Hypostome (trilobite) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The hypostome is the hard mouthpart of
trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s found on the ventral side of the cephalon (head). The hypostome can be classified into three types based on whether they are permanently attached to the rostrum or not and whether they are aligned to the anterior dorsal tip of the glabella
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to ...
.
Morphology
The center of the hypostome is an ovoid, typically convex part called the median body, often divided into an anterior lobe and a posterior lobe. Either side of the median body is a border with various extensions, including anterior and posterior wings, sometimes bearing knob-like processes. The hypostome is hollow, and encloses the mouthparts, the anterior digestive tract, and the bases of the antennae. Trilobite antennae pass through notches between the anterior and posterior wings, then forward. The anterior wings are designed to rest firmly against internal structures (ventral apodemes) on theglabella
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to ...
.
Variation in trilobite hypostome morphology is crucial in modern discussions of trilobite phylogeny. Functional interpretations of hypostome shape also allow for reasonable speculation on the feeding habits of trilobite species.
Types
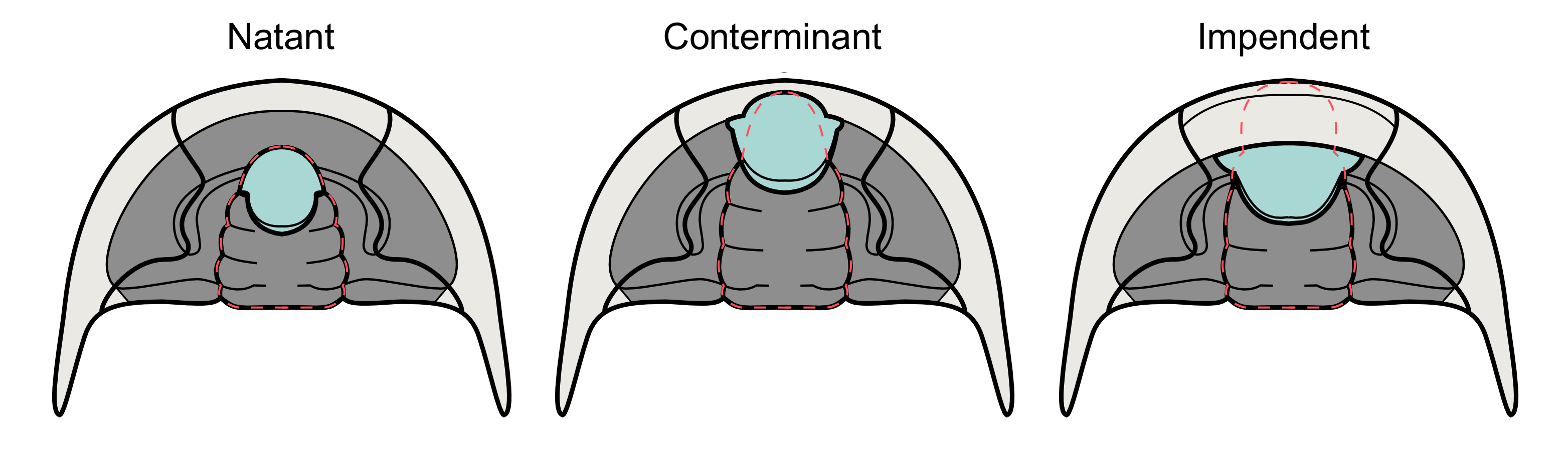
Although hypostome morphology is highly variable, three broad types are generally recognized:
Natant
A natant hypostome is not attached to the anterior doublure, with support assumed to be provided by a non-mineralised membrane. Natant hypostomes appear to have been conservative over the course of the evolution of trilobites with overall form and shape of a simple ovoid without posterior extensions or ornamentation. Natant hypostomes are thought to be ancestral to other hypostome forms and thought to belong to trilobites with generalized particle feeding habits (''i.e.'' little need to modify mouth-parts to deal with specialized food items).Conterminant
A conterminant hypostome is attached to the anterior doublure, aligned with the front edge of theglabella
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to ...
and found on trilobites thought of as predators. Anchoring the hypostome against the anterior doublure and cephalon provides structural bracing against which to tear apart prey. Different specializations of hypostome form might reflect different kinds of prey, or different feeding behaviors.
Impendent
An impendent hypostome is attached to the anterior doublure but not aligned with the front edge of the glabella. Many impendent hypostomes have prongs, grooves and other adaptations thought to relate to feeding on complex food sources.See also
*Mandible (arthropod)
250px, The mandibles of a bull ant
The mandible (from la, mandibula or mandĭbŭ-lum, a jaw) of an arthropod is a pair of mouthparts used either for biting or cutting and holding food. Mandibles are often simply called jaws. Mandibles are p ...
References
{{reflist Trilobite anatomy