Industry In Bangladesh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The economy of Bangladesh is a major economy of South Asia and a
—
—Siddiqi, Dina M. “Miracle Worker or Womanmachine? Tracking (Trans)National Realities in Bangladeshi Factories.”
—Paksha Paul, B. (2010), "Does corruption foster growth in Bangladesh?", International Journal of Development Issues, Vol. 9 No. 3, pp. 246-262.
—Chowdhury, M.S. (2007), "Overcoming entrepreneurship development constraints: the case of Bangladesh", Journal of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the Global Economy, Vol. 1 No. 3, pp. 240-251.
—Bashar, Omar K. M. R., and Habibullah Khan. “Liberalisation and Growth in Bangladesh: An Empirical Investigation.” The Bangladesh Development Studies, vol. 32, no. 1,
—Ahamed, Md Mostak. “Market Structure and Performance of Bangladesh Banking Industry: A Panel Data Analysis.” The Bangladesh Development Studies, vol. 35, no. 3,
—Abdin, MD. Joynal, The Nature and Evolution of Capitalism in Bangladesh (March 16, 2016). Abdin, M.J. (2016). The Nature and Evolution of Capitalism in Bangladesh, “The Nature and Evolution of Capitalism in All World”, March 16, 2016., . . As the second-largest economy in South Asia,
/ref> Between 1947 and 1971,



 Punch-marked coins are the earliest form of currency found in Bangladesh, dating back to the
Punch-marked coins are the earliest form of currency found in Bangladesh, dating back to the
''A Country Study: Bangladesh''
(James Heitzman and Robert Worden, editors).
About the Country Studies / Area Handbooks Program: Country Studies – Federal Research Division, Library of Congress
/ref> The Ganges Delta provided advantages of a mild, almost tropical climate, fertile soil, ample water, and an abundance of fish, wildlife, and fruit. Living standards for the elite were comparatively better than other parts of the
About the Country Studies / Area Handbooks Program: Country Studies – Federal Research Division, Library of Congress
/ref> There were critical shortages of essential food grains and other staples because of wartime disruptions. External markets for jute had been lost because of the instability of supply and the increasing popularity of synthetic substitutes. Foreign exchange resources were minuscule, and the banking and monetary systems were unreliable. Although Bangladesh had a large work force, the vast reserves of under trained and underpaid workers were largely illiterate, unskilled, and underemployed. Commercially exploitable industrial resources, except for natural gas, were lacking. Inflation, especially for essential consumer goods, ran between 300 and 400 percent. The war of independence had crippled the transportation system. Hundreds of road and railroad bridges had been destroyed or damaged, and rolling stock was inadequate and in poor repair. The new country was still recovering from a severe cyclone that hit the area in 1970 and caused 250,000 deaths. India came forward immediately with critically measured economic assistance in the first months after Bangladesh achieved independence from Pakistan. Between December 1971 and January 1972, India committed US$232 million in aid to Bangladesh from the politico-economic aid India received from the US and From 1991 to 1993, the government engaged in an
From 1991 to 1993, the government engaged in an  In the last decade, poverty dropped by around one third with significant improvements in the
In the last decade, poverty dropped by around one third with significant improvements in the
developing
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
.
——
—Siddiqi, Dina M. “Miracle Worker or Womanmachine? Tracking (Trans)National Realities in Bangladeshi Factories.”
Economic and Political Weekly
The ''Economic and Political Weekly'' (''EPW'') is a weekly peer-reviewed academic journal covering all social sciences, and is published by the Sameeksha Trust. In January 2018, academic Gopal Guru was named the new Editor of the journal. Guru wil ...
, vol. 35, no. 21/22, Economic and Political Weekly
The ''Economic and Political Weekly'' (''EPW'') is a weekly peer-reviewed academic journal covering all social sciences, and is published by the Sameeksha Trust. In January 2018, academic Gopal Guru was named the new Editor of the journal. Guru wil ...
, 2000, pp. L11–17, .—Paksha Paul, B. (2010), "Does corruption foster growth in Bangladesh?", International Journal of Development Issues, Vol. 9 No. 3, pp. 246-262.
—Chowdhury, M.S. (2007), "Overcoming entrepreneurship development constraints: the case of Bangladesh", Journal of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the Global Economy, Vol. 1 No. 3, pp. 240-251.
—Bashar, Omar K. M. R., and Habibullah Khan. “Liberalisation and Growth in Bangladesh: An Empirical Investigation.” The Bangladesh Development Studies, vol. 32, no. 1,
Bangladesh Institute of Development Studies
The Bangladesh Institute of Development Studies (BIDS) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ উন্নয়ন গবেষণা প্রতিষ্ঠান (বিআইডিএস)) is an autonomous multi-disciplinary public research organi ...
, 2009, pp. 61–76, .—Ahamed, Md Mostak. “Market Structure and Performance of Bangladesh Banking Industry: A Panel Data Analysis.” The Bangladesh Development Studies, vol. 35, no. 3,
Bangladesh Institute of Development Studies
The Bangladesh Institute of Development Studies (BIDS) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ উন্নয়ন গবেষণা প্রতিষ্ঠান (বিআইডিএস)) is an autonomous multi-disciplinary public research organi ...
, 2012, pp. 1–18, .—Abdin, MD. Joynal, The Nature and Evolution of Capitalism in Bangladesh (March 16, 2016). Abdin, M.J. (2016). The Nature and Evolution of Capitalism in Bangladesh, “The Nature and Evolution of Capitalism in All World”, March 16, 2016., . . As the second-largest economy in South Asia,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
's economy is the 35th largest in the world in nominal terms, and 25th largest by purchasing power parity. Bangladesh is seen by various financial institutions as one of the Next Eleven, an emerging market, a middle income economy, and a frontier market A frontier market is a term for a type of developing country's market economy which is more developed than a least developing countries , least developed country's, but too small, risky, or illiquid to be generally classified as an emerging market ...
. Bangladesh is a member of the South Asian Free Trade Area
The South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) is a 2004 agreement that created a free-trade area of 1.6 billion people in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka with the vision of increasing economic cooper ...
and the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
. In fiscal year 2021–2022, Bangladesh registered a GDP growth rate of 7.2% after the global pandemic. Bangladesh is one of the fastest growing economies
This article includes a lists of countries and dependent territories sorted by their real gross domestic product growth rate; the rate of growth of the value of all final goods and services produced within a state in a given year. The statistics ...
in the world.
Industrialisation in Bangladesh received a strong impetus after the partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
due to labour reforms and new industries.The Bangladesh Economy Navigating the Turning Point/ref> Between 1947 and 1971,
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
generated between 70% and 50% of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
's exports. After independence in 1971, Bangladesh embarked on economic reforms in the late 1970s which promoted free markets and foreign direct investment. By the 1990s, the country had a booming ready-made garments industry. Remittances
A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland. Money sent home by migrants competes with ...
from the large Bangladeshi diaspora became a vital source of foreign exchange reserves. Agriculture in Bangladesh
Agriculture is the largest employment sector in Bangladesh, making up 14.2 percent of Bangladesh's GDP in 2017 and employing about 42.7 percent of the workforce. The performance of this sector has an overwhelming impact on major macroeconomic ...
is supported by government subsidies and ensures self-sufficiency in food production. Bangladesh has pursued export-oriented industrialisation.
Bangladesh experienced robust growth after the pandemic with macroeconomic stability, improvements in infrastructure, a growing digital economy, and growing trade flows. Tax collection remains very low, with tax revenues accounting for only 7.7% of GDP. Bangladesh's banking sector has a large amount of non-performing loans or loan defaults, which have caused a lot of concern. The private sector makes up 80% of GDP. The Dhaka Stock Exchange and Chittagong Stock Exchange are the two stock markets of the country. Most Bangladeshi businesses are privately owned small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) which make up 90% of all businesses.
Economic history




 Punch-marked coins are the earliest form of currency found in Bangladesh, dating back to the
Punch-marked coins are the earliest form of currency found in Bangladesh, dating back to the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
and the first millennium BCE. 1st century Roman coins with images of Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
have been excavated in Bangladesh and point to trade links with the Roman world. The Wari-Bateshwar ruins
The Wari-Bateshwar (Bengali: উয়ারী-বটেশ্বর,''Uari-Bôṭeshshor'') ruins in Narsingdi, Dhaka Division, Bangladesh is one of the earliest urban archaeological sites in Bangladesh. Excavation in the site unearthed a ...
are believed to be the emporium (trading center) of Sounagoura mentioned by Roman geographer Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
. The eastern segment of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
was a historically prosperous region.Lawrence B. Lesser. "Historical Perspective"''A Country Study: Bangladesh''
(James Heitzman and Robert Worden, editors).
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The library is ...
Federal Research Division
The Federal Research Division (FRD) is the research and analysis unit of the United States Library of Congress.
The Federal Research Division provides directed research and analysis on domestic and international subjects to agencies of the Unite ...
(September 1988). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.About the Country Studies / Area Handbooks Program: Country Studies – Federal Research Division, Library of Congress
/ref> The Ganges Delta provided advantages of a mild, almost tropical climate, fertile soil, ample water, and an abundance of fish, wildlife, and fruit. Living standards for the elite were comparatively better than other parts of the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. Trade routes like the Grand Trunk Road, Tea Horse Road
The Tea Horse Road or ''chamadao'' (), now generally referred to as the Ancient Tea Horse Road or ''chamagudao'' () was a network of caravan paths winding through the mountains of Sichuan, Yunnan and Tibet in Southwest China. This was also a tea t ...
and Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
connected the region to the wider neighborhood. Between 400 and 1200, the region had a well-developed economy in terms of land ownership, agriculture, livestock, shipping, trade, commerce, taxation, and banking. Muslim trade with Bengal increased after the fall of the Sasanian Empire and the Arab takeover of Persian trade routes. Much of this trade occurred east of the Meghna River
The Meghna River ( bn, মেঘনা নদী) is one of the major rivers in Bangladesh, one of the three that form the Ganges Delta, the largest delta on earth, which fans out to the Bay of Bengal. A part of the Surma-Meghna River System, ...
in southeastern Bengal. After 1204, Muslim conquerors inherited the gold and silver reserves of pre-Islamic kingdoms.
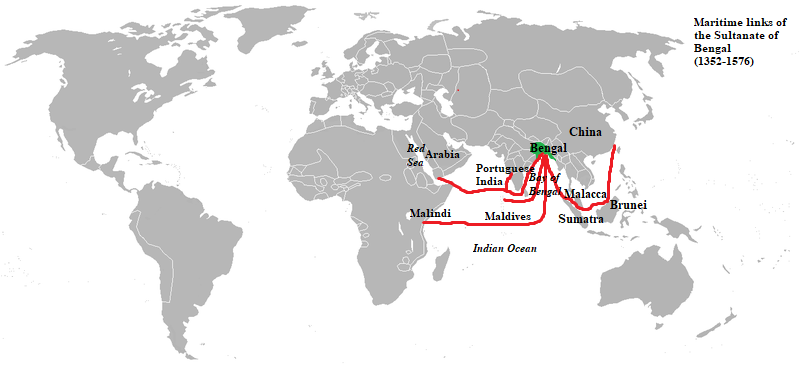
The Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominan ...
presided over a mercantile empire of its own. Bengali ships were the largest ships in the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
and other parts of the Indian Ocean trade network. Ship-owning merchants often acted as royal envoys of the Sultan. A large number of wealthy Bengali merchants and shipowners lived in Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
. A vessel from Bengal transported embassies from Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Bengal and the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
operated the largest shell currency
Shell money is a medium of trade, exchange similar to coin money and other forms of commodity money, and was once commonly used in many parts of the world. Shell money usually consisted of whole or partial sea shells, often worked into beads or o ...
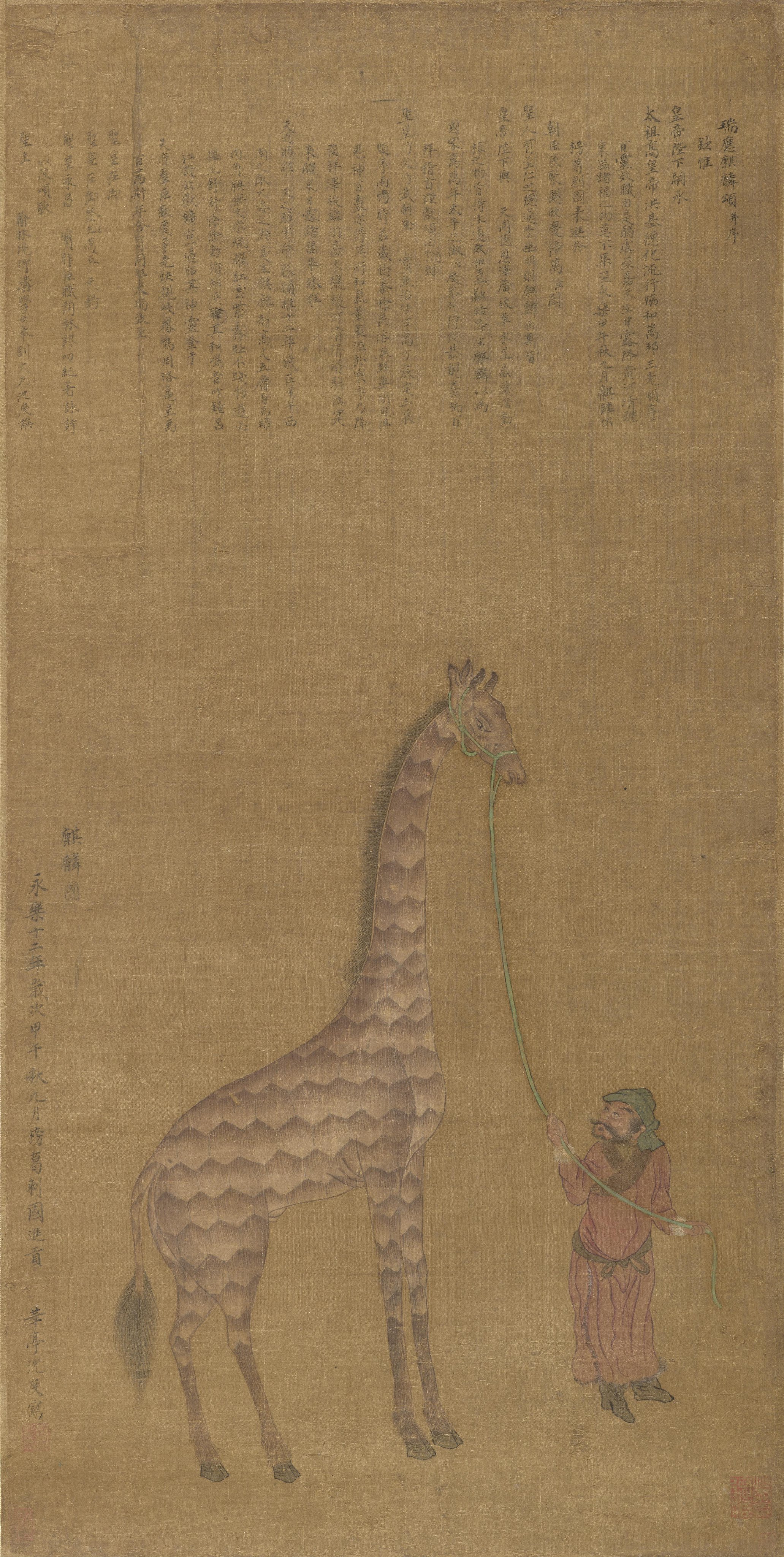
network in history. A Masai giraffe from Malindi in Africa was shipped to Bengal and later gifted to the Emperor of China as a gift from the Sultan of Bengal. The rulers of Arakan looked to Bengal for economic, political and cultural capital. The Sultan of Bengal financed projects in the Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provin ...
region of Arabia.
Under Mughal rule, Bengal operated as a centre of the worldwide muslin
Muslin () is a cotton fabric of plain weave. It is made in a wide range of weights from delicate sheers to coarse sheeting. It gets its name from the city of Mosul, Iraq, where it was first manufactured.
Muslin of uncommonly delicate handsp ...
, silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
and pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
trades. Domestically, much of India depended on Bengali products such as rice, silks and cotton textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
s. Overseas, Europeans depended on Bengali products such as cotton textiles, silks and opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
; Bengal accounted for 40% of Dutch imports from Asia, for example. Bengal shipped saltpeter to Europe, sold opium in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, exported raw silk to Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, and produced cotton and silk textiles for export to Europe, Indonesia and Japan. Real wages
Real wages are wages adjusted for inflation, or, equivalently, wages in terms of the amount of goods and services that can be bought. This term is used in contrast to nominal wages or unadjusted wages.
Because it has been adjusted to account f ...
and living standards
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
in 18th-century Bengal were comparable to Britain, which in turn had the highest living standards in Europe.
During the Mughal era, the most important centre of cotton production was Bengal, particularly around its capital city of Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
, leading to muslin being called "daka" in distant markets such as Central Asia. Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
agriculturalists rapidly learned techniques of mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 identif ...
cultivation and sericulture
Sericulture, or silk farming, is the cultivation of silkworms to produce silk. Although there are several commercial species of silkworms, ''Bombyx mori'' (the caterpillar of the domestic silkmoth) is the most widely used and intensively studie ...
, establishing Bengal as a major silk-producing region of the world. Bengal accounted for more than 50% of textiles and around 80% of silks imported by the Dutch from Asia, for example.
Bengal also had a large shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
industry. Indrajit Ray estimates shipbuilding output of Bengal during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries at 223,250tons annually, compared with 23,061tons produced in nineteen colonies in North America from 1769 to 1771. He also assesses ship repairing as very advanced in Bengal. Bengali shipbuilding was advanced compared to European shipbuilding at the time. An important innovation in shipbuilding was the introduction of a flushed deck design in Bengal rice ships, resulting in hulls that were stronger and less prone to leak than the structurally weak hulls of traditional European ships built with a stepped deck design. The English East India Company later duplicated the flushed-deck and hull designs of Bengal rice ships in the 1760s, leading to significant improvements in seaworthiness and navigation for European ships during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. Among the oldest businesses from the pre-colonial and Mughal periods, the biryani restaurant Fakhruddin's traces its history to the era of the Nawabs of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
.
The British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
, that took complete control of Bengal in 1793 by abolishing Nizamat (local rule), chose to develop Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
, now the capital city of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
, as their commercial and administrative center for the Company-held territories in South Asia. The development of East Bengal was thereafter limited to agriculture. The administrative infrastructure of the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries focused on East Bengal's function as a primarily agricultural producer—chiefly of rice, tea, teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panicl ...
, cotton, sugar cane and jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny bast fiber that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', which is in the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is ''Corchorus olit ...
— for processors and traders in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
. British rule saw the introduction of railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
. The Hardinge Bridge was built to carry trains across the Padma River. In the early 20th century, Eastern Bengal and Assam was established in the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
to promote jobs, education and investment in East Bengal. In 1928, the Port of Chittagong was declared to be a "Major Port" of British India. East Bengal extended its rice economy into Arakan Division
Arakan Division ( my, ရခိုင်တိုင်း) was an administrative division of the British Empire, covering modern-day Rakhine State, Myanmar, which was the historical region of Arakan. It bordered the Bengal Presidency of British ...
in British Burma
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. The river and sea ports of East Bengal, including Goalundo Ghat
Goalundo Ghat (also spelled Goalanda and Goalondo; bn, গোয়ালন্দঘাট) is a small town and pourasabha in Goalandaghat Upazila, Rajbari District, Dhaka Division, Bangladesh, South Asia. There are two railway stops one a ...
, the Port of Dhaka
The Port of Dhaka is a major river port on the Buriganga River in Dhaka, the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. The port is located in the southern part of the city. It is Bangladesh's busiest port in terms of passenger traffic. The port has s ...
, the Port of Narayanganj, and the Port of Chittagong became entrepots for trade between Bengal, Assam and Burma. Some of Bangladesh's venerable and oldest companies were born in British Bengal, including A K Khan & Company
A K Khan & Co. Ltd. is one of the oldest Bangladeshi conglomerates headquartered in Chittagong. It was established in 1945 by Abul Kashem Khan during the Second World War.
Projects
The company is planning to setup a tyre plant under joint collab ...
, M. M. Ispahani Limited
M.M. Ispahani Limited ( bn, এম এম ইস্পাহানি লিমিটেড), also known as The Ispahani Group, is a Bangladeshi conglomerate headquartered in Chittagong. Founded in 1820, it is the oldest company in Bangladesh and ...
, James Finlay Bangladesh, and Anwar Group of Industries
Anwar Group of Industries is one of the largest and oldest Bangladeshi conglomerates company consists of 18 subsidiaries that are servicing consumer goods, steels, cement, textile, finance and automotive industry. Manwar Hossain is the Chairman o ...
.
The partition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
changed the economic geography of the region. The Pakistani government in East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = East ...
prioritized industries based on local raw materials like jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny bast fiber that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', which is in the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is ''Corchorus olit ...
, cotton, and leather. The Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
drove up demand for jute products. Adamjee Jute Mills, the world's largest jute processing plant, was built in the Port of Narayanganj. The plant was a symbol of East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
's industrialization. Living standards began to gradually improve. Labor reforms in 1958 eventually benefitted a future independent Bangladesh to develop industry. Free market principles were generally accepted. The government promoted an industrial policy which aimed to produce consumer goods as quickly as possible in order to avoid dependence on imports. Certain sectors, like public utilities, fell under state ownership. Natural gas in Sylhet was discovered by the Burmah Oil Company
The Burmah Oil Company was a leading British oil company which was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. In 1966, Castrol was acquired by Burmah, which was renamed "Burmah-Castrol". BP Amoco (now BP) purchased the company in 2000.
History ...
in 1955. By the late 1960s, East Pakistan's share of Pakistan's exports went down from 70% to 50%. Pakistan's rulers launched a so-called "Decade of Development" that "resulted in numerous economic and social contradictions, which played themselves out, not just in the 1960s, but beyond, where Ayub Khan’s rule created the social and economic conditions leading to the separation of East Pakistan". According to the World Bank, economic discrimination against East Pakistan included diverting foreign aid and other funds to West Pakistan, the use of East Pakistan's foreign-exchange surpluses to finance West Pakistani imports, and refusal by the central government to release funds allocated to East Pakistan. Rehman Sobhan paraphrased the Two-Nation Theory into the Two Economies Theory by arguing that East and West Pakistan diverged and became two different economies within one country.
After its independence from Pakistan, Bangladesh initially followed a socialist economy for five years, which proved to be a blunder by the Awami League In Urdu language, Awami is the adjectival form for '' Awam'', the Urdu language word for common people.
The adjective appears in the following proper names:
*Awami Colony, a neighbourhood of Landhi Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
*Awami Front, wa ...
government. The state nationalized all banks, insurance companies, and 580 industrial plants. Private companies had to operate under heavy regulation and restrictions. For example, profit limits were imposed on companies. Any company with revenues or profits above the limit were susceptible to nationalization. Many of the nationalized industries were abandoned by West Pakistanis during the war; while many pro-Awami League and other Bengali businesses also suffered nationalization of properties and industries. Land ownership was restricted to less than 25 ''bighas''. Land owners with more than 25 ''bighas'' were subjected to taxes. Farmers had to sell their products at prices set by the government instead of the market. There was hardly any foreign investment. Since Bangladesh followed a socialist economy, it underwent a slow growth of producing experienced entrepreneurs, managers, administrators, engineers, and technicians. ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. About the Country Studies / Area Handbooks Program: Country Studies – Federal Research Division, Library of Congress
/ref> There were critical shortages of essential food grains and other staples because of wartime disruptions. External markets for jute had been lost because of the instability of supply and the increasing popularity of synthetic substitutes. Foreign exchange resources were minuscule, and the banking and monetary systems were unreliable. Although Bangladesh had a large work force, the vast reserves of under trained and underpaid workers were largely illiterate, unskilled, and underemployed. Commercially exploitable industrial resources, except for natural gas, were lacking. Inflation, especially for essential consumer goods, ran between 300 and 400 percent. The war of independence had crippled the transportation system. Hundreds of road and railroad bridges had been destroyed or damaged, and rolling stock was inadequate and in poor repair. The new country was still recovering from a severe cyclone that hit the area in 1970 and caused 250,000 deaths. India came forward immediately with critically measured economic assistance in the first months after Bangladesh achieved independence from Pakistan. Between December 1971 and January 1972, India committed US$232 million in aid to Bangladesh from the politico-economic aid India received from the US and
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. The Awami League initiated work for the Ghorashal Fertilizer Factory and the Ashuganj Power Station Ashuganj Power Station is located near to the Titas Gas field and at the bank of river Meghna, Bangladesh. It consists of 1627 megawatt units. An agreement was signed in 1966 with a foreign construction company to establish a Thermal Power Plant in ...
. In spite of restrictions, several of Bangladesh's leading companies in the future were founded during this period, including BEXIMCO and Advanced Chemical Industries
In 1968, Imperial Chemical Industries, a British multinational company established a branch in then-East Pakistan. After Bangladesh gained independence in 1971, the company was incorporated on 24 January 1973 as ICI Bangladesh Manufacturers Limi ...
.
After 1975, Bangladeshi leaders began to promote private industry and turned their attention to developing new industrial capacity and rehabilitating the economy. ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work
A creative work is a manifestation of creative effort including fine artwork (sculpture, paintings, drawing, sketching, performance art), dance, writing (literature), filmmaking, ...
.'' The socialist economic model adopted by early leaders had resulted in inefficiency and economic stagnation. Beginning in late 1975, the government gradually gave greater scope to private sector participation in the economy, a pattern that has continued. The Dhaka Stock Exchange was re-opened in 1976. The government established special economic zones called Export Processing Zones (EPZs) to attract investors and promote export industries. These zones have played a key role in Bangladesh's export economy. The government also de-nationalized and privatized state-owned industries by either returning them to their original owners or selling them to private buyers. Inefficiency in the public sector gradually increased; and left-wing opposition grew against the export of natural gas.
The 1980s saw the emergence of dynamic local brands like PRAN Pran most often refers to , the concept of a "life force" in Hindu philosophy.
Pran may also refer to:
People
*Pran Kishore Kaul, Kashmiri actor
*Pran Nath Lekhi (1924/1925–2010), Indian lawyer
*Pran Nath (musician) (1918–1996), Hindustani cl ...
. Muhammad Yunus began experimenting with microcredit
:''This article is specific to small loans, often provided in a pooled manner. For direct payments to individuals for specific projects, see Micropatronage. For financial services to the poor, see Microfinance. For small payments, see Micropayme ...
in the late 1970s. In 1983, the Grameen Bank
Grameen Bank ( bn, গ্রামীণ ব্যাংক) is a microfinance organisation and community development bank founded in Bangladesh. It makes small loans (known as microcredit or "grameencredit") to the impoverished without requi ...
was established. Bangladesh became the pioneer of the modern microcredit industry, with leading players like Grameen Bank, BRAC and Proshika
Proshika (Proshika Centre for Human Development) is a Bangladesh-based organization. It was founded in 1976 by Dr. Qazi Faruque Ahmed. Proshika promotes self-reliance among the poor through a network of local organizations. Major emphasis is placed ...
. In the industrial sector, two policy innovations in the mid-1980s helped exporters. The reforms introduced the back-to-back letter of credit and duty-drawback facilities through bonded warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities ...
s. These reforms removed major constraints for the country's fledgling garment industry. The reforms allowed a garment manufacturer to obtain letters of credit from domestic banks to finance its import of inputs, by showing letters of credit from foreign buyers of garments. The reforms also reimbursed manufacturers the duty paid on imported inputs on proof that the inputs, stored in bonded warehouses, had been used to manufacture the exports. These reforms spurred the growth of industry into the world's second largest textile exporting sector. In the mid-1980s, there were encouraging signs of progress. Economic policies aimed at encouraging private enterprise and investment, privatising public industries, reinstating budgetary discipline, and liberalising the import regime were accelerated. The International Finance Investment and Commerce Bank was set up as a multinational bank for Bangladesh, Nepal and the Maldives.
 From 1991 to 1993, the government engaged in an
From 1991 to 1993, the government engaged in an enhanced structural adjustment facility The Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility (ESAF) was a program of financial assistance given to poor countries from December 1987 through 1999 through the International Monetary Fund. It replaced the Structural Adjustment Facility (SAF) and was i ...
(ESAF) with the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
(IMF). A series of economic liberalization measures was introduced by finance minister Saifur Rahman, including opening up sectors like telecom to foreign investment. The Chittagong Stock Exchange was also set up. The 1990s was a boon for the private sector. Banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
, telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that fe ...
, aviation and tertiary education saw new private players and increased competition. The pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh
The pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh is one of the most developed technology sectors within the country. Manufacturers produce insulin, hormones, and cancer drugs. This sector provides 97% of the total medicinal requirement of the local mark ...
grew to meet 98% of domestic demand. The ceramics industry in Bangladesh
The ceramics industry is a growing manufacturing sector in Bangladesh. The industry started during the late 1950s when the first ceramic industrial plants were established. The industry mainly produces tableware, sanitaryware and tiles. As of 2011, ...
developed to meet local demand for 96% of tableware ceramics, 77% of tiles and 89% of sanitary ceramics. The Chittagong-based steel industry in Bangladesh
The steel industry is an established and growing industry in Bangladesh. Predominantly based in the port city of Chittagong, the industry has emerged as a major contributor to the national economy. According to the experts, the growth of steel indu ...
exploited scrap steel from ship-breaking yards and started contributing to shipbuilding in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a major shipbuilding nation. It has a long history of shipbuilding. The industry has been growth in recent years when locally made ships began to be exported. Bangladesh has now over 200 shipbuilding companies, mostly concentrated in ...
.
But the government failed to sustain reforms in large part because of preoccupation with the government's domestic political troubles, including tensions between the Awami League, the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and Jatiya Party. Frequent hartal
Hartal () is a term in many Indian languages for a strike action that was first used during the Indian independence movement (also known as the nationalist movement) of the early 20th century. A hartal is a mass protest, often involving a total sh ...
s and strikes disrupted the economy. In the late 1990s the government's economic policies became more entrenched, and some gains were lost, which was highlighted by a precipitous drop in foreign direct investment in 2000 and 2001. Many new private commercial banks were given licenses to operate. Between 2001 and 2006, annual GDP growth touched an average of 5-6%. In June 2003 the IMF approved 3-year, $490-million plan as part of the Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF) for Bangladesh that aimed to support the government's economic reform programme up to 2006. Seventy million dollars was made available immediately. In the same vein the World Bank approved $536 million in interest-free loans. The economy saw continuous real GDP growth of at least 6% since 2009. Bangladesh emerged as one of the fastest growing economies
This article includes a lists of countries and dependent territories sorted by their real gross domestic product growth rate; the rate of growth of the value of all final goods and services produced within a state in a given year. The statistics ...
.
According to economist Syed Akhtar Mahmood, the Bangladeshi government is often seen as the villain in the country's economic story. But government has played an important role in stimulating the economy through building infrastructure, liberalizing regulations, and promoting high yielding crops in agriculture. According to Mahmood, " st roads linking the villages with one another, and with the cities, were not paved and not accessible throughout the year. This situation was remarkably transformed within a span of 10 years, from 1988 to 1997, with the construction of the so-called feeder roads. In 1988, Bangladesh had about 3,000 kilometers of feeder roads. By 1997, this network expanded to 15,500 kilometers. These “last-mile” all-weather roads helped connect the villages of Bangladesh to the rest of the country".
As a result of export-led growth, Bangladesh has enjoyed a trade surplus
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance ...
in recent years. Bangladesh historically has run a large trade deficit, financed largely through aid receipts and remittances from workers overseas. Foreign reserves dropped markedly in 2001 but stabilised in the US$3 to US$4 billion range (or about 3 months' import cover). In January 2007, reserves stood at $3.74 billion, and then increased to $5.8 billion by January 2008, in November 2009 it surpassed $10.0 billion, and as of April 2011 it surpassed the US$12 billion according to the Bank of Bangladesh, the central bank. The dependence on foreign aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another.
Ai ...
and imports has also decreased gradually since the early 1990s. Foreign aid now accounts for only 2% of GDP.
 In the last decade, poverty dropped by around one third with significant improvements in the
In the last decade, poverty dropped by around one third with significant improvements in the human development index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
, literacy, life expectancy and per capita food consumption. With the economy growing annually at an average rate of 6% over a prolonged period, more than 15 million people have moved out of poverty since 1992. The poverty rate
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little went down from 80% in 1971 to 44.2% in 1991 to 12.9% in 2021. In recent years, Bangladesh has focused on promoting regional trade and transport links. The
 This is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Bangladesh at market price
This is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Bangladesh at market price
estimated
by the International Monetary Fund with figures in millions of Bangladeshi Taka. However, this reflects only the formal sector of the economy. Mean wages were $0.58 per man-hour in 2009. The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green. The annual unemployment rate is extracted from the
 Many new jobs – mostly for women – have been created by the country's dynamic private ready-made garment industry, which grew at double-digit rates through most of the 1990s. By the late 1990s, about 1.5 million people, mostly women, were employed in the garments sector as well as Leather products specially Footwear (Shoe manufacturing unit). During 2001–2002, export earnings from ready-made garments reached $3,125 million, representing 52% of Bangladesh's total exports. Bangladesh has overtaken India in apparel exports in 2009, its exports stood at 2.66 billion US dollar, ahead of India's 2.27 billion US dollar and in 2014 the export rose to $3.12 billion every month. At the fiscal year 2018, Bangladesh has been able to garner US$36.67 billion export earnings by exporting manufactured goods, of which, 83.49 percent has come from the apparel manufacturing sector.
Eastern Bengal was known for its fine muslin and silk fabric before the British period. The dyes, yarn, and cloth were the envy of much of the premodern world. Bengali muslin, silk, and brocade were worn by the aristocracy of Asia and Europe. The introduction of machine-made textiles from England in the late eighteenth century spelled doom for the costly and time-consuming hand loom process. Cotton growing died out in East Bengal, and the
Many new jobs – mostly for women – have been created by the country's dynamic private ready-made garment industry, which grew at double-digit rates through most of the 1990s. By the late 1990s, about 1.5 million people, mostly women, were employed in the garments sector as well as Leather products specially Footwear (Shoe manufacturing unit). During 2001–2002, export earnings from ready-made garments reached $3,125 million, representing 52% of Bangladesh's total exports. Bangladesh has overtaken India in apparel exports in 2009, its exports stood at 2.66 billion US dollar, ahead of India's 2.27 billion US dollar and in 2014 the export rose to $3.12 billion every month. At the fiscal year 2018, Bangladesh has been able to garner US$36.67 billion export earnings by exporting manufactured goods, of which, 83.49 percent has come from the apparel manufacturing sector.
Eastern Bengal was known for its fine muslin and silk fabric before the British period. The dyes, yarn, and cloth were the envy of much of the premodern world. Bengali muslin, silk, and brocade were worn by the aristocracy of Asia and Europe. The introduction of machine-made textiles from England in the late eighteenth century spelled doom for the costly and time-consuming hand loom process. Cotton growing died out in East Bengal, and the  Bangladesh's textile industry, which includes knitwear and ready-made garments (RMG) along with specialised textile products, is the nation's number one export earner, accounting for $21.5 billion in 2013 – 80% of Bangladesh's total exports of $27 billion.
Bangladesh is 2nd in world textile exports, behind China, which exported $120.1 billion worth of textiles in 2009. The industry employs nearly 3.5 million workers. Current exports have doubled since 2004. Wages in Bangladesh's textile industry were the lowest in the world as of 2010. The country was considered the most formidable rival to China where wages were rapidly rising and currency was appreciating. As of 2012 wages remained low for the 3 million people employed in the industry, but labour unrest was increasing despite vigorous government action to enforce labour peace. Owners of textile firms and their political allies were a powerful political influence in Bangladesh.
The urban garment industry has created more than one million formal sector jobs for women, contributing to the high female labour participation in Bangladesh. While it can be argued that women working in the garment industry are subjected to unsafe labour conditions and low wages, Dina M. Siddiqi argues that even though conditions in Bangladesh garment factories "are by no means ideal," they still give women in Bangladesh the opportunity to earn their own wages. As evidence she points to the fear created by the passage of the 1993 Harkins Bill ( Child Labor Deterrence Bill), which caused factory owners to dismiss "an estimated 50,000 children, many of whom helped support their families, forcing them into a completely unregulated informal sector, in lower-paying and much less secure occupations such as brick-breaking, domestic service and rickshaw pulling."
Even though the working conditions in garment factories are not ideal, they tend to financially be more reliable than other occupations and, "enhance women's economic capabilities to spend, save and invest their incomes." Both married and unmarried women send money back to their families as remittances, but these earned wages have more than just economic benefits. Many women in the garment industry are marrying later, have lower fertility rates, and attain higher levels of education, then women employed elsewhere.
After massive labour unrest in 2006 the government formed a Minimum Wage Board including business and worker representatives which in 2006 set a minimum wage equivalent to 1,662.50 taka, $24 a month, up from Tk950. In 2010, following widespread labour protests involving 60,000 workers in June 2010, a controversial proposal was being considered by the Board which would raise the monthly minimum to the equivalent of $50 a month, still far below worker demands of 5,000 taka, $72, for entry level wages, but unacceptably high according to textile manufacturers who are asking for a wage below $30. On 28 July 2010 it was announced that the minimum entry level wage would be increased to 3,000 taka, about $43.
The government also seems to believe some change is necessary. On 21 September 2006 then ex-Prime Minister Khaleda Zia called on textile firms to ensure the safety of workers by complying with international labour law at a speech inaugurating the Bangladesh Apparel & Textile Exposition (BATEXPO).
Many Western multinationals use labour in Bangladesh, which is one of the cheapest in the world: 30 euros per month compared to 150 or 200 in China. Four days is enough for the CEO of one of the top five global textile brands to earn what a Bangladeshi garment worker will earn in her lifetime. In April 2013, at least 1,135 textile workers died in the collapse of their factory. Other fatal accidents due to unsanitary factories have affected Bangladesh: in 2005 a factory collapsed and caused the death of 64 people. In 2006, a series of fires killed 85 people and injured 207 others. In 2010, some 30 people died of asphyxiation and burns in two serious fires.
In 2006, tens of thousands of workers mobilized in one of the country's largest strike movements, affecting almost all of the 4,000 factories. The Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) uses police forces to crack down. Three workers were killed, hundreds more were wounded by bullets, or imprisoned. In 2010, after a new strike movement, nearly 1,000 people were injured among workers as a result of the repression.
Bangladesh's textile industry, which includes knitwear and ready-made garments (RMG) along with specialised textile products, is the nation's number one export earner, accounting for $21.5 billion in 2013 – 80% of Bangladesh's total exports of $27 billion.
Bangladesh is 2nd in world textile exports, behind China, which exported $120.1 billion worth of textiles in 2009. The industry employs nearly 3.5 million workers. Current exports have doubled since 2004. Wages in Bangladesh's textile industry were the lowest in the world as of 2010. The country was considered the most formidable rival to China where wages were rapidly rising and currency was appreciating. As of 2012 wages remained low for the 3 million people employed in the industry, but labour unrest was increasing despite vigorous government action to enforce labour peace. Owners of textile firms and their political allies were a powerful political influence in Bangladesh.
The urban garment industry has created more than one million formal sector jobs for women, contributing to the high female labour participation in Bangladesh. While it can be argued that women working in the garment industry are subjected to unsafe labour conditions and low wages, Dina M. Siddiqi argues that even though conditions in Bangladesh garment factories "are by no means ideal," they still give women in Bangladesh the opportunity to earn their own wages. As evidence she points to the fear created by the passage of the 1993 Harkins Bill ( Child Labor Deterrence Bill), which caused factory owners to dismiss "an estimated 50,000 children, many of whom helped support their families, forcing them into a completely unregulated informal sector, in lower-paying and much less secure occupations such as brick-breaking, domestic service and rickshaw pulling."
Even though the working conditions in garment factories are not ideal, they tend to financially be more reliable than other occupations and, "enhance women's economic capabilities to spend, save and invest their incomes." Both married and unmarried women send money back to their families as remittances, but these earned wages have more than just economic benefits. Many women in the garment industry are marrying later, have lower fertility rates, and attain higher levels of education, then women employed elsewhere.
After massive labour unrest in 2006 the government formed a Minimum Wage Board including business and worker representatives which in 2006 set a minimum wage equivalent to 1,662.50 taka, $24 a month, up from Tk950. In 2010, following widespread labour protests involving 60,000 workers in June 2010, a controversial proposal was being considered by the Board which would raise the monthly minimum to the equivalent of $50 a month, still far below worker demands of 5,000 taka, $72, for entry level wages, but unacceptably high according to textile manufacturers who are asking for a wage below $30. On 28 July 2010 it was announced that the minimum entry level wage would be increased to 3,000 taka, about $43.
The government also seems to believe some change is necessary. On 21 September 2006 then ex-Prime Minister Khaleda Zia called on textile firms to ensure the safety of workers by complying with international labour law at a speech inaugurating the Bangladesh Apparel & Textile Exposition (BATEXPO).
Many Western multinationals use labour in Bangladesh, which is one of the cheapest in the world: 30 euros per month compared to 150 or 200 in China. Four days is enough for the CEO of one of the top five global textile brands to earn what a Bangladeshi garment worker will earn in her lifetime. In April 2013, at least 1,135 textile workers died in the collapse of their factory. Other fatal accidents due to unsanitary factories have affected Bangladesh: in 2005 a factory collapsed and caused the death of 64 people. In 2006, a series of fires killed 85 people and injured 207 others. In 2010, some 30 people died of asphyxiation and burns in two serious fires.
In 2006, tens of thousands of workers mobilized in one of the country's largest strike movements, affecting almost all of the 4,000 factories. The Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) uses police forces to crack down. Three workers were killed, hundreds more were wounded by bullets, or imprisoned. In 2010, after a new strike movement, nearly 1,000 people were injured among workers as a result of the repression.

 Most banks in Bangladesh are privately owned. Until the 1980s, the financial sector of Bangladesh was dominated by state-owned banks. With the grand-scale reform made in finance, private commercial banks were established through privatisation. The next finance sector reform programme was launched from 2000 to 2006 with focus on the development of financial institutions and adoption of risk-based regulations and supervision by Bangladesh Bank. As of date, the banking sector consisted of 4 SCBs, 4 government-owned specialized banks dealing in development financing, 39 private commercial banks, and 9 foreign commercial banks.
Most banks in Bangladesh are privately owned. Until the 1980s, the financial sector of Bangladesh was dominated by state-owned banks. With the grand-scale reform made in finance, private commercial banks were established through privatisation. The next finance sector reform programme was launched from 2000 to 2006 with focus on the development of financial institutions and adoption of risk-based regulations and supervision by Bangladesh Bank. As of date, the banking sector consisted of 4 SCBs, 4 government-owned specialized banks dealing in development financing, 39 private commercial banks, and 9 foreign commercial banks.
 The Bangladesh Garments Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) has predicted textile exports will rise from US$7.90 billion earned in 2005–06 to US$15
billion by 2011. In part this optimism stems from how well the sector has fared since the end of textile and clothing quotas, under the Multifibre Agreement, in early 2005.
According to a
The Bangladesh Garments Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) has predicted textile exports will rise from US$7.90 billion earned in 2005–06 to US$15
billion by 2011. In part this optimism stems from how well the sector has fared since the end of textile and clothing quotas, under the Multifibre Agreement, in early 2005.
According to a
 Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a heavy toll on almost all sectors of the economy, inter alia, most notably, it has caused a reduction of exports by 16.93 percent, and imports by 17 percent in the FY2019-20.
In 2015, the top exports of Bangladesh are Non-Knit Men's Suits ($5.6B), Knit T-shirts ($5.28B), Knit Sweaters ($4.12B), Non-Knit Women's Suits ($3.66B) and Non-Knit Men's Shirts ($2.52B).
Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a heavy toll on almost all sectors of the economy, inter alia, most notably, it has caused a reduction of exports by 16.93 percent, and imports by 17 percent in the FY2019-20.
In 2015, the top exports of Bangladesh are Non-Knit Men's Suits ($5.6B), Knit T-shirts ($5.28B), Knit Sweaters ($4.12B), Non-Knit Women's Suits ($3.66B) and Non-Knit Men's Shirts ($2.52B).  Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported
license. In 2015, the top imports of Bangladesh are Heavy Pure Woven Cotton ($1.33B), Refined Petroleum ($1.25B), Light Pure Woven Cotton ($1.12B), Raw Cotton ($1.01B) and Wheat ($900M). In 2015, the top export destinations of Bangladesh are the United States ($6.19B), Germany ($5.17B), the United Kingdom ($3.53B), France ($2.37B) and Spain ($2.29B). In 2015, the top import origins are China ($13.9B), India ($5.51B), Singapore ($2.22B), Hong Kong ($1.47B) and Japan ($1.36B).
 As of 2014, female participation in the labour force is 58% as per World Bank data, and male participation at 82%.
A 2007 World Bank report stated that the areas in which women's work force participation have increased the most are in the fields of agriculture, education and health and social work. Over three-quarters of women in the labour force work in the agricultural sector. On the other hand, the International Labour Organization reports that women's workforce participation has only increased in the professional and administrative areas between 2000 and 2005, demonstrating women's increased participation in sectors that require higher education. Employment and labour force participation data from the World Bank, the UN, and the ILO vary and often under report on women's work due to unpaid labour and informal sector jobs. Though these fields are mostly paid, women experience very different work conditions than men, including wage differences and work benefits. Women's wages are significantly lower than men's wages for the same job with women being paid as much as 60–75 percent less than what men make.
One example of action that is being taken to improve female conditions in the work force is Non-Governmental Organisations. These NGOs encourage women to rely on their own self-savings, rather than external funds provide women with increased decision-making and participation within the family and society. However, some NGOs that address microeconomic issues among individual families fail to deal with broader macroeconomic issues that prevent women's complete autonomy and advancement.
As of 2014, female participation in the labour force is 58% as per World Bank data, and male participation at 82%.
A 2007 World Bank report stated that the areas in which women's work force participation have increased the most are in the fields of agriculture, education and health and social work. Over three-quarters of women in the labour force work in the agricultural sector. On the other hand, the International Labour Organization reports that women's workforce participation has only increased in the professional and administrative areas between 2000 and 2005, demonstrating women's increased participation in sectors that require higher education. Employment and labour force participation data from the World Bank, the UN, and the ILO vary and often under report on women's work due to unpaid labour and informal sector jobs. Though these fields are mostly paid, women experience very different work conditions than men, including wage differences and work benefits. Women's wages are significantly lower than men's wages for the same job with women being paid as much as 60–75 percent less than what men make.
One example of action that is being taken to improve female conditions in the work force is Non-Governmental Organisations. These NGOs encourage women to rely on their own self-savings, rather than external funds provide women with increased decision-making and participation within the family and society. However, some NGOs that address microeconomic issues among individual families fail to deal with broader macroeconomic issues that prevent women's complete autonomy and advancement.
Bangladesh Economic News
Bangladesh Budget 2007 – 2008
Budget in Brief 2016–17
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Bangladesh
2007 {{Asia topic, Urbanisation in
Bangladesh Bhutan India Nepal
The Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal (BBIN) Initiative is a subregional architecture of countries in Eastern South Asia, a subregion of South Asia. It meets through official representation of member states to formulate, implement and review qu ...
Motor Vehicles Agreement seeks to create hassle free road transport across international borders. Bangladesh also signed a coastal shipping agreement with India. While prioritizing food security in the domestic market, Bangladesh exports more than US$1 billion worth of processed food products. As the result of a robust agricultural supply chain, supermarket
A supermarket is a self-service Retail#Types of outlets, shop offering a wide variety of food, Drink, beverages and Household goods, household products, organized into sections. This kind of store is larger and has a wider selection than earli ...
s have sprung up in cities and towns across the country.
Bangladesh became the second largest textile exporter in the world. An estimated 4.4 million workers are employed in the garments industry, with the majority being women. The sector contributes 11% of Bangladesh's GDP. The 2013 Rana Plaza factory collapse
The 2013 Rana Plaza factory collapse (also referred to as the 2013 Savar building collapse or the Collapse of Rana Plaza) was a structural failure that occurred on 24 April 2013 in the Savar Upazila of Dhaka District, Bangladesh, where an eigh ...
caused global concern on industrial safety in Bangladesh, leading to the formation of the Accord on Fire and Building Safety in Bangladesh
The Accord on Fire and Building Safety in Bangladesh (the Accord) was signed on 24 April 2013. It is a five-year independent, legally binding Global Framework Agreement between global brands, retailers and trade unions designed to build a safe a ...
and the Alliance for Bangladesh Worker Safety
The Alliance for Bangladesh Worker Safety, also known as "the Alliance" or AFBWS, is a group of 28 major global retailers formed to develop and launch the Bangladesh Worker Safety Initiative, a binding, five-year undertaking with the intent of im ...
. The local clothing industry has seen fiercely competitive brands vying for the market, including Aarong
Aarong ( bn, আড়ং, lit=Village Fair) is a chain of Bangladeshi department stores specializing in Bengali ethnic wear and handicrafts. It is owned by the non-profit development agency BRAC, and employs thousands of rural artisans acr ...
, Westecs, Ecstasy
Ecstasy may refer to:
* Ecstasy (emotion), a trance or trance-like state in which a person transcends normal consciousness
* Religious ecstasy, a state of consciousness, visions or absolute euphoria
* Ecstasy (philosophy), to be or stand outside o ...
, and Yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In the R ...
among many others.
The World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
notes the economic progress of the country by stating that " en the newly independent country of Bangladesh was born on December 16, 1971, it was the second poorest country in the world—making the country's transformation over the next 50 years one of the great development stories. Since then, poverty has been cut in half at record speed. Enrolment in primary school is now nearly universal. Hundreds of thousands of women have entered the workforce. Steady progress has been made on maternal and child health. And the country is better buttressed against the destructive forces posed by climate change and natural disasters. Bangladesh's success comprises many moving parts—from investing in human capital to establishing macroeconomic stability. Building on this success, the country is now setting the stage for further economic growth and job creation by ramping up investments in energy, inland connectivity, urban projects, and transport infrastructure, as well as prioritizing climate change adaptation and disaster preparedness on its path toward sustainable growth".
As of 2022, Bangladesh had the second largest foreign-exchange reserves
Foreign exchange reserves (also called forex reserves or FX reserves) are cash and other reserve assets such as gold held by a central bank or other monetary authority that are primarily available to balance payments of the country, influence ...
in South Asia. In 2021, Bangladesh surpassed both India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
in terms of per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
. The country achieved 100% electricity coverage for households in 2022. Megaprojects like the Padma Bridge, Dhaka Metro
Dhaka Metro Rail ( bn, ঢাকা মেট্রোরেল), colloquially known as the Dhaka Metro ( bn, ঢাকা মেট্রো) is a mass rapid transit (MRT) system serving Dhaka, Bangladesh. Together with the city's planned sub ...
, Matarbari Port, and Karnaphuli Tunnel
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Tunnel (or Karnaphuli Tunnel) ( bn, কর্ণফুলী সুড়ঙ্গ) is an underwater expressway tunnel in the port city of Chittagong, Bangladesh under the Karnaphuli river. The length of the enti ...
have been planned to stimulate economic activity. The completion of Padma Bridge was expected to boost Bangladeshi GDP by 1.23%. During the Russia-Ukraine War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Revo ...
, Bangladesh experienced pressure on its foreign exchange reserves due to rising import costs; this affected the country's electricity sector which relies on imported fuel; rising import prices also contributed to inflation.
Macro-economic trend
 This is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Bangladesh at market price
This is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Bangladesh at market priceestimated
by the International Monetary Fund with figures in millions of Bangladeshi Taka. However, this reflects only the formal sector of the economy. Mean wages were $0.58 per man-hour in 2009. The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green. The annual unemployment rate is extracted from the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
, although the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
find them unreliable.
Economic sectors
Agriculture
Manufacturing and industry
 Many new jobs – mostly for women – have been created by the country's dynamic private ready-made garment industry, which grew at double-digit rates through most of the 1990s. By the late 1990s, about 1.5 million people, mostly women, were employed in the garments sector as well as Leather products specially Footwear (Shoe manufacturing unit). During 2001–2002, export earnings from ready-made garments reached $3,125 million, representing 52% of Bangladesh's total exports. Bangladesh has overtaken India in apparel exports in 2009, its exports stood at 2.66 billion US dollar, ahead of India's 2.27 billion US dollar and in 2014 the export rose to $3.12 billion every month. At the fiscal year 2018, Bangladesh has been able to garner US$36.67 billion export earnings by exporting manufactured goods, of which, 83.49 percent has come from the apparel manufacturing sector.
Eastern Bengal was known for its fine muslin and silk fabric before the British period. The dyes, yarn, and cloth were the envy of much of the premodern world. Bengali muslin, silk, and brocade were worn by the aristocracy of Asia and Europe. The introduction of machine-made textiles from England in the late eighteenth century spelled doom for the costly and time-consuming hand loom process. Cotton growing died out in East Bengal, and the
Many new jobs – mostly for women – have been created by the country's dynamic private ready-made garment industry, which grew at double-digit rates through most of the 1990s. By the late 1990s, about 1.5 million people, mostly women, were employed in the garments sector as well as Leather products specially Footwear (Shoe manufacturing unit). During 2001–2002, export earnings from ready-made garments reached $3,125 million, representing 52% of Bangladesh's total exports. Bangladesh has overtaken India in apparel exports in 2009, its exports stood at 2.66 billion US dollar, ahead of India's 2.27 billion US dollar and in 2014 the export rose to $3.12 billion every month. At the fiscal year 2018, Bangladesh has been able to garner US$36.67 billion export earnings by exporting manufactured goods, of which, 83.49 percent has come from the apparel manufacturing sector.
Eastern Bengal was known for its fine muslin and silk fabric before the British period. The dyes, yarn, and cloth were the envy of much of the premodern world. Bengali muslin, silk, and brocade were worn by the aristocracy of Asia and Europe. The introduction of machine-made textiles from England in the late eighteenth century spelled doom for the costly and time-consuming hand loom process. Cotton growing died out in East Bengal, and the textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturi ...
became dependent on imported yarn. Those who had earned their living in the textile industry were forced to rely more completely on farming. Only the smallest vestiges of a once-thriving cottage industry survived.
Other industries which have shown very strong growth include the pharmaceutical industry, shipbuilding industry, information technology, leather industry, steel industry, and light engineering industry.
 Bangladesh's textile industry, which includes knitwear and ready-made garments (RMG) along with specialised textile products, is the nation's number one export earner, accounting for $21.5 billion in 2013 – 80% of Bangladesh's total exports of $27 billion.
Bangladesh is 2nd in world textile exports, behind China, which exported $120.1 billion worth of textiles in 2009. The industry employs nearly 3.5 million workers. Current exports have doubled since 2004. Wages in Bangladesh's textile industry were the lowest in the world as of 2010. The country was considered the most formidable rival to China where wages were rapidly rising and currency was appreciating. As of 2012 wages remained low for the 3 million people employed in the industry, but labour unrest was increasing despite vigorous government action to enforce labour peace. Owners of textile firms and their political allies were a powerful political influence in Bangladesh.
The urban garment industry has created more than one million formal sector jobs for women, contributing to the high female labour participation in Bangladesh. While it can be argued that women working in the garment industry are subjected to unsafe labour conditions and low wages, Dina M. Siddiqi argues that even though conditions in Bangladesh garment factories "are by no means ideal," they still give women in Bangladesh the opportunity to earn their own wages. As evidence she points to the fear created by the passage of the 1993 Harkins Bill ( Child Labor Deterrence Bill), which caused factory owners to dismiss "an estimated 50,000 children, many of whom helped support their families, forcing them into a completely unregulated informal sector, in lower-paying and much less secure occupations such as brick-breaking, domestic service and rickshaw pulling."
Even though the working conditions in garment factories are not ideal, they tend to financially be more reliable than other occupations and, "enhance women's economic capabilities to spend, save and invest their incomes." Both married and unmarried women send money back to their families as remittances, but these earned wages have more than just economic benefits. Many women in the garment industry are marrying later, have lower fertility rates, and attain higher levels of education, then women employed elsewhere.
After massive labour unrest in 2006 the government formed a Minimum Wage Board including business and worker representatives which in 2006 set a minimum wage equivalent to 1,662.50 taka, $24 a month, up from Tk950. In 2010, following widespread labour protests involving 60,000 workers in June 2010, a controversial proposal was being considered by the Board which would raise the monthly minimum to the equivalent of $50 a month, still far below worker demands of 5,000 taka, $72, for entry level wages, but unacceptably high according to textile manufacturers who are asking for a wage below $30. On 28 July 2010 it was announced that the minimum entry level wage would be increased to 3,000 taka, about $43.
The government also seems to believe some change is necessary. On 21 September 2006 then ex-Prime Minister Khaleda Zia called on textile firms to ensure the safety of workers by complying with international labour law at a speech inaugurating the Bangladesh Apparel & Textile Exposition (BATEXPO).
Many Western multinationals use labour in Bangladesh, which is one of the cheapest in the world: 30 euros per month compared to 150 or 200 in China. Four days is enough for the CEO of one of the top five global textile brands to earn what a Bangladeshi garment worker will earn in her lifetime. In April 2013, at least 1,135 textile workers died in the collapse of their factory. Other fatal accidents due to unsanitary factories have affected Bangladesh: in 2005 a factory collapsed and caused the death of 64 people. In 2006, a series of fires killed 85 people and injured 207 others. In 2010, some 30 people died of asphyxiation and burns in two serious fires.
In 2006, tens of thousands of workers mobilized in one of the country's largest strike movements, affecting almost all of the 4,000 factories. The Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) uses police forces to crack down. Three workers were killed, hundreds more were wounded by bullets, or imprisoned. In 2010, after a new strike movement, nearly 1,000 people were injured among workers as a result of the repression.
Bangladesh's textile industry, which includes knitwear and ready-made garments (RMG) along with specialised textile products, is the nation's number one export earner, accounting for $21.5 billion in 2013 – 80% of Bangladesh's total exports of $27 billion.
Bangladesh is 2nd in world textile exports, behind China, which exported $120.1 billion worth of textiles in 2009. The industry employs nearly 3.5 million workers. Current exports have doubled since 2004. Wages in Bangladesh's textile industry were the lowest in the world as of 2010. The country was considered the most formidable rival to China where wages were rapidly rising and currency was appreciating. As of 2012 wages remained low for the 3 million people employed in the industry, but labour unrest was increasing despite vigorous government action to enforce labour peace. Owners of textile firms and their political allies were a powerful political influence in Bangladesh.
The urban garment industry has created more than one million formal sector jobs for women, contributing to the high female labour participation in Bangladesh. While it can be argued that women working in the garment industry are subjected to unsafe labour conditions and low wages, Dina M. Siddiqi argues that even though conditions in Bangladesh garment factories "are by no means ideal," they still give women in Bangladesh the opportunity to earn their own wages. As evidence she points to the fear created by the passage of the 1993 Harkins Bill ( Child Labor Deterrence Bill), which caused factory owners to dismiss "an estimated 50,000 children, many of whom helped support their families, forcing them into a completely unregulated informal sector, in lower-paying and much less secure occupations such as brick-breaking, domestic service and rickshaw pulling."
Even though the working conditions in garment factories are not ideal, they tend to financially be more reliable than other occupations and, "enhance women's economic capabilities to spend, save and invest their incomes." Both married and unmarried women send money back to their families as remittances, but these earned wages have more than just economic benefits. Many women in the garment industry are marrying later, have lower fertility rates, and attain higher levels of education, then women employed elsewhere.
After massive labour unrest in 2006 the government formed a Minimum Wage Board including business and worker representatives which in 2006 set a minimum wage equivalent to 1,662.50 taka, $24 a month, up from Tk950. In 2010, following widespread labour protests involving 60,000 workers in June 2010, a controversial proposal was being considered by the Board which would raise the monthly minimum to the equivalent of $50 a month, still far below worker demands of 5,000 taka, $72, for entry level wages, but unacceptably high according to textile manufacturers who are asking for a wage below $30. On 28 July 2010 it was announced that the minimum entry level wage would be increased to 3,000 taka, about $43.
The government also seems to believe some change is necessary. On 21 September 2006 then ex-Prime Minister Khaleda Zia called on textile firms to ensure the safety of workers by complying with international labour law at a speech inaugurating the Bangladesh Apparel & Textile Exposition (BATEXPO).
Many Western multinationals use labour in Bangladesh, which is one of the cheapest in the world: 30 euros per month compared to 150 or 200 in China. Four days is enough for the CEO of one of the top five global textile brands to earn what a Bangladeshi garment worker will earn in her lifetime. In April 2013, at least 1,135 textile workers died in the collapse of their factory. Other fatal accidents due to unsanitary factories have affected Bangladesh: in 2005 a factory collapsed and caused the death of 64 people. In 2006, a series of fires killed 85 people and injured 207 others. In 2010, some 30 people died of asphyxiation and burns in two serious fires.
In 2006, tens of thousands of workers mobilized in one of the country's largest strike movements, affecting almost all of the 4,000 factories. The Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) uses police forces to crack down. Three workers were killed, hundreds more were wounded by bullets, or imprisoned. In 2010, after a new strike movement, nearly 1,000 people were injured among workers as a result of the repression.
Shipbuilding and shipbreaking

Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
is a growing industry in Bangladesh with great potential. Due to the potential of shipbuilding in Bangladesh, the country has been compared to countries like China, Japan and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
. Referring to the growing amount of export deals secured by the shipbuilding companies as well as the low cost labour available in the country, experts suggest that Bangladesh could emerge as a major competitor in the global market of small to medium ocean-going vessels.
Bangladesh also has the world's largest ship breaking
Ship-breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for either a source of parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction ...
industry which employs over 200,000 Bangladeshis and accounts for half of all the steel in Bangladesh. Chittagong Ship Breaking Yard is the world's second-largest ship breaking area.
Khulna Shipyard Limited (KSY) with over five decades of reputation has been leading the Bangladesh Shipbuilding industry and had built a wide spectrum of ships for domestic and international clients. KSY built ships for Bangladesh Navy, Bangladesh Army and Bangladesh Coast Guard under the contract of ministry of defence.
Finance
 Most banks in Bangladesh are privately owned. Until the 1980s, the financial sector of Bangladesh was dominated by state-owned banks. With the grand-scale reform made in finance, private commercial banks were established through privatisation. The next finance sector reform programme was launched from 2000 to 2006 with focus on the development of financial institutions and adoption of risk-based regulations and supervision by Bangladesh Bank. As of date, the banking sector consisted of 4 SCBs, 4 government-owned specialized banks dealing in development financing, 39 private commercial banks, and 9 foreign commercial banks.
Most banks in Bangladesh are privately owned. Until the 1980s, the financial sector of Bangladesh was dominated by state-owned banks. With the grand-scale reform made in finance, private commercial banks were established through privatisation. The next finance sector reform programme was launched from 2000 to 2006 with focus on the development of financial institutions and adoption of risk-based regulations and supervision by Bangladesh Bank. As of date, the banking sector consisted of 4 SCBs, 4 government-owned specialized banks dealing in development financing, 39 private commercial banks, and 9 foreign commercial banks.
Tourism
The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) reported in 2013 that the travel and tourism industry in Bangladesh directly generated 1,281,500 jobs in 2012 or 1.8 percent of the country's total employment, which ranked Bangladesh 157 out of 178 countries worldwide. Direct and indirect employment in the industry totalled 2,714,500 jobs, or 3.7 percent of the country's total employment. The WTTC predicted that by 2023, travel and tourism will directly generate 1,785,000 jobs and support an overall total of 3,891,000 jobs, or 4.2 percent of the country's total employment. This would represent an annual growth rate in direct jobs of 2.9 percent. Domestic spending generated 97.7 percent of direct travel and tourism gross domestic product (GDP) in 2012. Bangladesh's world ranking in 2012 for travel and tourism's direct contribution to GDP, as a percentage of GDP, was 142 out of 176. in 2014 125,000 tourists visited Bangladesh. This number is extremely low relative to total population. As of 22 May 2019 the total local population numbering 166,594,000 inhabitants. This gives a ratio of 1 tourist for every 1,333 locals.Information and communication technology
Bangladesh's information technology sector is growing example of what can be achieved after the current government's relentless effort to create a skilled workforce in ICT sector. The ICT workforce consisted of private sector and freelance skilled ICT workforce. The ICT sector also contributed to Bangladesh's economic growth. The ICT adviser to the prime minister, Sajeeb Wazed Joy is hopeful that Bangladesh will become a major player in the ICT sector in the future. In the last 3 years, Bangladesh has seen a tremendous growth in the ICT sector. Bangladesh is a market of 160 million people with vast consumer spending around mobile phones, telco and internet. Bangladesh has 80 million internet users, an estimated 9% growth in internet use by June 2017 powered by mobile internet. Bangladesh currently has an active 23 million Facebook users. Bangladesh currently has 143.1 million mobile phone customers. Bangladesh has exported $800 million worth of software, games, outsourcing and services to European countries, the United States, Canada, Russia and India by 30 June 2017. The Junior Minister for ICT division of the Ministry of Post, Telecommunications and Information Technology said that Bangladesh aims to raise its export earnings from the information and communications technology (ICT) sector to $5 billion by 2021.Investment
The stockmarket capitalisation
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by t ...
of the Dhaka Stock Exchange in Bangladesh crossed $10 billion in November 2007 and the $30 billion mark in 2009, and US$50 billion in August 2010. Bangladesh had the best performing stock market in Asia during the recent global recession between 2007 and 2010, due to relatively low correlations with developed country stock markets.
Major investment in real estate by domestic and foreign-resident Bangladeshis has led to a massive building boom in Dhaka and Chittagong.
Recent (2011) trends for investing in Bangladesh as Saudi Arabia trying to secure public and private investment in oil and gas, power and transportation projects, United Arab Emirates (UAE) is keen to invest in growing shipbuilding industry in Bangladesh encouraged by comparative cost advantage, Tata, an India-based leading industrial multinational to invest Taka 1500 crore to set up an automobile industry in Bangladesh, World Bank to invest in rural roads improving quality of live, the Rwandan entrepreneurs are keen to invest in Bangladesh's pharmaceuticals sector considering its potentiality in international market, Samsung sought to lease 500 industrial plots from the export zones authority to set up an electronics hub in Bangladesh with an investment of US$1.25 billion, National Board of Revenue (NBR) is set to withdraw tax rebate facilities on investment in the capital market by individual taxpayers from the fiscal 2011–12. In 2011, Japan Bank for International Cooperation
The , JBIC, is a Japanese public financial institution and export credit agency that was created on October 1, 1999, through the merger of the Japan Export-Import Bank (JEXIM) and the Overseas Economic Cooperation Fund (OECF).
JBIC became the in ...
ranked Bangladesh as the 15th best investment destination for foreign investors.
2010–11 market crash
The bullish capital market turned bearish during 2010, with the exchange losing 1,800 points between December 2010 and January 2011. Millions of investors have been rendered bankrupt as a result of the market crash. The crash is believed to be caused artificially to benefit a handful of players at the expense of the big players.Companies
The list includes ten largest Bangladeshi companies by trading value (millions in BDT) in 2018.Composition of economic sectors
 The Bangladesh Garments Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) has predicted textile exports will rise from US$7.90 billion earned in 2005–06 to US$15
billion by 2011. In part this optimism stems from how well the sector has fared since the end of textile and clothing quotas, under the Multifibre Agreement, in early 2005.
According to a
The Bangladesh Garments Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) has predicted textile exports will rise from US$7.90 billion earned in 2005–06 to US$15
billion by 2011. In part this optimism stems from how well the sector has fared since the end of textile and clothing quotas, under the Multifibre Agreement, in early 2005.
According to a United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human dev ...
report "Sewing Thoughts: How to Realize Human Development Gains in the Post-Quota World" Bangladesh has been able to offset a decline in European sales by cultivating new markets in the United States.
"n 2005
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
we had tremendous growth. The quota-free textile regime has proved to be a big boost for our factories," said BGMEA president S.M. Fazlul Hoque told reporters, after the
sector's 24 per cent growth rate was revealed.
The Bangladesh Knitwear Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BKMEA) president Md Fazlul Hoque has also struck an optimistic tone. In an interview with United News Bangladesh he lauded the blistering growth rate, saying "The quality of our products and its competitiveness in terms of prices helped the sector achieve such... tremendous success."
Knitwear posted the strongest growth of all textile products in 2005–06, surging 35.38 per cent to US$2.82 billion. On the downside however, the sector's strong growth came amid sharp falls in prices for textile products on the world market, with growth subsequently dependent upon large increases in volume.
Bangladesh's quest to boost the quantity of textile trade was also helped by US and EU caps on Chinese textiles. The US cap restricts growth in imports of Chinese textiles to 12.5 per cent next year and between 15 and 16 per cent in 2008. The EU deal similarly manages import growth until 2008.
Bangladesh may continue to benefit from these restrictions over the next two years, however a climate of falling global textile prices forces wage rates the centre of the nation's efforts to increase market share.
They offer a range of incentives to potential investors including 10-year tax holidays, duty-free import of capital goods, raw materials and building materials, exemptions on income tax on salaries paid to foreign nationals for three years and dividend tax exemptions for the period of the tax holiday.
All goods produced in the zones are able to be exported duty-free, in addition to which Bangladesh benefits from the Generalised System of Preferences in US, European and Japanese markets and is also endowed with Most Favoured Nation status from the United States.
Furthermore, Bangladesh imposes no ceiling on investment in the EPZs and allows full repatriation of profits.
The formation of labour unions within the EPZs is prohibited as are strikes.
Bangladesh has been a world leader in its efforts to end the use of child labour in garment factories. On 4 July 1995, the Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers and Exporters Association, International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
, and UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Devel ...
signed a memorandum of understanding on the elimination of child labour in the garment sector. Implementation of this pioneering agreement began in fall 1995, and by the end of 1999, child labour in the garment trade virtually had been eliminated. The labour-intensive process of ship breaking for scrap has developed to the point where it now meets most of Bangladesh's domestic steel needs. Other industries include sugar, tea, leather goods, newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has an ...
, pharmaceutical, and fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
production.
The Bangladesh government continues to court foreign investment, something it has done fairly successfully in private power generation and gas exploration and production, as well as in other sectors such as cellular telephony, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. In 1989, the same year it signed a bilateral investment treaty with the United States, it established a Board of Investment to simplify approval and start-up procedures for foreign investors, although in practice the board has done little to increase investment. The government created the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority to manage the various export processing zones. The agency currently manages EPZs in Adamjee, Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in B ...
, Comilla, Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
, Ishwardi, Karnaphuli, Mongla, and Uttara. An EPZ has also been proposed for Sylhet
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট) is a metropolitan city in northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative seat of the Sylhet Division. Located on the north bank of the Surma River at the eastern tip of Bengal, Sylhet has a subtropical climate an ...
. The government has given the private sector permission to build and operate competing EPZs-initial construction on a Korean EPZ started in 1999. In June 1999, the AFL–CIO petitioned the U.S. Government to deny Bangladesh access to U.S. markets under the Generalized System of Preferences
The Generalized System of Preferences, or GSP, is a preferential tariff system which provides tariff reduction on various products. The concept of GSP is very different from the concept of " most favored nation" (MFN). MFN status provides equal tre ...
(GSP), citing the country's failure to meet promises made in 1992 to allow freedom of association in EPZs.
International trade
 Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a heavy toll on almost all sectors of the economy, inter alia, most notably, it has caused a reduction of exports by 16.93 percent, and imports by 17 percent in the FY2019-20.
In 2015, the top exports of Bangladesh are Non-Knit Men's Suits ($5.6B), Knit T-shirts ($5.28B), Knit Sweaters ($4.12B), Non-Knit Women's Suits ($3.66B) and Non-Knit Men's Shirts ($2.52B).
Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a heavy toll on almost all sectors of the economy, inter alia, most notably, it has caused a reduction of exports by 16.93 percent, and imports by 17 percent in the FY2019-20.
In 2015, the top exports of Bangladesh are Non-Knit Men's Suits ($5.6B), Knit T-shirts ($5.28B), Knit Sweaters ($4.12B), Non-Knit Women's Suits ($3.66B) and Non-Knit Men's Shirts ($2.52B). Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported
license. In 2015, the top imports of Bangladesh are Heavy Pure Woven Cotton ($1.33B), Refined Petroleum ($1.25B), Light Pure Woven Cotton ($1.12B), Raw Cotton ($1.01B) and Wheat ($900M). In 2015, the top export destinations of Bangladesh are the United States ($6.19B), Germany ($5.17B), the United Kingdom ($3.53B), France ($2.37B) and Spain ($2.29B). In 2015, the top import origins are China ($13.9B), India ($5.51B), Singapore ($2.22B), Hong Kong ($1.47B) and Japan ($1.36B).
Bangladeshi women and the economy
 As of 2014, female participation in the labour force is 58% as per World Bank data, and male participation at 82%.
A 2007 World Bank report stated that the areas in which women's work force participation have increased the most are in the fields of agriculture, education and health and social work. Over three-quarters of women in the labour force work in the agricultural sector. On the other hand, the International Labour Organization reports that women's workforce participation has only increased in the professional and administrative areas between 2000 and 2005, demonstrating women's increased participation in sectors that require higher education. Employment and labour force participation data from the World Bank, the UN, and the ILO vary and often under report on women's work due to unpaid labour and informal sector jobs. Though these fields are mostly paid, women experience very different work conditions than men, including wage differences and work benefits. Women's wages are significantly lower than men's wages for the same job with women being paid as much as 60–75 percent less than what men make.
One example of action that is being taken to improve female conditions in the work force is Non-Governmental Organisations. These NGOs encourage women to rely on their own self-savings, rather than external funds provide women with increased decision-making and participation within the family and society. However, some NGOs that address microeconomic issues among individual families fail to deal with broader macroeconomic issues that prevent women's complete autonomy and advancement.
As of 2014, female participation in the labour force is 58% as per World Bank data, and male participation at 82%.
A 2007 World Bank report stated that the areas in which women's work force participation have increased the most are in the fields of agriculture, education and health and social work. Over three-quarters of women in the labour force work in the agricultural sector. On the other hand, the International Labour Organization reports that women's workforce participation has only increased in the professional and administrative areas between 2000 and 2005, demonstrating women's increased participation in sectors that require higher education. Employment and labour force participation data from the World Bank, the UN, and the ILO vary and often under report on women's work due to unpaid labour and informal sector jobs. Though these fields are mostly paid, women experience very different work conditions than men, including wage differences and work benefits. Women's wages are significantly lower than men's wages for the same job with women being paid as much as 60–75 percent less than what men make.
One example of action that is being taken to improve female conditions in the work force is Non-Governmental Organisations. These NGOs encourage women to rely on their own self-savings, rather than external funds provide women with increased decision-making and participation within the family and society. However, some NGOs that address microeconomic issues among individual families fail to deal with broader macroeconomic issues that prevent women's complete autonomy and advancement.
Historical statistics
Bangladesh has made significant strides in its economic sector performance since independence in 1971. Although the economy has improved vastly in the 1990s, Bangladesh still suffers in the area of foreign trade in South Asian. Despite major impediments to growth like the inefficiency ofstate-owned enterprise
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a Government, government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn Profit (econom ...
s, a rapidly growing labour force that cannot be absorbed by agriculture, inadequate power supplies, and slow implementation of economic reforms, Bangladesh has made some headway improving the climate for foreign investors and liberalising the capital market
A capital market is a financial market in which long-term debt (over a year) or equity-backed securities are bought and sold, in contrast to a money market where short-term debt is bought and sold. Capital markets channel the wealth of savers t ...
s; for example, it has negotiated with foreign firms for oil and gas exploration, bettered the countrywide distribution of cooking gas, and initiated the construction of natural gas pipelines and power station
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.
Many p ...
s. Progress on other economic reforms has been halting because of opposition from the bureaucracy, public sector unions, and other vested interest groups.
The especially severe floods of 1998 increased the flow of international aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another.
Ai ...
. So far the global financial crisis has not had a major impact on the economy. Foreign aid has seen a gradual decline over the last few decades but economists see this as a good sign for self-reliance. There has been a dramatic growth in exports and remittance inflow which has helped the economy to expand at a steady rate.
Bangladesh has been on the list of UN Least Developed Countries (LDC) since 1975. Bangladesh met the requirements to be recognised as a developing country in March, 2018 with Bangladesh's Gross National Income (GNI) US$1,724 per capita, the Human Assets Index (HAI) 72 and the Economic Vulnerability (EVI) Index 25.2 then. Bangladesh's GNI is now forecasted to reach at US$4,753.39 in 2030.
Gross export and import
See also
*Bangladesh Academy for Rural Development
Bangladesh Academy for Rural Development (BARD) ( bn, বাংলাদেশ পল্লী উন্নয়ন একাডেমী (বার্ড)) Bangladesh Academy for Rural Development (BARD) started its journey on 27 May 1959 as a ...
* Electricity sector in Bangladesh
The utility electricity sector in Bangladesh has one national grid with an installed capacity of 25,700 MW as of June 2022. Bangladesh's energy sector is not up to the mark. However, per capita energy consumption in Bangladesh is considered hi ...
* Automotive industry in Bangladesh
* Bangladeshi RMG Sector
The textile and clothing industries provide a single source of growth in Bangladesh's rapidly developing economy. Exports of textiles and garments are the principal source of foreign exchange earnings. By 2002 exports of textiles, clothing, a ...
* Ceramics industry in Bangladesh
The ceramics industry is a growing manufacturing sector in Bangladesh. The industry started during the late 1950s when the first ceramic industrial plants were established. The industry mainly produces tableware, sanitaryware and tiles. As of 2011, ...
* Electronics industry in Bangladesh
* Federation of Bangladesh Chambers of Commerce & Industries
* List of companies of Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, (with over 166 million people).
It is one of the emerging and growth-leading economies of the world. It is listed among the Next Eleven countries, it ...
*List of megaprojects in Bangladesh
This is a list of megaprojects. "(i.e. projects) characterized by: large investment commitment, vast complexity (especially in organizational terms), and long-lasting impact on the economy, the environment, and society". The number of such projects ...
* List of the largest trading partners of Bangladesh
This is a list of the largest trading partners of Bangladesh based on data from The Observatory of Economic Complexity (OEC).(1)
* Ministry of Industries (Bangladesh)
The Ministry of Industries ( bn, শিল্প মন্ত্রণালয়) (abbreviated as MoInd) is primarily responsible for developing new policies and strategies for promotion, expansion and sustainable development of Industrial secto ...
* 3G (countries)
3G countries or Global Growth Generating countries are 11 countries which have been identified as sources of growth potential and of profitable investment opportunities.
Background
Prepared in February 2011, a Citigroup report prepared by analy ...
* Corruption in Bangladesh
Corruption in Bangladesh has been a continuing problem. According to all major ranking institutions, Bangladesh routinely finds itself among the most corrupt countries in the world.
The public sectors conducted by the Government are the most co ...
* Poverty in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a developing nation. Despite rapid economic growth, poverty remains a major issue. However, poverty has declined sharply in recent history. Shortly after its independence, approximately 90% of the population lived under the poverty ...
* Prostitution in Bangladesh
Prostitution is legal and regulated in Bangladesh. Prostitutes must register and state an affidavit stating that they are entering prostitution of their own free choice and that they are unable to find any other work. Bangladeshi prostitutes o ...
* Crime in Bangladesh
Crime in Bangladesh is present in various forms such as drug trafficking, money laundering, extortion, contract killing, fraud, human trafficking, robbery, corruption, black marketeering, political violence, terrorism and abduction, wildlife traff ...
* Human rights in Bangladesh
Human rights in Bangladesh are enshrined as fundamental rights in Part III of the Constitution of Bangladesh. However, constitutional and legal experts believe many of the country's laws require reform to enforce fundamental rights and reflect de ...
* Child labour in Bangladesh
References
External links
*Bangladesh Economic News
Bangladesh Budget 2007 – 2008
Budget in Brief 2016–17
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Bangladesh
2007 {{Asia topic, Urbanisation in
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...