ICOCA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The card is a rechargeable contactless
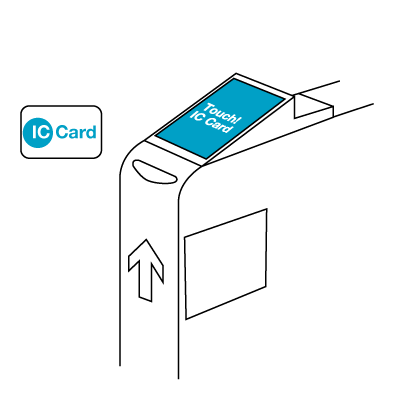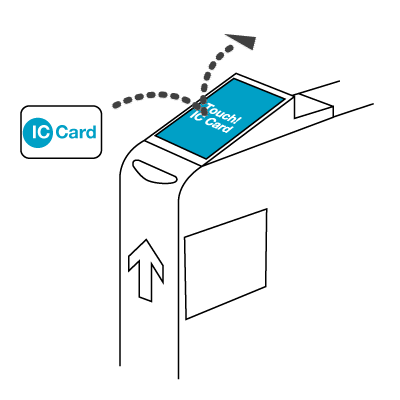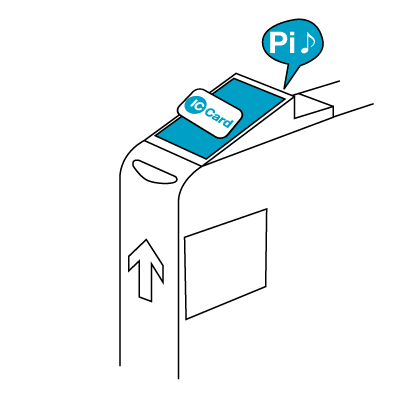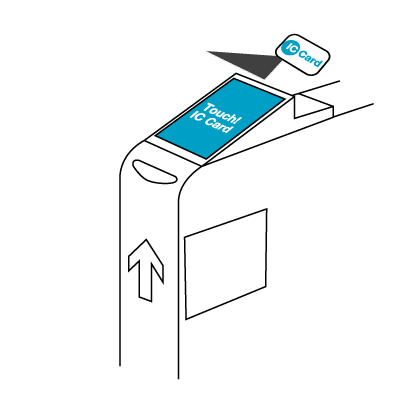 Usage of the card involves passing it over a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at some distance from the reader, so contact is not required, and many people leave the card in their wallet and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
Usage of the card involves passing it over a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at some distance from the reader, so contact is not required, and many people leave the card in their wallet and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
File:ICOCA-Gate1.jpg, alt=An ICOCA Ticket Gate, An ICOCA Ticket Gate.
File:ICOCA-Gate2.jpg, alt=Closeup of an ICOCA Gate reader, Closeup of an ICOCA Gate reader.
The balance on the card is displayed when you enter the ticket gate this way. The balance is also displayed whenever the card is inserted into the ticket or fare adjustment machines as well. A travel record is stored on the card, and can be displayed or printed out as well, at the fare adjustment machines.
On occasion, when travelling to a station where ICOCA is not supported, the card must be handed over to the staff at the exiting station, so that they can calculate the remaining fare, and also so that they can return a slip of paper which must be given to the staff at the next station where ICOCA is used.
ICOCA functions as a , and also has a added to it. However, for express services, such as the Haruka service to Kansai airport, on which an additional fee is required, ICOCA can only be used as (for passing the ticket gate) for non-reserved travel, with the express ticket purchased from the conductor on board the train – see train tickets in Japan.
File:Kips Icoca.png, alt=KIPS ICOCA Card, KIPS ICOCA Card
 Via a number of reciprocal agreements, for ordinary fares, ICOCA can be used interoperably with various other mass transit smart card systems. As of 2014, ICOCA has interoperability with Kitaca,
Via a number of reciprocal agreements, for ordinary fares, ICOCA can be used interoperably with various other mass transit smart card systems. As of 2014, ICOCA has interoperability with Kitaca,
Official homepage
{{Osaka transit Rail transport in Osaka Prefecture Fare collection systems in Japan E-commerce in Japan Contactless smart cards West Japan Railway Company Fictional monotremes 2003 introductions 2003 establishments in Japan
smart card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) c ...
used on the JR West
, also referred to as , is one of the Japan Railways Group (JR Group) companies and operates in western Honshu. It has its headquarters in Kita-ku, Osaka. It is listed in the Tokyo Stock Exchange, is a constituent of the TOPIX Large70 index, and ...
rail network in Japan. The card was launched on November 1, 2003 for usage on the Urban Network, which encompasses the major cities of Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
, Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
and Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, w ...
(Keihanshin
is a metropolitan region in the Kansai region of Japan encompassing the metropolitan areas of the cities of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture, Osaka in Osaka Prefecture and Kobe in Hyōgo Prefecture. The entire region has a population () of 19,302, ...
). It is now usable on many other networks. The ICOCA area has gradually been expanded, and now includes the San'yo region through the Okayama
is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889. , the city has an estimated population of 720,841 and a population density of 910 persons per km2. The total area is .
The city is ...
and Hiroshima urban areas, and some lines in northern Shikoku, San'in and Hokuriku regions as of 2020.
ICOCA stands for IC Operating CArd, but it is also a play on the phrase , an informal, Kansai dialect
The is a group of Japanese dialects in the Kansai region (Kinki region) of Japan. In Japanese, is the common name and it is called in technical terms. The dialects of Kyoto and Osaka are known as , and were particularly referred to as su ...
invitation meaning "Shall we go?" in Japanese (the standard, Tokyo dialect equivalent is ).
The mascots for the ICOCA program consists of a blue platypus
The platypus (''Ornithorhynchus anatinus''), sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or monot ...
(or duckbill) called and .
Functions/services
 Usage of the card involves passing it over a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at some distance from the reader, so contact is not required, and many people leave the card in their wallet and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
Usage of the card involves passing it over a card reader. The technology allows for the card to be read at some distance from the reader, so contact is not required, and many people leave the card in their wallet and just pass the wallet over the reader as they enter the ticket gate.
Variants
*Standard ICOCA rechargeable card *ICOCA 定期券 (''teikiken'') – rechargeable card with added commuter pass *こどもICOCA (''kodomo'') – children's ICOCA *こどもICOCA 定期券 – children's ICOCA with added commuter pass *Smart ICOCA *Smart ICOCA 定期券 *KIPS ICOCA – this card is sold by Kintetsu *KIPS ICOCA 定期券 – this card is sold by Kintetsu *Shikoku ICOCA - this card is sold byJR Shikoku
The , commonly known as , is the smallest of the seven constituent companies of the Japan Railways Group (JR Group). It operates of intercity and local rail services in the four prefectures on the island of Shikoku in Japan. The company has it ...
Interoperation
Suica
is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card, electronic money used as a fare card on train lines in Japan, launched on November 18, 2001. The card can be used interchangeably with JR West's ICOCA in the Kansai region and San'yō region i ...
, PASMO
is a rechargeable contactless smart card electronic money system. It is primarily used for public transport in Tokyo, Japan, where it was introduced on 18 March 2007. Pasmo can also be used as a payment card for vending machines and store ...
, TOICA, manaca
Manaca, written in lower-case letters, is a rechargeable contactless smart card used in Nagoya, Japan and the surrounding area since February 11, 2011, when it replaced the Tranpass magnetic fare card system. As of March 23, 2013, it became ...
, PiTaPa
is a contactless smart card ticketing and electronic money system used in the Kansai region (and may also be used in some areas of Okayama Prefecture, Hiroshima Prefecture, and Shizuoka Prefecture) of Japan. The name ''PiTaPa'' is an acro ...
, SUGOCA
is a Japanese rechargeable contactless smart card ticketing system for public transport in Fukuoka Prefecture and environs. The Kyūshū Railway Company (JR Kyūshū) introduced the system on 1 March 2009. The name is an acronym of "Smart Urban ...
, nimoca
Nimoka, stylized as , is a rechargeable contactless smart card ticketing system for public transport in Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. Nishi-Nippon Railroad (Nishitetsu) introduced the system on May 18, 2008. Its name is an acronym of "nice money ...
, hayakaken and several other local smart cards.
* Since August 1, 2004, in a reciprocal agreement with JR East
The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and is the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as in Japanese. The company's headquarters ar ...
, ICOCA is also usable in the Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
- Kantō area. Conversely, the Suica
is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card, electronic money used as a fare card on train lines in Japan, launched on November 18, 2001. The card can be used interchangeably with JR West's ICOCA in the Kansai region and San'yō region i ...
card of JR East can also be used on JR West rail services.
* Since January 21, 2006, ICOCA cards can also be used at all locations accepting Osaka PiTaPa
is a contactless smart card ticketing and electronic money system used in the Kansai region (and may also be used in some areas of Okayama Prefecture, Hiroshima Prefecture, and Shizuoka Prefecture) of Japan. The name ''PiTaPa'' is an acro ...
smart cards.
* Since September 1, 2007, ICOCA is also usable in the Hiroshima-Okayama
is the capital city of Okayama Prefecture in the Chūgoku region of Japan. The city was founded on June 1, 1889. , the city has an estimated population of 720,841 and a population density of 910 persons per km2. The total area is .
The city is ...
area.
* Since March 29, 2008, in a reciprocal agreement with JR Central
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
, ICOCA is also usable in the Nagoya metropolitan area. Similarly, the TOICA card of JR Central can also be used on JR West rail services.
* Since March 5, 2011, in a reciprocal agreement with JR Kyushu
The , also referred to as , is one of the seven constituent companies of Japan Railways Group (JR Group). It operates intercity rail services within Kyushu, Japan and the JR Kyushu Jet Ferry Beetle hydrofoil service across the Tsushima Stra ...
, ICOCA is also usable in the Fukuoka
is the List of Japanese cities by population, sixth-largest city in Japan, the second-largest port city after Yokohama, and the capital city of Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. The city is built along the shores of Hakata Bay, and has been a center ...
-Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the Pl ...
area. Similarly, the SUGOCA
is a Japanese rechargeable contactless smart card ticketing system for public transport in Fukuoka Prefecture and environs. The Kyūshū Railway Company (JR Kyūshū) introduced the system on 1 March 2009. The name is an acronym of "Smart Urban ...
card of JR Kyushu can also be used on JR West rail services.
* Since June 1, 2011, Keihan started selling its ICOCA.
* Since March 17, 2012, ICOCA became usable in some stations of JR Shikoku
The , commonly known as , is the smallest of the seven constituent companies of the Japan Railways Group (JR Group). It operates of intercity and local rail services in the four prefectures on the island of Shikoku in Japan. The company has it ...
.
* Since December 1, 2012, Kintetsu started selling its ICOCA.
* Since March 23, 2013, nationwide inter-operation among 10 transportation smart cards started.
Retail
These cards are available at cardvending machine
A vending machine is an automated machine that provides items such as snacks, beverages, cigarettes, and lottery tickets to consumers after cash, a credit card, or other forms of payment are inserted into the machine or otherwise made. The fir ...
s at the train stations. The card costs 2000 yen, which includes a 500 yen deposit that will be returned if the card is turned in. The remaining 1500 yen is immediately available for train rides, and more money can be charged on to the card at similar ticket vending machines or fare adjustment machines inside each station.
The card may only be returned in JR West stations, however, so travelers who start their trip in JR west area and finish their trip elsewhere may not be able to return it before departure. Shikoku ICOCA cards are sold at several stations in Shikoku and can only be returned at those stations.
Technology
The card incorporates contactlessRFID
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electroma ...
technology developed by Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
, called FeliCa
FeliCa is a contactless RFID smart card system from Sony in Japan, primarily used in electronic money cards. The name stands for ''Felicity Card''. First utilized in the Octopus card system in Hong Kong, the technology is used in a variety of card ...
. The same technology is also deployed in the Edy
Edy, provided by Rakuten, Inc. in Japan is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card. While the name derives from euro, dollar, and yen, it works with yen only.
History
Edy was launched on January 18, 2001 by BitWallet, with fincanin ...
electronic cash cards used in Japan, the Octopus card in Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
& the old ezlink Card in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
.
See also
* Mass transit systems * Electronic money * List of smart cardsReferences
External links
Official homepage
{{Osaka transit Rail transport in Osaka Prefecture Fare collection systems in Japan E-commerce in Japan Contactless smart cards West Japan Railway Company Fictional monotremes 2003 introductions 2003 establishments in Japan