ITMO University on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ITMO University (russian: –£–Ĺ–ł–≤–Ķ—Ä—Ā–ł—ā–Ķ—ā –ė–Ę–ú–ě) is a state-supported university in
 The university began to actively develop after the war. In the fall of 1945 it opened a new faculty ‚Äď Electrical Instrumentation, which was soon reorganized into Radio Engineering. Here was established Department of Quantum Radio Electronics, which began to train specialists in this field. Engineering Physics Department was established here in 1946. From this department in 1954 graduated Dr. Yuri Denisjuk, a future scientist, author of discoveries in holography, and laureate of the state award.
In 1956, the researchers of the Computing Devices Department began to work on the first calculating machine ‚ÄúLITMO-1‚ÄĚ that was finished in 1958. It did binary engineering calculations but the data was entered and the results were presented in the familiar decimal system. A laboratory for laser technologies was opened in the 1960s. The building on Sablinskaya Street, which is now the main campus, was built in the 1970s. The following decade saw the beginning of
The university began to actively develop after the war. In the fall of 1945 it opened a new faculty ‚Äď Electrical Instrumentation, which was soon reorganized into Radio Engineering. Here was established Department of Quantum Radio Electronics, which began to train specialists in this field. Engineering Physics Department was established here in 1946. From this department in 1954 graduated Dr. Yuri Denisjuk, a future scientist, author of discoveries in holography, and laureate of the state award.
In 1956, the researchers of the Computing Devices Department began to work on the first calculating machine ‚ÄúLITMO-1‚ÄĚ that was finished in 1958. It did binary engineering calculations but the data was entered and the results were presented in the familiar decimal system. A laboratory for laser technologies was opened in the 1960s. The building on Sablinskaya Street, which is now the main campus, was built in the 1970s. The following decade saw the beginning of
 The university has a multi-level system of higher education: bachelor ‚Äď 4 years, specialist ‚Äď 5 years, master ‚Äď 2 years, post-graduate ‚Äď 3‚Äď4 years.
Since 2013/14 ITMO is partnering with universities in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland, France, among others, to participate in ‚Äúdouble degree‚ÄĚ international educational programs. ITMO graduates of these programs receive a second degree from a partner university.
The university collaborates with large St. Petersburg companies, including Elektropribor,
The university has a multi-level system of higher education: bachelor ‚Äď 4 years, specialist ‚Äď 5 years, master ‚Äď 2 years, post-graduate ‚Äď 3‚Äď4 years.
Since 2013/14 ITMO is partnering with universities in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland, France, among others, to participate in ‚Äúdouble degree‚ÄĚ international educational programs. ITMO graduates of these programs receive a second degree from a partner university.
The university collaborates with large St. Petersburg companies, including Elektropribor,
National Student Forum
The university has participated in student and instructor exchange programs financed by organizations, including the DAAD. ITMO is a member of the Association of European Universities. It also collaborates with foreign universities, including ITMO University maintains ties with IT companies. In 2011,
ITMO University maintains ties with IT companies. In 2011,
 Since 1996, the Rector of the university is the Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, Chairman of the Council of Rectors of St. Petersburg (2004), vice-president of the Russian Union of Rectors (2006), corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Education, corresponding member Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Vladimir Vasilyev.
Since 1996, the Rector of the university is the Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, Chairman of the Council of Rectors of St. Petersburg (2004), vice-president of the Russian Union of Rectors (2006), corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Education, corresponding member Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Vladimir Vasilyev.
 In 2012, a ‚Äú Skolkovo‚ÄĚ communications center was supposed to open on the campus of the former Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnologies of ITMO, but the plans were altered. That same year the university signed a memorandum with RSV Venture Partners Foundation to establish a $6 million fund for IT startups. In 2013, Internet Initiatives Development Fund offered ITMO University to collaborate in opening regional accelerators to support commercially promising internet startups.
University's list of international partners over the years includes General Motors Corp., PPG, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, Nokia and others.
Students and staff members of over 80 departments participate in research. Many of them are working in ‚Äúsmall innovative enterprises,‚ÄĚ or startups, located at ITMO Technopark on Birzhevaya Liniya, offering access to high-tech equipment.
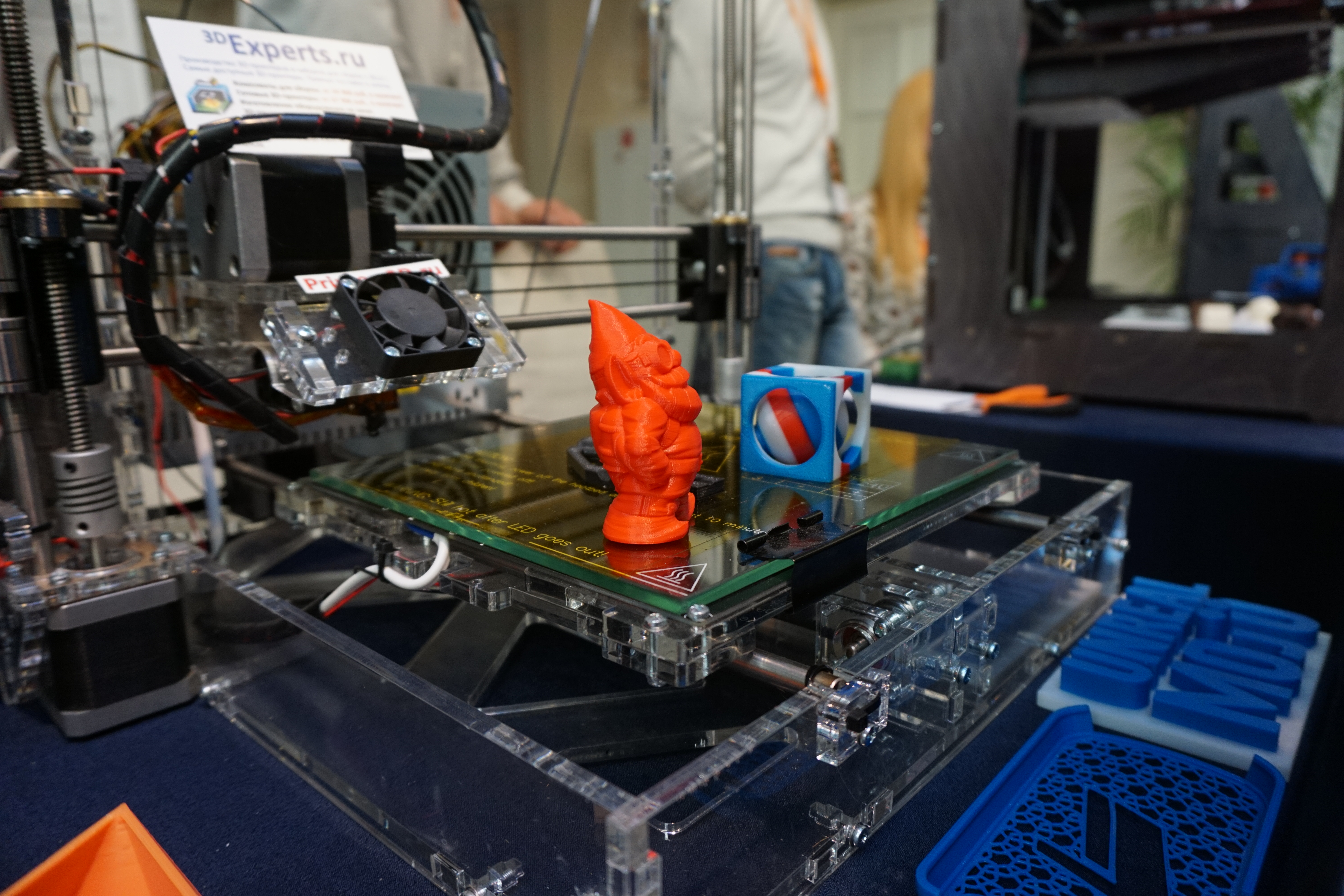
As part of the Project 5‚Äď100, Technopark opened a coworking space called FabLab in 2015, which also offered facilities and resources, including a 3D printer, a laser engraver, a milling machine, etc. The equipment is offered free of charge to the ITMO University specialists and students.
In 2012, a ‚Äú Skolkovo‚ÄĚ communications center was supposed to open on the campus of the former Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnologies of ITMO, but the plans were altered. That same year the university signed a memorandum with RSV Venture Partners Foundation to establish a $6 million fund for IT startups. In 2013, Internet Initiatives Development Fund offered ITMO University to collaborate in opening regional accelerators to support commercially promising internet startups.
University's list of international partners over the years includes General Motors Corp., PPG, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, Nokia and others.
Students and staff members of over 80 departments participate in research. Many of them are working in ‚Äúsmall innovative enterprises,‚ÄĚ or startups, located at ITMO Technopark on Birzhevaya Liniya, offering access to high-tech equipment.
As part of the Project 5‚Äď100, Technopark opened a coworking space called FabLab in 2015, which also offered facilities and resources, including a 3D printer, a laser engraver, a milling machine, etc. The equipment is offered free of charge to the ITMO University specialists and students.
 In 2009, the university was granted the status of National Research University. It implies carrying out research in areas considered key to the development of Russia's economy, including IT, photonics, optoinformatics, and urban science.
In 2009, the university was granted the status of National Research University. It implies carrying out research in areas considered key to the development of Russia's economy, including IT, photonics, optoinformatics, and urban science.
 Since 15 August 2009 Russian universities are able to form small innovative enterprises according to Federal Law No.217 of August 2, 2009 N 217-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on the establishment of budget scientific and educational institutions, business entities for the purpose of practical application (implementation) of the results of intellectual activity".
By 2015 ITMO University has become the Launchpad for 43 small innovative enterprises. A special department is designated to helping them find funding, offers legal support for registering, partner search, placement in university's Technopark and business incubator. Other types of support include education initiatives
Since 15 August 2009 Russian universities are able to form small innovative enterprises according to Federal Law No.217 of August 2, 2009 N 217-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on the establishment of budget scientific and educational institutions, business entities for the purpose of practical application (implementation) of the results of intellectual activity".
By 2015 ITMO University has become the Launchpad for 43 small innovative enterprises. A special department is designated to helping them find funding, offers legal support for registering, partner search, placement in university's Technopark and business incubator. Other types of support include education initiatives
classes in social entrepreneurship and projects
fundraising school ''FundIT'', soft skill training, lectures in marketing and management, interdisciplinary seminars ''Brainexplain'', as well as lectures by guest experts. The university holds an annual international forum where its partners and business stakeholders discuss issues in technology transfer and development of innovations ecosystem. Other events are festival o
social entrepreneurship
a competition of socially valuable projects ‚ÄúPeople need you!‚ÄĚ, and a business game ‚ÄúInnovations marketing‚Ä̬Ľ. ITMO University was as of 2015 developing a network of startup accelerators in Russia‚Äôs regions as part of the program for development of research and entrepreneurship potential of Russian universities ‚ÄúEURECA‚ÄĚ and in partnership with the U.S. Russia Foundation and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). To promote building an innovation ecosystem from the ground up, ITMO partnered with "Xmas Ventures" and St. Petersburg Polytechnic University to establish
Demola Innovations Center
in St. Petersburg, the only one in Russia. German company
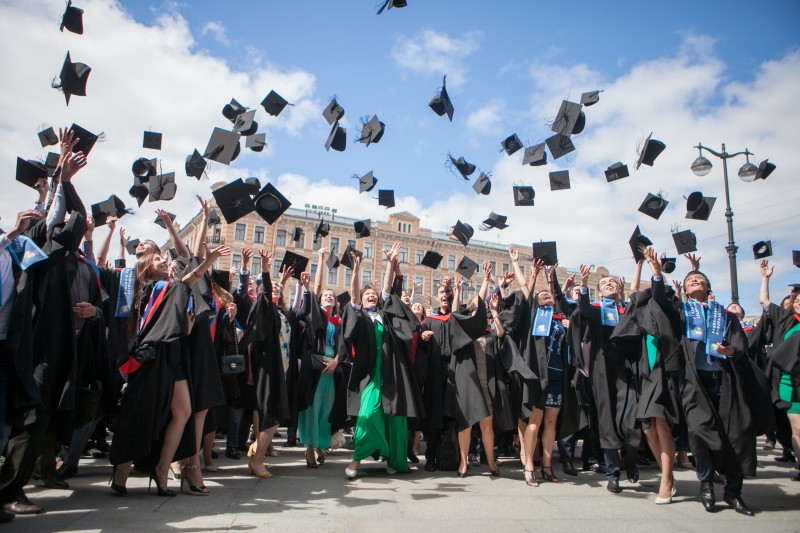
 In 2004, ITMO University scored its first victory in the International Collegiate Programming Contest ACM-ICPC, and by 2017 it became the first in history seven-time winner of the competition.
In 2013, ITMO University was the first Russian university to host the ACM-ICPC Finals. Some 120 teams representing 2,322 universities from 36 countries participated in selection rounds. Russia was represented by 15 student teams. ITMO University scored a victory in the finals.
In 2004, ITMO University scored its first victory in the International Collegiate Programming Contest ACM-ICPC, and by 2017 it became the first in history seven-time winner of the competition.
In 2013, ITMO University was the first Russian university to host the ACM-ICPC Finals. Some 120 teams representing 2,322 universities from 36 countries participated in selection rounds. Russia was represented by 15 student teams. ITMO University scored a victory in the finals.
 ITMO University has three museums. ''‚ÄúMuseum of ITMO University History‚ÄĚ'' is located in the building on Pereulok Grivtzova.
The ''Museum of Optics'' was established in 2006 and is located on the first floor of the Eliseev House on Birzhevaya Linia. With support from the Hellenic Institute of Holography, ITMO University opened an exhibition ‚ÄúMagic of Light‚ÄĚ in 2015. The Eliseev House was selected for the exhibition because it used to house the office of Prof. Denisuk, the founder of image holography. It features over 200 holograms, including OptoClones of Imperial
ITMO University has three museums. ''‚ÄúMuseum of ITMO University History‚ÄĚ'' is located in the building on Pereulok Grivtzova.
The ''Museum of Optics'' was established in 2006 and is located on the first floor of the Eliseev House on Birzhevaya Linia. With support from the Hellenic Institute of Holography, ITMO University opened an exhibition ‚ÄúMagic of Light‚ÄĚ in 2015. The Eliseev House was selected for the exhibition because it used to house the office of Prof. Denisuk, the founder of image holography. It features over 200 holograms, including OptoClones of Imperial
 The university has student unions, including those for foreign students, student clubs, a student orchestra, student radio, a student scientific society, and volunteer center. Many of these organizations get together in coworking spaces around the campus. The students can use these spaces for their own projects, but some, such as SumIT, require a prior interview.
The university has two assembly halls that can hold up to 500 people each. Other activity spaces include a soundproof room for singing lessons, an audio recording studio, a studio for ‚ÄúMegabyte‚ÄĚ internet radio and editorial office of ‚ÄúNewTone‚ÄĚ magazine.
The university has student unions, including those for foreign students, student clubs, a student orchestra, student radio, a student scientific society, and volunteer center. Many of these organizations get together in coworking spaces around the campus. The students can use these spaces for their own projects, but some, such as SumIT, require a prior interview.
The university has two assembly halls that can hold up to 500 people each. Other activity spaces include a soundproof room for singing lessons, an audio recording studio, a studio for ‚ÄúMegabyte‚ÄĚ internet radio and editorial office of ‚ÄúNewTone‚ÄĚ magazine.
 The university has its own sporting infrastructure. Sports clubs are located on Vjazemsky Pereulok and Lomonosova Street, and there's also a sportsground by the main building. The university also owns a recreational facility, Yagodnoe, located by the Berestovoe Lake, near Losevo, in the
The university has its own sporting infrastructure. Sports clubs are located on Vjazemsky Pereulok and Lomonosova Street, and there's also a sportsground by the main building. The university also owns a recreational facility, Yagodnoe, located by the Berestovoe Lake, near Losevo, in the
 *
*
University Homepage
{{Authority control Educational institutions established in 1900 1900 establishments in the Russian Empire National research universities in Russia Universities in Saint Petersburg Engineering universities and colleges in Russia
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, –°–į–Ĺ–ļ—ā-–ü–Ķ—ā–Ķ—Ä–Ī—É—Ä–≥, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ňąsankt p ≤…™t ≤…™rňąburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914‚Äď1924) and later Leningrad (1924‚Äď1991), i ...
and is one of Russia's National Research Universities. ITMO University is one of 15 Russian universities that were selected to participate in Russian Academic Excellence ''Project 5-100
Project 5-100 was a special government run program to develop major Russian universities. The program was launched by the Russian Ministry of Education and Science in 2013. It was aimed at improving the prestige of Russian higher education and br ...
'' by the government of the Russian Federation to improve their international standing among the world's research and educational centers.
In 2022, the university was ranked #365 in the world by QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
, and #601 by World University Rankings by ''Times Higher Education
''Times Higher Education'' (''THE''), formerly ''The Times Higher Education Supplement'' (''The Thes''), is a British magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
Ownership
TPG Capital acquired TSL Education ...
''. In 2021, it was ranked #718 in the world by Best Global Universities Rankings by '' U.S. News & World Report'', and #901 by Academic Ranking of World Universities by Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU; ) is a public research university in Shanghai, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education of China.
The university was established on April 8, 1896 as Nanyang Public School (ŚćóśīčŚÖ ...
.
Research priorities of ITMO University are concentrated in information and photonic technologies. The university consists of four main schools, 14 faculties, and a number of institutes and research centers. As of 2020, the total number of students was over 12,500, with 2,450 being foreign nationals. In 2014, the university employed 1,163 instructors, including over 800 PhDs. Many of its staff members and researchers have received government awards and designations of ‚Äúhonored science worker,‚ÄĚ the highest in Russia.
Vladimir Vasilyev Vladimir Vasiliev may refer to:
* Vladimir Vasiliev (dancer) (born 1940), dancer with the Bolshoi Ballet
* Vladimir Vasilyev (rower) (born 1948), Soviet Olympic rower
* Vladimir Vasilyev (politician) (born 1949), Russian politician
* Vladimir Vas ...
has been the university's Rector since 1996.
History
The university's birthday is considered to be 26 March 1900, when a ''Mechanics, Optics and Watchmaking Department'' was opened in the ''Prince Nicholas
Nicholas Teo () is a Malaysian Chinese singer under Good Tengz Entertainment Sdn Bhd. (Malaysia)
Career
Pre debut
Before returning to Malaysia, Nicholas was studying in Taiwan, where he won the Best Singer in a competition among all the Tai ...
Vocational School''. At the time it was the only school in the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
that prepared specialists in these areas. The first year, some 65 applications were received for 30 places. Eighteen students were admitted to Watchmaking and 18 to Mechanics and Optics sections.
1917 ‚Äď 1941
In 1917 the Mechanics, Optics and Watchmaking Department became its own entity - ''Petrograd Technical College for Mechanics, Optics and Watchmaking''. Norbert Boleslavovich Zavodsky became its headmaster. In 1920, most of its classes were transformed into ''Petrograd College for Fine Mechanics and Optics'' (later ‚Äď Leningrad). The municipalities allocated a building for it in Demidov Pereulok ( Pereulok Grivtzova). The colleges‚Äô manufacturing facilities made a variety of complex optical and fine mechanics products. The first in USSR group of instrument engineers graduated here in 1931. In 1930, the college was transformed into ''Leningrad Training Center'', and in 1933, ''Leningrad Institute of Fine Mechanics and Optics'' (LIFMO) became a separate college. Its first research laboratory was established in the Department of Optical Glass Technologies. Thanks to research here the USSR could get away from importing expensive foreignabrasives
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflec ...
.
In 1937, LITMO opened the first in the USSR laboratory for calculating machinery that was later transformed into the Department of Mathematical and Computing Devices. By the autumn of 1939 it became one of the institute's top departments and focused on developing electromechanical computing devices and control devices. By 1940, it had over 1,400 students and employed 27 professors as well as 80 associated professors and PhDs.
1941 ‚Äď 1945
With the beginning of theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries‚ÄĒincluding all of the great powers‚ÄĒforming two opposin ...
, 189 students and 85 staff members went to the front lines, while over 450 joined the People's Militia. Classes continued and only at the end of 1942 the students and instructors were evacuated to the town of Cherapanovo by Novosibirsk.
During the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, –Ď–Ľ–ĺ–ļ–į–ī–į –õ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī–į; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
, LIFMO continued to operate a military repair facility for the Leningrad front
The Leningrad Front (russian: –õ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ —Ą—Ä–ĺ–Ĺ—ā) was formed during the 1941 German approach on Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) by dividing the Northern Front into the Leningrad Front and Karelian Front
The Karelian Front ...
. It fabricated test and measurement instruments for army and navy units. During the Siege, the facility developed improved optical sights, fixed artillery binoculars, gun panoramas, anti-aircraft sighting telescopes, periscopes, machined ‚Äúcups‚ÄĚ for anti-aircraft shells and parts for land and sea mines.
After the Siege was lifted, the re-evacuation document was signed on August 10, 1944. The students and instructors returned to the city, and classes started again that October.
1945 ‚Äď 1992
 The university began to actively develop after the war. In the fall of 1945 it opened a new faculty ‚Äď Electrical Instrumentation, which was soon reorganized into Radio Engineering. Here was established Department of Quantum Radio Electronics, which began to train specialists in this field. Engineering Physics Department was established here in 1946. From this department in 1954 graduated Dr. Yuri Denisjuk, a future scientist, author of discoveries in holography, and laureate of the state award.
In 1956, the researchers of the Computing Devices Department began to work on the first calculating machine ‚ÄúLITMO-1‚ÄĚ that was finished in 1958. It did binary engineering calculations but the data was entered and the results were presented in the familiar decimal system. A laboratory for laser technologies was opened in the 1960s. The building on Sablinskaya Street, which is now the main campus, was built in the 1970s. The following decade saw the beginning of
The university began to actively develop after the war. In the fall of 1945 it opened a new faculty ‚Äď Electrical Instrumentation, which was soon reorganized into Radio Engineering. Here was established Department of Quantum Radio Electronics, which began to train specialists in this field. Engineering Physics Department was established here in 1946. From this department in 1954 graduated Dr. Yuri Denisjuk, a future scientist, author of discoveries in holography, and laureate of the state award.
In 1956, the researchers of the Computing Devices Department began to work on the first calculating machine ‚ÄúLITMO-1‚ÄĚ that was finished in 1958. It did binary engineering calculations but the data was entered and the results were presented in the familiar decimal system. A laboratory for laser technologies was opened in the 1960s. The building on Sablinskaya Street, which is now the main campus, was built in the 1970s. The following decade saw the beginning of microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
technology research and the opening of the Interdisciplinary Institute of Advanced Studies to train manufacturing professionals in new areas of engineering and technology.
1992 ‚Äď present
In 1992, LIFMO became ''Saint Petersburg Institute of Fine Mechanics and Optics'', and in 1994 it acquired the university status. The Faculty of Computer Technologies and Controls opened in 1994. In 1994 the institute was the initiator and key developer ofRUNNET
RUNNet (Russian university network) was established in 1994 on the initiative of the State University of Fine Mechanics and Optics by the State Committee of Higher Education as a very important branch of the Russian Universities program. In the ...
, an IP network that unites all large research and education centers in Russia. The work was overseen by Dr. Vasilyev. The institute placed satellite dishes ‚ÄúRussia‚Äô Rainbow,‚ÄĚ rented from the military, on other universities. In 1995, the research center ‚ÄúComputer Optics‚ÄĚ was established. In 2003 the institute was renamed into ''Saint Petersburg State University of Information Technologies, Mechanics and Optics''.
''Academy of Management Methods and Technologies'' (LIMTU) was added to the ITMO structure as well as ''Interdisciplinary Institute of Professional Training in New Areas of Science and Technology'' and the ''State Scientific Center of Computer Telecommunication Networks of Higher Education'', followed by ''St. Petersburg College of Marine Instrument Making'', '' St. Petersburg State University of Refrigeration and Biotechnology'' and ''St. Petersburg Economic and Technological College of D.I. Mendeleev''.
In 2009 the university gained the status of ''National Research University'' and was renamed ''National Research University ITMO'' in 2011. In 2013 it was selected to join the Project 5‚Äď100.
From January 9, 2013, to November 3, 2014, a tribute to Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 ‚Äď October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
in a form of a giant iPhone graced the courtyard of the university's building on Birzhevaya Linija.
On November 26, 2014, the university opened its representative office in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
.
Since 2014 the university holds the name of ''ITMO University''.
Chronology of names
* 1900 - 1917 - Mechanics, Optics and Watchmaking Department of the Prince Nicholas Vocational School * 1917 - 1920 - Petrograd Technical College for Mechanics, Optics and Watchmaking. * 1920 - 1930 - Petrograd College for Fine Mechanics and Optics * 1930 - 1992 - Leningrad Institute of Fine Mechanics and Optics (LIFMO) * 1992 - 1994 - Saint Petersburg Institute of Fine Mechanics and Optics * 1994 - 2003 - Saint Petersburg University of Fine Mechanics and Optics * 2003 - 2011 - Saint Petersburg State University of Information Technologies, Mechanics and Optics * 2011 - 2014 - National Research University ITMO * Since 2014 - ITMO UniversityPresent
 The university has a multi-level system of higher education: bachelor ‚Äď 4 years, specialist ‚Äď 5 years, master ‚Äď 2 years, post-graduate ‚Äď 3‚Äď4 years.
Since 2013/14 ITMO is partnering with universities in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland, France, among others, to participate in ‚Äúdouble degree‚ÄĚ international educational programs. ITMO graduates of these programs receive a second degree from a partner university.
The university collaborates with large St. Petersburg companies, including Elektropribor,
The university has a multi-level system of higher education: bachelor ‚Äď 4 years, specialist ‚Äď 5 years, master ‚Äď 2 years, post-graduate ‚Äď 3‚Äď4 years.
Since 2013/14 ITMO is partnering with universities in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland, Finland, France, among others, to participate in ‚Äúdouble degree‚ÄĚ international educational programs. ITMO graduates of these programs receive a second degree from a partner university.
The university collaborates with large St. Petersburg companies, including Elektropribor, LOMO
LOMO (russian: –õ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ķ O–Ņ—ā–ł–ļ–ĺ-M–Ķ—Ö–į–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ķ O–Ī—ä–Ķ–ī–ł–Ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ķ, Leningradskoye Optiko-Mekhanicheskoye Obyedinenie, Leningrad Optical Mechanical Association) is a manufacturer of medical and motion-picture lens ...
, Mendeleev Institute for Metrology. The university supports a variety of scholarships: President of the Russian Federation, The Government of the Russian Federation, the Government of St. Petersburg, special scholarships in math, physics, IT, Research Council scholarship, name scholarship by LOMO and other companies. Students and staff carry out research and project activities on their own and as part of programs funded by the state and international contracts, federal and industry targeted programs. The university organizes and hosts competitions, congresses (for example, the annual ‚ÄúYoung Scientists Congress‚ÄĚ), forums, research conferences, including international (‚ÄúSensorica,‚ÄĚ ‚ÄúFundamental Problems of Optics,‚ÄĚ etc.). In 2013, the university was one of the venues for the RussiaNational Student Forum
The university has participated in student and instructor exchange programs financed by organizations, including the DAAD. ITMO is a member of the Association of European Universities. It also collaborates with foreign universities, including
UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California St ...
and ITESM
Instituto Tecnológico y de Estudios Superiores de Monterrey (ITESM) ( en, Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education), also known as Tecnológico de Monterrey or just Tec, is a secular and Mixed-sex education, coeducational private ...
.
ITMO University is one of two St. Petersburg universities - members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian politics, political, economy, economic and security organization. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geography, geographic scope and world population, population, c ...
. SCO University offers involved learning where students work based on individual plans, learn about life in a different country and thus add to their education at their ‚Äúhome‚ÄĚ university. At graduation, SCO University students receive a regular diploma and a special certificate.
The university is part of the Association of Technical Universities of Russia and China, founded in 2011, and participates in joint educational programs with the leading universities in China. This non-commercial organization unites technical universities of both countries and facilities student and instructor exchange. It was originally established at Harbin Institute of Technology
Harbin Institute of Technology (; abbreviation: HIT or ) is a public research university and a member of China's elite C9 League and a member of the University Alliance of the Silk Road. HIT is a Chinese Ministry of Education Class A Doubl ...
and Bauman Technical University
The Bauman Moscow State Technical University, BMSTU (russian: link=no, –ú–ĺ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–≤—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ –≥–ĺ—Ā—É–ī–į—Ä—Ā—ā–≤–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č–Ļ —ā–Ķ—Ö–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ —É–Ĺ–ł–≤–Ķ—Ä—Ā–ł—ā–Ķ—ā –ł–ľ. –Ě. –≠. –Ď–į—É–ľ–į–Ĺ–į (–ú–ď–Ę–£ –ł–ľ. –Ě. –≠. –Ď–į—É–ľ–į–Ĺ–į)), some ...
in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, –ú–ĺ—Ā–ļ–≤–į, r=Moskva, p=m…źskňąva, a=–ú–ĺ—Ā–ļ–≤–į.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
.
Several times ITMO University students won “Yandex
Yandex LLC (russian: link=no, –Į–Ĺ–ī–Ķ–ļ—Ā, p=ňąjand…ôks) is a Russian multinational technology company providing Internet-related products and services, including an Internet search engine, information services, e-commerce, transportation, maps ...
. Algorithm‚ÄĚ programming championship, organized by one of Russia's internet companies. It's not a student competition per se but open to participants over 17. In 2013, it welcomed over 3,000 programmers from 84 countries and several large companies, including Google, Facebook and Vkontakte
VK (short for its original name ''VKontakte''; russian: –í–ö–ĺ–Ĺ—ā–į–ļ—ā–Ķ, meaning ''InContact'') is a Russian online social media and social networking service based in Saint Petersburg. VK is available in multiple languages but it is predomin ...
. That same year ITMO students took gold and silver, and in 2014 ‚Äď gold again, followed by another gold in 2015.
ITMO team also regularly participates in ACM ICPC programming championship under the general sponsorship by IBM since 1997. In 2013, the university hosted the 37th championship and its student won the top prize. ITMO students received medals in this championship since 1999 and from 2004 till 2015 became absolute winners six times.
In 2013, after their fifth win, Russia's Ministry of Defense
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in states ...
signed a contract with ITMO University to develop software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...
for unmanned airplanes
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller ...
and robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrat ...
, to name a few. The same year Minister Sergey Shoygu
Sergei Kuzhugetovich Shoigu, ; tyv, –°–Ķ—Ä–≥–Ķ–Ļ –ö“Į–∂“Į–≥–Ķ—ā –ĺ–≥–Ľ—É –®–ĺ–Ļ–≥—É, translit=Sergey Kyzhyget oglu Shoygu, . (russian: –°–Ķ—Ä–≥–Ķ–Ļ –ö—É–∂—É–≥–Ķ—ā–ĺ–≤–ł—á –®–ĺ–Ļ–≥—É; born 21 May 1955) is a Russian politician who has served as ...
offered talented students jobs in scientific military units as an alternative to mandatory military service.
 ITMO University maintains ties with IT companies. In 2011,
ITMO University maintains ties with IT companies. In 2011, Dmitry Grishin
Dmitry Grishin (born 15 October 1978) is a businessman, investor and Internet entrepreneur. He is best known as the co-founder and former Chairman and CEO of Mail.ru Group. Grishin also made significant contributions to Russia’s internet presence ...
, the general director of Mail.Ru
VK, known as Mail.ru Group until 12 October 2021, is a Russian technology company. It started in 1998 as an e-mail service and went on to become a major corporate figure in the Russian-speaking segment of the Internet.
VK operates an e-mail s ...
, became the head of the department of internet technologies founded by the company. Later it was reorganized. In 2012, Russian programmers working for Facebook held a series of lectures at the leading technical universities in Russia, including ITMO. In 2015, Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
winner Zhores Alferov
Zhores Ivanovich Alferov (russian: link=no, –Ė–ĺ—Ä–ĶŐĀ—Ā –ė–≤–įŐĀ–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–ł—á –ź–Ľ—Ą—Ď—Ä–ĺ–≤, ; be, –Ė–į—Ä—ć—Ā –Ü–≤–įŐĀ–Ĺ–į–≤—Ė—á –ź–Ľ—Ą—Ď—Ä–į—ě; 15 March 19301 March 2019) was a Soviet and Russian physicist and academic who contributed signific ...
opened the ''International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies'' in St. Petersburg and held an open lecture at the university.
In November 2014, the association of software manufacturers Russoft
Russoft, headquartered in Saint-Petersburg, is an association of software companies from Russia, Ukraine and Belarus. It was founded on September 9, 1999 and has merged with the Fort-Ross Consortium in May 2004. Today Russoft unites more than 80 ...
published a ranking of Russian universities by the level of success in training of the IT specialists. ITMO University placed first. Around the same time the university held a conference together with the association about the advantages of successful performance at international programming competitions.
In 2015, the Ministry of Education offered several universities, including ITMO to participate in the ‚ÄúNational Platform for Open Education‚ÄĚ Association and develop a pilot for online education with an opportunity to graduate at the completion of the courses. Currently this project still requires changes when it comes to licenses and university accreditations. Every participating university has to present no fewer than four online courses by September 2015.
Russian President Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
congratulated the team of ITMO University with its sixth victory in ACM ICPC programming championship at the plenary session during the second day of the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum in May 2015.
Rankings
In 2022, the university was ranked #365 in the world byQS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
, and #601 by World University Rankings by ''Times Higher Education
''Times Higher Education'' (''THE''), formerly ''The Times Higher Education Supplement'' (''The Thes''), is a British magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
Ownership
TPG Capital acquired TSL Education ...
''. In 2021, it was ranked #718 in the world by Best Global Universities Rankings by '' U.S. News & World Report'', and #901 by Academic Ranking of World Universities by Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU; ) is a public research university in Shanghai, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education of China.
The university was established on April 8, 1896 as Nanyang Public School (ŚćóśīčŚÖ ...
.
ITMO University is one of the 21 Russian institutions of higher education that were selected for participation in the Russian Academic Excellence Project 5-100, launched in 2013 by the Russian Ministry of Education and Science
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (russian: –ú–ł–Ĺ–ł—Ā—ā–Ķ—Ä—Ā—ā–≤–ĺ –ĺ–Ī—Ä–į–∑–ĺ–≤–į–Ĺ–ł—Ź –ł –Ĺ–į—É–ļ–ł –†–ĺ—Ā—Ā–ł–Ļ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ļ –§–Ķ–ī–Ķ—Ä–į—Ü–ł–ł or Minobrnauki of Russia) existed from March 2004 till May 2018. It oversaw ...
. The aim of the project is to have at least five Russian universities included in the top-100 lists of three major international university rankings: the Academic Ranking of World Universities
The ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'' (''ARWU''), also known as the Shanghai Ranking, is one of the annual publications of world university rankings. The league table was originally compiled and issued by Shanghai Jiao Tong University ...
, QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
, and THE World University Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'' (often referred to as the THE Rankings) is an annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli ...
, compiled annually by the ranking agencies ShanghaiRanking Consultancy, Quacquarelli Symonds
Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) is a British company specialising in the analysis of higher education institutions around the world. The company was founded in 1990 by Nunzio Quacquarelli.
History
On 5 October 2017, QS Quacquarelli Symonds acquired Hob ...
, and the ''Times Higher Education
''Times Higher Education'' (''THE''), formerly ''The Times Higher Education Supplement'' (''The Thes''), is a British magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
Ownership
TPG Capital acquired TSL Education ...
'' magazine, respectively.
Universities participating in the project regularly compile development roadmaps in which they outline their goals in regard to enhancing their position in international rankings. The project's council reviews these roadmaps and consults the Ministry of Science and Higher Education
{{Unreferenced, date=March 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
A Ministry of Higher Education is a government department that focuses on the provision or regulation of institutions of higher education. In some countries these exist as ministries compounde ...
, which in turn distributes funding among the participating universities.
ITMO University has been one of the project's top participants; these universities receive subsidies of up to 1 billion rubles
The ruble (American English) or rouble (Commonwealth English) (; rus, —Ä—É–Ī–Ľ—Ć, p=rubl ≤) is the currency unit of Belarus and Russia. Historically, it was the currency of the Russian Empire and of the Soviet Union.
, currencies named ''rub ...
.
In September 2016, ITMO University made its debut in THE World University Rankings within the 350-400 range, and was ranked 56th in computer science (but it dropped to the 101-125 range in 2020 in computer science), but it dropped to #601 in the world ranking in 2022. In June 2017, ITMO debuted in the QS World University Rankings within the 601-650 range, but it was ranked #901 in the world in 2022. ITMO made its debut in the ARWU
The ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'' (''ARWU''), also known as the Shanghai Ranking, is one of the annual publications of world university rankings. The league table was originally compiled and issued by Shanghai Jiao Tong University ...
in August 2018 within the 801-900 range. As of the start of 2020, ITMO University featured in 13 subject rankings published by THE, QS, and ARWU.
The university is also included in a number of other Russian and international rankings compiled by various analytics agencies, companies, and magazines. Since 2018, the Russian edition of the ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also re ...
'' magazine has been publishing its ranking of the top 100 Russian institutions of higher education, in which ITMO University has consistently been placing among the top ten.
Structure, university institutes and departments
* Institute of Design & Urban Studies * Institute of Translational Medicine * Department of Higher Qualification Expert Training * Department of Computer Technologies and Control Systems ** Department of Control Systems and Industrial Robotics ** Department of Software Engineering and Computer Systems ** Department of Information Security and Computer Technologies * Information Technologies and Programming Department * Department of Infocommunication Technologies * Department of Photonics and Optical Information * Department of Laser and Light Engineering * Department of Technological Management and Innovations * Institute of International Development and Partnership * Department of Cryogenic Techniques and Air Conditioning * Department of Food Biotechnologies and Engineering * Department of International Business and Law * Department of Management and Automation Controls * Department of Natural Sciences * Department of Integrated Military Education * Department of Distance Education * Department of Secondary Vocational Education * Department of Career Development and Pre-Entry Preparatory Training * Department of Advanced Training of TeachersLeadership
 Since 1996, the Rector of the university is the Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, Chairman of the Council of Rectors of St. Petersburg (2004), vice-president of the Russian Union of Rectors (2006), corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Education, corresponding member Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Vladimir Vasilyev.
Since 1996, the Rector of the university is the Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, Chairman of the Council of Rectors of St. Petersburg (2004), vice-president of the Russian Union of Rectors (2006), corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Education, corresponding member Russian Academy of Sciences, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Vladimir Vasilyev.
Research and partnerships
ITMO University collaborates on research and innovations projects with several large Russian companies, includingLOMO
LOMO (russian: –õ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ķ O–Ņ—ā–ł–ļ–ĺ-M–Ķ—Ö–į–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ķ O–Ī—ä–Ķ–ī–ł–Ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ķ, Leningradskoye Optiko-Mekhanicheskoye Obyedinenie, Leningrad Optical Mechanical Association) is a manufacturer of medical and motion-picture lens ...
, D.I. Mendeleyev Institute for Metrology (VNIIM), Techpribor, Elektropribor, etc. The university signed an agreement to create the Northwestern Center for Technology Transfer to become one of 12 nano-centers around Russia. Originally it was supposed to be in the town of Gatchina
The town of Gatchina ( rus, –ď–įŐĀ—ā—á–ł–Ĺ–į, , ňą…°atňź…ē…™n…ô, links=y) serves as the administrative center of the Gatchinsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies south-south-west of St. Petersburg, along the E95 highway which ...
. In 2015 it was opened in St. Petersburg on Malookhtenskii Prospect. Another joint project with Rusnano
Rusnano Group (russian: –†–ĺ—Ā–Ĺ–į–Ĺ–ĺ –ź–ě, lit=Rosnano plc.) is a Russian state-established and funded company. The Rusnano Group's mission is to create competitive nanotechnology-based industry in Russia. Rusnano invests directly and through i ...
is ''‚ÄúInnograd of Science and Technologies.‚ÄĚ'' It was expected to open by 2019 in the satellite city Yuzhni. Rusnano was investing 690 million rubles in its equipment. Construction was scheduled to begin in 2015 in the town of Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, –ź–Ľ–Ķ–ļ—Ā–į–Ĺ–ī—Ä –°–Ķ—Ä–≥–Ķ–Ķ–≤–ł—á –ü—É—ą–ļ–ł–ĹIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=…źl ≤…™kňąsandr s ≤…™rňą…° ≤e(j)…™v ≤…™t…ē ňąpu āk ≤…™n, ...
, near St. Petersburg.
 In 2012, a ‚Äú Skolkovo‚ÄĚ communications center was supposed to open on the campus of the former Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnologies of ITMO, but the plans were altered. That same year the university signed a memorandum with RSV Venture Partners Foundation to establish a $6 million fund for IT startups. In 2013, Internet Initiatives Development Fund offered ITMO University to collaborate in opening regional accelerators to support commercially promising internet startups.
University's list of international partners over the years includes General Motors Corp., PPG, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, Nokia and others.
Students and staff members of over 80 departments participate in research. Many of them are working in ‚Äúsmall innovative enterprises,‚ÄĚ or startups, located at ITMO Technopark on Birzhevaya Liniya, offering access to high-tech equipment.
As part of the Project 5‚Äď100, Technopark opened a coworking space called FabLab in 2015, which also offered facilities and resources, including a 3D printer, a laser engraver, a milling machine, etc. The equipment is offered free of charge to the ITMO University specialists and students.
In 2012, a ‚Äú Skolkovo‚ÄĚ communications center was supposed to open on the campus of the former Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnologies of ITMO, but the plans were altered. That same year the university signed a memorandum with RSV Venture Partners Foundation to establish a $6 million fund for IT startups. In 2013, Internet Initiatives Development Fund offered ITMO University to collaborate in opening regional accelerators to support commercially promising internet startups.
University's list of international partners over the years includes General Motors Corp., PPG, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, Nokia and others.
Students and staff members of over 80 departments participate in research. Many of them are working in ‚Äúsmall innovative enterprises,‚ÄĚ or startups, located at ITMO Technopark on Birzhevaya Liniya, offering access to high-tech equipment.
As part of the Project 5‚Äď100, Technopark opened a coworking space called FabLab in 2015, which also offered facilities and resources, including a 3D printer, a laser engraver, a milling machine, etc. The equipment is offered free of charge to the ITMO University specialists and students.
National Research University Program
 In 2009, the university was granted the status of National Research University. It implies carrying out research in areas considered key to the development of Russia's economy, including IT, photonics, optoinformatics, and urban science.
In 2009, the university was granted the status of National Research University. It implies carrying out research in areas considered key to the development of Russia's economy, including IT, photonics, optoinformatics, and urban science.
International research centers
As part of the Project 5‚Äď100, the university created international research centers to carry out joint research between scientists at ITMO and their peers at foreign research and education centers. By 2014 the university had established 49 such entities with co-heads from the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Australia, China, etc. In order to strengthen governmental support for the development of science and innovations in higher education and to improve the quality of higher education, on April 9, 2010, theGovernment of the Russian Federation
The Government of Russia exercises executive power in the Russia, Russian Federation. The members of the government are the Prime Minister of Russia, prime minister, the Deputy Chairman of the Government, deputy prime ministers, and the federa ...
instituted monetary grants that were made available on a competitive basis to support of scientific research projects implemented by the world's scientists at Russian institutions of higher learning. From some 507 applications, 39 were awarded funding, including two from ITMO University. In 2013 ITMO University won two more mega-grants from the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia Federation.
Small innovative enterprises (start-ups)
 Since 15 August 2009 Russian universities are able to form small innovative enterprises according to Federal Law No.217 of August 2, 2009 N 217-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on the establishment of budget scientific and educational institutions, business entities for the purpose of practical application (implementation) of the results of intellectual activity".
By 2015 ITMO University has become the Launchpad for 43 small innovative enterprises. A special department is designated to helping them find funding, offers legal support for registering, partner search, placement in university's Technopark and business incubator. Other types of support include education initiatives
Since 15 August 2009 Russian universities are able to form small innovative enterprises according to Federal Law No.217 of August 2, 2009 N 217-FZ "On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on the establishment of budget scientific and educational institutions, business entities for the purpose of practical application (implementation) of the results of intellectual activity".
By 2015 ITMO University has become the Launchpad for 43 small innovative enterprises. A special department is designated to helping them find funding, offers legal support for registering, partner search, placement in university's Technopark and business incubator. Other types of support include education initiativesclasses in social entrepreneurship and projects
fundraising school ''FundIT'', soft skill training, lectures in marketing and management, interdisciplinary seminars ''Brainexplain'', as well as lectures by guest experts. The university holds an annual international forum where its partners and business stakeholders discuss issues in technology transfer and development of innovations ecosystem. Other events are festival o
social entrepreneurship
a competition of socially valuable projects ‚ÄúPeople need you!‚ÄĚ, and a business game ‚ÄúInnovations marketing‚Ä̬Ľ. ITMO University was as of 2015 developing a network of startup accelerators in Russia‚Äôs regions as part of the program for development of research and entrepreneurship potential of Russian universities ‚ÄúEURECA‚ÄĚ and in partnership with the U.S. Russia Foundation and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). To promote building an innovation ecosystem from the ground up, ITMO partnered with "Xmas Ventures" and St. Petersburg Polytechnic University to establish
Demola Innovations Center
in St. Petersburg, the only one in Russia. German company
SAP SE
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a sepa ...
was instrumental in supporting the university's startups. What started with joint business incubator events and accelerator programs in 2013 grew into a partnership.
Accelerators
In spring of 2015, ITMO University launched the ''Future Technologies accelerator'' for startups in instrumentation, robotics, optics and photonics, biotechnologies and energy efficiency. In the future, the organizers hoped to attract companies working in new materials and alternative energy. The participants receive a three-month training course as well as free office space, supplies and consultations with experts in research and business. They can apply for a 300,000 ruble grant that covers expenses for research and development. In the first session, 10 companies were selected to participate out of 70 that applied. At the end of June, the startups presented their projects at the international conference ''Russia-EU Startup Match-making Event'' in Brussels. SumIT startup accelerator takes place at the university every six months since 2012. The top ten teams from the previous sessions from Russia, Finland, France and USA secured funding from $20,000 to $200,000 and several settled in the startup accelerator ''iDealMachine''.World Programming Championship
 In 2004, ITMO University scored its first victory in the International Collegiate Programming Contest ACM-ICPC, and by 2017 it became the first in history seven-time winner of the competition.
In 2013, ITMO University was the first Russian university to host the ACM-ICPC Finals. Some 120 teams representing 2,322 universities from 36 countries participated in selection rounds. Russia was represented by 15 student teams. ITMO University scored a victory in the finals.
In 2004, ITMO University scored its first victory in the International Collegiate Programming Contest ACM-ICPC, and by 2017 it became the first in history seven-time winner of the competition.
In 2013, ITMO University was the first Russian university to host the ACM-ICPC Finals. Some 120 teams representing 2,322 universities from 36 countries participated in selection rounds. Russia was represented by 15 student teams. ITMO University scored a victory in the finals.
ITMO Highpark
In 2017, the university initiated the ITMO Highpark project, which entails the creation of a research, education, and innovation center with the university's second campus as its core. The future campus will be situated in the south of St. Petersburg, in the vicinity ofPulkovo Airport
Pulkovo ( rus, links=no, –ü—É–Ľ–ļ–ĺ–≤–ĺ, p=ňąpulk…ôv…ô) is an international airport serving St. Petersburg, Russia. It consists of one terminal which is located south of the city centre. The airport serves as a airline hub, hub for Rossiya Ai ...
. The university administration's proposal was supported by the Governor of St. Petersburg and the Russian Government. On October 13, 2017, the Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev
Dmitry Anatolyevich Medvedev ( rus, links=no, –Ē–ľ–ł—ā—Ä–ł–Ļ –ź–Ĺ–į—ā–ĺ–Ľ—Ć–Ķ–≤–ł—á –ú–Ķ–ī–≤–Ķ–ī–Ķ–≤, p=ňądm ≤itr ≤…™j …źn…źňątol ≤j…™v ≤…™t…ē m ≤…™dňąv ≤ed ≤…™f; born 14 September 1965) is a Russian politician who has been serving as the dep ...
signed the corresponding executive order; on October 17, he made an official announcement of the project's launch at the Open Innovations forum.
ITMO University's second campus, along with a Techno Valley and a Business Park, will be situated on an area of 87 hectares. The second campus, which will include an academic building, three research centers, a student club, a sports facility, dormitories, and a science museum, will cover an area of 41 hectares, with the total area of all interior spaces being approximately 100,000 sq.m. The campus will be home to ITMO's Master's and doctoral programs that are focused on applied research and its commercialization. The university's buildings in central St. Petersburg will remain in use by Bachelor's programs and Master's programs focused on fundamental science.
The Techno Valley is described as ‚Äúa site for objects of scientific, innovative, and production infrastructure established by businesses and startups‚ÄĚ. Its total area will equal 16 hectares. In the future, it is planned to become an Innovative Research and Technology Center (IRTC), which will offer tax concessions to businesses.
The Business Park will be the site of a National Center for Urban Studies, a Data Processing Center, a business incubator, and various other objects of business and cultural infrastructure. The total area allocated for the Business Park is 4 hectares.
By 2024, 3,600 students are expected to study at ITMO Highpark; the campus is said to provide 12,000 jobs and host 5 innovative production facilities and approximately 50 international laboratories.
The project's scientific area of focus is in applied research and fields such as intelligent technologies, cyberphysical systems, photonics, quantum technologies, and biochemistry. The resident businesses’ areas of activity will aim to develop the markets of urban studies, safe/smart cities, the exploration of new territories, extreme environments and virtual worlds, and creative industries.
ITMO Highpark's cost is estimated to be more than 41 billion rubles; of that amount, 53% is said to be invested from the federal budget, 12% from the city's budget, and 35% provided by private investors.
In 2019, ITMO Highpark's architectural concept design, developed by Russian and British architects, was shortlisted for the World Architecture Festival Award, one of the most prestigious prizes in the field of architecture.
In May 2020, the Government of St. Petersburg approved the plan for the first stage of construction of ITMO Highpark. The construction was expected to start in late 2020 - early 2021. The first stage, which includes the main academic building, a dormitory, the student club, the science museum, and street infrastructure, was to be completed in 2022. The second stage (which includes research centers, a second dormitory, a sports facility, and a business incubator as part of the Techno Valley) was to be finished by the end of 2023; the third stage (includes the National Center for Urban Studies, the Data Processing Center, a business incubator as part of the Business Park, and the social infrastructure of Yuzhny) was to be completed in 2027.
Publishing, library, museum
Publishing
Along with training aids, ITMO University produces a variety of publications. To celebrate the university's 100 anniversary in 2000 it launched two series of books: ''‚ÄúNational Research University ITMO: Years and People,‚ÄĚ'' and monographs ''‚ÄúOutstanding People of ITMO University.‚ÄĚ'' The official newspaper ‚ÄúITMO University‚ÄĚ has been in print since 1931. Launched as ''‚ÄúNew Talent,‚ÄĚ'' it has changed its name several times over the eras: ‚ÄúFor Precise Instrumentation,‚ÄĚ ‚ÄúInstrument Builder,‚ÄĚ ‚ÄúNew Talent for Instrumentation.‚ÄĚ In 1956 it was halted due to budget cuts and reemerged in 1994 as ‚ÄúTechnical University ITMO‚ÄĚ but was not produced on a regular basis. In 2013, it came out twice a year. Since 2015 it became a monthly, with the exception of summer months, and offers an extended version online. : Scientific journals * ''"Proceedings of Higher Educational Institutions. Instrumentation.‚ÄĚ'' The journal was among the scientific publications launched by the Ministry of Higher Education in 1957. The first issue ‚ÄúProceedings of USSR Universities ‚Äď Instrumentation‚ÄĚ came out in January 1958. In 1991, some 3,000 copies of 12 issues were published annually and delivered by subscription. In 1992 the circulation dropped sharply and by 1997 only 9 issues were published annually. Since 2015 it's back to 12 issues a year. * ''‚ÄúScientific and Technical Gazette of IT, Mechanics and Optics.‚ÄĚ'' Originally launched in 1936, it was reestablished in 2001. It 2011 it got its current name. It comes out 6 times a year and is indexed. * ''‚ÄúNanosystems: Physics, Chemistry, Math.‚ÄĚ'' 6 issues a year. Indexed. * ''‚ÄúOptical Journal.‚ÄĚ'' Launched in 1931. 12 issues a year. Indexed. * ''‚ÄúScientific Journal of NRU ITMO.‚ÄĚ'' Series ‚ÄúRefrigeration technology and air conditioning.‚ÄĚ Electronic edition comes out twice a year. Launched in 2007. Since 2013 titled ‚ÄúThe Journal of the Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnology‚ÄĚ. * ''‚ÄúScientific Journal of NRU ITMO.‚ÄĚ'' Series ‚ÄúProcesses and Food Processing Equipment.‚ÄĚ Electronic edition comes out four times a year. Launched in 2006 as a collection of papers, it became a scientific periodical in 2008. Before 2013 it was titled ‚ÄúThe Journal of the Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnology.‚ÄĚ Indexed. * ''‚ÄúScientific Journal of NRU ITMO.‚ÄĚ'' Series ‚ÄúEconomics and Eco Management.‚ÄĚ Electronic edition comes out four times a year. Launched in 2007. Before 2013 it was titled ‚ÄúThe Journal of the Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnology.‚ÄĚ Indexed.Library
The university is a member of the'' Library Association of Russia'', ''St. Petersburg Library Society'', ''National Electronic Information Consortium'', and the ''Association of Regional Library Consortiums''. The ITMO University library offers access to Russian and foreign full-text and reference electronic resources, including Web of Science, Conference Proceedings Citation,Journal Citation Reports
''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publicationby Clarivate Analytics (previously the intellectual property of Thomson Reuters). It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science-Core Collect ...
, Scopus
Scopus is Elsevier's abstract and citation database launched in 2004. Scopus covers nearly 36,377 titles (22,794 active titles and 13,583 inactive titles) from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in top-l ...
, ScienceDirect
ScienceDirect is a website which provides access to a large bibliographic database of scientific and medical publications of the Dutch publisher Elsevier. It hosts over 18 million pieces of content from more than 4,000 academic journals and 30,0 ...
, Springer
Springer or springers may refer to:
Publishers
* Springer Science+Business Media, aka Springer International Publishing, a worldwide publishing group founded in 1842 in Germany formerly known as Springer-Verlag.
** Springer Nature, a multinationa ...
, ACM, OSA, SPIE
SPIE (formerly the Society of Photographic Instrumentation Engineers, later the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers) is an international not-for-profit professional society for optics and photonics technology, founded in 1955. It ...
, eLibrary
HighBeam Research was a paid search engine and full text online archive owned by Gale, a subsidiary of Cengage, for thousands of newspapers, magazines, academic journals, newswires, trade magazines, and encyclopedias in English. It was headquart ...
, etc.
The year 1900 is considered the library's foundation year. By 1925, it contained 2,600 books and by 1945 ‚Äď over 90,000. Initially the library was situated in a building on Pereulok Grivtzova. During the WWII it was evacuated to Cherepanovo and returned with re-evacuation. In 1970 it got a dedicated space in the university's main building on Ulitza Sablina.
In 1998 the library created a department for computerization of library processes and adopted ‚ÄúIrbis‚ÄĚ library information system. In 2002 the university got a grant from the ''National Fund for Personnel Development'' for ‚ÄúImproving management of library resources and forming an open educational environment of the university.‚ÄĚ The library as of 2015 was working on forming an electronic catalogue.
The library of the Faculty of Associate Level Education became a department of the main library in 2003 and contains the books from the former Mechanical College #1 that merged with the university that year. The readers who had been in Leningrad during the Siege of the WWII donated the first books to the college in 1945. By 2000, it contained over 44,000 books and grew to 56,000 by 2008 with the addition of the library of the Marine Instrumentation College.
In 2005 the library absorbed the collection from the library of the State Optical Institute, which dates back to 1918. In 1974 the State Optical Institute library was granted a status of a collection on optics and optical instrumentation of state importance and became a resource for several university libraries as well as industry. In 2006 the library received over 10,000 books from the Academy of Management that also became part of the university. In 2011 it also got the books from the library of the Institute of Refrigeration and Food Processing that dates back to 1931, survived the Siege and by 1980 contained over 550,000 books and over a million by the time of merger.
Museums
 ITMO University has three museums. ''‚ÄúMuseum of ITMO University History‚ÄĚ'' is located in the building on Pereulok Grivtzova.
The ''Museum of Optics'' was established in 2006 and is located on the first floor of the Eliseev House on Birzhevaya Linia. With support from the Hellenic Institute of Holography, ITMO University opened an exhibition ‚ÄúMagic of Light‚ÄĚ in 2015. The Eliseev House was selected for the exhibition because it used to house the office of Prof. Denisuk, the founder of image holography. It features over 200 holograms, including OptoClones of Imperial
ITMO University has three museums. ''‚ÄúMuseum of ITMO University History‚ÄĚ'' is located in the building on Pereulok Grivtzova.
The ''Museum of Optics'' was established in 2006 and is located on the first floor of the Eliseev House on Birzhevaya Linia. With support from the Hellenic Institute of Holography, ITMO University opened an exhibition ‚ÄúMagic of Light‚ÄĚ in 2015. The Eliseev House was selected for the exhibition because it used to house the office of Prof. Denisuk, the founder of image holography. It features over 200 holograms, including OptoClones of Imperial Faberg√© egg
A Faberg√© egg (russian: link=no, —Ź–Ļ—Ü–ĺ –§–į–Ī–Ķ—Ä–∂–ĶŐĀ, translit=yaytso Faberzhe) is a jewelled egg created by the jewellery firm House of Faberg√©, in Saint Petersburg, Russia. As many as 69 were created, of which 57 survive today. Virtual ...
s, Oculus Rift
Oculus Rift is a discontinued line of virtual reality headsets developed and manufactured by Oculus VR, a division of Meta Platforms, released on March 28, 2016.
In 2012 Oculus initiated a Kickstarter campaign to fund the Rift's development, af ...
virtual reality glasses and more. The inner courtyard houses ''Lux Aeterna Laser Theater''.
The ''Museum of the Institute of Refrigeration and Biotechnologies'', dating back to 1936, is located in a historic building on Lomonosova Street.
In 2012 the university won a competition by a Committee on Investments to come up with a concept of an interactive museum of science and technology that will be built on the grounds of the former tram park on Vasilyevsky Island
Vasilyevsky Island (russian: –í–į—Ā–łŐĀ–Ľ—Ć–Ķ–≤—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ –ĺŐĀ—Ā—ā—Ä–ĺ–≤, Vasilyevsky Ostrov, V.O.) is an island in St. Petersburg, Russia, bordered by the Bolshaya Neva and Malaya Neva Rivers (in the delta of the Neva River) in the south a ...
.
In Lakhta Center
The Lakhta Center () is an 87-story skyscraper built in the northwestern neighbourhood of Lakhta, Saint Petersburg, Lakhta in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Standing tall, it is the List of tallest buildings in Russia, tallest building in Russia, t ...
, ITMO University was as of 2013 building one of the largest children's science museums in the country, around 7,000 sq. m., with support of Saint Petersburg government.
Student life
 The university has student unions, including those for foreign students, student clubs, a student orchestra, student radio, a student scientific society, and volunteer center. Many of these organizations get together in coworking spaces around the campus. The students can use these spaces for their own projects, but some, such as SumIT, require a prior interview.
The university has two assembly halls that can hold up to 500 people each. Other activity spaces include a soundproof room for singing lessons, an audio recording studio, a studio for ‚ÄúMegabyte‚ÄĚ internet radio and editorial office of ‚ÄúNewTone‚ÄĚ magazine.
The university has student unions, including those for foreign students, student clubs, a student orchestra, student radio, a student scientific society, and volunteer center. Many of these organizations get together in coworking spaces around the campus. The students can use these spaces for their own projects, but some, such as SumIT, require a prior interview.
The university has two assembly halls that can hold up to 500 people each. Other activity spaces include a soundproof room for singing lessons, an audio recording studio, a studio for ‚ÄúMegabyte‚ÄĚ internet radio and editorial office of ‚ÄúNewTone‚ÄĚ magazine.
Accommodations
The university offers accommodations in six dorms. Depending on a student's individual circumstances, accommodation may also be provided at the Inter-university student campus on Novoizmailovskii Prospect, 16.Main Building
; Campus and dorms * Kronverksky prospect, d. 49 * Birzhevaya linia, d. 4 * Birzhevaya linia, d. 16 * Birzhevaya linia, d. 14 * Grivtsova per.,d. 14-16 * Pesochnaya nab., d. 14 * Chaikovskogo ul., d. 11/2 * Gastello ul., d. 12 * Kadetskaya Linia V.–ě., d. 3,k.2 * Novoizmailovsky prospect, d. 34, k. 3 * Vyazemsky per., d. 5-7 * 2 Komsomolskaya ul., d. 5 * 2 Komsomolskaya ul, d. 7, k. 1 * Serebristiy bul., d. 29, k. 1 * Khrustalnaya ul, d. 14 * Lomonosova ul, d. 9 * Alpiysky per., d. 15,k.2 * Belorusskaya ul, d. 6 * Lensoveta ul, d.23Sports
 The university has its own sporting infrastructure. Sports clubs are located on Vjazemsky Pereulok and Lomonosova Street, and there's also a sportsground by the main building. The university also owns a recreational facility, Yagodnoe, located by the Berestovoe Lake, near Losevo, in the
The university has its own sporting infrastructure. Sports clubs are located on Vjazemsky Pereulok and Lomonosova Street, and there's also a sportsground by the main building. The university also owns a recreational facility, Yagodnoe, located by the Berestovoe Lake, near Losevo, in the Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, –õ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ĺ–Ī–Ľ–į—Ā—ā—Ć, Leningradskaya oblast‚Äô, l ≤…™n ≤…™nňągratsk…ôj…ô ňąobl…ôs ≤t ≤, , ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, a ...
.
The university's futsal team won a silver medal at 2013 ‚ÄúGolden League‚ÄĚ championship and took bronze in 2015.
Since 2014, the university's rector Vladimir Vasilyev has been heading a series of bi-annual bike rides for students and staff in the vicinity of the Krestovsky Island
Krestovsky Island (russian: –ö—Ä–Ķ—Ā—ā–ĺ–≤—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ –ĺ—Ā—ā—Ä–ĺ–≤) is a 3.4 km2 island in Saint Petersburg, Russia, between several tributaries of the Neva: the Srednyaya Nevka, the Malaya Nevka and the Krestovka. The island is served by ...
.
Building collapse
On February 16, 2019, multiple news sources reported a building collapse at one of ITMO University's buildings on Lomonosova Street 9. Initial reports indicated that four floors of the building ‚Äď floors two through five ‚Äď had collapsed. 80 people were evacuated, and emergency crews were on the scene. Other news outlets initially reported that the collapse occurred as the result of construction work in the building.Honored doctors
 *
* Askar Akayev
Askar Akayevich Akayev ( ky, –ź—Ā–ļ–į—Ä –ź–ļ–į–Ķ–≤–ł—á (–ź–ļ–į–Ļ —É—É–Ľ—É) –ź–ļ–į–Ķ–≤, translit=Askar Akayevich (Akay Uulu) Akayev ; ; born 10 November 1944) is a Kyrgyz politician who served as President of Kyrgyzstan from 1990 until being ov ...
, Kyrgyz Professor, foreign member of the Russian Academy of Sciences (2000), President Kyrgyz Republic
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east ...
, graduated from LITMO (1968)
* Wilfred Joseph Goodman, Doctor of Electrical Engineering (Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
), former president of the American Optical Society (OSA), ex-president of the International Commission for Optics (ICO), former chief editor of OSA
* Yuri Denisyuk
Yuri Nikolayevich Denisyuk ( Russian: –ģ—Ä–ł–Ļ –Ē–Ķ–Ĺ–ł—Ā—é“Ě; July 27, 1927 in Sochi ‚ÄĒ May 14, 2006 in Saint Petersburg) was a Russian physicist and one of the founders of optical holography in the former Soviet Union. He is known for his grea ...
, member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, graduate LITMO (1954), one of the founders of optical holography
* Robert Elliot Kahn, American inventor of protocols TCP and IP, underlying the functioning of the Internet
* Ilya Klebanov
Ilya Iosifovich Klebanov (russian: –ė–Ľ—Ć—Ź –ė–ĺ—Ā–ł—Ą–ĺ–≤–ł—á –ö–Ľ–Ķ–Ī–į–Ĺ–ĺ–≤; born 7 May 1951 in Leningrad) is a Russian politician. He was the Plenipotentiary Presidential Envoy to the Northwestern Federal District of the Russian Federation ...
, authorized representative President in Northwestern Federal District
Northwestern Federal District,, ''Severo-Zapadny federalny okrug'' is one of the federal districts of Russia, eight federal districts of Russia. It covers most of Northwest Russia. Its population was 13.6 million, of which 83.5% was urban, livi ...
(2003-2011), Director General JSC "LOMO
LOMO (russian: –õ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ķ O–Ņ—ā–ł–ļ–ĺ-M–Ķ—Ö–į–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ĺ–Ķ O–Ī—ä–Ķ–ī–ł–Ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ–ł–Ķ, Leningradskoye Optiko-Mekhanicheskoye Obyedinenie, Leningrad Optical Mechanical Association) is a manufacturer of medical and motion-picture lens ...
" (1992-1997)
* Bertrand Meyer
Bertrand Meyer (; ; born 21 November 1950) is a French academic, author, and consultant in the field of computer languages. He created the Eiffel programming language and the idea of design by contract.
Education and academic career
Meyer recei ...
, French Professor, Head of Software Engineering in ETH Zurich
(colloquially)
, former_name = eidgenössische polytechnische Schule
, image = ETHZ.JPG
, image_size =
, established =
, type = Public
, budget = CHF 1.896 billion (2021)
, rector = G√ľnther Dissertori
, president = Jo√ęl Mesot
, ac ...
* , scientific consultant of the Department of Computer photonics
* , Professor, Director General Vavilov State Optical Institute The Vavilov State Optical Institute in St Petersburg, Russia (named after Sergey Ivanovich Vavilov) is the largest research institute in optics in Russia. It works both in pure and applied optics, and has a high reputation in the field of holograph ...
(1994-2002)
* , first deputy governor of St. Petersburg, a graduate LITMO (1963)
* Bjarne Stroustrup
Bjarne Stroustrup (; ; born 30 December 1950) is a Danish computer scientist, most notable for the invention and development of the C++ programming language. As of July 2022, Stroustrup is a professor of Computer Science at Columbia University. ...
, Danish professor of the Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, or TAMU) is a public, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of the Texas A&M University System in 1948. As of late 2021, T ...
, Master of Computer Science, University of Aarhus
Aarhus University ( da, Aarhus Universitet, abbreviated AU) is a public research university with its main campus located in Aarhus, Denmark. It is the second largest and second oldest university in Denmark. The university is part of the Coimbra Gr ...
, founder of language C ++
* Joseph Feliksberger, Doctor of Science, Head of Applied Technology Degussa
Evonik Industries AG is a stock-listed German specialty chemicals company headquartered in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the second largest chemicals company in Germany, and one of the largest specialty chemicals companies in the ...
, PCI Augsburg
* Dale Fuller, American president and CEO "Borland Labs, Inc"
* Gunter Hyun, Professor, Ph.D., Dean of the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering of the Technische Universität Ilmenau
The Technische Universität Ilmenau (''Ilmenau University of Technology'', TU Ilmenau) is a German public research university located in Ilmenau, Thuringia, central Germany. Founded in 1894, it has five academic departments (faculties) with abo ...
* Tony Hoare
Sir Charles Antony Richard Hoare (Tony Hoare or C. A. R. Hoare) (born 11 January 1934) is a British computer scientist who has made foundational contributions to programming languages, algorithms, operating systems, formal verification, and c ...
, British, one of the founders of discrete mathematics
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" (in a way analogous to discrete variables, having a bijection with the set of natural numbers) rather than "continuous" (analogously to continuous f ...
, author of the algorithm Quicksort
Quicksort is an efficient, general-purpose sorting algorithm. Quicksort was developed by British computer scientist Tony Hoare in 1959 and published in 1961, it is still a commonly used algorithm for sorting. Overall, it is slightly faster than ...
, the theory of communicating sequential processes
In computer science, communicating sequential processes (CSP) is a formal language for describing patterns of interaction in concurrent systems. It is a member of the family of mathematical theories of concurrency known as process algebras, or pro ...
(CSP), Hoare logic
Hoare logic (also known as Floyd–Hoare logic or Hoare rules) is a formal system with a set of logical rules for reasoning rigorously about the correctness of computer programs. It was proposed in 1969 by the British computer scientist and log ...
, widely used for software verification Software verification is a discipline of software engineering whose goal is to assure that software fully satisfies all the expected requirements.
Broad scope and classification
A broad definition of verification makes it equivalent to software t ...
* John Edward Hopcroft, American specialist in computer science at Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach an ...
* Yang Shichin, rector of Harbin Institute of Technology
Harbin Institute of Technology (; abbreviation: HIT or ) is a public research university and a member of China's elite C9 League and a member of the University Alliance of the Silk Road. HIT is a Chinese Ministry of Education Class A Doubl ...
in 1985‚Äď2002.
* Klaus-Peter Tsoher, Professor of Technology Faculty of Mechanical Engineering of the Technische Universität Ilmenau
The Technische Universität Ilmenau (''Ilmenau University of Technology'', TU Ilmenau) is a German public research university located in Ilmenau, Thuringia, central Germany. Founded in 1894, it has five academic departments (faculties) with abo ...
* Niklaus Wirth
Niklaus Emil Wirth (born 15 February 1934) is a Swiss computer scientist. He has designed several programming languages, including Pascal (programming language), Pascal, and pioneered several classic topics in software engineering. In 1984, he w ...
, Swiss computer science professor, Honorary Doctor of Sciences
Notable alumni
; Scientists * Nadezhda Agaltzeva * Aleksandr Aronov * Aziz Azizov *Pavel Belov
Pavel Alexeyevich Belov (Russian: –ü–į–≤–Ķ–Ľ –ź–Ľ–Ķ–ļ—Ā–Ķ–Ķ–≤–ł—á –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–ĺ–≤; 18 February 1897 ‚Äď 3 December 1963) was a Soviet Army, Soviet Army colonel Colonel general, general and a Hero of the Soviet Union. He was nicknamed the "Fox" by the ...
* Gennadi Dulnev
* Aleksandr Grammatin
* Leonid Konopolko
* Dmitri Sergeev
* Vladimir Vasilyev Vladimir Vasiliev may refer to:
* Vladimir Vasiliev (dancer) (born 1940), dancer with the Bolshoi Ballet
* Vladimir Vasilyev (rower) (born 1948), Soviet Olympic rower
* Vladimir Vasilyev (politician) (born 1949), Russian politician
* Vladimir Vas ...
* Mark Veyngerov
* Aleksandr Zapesotzki
* Viktor Zverev
; Political leaders
* Askar Akaev
Askar Akayevich Akayev ( ky, –ź—Ā–ļ–į—Ä –ź–ļ–į–Ķ–≤–ł—á (–ź–ļ–į–Ļ —É—É–Ľ—É) –ź–ļ–į–Ķ–≤, translit=Askar Akayevich (Akay Uulu) Akayev ; ; born 10 November 1944) is a Kyrgyz politician who served as President of Kyrgyzstan from 1990 until being ov ...
; Musicians
* Dmitri Tikhonov
* Vasilii Vasin
; Athletes
* Boris Lukomsky
Boris Lukomsky (russian: –Ď–ĺ—Ä–ł—Ā –°–Ķ–ľ—Ď–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–ł—á –õ—É–ļ–ĺ–ľ—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ; born 6 June 1951) is a Soviet fencer. He won a bronze medal in the team √©p√©e event at the 1980 Summer Olympics
The 1980 Summer Olympics (russian: –õ–Ķ—ā–Ĺ–ł–Ķ –ě– ...
* Ekaterina Mamleeva
* Tamara Manina
Tamara Ivanovna Manina (russian: –Ę–į–ľ–įŐĀ—Ä–į –ė–≤–įŐĀ–Ĺ–ĺ–≤–Ĺ–į –ú–įŐĀ–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–į; born 16 September 1934) is a retired Soviet Olympic gymnast and a sports scientist.
Biography
Her family lived in Petersburg (and later in Leningrad), but Manin ...
* Valentin Zanin
; Special services
* Sergei Verevkin-Rahalski
* Boris Mylnikov
References
External links
University Homepage
{{Authority control Educational institutions established in 1900 1900 establishments in the Russian Empire National research universities in Russia Universities in Saint Petersburg Engineering universities and colleges in Russia