:GhinggisKhanMausoleumGate.jpg, Genghis Khan Mausoleum (1954)
File:AlshaaUul.jpg, Helan Mountains scenery
File:AlshaaBaruunHiid.jpg, Alxa Western Monastery (Alshaa Baruun Hiid) built in 1756
See also
* Leagues of China, Leagues of Inner Mongolia * List of administrative divisions of Inner Mongolia * Major national historical and cultural sites (Inner Mongolia), Major national historical and cultural sites in Inner Mongolia * Winter storms of 2009–10 in East AsiaNotes
References
Further reading
* Wang, Liping. "From Masterly Brokers to Compliant Protégées: The Frontier Governance System and the Rise of Ethnic Confrontation in China–Inner Mongolia, 1900–1930." ''American Journal of Sociology'' 120.6 (2015): 1641–1689. * Williams, Dee Mack. ''Beyond great walls: environment, identity, and development on the Chinese grasslands of Inner Mongolia'' (Stanford University Press, 2002)Online
* Borjigin, Monkbat.
A case study of Language education in the Inner Mongolia
Archive
Japanese title: ). ''Journal of Chiba University Eurasian Society'' () 16, 261–266, 2014-09-25. Chiba University Eurasian Society ()
See profile at
Chiba University Repository
See profile at
CiNii. – In English with a Japanese abstract. *
External links
*Inner Mongolia Government website
*
Welcome to Inner Mongolia-Mongolia Tours with Samar Magic Tours
* {{Authority control Inner Mongolia, Autonomous regions of China Mongols in China 1947 establishments in China States and territories established in 1947 Inner Asia Historical regions