informational era on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the
The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the

 The world's technological capacity to store information grew from 2.6 (optimally compressed)
The world's technological capacity to store information grew from 2.6 (optimally compressed)
Technological Progress
." ''
 There are different conceptualizations of the Information Age. Some focus on the evolution of information over the ages, distinguishing between the Primary Information Age and the Secondary Information Age. Information in the Primary Information Age was handled by
There are different conceptualizations of the Information Age. Some focus on the evolution of information over the ages, distinguishing between the Primary Information Age and the Secondary Information Age. Information in the Primary Information Age was handled by 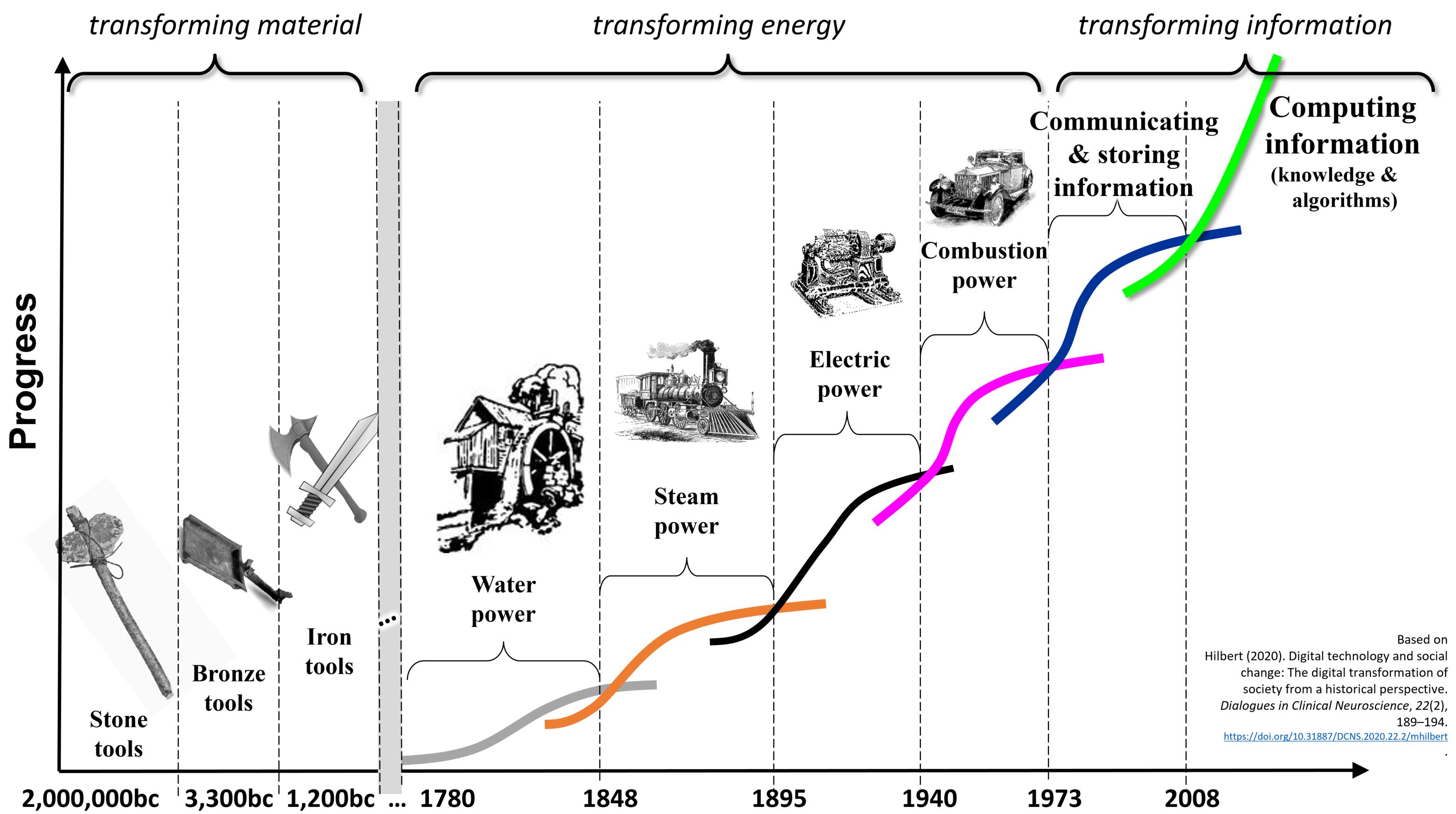 Others classify it in terms of the well-established Schumpeterian long waves or Kondratiev waves. Here authors distinguish three different long-term meta paradigms, each with different long waves. The first focused on the transformation of material, including
Others classify it in terms of the well-established Schumpeterian long waves or Kondratiev waves. Here authors distinguish three different long-term meta paradigms, each with different long waves. The first focused on the transformation of material, including
 The Information Age was enabled by technology developed in the Digital Revolution, which was itself enabled by building on the developments of the Technological Revolution.
The Information Age was enabled by technology developed in the Digital Revolution, which was itself enabled by building on the developments of the Technological Revolution.
 Steve Wozniak (known as "Woz"), a regular visitor to Homebrew Computer Club meetings, designed the single-board Apple I computer and first demonstrated it there. With specifications in hand and an order for 100 machines at US$500 each from Paul Terrell, the Byte Shop, Woz and his friend Steve Jobs founded Apple Computer.
About 200 of the machines sold before the company announced the Apple II as a complete computer. It had color graphics, a full QWERTY keyboard, and internal slots for expansion, which were mounted in a high quality streamlined plastic case. The monitor and I/O devices were sold separately. The original Apple II operating system was only the built-in BASIC interpreter contained in ROM. Apple DOS was added to support the diskette drive; the last version was "Apple DOS 3.3".
Its higher price and lack of floating point BASIC, along with a lack of retail distribution sites, caused it to lag in sales behind the other Trinity machines until 1979, when it surpassed the PET. It was again pushed into 4th place when Atari introduced its popular Atari 8-bit systems.
Despite slow initial sales, the Apple II's lifetime was about eight years longer than other machines, and so accumulated the highest total sales. By 1985 2.1 million had sold and more than 4 million Apple II's were shipped by the end of its production in 1993.
Steve Wozniak (known as "Woz"), a regular visitor to Homebrew Computer Club meetings, designed the single-board Apple I computer and first demonstrated it there. With specifications in hand and an order for 100 machines at US$500 each from Paul Terrell, the Byte Shop, Woz and his friend Steve Jobs founded Apple Computer.
About 200 of the machines sold before the company announced the Apple II as a complete computer. It had color graphics, a full QWERTY keyboard, and internal slots for expansion, which were mounted in a high quality streamlined plastic case. The monitor and I/O devices were sold separately. The original Apple II operating system was only the built-in BASIC interpreter contained in ROM. Apple DOS was added to support the diskette drive; the last version was "Apple DOS 3.3".
Its higher price and lack of floating point BASIC, along with a lack of retail distribution sites, caused it to lag in sales behind the other Trinity machines until 1979, when it surpassed the PET. It was again pushed into 4th place when Atari introduced its popular Atari 8-bit systems.
Despite slow initial sales, the Apple II's lifetime was about eight years longer than other machines, and so accumulated the highest total sales. By 1985 2.1 million had sold and more than 4 million Apple II's were shipped by the end of its production in 1993.
In the Depths of the Digital Age
'' The New York Review of Books * Bollacker, Kurt D. (2010)
Avoiding a Digital Dark Age
', American Scientist, March–April 2010, Volume 98, Number 2, p. 106ff * Manuel Castells, Castells, Manuel. (1996–98). ''The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture'', 3 vols. Oxford: Blackwell. * Gelbstein, E. (2006) ''Crossing the Executive Digital Divide''.
Articles on the impact of the Information Age on business
nbsp;– at ''Information Age'' magazine
Beyond the Information Age
by Dave Ulmer
Information Age Anthology Vol I
by Alberts and Papp (CCRP, 1997) (PDF)
Information Age Anthology Vol II
by Alberts and Papp (CCRP, 2000) (PDF)
Information Age Anthology Vol III
by Alberts and Papp (CCRP, 2001) (PDF)
Understanding Information Age Warfare
by Alberts et al. (CCRP, 2001) (PDF)
Information Age Transformation
by Alberts (CCRP, 2002) (PDF)
The Unintended Consequences of Information Age Technologies
by Alberts (CCRP, 1996) (PDF)
History & Discussion of the Information Age
Science Museum - Information Age
{{portal bar, Internet, Technology Information Age, Digital media Digital divide Contemporary history Historical eras Postmodernism Cultural trends
 The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the
The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, to an economy centered on information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of Data (computing), data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information te ...
. The onset of the Information Age has been linked to the development of the transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
in 1947, the optical amplifier in 1957, and Unix time
Current Unix time ()
Unix time is a date and time representation widely used in computing. It measures time by the number of seconds that have elapsed since 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970, the beginning of the Unix epoch, less adjustments m ...
, which began on January 1, 1970 and serves as the basis for Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently use ...
and the Network Time Protocol. These technological advances have had a significant impact on the way information is processed and transmitted.
According to the United Nations Public Administration Network
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Econ ...
, the Information Age was formed by capitalizing on computer microminiaturization advances, which led to modernized information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random ...
systems and internet communications as the driving force of social evolution.
Overview of early developments

Library expansion and Moore's law
Library expansion was calculated in 1945 byFremont Rider
Arthur Fremont Rider (May 25, 1885 – October 26, 1962) was an American writer, poet, editor, inventor, genealogist, and librarian. He studied under Melvil Dewey, of whom he wrote a biography for the ALA. Throughout his life he wrote in se ...
to double in capacity every 16 years where sufficient space made available. He advocated replacing bulky, decaying printed works with miniaturized
Miniaturization ( Br.Eng.: ''Miniaturisation'') is the trend to manufacture ever smaller mechanical, optical and electronic products and devices. Examples include miniaturization of mobile phones, computers and vehicle engine downsizing. In ele ...
microform
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the original document size. ...
analog photographs, which could be duplicated on-demand for library patrons and other institutions.
Rider did not foresee, however, the digital technology Digital technology may refer to:
* Application of digital electronics
* Any significant piece of knowledge from information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange a ...
that would follow decades later to replace analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
microform with digital imaging
Digital imaging or digital image acquisition is the creation of a digital representation of the visual characteristics of an object, such as a physical scene or the interior structure of an object. The term is often assumed to imply or include t ...
, storage, and transmission media
A transmission medium is a system or substance that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication. Signals are typically imposed on a wave of some kind suitable for the chosen medium. For example, data can modulate ...
, whereby vast increases in the rapidity of information growth would be made possible through automated
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
, potentially-lossless
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistic ...
digital technologies. Accordingly, '' Moore's law'', formulated around 1965, would calculate that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years.
By the early 1980s, along with improvements in computing power
In computing, computer performance is the amount of useful work accomplished by a computer system. Outside of specific contexts, computer performance is estimated in terms of accuracy, efficiency and speed of executing computer program instructio ...
, the proliferation of the smaller and less expensive personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
s allowed for immediate access to information
Access may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* ACCESS (Australia), an Australian youth network
* Access (credit card), a former credit card in the United Kingdom
* Access Co., a Japanese software company
* Access Healthcare, an Indian BPO s ...
and the ability to share and store it. Connectivity between computers within organizations enabled access to greater amounts of information.
Information storage and Kryder's law
 The world's technological capacity to store information grew from 2.6 (optimally compressed)
The world's technological capacity to store information grew from 2.6 (optimally compressed) exabyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
s (EB) in 1986 to 15.8 EB in 1993; over 54.5 EB in 2000; and to 295 (optimally compressed) EB in 2007. This is the informational equivalent to less than one 730- megabyte (MB) CD-ROM per person in 1986 (539 MB per person); roughly four CD-ROM per person in 1993; twelve CD-ROM per person in the year 2000; and almost sixty-one CD-ROM per person in 2007. It is estimated that the world's capacity to store information has reached 5 zettabyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
s in 2014, the informational equivalent of 4,500 stacks of printed books from the earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
to the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
.
The amount of digital data stored appears to be growing approximately exponentially
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including:
*Exponential function, also:
**Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above
*Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value
*Expo ...
, reminiscent of Moore's law. As such, ''Kryder's law'' prescribes that the amount of storage space available appears to be growing approximately exponentially. Roser, Max, and Hannah Ritchie. 2013.Technological Progress
." ''
Our World in Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a re ...
.'' Retrieved on 9 June 2020.
Information transmission
The world's technological capacity to receive information through one-way broadcast networks was 432exabyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
s of (optimally compressed) information in 1986; 715 (optimally compressed) exabytes in 1993; 1.2 (optimally compressed) zettabytes
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
in 2000; and 1.9 zettabytes in 2007, the information equivalent of 174 newspaper
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as p ...
s per person per day.
The world's effective capacity to exchange information through two-way
Two-way or Two Way may refer to:
* " 2-Way", single by rapper Lil' Romeo
* Two-way, Cincinnati chili topped on spaghetti
* "Two Way" (KT Tunstall and James Bay duet), 2016
See also
*
*
*
* 3-Way (disambiguation)
{{Disambiguation ...
telecommunication networks was 281 petabytes
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
of (optimally compressed) information in 1986; 471 petabytes in 1993; 2.2 (optimally compressed) exabytes in 2000; and 65 (optimally compressed) exabytes in 2007, the information equivalent of 6 newspapers per person per day. In the 1990s, the spread of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
caused a sudden leap in access to and ability to share information in businesses and homes globally. Technology was developing so quickly that a computer costing $3000 in 1997 would cost $2000 two years later and $1000 the following year.
Computation
The world's technological capacity to compute information with humanly guided general-purpose computers grew from 3.0 × 108 MIPS in 1986, to 4.4 × 109 MIPS in 1993; to 2.9 × 1011 MIPS in 2000; to 6.4 × 1012 MIPS in 2007. An article featured in thejournal
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to:
*Bullet journal, a method of personal organization
*Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period
*Daybook, also known as a general journal, a ...
''Trends in Ecology and Evolution
A fad or trend is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short period.
Fads are objects or behaviors that achieve short-l ...
'' in 2016 reported that:
Genetic information
Genetic code may also be considered part of theinformation revolution
The term information revolution describes current economic, social and technological trends beyond the Industrial Revolution.
Many competing terms have been proposed that focus on different aspects of this societal development.
The British polymat ...
. Now that sequencing has been computerized, genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
can be rendered and manipulated as data. This started with DNA sequencing, invented by Walter Gilbert and Allan Maxam in 1976-1977 and Frederick Sanger in 1977, grew steadily with the Human Genome Project, initially conceived by Gilbert and finally, the practical applications of sequencing, such as gene testing, after the discovery by Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics, Inc. is an American genetic testing and precision medicine company based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. Myriad employs a number of proprietary technologies that permit doctors and patients to understand the genetic bas ...
of the BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a ...
breast cancer gene mutation. Sequence data in Genbank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. It is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; a part ...
has grown from the 606 genome sequences registered in December 1982 to the 231 million genomes in August 2021. An additional 13 trillion incomplete sequences are registered in the Whole Genome Shotgun submission database as of August 2021. The information contained in these registered sequences has doubled every 18 months.
Different stage conceptualizations
During rare times in human history, there have been periods of innovation that have transformed human life. TheNeolithic Age
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
, the Scientific Age and the Industrial Age all, ultimately, induced discontinuous and irreversible changes in the economic, social and cultural elements of the daily life of most people. Traditionally, these epochs have taken place over hundreds, or in the case of the Neolithic Revolution, thousands of years, whereas the Information Age swept to all parts of the globe in just a few years. The reason for its rapid adoption is the rapidly advancing speed of information exchange.
Between 7,000 and 10,000 years ago during the Neolithic period, humans began to domesticate animals, began to farm grains and to replace stone tools with ones made of metal. These innovations allowed nomadic hunter-gatherers to settle down. Villages formed along the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
in China in 6,500 B.C., the Nile River region of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
(Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
) in 6,000 B.C. Cities emerged between 6,000 B.C. and 3,500 B.C. The development of written communication (cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
in Sumeria
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
and hieroglyphs
A hieroglyph (Greek for "sacred carvings") was a character of the ancient Egyptian writing system. Logographic scripts that are pictographic in form in a way reminiscent of ancient Egyptian are also sometimes called "hieroglyphs". In Neoplatonis ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
in 3,500 B.C. and writing in Egypt in 2,560 B.C. and in Minoa
Minoa was the name of several Bronze-Age port cities on the coasts of the Aegean islands Crete, Paros, Siphnos, Amorgos and Corfu in Greece, as well as the Italian island of Sicily.F. Schachermeyer (1964). ''Die Minoische Kultur des alten Kret ...
and China around 1,450 B.C.) enabled ideas to be preserved for extended periods to spread extensively. In all, Neolithic developments, augmented by writing as an information tool, laid the groundwork for the advent of civilization.
The Scientific Age began in the period between Galileo's 1543 proof that the planets orbit the sun and Newton's publication of the laws of motion and gravity in '' Principia'' in 1697. This age of discovery continued through the 18th Century, accelerated by widespread use of the moveable type printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in wh ...
by Johannes Gutenberg.
The Industrial Age began in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
in 1760 and continued into the mid-19th Century. It altered many aspects of life around the world. The invention of machines such as the mechanical textile weaver by Edmund Cartwrite, the rotating shaft steam engine by James Watt and the cotton gin by Eli Whitney, along with processes for mass manufacturing, came to serve the needs of a growing global population. The Industrial Age harnessed steam and waterpower to reduce the dependence on animal and human physical labor as the primary means of production. Thus, the core of the Industrial Revolution was the generation and distribution of energy from coal and water to produce steam and, later in the 20th Century, electricity.
The Information Age also requires electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
to power the global networks of computers that process and store data. However, what dramatically accelerated the pace of adoption of The Information Age, as compared to previous ones, was the speed by which knowledge could be transferred and pervaded the entire human family in a few short decades. This acceleration came about with the adoptions of a new form of power. Beginning in 1972, engineers devised ways to harness light to convey data through fiber optic cable. Today, light-based optical networking
Optical networking is a means of communication that uses signals encoded in light to transmit information in various types of telecommunications networks. These include limited range Local area network, local-area networks (LAN) or Wide area networ ...
systems at the heart of telecom networks and the Internet span the globe and carry most of the information traffic to and from users and data storage systems.
 There are different conceptualizations of the Information Age. Some focus on the evolution of information over the ages, distinguishing between the Primary Information Age and the Secondary Information Age. Information in the Primary Information Age was handled by
There are different conceptualizations of the Information Age. Some focus on the evolution of information over the ages, distinguishing between the Primary Information Age and the Secondary Information Age. Information in the Primary Information Age was handled by newspapers
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports ...
, radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
and television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ...
. The Secondary Information Age was developed by the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
, satellite television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna comm ...
s and mobile phones. The Tertiary Information Age was emerged by media of the Primary Information Age interconnected with media of the Secondary Information Age as presently experienced.
 Others classify it in terms of the well-established Schumpeterian long waves or Kondratiev waves. Here authors distinguish three different long-term meta paradigms, each with different long waves. The first focused on the transformation of material, including
Others classify it in terms of the well-established Schumpeterian long waves or Kondratiev waves. Here authors distinguish three different long-term meta paradigms, each with different long waves. The first focused on the transformation of material, including stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
, bronze, and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
. The second, often referred to as industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, was dedicated to the transformation of energy, including water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
, steam, electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
, and combustion power. Finally, the most recent metaparadigm aims at transforming information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random ...
. It started out with the proliferation of communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
and stored data
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, Phonograph record, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA a ...
and has now entered the age of algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
, which aims at creating automated processes to convert the existing information into actionable knowledge.
Economics
Eventually,Information and communication technology
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications ( telephone lines and wireless signals) and computer ...
(ICT)—i.e. computers, computerized machinery, fiber optics, communication satellites
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
, the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
, and other ICT tools—became a significant part of the world economy, as the development of optical networking
Optical networking is a means of communication that uses signals encoded in light to transmit information in various types of telecommunications networks. These include limited range Local area network, local-area networks (LAN) or Wide area networ ...
and microcomputers greatly changed many businesses and industries. Nicholas Negroponte
Nicholas Negroponte (born December 1, 1943) is a Greek American architect. He is the founder and chairman Emeritus of Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Media Lab, and also founded the One Laptop per Child Association (OLPC). Negroponte ...
captured the essence of these changes in his 1995 book, '' Being Digital,'' in which he discusses the similarities and differences between products made of atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s and products made of bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represente ...
s.
Jobs and income distribution
The Information Age has affected theworkforce
The workforce or labour force is a concept referring to the pool of human beings either in employment or in unemployment. It is generally used to describe those working for a single company or industry, but can also apply to a geographic reg ...
in several ways, such as compelling workers to compete in a global job market. One of the most evident concerns is the replacement of human labor by computers that can do their jobs faster and more effectively, thus creating a situation in which individuals who perform tasks that can easily be automated
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
are forced to find employment where their labor is not as disposable. This especially creates issue for those in industrial cities
An industrial city or industrial town is a town or city in which the municipal economy, at least historically, is centered around industry, with important factories or other production facilities in the town. It has been part of most countries' i ...
, where solutions typically involve lowering working time
Working(laboring) time is the period of time that a person spends at paid labor. Unpaid labor such as personal housework or caring for children or pets is not considered part of the working week.
Many countries regulate the work week by law, ...
, which is often highly resisted. Thus, individuals who lose their jobs may be pressed to move up into joining "mind workers" (e.g. engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limit ...
s, doctors, lawyers, teachers
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching.
''Informally'' the role of teacher may be taken on by anyone (e.g. wh ...
, professors
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an academic rank at universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who professes". Professors ...
, scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosoph ...
s, executives, journalist
A journalist is an individual that collects/gathers information in form of text, audio, or pictures, processes them into a news-worthy form, and disseminates it to the public. The act or process mainly done by the journalist is called journalis ...
s, consultants), who are able to compete successfully in the world market and receive (relatively) high wages.
Along with automation, jobs traditionally associated with the middle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Com ...
(e.g. assembly line
An assembly line is a manufacturing process (often called a ''progressive assembly'') in which parts (usually interchangeable parts) are added as the semi-finished assembly moves from workstation to workstation where the parts are added in se ...
, data processing, management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a Government agency, government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includ ...
, and supervision) have also begun to disappear as result of outsourcing.McGowan, Robert. 1991. "The Work of Nations by Robert Reich" (book review). '' Human Resource Management'' 30(4):535–38. . . Unable to compete with those in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, production
Production may refer to:
Economics and business
* Production (economics)
* Production, the act of manufacturing goods
* Production, in the outline of industrial organization, the act of making products (goods and services)
* Production as a stati ...
and service workers in post-industrial (i.e. developed) societies either lose their jobs through outsourcing, accept wage
A wage is payment made by an employer to an employee for work done in a specific period of time. Some examples of wage payments include compensatory payments such as ''minimum wage'', '' prevailing wage'', and ''yearly bonuses,'' and remune ...
cuts, or settle for low-skill, low-wage service jobs. In the past, the economic fate of individuals would be tied to that of their nation's. For example, workers in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
were once well paid in comparison to those in other countries. With the advent of the Information Age and improvements in communication, this is no longer the case, as workers must now compete in a global job market, whereby wages are less dependent on the success or failure of individual economies.
In effectuating a globalized workforce, the internet has just as well allowed for increased opportunity in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, making it possible for workers in such places to provide in-person services, therefore competing directly with their counterparts in other nations. This competitive advantage
In business, a competitive advantage is an attribute that allows an organization to outperform its competitors.
A competitive advantage may include access to natural resources, such as high-grade ores or a low-cost power source, highly skilled ...
translates into increased opportunities and higher wages.
Automation, productivity, and job gain
The Information Age has affected the workforce in thatautomation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
and computerization have resulted in higher productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
coupled with net job loss in manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
. In the United States, for example, from January 1972 to August 2010, the number of people employed in manufacturing jobs fell from 17,500,000 to 11,500,000 while manufacturing value rose 270%.
Although it initially appeared that job loss in the industrial sector might be partially offset by the rapid growth of jobs in information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of Data (computing), data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information te ...
, the recession of March 2001 foreshadowed a sharp drop in the number of jobs in the sector. This pattern of decrease in jobs would continue until 2003, and data has shown that, overall, technology creates more jobs than it destroys even in the short run.
Information-intensive industry
Industry has become more information-intensive while lesslabor
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the la ...
- and capital-intensive. This has left important implications for the workforce
The workforce or labour force is a concept referring to the pool of human beings either in employment or in unemployment. It is generally used to describe those working for a single company or industry, but can also apply to a geographic reg ...
, as workers have become increasingly productive
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
as the value of their labor decreases. For the system of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
itself, the value of labor decreases, the value of capital increases.
In the classical model, investments in human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
and financial capital
Financial capital (also simply known as capital or equity in finance, accounting and economics) is any economic resource measured in terms of money used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy what they need to make their products or to provi ...
are important predictors of the performance of a new venture
Venture may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
*The Ventures, an American instrumental rock band formed in 1958
*"A Venture", 1971 song by the band Yes
*''Venture'', a 2010 EP by AJR
Games
* ''Venture'' (video game), a 1981 arcade gam ...
. However, as demonstrated by Mark Zuckerberg and Facebook
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin Mosk ...
, it now seems possible for a group of relatively inexperienced people with limited capital to succeed on a large scale.
Innovations
 The Information Age was enabled by technology developed in the Digital Revolution, which was itself enabled by building on the developments of the Technological Revolution.
The Information Age was enabled by technology developed in the Digital Revolution, which was itself enabled by building on the developments of the Technological Revolution.
Transistors
The onset of the Information Age can be associated with the development oftransistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
technology. The concept of a field-effect transistor was first theorized by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925. The first practical transistor was the point-contact transistor, invented by the engineers Walter Houser Brattain and John Bardeen while working for William Shockley at Bell Labs in 1947. This was a breakthrough that laid the foundations for modern technology. Shockley's research team also invented the bipolar junction transistor in 1952. The most widely used type of transistor is the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), invented by Mohamed M. Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in 1960. The complementary MOS (CMOS) fabrication process was developed by Frank Wanlass and Chih-Tang Sah in 1963.
Computers
Before the advent of electronics, mechanical computers, like the Analytical Engine in 1837, were designed to provide routine mathematical calculation and simple decision-making capabilities. Military needs during World War II drove development of the first electronic computers, based on vacuum tubes, including the Z3 (computer), Z3, the Atanasoff–Berry Computer, Colossus computer, and ENIAC. The invention of the transistor enabled the era of mainframe computers (1950s–1970s), typified by the IBM 360. These large, History of computing hardware, room-sized computers provided data calculation and Data manipulation language, manipulation that was much faster than humanly possible, but were expensive to buy and maintain, so were initially limited to a few scientific institutions, large corporations, and government agencies. The germanium integrated circuit (IC) was invented by Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments in 1958. The silicon integrated circuit was then invented in 1959 by Robert Noyce at Fairchild Semiconductor, using the planar process developed by Jean Hoerni, who was in turn building on Mohamed Atalla's silicon surface passivation method developed at Bell Labs in 1957. Following the invention of the MOS transistor by Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in 1959, the MOSFET, MOS integrated circuit was developed by Fred Heiman and Steven Hofstein at RCA in 1962. The silicon-gate MOS IC was later developed by Federico Faggin at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1968. With the advent of the MOS transistor and the MOS IC, transistor technology Moore's Law, rapidly improved, and the ratio of computing power to size increased dramatically, giving direct access to computers to ever smaller groups of people. The first commercial single-chip microprocessor launched in 1971, the Intel 4004, which was developed by Federico Faggin using his silicon-gate MOS IC technology, along with Marcian Hoff, Masatoshi Shima and Stan Mazor. Along with electronic arcade machines and home video game consoles pioneered by Nolan Bushnell in the 1970s, the development ofpersonal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
s like the Commodore PET and Apple II (both in 1977) gave individuals access to the computer. But data sharing between individual computers was either non-existent or largely sneaker net, manual, at first using punched cards and magnetic tape, and later floppy disks.
Data
The first developments for storing data were initially based on photographs, starting with microphotography in 1851 and thenmicroform
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the original document size. ...
in the 1920s, with the ability to store documents on film, making them much more compact. Early information theory and Hamming codes were developed about 1950, but awaited technical innovations in data transmission and storage to be put to full use.
Magnetic-core memory was developed from the research of Frederick W. Viehe in 1947 and An Wang at Harvard University in 1949. With the advent of the MOS transistor, MOS semiconductor memory was developed by John Schmidt at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1964. In 1967, Dawon Kahng and Simon Sze at Bell Labs described in 1967 how the floating gate of an MOS semiconductor device could be used for the cell of a reprogrammable ROM. Following the invention of flash memory by Fujio Masuoka at Toshiba in 1980, Toshiba commercialized NAND flash memory in 1987.
Copper wire cables transmitting digital data connected computer terminals and Peripheral, peripherals to mainframes, and special message-sharing systems leading to email, were first developed in the 1960s. Independent computer-to-computer networking began with ARPANET in 1969. This expanded to become the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
(coined in 1974). Access to the Internet improved with the invention of the World Wide Web in 1991. The capacity expansion from Wavelength-division multiplexing, dense wave division multiplexing, optical amplification and optical networking
Optical networking is a means of communication that uses signals encoded in light to transmit information in various types of telecommunications networks. These include limited range Local area network, local-area networks (LAN) or Wide area networ ...
in the mid-1990s led to record data transfer rates. By 2018, optical networks routinely delivered 30.4 terabits/s over a fiber optic pair, the data equivalent of 1.2 million simultaneous 4K HD video streams.
MOSFET scaling, the rapid miniaturization of MOSFETs at a rate predicted by Moore's law, led to computers becoming smaller and more powerful, to the point where they could be carried. During the 1980s1990s, laptops were developed as a form of portable computer, and personal digital assistants (PDAs) could be used while standing or walking. Pagers, widely used by the 1980s, were largely replaced by mobile phones beginning in the late 1990s, providing mobile networking features to some computers. Now commonplace, this technology is extended to digital cameras and other wearable devices. Starting in the late 1990s, Tablet computer, tablets and then smartphones combined and extended these abilities of computing, mobility, and information sharing. Metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) image sensors, which first began appearing in the late 1960s, led to the transition from analog to digital imaging
Digital imaging or digital image acquisition is the creation of a digital representation of the visual characteristics of an object, such as a physical scene or the interior structure of an object. The term is often assumed to imply or include t ...
, and from analog to digital cameras, during the 1980s–1990s. The most common image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) sensor and the CMOS (complementary MOS) active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor).
Electronic paper, which has origins in the 1970s, allows digital information to appear as paper documents.
Personal computers
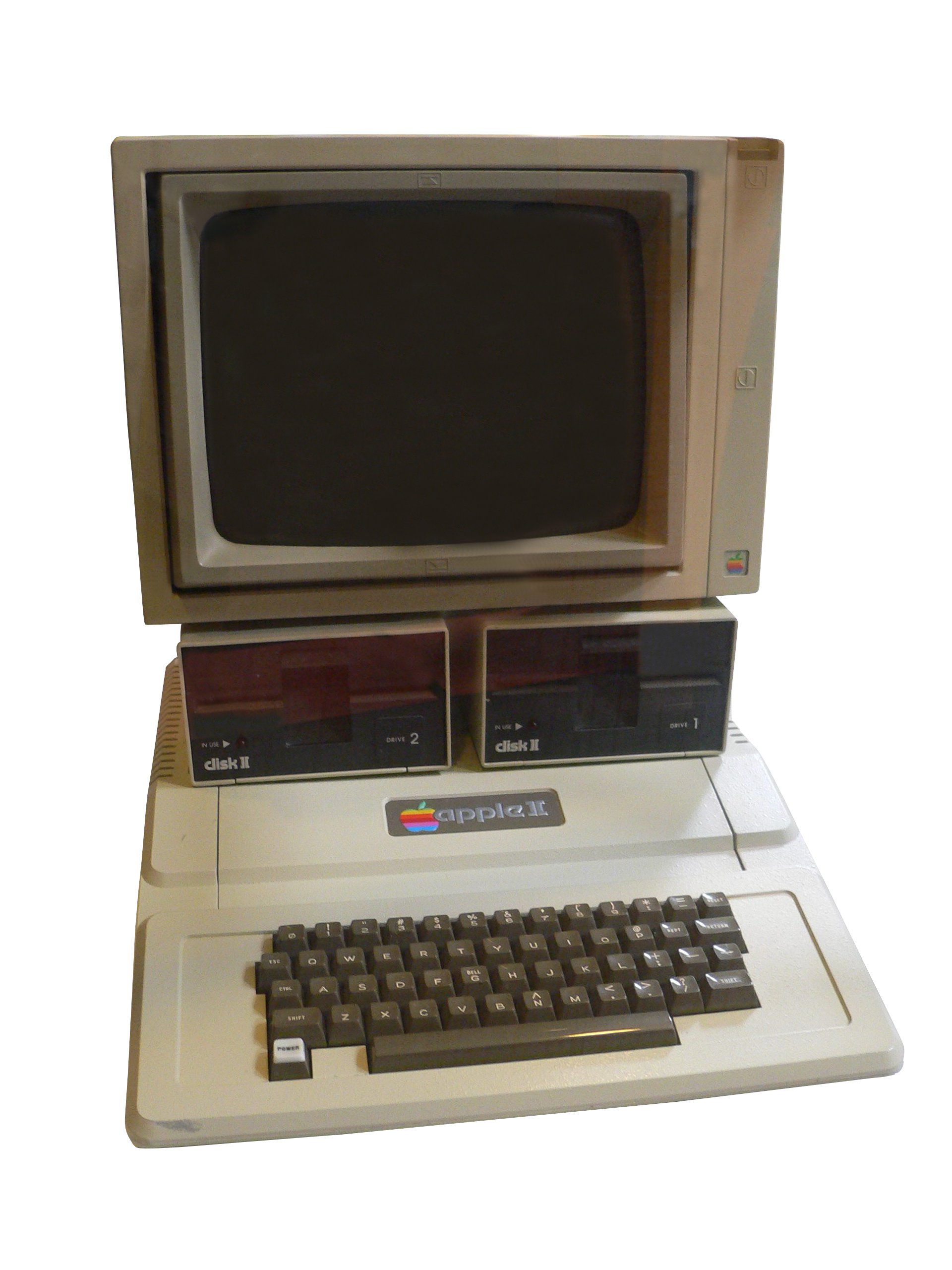
By 1976, there were several firms racing to introduce the first truly successful commercial personal computers. Three machines, the Apple II family, Apple II, PET 2001 and TRS-80 were all released in 1977, becoming the most popular by late 1978. ''Byte'' magazine later referred to Commodore, Apple, and Tandy as the "1977 Trinity". Also in 1977, Sord Computer Corporation released the Sord M200 Smart Home Computer in Japan.Apple II
 Steve Wozniak (known as "Woz"), a regular visitor to Homebrew Computer Club meetings, designed the single-board Apple I computer and first demonstrated it there. With specifications in hand and an order for 100 machines at US$500 each from Paul Terrell, the Byte Shop, Woz and his friend Steve Jobs founded Apple Computer.
About 200 of the machines sold before the company announced the Apple II as a complete computer. It had color graphics, a full QWERTY keyboard, and internal slots for expansion, which were mounted in a high quality streamlined plastic case. The monitor and I/O devices were sold separately. The original Apple II operating system was only the built-in BASIC interpreter contained in ROM. Apple DOS was added to support the diskette drive; the last version was "Apple DOS 3.3".
Its higher price and lack of floating point BASIC, along with a lack of retail distribution sites, caused it to lag in sales behind the other Trinity machines until 1979, when it surpassed the PET. It was again pushed into 4th place when Atari introduced its popular Atari 8-bit systems.
Despite slow initial sales, the Apple II's lifetime was about eight years longer than other machines, and so accumulated the highest total sales. By 1985 2.1 million had sold and more than 4 million Apple II's were shipped by the end of its production in 1993.
Steve Wozniak (known as "Woz"), a regular visitor to Homebrew Computer Club meetings, designed the single-board Apple I computer and first demonstrated it there. With specifications in hand and an order for 100 machines at US$500 each from Paul Terrell, the Byte Shop, Woz and his friend Steve Jobs founded Apple Computer.
About 200 of the machines sold before the company announced the Apple II as a complete computer. It had color graphics, a full QWERTY keyboard, and internal slots for expansion, which were mounted in a high quality streamlined plastic case. The monitor and I/O devices were sold separately. The original Apple II operating system was only the built-in BASIC interpreter contained in ROM. Apple DOS was added to support the diskette drive; the last version was "Apple DOS 3.3".
Its higher price and lack of floating point BASIC, along with a lack of retail distribution sites, caused it to lag in sales behind the other Trinity machines until 1979, when it surpassed the PET. It was again pushed into 4th place when Atari introduced its popular Atari 8-bit systems.
Despite slow initial sales, the Apple II's lifetime was about eight years longer than other machines, and so accumulated the highest total sales. By 1985 2.1 million had sold and more than 4 million Apple II's were shipped by the end of its production in 1993.
Optical networking
Optical communication plays a crucial role in Communication network, communication networks. Optical communication provides the transmission backbone for the telecommunications and computer networks that underlie theInternet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
, the foundation for the Digital Revolution and Information Age.
The two core technologies are the optical fiber and light amplification (the optical amplifier). In 1953, Bram van Heel demonstrated image transmission through bundles of Optical fiber, optical fibers with a transparent cladding. The same year, Harold Hopkins (physicist), Harold Hopkins and Narinder Singh Kapany at Imperial College succeeded in making image-transmitting bundles with over 10,000 optical fibers, and subsequently achieved image transmission through a 75 cm long bundle which combined several thousand fibers.
Gordon Gould invented the optical amplifier and the laser, and also established the first optical telecommunications company, Optelecom, to design communication systems. The firm was a co-founder in Ciena Corp., the venture that popularized the optical amplifier with the introduction of the first Wavelength-division multiplexing, dense wave division multiplexing system. This massive scale communication technology has emerged as the common basis of all telecommunication networks and, thus, a foundation of the Information Age.
Economy, society and culture
Manuel Castells captures the significance of the Information Age in ''The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture'' when he writes of our global interdependence and the new relationships between economy, state and society, what he calls "a new society-in-the-making." He cautions that just because humans have dominated the material world, does not mean that the Information Age is the end of history:See also
* Attention economy * Attention inequality * Big data * Cognitive-cultural economy * Computer crime * Cyberterrorism * Cyberwarfare * Datamation – first print magazine dedicated solely to covering information technology * Digital dark age * Digital detox * Digital divide * Digital transformation * Digital world * Imagination age, the hypothesized successor of the information age: a period in which creativity and imagination become the primary creators of economic value * Indigo Era * Information explosion * Information revolution * Information society * Internet governance * Netocracy * Social Age * Technological determinism * Telecommunications * Zettabyte Era * The Hacker Ethic and the Spirit of the Information Age * Information and communication technologies for environmental sustainabilityReferences
Further reading
* Oliver Stengel et al. (2017). ''Digitalzeitalter - Digitalgesellschaft'', Springer * Edward Mendelson, Mendelson, Edward (June 2016).In the Depths of the Digital Age
'' The New York Review of Books * Bollacker, Kurt D. (2010)
Avoiding a Digital Dark Age
', American Scientist, March–April 2010, Volume 98, Number 2, p. 106ff * Manuel Castells, Castells, Manuel. (1996–98). ''The Information Age: Economy, Society and Culture'', 3 vols. Oxford: Blackwell. * Gelbstein, E. (2006) ''Crossing the Executive Digital Divide''.
External links
Articles on the impact of the Information Age on business
nbsp;– at ''Information Age'' magazine
Beyond the Information Age
by Dave Ulmer
Information Age Anthology Vol I
by Alberts and Papp (CCRP, 1997) (PDF)
Information Age Anthology Vol II
by Alberts and Papp (CCRP, 2000) (PDF)
Information Age Anthology Vol III
by Alberts and Papp (CCRP, 2001) (PDF)
Understanding Information Age Warfare
by Alberts et al. (CCRP, 2001) (PDF)
Information Age Transformation
by Alberts (CCRP, 2002) (PDF)
The Unintended Consequences of Information Age Technologies
by Alberts (CCRP, 1996) (PDF)
History & Discussion of the Information Age
Science Museum - Information Age
{{portal bar, Internet, Technology Information Age, Digital media Digital divide Contemporary history Historical eras Postmodernism Cultural trends