Indian Force on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the
 In 1776, a Military Department was created within the government of the East India Company at Kolkata. Its main function was to record orders that were issued to the army by various departments of the East India Company for the territories under its control.
With the Charter Act of 1833, the Secretariat of the government of the East India Company was reorganised into four departments, including a Military Department. The army in the presidencies of Bengal, Bombay and
In 1776, a Military Department was created within the government of the East India Company at Kolkata. Its main function was to record orders that were issued to the army by various departments of the East India Company for the territories under its control.
With the Charter Act of 1833, the Secretariat of the government of the East India Company was reorganised into four departments, including a Military Department. The army in the presidencies of Bengal, Bombay and
 The Kitchener Reforms brought the British Army to a new century. In the 20th century, the British Indian Army was a crucial adjunct to British forces in both world wars. 1.3 million Indian soldiers served in World War I (1914–1918) with the
The Kitchener Reforms brought the British Army to a new century. In the 20th century, the British Indian Army was a crucial adjunct to British forces in both world wars. 1.3 million Indian soldiers served in World War I (1914–1918) with the
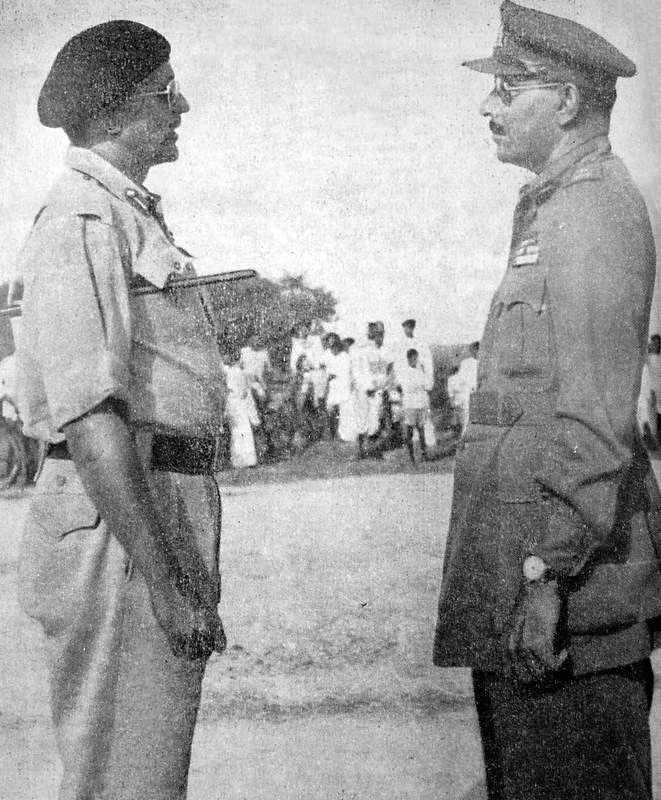 After the partition of India,
After the partition of India,  The cause of this war was a dispute over the sovereignty of the widely separated Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh border regions. Aksai Chin, claimed by India as part of Kashmir, and by China as part of Xinjiang, contains an important road link that connects the Chinese regions of Tibet and Xinjiang. China's construction of this road was one of the triggers of the conflict.
Small-scale clashes between Indian and Chinese forces broke out as India insisted on the disputed McMahon Line being regarded as the international border between the two countries. Chinese troops claimed not to have retaliated to the cross-border firing by Indian troops, despite sustaining losses. China's suspicion of India's involvement in Tibet created more rifts between the two countries.
In 1962, the Indian Army was ordered to move to the Thag La ridge, located near the border between Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh and about north of the disputed McMahon Line. Meanwhile, Chinese troops had also made incursions into Indian-held territory, and tensions between the two reached a new high when Indian forces discovered the road constructed by China in Aksai Chin. After a series of failed negotiations, the
The cause of this war was a dispute over the sovereignty of the widely separated Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh border regions. Aksai Chin, claimed by India as part of Kashmir, and by China as part of Xinjiang, contains an important road link that connects the Chinese regions of Tibet and Xinjiang. China's construction of this road was one of the triggers of the conflict.
Small-scale clashes between Indian and Chinese forces broke out as India insisted on the disputed McMahon Line being regarded as the international border between the two countries. Chinese troops claimed not to have retaliated to the cross-border firing by Indian troops, despite sustaining losses. China's suspicion of India's involvement in Tibet created more rifts between the two countries.
In 1962, the Indian Army was ordered to move to the Thag La ridge, located near the border between Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh and about north of the disputed McMahon Line. Meanwhile, Chinese troops had also made incursions into Indian-held territory, and tensions between the two reached a new high when Indian forces discovered the road constructed by China in Aksai Chin. After a series of failed negotiations, the  Initially, the Indian Army met with considerable success in the northern sector. After launching prolonged artillery barrages against Pakistan, India was able to capture three important mountain positions in Kashmir. By 9 September, the Indian Army had made considerable inroads into Pakistan. India had its largest haul of Pakistani tanks when an offensive by Pakistan's 1st Armoured Division was blunted at the Battle of Asal Uttar, which took place on 10 September near Khemkaran. The biggest tank battle of the war was the
Initially, the Indian Army met with considerable success in the northern sector. After launching prolonged artillery barrages against Pakistan, India was able to capture three important mountain positions in Kashmir. By 9 September, the Indian Army had made considerable inroads into Pakistan. India had its largest haul of Pakistani tanks when an offensive by Pakistan's 1st Armoured Division was blunted at the Battle of Asal Uttar, which took place on 10 September near Khemkaran. The biggest tank battle of the war was the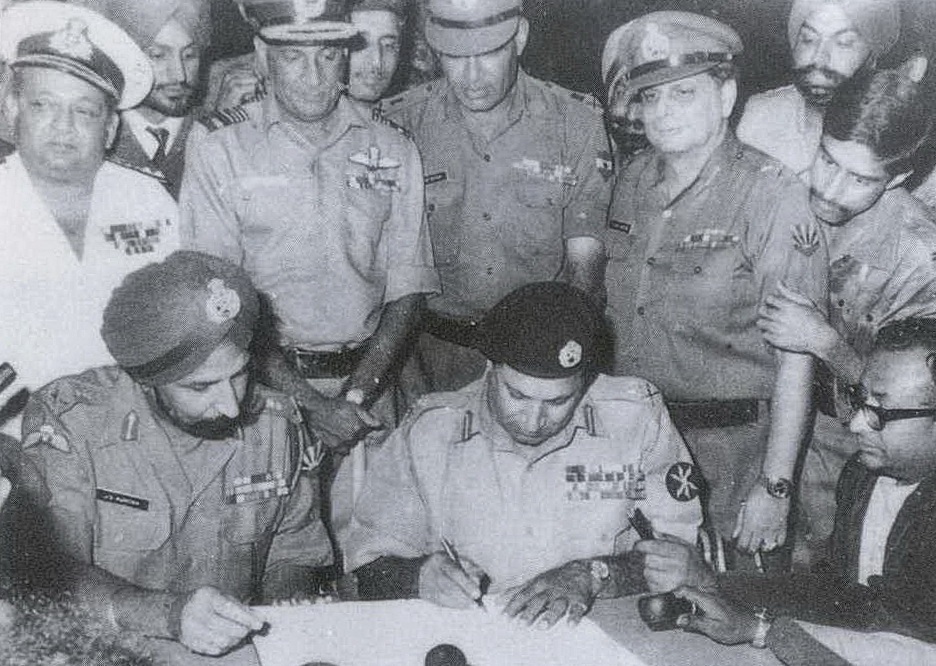  Pakistan launched a counterattack against India on the western front. On 4 December 1971, A Company of the 23rd Battalion of India's
Pakistan launched a counterattack against India on the western front. On 4 December 1971, A Company of the 23rd Battalion of India's  The Siachen Glacier, although a part of the Kashmir region, was not demarcated on maps prepared and exchanged between the two sides in 1947. In consequence, before the 1980s neither India nor Pakistan maintained a permanent military presence in the region. However, beginning in the 1950s, Pakistan began sending mountaineering expeditions to the glacier. By the early 1980s, the Government of Pakistan was granting special expedition permits to mountaineers and United States Army maps showed Siachen as a part of Pakistan. This practice gave rise to the term ''
The Siachen Glacier, although a part of the Kashmir region, was not demarcated on maps prepared and exchanged between the two sides in 1947. In consequence, before the 1980s neither India nor Pakistan maintained a permanent military presence in the region. However, beginning in the 1950s, Pakistan began sending mountaineering expeditions to the glacier. By the early 1980s, the Government of Pakistan was granting special expedition permits to mountaineers and United States Army maps showed Siachen as a part of Pakistan. This practice gave rise to the term '' Once the scale of the Pakistani incursion was realised, the Indian Army quickly mobilised about 200,000 troops, and Operation Vijay was launched. However, since the heights were under Pakistani control, India was at a clear strategic disadvantage. From their observation posts, the Pakistani forces had a clear line-of-sight to lay down indirect artillery fire on NH 1A, inflicting heavy casualties on the Indians.Indian general praises Pakistani valour at Kargil
Once the scale of the Pakistani incursion was realised, the Indian Army quickly mobilised about 200,000 troops, and Operation Vijay was launched. However, since the heights were under Pakistani control, India was at a clear strategic disadvantage. From their observation posts, the Pakistani forces had a clear line-of-sight to lay down indirect artillery fire on NH 1A, inflicting heavy casualties on the Indians.Indian general praises Pakistani valour at Kargil
5 May 2003 Daily Times, Pakistan This was a serious problem for the Indian Army as the highway was its main supply route. Thus, the Indian Army's priority was to recapture peaks near NH 1A. This resulted in Indian troops first targeting the Tiger Hill and Tololing complex in Dras. This was soon followed by more attacks on the Batalik–Turtok sub-sector, which provided access to Siachen Glacier. Point 4590, which had the nearest view of the NH 1A, was successfully recaptured by Indian forces on 14 June. Though most of the posts in the vicinity of the highway were cleared of the enemy by mid-June, some posts near Dras endured sporadic shelling until the end of the war. Once the NH 1A area was cleared, the Indian Army turned to drive the invading force back across the Line of Control. The Battle of Tololing, among others, slowly tilted the war in India's favour. Nevertheless, some Pakistani posts put up a stiff resistance, including Tiger Hill (Point 5140), which fell only later in the war. As the operation was fully underway, about 250 artillery guns were brought in to clear the infiltrators in posts that were in the line-of-sight. At many vital points, neither artillery nor air power could dislodge the Pakistan soldiers, who were out of visible range. The Indian Army mounted some direct frontal ground assaults, which were slow and took a heavy toll, given the steep ascents that had to be made on peaks as high as . Two months into the conflict, Indian troops had slowly retaken most of the ridges they had lost. According to official accounts, an estimated 75%–80% of the enemy-occupied area, and nearly all the high ground, was back under Indian control.
Following the
Though most of the posts in the vicinity of the highway were cleared of the enemy by mid-June, some posts near Dras endured sporadic shelling until the end of the war. Once the NH 1A area was cleared, the Indian Army turned to drive the invading force back across the Line of Control. The Battle of Tololing, among others, slowly tilted the war in India's favour. Nevertheless, some Pakistani posts put up a stiff resistance, including Tiger Hill (Point 5140), which fell only later in the war. As the operation was fully underway, about 250 artillery guns were brought in to clear the infiltrators in posts that were in the line-of-sight. At many vital points, neither artillery nor air power could dislodge the Pakistan soldiers, who were out of visible range. The Indian Army mounted some direct frontal ground assaults, which were slow and took a heavy toll, given the steep ascents that had to be made on peaks as high as . Two months into the conflict, Indian troops had slowly retaken most of the ridges they had lost. According to official accounts, an estimated 75%–80% of the enemy-occupied area, and nearly all the high ground, was back under Indian control.
Following the
, 157 Indians have been killed during such missions. The Indian army has also provided paramedical units to facilitate the withdrawal of the sick and wounded. Indo-China Doklam issue
 The eighth edition of Yudh Abhyas was conducted from 3 to 17 May 2013 as a U.S.-Army-Pacific-sponsored bilateral training exercise with the Indian Army, an exercise that focused on the two countries' cultures, weapons training, and tactics. Units from the United States included the 1st Brigade Combat Team,
The eighth edition of Yudh Abhyas was conducted from 3 to 17 May 2013 as a U.S.-Army-Pacific-sponsored bilateral training exercise with the Indian Army, an exercise that focused on the two countries' cultures, weapons training, and tactics. Units from the United States included the 1st Brigade Combat Team,
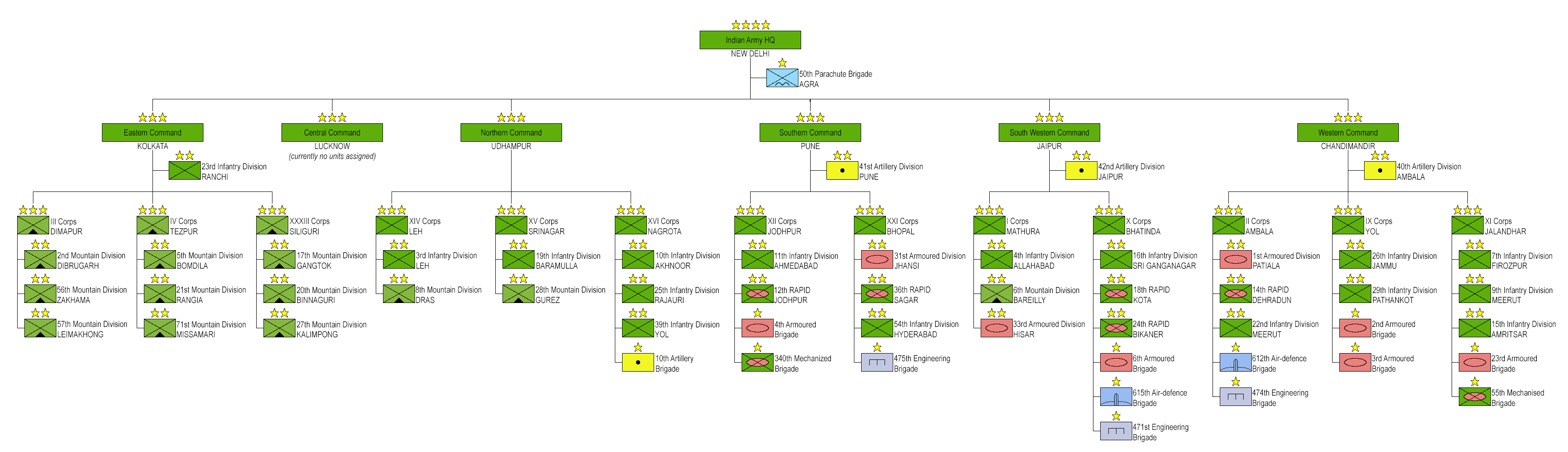 The troops are organized into 40 Divisions in 14 Corps. Army headquarters is located in the Indian capital, New Delhi, and it is under the overall command of the
The troops are organized into 40 Divisions in 14 Corps. Army headquarters is located in the Indian capital, New Delhi, and it is under the overall command of the
 Not to be confused with the field corps listed above, the corps mentioned below are divisions entrusted with specific pan-Army tasks.
The
Not to be confused with the field corps listed above, the corps mentioned below are divisions entrusted with specific pan-Army tasks.
The  Armoured Corps
Armoured Corps
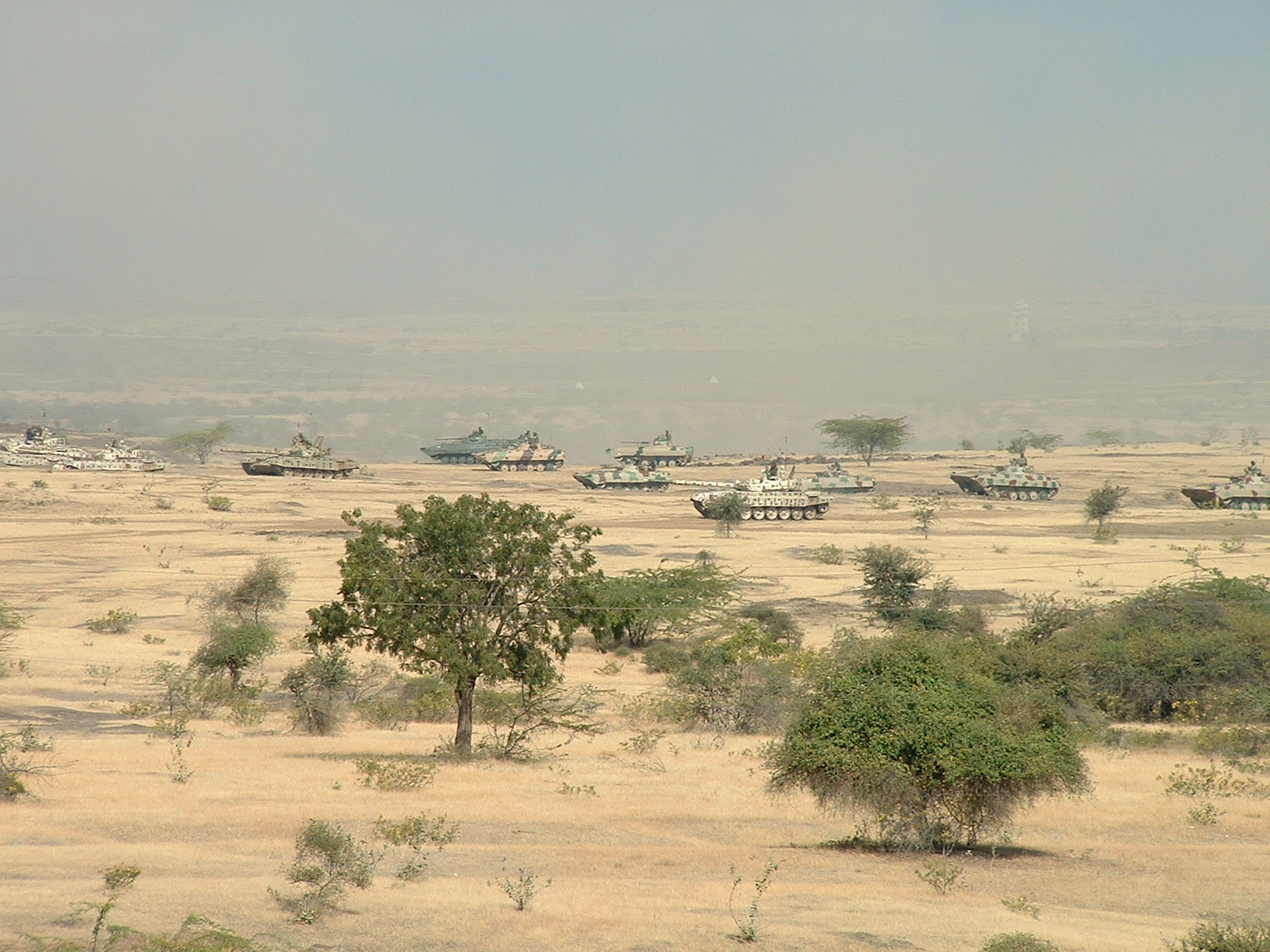 There are 65 armoured regiments in the Indian Army (including). These include the President's Bodyguard and 61st Cavalry the as well as the following historic regiments dating back to the nineteenth century or earlier: 1st (Skinner's) Horse, the
There are 65 armoured regiments in the Indian Army (including). These include the President's Bodyguard and 61st Cavalry the as well as the following historic regiments dating back to the nineteenth century or earlier: 1st (Skinner's) Horse, the 


 Upon its inception, the Indian Army inherited the British Army's organisational structure, which is still maintained today. Therefore, like its predecessor, an Indian infantry regiment's responsibility is not to undertake field operations but to provide battalions and well-trained personnel to the field formations. As such, it is common to find battalions of the same regiment spread across several brigades, divisions, corps, commands, and even theatres. Like its British and Commonwealth counterparts, troops enlisted within the regiment are immensely loyal, take great pride in the regiment to which they are assigned, and generally spend their entire career within the regiment.
Most Indian Army infantry regiments recruit based on certain selection criteria, such as region (for example, the Assam Regiment), caste/community ( Jat Regiment), or religion (
Upon its inception, the Indian Army inherited the British Army's organisational structure, which is still maintained today. Therefore, like its predecessor, an Indian infantry regiment's responsibility is not to undertake field operations but to provide battalions and well-trained personnel to the field formations. As such, it is common to find battalions of the same regiment spread across several brigades, divisions, corps, commands, and even theatres. Like its British and Commonwealth counterparts, troops enlisted within the regiment are immensely loyal, take great pride in the regiment to which they are assigned, and generally spend their entire career within the regiment.
Most Indian Army infantry regiments recruit based on certain selection criteria, such as region (for example, the Assam Regiment), caste/community ( Jat Regiment), or religion ( For some time, the Regiment of Artillery commanded a significantly larger share of the Army's personnel than it does now, as it was also responsible for air defence artillery and some aviation assets. The 1990s saw the formation of the Corps of Army Air Defence and the coalescing of all aviation assets into the Army Aviation Corps. The arm is now focused on field artillery and supplies regiments and batteries to each of the operational commands. The home of the Regiment is in Nashik,
For some time, the Regiment of Artillery commanded a significantly larger share of the Army's personnel than it does now, as it was also responsible for air defence artillery and some aviation assets. The 1990s saw the formation of the Corps of Army Air Defence and the coalescing of all aviation assets into the Army Aviation Corps. The arm is now focused on field artillery and supplies regiments and batteries to each of the operational commands. The home of the Regiment is in Nashik,
 The Indian Army is a voluntary service, and although a provision for military
The Indian Army is a voluntary service, and although a provision for military
 To make themselves less of a target, the forces of the East India Company in India dyed their white summer tunics to neutral tones initially a tan called khaki (from the Hindi word for "dusty"). This was a temporary measure that became standard in the Indian service in the 1880s. Only during the Second Boer War in 1902, did the entire British Army standardise on dun for Service Dress. The Indian Army uniform standardises on dun for khaki.
The 2006 standard issued camouflage uniform of the Indian Army was the PC-DPM which consists of French Camouflage Europe Centrale featuring a forest camouflage pattern and is designed for use in woodland environments being printed on BDU. The Desert variant issued in 2006 was based on the French Camouflage Daguet printed on BDU, which features a desert camouflage pattern, is used by artillery and infantry posted in dusty, semi-desert, and desert areas of Rajasthan and its vicinity. Starting in 2022, a digital pixelated camouflage pattern uniform designed by
To make themselves less of a target, the forces of the East India Company in India dyed their white summer tunics to neutral tones initially a tan called khaki (from the Hindi word for "dusty"). This was a temporary measure that became standard in the Indian service in the 1880s. Only during the Second Boer War in 1902, did the entire British Army standardise on dun for Service Dress. The Indian Army uniform standardises on dun for khaki.
The 2006 standard issued camouflage uniform of the Indian Army was the PC-DPM which consists of French Camouflage Europe Centrale featuring a forest camouflage pattern and is designed for use in woodland environments being printed on BDU. The Desert variant issued in 2006 was based on the French Camouflage Daguet printed on BDU, which features a desert camouflage pattern, is used by artillery and infantry posted in dusty, semi-desert, and desert areas of Rajasthan and its vicinity. Starting in 2022, a digital pixelated camouflage pattern uniform designed by 
 The new camouflage pattern retains the mix of colours including olive green and earthen, and has been designed keeping in mind aspects like areas of deployment of the troops and climatic conditions they operate in. According to the officials, the fabric of the new material makes it lighter, sturdier, more breathable, and more suitable for the different terrains that the soldiers are posted in.
The new uniform, unlike the old one, has a combat T-shirt worn underneath and a
The new camouflage pattern retains the mix of colours including olive green and earthen, and has been designed keeping in mind aspects like areas of deployment of the troops and climatic conditions they operate in. According to the officials, the fabric of the new material makes it lighter, sturdier, more breathable, and more suitable for the different terrains that the soldiers are posted in.
The new uniform, unlike the old one, has a combat T-shirt worn underneath and a

 The role of women in the Indian Army began when the Indian Military Nursing Service was formed in 1888. Nurses served in World Wars I and II, where 350 Indian Army nurses either died, were taken prisoner of war, or declared missing in action; this includes nurses who died when SS Kuala was sunk by Japanese Bombers in 1942. In 1992, the Indian Army began inducting women officers in non-medical roles.
The role of women in the Indian Army began when the Indian Military Nursing Service was formed in 1888. Nurses served in World Wars I and II, where 350 Indian Army nurses either died, were taken prisoner of war, or declared missing in action; this includes nurses who died when SS Kuala was sunk by Japanese Bombers in 1942. In 1992, the Indian Army began inducting women officers in non-medical roles.
 Most of the army equipment is imported, but efforts are being made to manufacture indigenous equipment. The Defence Research and Development Organisation has developed a range of weapons for the Indian Army, including small arms, artillery, radars, and the Arjun tank. All Indian military small-arms are manufactured under the umbrella administration of the
Most of the army equipment is imported, but efforts are being made to manufacture indigenous equipment. The Defence Research and Development Organisation has developed a range of weapons for the Indian Army, including small arms, artillery, radars, and the Arjun tank. All Indian military small-arms are manufactured under the umbrella administration of the  Aircraft
The Army Aviation Corps is the main body of the Indian Army for tactical air transport, reconnaissance, and medical evacuation, while the
Aircraft
The Army Aviation Corps is the main body of the Indian Army for tactical air transport, reconnaissance, and medical evacuation, while the


 ;Aviation
* The procurement process for 197 light utility helicopters (LUH) has been scrapped; only 64 will be inducted in the Army Aviation to replace the Cheetak and Cheetah Helicopters.
* HAL Light Utility Helicopter (LUH) – requirement for 384 helicopters for both the army and air force.
* HAL has obtained a firm order to deliver 114
;Aviation
* The procurement process for 197 light utility helicopters (LUH) has been scrapped; only 64 will be inducted in the Army Aviation to replace the Cheetak and Cheetah Helicopters.
* HAL Light Utility Helicopter (LUH) – requirement for 384 helicopters for both the army and air force.
* HAL has obtained a firm order to deliver 114  * Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles
**
* Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles
**
excerpt and text search
*
Army and Nation: The Military and Indian Democracy since Independence
Harvard University Press.
Indian Army
at Bharat Rakshak {{Authority control 1895 establishments in India 1947 establishments in India Cantonments of India Defence agencies of India Government agencies established in 1947 Articles containing video clips Military units and formations established in 1895 Recipients of the Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar
Chief of Army Staff
Chief of Army Staff or Chief of the Army Staff which is generally abbreviated as COAS is a title commonly used for the appointment held by the most senior staff officer or the chief commander in several nations' armies.
* Chief of Army (Australia ...
(COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army was formed in 1895 alongside the long established presidency armies of the East India Company, which too were absorbed into it in 1903. The princely states had their own armies, which were merged into the national army after independence. The units and regiments of the Indian Army have diverse histories and have participated in several battles and campaigns around the world, earning many battle and theatre honours before and after Independence.
The primary mission of the Indian Army is to ensure national security and national unity, to defend the nation from external aggression and internal threats, and to maintain peace and security within its borders. It conducts humanitarian rescue operations during natural calamities and other disturbances, such as Operation Surya Hope
Operation Surya Hope was the Indian Army’s Central Command response to the June 2013 North India floods in Uttarakhand. The Uttarakhand flood was caused by record off-season monsoon rains, cloud burst, floods, flash floods, and glacial lak ...
, and can also be requisitioned by the government to cope with internal threats. It is a major component of national power, alongside the Indian Navy and the Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
. The army has been involved in four wars with neighbouring Pakistan and one with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Other major operations undertaken by the army include Operation Vijay, Operation Meghdoot, and Operation Cactus
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Man ...
. The army has conducted large peacetime exercises such as Operation Brasstacks and Exercise Shoorveer, and it has also been an active participant in numerous United Nations peacekeeping missions, including those in Cyprus, Lebanon, Congo
Congo or The Congo may refer to either of two countries that border the Congo River in central Africa:
* Democratic Republic of the Congo, the larger country to the southeast, capital Kinshasa, formerly known as Zaire, sometimes referred to a ...
, Angola, Cambodia, Vietnam, Namibia, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south b ...
, Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
, Mozambique, South Sudan, and Somalia.
The Indian Army is operationally and geographically divided into seven commands, with the basic field formation being a division. Below the division level are permanent regiments that are responsible for their own recruiting and training. The army is an all-volunteer force and comprises more than 80% of the country's active defence personnel. It is the largest standing army in the world, with 1,237,117 active troops and 960,000 reserve troops. The army has embarked on an infantry modernisation program known as Futuristic Infantry Soldier As a System (F-INSAS
F-INSAS is India's programme to equip its infantry with state-of-the-art equipment, F-INSAS standing for Future Infantry Soldier As a System. However the Indian Army has decided to drop the F-INSAS program in favour of two separate projects. The ...
), and is also upgrading and acquiring new assets for its armoured, artillery, and aviation branches.
History
Until the independence of India, the "Indian Army" was a British-commanded force defined as "the force recruited locally and permanently based in India, together with its expatriate British officers"; the "British Army in India" referred to British Army units posted to India for a tour of duty. The "Army of India" meant the combined Indian Army and the British Army in India.British Indian Army
 In 1776, a Military Department was created within the government of the East India Company at Kolkata. Its main function was to record orders that were issued to the army by various departments of the East India Company for the territories under its control.
With the Charter Act of 1833, the Secretariat of the government of the East India Company was reorganised into four departments, including a Military Department. The army in the presidencies of Bengal, Bombay and
In 1776, a Military Department was created within the government of the East India Company at Kolkata. Its main function was to record orders that were issued to the army by various departments of the East India Company for the territories under its control.
With the Charter Act of 1833, the Secretariat of the government of the East India Company was reorganised into four departments, including a Military Department. The army in the presidencies of Bengal, Bombay and Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
functioned as respective Presidency Armies until 1 April 1895, when they were unified into a single force known as the Indian Army. For administrative convenience, it was divided into four commands, namely Punjab (including the North West Frontier), Bengal, Madras (including Burma), and Bombay (including Sind, Quetta and Aden).
The British Indian Army was a critical force for maintaining the primacy of the British Empire, both in India and throughout the world. Besides maintaining the internal security of the British Raj, the Army fought in many other theatres: the Anglo-Burmese Wars; the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
Anglo-Sikh wars; the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
, Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
, and Third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* Second#Sexagesimal divisions of calendar time and day, 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (d ...
Anglo-Afghan wars; the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
opium wars, and the Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
in China; and in Abyssinia.
World wars
 The Kitchener Reforms brought the British Army to a new century. In the 20th century, the British Indian Army was a crucial adjunct to British forces in both world wars. 1.3 million Indian soldiers served in World War I (1914–1918) with the
The Kitchener Reforms brought the British Army to a new century. In the 20th century, the British Indian Army was a crucial adjunct to British forces in both world wars. 1.3 million Indian soldiers served in World War I (1914–1918) with the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, in which 74,187 Indian troops were killed or missing in action. In 1915 there was a mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among member ...
by Indian soldiers in Singapore. The United Kingdom made promises of self-governance to the Indian National Congress in return for its support but reneged on them after the war, following which the Indian Independence movement gained strength.
The " Indianisation" of the British Indian Army began with the formation of the Prince of Wales Royal Indian Military College
The Rashtriya Indian Military College (abbreviated RIMC; formerly known as Prince of Wales Royal Indian Military College) is a military school for boys and girls situated in Doon Valley, Dehradun in India. The RIMC is a feeder institution for ...
at Dehradun, in March 1912, to provide education to the scions of aristocratic and well-to-do Indian families and to prepare selected Indian boys for admission into the Royal Military College, Sandhurst. Cadets were given a King's commission, after passing out, and were posted to one of the eight units selected for Indianisation. Because of the slow pace of Indianisation, with just 69 officers being commissioned between 1918 and 1932, political pressure was applied, leading to the formation of the Indian Military Academy in 1932 and greater numbers of officers of Indian origin being commissioned. On the eve of World War II, the officer corps consisted of roughly 500 Indians holding regular commissions against approximately 3,000 British officers.
In World War II Indian soldiers fought alongside the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
. In 1939, British officials had no plan for expansion and training of Indian forces, which comprised about 130,000 men (in addition there were 44,000 men in British units in India in 1939), whose mission was internal security and defence against a possible Soviet threat through Afghanistan. As the war progressed, the size and role of the Indian Army expanded dramatically, and troops were sent to battlefronts as soon as possible. The most serious problem was the lack of equipment. Indian units served in Burma, wherein 1944–45, five Indian divisions were engaged along with one British and three African divisions. Even larger numbers operated in the Middle East. Some 87,000 Indian soldiers died in the war. By the end of the war, it had become the largest volunteer army in history, rising to over 2.5 million men in August 1945.Sumner, p.25
In the African and Middle East campaigns, captured Indian troops were given a choice to join the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
, to eventually "liberate" India from Great Britain, instead of being sent to POW camps. These men, along with Indian students who were in Germany when the war broke out, made up what was called the Free India Legion
, image = Flag of the Indian Legion.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = Flag of the Indian Legion
, country =
, allegiance = Adolf ...
. They were originally intended as pathfinders for German forces in Asia but were soon sent to help guard the Atlantic Wall
The Atlantic Wall (german: link=no, Atlantikwall) was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticip ...
. Few who were part of the Free India Legion ever saw any combat, and very few were ever stationed outside Europe. At its height, the Free India Legion had over 3,000 troops in its ranks.
Indian POWs also joined the Indian National Army
The Indian National Army (INA; ''Azad Hind Fauj'' ; 'Free Indian Army') was a collaborationist armed force formed by Indian collaborators and Imperial Japan on 1 September 1942 in Southeast Asia during World War II. Its aim was to secure In ...
, which was allied with the Empire of Japan. It was raised by a former colonel of the British Indian Army, General Mohan Singh, but was later led by Subhas Chandra Bose
Subhas Chandra Bose ( ; 23 January 1897 – 18 August 1945
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*) was an Indian nationalist whose defiance of British authority in India made him a hero among Indians, but his wartime alliances with Nazi Germany and Imperia ...
and Rash Bihari Bose. With the fall of Singapore in 1942, about 40,000 Indian soldiers were captured. When given the choice, over 30,000 joined the Indian National Army. Those who refused became POWs and were mostly shipped to New Guinea. After initial success, this army was defeated, along with the Japanese; but it had a huge impact on the Indian independence movement.
Indian independence
Upon thePartition of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: ...
and Indian independence in 1947, four of the ten Gurkha regiments were transferred to the British Army. The rest of the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
was divided between the newly created nations of India and Pakistan. The Punjab Boundary Force, which had been formed to help police Punjab during the partition period, was disbanded. Headquarters Delhi and the East Punjab Command were formed to administer the area.
The departure of virtually all senior British officers following independence, and their replacement by Indian officers, meant many of the latter held acting ranks several ranks above their substantive ones. For instance, S. M. Shrinagesh
General Satyawant Mallanna Shrinagesh (also known as Satyavant Shrinagule Mallannah) (11 May 1903 – 27 December 1977) was an Indian military officer who served as 3rd Chief of Army Staff of the Indian Army from 14 May 1955 till 7 May 1957. Af ...
, the ground-forces commander of Indian forces during the first Indo-Pak War of 1947–49 (and the future third COAS), was first an acting major-general and then an acting lieutenant-general during the conflict while holding the substantive rank of major, and only received a substantive promotion to lieutenant-colonel in August 1949. Gopal Gurunath Bewoor, the future ninth COAS, was an acting colonel at his promotion to substantive major from substantive captain in 1949, while future Lieutenant General K. P. Candeth
Lieutenant General Kunhiraman Palat Candeth, PVSM (Hindi: कुँहिरामन पलट कंडेथ; 23 October 1916 – 19 May 2003) was a senior army officer in the Indian Army who played a commanding role in Liberation of Go ...
was an acting brigadier (substantive captain) at the same time. In April 1948, the former Viceroy's Commissioned Officers (VCO) were re-designated Junior Commissioned Officers, while the former King's Commissioned Indian Officers (KCIO) and Indian Commissioned Officers (ICO), along with the former Indian Other Ranks (IOR), were respectively re-designated as Officers and Other Ranks.
Army Day is celebrated on 15 January every year in India, in recognition of Lieutenant General K. M. Cariappa
'
Field Marshal Kodandera Madappa Cariappa (28 January 1899 – 15 May 1993) was the first Indian Commander-in-Chief (C-in-C) of the Indian Army. He led Indian forces on the Western Front during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947. He was appoin ...
's taking over as the first commander-in-chief of the Indian Army from General Sir Francis Butcher, the last British commander-in-chief of India, on 15 January 1949. With effect from 26 January 1950, the date India became a republic, all active-duty Indian Army officers formerly holding the King's Commission were recommissioned and confirmed in their substantive ranks.
Conflicts and operations
First Kashmir War (1947) Immediately after independence, tensions between India and Pakistan erupted into the first of three full-scale wars between the two nations over the thenprincely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
of Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
. The Maharaja of Kashmir wanted to have a standstill position. Since Kashmir was a Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
majority state, Pakistan wanted to make Kashmir a Pakistani territory. As a result, Pakistan invaded Kashmir on 22 October 1947, causing Maharaja Hari Singh to look to India, specifically to Lord Mountbatten of Burma
Louis Francis Albert Victor Nicholas Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (25 June 1900 – 27 August 1979) was a British naval officer, colonial administrator and close relative of the British royal family. Mountbatten, who was of German ...
, the governor-general, for help. He signed the Instrument of Accession to India on 26 October 1947. Indian troops were airlifted to Srinagar from dawn on 27 October. This contingent included General Thimayya
General Kodendera Subayya Thimayya (31 March 1906 - 18 December 1965) was a distinguished soldier of the Indian Army who served as Chief of Army Staff from 1957 to 1961 in the crucial years leading up to the conflict with China in 1962. Gen. ...
who distinguished himself in the operation and in the years that followed became a Chief of the Indian Army. An intense war was waged across the state and former comrades found themselves fighting each other. Pakistan suffered significant losses. Its forces were stopped on the line formed which is now called the Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but serve ...
(LOC).
An uneasy peace, sponsored by the UN, returned by the end of 1948, with Indian and Pakistani soldiers facing each other across the Line of Control, which has since divided Indian-held Kashmir from that part held by Pakistan. Several UN Security Council resolutions
A United Nations Security Council resolution is a United Nations resolution adopted by the fifteen members of the Security Council (UNSC); the United Nations (UN) body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peac ...
were passed, with Resolution 47 calling for a plebiscite to be held in Kashmir to determine accession to India or Pakistan, only after Pakistan withdrew its army from Kashmir. A precondition to the resolution was for Pakistan and India to return to a state of "as was" before the conflict. Pakistan would withdraw all tribesmen and Pakistani nationals brought in to fight in Kashmir. Pakistan refused to pull back, and there could be no further dialogue on fulfilling the UN resolution. Tensions between India and Pakistan, largely over Kashmir, have never been eliminated.
Annexation of Hyderabad (1948)
 After the partition of India,
After the partition of India, Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
, a princely state under the rule of the Nizam of Hyderabad
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, chose to remain independent. The following stand-off between the Government of India and the Nizam ended on 12 September 1948, when India's then Deputy Prime Minister Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
Vallabhbhai Jhaverbhai Patel (; ; 31 October 1875 – 15 December 1950), commonly known as Sardar, was an Indian lawyer, influential political leader, barrister and statesman who served as the first Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister of I ...
ordered Indian troops to secure Hyderabad State. During five days of fighting, the Indian Army, backed by an Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
squadron of Hawker Tempest aircraft, routed the Hyderabad State forces. Five Indian Army infantry battalions and one armoured squadron were engaged in the operation. The following day, Hyderabad was proclaimed part of India. Major General Joyanto Nath Chaudhuri, who led the operation, and accepted the surrender of the Nizam's forces on 18 September 1948, was appointed the military governor of Hyderabad, to restore law and order, and served until 1949.
Assistance during the Korean War (1950–1953)
During the Korean War, although deciding against sending combat forces, India sent its 60th Parachute Field Ambulance unit to aid the UN troops fighting against the North Korean invasion of South Korea, as part of the 1st Commonwealth Division
The 1st Commonwealth Division was the military unit that commanded Commonwealth land forces in the Korean War. The division was a part of the multinational British Commonwealth Forces Korea, with infantry units of the British Army, Canadian Arm ...
. In the aftermath of the war, an Indian infantry brigade formed the Custodian Force of India, some of whose soldiers were also part of the Neutral Nations Repatriation Commission
After the Korean War, prisoner exchange was important for both sides. The UN wanted voluntary repatriation, while People's Republic of China wanted forced repatriation. By May 1952, despite several efforts the issue was deadlocked. Several plans w ...
, which assisted in the exchange of prisoners of war and was headed by Lieutenant General K. S. Thimayya
General Kodendera Subayya Thimayya (31 March 1906 - 18 December 1965) was a distinguished soldier of the Indian Army who served as Chief of Army Staff from 1957 to 1961 in the crucial years leading up to the conflict with China in 1962. Gen. ...
.
Annexation of Goa, Daman and Diu (1961)
Even though the British and French vacated all their colonial possessions in the Indian subcontinent, Portugal refused to relinquish control of its colonies of Goa, Daman, and Diu. After repeated attempts by India to negotiate were spurned by Portuguese prime minister and dictator, António de Oliveira Salazar, on 12 December 1961 India launched Operation Vijay to capture the Portuguese colonies, which was accomplished by small contingents of Indian troops. After a brief conflict that lasted twenty-six hours—during which 31 Portuguese soldiers were killed, the Portuguese Navy frigate NRP Afonso de Albuquerque
NRP ''Afonso de Albuquerque'' was a warship of the Portuguese Navy, named after the 16th-century Portuguese navigator Afonso de Albuquerque. She was destroyed in combat on 18 December 1961, defending Goa against the Indian Armed Forces Annexatio ...
was destroyed, and over 3,000 Portuguese were captured—Portuguese General Manuel António Vassalo e Silva
Manuel António Vassalo e Silva (8 November 1899 – 11 August 1985) was an officer of the Portuguese Army and an overseas administrator. He was the 128th and the last Governor-General of Portuguese India.
Background
He was the only son of Manu ...
surrendered to Major General Kunhiraman Palat Kandoth of the Indian Army. Goa, Daman, and Diu became a part of the Republic of India.
Sino-Indian War (1962)
 The cause of this war was a dispute over the sovereignty of the widely separated Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh border regions. Aksai Chin, claimed by India as part of Kashmir, and by China as part of Xinjiang, contains an important road link that connects the Chinese regions of Tibet and Xinjiang. China's construction of this road was one of the triggers of the conflict.
Small-scale clashes between Indian and Chinese forces broke out as India insisted on the disputed McMahon Line being regarded as the international border between the two countries. Chinese troops claimed not to have retaliated to the cross-border firing by Indian troops, despite sustaining losses. China's suspicion of India's involvement in Tibet created more rifts between the two countries.
In 1962, the Indian Army was ordered to move to the Thag La ridge, located near the border between Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh and about north of the disputed McMahon Line. Meanwhile, Chinese troops had also made incursions into Indian-held territory, and tensions between the two reached a new high when Indian forces discovered the road constructed by China in Aksai Chin. After a series of failed negotiations, the
The cause of this war was a dispute over the sovereignty of the widely separated Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh border regions. Aksai Chin, claimed by India as part of Kashmir, and by China as part of Xinjiang, contains an important road link that connects the Chinese regions of Tibet and Xinjiang. China's construction of this road was one of the triggers of the conflict.
Small-scale clashes between Indian and Chinese forces broke out as India insisted on the disputed McMahon Line being regarded as the international border between the two countries. Chinese troops claimed not to have retaliated to the cross-border firing by Indian troops, despite sustaining losses. China's suspicion of India's involvement in Tibet created more rifts between the two countries.
In 1962, the Indian Army was ordered to move to the Thag La ridge, located near the border between Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh and about north of the disputed McMahon Line. Meanwhile, Chinese troops had also made incursions into Indian-held territory, and tensions between the two reached a new high when Indian forces discovered the road constructed by China in Aksai Chin. After a series of failed negotiations, the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
attacked Indian Army positions on the Thag La ridge. This move by China caught India by surprise, and on 12 October Nehru gave orders for the Chinese to be expelled from Aksai Chin. However, poor coordination among various divisions of the Indian Army, and the late decision to mobilise the Indian Air Force in vast numbers, gave China a crucial tactical and strategic advantage over India. On 20 October, Chinese soldiers attacked India from both the northwest and northeast; and captured large portions of Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh.
As the fighting moved beyond disputed territories, China called on the Indian government to negotiate; however, India remained determined to regain lost territory. With no agreement in sight, China unilaterally withdrew its forces from Arunachal Pradesh. The reasons for the withdrawal are disputed, with India claiming various logistical problems for China and diplomatic support from the United States, while China stated that it still held territory it had staked a claim on. The dividing line between the Indian and Chinese forces was named the Line of Actual Control.
The poor decisions made by India's military commanders, and the political leadership, raised several questions. The Henderson-Brooks and Bhagat committee was soon set up by the government of India to determine the causes of the poor performance of the Indian Army. Its report criticised the decision not to allow the Indian Air Force to target Chinese transport lines, out of fear of a Chinese aerial counter-attack on Indian civilian areas. Much of the blame was placed on the then–defence minister, Krishna Menon, who resigned from his post soon after the war ended. Despite frequent calls for its release, the Henderson-Brooks report remains classified. Neville Maxwell
Neville Maxwell (1926 – 23 September 2019) was a British journalist and scholar who authored the 1970 book ''India's China War'', which is considered a revisionist analysis of the 1962 Sino-Indian War, putting the blame for it on India. Maxwe ...
has written an account of the war.
Indo-Pakistani War of 1965
A second confrontation with Pakistan took place in 1965. Although the war is described as inconclusive, India had the better of the war and was the clear winner in tactical and strategic terms. Pakistani president Ayub Khan
Ayub Khan is a compound masculine name; Ayub is the Arabic version of the name of the Biblical figure Job, while Khan or Khaan is taken from the title used first by the Mongol rulers and then, in particular, their Islamic and Persian-influenced s ...
launched Operation Gibraltar in August 1965, during which Pakistani paramilitary troops infiltrated into Indian-administered Kashmir and attempted to ignite anti-India agitation in Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
. Pakistani leaders believed that India, which was still recovering from the Sino-Indian War, would be unable to deal with a military thrust and a Kashmiri rebellion. India reacted swiftly and launched a counter-offensive against Pakistan. In reply, on 1 September Pakistan launched Operation Grand Slam, invading India's Chamb-Jaurian sector. In retaliation, the Indian Army launched a major offensive all along its border with Pakistan, with Lahore as its prime target.
 Initially, the Indian Army met with considerable success in the northern sector. After launching prolonged artillery barrages against Pakistan, India was able to capture three important mountain positions in Kashmir. By 9 September, the Indian Army had made considerable inroads into Pakistan. India had its largest haul of Pakistani tanks when an offensive by Pakistan's 1st Armoured Division was blunted at the Battle of Asal Uttar, which took place on 10 September near Khemkaran. The biggest tank battle of the war was the
Initially, the Indian Army met with considerable success in the northern sector. After launching prolonged artillery barrages against Pakistan, India was able to capture three important mountain positions in Kashmir. By 9 September, the Indian Army had made considerable inroads into Pakistan. India had its largest haul of Pakistani tanks when an offensive by Pakistan's 1st Armoured Division was blunted at the Battle of Asal Uttar, which took place on 10 September near Khemkaran. The biggest tank battle of the war was the Battle of Chawinda
{{Infobox military conflict
, width = 380px
, image = File:Sculpture showing Indo-Pak war.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Sculpture showing the Indo-Pakistani War
{{clear
{{OSM Location map
, co ...
, the largest tank battle in history after World War II. Pakistan's defeat at the Battle of Asal Uttar hastened the end of the conflict.
At the time of the ceasefire declaration, India reported casualties of about 3,000. On the other hand, it was estimated that more than 3,800 Pakistani soldiers were killed in the conflict. About 200–300 Pakistani tanks were either destroyed or captured by India. India lost a total of 150-190 tanks during the conflict. The decision to return to pre-war positions, following the Tashkent Declaration, caused an outcry in New Delhi. It was widely believed that India's decision to accept the ceasefire was due to political factors, not military, since it was facing considerable pressure from the United States and the United Nations to cease hostilities.
1967 Sino-Indian conflict
The 1967 Sino-Indian skirmish, also known as the Cho La incident, was a military conflict between Indian troops and members of the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
who, on 1 October 1967, invaded Sikkim, which was then a protectorate of India. On 10 October, both sides clashed again. Defence minister Sardar Swaran Singh
Sardar Swaran Singh (19 August 1907 – 30 October 1994) was an Indian politician. He was India's longest-serving union cabinet minister.
Early life
Swaran Singh Purewal was born on 19 August 1907 in Shankar (village) in Jalandhar distric ...
assured the Indian people that the government was taking care of developments along the border. Indian losses were 88 killed, and 163 wounded, while Chinese casualties were 300 killed and 450 wounded in Nathula, and 40 in Chola. The Chinese Army left Sikkim after this defeat.
Operation against the Naxalites during 1971
Under Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhi (; Given name, ''née'' Nehru; 19 November 1917 – 31 October 1984) was an Indian politician and a central figure of the Indian National Congress. She was elected as third prime minister of India in 1966 ...
, during the president's rule
In India, President's rule is the suspension of state government and imposition of direct Union government rule in a state. Under Article 356 of the Constitution of India, if a state government is unable to function according to Constitutional ...
in 1971, the Indian Army and the Indian police launched Operation Steeplechase, a gigantic "counter-insurgency" operation against the Naxalites, which resulted in the death of hundreds of Naxalites and the imprisonment of more than 20,000 suspects and cadres, including senior leaders. The army was also assisted by a brigade of para commandos and the Indian paramilitary
India maintains 10 paramilitary forces.
List of Paramilitary forces
From 1986 to 2011 the Central Armed Police Forces were considered as Central Police Forces (CPF). However, as per their respective acts they all are Armed Police Forces.
...
. The operation was organised in October 1969, and Lieutenant General J.F.R. Jacob
Lieutenant General Jack Farj Rafael Jacob, PVSM (2May 1921 – 13January 2016), was a general officer in the Indian Army. He was best known for the role he played in the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971. Jacob, then a major general, served as ...
was enjoined by Govind Narain, the Home Secretary, that "there should be no publicity and no records". Jacob's request to be presented with written orders was also refused by Sam Manekshaw.
Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971
An independence movement broke out in East Pakistan which was crushed
Crushed may refer to:
* "Crushed" (''Ms. Marvel''), a 2022 episode of the American television series ''Ms. Marvel''
* "Crushed" (Roland Lee Gift song) a 2009 single by Roland Lee Gift
* "Crushed" (''The Suite Life of Zack & Cody'' episode), an ...
by Pakistani forces. Due to large-scale atrocities against them, thousands of Bengalis took refuge in neighbouring India causing a major refugee crisis there. In early 1971, India declared its full support for the Bengali freedom fighters, known as Mukti Bahini, and Indian agents were extensively involved in covert operations to aid them.
On 20 November 1971, the Indian Army moved 14 Punjab Battalion, of the 45th Cavalry
45 Cavalry is an armoured regiment in the Armoured Corps of the Indian Army. The regiment distinguished itself in operations during the 1971 Indo-Pakistan War winning one Maha Vir Chakra.
Raising
The first 45th Cavalry was formed in August 1 ...
regiment, into Garibpur, a strategically important town in East Pakistan, near India's border, and successfully captured it. The following day, more clashes took place between Indian and Pakistani forces. Wary of India's growing involvement in the Bengali rebellion, the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) launched a preemptive strike on 10 Indian air bases—at Srinagar, Jammu, Pathankot, Amritsar, Agra, Adampur, Jodhpur, Jaisalmer, Uttarlai, and Sirsa—at 17:45 hours on 3 December. However, this aerial offensive failed to accomplish its objectives and gave India an excuse to declare a full-scale war against Pakistan the same day. By midnight, the Indian Army, accompanied by the Indian Air Force, launched a major three-pronged assault into East Pakistan. The Indian Army won several battles on the eastern front including the decisive Battle of Hilli
The Battle of Hilli or the Battle of Bogura was a major battle fought in the Bangladesh Liberation War. It is generally regarded as the most severe pitched battle that took place in East Pakistan, now Bangladesh. The battle of Hilli took place ...
. The operation also included a battalion-level airborne operation on Tangail, which resulted in the capitulation of all resistance within five days. India's massive early gains were attributed largely to the speed and flexibility with which Indian armoured divisions moved across East Pakistan.
 Pakistan launched a counterattack against India on the western front. On 4 December 1971, A Company of the 23rd Battalion of India's
Pakistan launched a counterattack against India on the western front. On 4 December 1971, A Company of the 23rd Battalion of India's Punjab Regiment Punjab Regiment may refer to the following existing units:
*Punjab Regiment (India)
*Punjab Regiment (Pakistan)
From 1922 to 1947, the British Indian Army included 6 numbered Punjab Regiments:
*1st Punjab Regiment
* 2nd Punjab Regiment
*8th Punj ...
intercepted the Pakistani 51st Infantry Brigade near Ramgarh, Rajasthan. The Battle of Longewala ensued, during which A Company, though outnumbered, thwarted the Pakistani advance until the Indian Air Force directed its fighters to engage the Pakistani tanks. By the time the battle had ended, 38 Pakistani tanks and 100 armoured vehicles were either destroyed or abandoned. About 200 Pakistani troops were killed in action, while only two Indian soldiers died. Pakistan suffered another major defeat on the western front at the Battle of Basantar
The Battle of Basantar also known as the Battle of Shakargarh or Battle of Barapind (December 4–16, 1971) was one of the vital battles fought as part of the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 in the western sector of India. The Indian troops won a har ...
, which was fought from 4 to 16 December. During the battle, about 66 Pakistani tanks were destroyed and 40 more were captured. Pakistani forces destroyed only 11 Indian tanks. By 16 December, Pakistan had lost sizeable territory on both the eastern and western fronts.
On 16 December 1971, under the command of Lt. General J. S. Arora, elements of the three corps of the Indian Army that had invaded East Pakistan entered Dhaka as a part of the Indo-Bangladesh allied force and forced Pakistani forces to surrender, one day after the conclusion of the Battle of Basantar. After Pakistan's Lt General A. A. K. Niazi
Lieutenant General Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi (1915 – 1 February 2004) was a Pakistan Army general. During the Bangladesh Liberation War and the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, he commanded the Pakistani Eastern Command in East Pakistan (now Ba ...
signed the Instrument of Surrender, India, as a part of the allied forces, took more than 90,000 Pakistani prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
. By the time of the signing, 11,000 Pakistani soldiers had been killed in action, while India suffered 3,500 battle-related deaths. In addition, Pakistan lost 220 tanks during the battle compared to India's 69.
In 1972, the Simla Agreement was signed between the two countries, although subsequent incidences of heightened tensions have resulted in continued military vigilance on both sides.
Siachen conflict (1984)
 The Siachen Glacier, although a part of the Kashmir region, was not demarcated on maps prepared and exchanged between the two sides in 1947. In consequence, before the 1980s neither India nor Pakistan maintained a permanent military presence in the region. However, beginning in the 1950s, Pakistan began sending mountaineering expeditions to the glacier. By the early 1980s, the Government of Pakistan was granting special expedition permits to mountaineers and United States Army maps showed Siachen as a part of Pakistan. This practice gave rise to the term ''
The Siachen Glacier, although a part of the Kashmir region, was not demarcated on maps prepared and exchanged between the two sides in 1947. In consequence, before the 1980s neither India nor Pakistan maintained a permanent military presence in the region. However, beginning in the 1950s, Pakistan began sending mountaineering expeditions to the glacier. By the early 1980s, the Government of Pakistan was granting special expedition permits to mountaineers and United States Army maps showed Siachen as a part of Pakistan. This practice gave rise to the term ''oropolitics Oropolitics comes from the Greek ''oros'' meaning mountain and ''politikos'' meaning citizen. In modern usage it denotes the use of mountaineering for political purposes.
Origin of term
The term "oropolitics" was coined by Joydeep Sircar in the ear ...
''.
India, possibly irked by these developments, launched Operation Meghdoot in April 1984. An entire battalion of the Kumaon Regiment was airlifted to the glacier. Pakistani forces responded quickly, and clashes between the two followed. The Indian Army secured the strategic Sia La and Bilafond La
Bilafond La (meaning "Pass of the Butterflies" in Balti language, also known as the Saltoro Pass, is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, sitting immediately west of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ 980420 wh ...
mountain passes, and by 1985 more than of territory claimed by Pakistan was under Indian control. The Indian Army continues to control all of the Siachen Glacier and its tributary glaciers. Pakistan has made several unsuccessful attempts to regain control over Siachen. In late 1987, Pakistan mobilised about 8,000 troops and garrisoned them near Khapalu, aiming to capture Bilafond La. However, they were repulsed by Indian Army personnel guarding Bilafond. During the battle, about 23 Indian soldiers lost their lives, while more than 150 Pakistani troops perished. Further unsuccessful attempts to reclaim positions were launched by Pakistan in 1990, 1995, 1996, and 1999, most notably in Kargil in the latter year.
India continues to maintain a strong military presence in the region, despite inhospitable conditions. The conflict over Siachen is regularly cited as an example of mountain warfare. The highest peak in the Siachen Glacier region, Saltoro Kangri, could be viewed as strategically important for India because of its height, which would enable Indian forces to monitor Pakistani or Chinese movements in the area. Maintaining control over Siachen poses several logistical challenges for the Indian Army. Several infrastructure projects were constructed in the region, including a helipad at an elevation of . In 2004, the Indian Army was spending an estimated US$2 million a month to support its personnel stationed in the region.
Counter-insurgency activities
The Indian Army has played a crucial role in fighting insurgents and terrorists within the nation. The army launched Operation Blue Star and Operation Woodrose
Operation Woodrose was a military operation carried out by the Indira Gandhi-led Indian government in the months after Operation Blue Star to "prevent the outbreak of widespread public protest" in the state of Punjab. The government arrested all ...
in the 1980s to combat Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
insurgents. The army, along with some paramilitary forces, has the prime responsibility of maintaining law and order in the troubled Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
region, under Northern Command. The Indian Army sent a contingent to Sri Lanka in 1987 as a part of the Indian Peace Keeping Force
Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) was the Indian military contingent performing a peacekeeping operation in Sri Lanka between 1987 and 1990. It was formed under the mandate of the 1987 Indo-Sri Lankan Accord that aimed to end the Sri Lankan ...
. The Indian Army also successfully conducted Operation Golden Bird
Operation Golden Bird was an Indian-Myanmar military operation conducted by the Indian Army in April–May 1995.
The operation was initiated by the 57th Mountain Division of the Indian Army, which tracked down and decapitated a rebel column ...
in 1995, as a counter-insurgency operation in northeast India.
Kargil war (1999)
In 1998, India carried out nuclear tests; and a few days later, Pakistan responded with nuclear tests of its own, giving both countries nuclear deterrence
Deterrence theory refers to the scholarship and practice of how threats or limited force by one party can convince another party to refrain from initiating some other course of action. The topic gained increased prominence as a military strategy ...
capability, although India had tested a hydrogen bomb, which Pakistan lacked. Diplomatic tensions eased after the Lahore Summit was held in 1999. However, the sense of optimism was short-lived. In mid-1999, Pakistani paramilitary forces and Kashmiri insurgents captured the deserted, but strategic, Himalayan heights in the Kargil district of India. These had been vacated by the Indian Army during the onset of the inhospitable winter and were to be reoccupied in spring. The troops that took control of these areas received important support, of both arms and supplies, from Pakistan. Some of the heights under their control, which also included the Tiger Hill, overlooked the vital Srinagar
Srinagar (English: , ) is the largest city and the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It lies in the Kashmir Valley on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus, and Dal and Anchar lakes. The city is known for its natu ...
–Leh
Leh () ( lbj, ) is the joint capital and largest city of Ladakh, a union territory of India. Leh, located in the Leh district, was also the historical capital of the Kingdom of Ladakh, the seat of which was in the Leh Palace, the former res ...
Highway ( NH 1A), Batalik
Batalik is a town in Ladakh, India, located on the upper reaches of the Indus river. It was a focal point in the Kargil War because of its strategic location between Kargil, Leh and Baltistan. In 1999, the Kargil war was fought in this region.
...
, and Dras
Dras (also spelt Drass, ISO transliteration: '), also known locally in Shina as Himababs, Hembabs, or Humas, is a town and hill station, near Kargil city in the Kargil district of the union territory of Ladakh in India. It is on the Nationa ...
.
 Once the scale of the Pakistani incursion was realised, the Indian Army quickly mobilised about 200,000 troops, and Operation Vijay was launched. However, since the heights were under Pakistani control, India was at a clear strategic disadvantage. From their observation posts, the Pakistani forces had a clear line-of-sight to lay down indirect artillery fire on NH 1A, inflicting heavy casualties on the Indians.Indian general praises Pakistani valour at Kargil
Once the scale of the Pakistani incursion was realised, the Indian Army quickly mobilised about 200,000 troops, and Operation Vijay was launched. However, since the heights were under Pakistani control, India was at a clear strategic disadvantage. From their observation posts, the Pakistani forces had a clear line-of-sight to lay down indirect artillery fire on NH 1A, inflicting heavy casualties on the Indians.Indian general praises Pakistani valour at Kargil5 May 2003 Daily Times, Pakistan This was a serious problem for the Indian Army as the highway was its main supply route. Thus, the Indian Army's priority was to recapture peaks near NH 1A. This resulted in Indian troops first targeting the Tiger Hill and Tololing complex in Dras. This was soon followed by more attacks on the Batalik–Turtok sub-sector, which provided access to Siachen Glacier. Point 4590, which had the nearest view of the NH 1A, was successfully recaptured by Indian forces on 14 June.
 Though most of the posts in the vicinity of the highway were cleared of the enemy by mid-June, some posts near Dras endured sporadic shelling until the end of the war. Once the NH 1A area was cleared, the Indian Army turned to drive the invading force back across the Line of Control. The Battle of Tololing, among others, slowly tilted the war in India's favour. Nevertheless, some Pakistani posts put up a stiff resistance, including Tiger Hill (Point 5140), which fell only later in the war. As the operation was fully underway, about 250 artillery guns were brought in to clear the infiltrators in posts that were in the line-of-sight. At many vital points, neither artillery nor air power could dislodge the Pakistan soldiers, who were out of visible range. The Indian Army mounted some direct frontal ground assaults, which were slow and took a heavy toll, given the steep ascents that had to be made on peaks as high as . Two months into the conflict, Indian troops had slowly retaken most of the ridges they had lost. According to official accounts, an estimated 75%–80% of the enemy-occupied area, and nearly all the high ground, was back under Indian control.
Following the
Though most of the posts in the vicinity of the highway were cleared of the enemy by mid-June, some posts near Dras endured sporadic shelling until the end of the war. Once the NH 1A area was cleared, the Indian Army turned to drive the invading force back across the Line of Control. The Battle of Tololing, among others, slowly tilted the war in India's favour. Nevertheless, some Pakistani posts put up a stiff resistance, including Tiger Hill (Point 5140), which fell only later in the war. As the operation was fully underway, about 250 artillery guns were brought in to clear the infiltrators in posts that were in the line-of-sight. At many vital points, neither artillery nor air power could dislodge the Pakistan soldiers, who were out of visible range. The Indian Army mounted some direct frontal ground assaults, which were slow and took a heavy toll, given the steep ascents that had to be made on peaks as high as . Two months into the conflict, Indian troops had slowly retaken most of the ridges they had lost. According to official accounts, an estimated 75%–80% of the enemy-occupied area, and nearly all the high ground, was back under Indian control.
Following the Washington Accord Washington Agreement or Washington Accords may refer to:
* Washington Agreement (1994), peace agreement of Bosnia and Herzegovina (March 1 1994)
* Washington Accords (1942), the Brazil-United States Political-Military Agreement leading to Brazil e ...
of 4 July, where Sharif agreed to withdraw Pakistani troops, most of the fighting came to a gradual halt; but some Pakistani forces remained in positions on the Indian side of the LOC. In addition, the United Jihad Council (an umbrella group for all extremists) rejected Pakistan's plan for a draw-down, deciding instead to fight on. The Indian Army launched its final attacks in the last week of July. As soon as the Dras sub-sector had been cleared of Pakistani forces, the fighting ceased on 26 July, which has since been celebrated as Kargil Vijay Diwas (Kargil Victory Day) in India. By the end of the war, India had resumed control of all the territory south and east of the Line of Control, as was established in July 1972 per the Shimla Accord. By the time all hostilities had ended, the number of Indian soldiers killed during the conflict stood at 527, while more than 700 regular members of the Pakistani Army had been killed. The number of Islamist fighters, also known as Mujahideen, killed by Indian armed forces during the conflict stood at about 3,000.
2016 Surgical Strikes on Kashmir and the 2016–2018 India-Pakistan conflict
On 18 September 2016, a ''fedayeen'' attack was made by four armed militants on an army base near the town of Uri Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), an island off Malakula Islan ...
. Nineteen Indian Army soldiers were killed. India accused Jaish-e-Muhammad, a Pakistan-based terrorist organisation. On 29 September 2016, the India Army announced that it conducted "surgical strike
A surgical strike is a military attack which is intended to damage only a legitimate military target, with no or minimal collateral damage to surrounding structures, vehicles, buildings, or the general public infrastructure and utilities.
Descr ...
s" against militant launch pads across the Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but serve ...
, in Pakistani-administered Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, and inflicted "significant casualties". Indian media reported the casualty figures variously from 35 to 70 killed. Partial footage of the strikes was released to the Indian media on 27 June 2018 as proof of the strike. The incident triggered the 2016–2018 India-Pakistan border conflict, which ended on 16 June 2018 with both India and Pakistan agreeing on a ceasefire.
United Nations peacekeeping missions
India has been the largest troop contributor to UN peacekeeping missions
This is a list of United Nations peacekeeping missions since the United Nations was founded in 1945, organized by region, with the dates of deployment, the name of the related conflict, and the name of the UN operation.
Peacekeeping, as defin ...
since its inception. So far, India has taken part in 43 Peacekeeping missions, with a total contribution exceeding 160,000 troops and a significant number of police personnel having been deployed. In 2014, India was the third largest troop contributor (TCC), with 7,860 personnel deployed, of which 995 were police personnel, including the first UN Female Formed Police Unit
So far India has taken part in 49 Peacekeeping missions with a total contribution exceeding troops and a significant number of police personnel having been deployed and more than 160 Indian peacekeepers have paid the ultimate price in service ...
, serving with ten UN peacekeeping missions., 157 Indians have been killed during such missions. The Indian army has also provided paramedical units to facilitate the withdrawal of the sick and wounded. Indo-China Doklam issue
Major exercises
Operation Brasstacks Operation Brasstacks was launched by the Indian Army in November 1986 to simulate a full-scale war on India's western border. The exercise was the largest ever conducted in India; it included nine infantry, three mechanised, three armoured divisions, and one air assault division, as well as three independent armoured brigades. Amphibious assault exercises were also conducted with the Indian Navy. Brasstacks also allegedly incorporated nuclear attack drills. It led to tensions with Pakistan and a subsequent rapprochement in mid-1987. Exercise Nomadic Elephant Since 2004, and every year since, the Indian Army has been conducting training exercises with the Mongolian Army. In 2012, the exercise took place inBelgaum
Belgaum (ISO 15919, ISO: ''Bēḷagāma''; also Belgaon and officially known as Belagavi) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka located in its northern part along the Western Ghats. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous ...
; in June 2013, it was held in Mongolia. The aim of the exercises is to enhance counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations, and to train in conducting peacekeeping operations under the mandate of the United Nations.
Exercise Ashwamedha
Indian Army tested its network-centric warfare capabilities in the Ashwamedha exercise. The exercise was held in the Thar desert, and over 300,000 troops participated. Asymmetric warfare capability was also tested by the Indian Army during the exercise.
Exercise Yudh Abhyas
The Yudh Abhyas exercise is an ongoing series, since 2005, of joint exercises between the Indian and United States armies, agreed upon under the New Framework of the India-US Defence Relationship. Commencing at the platoon level, the exercise has graduated to a command post (CPX) and field training exercise (FTX).
The seventh edition of Yudh Abhyas began on 5 March 2012, in two locations under the South Western Command. The US Army contingent is from the US Army Pacific (USARPAC), part of the United States Pacific Command (USPACOM). The command post exercise has an engineer brigade headquarters, with its planners drawn from both countries, while the field training exercise comprises troops of the United States' 2nd Squadron, 14th Cavalry Regiment
The 14th Cavalry Regiment is a cavalry regiment of the United States Army. It has two squadrons that provide reconnaissance, surveillance, and target acquisition for Stryker brigade combat teams. Constituted in 1901, it has served in conflicts ...
, from the 25th Infantry Division, Hawaii, along with a Stryker platoon, and a similarly sized Indian Army contingent of mechanised infantry. Several key surveillance, communications, and IED detection and neutralisation technologies, available to both sides, were fielded in the exercise.

 The eighth edition of Yudh Abhyas was conducted from 3 to 17 May 2013 as a U.S.-Army-Pacific-sponsored bilateral training exercise with the Indian Army, an exercise that focused on the two countries' cultures, weapons training, and tactics. Units from the United States included the 1st Brigade Combat Team,
The eighth edition of Yudh Abhyas was conducted from 3 to 17 May 2013 as a U.S.-Army-Pacific-sponsored bilateral training exercise with the Indian Army, an exercise that focused on the two countries' cultures, weapons training, and tactics. Units from the United States included the 1st Brigade Combat Team, 82nd Airborne Division
The 82nd Airborne Division is an Airborne forces, airborne infantry division (military), division of the United States Army specializing in Paratrooper, parachute assault operations into denied areasSof, Eric"82nd Airborne Division" ''Spec Ops ...
, from Fort Bragg
Fort Bragg is a military installation of the United States Army in North Carolina, and is one of the largest military installations in the world by population, with around 54,000 military personnel. The military reservation is located within Cum ...
, N.C., and the 3rd Squadron, 73rd Cavalry Regiment. Units from India were the Indian Army's 99th Mountain Brigade
The 99th Mountain Brigade, formerly the 99th Indian Infantry Brigade, is an infantry formation of the Indian Army.
The brigade was formed in April 1941 at Lucknow. The brigade was then assigned to the 34th Indian Infantry Division in October 194 ...
; the 2nd Battalion, 5th Gurka Rifles; the
50th Independent Parachute Brigade; and the 54th Engineers Regiment.
Exercise Shakti
The Shakti exercise is an ongoing series, since 2011, of joint exercises between the Indian and French armies. The exercise is conducted to practice and validate anti-terrorist operations in snowbound and mountainous areas. The first joint exercise was held in India in October 2011 and the second one in September 2013. The theme of the exercise is to conduct joint platoon-level counter-insurgency operations in high-altitude mountainous terrain under the UN Charter, thus emphasising the shared concerns of both countries regarding global terrorism. An added aim of the exercise is to qualitatively enhance knowledge of each other's military procedures, thus increasing the scope for interoperability and the ability to respond to a common threat. The twelve-day exercise with the French Army is scheduled to be conducted in multiple modules in order to achieve complete integration between the two contingents at every stage.
Exercise Shoorveer
From the first week of April to the first week of May 2012, the Indian Army launched a massive summer exercise in the Rajasthan desert, involving over 50,000 troops and several hundred artillery pieces and infantry combat vehicles, as part of its efforts to shore up its battle worthiness on the western front, the border with Pakistan. The exercise, code-named "Shoorveer", was being conducted by the Jaipur-based South Western Command. This was the largest ever exercise conducted by the Indian army since 1947. The collective training started with the honing of basic battle procedures and tactical drills.
Several field firings were carried out to check the accuracy and lethality of weapon systems. Many innovations, adopted by units and formations to enhance combat power, were tested in the field. The troops built on the training momentum gradually, with increasing combat tempo, to set the stage for a major joint army–air force exercise in the latter part of the exercise.
Exercise Rudra Akrosh
In May 2012, the Indian Army conducted several war games aimed (according to officials) at validating "the operational and transformational effectiveness of various formations under the Western Army Command". The exercise involved approximately 20,000 troops and support from the Indian Air Force.
Exercise Shatrujeet
In April 2016, the Indian Army conducted a major exercise called Shatrujeet, with the elite Mathura-based Strike Corps in the desert area of the Mahajan Field Firing Range in Rajasthan, whose object was to evaluate the capability to strike deep into enemy territory, to deliver a quick, lethal strike against the enemy in an integrated air-land battle environment, with co-ordination among all the forces in a nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare scenario.
Mission and doctrine
Initially, the army's main objective was to defend the nation's frontiers. However, over the years, the army has also taken up the responsibility of providing internal security, especially against insurgencies inKashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
and Northeast India. Currently, the army is also looking at enhancing its special forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
capabilities. With India's increasing international role, and the requirement to protect its interests in far-off countries becoming important, the Indian Army and the Indian Navy are jointly planning to set up a marine brigade.
The current combat doctrine of the Indian Army is based on effectively utilising holding formations and strike formations. In the case of an attack, the holding formations would contain the enemy and strike formations would counter-attack to neutralise enemy forces. In the case of an Indian attack, the holding formations would pin enemy forces down, whilst the strike formations would attack at a point of India's choosing. The Indian Army is large enough to devote several corps to the strike role.
Organisation
 The troops are organized into 40 Divisions in 14 Corps. Army headquarters is located in the Indian capital, New Delhi, and it is under the overall command of the
The troops are organized into 40 Divisions in 14 Corps. Army headquarters is located in the Indian capital, New Delhi, and it is under the overall command of the Chief of Army Staff
Chief of Army Staff or Chief of the Army Staff which is generally abbreviated as COAS is a title commonly used for the appointment held by the most senior staff officer or the chief commander in several nations' armies.
* Chief of Army (Australia ...
(COAS).
Command structure
The army operates six operational commands and one training command. Each command is headed by General Officer Commanding-in-Chief with the rank of Lieutenant General. Each command directly reports to Army HQ in New Delhi. These commands are given below in order of creation, with location (city) and commanders listed. There is also the Army Training Command abbreviated ARTRAC. Besides these, army officers may head tri-service commands such as theStrategic Forces Command
The Strategic Forces Command (SFC), sometimes called Strategic Nuclear Command, forms part of India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA). It is responsible for the management and administration of the country's tactical and strategic nuclear weap ...
and Andaman and Nicobar Command
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is the first and only Joint warfare, tri-service Theater (warfare), theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was cre ...
, as well as institutions such as the Integrated Defence Staff.
''Note: ** = Currently being raised''
Combat Arms
 Not to be confused with the field corps listed above, the corps mentioned below are divisions entrusted with specific pan-Army tasks.
The
Not to be confused with the field corps listed above, the corps mentioned below are divisions entrusted with specific pan-Army tasks.
The Indian Territorial Army
The Territorial Army (TA) of India is an auxiliary military organisation of part-time volunteers that provides support service to the Indian Army. It is composed of officers, junior commissioned officers, non-commissioned officers and other per ...
has battalions affiliated with different infantry regiments and some department units that are from the Corps of Engineers, Army Medical Corps, or the Army Service Corps. They serve as a part-time reserve. On 4 June 2017, the chief of staff announced that the Army was planning to open combat positions to women, who would first be appointed to positions in the military police.
 Armoured Corps
Armoured Corps
 There are 65 armoured regiments in the Indian Army (including). These include the President's Bodyguard and 61st Cavalry the as well as the following historic regiments dating back to the nineteenth century or earlier: 1st (Skinner's) Horse, the
There are 65 armoured regiments in the Indian Army (including). These include the President's Bodyguard and 61st Cavalry the as well as the following historic regiments dating back to the nineteenth century or earlier: 1st (Skinner's) Horse, the 2nd Lancers (Gardner's Horse)
The 2nd Lancers (Gardner's Horse) is one of the oldest and a highly decorated armoured regiment of the Indian Army. The regiment was formed by the amalgamation of two of the oldest regiments of the Bengal Army – the 2nd Royal Lancers (Gardner' ...
, the 3rd Cavalry, the 4th (Hodson's) Horse, the 7th Light Cavalry, the 8th Light Cavalry
The 8th Light Cavalry traces its origins from the 8th King George's Own Light Cavalry which was formed in 1922 by the amalgamation of the 26th King George's Own Light Cavalry and the 30th Lancers following a re-organisation of the Indian Cavalry C ...
, the 9th (Deccan) Horse, the 14th (Scinde) Horse, the 17th (Poona) Horse, the 15th Lancers
The 15th Lancers (Baloch) is an armoured regiment of the Pakistan Army. It was formed in 1922 by the amalgamation of the 17th Cavalry and the 37th Lancers (Baluch Horse).Ahmad, Lt Col RN. (2010). ''Battle Honours of the Baloch Regiment''. Abbottaba ...
, the 16th Light Cavalry
The 16th Light Cavalry is a regiment of the Armoured Corps, a primary combat arm of the Indian Army. Prior to India gaining independence from the British in 1947, it was a regular cavalry regiment of the British Indian Army. It was formed in 1776 ...
, the 18th Cavalry
The 18th King Edward's Own Cavalry was a regular cavalry regiment in the British Indian Army. Following the independence of India, the regiment was allotted to the Indian Army and redesignated as the 18th Cavalry.
Formation
Tracing its orig ...
, the 20th Lancers and the 21st (Central India) Horse. A substantial number of additional units designated as either "Cavalry" or "Armoured" Regiments have been raised since Independence.
Mechanised Infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also mechanized force).
As defined by the United States Army, mechanized infantry is di ...
The Mechanised Infantry is the newest combat arm of the Indian Army. Often referred to as "tomorrow's arm in today's army", it is formed of two regiments— The Brigade of the Guards and Mechanised Infantry Regiment—and comprises 48 Mechanised Infantry battalions in all. It is the brainchild of General Krishnaswamy Sundarji (28 April 1930 – 8 February 1999), who was the Chief of Army Staff of the Indian Army from 1986 to 1988. During the late 70s, as part of Indian Army modernisation, there was an urgent need to re-calibrate the Indian Mechanised Forces, which led to the forming of Mechanised Infantry units to further the shock-action, fire-power, flexibility, and mobility of armoured formations by including ground-holding ability. The Mechanised Infantry regiments were first created with carefully selected existing Infantry battalions, based on their operational performance. As the need for more mechanised battalions grew, the elite Brigade of The Guards was also converted to the mechanised profile. The two regiments along with the Armoured Corps form part of the Indian Army's elite "Mechanised Forces".
Infantry



 Upon its inception, the Indian Army inherited the British Army's organisational structure, which is still maintained today. Therefore, like its predecessor, an Indian infantry regiment's responsibility is not to undertake field operations but to provide battalions and well-trained personnel to the field formations. As such, it is common to find battalions of the same regiment spread across several brigades, divisions, corps, commands, and even theatres. Like its British and Commonwealth counterparts, troops enlisted within the regiment are immensely loyal, take great pride in the regiment to which they are assigned, and generally spend their entire career within the regiment.
Most Indian Army infantry regiments recruit based on certain selection criteria, such as region (for example, the Assam Regiment), caste/community ( Jat Regiment), or religion (
Upon its inception, the Indian Army inherited the British Army's organisational structure, which is still maintained today. Therefore, like its predecessor, an Indian infantry regiment's responsibility is not to undertake field operations but to provide battalions and well-trained personnel to the field formations. As such, it is common to find battalions of the same regiment spread across several brigades, divisions, corps, commands, and even theatres. Like its British and Commonwealth counterparts, troops enlisted within the regiment are immensely loyal, take great pride in the regiment to which they are assigned, and generally spend their entire career within the regiment.
Most Indian Army infantry regiments recruit based on certain selection criteria, such as region (for example, the Assam Regiment), caste/community ( Jat Regiment), or religion (Sikh Regiment
The Sikh Regiment is an infantry regiment of the Indian Army. Sikh regiment is the highest decorated regiment of the Indian Army and in 1979, the 1st battalion was the Commonwealth's most decorated battalion with 245 pre-independence and 82 ...
). Most regiments continue the heritage of regiments raised under the British Raj, but some have been raised after independence, some of which have specialised in border defence, in particular the Ladakh Scouts, the Arunachal Scouts, and the Sikkim Scouts.
Over the years there have been fears that troops' allegiance lay more with their regiments and the regions/castes/communities/religions from which they were recruited, as opposed to the Indian union as a whole. Thus some "all India" or "all class" regiments have been created, which recruit troops from all over India, regardless of region, caste, community, or religion: such as the Brigade of the Guards (which later converted to the Mechanised Infantry profile) and the Parachute Regiment.
Artillery
The Regiment of Artillery is the second-largest arm of the Indian Army, constituting nearly one-sixth of the Army's total strength. Originally raised in 1935 as part of the Royal Indian Artillery of the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
, the Regiment is now tasked with providing the Army's towed and self-propelled field artillery
Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement.
Until the early 20t ...
, including guns, howitzers, heavy mortars, rockets, and missiles.
As an integral part of nearly all combat operations conducted by the Indian Army, the Regiment of Artillery has a history of being a major contributor to its military success. During the Kargil War, it was the Indian Artillery that inflicted the most damage. Over the years, five artillery officers have gone on to the Army's highest post as Chief of Army Staff.
 For some time, the Regiment of Artillery commanded a significantly larger share of the Army's personnel than it does now, as it was also responsible for air defence artillery and some aviation assets. The 1990s saw the formation of the Corps of Army Air Defence and the coalescing of all aviation assets into the Army Aviation Corps. The arm is now focused on field artillery and supplies regiments and batteries to each of the operational commands. The home of the Regiment is in Nashik,
For some time, the Regiment of Artillery commanded a significantly larger share of the Army's personnel than it does now, as it was also responsible for air defence artillery and some aviation assets. The 1990s saw the formation of the Corps of Army Air Defence and the coalescing of all aviation assets into the Army Aviation Corps. The arm is now focused on field artillery and supplies regiments and batteries to each of the operational commands. The home of the Regiment is in Nashik, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
, where their headquarters is located, along with the service's museum. The School of Artillery of the Indian Army is located nearby, in Devlali
Deolali, or Devlali (), is a small hill station and a census town in Nashik district of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Now it is part of Nashik Metropolitan Region.
Deolali has an important army base. Deolali Camp, one of the oldest Indian ...
.
After suffering consistent failure to import or produce modern artillery for three decades, the Regiment of Artillery is finally going ahead with procurement of brand new 130-mm and 155-mm guns. The Army is also putting large numbers of rocket launchers into service, with 22 regiments to be equipped with the indigenously developed Pinaka multi barrel rocket launcher by the end of the next decade.
Corps of Engineers
The Indian Army Corps of Engineers has a long history dating back to the mid-18th century. The earliest existing subunit of the Corps (18 Field Company) dates back to 1777, while the Corps officially recognises its birth as 1780, when the senior-most group of the Corps, the Madras Sappers, were raised. The Corps consists of three groups of combat engineers, namely the Madras Sappers, the Bengal Sappers, and the Bombay Sappers. A group is roughly analogous to a regiment of the Indian infantry, each group consisting of several engineer regiments. The engineer regiment is the basic combat-engineer unit, analogous to an infantry battalion.
Corps of Signals
Indian Army Corps of Signals
Indian Army Corps of Signals is a corps and a combat support arm of the Indian Army, which handles its military communications. It was formed on 15 February 1911 as a separate entity under Lieutenant Colonel S H Powell, and went on to make import ...
is a corps and the arm of the Indian Army which handles its military communications
Military communications or military signals involve all aspects of communications, or conveyance of information, by armed forces. Military communications span from pre-history to the present. The earliest military communications were delivered b ...
. It was formed on 15 February 1911 as a separate entity under Lieutenant Colonel S. H. Powell and went on to make important contributions during World War I and World War II. On 15 February 2011, the corps celebrated the 100th anniversary of its raising.
Army Aviation Corps
The Army Aviation Corps, formed on 1 November 1986, is the aviation arm of the Indian Army. It is headed by a Director-General with the rank of Lieutenant General at Army HQ in New Delhi.
Corps of Army Air Defence
The Corps of Army Air Defence
The Corps of Army Air Defence (abbreviated as AAD), is an active corps of the Indian Army and a major combat support arm tasked with Anti-aircraft warfare, air defence of the country from foreign threats. The AAD is responsible for the protection ...
(abbreviated AAD) is an active corps of the Indian Army, and a major combat formation tasked with the air defences
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, ...
of the country from foreign threats. The Corps is responsible for the protection of Indian air space from enemy aircraft and missiles, especially those below 5,000 feet.
The history of the AAD dates back to 1939, during the times of the British Raj in India. The corps actively took part in the Second World War, fighting on behalf of the British Empire. Post-independence, the corps has participated in all the wars involving India
This is a list of known wars, conflicts, battles/sieges, missions and operations involving former kingdoms and states in the Indian subcontinent and the modern day Republic of India and it's predecessors.
Ancient India (c. 15th to 1st centu ...
, starting with the 1947 Indo-Pakistani War
It was the first year of the Cold War, which would last until 1991, ending with the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Events
January
* January– February – Winter of 1946–47 in the United Kingdom: The worst snowfall in the countr ...
, up to the 1999 Kargil conflict
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referred ...
. The corps enjoyed autonomous status from 1994, after the bifurcation of the Corps of Air Defence Artillery from the Army's artillery regiment. A separate training school, the Army Air Defence College (AADC), was established to train its personnel.
Services
Recruitment and Training
Pre-commission training of Gentlemen Cadets is carried out at the Indian Military Academy atDehradun
Dehradun () is the capital and the most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and is governed by the Dehradun Municipal Corporation, with the Uttarakhand Legislative As ...
and the Officers Training Academy
The Officers Training Academy (OTA) is a training establishment of the Indian Army that trains officers for the Short Service Commission (SSC). The 49-week course at the OTA prepares graduates for all branches of the Army, except for the Army Me ...
at Chennai. There are also specialised training institutions such as the Army War College, at Mhow, Madhya Pradesh; the High Altitude Warfare School
The High Altitude Warfare School (HAWS) is a National security, defence service training and research establishment of the Indian Army. In 1948, the Indian Army established a ski school in Gulmarg that later became the High Altitude Warfare Scho ...
(HAWS), at Gulmarg, Jammu and Kashmir; the Counter Insurgency and Jungle Warfare School
The Counter-Insurgency and Jungle Warfare School (CIJWS) in Vairengte, Mizoram, India is a training and research establishment of the Indian Army specialising in unconventional warfare, especially counter-insurgency and guerrilla warfare. CIJ ...
(CIJW), in Vairengte, Mizoram; and the College of Military Engineering (CME), in Pune.
The Army Training Command (ARTRAC), at Shimla, supervises training of personnel.
In 2020 a 'Tour of Duty' scheme was proposed for voluntary recruitment into the forces for civilians, to enable them to join for three years of short service. The scheme is on a trial basis and will start with a test group of 100 officers and 1000 jawans.
Agnipath Scheme
Agnipath Scheme (also spelled Agneepath Scheme) ( hi, Agnīpath Yojanā, ) is a tour of duty style scheme introduced by the Government of India on 14 June 2022, for recruitment of soldiers below the rank of commissioned officers into the three se ...
is a new scheme introduced by the Government of India on 14 June 2022, for recruitment of soldiers below the rank of commissioned officers into the three services of the armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
.
Intelligence
The Directorate of Military Intelligence (DMI) is an intelligence-gathering arm of the Indian Army. The MI (as it is commonly referred to) was constituted in 1941. It was initially created to check corruption in the Army's ranks. With time, its role has evolved into cross-border intelligence, intelligence sharing with friendly nations, infiltrating insurgent groups, and counter-terrorism. In the late 1970s, the MI was embroiled in theSamba spy scandal
The Samba Military Spy Scandal was a cold war military intelligence program which eventually emerged as a scandal in 1979. According to the Indian Army, the military program was run by the MI of Pakistan to seek information on the Indian Army's ...
, wherein three Indian Army officers were falsely implicated as Pakistani spies. The organisation has since emerged from the scandal as a prime intelligence organisation of the Indian Army.
, the MI has seen many of its roles taken away by the newly created National Technical Research Organisation and the Defence Intelligence Agency. Since it was set up in 2004 as a premier scientific agency under the National Security Adviser in the Prime Minister's Office, it also includes the National Institute of Cryptology Research and Development (NICRD), which is the first of its kind in Asia.
Field formations
Below are the basic field formations of the Indian Army: * Command: Indian Army has six operational commands and one training command. Each one is headed by a general officer commanding-in-chief (GOC-in-C), known as the army commander, who is among the seniormost Lieutenant General officers in the army. * Corps: A command generally consists of two or more corps. Indian Army has 14 Corps each one commanded by a general officer commanding (GOC), known as the corps commander, who holds the rank of Lieutenant General. Each corps is composed of three or four divisions. There are three types of corps in the Indian Army: Strike, Holding and Mixed. The Corps HQ is the highest field formation in the army. * Division: Each division is headed by GOC (division commander) in the rank of major general. It usually consists of three to four Brigades. Currently, the Indian Army has 40 Divisions including four RAPIDs (Re-organised Army Plains Infantry Division), 18 Infantry Divisions, 12 Mountain Divisions, three Armoured Divisions and three Artillery Divisions. * Brigade: A brigade generally consists of around 3,000 combat troops with supporting elements. An Infantry Brigade usually has three Infantry battalions along with various Support Elements. It is commanded by a brigade commander who is a Brigadier, equivalent to a brigadier general in some armies. In addition to the Brigades in various Army Divisions, the Indian Army also has five Independent Armoured Brigades, 15 Independent Artillery Brigades, seven Independent Infantry Brigades, one Independent Parachute Brigade, three Independent Air Defence Brigades, two Independent Air Defence Groups and four Independent Engineer Brigades. These Independent Brigades operate directly under the Corps Commander (GOC Corps). * Battalion: Composed of four rifle companies. Commanded by a battalion commander who is a Colonel and is the Infantry's main fighting unit. Every infantry battalion also possesses oneGhatak Platoon
A Ghatak Platoon, or Ghatak Commandos, is a special operations capable reconnaissance platoon that is present in every infantry battalion in the Indian Army. Ghatak is a Sanskrit word meaning "killer" or "lethal". Their name was given to them by ...
.
* Company
A company, abbreviated as co., is a Legal personality, legal entity representing an association of people, whether Natural person, natural, Legal person, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common p ...
: Composed of three platoons. Commanded by a company commander who is a major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
or lieutenant-colonel.
* Battery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
: Comprising either 3 or 4 sections, in artillery and air defence units. Every battery has two officers, the senior of which is the Battery Commander.
* Platoon: Composed of three sections. Commanded by a platoon commander who is a JCO.
* Section: Smallest military outfit, with a strength of 10 personnel. Commanded by a section commander of the rank of Havaldar.
Indian Army forts
* Fort William, Kolkata: Garrison of Eastern Army Command * Fort St George, Chennai: Garrison of ATNK&K Army Area * OD Fort,Allahabad
Allahabad (), officially known as Prayagraj, also known as Ilahabad, is a metropolis in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.The other five cities were: Agra, Kanpur (Cawnpore), Lucknow, Meerut, and Varanasi (Benares). It is the administrat ...
, Ordnance Depot
Personnel
 The Indian Army is a voluntary service, and although a provision for military
The Indian Army is a voluntary service, and although a provision for military conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
exists in the Indian constitution, conscription has never been imposed. , the Indian Army has a sanctioned strength of 49,932 officers (42,253 serving, being 7,679 under strength), and 1,215,049 enlisted personnel (1,194,864 serving, being 20,185 under strength). Recently, it has been proposed to increase the strength of the army by more than 90,000, to counter the increasing presence of Chinese troops along the Line of Actual Control. According to the International Institute for Strategic Studies, in 2020 the army had a strength of 1,237,000 active personnel and 960,000 reserve personnel. Of those in reserve, 300,000 are first-line reserves (within 5 years of active service), 500,000 are committed to return if called until the age of 50, and 160,000 were in the Indian Territorial Army
The Territorial Army (TA) of India is an auxiliary military organisation of part-time volunteers that provides support service to the Indian Army. It is composed of officers, junior commissioned officers, non-commissioned officers and other per ...
, with 40,000 in regular establishment. This makes the Indian Army the world's largest standing volunteer army.
Rank structure
The ranks of the Indian Army for the most part follow the British Army tradition. Commissioned Officers Commissioned officers are the leaders of the army and command units from platoon/company to brigade, division, corps, and above. Indian Army officers are continually put through different courses of training, and assessed on merit, for promotions and appointments. Substantive promotions up to lieutenant colonel, or equivalent, are based on time in service, whereas those for the colonel and above are based on selection, with promotion to colonel being also based on time served. Other RanksUniforms
 To make themselves less of a target, the forces of the East India Company in India dyed their white summer tunics to neutral tones initially a tan called khaki (from the Hindi word for "dusty"). This was a temporary measure that became standard in the Indian service in the 1880s. Only during the Second Boer War in 1902, did the entire British Army standardise on dun for Service Dress. The Indian Army uniform standardises on dun for khaki.
The 2006 standard issued camouflage uniform of the Indian Army was the PC-DPM which consists of French Camouflage Europe Centrale featuring a forest camouflage pattern and is designed for use in woodland environments being printed on BDU. The Desert variant issued in 2006 was based on the French Camouflage Daguet printed on BDU, which features a desert camouflage pattern, is used by artillery and infantry posted in dusty, semi-desert, and desert areas of Rajasthan and its vicinity. Starting in 2022, a digital pixelated camouflage pattern uniform designed by
To make themselves less of a target, the forces of the East India Company in India dyed their white summer tunics to neutral tones initially a tan called khaki (from the Hindi word for "dusty"). This was a temporary measure that became standard in the Indian service in the 1880s. Only during the Second Boer War in 1902, did the entire British Army standardise on dun for Service Dress. The Indian Army uniform standardises on dun for khaki.
The 2006 standard issued camouflage uniform of the Indian Army was the PC-DPM which consists of French Camouflage Europe Centrale featuring a forest camouflage pattern and is designed for use in woodland environments being printed on BDU. The Desert variant issued in 2006 was based on the French Camouflage Daguet printed on BDU, which features a desert camouflage pattern, is used by artillery and infantry posted in dusty, semi-desert, and desert areas of Rajasthan and its vicinity. Starting in 2022, a digital pixelated camouflage pattern uniform designed by NIFT
National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) is an autonomous institute that offers courses in fashion, designing, technology, and management. Its head office is located in New Delhi, India.
History
NIFT was established in 1986 under the M ...
has been adopted, while the uniform style is similar to the US Marine MMCUU uniform.

 The new camouflage pattern retains the mix of colours including olive green and earthen, and has been designed keeping in mind aspects like areas of deployment of the troops and climatic conditions they operate in. According to the officials, the fabric of the new material makes it lighter, sturdier, more breathable, and more suitable for the different terrains that the soldiers are posted in.
The new uniform, unlike the old one, has a combat T-shirt worn underneath and a
The new camouflage pattern retains the mix of colours including olive green and earthen, and has been designed keeping in mind aspects like areas of deployment of the troops and climatic conditions they operate in. According to the officials, the fabric of the new material makes it lighter, sturdier, more breathable, and more suitable for the different terrains that the soldiers are posted in.
The new uniform, unlike the old one, has a combat T-shirt worn underneath and a jacket
A jacket is a garment for the upper body, usually extending below the hips. A jacket typically has sleeves, and fastens in the front or slightly on the side. A jacket is generally lighter, tighter-fitting, and less insulating than a coat, which ...
over it. Also unlike the older uniform, the shirt will not be tucked in. The jacket has angular top pockets, lower pockets with vertical openings, knife pleat
A pleat (plait in older English) is a type of fold formed by doubling fabric back upon itself and securing it in place. It is commonly used in clothing and upholstery to gather a wide piece of fabric to a narrower circumference.
Pleats are cat ...
s at the back, a pocket on the left sleeve & a pen holder on the left forearm, and improved-quality buttons. The trousers will be adjustable at the waist with elastic and buttons, and has a double layer at the groin. For the caps, the girth
Girth may refer to:
;Mathematics
* Girth (functional analysis), the length of the shortest centrally symmetric simple closed curve on the unit sphere of a Banach space
* Girth (geometry), the perimeter of a parallel projection of a shape
* Girth ...
will be adjustable, and the logo of the Army will be of better quality than earlier.
The new uniforms would not be available in the open market. The uniforms will be barcoded and QR coded to maintain their uniqueness, and will be available only through the ordnance chain or military canteens. To control random proliferation, they will come in over a dozen pre-stitched standard sizes. The new uniform will be made available in a phased manner to the nearly 1.2 million personnel of the Indian Army.
The modern Indian Army wears distinctive parade uniforms characterised by variegated turbans and waist-sashes in regimental colours. The Gurkha and Garhwal Rifles and the Assam, Kumaon, and Naga Regiments wear broad-brimmed hats of traditional style. Traditionally, all rifle regiments (the Jammu and Kashmir Rifles, the Garhwal Rifles, all Gorkha Rifles, and the Rajputana Rifles), as well as the Jammu and Kashmir Light Infantry, wear rank badge
A mandarin square ( zh, t=補子, s=补子, hp=bŭzi, w=putzŭ; mnc, m=, v=sabirgi; vi, Bổ tử; Chữ Nho: 補子; ko, 흉배/胸背, hyungbae), also known as a rank badge, was a large embroidered badge sewn onto the surcoat of Mandarin ( ...
s, buttons, and wire-embroidered articles in black, instead of the usual brass (or gold) colour, as the original role of the rifle regiments was camouflage and concealment.
Medals and awards
The medals awarded by the President of India for gallantry displayed on the battlefield, in order of precedence, are Param Vir Chakra, Maha Vir Chakra, and Vir Chakra. The medals awarded by the President for gallantry displayed away from the battlefield, in order of precedence, are Ashoka Chakra,Kirti Chakra
The Kirti Chakra is an Indian military decoration awarded for valour, courageous action or self-sacrifice away from the field of battle. It may be awarded to civilians as well as military personnel, including posthumous awards. It is the ''pe ...
, and Shaurya Chakra.
Many of the recipients of these awards have been Indian Army personnel.
Women

 The role of women in the Indian Army began when the Indian Military Nursing Service was formed in 1888. Nurses served in World Wars I and II, where 350 Indian Army nurses either died, were taken prisoner of war, or declared missing in action; this includes nurses who died when SS Kuala was sunk by Japanese Bombers in 1942. In 1992, the Indian Army began inducting women officers in non-medical roles.
The role of women in the Indian Army began when the Indian Military Nursing Service was formed in 1888. Nurses served in World Wars I and II, where 350 Indian Army nurses either died, were taken prisoner of war, or declared missing in action; this includes nurses who died when SS Kuala was sunk by Japanese Bombers in 1942. In 1992, the Indian Army began inducting women officers in non-medical roles.
Equipment
 Most of the army equipment is imported, but efforts are being made to manufacture indigenous equipment. The Defence Research and Development Organisation has developed a range of weapons for the Indian Army, including small arms, artillery, radars, and the Arjun tank. All Indian military small-arms are manufactured under the umbrella administration of the
Most of the army equipment is imported, but efforts are being made to manufacture indigenous equipment. The Defence Research and Development Organisation has developed a range of weapons for the Indian Army, including small arms, artillery, radars, and the Arjun tank. All Indian military small-arms are manufactured under the umbrella administration of the Ordnance Factories Board
Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), consisting of the Indian Ordnance Factories, now known as Directorate of Ordnance (Coordination & Services) was an organisation, under the Department of Defence Production (DDP) of Ministry of Defence (MoD), Gove ...
, with principal firearm manufacturing facilities in Ichhapore, Cossipore, Kanpur, Jabalpur, and Tiruchirapalli. The Indian Small Arms System (INSAS
INSAS or Indian Small Arms System is a family of infantry arms consisting of an assault rifle and a light machine gun (LMG). It was designed by the Armament Research and Development Establishment and manufactured by the Ordnance Factories Boa ...
) rifle, which has been successfully deployed since 1997, is a product of Rifle Factory Ishapore, while ammunition is manufactured at Khadki, and possibly at Bolangir.
In 2014, Army chief General Bikram Singh
General Bikram Singh, (born 1952) is a retired Indian army officer who served as the 24th Chief of Army Staff (COAS) of the Indian Army. Previously the General Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the army's Eastern Command, he succeeded General ...
said that if given sufficient budget support, the Indian Army might be able to acquire half the ammunition needed to fight in a major conflict by the next year.
 Aircraft
The Army Aviation Corps is the main body of the Indian Army for tactical air transport, reconnaissance, and medical evacuation, while the
Aircraft
The Army Aviation Corps is the main body of the Indian Army for tactical air transport, reconnaissance, and medical evacuation, while the Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial w ...
's helicopter assets are responsible for assisting army troop transport and close air support. The Aviation Corps operates approximately 150 helicopters. The Indian army had projected a requirement for a helicopter that can carry loads of up to to heights of on the Siachen Glacier in Jammu and Kashmir. Flying at these heights poses unique challenges due to the rarefied atmosphere. The Indian Army will induct the HAL Light Utility Helicopter to replace its ageing fleet of Chetaks and Cheetahs, some of which were deployed more than three decades ago.
On 13 October 2012, the defence minister gave control of attack helicopters to the Indian Army, which had formerly rested the Indian Air force.
Future developments
*F-INSAS
F-INSAS is India's programme to equip its infantry with state-of-the-art equipment, F-INSAS standing for Future Infantry Soldier As a System. However the Indian Army has decided to drop the F-INSAS program in favour of two separate projects. The ...
is the Indian Army's principal infantry modernisation programme, which aims to modernise the army's 465 infantry and paramilitary battalions by 2020. The programme aims to upgrade the infantry to a multi-calibre rifle with an under-barrel grenade launcher, as well as bulletproof jackets and helmets. The helmet would include a visor, flashlight, thermal sensors, night vision devices, and a miniature computer with an audio headset. There would also be a new lightweight and waterproof uniform, which would help the soldier in carrying extra loads and fighting in an NBC environment.
* India is currently re-organising its mechanised forces to achieve strategic mobility and high-volume firepower for rapid thrusts into enemy territory. India proposes to progressively deploy as many as 248 Arjun main battle tanks (MBT) and to develop and deploy the Arjun MK-II variant, as well as 1,657 Russian-made T-90S MBTs. The army is procuring 2,000 night vision devices for T-72 tanks, for Rs 10 billion; 1,200 for T-90 tanks, for Rs 9.60 billion; and 1,780 for infantry combat vehicles, for Rs 8.60 billion. It is also acquiring 700 TISAS (thermal imaging stand alone systems) and 418 TIFACS (thermal fire control systems) for its T-72 fleet, at a cost of around $230 million. 300 Israeli TISAS were installed as part of several T-72 upgrade phases, followed by 3,860 image intensifier-based night-vision devices. 310 Russian produced T-90S Main Battle Tanks were also fitted with French Catherine TI cameras.
*In 2008, the Cabinet Committee on Security
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) of the Government of India discusses, debates and is the final decision-making body on senior appointments in the national security apparatus, defence policy and expenditure, and generally all matters of Ind ...
approved raising two new infantry mountain divisions (with around 15,000 combat soldiers each) and an artillery brigade. These divisions were likely to be armed with ultralight howitzers. In July 2009, it was reported that the Army was advocating a new artillery division. The proposed artillery division, to be under the Kolkata-based Eastern Command, was to have three brigades – two armed with 155 mm howitzers and one with the Russian "Smerch" and indigenous "Pinaka" multiple-launch rocket systems.
The major ongoing weapons programmes of the Indian Army are as follows:
;Tanks and Armoured vehicles
* Arjun MK-IA – main battle tank
* Futuristic Battle Tank (FMBT) – The FMBT will be a lighter tank of 50 tons. At the conceptual stage.
* Abhay IFV – Future Infantry Combat Vehicle
* TATA Kestrel – A modern armoured personnel carrier (APC) developed by Tata Motors and the Defence Research and Development Organisation ( DRDO). It was developed to replace old Soviet-era infantry fighting vehicles (BMP) and APCs in service with the Indian army. It is expected to join the Indian Army by 2017.

 ;Aviation
* The procurement process for 197 light utility helicopters (LUH) has been scrapped; only 64 will be inducted in the Army Aviation to replace the Cheetak and Cheetah Helicopters.
* HAL Light Utility Helicopter (LUH) – requirement for 384 helicopters for both the army and air force.
* HAL has obtained a firm order to deliver 114
;Aviation
* The procurement process for 197 light utility helicopters (LUH) has been scrapped; only 64 will be inducted in the Army Aviation to replace the Cheetak and Cheetah Helicopters.
* HAL Light Utility Helicopter (LUH) – requirement for 384 helicopters for both the army and air force.
* HAL has obtained a firm order to deliver 114 HAL Light Combat Helicopter
The HAL Prachand (IPA: prəcəɳɖ, lit.''"Fierce"'') is an Indian multi-role, light attack helicopter designed and manufactured by the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) under project LCH. It has been ordered by the Indian Air Force and the ...
s to the Indian Army.
;Missiles
 * Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles
**
* Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles
** Agni-V
Agni-V is a nuclear capable intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation RDOof India. The missile is believed to have a range of around 5,000 to 5,500 kilometers. Scientists and experts say ...
– – Successfully Tested third time canistered version by DRDO on 31 January 2015.
** Agni-VI – – range with MIRVed warheads. Currently in planning stage.
*Cruise Missiles
** Hypersonic missile
** Nirbhay Missile
Nirbhay (meaning ''Dauntless/Fearless'') is a long range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile designed and developed in India by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) which is under Defence Research and Development Organisation (D ...
** BrahMos
The BrahMos (also designated as PJ-10)Prahaar (missile)
Prahaar ("Strike") is an Indian solid-fuel rocket, solid-fuel road-mobile tactical ballistic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Prahaar is expected to replace the Prithvi-I SRBM , short-range ballistic ...
– With a range of .
** Agni-II (missile) – It a ballistic missile with a range of 2000–3500 km with a speed of 3.5 km/s.
** Agni-III (missile) – It is the successor to the Agni-II missile with an effective range of 3500–5000 km with a speed of 5–6 km/s.
** Agni-IV – Also known as the Agni-II prime in the earlier times, it has an effective range of 4000 km and a cruise altitude of 900 km.
** Shaurya (missile) – It has a range of between -
* Anti-Tank Guided Missiles
** Nag Anti-tank guided missile – ground and air-launched variant.
* The Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme is an initiative to develop and deploy a multi-layered ballistic missile defence system to protect India from ballistic missile attacks. It is a double-tiered system consisting of two interceptor missiles, namely the Prithvi Air Defence (PAD) missile for high altitude interception, and the Advanced Air Defence (AAD) Missile for lower altitude interception.
;Artillery
* Under the Field Artillery Rationalisation Plan (FARP) of 2010, the army plans to procure 3000 to 4000 pieces of artillery at the cost of . This includes purchasing 1580 towed, 814 mounted, 180 self-propelled wheeled, 100 self-propelled tracked, and 145 ultra-light 155 mm/39 calibre guns. The requirement for artillery guns would be met with indigenous development and production. The FARP has resulted in a collaboration with Korea over the K-9 Vajra-T (an offshoot of the Korean K9 Thunder), some of which will be built domestically by Larsen & Toubro. The K9 contract was signed in the midst of the failure of the Dhanush (howitzer) programme. As well the fully indigenous towed artillery ATAGS howitzer
The Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) is a towed 155 mm/52 calibre howitzer that is being developed for the Indian Army by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE), Tata Advanced Systems and Kalyani Strategic System ...
had a successful field trials in spring 2022 at the Pokhran Field Firing Range. It is produced by Bharat Forge
Bharat Forge Limited is an Indian multinational company involved in forging, automotives, energy, construction and mining, railways, marine, aerospace and defence industries. The company was founded by Nilkanthrao A. Kalyani on 19 June 1961. He ...
and Tata Advanced Systems Limited
Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) is an Indian aerospace, defense, military engineering & construction and technology company. It is a fully owned subsidiary of Tata Sons, a holding company for the Tata Group.
History
TASL entered into a j ...
.
;Small Arms
Earlier development efforts of the DRDO to meet the Indian Army's small arms requirements—namely the Excalibur rifle, which was meant to replace the INSAS rifle in service; the Multi Caliber Individual Weapon System (MCIWS)
Multi Calibre Individual Weapon System (MCIWS) is an assault rifle developed in India by the Armament Research and Development Establishment, a laboratory of the Defence Research and Development Organisation. It was first seen at the DEFEXPO 2014 ...
; and the Modern Sub Machine Carbine, a combined venture of ARDE & OFB to develop an assault carbine for the Indian Army based on a platform of experiences from the INSAS rifle—have been halted.
The Indian Army has chosen instead to procure 72,400 Sig Sauer SIG 716 G2 Patrol high-performance assault rifles for its frontline troops engaged in counter-militancy operations, and the Caracal CAR 816 to meet a requirement of 94,000 close quarter battle carbines.
To meet the needs of the rest of its soldiers, the army has selected the Russian 7.62 mm AK-103/AK-203 assault rifle as a "Make in India" project to manufacture 650,000 rifles through a government-to-government agreement.
;Vehicles
* Tata Motors offers a full range of 6×6, 8×8, and 12×12 multi-purpose high mobility carriers, designed especially for integrating specialist rocket and missile systems. The Tata 2038 6×6 vehicle platform has, after rigorous field-firing evaluation trials, been qualified by the Indian Army to carry the GRAD BM21 Multi Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) application.
* Mahindra Axe – Light utility vehicle to be purchased.
* The army needs 3,000 light support vehicles and 1600 heavy motor vehicles for mounting rockets and radar, and for reconnaissance and transportation, at a cost of Rs 15 billion.
See also
* Centre for Land Warfare Studies * List of serving generals of the Indian Army * Paramilitary forces of India * Army Day (India) *Indian National Army
The Indian National Army (INA; ''Azad Hind Fauj'' ; 'Free Indian Army') was a collaborationist armed force formed by Indian collaborators and Imperial Japan on 1 September 1942 in Southeast Asia during World War II. Its aim was to secure In ...
* Indian Army United Nations peacekeeping missions
* Army Red Football Club
* Army Green Football Club
References
;Citations ;Bibliography * * * Praval, K.C. Praval ''Indian Army After Independence'' (3rd ed. 2013excerpt and text search
*
Further reading
* Wilkinson, Steven I. 2015Army and Nation: The Military and Indian Democracy since Independence
Harvard University Press.
External links
*Indian Army
at Bharat Rakshak {{Authority control 1895 establishments in India 1947 establishments in India Cantonments of India Defence agencies of India Government agencies established in 1947 Articles containing video clips Military units and formations established in 1895 Recipients of the Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar