Illyrian Provinces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Illyrian Provinces
sl, Ilirske province
hr, Ilirske provincije
sr, Илирске провинције
it, Province illiriche
german: Illyrische Provinzen, group=note were an
 The
The

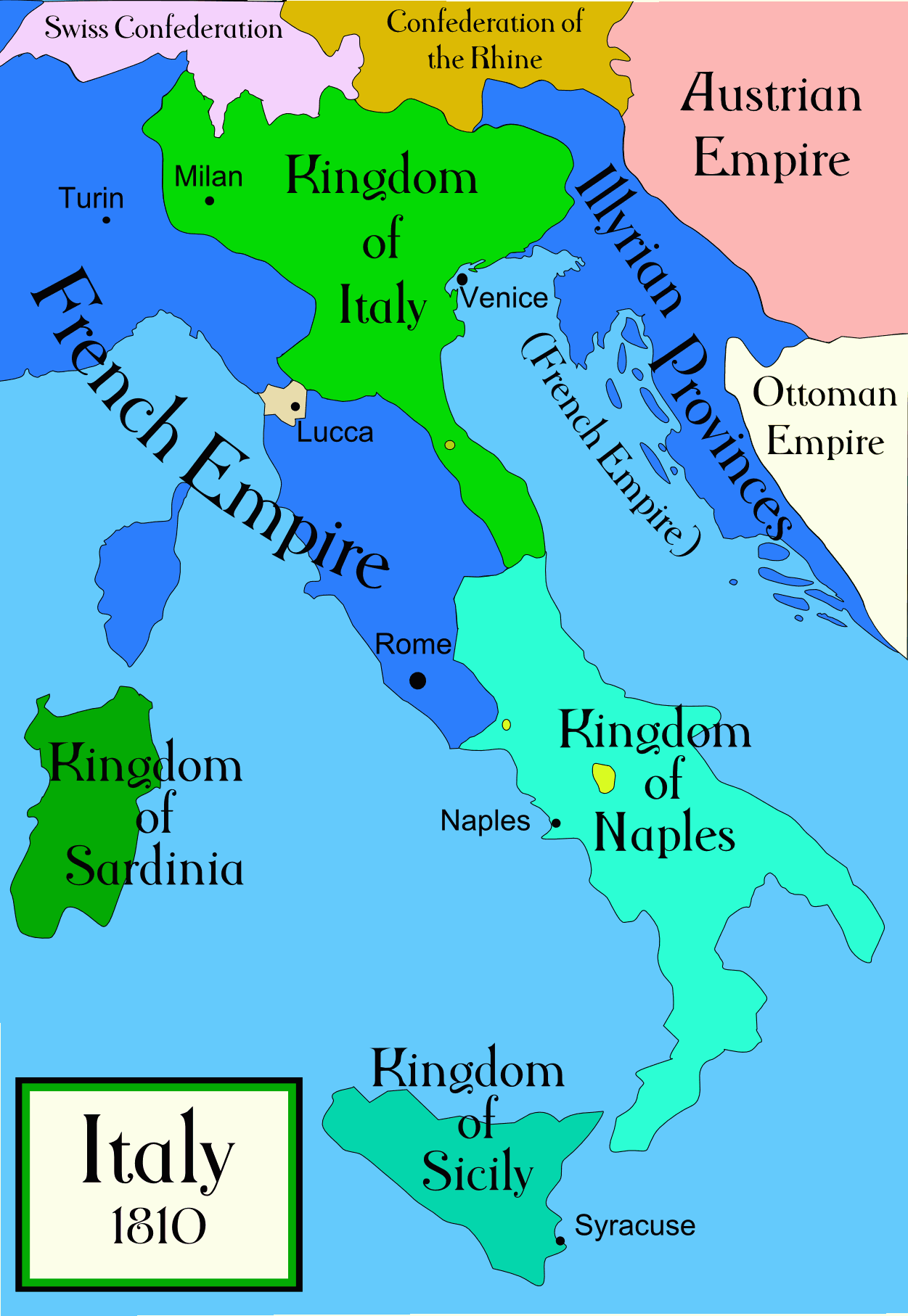 The capital was established at ''Laybach'', i.e.
The capital was established at ''Laybach'', i.e.
 Despite the fact that not all French laws applied to the territory of the Illyrian Provinces, Illyrian offices were accountable to ministries in Paris and to the Higher Court of Paris. Inhabitants of the Illyrian Provinces had Illyrian nationality. Initially the official languages were French, Italian and German, but in 1811 Croatian and Slovenian were further added, the latter becoming official for the first time in history. Among the main changes the French empire brought were the overhaul of administration, the changing of the schooling system – creating universities and making Slovene a learning language – and the usage of the
Despite the fact that not all French laws applied to the territory of the Illyrian Provinces, Illyrian offices were accountable to ministries in Paris and to the Higher Court of Paris. Inhabitants of the Illyrian Provinces had Illyrian nationality. Initially the official languages were French, Italian and German, but in 1811 Croatian and Slovenian were further added, the latter becoming official for the first time in history. Among the main changes the French empire brought were the overhaul of administration, the changing of the schooling system – creating universities and making Slovene a learning language – and the usage of the
sl, Ilirske province
hr, Ilirske provincije
sr, Илирске провинције
it, Province illiriche
german: Illyrische Provinzen, group=note were an
autonomous province
Autonomous province is a term for a type of province that has administrative autonomy.Collins Dictionar ...
of France during the First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Eu ...
that existed under Napoleonic Rule from 1809 to 1814. The province encompassed modern-day Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, Gorizia
Gorizia (; sl, Gorica , colloquially 'old Gorizia' to distinguish it from Nova Gorica; fur, label= Standard Friulian, Gurize, fur, label= Southeastern Friulian, Guriza; vec, label= Bisiacco, Gorisia; german: Görz ; obsolete English ''Gorit ...
, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into provi ...
, and parts of Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. Its capital was Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
(german: Laybach, Laibach) in Slovenia. It encompassed six ''départements'', making it a relatively large portion of territorial France at the time. Parts of Croatia were split up into Civil Croatia and Military Croatia, the former served as a residential space for French immigrants and Croatian inhabitants and the latter as a military base to check the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
In 1809, Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
invaded the region with his Grande Armée
''La Grande Armée'' (; ) was the main military component of the French Imperial Army commanded by Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte during the Napoleonic Wars. From 1804 to 1808, it won a series of military victories that allowed the French Empi ...
after key wins during the War of the Fifth Coalition
The War of the Fifth Coalition was a European conflict in 1809 that was part of the Napoleonic Wars and the Coalition Wars. The main conflict took place in central Europe between the Austrian Empire of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis ...
forced the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
to cede parts of its territory. Integrating the land into France was Bonaparte's way of controlling Austria's access to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
and Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
and expanding his empire east. Bonaparte installed four governors to disseminate French bureaucracy, culture, and language. The most famous and influential governor was Auguste de Marmont
Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont (20 July 1774 – 22 March 1852) was a French general and nobleman who rose to the rank of Marshal of the Empire and was awarded the title (french: duc de Raguse). In the Peninsular War Marmont succeede ...
, who undertook the bulk of Bonaparte's bidding in the area. Marmont was succeeded by Henri Gatien Bertrand
Henri-Gatien Bertrand (28 March 1773 – 31 January 1844) was a French general who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. Under the Empire he was the third and last Grand marshal of the palace, the head of the M ...
(1811–12), Jean-Andoche Junot (1812–13), and Joseph Fouché (1813–14).
Marmont pushed the Code Napoléon throughout the area and led a vast infrastructural expansion. During 1810, the French authorities established the ''Écoles centrales'' in Croatia and Slovenia. Although the respective states were allowed to speak and work in their native languages, French was designated as the official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
and much of the federal administration was conducted as such. French rule contributed significantly to the provinces even after the Austrian Empire recovered the area in 1814. Napoleon introduced a greater national self-confidence and awareness of freedoms, as well as numerous political reforms. He introduced equality before the law, compulsory military service
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
for men, a uniform tax system, abolished certain tax privileges, introduced modern administration, separated church and state and nationalized the judiciary. French presence in this region saw to a diffusion of French culture
The culture of France has been shaped by geography, by historical events, and by foreign and internal forces and groups. France, and in particular Paris, has played an important role as a center of high culture since the 17th century and from t ...
and the creation of the Illyrian Movement
The Illyrian movement ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Ilirski pokret, Илирски покрет; sl, Ilirsko gibanje) was a pan-South-Slavic cultural and political campaign with roots in the early modern period, and revived by a group of young Croatian inte ...
.
Etymology
The name "Illyrian" was probably suggested to Napoleon by Auguste de Marmont, who was influenced by the civic and revolutionary intelligentsia in Dalmatia, Dubrovnik and Carinthia, and wanted to use it to support the sense of commonality of the peoples living in the Provinces, which went beyond Napoleon's basic geostrategic rationale to form the provinces, though historians have discussed the extents of the influence of historical ideas of Illyrism both in France and locally, as well as aNeoclassicist
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was ...
allusion to the ancient names of the Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
n coast, known as Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
in antiquity and Illyricum during the Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
.
History
 The
The Slovene Lands
The Slovene lands or Slovenian lands ( sl, Slovenske dežele or in short ) is the historical denomination for the territories in Central and Southern Europe where people primarily spoke Slovene. The Slovene lands were part of the Illyrian provin ...
, ruled by the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, were first occupied by the French Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army (french: Armée révolutionnaire française) was the French land force that fought the French Revolutionary Wars from 1792 to 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary fervour, their poor equipme ...
after the Battle of Tarvis in March 1797, led by General Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
. The occupation caused huge civil disturbances. The French troops under the command of General Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte
sv, Karl Johan Baptist Julius
, spouse =
, issue = Oscar I of Sweden
, house = Bernadotte
, father = Henri Bernadotte
, mother = Jeanne de Saint-Jean
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Pau, ...
tried to calm the worried population by issuing special public notices that were published also in Slovene. During the withdrawal of the French army, the commanding general Bonaparte and his escort made a stop in Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
on April 28, 1797. Upon the 1805 Battle of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz i ...
and the Peace of Pressburg, French troops once again occupied parts of Slovene territory. Supply of the French troops and steep war dues were a huge burden for the population of the occupied territories. The foundation of the provincial brigades in June 1808 and extensive preparations for the new war did not stop Napoleon's Grande Armée
''La Grande Armée'' (; ) was the main military component of the French Imperial Army commanded by Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte during the Napoleonic Wars. From 1804 to 1808, it won a series of military victories that allowed the French Empi ...
, which completely defeated the Austrian
Austrian may refer to:
* Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent
** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law
* Austrian German dialect
* Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ...
troops at the Battle of Wagram
The Battle of Wagram (; 5–6 July 1809) was a military engagement of the Napoleonic Wars that ended in a costly but decisive victory for Emperor Napoleon's French and allied army against the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles ...
on July 6, 1809.
After the Austrian defeat, the Illyrian Provinces were created by the Treaty of Schönbrunn
The Treaty of Schönbrunn (french: Traité de Schönbrunn; german: Friede von Schönbrunn), sometimes known as the Peace of Schönbrunn or Treaty of Vienna, was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna on 14 October ...
on 14 October 1809, when the Austrian Empire ceded the territories of western ("Upper") Carinthia
Carinthia (german: Kärnten ; sl, Koroška ) is the southernmost States of Austria, Austrian state, in the Eastern Alps, and is noted for its mountains and lakes. The main language is German language, German. Its regional dialects belong to t ...
with Lienz
Lienz (; Southern Bavarian: ''Lianz'') is a medieval town in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is the administrative centre of the Lienz district, which covers all of East Tyrol. The municipality also includes the cadastral subdivision of ''Pat ...
in the East Tyrol
East Tyrol, occasionally East Tirol (german: Osttirol), is an exclave of the Austrian state of Tyrol, separated from the main North Tyrol part by the short common border of Salzburg and Italian South Tyrol (''Südtirol'', it, Alto Adige). It i ...
, Carniola, Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (german: Gefürstete Grafschaft Görz und Gradisca; it, Principesca Contea di Gorizia e Gradisca; sl, Poknežena grofija Goriška in Gradiščanska), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled " ...
, the Imperial Free City of Trieste
The Imperial Free City of Trieste and its Territory (german: Reichsunmittelbare Stadt Triest und ihr Gebiet, it, Città Imperiale di Trieste e Dintorni) was a possession of the Habsburg monarchy in the Holy Roman Empire from the 14th century to 1 ...
, the March of Istria
The March of Istria (or Margraviate of Istria ) was originally a Carolingian frontier march covering the Istrian peninsula and surrounding territory conquered by Charlemagne's son Pepin of Italy in 789. After 1364, it was the name of the Istrian ...
, and the Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
n lands southwest of the river Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally th ...
to the French Empire. These territories lying north and east of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
were amalgamated with the former Venetian territories of Dalmatia and Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
, annexed by Austria in the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The treat ...
, and the former Republic of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world"
, population_estimate = 90 000 in the XVI Century
, currency = ...
, which all had just been adjudicated to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
in 1805 and 1808, into the Illyrian Provinces, technically part of France.
The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
imposed a blockade of the Adriatic Sea after the signing of the Treaty of Tilsit
The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by French Emperor Napoleon in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Napoleon and Russian Emperor Alexander, when ...
(July 1807), which brought merchant shipping to a standstill, a measure which seriously affected the economy of the Dalmatian port cities. An attempt by joint Franco-Italian force to seize the British-held Dalmatian island of Vis (Lissa) failed on 22 October 1810.
In August 1813, the Austrian Empire again declared war on France. Austrian troops led by General Franz Tomassich invaded the Illyrian Provinces. Croat troops enrolled in the French army switched sides. Zara (now called Zadar
Zadar ( , ; historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian: ); see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar serv ...
) surrendered to Austrian and British forces after a 34-day siege on 6 December 1813. At Dubrovnik an insurrection expelled the French and a provisional Ragusan administration was established, hoping for the restoration of the Republic. It was occupied by Austrian troops on 20 September 1813. The Cattaro area (now called Bay of Kotor
The Bay of Kotor ( Montenegrin and Serbian: , Italian: ), also known as the Boka, is a winding bay of the Adriatic Sea in southwestern Montenegro and the region of Montenegro concentrated around the bay. It is also the southernmost part of the hi ...
) and its environs were occupied in 1813 by Montenegrin forces, which held it until 1814, when the appearance of an Austrian force caused the Prince of Montenegro to turn over the territory to Austrian administration on 11 June. The British withdrew from the Dalmatian islands as the final part of the handover of these islands to their Austrian allies in July 1815, following the conclusion of the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
.
Administration
 The capital was established at ''Laybach'', i.e.
The capital was established at ''Laybach'', i.e. Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
in modern Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
. According to Napoleon's Decree on the Organization of Illyria (''Decret sur l'organisation de l'Illyrie''), issued on April 15, 1811, the Central Government of the Illyrian Provinces (''Gouvernement general des provinces d'Illyrie'') in Ljubljana consisted of the governor-general (''gouverneur-général''), the general intendant of finance (''intendant général des finances'') and the commissioner of the judiciary (''commissaire de justice''). With two judges of the Appellate Court in Ljubljana they formed the Minor Council (''Petit conseil'') as the supreme judicial and administrative authority of the Provinces.
Subdivision
The area initially consisted of eleven departments, though the subdivision was never completely enacted: In 1811, the Illyrian provinces saw an administrative reorganization, when the country was divided initially in four - Laybach (Ljubljana), Karlstadt (Karlovac), Trieste (Trst), Zara (Zadar) - on 15 April in sevenprovinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
(''intendances'', similar to French ''départements''). Each province was further subdivided into districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
, and these into cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, t ...
. A province (''intendancy'') was governed by a provincial intendant, districts were administered by subdelegates (each district capital that was not a province capital had a subdelegation with a subdelegate, similar to French subprefect) and in cantons justices of the peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sa ...
had their seats. Municipalities - with municipal council, mayor and deputy mayors in larger municipalities; or council, municipality president-syndic and deputy president-deputy syndic - were units of local government. All officials and councillors were appointed by the emperor or the governor-general, depending on their relevance and/or size of the subdivision unit in which they served.
List of provinces
List of provinces (''intendances'') and districts: TwoChambers of Commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to a ...
were established, at Trieste and at Ragusa. The ecclesiastical administration was reorganized in accordance with the new political borders; two archdiocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
s were established with seats at Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
and Zara, with suffragan diocese
A suffragan diocese is one of the dioceses other than the metropolitan archdiocese that constitute an ecclesiastical province. It exists in some Christian denominations, in particular the Catholic Church, the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria ...
s at Gorizia
Gorizia (; sl, Gorica , colloquially 'old Gorizia' to distinguish it from Nova Gorica; fur, label= Standard Friulian, Gurize, fur, label= Southeastern Friulian, Guriza; vec, label= Bisiacco, Gorisia; german: Görz ; obsolete English ''Gorit ...
, Capodistria, Sebenico, Spalato
)''
, settlement_type = City
, anthem = ''Marjane, Marjane''
, image_skyline =
, imagesize = 267px
, image_caption = Top: Nighttime view of Split from Mosor; 2nd row: Cathedra ...
and Ragusa Ragusa is the historical name of Dubrovnik. It may also refer to:
Places Croatia
* the Republic of Ragusa (or Republic of Dubrovnik), the maritime city-state of Ragusa
* Cavtat (historically ' in Italian), a town in Dubrovnik-Neretva County, Cro ...
(1811).
Governors-general
The French administration, headed by a governor-general, introduced civil law (the Napoleonic '' Code civil'') across the provinces. The seat of the governor-general was at Laybach. The governors-general were: *Auguste de Marmont
Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont (20 July 1774 – 22 March 1852) was a French general and nobleman who rose to the rank of Marshal of the Empire and was awarded the title (french: duc de Raguse). In the Peninsular War Marmont succeede ...
(8 October 1809 – January 1811)
*Henri Gatien Bertrand
Henri-Gatien Bertrand (28 March 1773 – 31 January 1844) was a French general who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. Under the Empire he was the third and last Grand marshal of the palace, the head of the M ...
(9 April 1811 – 21 February 1813)
* Jean-Andoche Junot (21 February 1813 – July 1813)
* Joseph Fouché (July 1813 – August 1813)
Population
The population (1811) was given at 460,116 for the intendancy of Ljubljana, 381,000 for the intendancy of Karlovac, 357,857 for the intendancy of Trieste and 305,285 for the intendancy of Zara, in total 1,504,258 for all of Illyria. A French decree emancipated theJew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""Th ...
s; in effect the decree abolished a Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
regulation which had forbidden Jews to settle within Carniola.
Political arrangements
Napoleonic
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
code (the French Code Civil) and the Penal Code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might ...
. Although the French did not entirely abolish the feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
, their rule familiarized in more detail the inhabitants of the Illyrian Provinces with the achievements of the French revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
and with contemporary bourgeois society
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
. They introduced equality before the law, compulsory military service
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
and a uniform tax system, and also abolished certain tax privileges, introduced modern administration, separated powers between the state and the church (the introduction of the civil wedding
A wedding is a ceremony where two people are united in marriage. Wedding traditions and customs vary greatly between cultures, ethnic groups, religions, countries, and social classes. Most wedding ceremonies involve an exchange of marriag ...
, keeping civil registration of births etc.), and nationalized the judiciary. The occupants made all the citizens theoretically equal under the law for the first time.
The French also founded a university ("École centrale") in 1810 (which was disbanded in 1813, when Austria regained control, but whose Basic Decree of 4 July 1810, which ordered the reorganization of the former Austrian lycees in Ljubljana and Zara into écoles centrales, is now considered the charter of the University of Ljubljana). They established the first botanic garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
at the city's edge, redesigned the streets and made vaccination of children obligatory. At Karlovac, the headquarters of the Croatian military, a special French-language military school was established in 1811. The linguist Jernej Kopitar
Jernej Kopitar, also known as Bartholomeus Kopitar (21 August 1780 – 11 August 1844), was a Slovene linguist and philologist working in Vienna. He also worked as the Imperial censor for Slovene literature in Vienna. He is perhaps best known ...
and the poet Valentin Vodnik
Valentin Vodnik (3 February 1758 – 8 January 1819) was a Carniolan priest, journalist and poet of Slovene descent. He was active in the late Enlightenment period. He is well known for his contributions in writing materials that lifted the p ...
succeeded in instructing the authorities at that time that the language of the inhabitants living in the present-day Slovenian part of the Illyrian Provinces was actually Slovene. Although at the time of the Illyrian Provinces the educational reform
Education reform is the name given to the goal of changing public education. The meaning and education methods have changed through debates over what content or experiences result in an educated individual or an educated society. Historically, th ...
did not come to life to its fullest ability, it was nevertheless of considerable social significance. The plan for reorganisation of the school system provided for education in elementary and secondary schools in Slovene in Slovenian areas. There were 25 gymnasia in the Illyrian provinces.
Proclamations were published in the provinces' official newspaper, ''Official Telegraph of the Illyrian Provinces'' (). The newspaper was established by Marmont. In 1813, the French author Charles Nodier
Jean Charles Emmanuel Nodier (29 April 1780 – 27 January 1844) was a French author and librarian who introduced a younger generation of Romanticists to the ''conte fantastique'', gothic literature, and vampire tales. His dream related writings ...
worked in Ljubljana as the last editor of the journal, significantly renovated it, and published it in French, Italian, and German. The "French gift" of letting Slovene be used at school was one of the most important reforms and it won the sympathy of members of the so-called "Slovene National Awakening Movement". The Marmont's school reform introduced, in the fall of 1810, a uniform four-year primary school and an extended network of lower and upper gymnasiums and crafts schools. Valentin Vodnik
Valentin Vodnik (3 February 1758 – 8 January 1819) was a Carniolan priest, journalist and poet of Slovene descent. He was active in the late Enlightenment period. He is well known for his contributions in writing materials that lifted the p ...
, author of the poem "Illyria Arise", wrote numerous school books for primary schools and lower gymnasiums; since textbooks (and teachers) were scarce, these books made the realization of the idea of Slovene as a teaching language possible.
Legacy
Although French rule in the Illyrian Provinces was short-lived and did not enjoy great popular support, it significantly contributed to greater national self-confidence and awareness of freedoms, especially in the Slovene lands. The opinion ofNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's rule and the Illyrian Provinces changed significantly at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, when liberal Croatian and Slovene intellectuals began to praise the French for liberation from Austrian rule.
It could also be established today that the short period of the Illyrian Provinces marked the beginning of an enhanced awareness of the principles of liberty, equality and fraternity. The Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
confirmed Austria in the possession of the former Illyrian Provinces. In 1816 they were reconstituted without Dalmatia and Croatia, yet now with all of Carinthia, as a Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
, which was formally abolished only in 1849, even though the civil administration of the Croatian districts had already been placed under Hungarian administration in 1822.
The memory of the French and of the Emperor Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
is embedded in Croatian and Slovene traditions, in their folk art and folk songs. The presence of the French on Croatian and Slovene territories reflects also in the surnames and house names of French origin, in frescoes, and other paintings depicting French soldiers as well as in rich immovable cultural heritage (roads, bridges, fountains). In 1929, a national ceremony was held in Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
during which a monument was erected to Napoleon and Illyria at French Revolution Square. It was filmed by Janko Ravnik
Janko Ravnik (7 March 1891 – 2 September 1981) was a Slovenian pianist, teacher, film director and composer.Booklet to Bernarda Fink ''Slovenija!'' 2010 Harmonia Mundi
He was born in Bohinjska Bistrica and died in Ljubljana. In 1928 and 1929, he ...
.
One of the central streets in Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
city centre is named after marshal Marmont
Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont (20 July 1774 – 22 March 1852) was a French general and nobleman who rose to the rank of Marshal of the Empire and was awarded the title (french: duc de Raguse). In the Peninsular War Marmont succeede ...
, in appreciation of his enlightened rule in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
.
See also
*List of French possessions and colonies
From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire stretched from a total area at its peak in 1680 to over , the second largest empire in the world at the time behind only the Spanish Empire. During the 19th and 20th centuri ...
*Ionian Islands under Venetian rule
The Ionian Islands were an overseas possession of the Republic of Venice from the mid-14th century until the late 18th century. The conquest of the islands took place gradually. The first to be acquired was Cythera and the neighboring islet ...
*Septinsular Republic
The Septinsular Republic ( el, Ἑπτάνησος Πολιτεία, Heptanēsos Politeia; it, Repubblica Settinsulare) was an oligarchic republic that existed from 1800 to 1807 under nominal Russian and Ottoman sovereignty in the Ionian Islan ...
*Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (1805–1814; it, Regno d'Italia; french: Royaume d'Italie) was a kingdom in Northern Italy (formerly the Italian Republic) in personal union with Napoleon I's French Empire. It was fully influenced by revolutionary Franc ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* *Bradshaw, Mary Eloise. (1928). ''The Napoleonic Influence on the Illyrian Provinces''. University of Wisconsin—Madison Press.OCLC
OCLC, Inc., doing business as OCLC, See also: is an American nonprofit cooperative organization "that provides shared technology services, original research, and community programs for its membership and the library community at large". It was ...
: 54803367.
*Bradshaw, Mary Eloise. (1932) ''The Illyrian Provinces''. University of Wisconsin—Madison Press. OCLC
OCLC, Inc., doing business as OCLC, See also: is an American nonprofit cooperative organization "that provides shared technology services, original research, and community programs for its membership and the library community at large". It was ...
: 49491990 .
External links
* {{Authority control First French Empire Modern history of the Balkans History of Dalmatia 19th century in Croatia 19th century in Montenegro Austrian Empire 19th century in Italy States and territories established in 1809 1809 establishments in Europe 1816 disestablishments in Europe Former states and territories in Slovenia Use of the term Illyrian in modern history